Diagnosis and prognosis of acute hamstring injuries in athletes
|
|
|
- Sheryl Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: DO /s x SPORTS MEDCNE Diagnosis and prognosis of acute hamstring injuries in athletes Gino M. M. J. Kerkhoffs Nick van Es Thijs Wieldraaijer nger N. Sierevelt Jan Ekstrand C. Niek van Dijk Received: 17 December 2011 / Accepted: 10 May 2012 / Published online: 24 May 2012 Ó The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Abstract Purpose dentification of the most relevant diagnostic and prognostic factors of physical examination and imaging of hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes. Methods A literature search was conducted in MEDLNE and EMBASE for articles between 1950 and April A survey was distributed among the members of the European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy, which focused on physical examination, prognosis, imaging and laboratory tests of hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes. Results Medical history, inspection and palpation of the muscle bellies and imaging are most valuable at the initial assessment according to the literature. Experts considered medical history, posture and gait inspection, inspection and palpation of muscle bellies, range of motion tests, manual muscle testing, referred pain tests and imaging to be most important in the initial assessment of hamstring injuries. Magnetic resonance imaging (MR) is preferred over ultrasonography and should take place within 3 days posttrauma. mportant prognostic factors are injury grade, length of the muscle tear on MR images, MR-negative injuries and trauma mechanism. Conclusions Posture and gait inspection, inspection and palpation of muscle bellies, range of motion tests, manual G. M. M. J. Kerkhoffs (&) N. van Es T. Wieldraaijer. N. Sierevelt C. N. van Dijk ESSKA Sports Committee, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Academic Medical Center, 1105 AZ Amsterdam, The Netherlands g.m.kerkhoffs@amc.nl J. Ekstrand Department of Medical and Health Sciences, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden muscle testing and referred pain tests within 2 days posttrauma were identified as the most relevant diagnostic factors. Level of evidence Literature review and expert opinion, Level. Keywords Hamstring strain injury Sports injury Physical examination maging ntroduction Hamstring injuries are frequent in sports like football [1 17, 21, 27, 46, 59, 60], Australian rules football [43, 52], sprinting [65], American football [20] and rugby [10]. Considering the explosive character of sprinting, it is not surprising that the incidence of injuries (0.87/1,000 h of exposure) is comparable to the incidence in contact sports ( /1,000 h of exposure) [17, 18, 65]. At the top level, professional football team of 25 players can expect about 7 hamstring injuries per season [16]. These injuries frequently cause a significant loss of time from competition and have a high recurrence rate (12 43 %) [11, 17, 21, 24, 27, 30, 35, 39, 46, 52, 56, 58]. Elite football players sustaining a hamstring injury cannot participate in competition for a mean of 14 days [17]. The need for a quick and accurate diagnosis and prognosis of hamstring injuries in elite sports is evident and has been given greater emphasis. The number of games in elite sports has increased and the stakes are higher [63]. However, there is little evidence for the diagnostic and prognostic value of several physical tests [50, 61] and discussion continues on the optimal imaging technique [1, 8, 13, 14, 34, 50, 61]. The objective of this study was to identify the most relevant diagnostic and prognostic aspects of physical examination and additional studies of hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes.
2 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: Materials and methods Literature review A comprehensive literature study was conducted for articles between January 1950 and April 2011 on the diagnosis and prognosis of hamstring injuries. The strategies that were used consisted of searching online databases (MED- LNE and EMBASE) and scanning reference lists. The search terms used in MEDLNE were hamstring* or thigh[mesh] combined with the MeSH-terms Sprains and Strains/diagnosis, Muscle, Skeletal/injuries, Magnetic resonance imaging or Ultrasonography. n EMBASE, the terms hamstring /exp/mj or thigh/exp/mj and injury /exp combined with prognos*, diagnos*, assess*, ultrasonograph*, ultrasound, mri, magnetic resonance imaging or imag* were searched for. Articles concerning medical history, physical examination, prognosis and imaging of hamstring injuries were selected. Expert opinion As part of a project of the Sports Committee of the European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy (ESSKA), ESSKA Members (n = 800) were invited by to participate in an English web-based survey in June The survey focused on the physical examination, prognosis, imaging and laboratory tests for hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes. The questions were formulated by the authors on the basis of a comprehensive literature review. The survey was a mixture of open questions, multiple choice questions and Likert-scale questions. The five options from which the respondents could choose in the Likert-scale questions were (1) not important, (2) of little importance, (3) moderately important, (4) important and (5) very important. Additional information was provided on the way in which the physical tests were carried out. A pilot survey was distributed among the orthopaedic surgeons of the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam in order to identify indistinct, irrelevant and missing questions. One week after the first invitation to take part, a reminder was sent by to the ESSKA members in which they were asked to participate in the survey. Statistic analysis Data were analysed using SPSS version 16.0 (Chicago, USA). Results were mainly presented in a descriptive way as frequencies with corresponding percentages and averages with standard deviations. Likert scales were dichotomised by combining options 1 and 2 and options 3 5 to, respectively, the categories not important and important. Results One hundred and forty ESSKA members (18 % response rate) from 34 countries with 18 (SD 9.6) years of experience completed the questionnaire. The selected articles from the literature search are categorised according to the type of article and the level of evidence in Tables 1, 2. Timing of initial physical examination Traditionally, the clinical assessment of hamstring injuries is based on a thorough medical history and physical examination consisting of posture and gait inspection, inspection and palpation of muscle bellies, range of motion tests (ROM tests) and manual muscle testing. n the literature, the initial assessment is often carried out within 12 h to 2 days post-injury [5, 50, 58, 61]. Advantages of an assessment shortly post-injury are the possibility of quick intervention and a more reliable medical history. However, possible signs of swelling and ecchymosis may arise a few days later and consequently may not be noticed at the initial examination [4, 12, 31, 62]. 82 % of the respondents stated that the initial clinical assessment of an (elite) athlete with a suspected hamstring injury should take place within 2 days. This is confirmed in recent work where it is advised to measure active ROM at the end of the second day [38]. Palpation Palpation helps identify the site of injury in cranio-caudal direction, because of possible involvement of the free proximal tendon, and determines the injured muscles (lateral: m. biceps femoris, medial: m. semitendinosus and/or m. semimembranosus). njuries in the m. biceps femoris [13] and more cranially palpated injuries [5] might correlate with a longer rehabilitation interval. Flexibility Flexibility in acute and sub-acute phase was addressed. Flexibility is tested by means of hamstring ROM tests. n case of a hamstring injury, the range of motion of the hip and the knee of the injured leg is significantly decreased compared to the healthy leg [4]. However, the flexibility of the hip in the acute situation is often influenced by pain as a consequence of which the test may be less accurate. Active ROM is decreased in the acute phase of the injury and it is advised to be measured at the end of the second day [38]. Use of the classic sit-and-reach test is discouraged in the literature as the testing result is influenced by spinal mobility (i.e. lumbal flexion), leg length, scapular abduction and stretch on the peripheral nerves by dorsiflexion of
3 502 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: Table 1 Overview of the literature review source articles Article Article design (type) Level of evidence Allen et al. [1] Arnason et al. [2] Epidemiological review Retrospective cohort study Arnason et al. [3] Askling et al. [4] Askling et al. [5] Askling et al. [6] Askling et al. [7] Bencardino et al. [8] Blankerbaker et al. [9] Brooks et al. [10] Carling et al. [11] Prospective therapeutic study Prospective prognostic study Prognostic case series Prognostic case series Prognostic case series Cohort study (prevention) Epidemiological review Prognostic case series Cohen et al. [12] Literature review/background Connell et al. [13] Diagnostic case series Davis [14] Ekstrand et al. [15] Ekstrand et al. [16] Ekstrand et al. [17] Ekstrand et al. [18] Ekstrand et al. [19] Elliott et al. [20] Engebretsen et al. [21] Fleckenstein et al. [22] Fleckenstein et al. [23] Gibbs et al. [24] Gielen et al. [25] Prospective two-cohort study Descriptive epidemiology study Diagnostic case series (descriptive) Prospective diagnostic study Descriptive chapter Table 1 continued Article Article design (type) Level of evidence Guerrero et al. [26] Hägglund et al. [27] Heiderscheit et al. [29] Heiser et al. [30] Klingele et al. [31] Kornberg et al. [32] Koulouris et al. [33] Koulouris et al. [34] Koulouris et al. [35] Lempainen et al. [36] Liemohn et al. [37] Malliaropoulos et al. [38] Malliaropoulos et al. [39] Martínez Amat et al. [40] Miñarro et al. [41] Nikolaou et al. [42] Orchard et al. [43] Prognostic case series Prospective prognostic study Retrospective cohort study Retrospective cohort study Therapeutic cohort study Retrospective cohort study Prognostic cohort study Retrospective case series Therapeutic case series Prognostic cohort study Prognostic cohort study Diagnostic cohort study Diagnostic cohort study Biomechanical and histological evaluation of muscle Retrospective epidemiologic study Orchard et al. [44] Peetrons [45] Petersen et al. [46] Puranen et al. [47] Sallay et al. [48] Descriptive case series Sarimo et al. [49] Schneider-Kolsky et al. [50] Schneider-Kolsky et al. [51] Retrospective case series Diagnostic cohort study Author s reply
4 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: Table 1 continued Article Article design (type) Level of evidence Seward et al. [52] the ankle joint [37, 41]. Knee active range of motion deficit 48 h after a unilateral posterior thigh muscle injury is an objective and accurate measurement, predicting recovery time in elite athletes [38]. Flexibility tests were pointed out as important by a majority of the respondents. The sit-and-reach test was considered to be important despite the above-mentioned negative advice given in the literature. No difference in importance was found between active and passive ROM tests (n.s). Strength Shellock et al. [53] Slavotinek et al. [54] Prospective RCT Sorichter et al. [55] errall et al. [56] errall et al. [57] errall et al. [58] olpi et al. [59] Walden et al. [60] Warren et al. [61] Retrospective case control study Prospective prognostic cohort study Epidemiological review Retrospective cohort study Prospective observational study Wood et al. [62] Woods et al. [63] Epidemiological review Woods et al. [64] Yeung et al. [65] Zeren et al. [66] Epidemiological review Diagnostic cohort study Level of evidence is rendered as ranging from to in accordance with guidelines from the centre for evidence-based medicine, Oxford, UK Strength of the hamstring muscles can be tested by means of knee flexion and hip extension against resistance. Bilateral comparison is preferred to identify decreased strength of the injured muscle as a result of pain and/or Table 2 Summary of the articles used for this literature review and level of evidence Article type Number Level of evidence fibre disruption [4]. An alternative to measuring the strength of the hamstring muscles is the take-off-the-shoe test (TOST) (or hamstring-drag test) in which the patient is asked to take-off the shoe of the injured leg in a standing position with the help of the foot of the healthy leg [66]. Although this test is potentially a valuable addition to the physical examination, the true value should be studied by comparison with magnetic resonance imaging (MR) and recurrence rates [51]. Referred pain An acute disc prolapse at the L5/S1 level may present with hamstring and/or calf pain and limitations in hip joint flexibility, which may mimic a muscle strain. Subtle lumbosacral canal impingement of the L5 nerve root however may in fact also be a common underlying basis for the agerelated predisposition towards hamstring injuries [44]. The distinction between real hamstring injuries and backrelated or neural hamstring injuries can be made by the assessment of referred pain with help of an MR scan [44, 56]. f the distinction remains difficult, imaging-guided cortisone injections to the lumbosacral canal region (L5 nerve root) is a relatively painless and complication-free outpatient procedure with quick recovery that can be used to distinguish the hamstring-spine dilemma. Pain felt over the area of the ischial tuberosity and radiating down the back of the thigh is often labelled as the hamstring syndrome [47]. Laboratory tests Total Epidemiological review Prospective Retrospective Literature review 1 1 Expert opinion/ background Author s reply 1 1 Traditional biological markers creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), myoglobin (Mb) and uric acid should not be used for the diagnosis and prognosis of muscle injuries because of their low sensitivity and specificity [55]. More research is needed to determine the real
5 504 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: diagnostic and prognostic value of potential markers, such as fast myosin heavy chains (fast MHC) [26], skeletaltroponin (stn) [55] and alfa-actin [40]. Few of the respondents thought that laboratory tests can be of diagnostic or prognostic importance. The results of the survey are shown in Table 3. maging The imaging provides information on the nature and extent of hamstring injuries. The length of a muscle tear on MR images or the cross-sectional area of the muscle tear on ultrasonography (US) is valuable for estimating the convalescent period [13, 19, 24, 35, 50, 52]. 88 % of the respondents in this study use imaging for hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes. maging technique MR and US are the most suitable imaging techniques for depicting hamstring injuries [8, 34]. Connell et al. [13] concluded that MR and US are equally useful in diagnosing hamstring injuries at baseline. However, MR is more sensitive for identifying minimal injuries, with less than 5 % of muscle involved: the radiological definition of a grade- muscle injury [13, 33, 45]. When imaging is indicated, MR is used in % of cases, both MR and US in 7 40 % and US only in % of cases [10, 17, 19, 64]. The most important advantages and disadvantages of both imaging techniques are presented in Table 4. Table 3 mportance of different physical tests and additional studies for hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes according to experts Test mportant (%) Palpation to identify the site of injury 97 3 Palpation to identify the injured muscle(s) 95 5 Knee flexion against resistance 94 6 nspection of the posterior thigh 93 7 Posture and gait inspection Hip extension against resistance Assessing referred pain Active straight leg raise Sit-and-reach test Passive knee extension Active knee extension Passive straight leg raise Take-off-the-shoe test/hamstring-drag test Prognostic laboratory tests Diagnostic laboratory tests 4 96 Not important (%) Table 4 Advantages and disadvantages of MR and US as imaging technique for hamstring injuries Qualities MR US Low costs [13] -?? ndependence of the quality and experience of the?? - physician [13] Ease of use ±?? Ease of use for prognosis [13]??? Sensitivity for low-grade injuries [13, 33]? ± Diagnosis of avulsion fractures [33]? ± Reproducibility?? ± Dynamic assessment -?? Availability ±?? Evaluation of superficial structures [33]??? Evaluation of deep structures?? ± Correct reflection of the extent of the injury [13]?? ± Assessment time ±?? Follow-up imaging [13]????? = much applicable,? = applicable, ± = less applicable, -=not applicable Time of imaging There is currently no consensus in the literature on the ideal moment of imaging of hamstring injuries. Ekstrand et al. [19] are in favour of MR within h post-trauma, whereas Gielen et al. [25] argue that a hamstring injury can only be correctly graded h post-trauma. Signs of muscle injury on MR images are mainly seen on fat-suppressed T2 images or short-tau inversion recovery images (STR) and are most evident at 24 h to 5 days post-trauma [22, 23, 53]. n prospective studies, MR is often used out 2 5 days post-trauma [13, 35, 58]. Since the amount of oedema is histologically maximal after 24 h and already decreases after 48 h [42], imaging 1 2 days post-trauma seems to be the best moment. The respondents prefer imaging within 3 days posttrauma for MR (66 %) and for US (79 %). Follow-up imaging MR is more sensitive for follow-up imaging than US [13]. Follow-up imaging is useful in the case of complications and in order to follow the progression of the rehabilitation and consequently to support the decision for sports resumption for (elite) athletes [9]. After 6 weeks in % of all cases, signs of hamstring injury are still noticeable on MR images [5]. The ideal moment of followup imaging differs in every single case and is therefore difficult to generalise. 66 % of the respondents use follow-up imaging in the case of persisting bad rehabilitation and 61 % to assess the
6 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: progression of the rehabilitation. n total, 91 % of the respondents use follow-up imaging for hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes. Prognostic factors An accurate prognosis can be obtained on the basis of a thorough clinical assessment [50]. Different classification systems are provided in the literature. A clinical classification system resulting from the treatment for 165 elite track and field athletes with acute, first-time unilateral hamstring muscle strains was proposed in Strains were classified into 4 grades (,, and ) based on knee active range of motion deficit at 48 h [38]. maging is a valuable addition. There is the classic radiological grading system of a hamstring injury with grade (minimal muscle damage with \5 % of muscle length involved) or (partial rupture with 5 50 % of muscle length involved) on MR or US to correspond with the rehabilitation period [13, 19, 24, 50, 52]. Grade hamstring injuries (complete rupture or avulsion fracture) are serious injuries resulting in a convalescent period of 3 months up to 1.5 years, often requiring surgery [31, 36, 48, 49]. n 2002, an additional grading systems was introduced, specifically for US, grade 0 (normal US appearance), grade 1 (subtle ultrasound findings), grade 2 and grade 3 injuries (partial and complete muscle tears) [45]. n general, the grading should be done by a team consisting of an orthopaedic surgeon and/or a sports medicine physician and a radiologist. A substantial part of supposed hamstring injuries are negative on MR (14 45 %) [24, 50, 56, 57]. n these cases, the symptoms are probably not the result of muscle fibre disruption, but are caused by referred pain (e.g. from the lumbar spine) or abnormal neural tension [32, 44, 47]). t has been described that hamstring injuries that result from excessive slow-speed stretching require a much longer convalescent period compared to hamstring injuries sustained during high-speed running. n the former type of injury, the m. semimembranosus and the free proximal tendon are often involved, resulting in a rehabilitation period of weeks. [6, 7]. Athletes sustaining a recurrent hamstring injury have a longer convalescent period compared to a first-time hamstring injury [10, 17, 18, 35, 39]. The time to return to sports after re-injury was depending on the injury grade on average days longer [10, 17, 35, 39]. Over 50 % of re-injuries occur within 1 month after the initial injury [10]. This emphasises the risk of an early return to sport after a hamstring injury. The factors mentioned in the literature associated with a longer rehabilitation period are compared with the expert opinion in Table 5. Table 5 Prognostic factors during the injury period associated with a longer rehabilitation period for hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes?? = multiple randomised controlled trials (RCT) (strong evidence),?=one RCT (moderate evidence), ±=contradiction in the literature, -=no evidence Factors associated with a longer rehabilitation period Literature Expert opinion Complete rupture or avulsion fracture [12, 31, 48, 62]???? Greater length of muscle tear on MR images or larger cross-sectional???? area of muscle tear on ultrasound images [13, 24, 50, 54] MR-positive hamstring injury [13, 24, 57]??? Recurrent hamstring injury [10, 17, 18, 35, 39]??? Persisting pain/restriction at ROM tests, strength tests and sport??? exercises njury resulting from excessive slow-speed stretching [4]?? Persisting signs of injury on follow-up imaging [5]?? njury to the m. biceps femoris [13] ±? Sports type [5] ±? More cranially palpated injury [5] ±? Large and deep haematoma -?? Hamstring injury involving the free proximal tendon [6]? - Higher subjective pain score at the time of injury on a isual? - Analogue Scale (AS) [57] Being unable to walk pain-free within 24 h of injury [61]? - Long period until initial treatment -? Low quality of the rehabilitation programme and minimal willingness of the patient to rehabilitate -?
7 506 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: Discussion n this study, we identified posture and gait inspection, inspection of the muscle bellies, location and extent of the muscle tear, flexibility, strength of the hamstrings and assessing referred pain within 2 days as most relevant diagnostic factors of the physical examination. This is in line with the evidence from recent literature. Consensus between literature and experts was also observed for the use of MR to identify injuries with a longer rehabilitation time: (1) greater length of muscle tear on MR images, (2) MR-positive injuries and (3) persistent signs on follow-up injuries. Although both MR and US techniques are used, most experts prefer MR to US. MR is more sensitive than US [13, 33], easier to use for prognostic purposes [13, 52] and less operator-dependent [33]. Consequently, MR should be given the preference over US as imaging technique at the initial assessment. Although it has to be stated that US remains valuable in many cases because of its low costs, availability, dynamic character and secondly, that US is indeed still quite operator-dependent. Consensus between literature and experts was also found for the interpretation that apart from the MR results, trauma mechanism and injury grade are important prognostic factors and that laboratory tests are of minimal diagnostic and prognostic value. There was no consensus between literature and experts on the interpretation of a large and deep haematoma: experts interpret a large and deep haematoma as an important factor associated with a longer rehabilitation period; however, literature does not provide the evidence for this. This is also observed for a longer period to initial treatment and low quality of the rehabilitation programme. All three above-mentioned factors seem logical; however, literature does not support nor deny the prognostic value of these factors. There was also no consensus on the value of higher AS score [58] nor being able to walk pain-free within 24 h of injury [61], experts do not (yet) seem to link these factors to a longer rehabilitation period. Reason for Suspected hamstring injury Medical history MR < 3 days < 2 days Physical examination - posture and gait inspection - inspection of muscle bellies - palpation - ROM tests - manual muscle testing - referred pain assessment Diagnosis Negative factors - avulsion fracture - grade hamstring injury (complete rupture) - recurrent hamstring injury - MR-positive hamstring injury - involvement of proximal tendon - large and deep hematoma - injury resulting from excessive slow-speed stretching - high pain score on AS Prognosis Positive factors - grade or hamstring injury - MR-negative injury - short muscle tear on MR - walk pain free within 24 hours Follow-up MR Return to sports Fig. 1 Guideline for diagnosing hamstring injuries and estimating the convalescent period in elite athletes
8 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: this difference between literature and experts could be the subjective nature of these findings or simply that these findings are not widely known or accepted by other experts yet. There are obvious limitations of this research. Since many prospective studies evaluated hamstring injuries in only one type of sports, there is a selection bias [2, 3, 10, 11, 15 17, 20, 21, 27, 43, 46, 52, 59, 60, 64, 65]. The question rises whether the conclusions of these studies can be extrapolated to other sports types. n our survey, experts were not asked to specify for the sports types with which they deal in their daily practice. Caution is therefore recommended when adopting the results of this study. Also, there is the limited value of a questionnaire with low response rate, again a selection bias [28]; however, we feel that the research benefits from the information provided by the selection of ESSKA members with interest in muscle injuries that answered the questionnaire. We feel that there is a definite need for further research in this field. First, all prognostic factors identified in this review should be validated in a prospective cohort and even better in different cohorts of active sports participants, so the difference between the different sport types can also be monitored. Second, the anatomy of the hamstring (injuries) can be re-evaluated to see whether we can identify important prognostic factors on a basic level. Third, imaging provides numerous keystones to improve the understanding of the extent of the hamstring injury and to link this to an accurate prognosis: ideal moment of initial assessment, use of follow-up imaging in decision-making, US versus MR, optimalisation of MR modalities. With this combination of best evidence from the literature and experts from the field, the most relevant and explicit diagnostic and prognostic factors of physical examination, imaging and additional studies of hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes were identified and an assessment protocol for hamstring injuries in (elite) athletes (Fig. 1) was proposed. n this way, it was attempted to provide a guideline for diagnosing hamstring injuries and estimating the convalescent period in (elite) athletes. Conclusion Physical examination of an athlete with suspected acute hamstring injury should take place within 2 days posttrauma and consists of posture and gait inspection, location and extent of the muscle tear, flexibility and strength of the hamstrings and assessing referred pain. MR as imaging technique for acute hamstring injuries in elite athletes is preferred over ultrasound by both the experts and recent literature mainly based on its greater sensitivity for minor injuries and the ease of use for an accurate prognosis. mportant prognostic factors related to a longer rehabilitation period are MR-positive muscle tears, larger extent of the muscle tear as seen on MR, recurrent hamstring injury and injury mechanism. Acknowledgments We thank all ESSKA colleagues who participated in the questionnaire and the ESSKA Sports committee colleagues for their feedback on the research protocol. Conflict of interest No competing interests or funding reported. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited. References 1. Allen GM (2007) Ultrasound in sports medicine a critical evaluation. Eur J Radiol 62: Arnason A, Gudmundsson A, Dahl HA, Jóhannsson E (1996) Soccer injuries in celand. Scand J Med Sci Sports 6: Arnason A, Andersen TE, Holme, Engebretsen L, Bahr R (2008) Prevention of hamstring strains in elite football: an intervention study. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18: Askling C, Saartok T, Thorstensson A (2006) Type of acute hamstring strain affects flexibility, strength, and time to return to pre-injury level. Br J Sports Med 40: Askling CM, Tengvar M, Saartok T, Thorstensson A (2007) Acute first-time hamstring strains during high-speed running: a longitudinal study including clinical and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Am J Sports Med 35: Askling CM, Tengvar M, Saartok T, Thorstensson A (2007) Acute first-time hamstring strains during slow-speed stretching: clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, and recovery characteristics. Am J Sports Med 35: Askling CM, Tengvar M, Saartok T, Thorstensson A (2008) Proximal hamstring strains of stretching type in different sports: injury situations, clinical and magnetic resonance imaging characteristics, and return to sport. Am J Sports Med 36: Bencardino JT, Mellado JM (2005) Hamstring injuries of the hip. Magn Reson maging Clin N Am 13: , vi 9. Blankenbaker D, De Smet AA (2004) MR-imaging of muscle injuries. Appl Rad 33: Brooks JH, Fuller CW, Kemp SP, Reddin DB (2006) ncidence, risk, and prevention of hamstring muscle injuries in professional rugby union. Am J Sports Med 34: Carling C, Le Gall F, Orhant E (2011) A four-season prospective study of muscle strain reoccurrences in a professional football club. Res Sports Med 19: Cohen S, Bradley J (2007) Acute proximal hamstring rupture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 15: Connell DA, Schneider-Kolsky ME, Hoving JL, Malara F, Buchbinder R, Koulouris G, Burke F, Bass C (2004) Longitudinal study comparing sonographic and MR assessments of acute and healing hamstring injuries. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183: Davis KW (2008) maging of the hamstrings. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 12: Ekstrand J, Gillquist J (1983) Socces injuries and their mechanisms: a prospective study. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15: Ekstrand J, Timpka T, Hägglund M (2006) Risk of injury in elite football played on artificial turf versus natural grass: a prospective two-cohort study. Br J Sports Med 40:
9 508 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: Ekstrand J, Hägglund M, Waldén M (2011) Epidemiology of muscle injuries in professional football (Soccer). Am J Sports Med 39: Ekstrand J, Hägglund M, Waldén M (2011) njury incidence and injury patterns in professional football the UEFA injury study. Br J Sports Med 45: Ekstrand J, Healy JC, Waldén M, Lee JC, English B, Hägglund M (2012) Hamstring muscle injuries in professional football: the correlation of MR findings with return to play. Br J Sports Med 46: Elliott MC, Zarins B, Powell JW, Kenyon CD (2011) Hamstring muscle strains in professional football players: a 10-year review. Am J Sports Med 39: Engebretsen AH, Myklebust G, Holme, Engebretsen L, Bahr R (2010) ntrinsic risk factors for hamstring injuries among male soccer players: a prospective cohort study. Am J Sports Med 38: Fleckenstein JL, Weatherall PT, Parkey RW, Payne JA, Peshock RM (1989) Sports-related muscle injuries: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiology 172: Fleckenstein JL, Shellock FG (1991) Exertional muscle injuries: magnetic resonance imaging evaluation. Top Magn Reson maging 3: Gibbs NJ, Cross TM, Cameron M, Houang MT (2004) The accuracy of MR in predicting recovery and recurrence of acute grade one hamstring muscle strains within the same season in Australian Rules football players. J Sci Med Sport 7: Gielen JL, Robinson P, an Dyck P, an der Stappen A, anhoenacker FM (2007) Muscle injuries. n: anhoenacker FM, Maas MM, Gielen JL (eds) maging of orthopedic sports injuries, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp Guerrero M, Guiu-Comadevall M, Cadefau JA, Parra J, Ballius R, Estruch A, Rodas G, Bedini JL, Cussó R (2008) Fast and slow myosins as markers of muscle injury. Br J Sports Med 42: Hägglund M, Waldén M, Ekstrand J (2006) Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons. Br J Sports Med 40: Hasson G, Keeney S, McKenna H (2000) Research guidelines for the Delphi survey technique. J Adv Nurs 32: Heiderscheit BC, Sherry MA, Silder A, Chumanov ES, Thelen DG (2010) Hamstring strain injuries: recommendations for diagnosis, rehabilitation, and injury prevention. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 40: Heiser TM, Weber J, Sullivan G, Clare P, Jacobs RR (1984) Prophylaxis and management of hamstring muscle injuries in intercollegiate football players. Am J Sports Med 12: Klingele KE, Sallay P (2002) Surgical repair of complete proximal hamstring tendon rupture. Am J Sports Med 30: Kornberg C, Lew P (1989) The effect of stretching neural structures on grade one hamstring injuries. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 10: Koulouris G, Connell D (2003) Evaluation of the hamstring muscle complex following acute injury. Skeletal Radiol 32: Koulouris G, Connell D (2005) Hamstring muscle complex: an imaging review. Radiographics 25: Koulouris G, Connell DA, Brukner P, Schneider-Kolsky M (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging parameters for assessing risk of recurrent hamstring injuries in elite athletes. Am J Sports Med 35: Lempainen L, Sarimo J, Heikkila J, Mattila K, Orava S (2007) Distal tears of the hamstring muscles: review of the literature and our results of surgical treatment. Br J Sports Med 41: Liemohn W, Martin SB, Pariser GL (1997) The effect of ankle posture on sit-and-reach test performance. J Strength Cond Res 11: Malliaropoulos N, Papacostas E, Kiritsi O, Papalada A, Gougoulias N, Maffulli N (2010) Posterior thigh muscle injuries in elite track and field athletes. Am J Sports Med 38: Malliaropoulos N, sinkaye T, Tsitas K, Maffulli N (2011) Reinjury after acute posterior thigh muscle injuries in elite track and field athletes. Am J Sports Med 39: Martínez Amat A, Marchal Corrales JA, Rodríguez Serrano F, Boulaiz H, Prados Salazar JC, Hita Contreras F, Caba Perez O, Carrillo Delgado E, Martiín, Aranega Jimenez A (2007) Role of alpha-actin in muscle damage of injured athletes in comparison with traditional markers. Br J Sports Med 41: Miñarro PA, Andújar PS, García PL, Toro EO (2007) A comparison of the spine posture among several sit-and-reach test protocols. J Sci Med Sport 10: Nikolaou PK, Macdonald BL, Glisson RR, Seaber A, Garrett WE Jr (1987) Biomechanical and histological evaluation of muscle after controlled strain injury. Am J Sports Med 15: Orchard J, Seward H (2002) Epidemiology of injuries in the Australian Football League, seasons Br J Sports Med 36: Orchard JW, Farhart P, Leopold C (2004) Lumbar spine region pathology and hamstring and calf injuries in athletes: is there a connection? Br J Sports Med 38: Peetrons P (2002) Ultrasound of muscles. Eur Radiol 12: Petersen J, Thorborg K, Nielsen MB, Hölmich P (2010) Acute hamstring injuries in Danish elite football: a 12-month prospective registration study among 374 players. Scand J Med Sci Sports 20: Puranen J, Orava S (1988) The hamstring syndrome. A new diagnosis of gluteal sciatic pain. Am J Sports Med 16: Sallay P, Friedman RL, Coogan PG, Garrett WE (1996) Hamstring muscle injuries among water skiers. Functional outcome and prevention. Am J Sports Med 24: Sarimo J, Lempainen L, Mattila K, Orava S (2008) Complete proximal hamstring avulsions: a series of 41 patients with operative treatment. Am J Sports Med 36: Schneider-Kolsky ME, Hoving JL, Warren P, Connell DA (2006) A comparison between clinical assessment and magnetic resonance imaging of acute hamstring injuries. Am J Sports Med 34: Schneider-Kolsky M, Warren P, Connell D (2007) Author s reply on comment on: a comparison between clinical assessment and magnetic resonance imaging of acute hamstring injuries. Am J Sports Med 35: Seward H, Orchard J, Hazard H, Collinson D (1993) Football injuries in Australia at the elite level. Med J Aust 159: Shellock FG, Fleckenstein JL (2000) Muscle physiology and pathophysiology: magnetic resonance imaging evaluation. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 4: Slavotinek JP, errall GM, Fon GT (2002) Hamstring injury in athletes: using MR imaging measurements to compare extent of muscle injury with amount of time lost from competition. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179: Sorichter S, Mair J, Koller A, Gebert W, Rama D, Calzolari C, Artner-Dworzak E, Puschendorf B (1997) Skeletal troponin as a marker of exercise-induced muscle damage. J Appl Physiol 83: errall GM, Slavotinek JP, Barnes PG, Fon GT, Spriggins AJ (2001) Clinical risk factors for hamstring muscle strain injury: a prospective study with correlation of injury by magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Sports Med 35: errall GM, Slavotinek JP, Barnes PG, Fon GT (2003) Diagnostic and prognostic value of clinical findings in 83 athletes with posterior thigh injury: comparison of clinical findings with magnetic resonance imaging documentation of hamstring muscle strain. Am J Sports Med 31:
10 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2013) 21: errall GM, Slavotinek JP, Barnes PG, Fon GT, Esterman A (2006) Assessment of physical examination and magnetic resonance imaging findings of hamstring injury as predictors for recurrent injury. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 36: olpi P, Melegati G, Tornese D, Bandi M (2004) Muscle strains in soccer: a five-year survey of an talian major league team. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 12: Walden M, Hagglund M, Ekstrand J (2005) UEFA champions League study: a prospective study of injuries in professional football during the season. Br J Sports Med 39: Warren P, Gabbe BJ, Schneider-Kolsky M, Bennell KL (2010) Clinical predictors of time to return to competition and of recurrence following hamstring strain in elite Australian footballers. Br J Sports Med 44: Wood DG, Packham, Trikha SP, Linklater J (2008) Avulsion of the proximal hamstring origin. J Bone Jt Surg Am 90: Woods C, Hawkins R, Hulse M, Hodson A (2002) The football association medical research programme: an audit of injuries in professional football-analysis of preseason injuries. Br J Sports Med 36: Woods C, Hawkins RD, Maltby S, Hulse M, Thomas A, Hodson A (2004) The football association medical research programme: an audit of injuries in professional football analysis of hamstring injuries. Br J Sports Med 38: Yeung SS, Suen AM, Yeung EW (2009) A prospective cohort study of hamstring injuries in competitive sprinters: preseason muscle imbalance as a possible risk factor. Br J Sports Med 43: Zeren B, Oztekin HH (2006) A new self-diagnostic test for biceps femoris muscle strains. Clin J Sport Med 16:
Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair
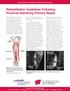 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair The hamstring muscle group consists of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus.
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair The hamstring muscle group consists of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus.
The correlation between the imaging characteristics of hamstring injury and time required before returning to sports: a literature review
 Review Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2016;12(3):134-142 The correlation between the imaging characteristics of hamstring injury and time returning to sports: a literature review Kjell Svensson
Review Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2016;12(3):134-142 The correlation between the imaging characteristics of hamstring injury and time returning to sports: a literature review Kjell Svensson
T his review is based on computerised searches
 319 REVIEW Evidence based prevention of hamstring injuries in sport J Petersen, P Hölmich... A common soft tissue injury in sports involving sprinting and jumping is the hamstring strain. A major problem
319 REVIEW Evidence based prevention of hamstring injuries in sport J Petersen, P Hölmich... A common soft tissue injury in sports involving sprinting and jumping is the hamstring strain. A major problem
Original article. Muscle injuries in Chilean professional soccer players
 ABSTRACT Muscle injuries in Chilean professional soccer players N. Garcίa 1, C. Sáez 2, J. P. Guarachi 3, J. Rosales 4, M. Verdugo 4, R. Yáñez 2 1Clínica Meds, Santiago, Chile. Sports Medicine Department
ABSTRACT Muscle injuries in Chilean professional soccer players N. Garcίa 1, C. Sáez 2, J. P. Guarachi 3, J. Rosales 4, M. Verdugo 4, R. Yáñez 2 1Clínica Meds, Santiago, Chile. Sports Medicine Department
Hamstring muscle injuries in professional football: the correlation of MRI findings with return to play
 Hamstring muscle injuries in professional football: the correlation of MRI findings with return to play Jan Ekstrand, Jeremiah C Healy, Markus Waldén, Justin C Lee, Bryan English and Martin Hägglund Linköping
Hamstring muscle injuries in professional football: the correlation of MRI findings with return to play Jan Ekstrand, Jeremiah C Healy, Markus Waldén, Justin C Lee, Bryan English and Martin Hägglund Linköping
Hamstring injuries in professional football players: magnetic resonance imaging correlation with return to play.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Rothman Institute Rothman Institute 9-1-2011 Hamstring injuries in professional football players: magnetic resonance imaging correlation with return
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Rothman Institute Rothman Institute 9-1-2011 Hamstring injuries in professional football players: magnetic resonance imaging correlation with return
Injury rate, mechanism, and risk factors of hamstring strain injuries in sports: A review of the literature
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Sport and Health Science 1 (2012) 92e101 Review Injury rate, mechanism, and risk factors of hamstring strain injuries in sports: A review of the literature
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Sport and Health Science 1 (2012) 92e101 Review Injury rate, mechanism, and risk factors of hamstring strain injuries in sports: A review of the literature
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Parameters for Assessing Risk of Recurrent Hamstring Injuries in Elite Athletes
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Parameters for Assessing Risk of Recurrent Hamstring Injuries in Elite Athletes George Koulouris, * FRANZCR, David A. Connell, FRANZCR, Peter Brukner, FACSP, and Michal Schneider-Kolsky,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Parameters for Assessing Risk of Recurrent Hamstring Injuries in Elite Athletes George Koulouris, * FRANZCR, David A. Connell, FRANZCR, Peter Brukner, FACSP, and Michal Schneider-Kolsky,
Clinical predictors of time to return to competition and of recurrence following hamstring strain in elite Australian footballers
 Clinical predictors of time to return to competition and of recurrence following hamstring strain in elite Australian footballers Price Warren 1, Belinda J Gabbe 2, Michal SchneiderKolsky 3, Kim L Bennell
Clinical predictors of time to return to competition and of recurrence following hamstring strain in elite Australian footballers Price Warren 1, Belinda J Gabbe 2, Michal SchneiderKolsky 3, Kim L Bennell
A cute hamstring strains are common injuries in sport.1
 4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Type of acute hamstring strain affects flexibility, strength, and time to return to pre-injury level C Askling, T Saartok, A Thorstensson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Type of acute hamstring strain affects flexibility, strength, and time to return to pre-injury level C Askling, T Saartok, A Thorstensson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
NORDIC HAMSTRING PROGRAM
 NORDIC HAMSTRING PROGRAM Injury Prevention Sport Med 18 January 26 Dave Wright CAT(c) University of Guelph Hamstring Injury Prevention Injury Prevention: Evidence Based Literature Hamstring injuries are
NORDIC HAMSTRING PROGRAM Injury Prevention Sport Med 18 January 26 Dave Wright CAT(c) University of Guelph Hamstring Injury Prevention Injury Prevention: Evidence Based Literature Hamstring injuries are
Original article. high risk of sustaining a reinjury. Sports Medicine Hospital, Doha, Qatar
 Editor s choice Scan to access more free content 1 Aspetar Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital, Doha, Qatar 2 Department of Sports Medicine, Oslo Sports Trauma Research Center, Norwegian School of
Editor s choice Scan to access more free content 1 Aspetar Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital, Doha, Qatar 2 Department of Sports Medicine, Oslo Sports Trauma Research Center, Norwegian School of
MR observations of long-term musculotendon remodeling following a hamstring strain injury
 Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:1101 1109 DOI 10.1007/s00256-008-0546-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE MR observations of long-term musculotendon remodeling following a hamstring strain injury Amy Silder & Bryan C. Heiderscheit
Skeletal Radiol (2008) 37:1101 1109 DOI 10.1007/s00256-008-0546-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE MR observations of long-term musculotendon remodeling following a hamstring strain injury Amy Silder & Bryan C. Heiderscheit
The predictive validity of a single leg bridge test for hamstring injuries in Australian Rules Football Players
 Editor s choice Scan to access more free content 1 Department of Physiotherapy, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 2 Department of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Monash University,
Editor s choice Scan to access more free content 1 Department of Physiotherapy, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 2 Department of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Monash University,
Return to play after thigh muscle injury in elite football players: implementation and validation of the Munich muscle injury classification
 Return to play after thigh muscle injury in elite football players: implementation and validation of the Munich muscle injury classification The Harvard community has made this article openly available.
Return to play after thigh muscle injury in elite football players: implementation and validation of the Munich muscle injury classification The Harvard community has made this article openly available.
Hamstring strains and prevention
 Research Center of Movement Science Department of Physiotherapy University of Iceland UIVERSITY OF ICELAD DEPARTMET OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Hamstring strains and prevention Árni Árnason PT, PhD University of
Research Center of Movement Science Department of Physiotherapy University of Iceland UIVERSITY OF ICELAD DEPARTMET OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Hamstring strains and prevention Árni Árnason PT, PhD University of
That Tricky Hamstring. Ulrik Sandstrøm
 That Tricky Hamstring Ulrik Sandstrøm Language Experience Audience Roadmap Incidence and risk factors When it s not a hamstring Assessment Incl practical Treatment Incl practical Management Incl R2P protocols
That Tricky Hamstring Ulrik Sandstrøm Language Experience Audience Roadmap Incidence and risk factors When it s not a hamstring Assessment Incl practical Treatment Incl practical Management Incl R2P protocols
Manual or exercise therapy for long-standing adductor-related groin pain: Mid-term follow-up of a randomised controlled clinical trial
 Manual or exercise therapy for long-standing adductor-related groin pain: Mid-term follow-up of a randomised controlled clinical trial Weir A 1, Jansen N 2, Dijkstra SD 3, Backx FJG 4, Tol JL 1 1Aspetar
Manual or exercise therapy for long-standing adductor-related groin pain: Mid-term follow-up of a randomised controlled clinical trial Weir A 1, Jansen N 2, Dijkstra SD 3, Backx FJG 4, Tol JL 1 1Aspetar
Can a Clinical Examination Demonstrate Intramuscular Tendon Involvement in Acute Hamstring Injuries?
 Original Research Can a Clinical Examination Demonstrate Intramuscular Tendon Involvement in Acute Hamstring Injuries? Michel D. Crema,* MD, Ali Guermazi, MD, PhD, Gustaaf Reurink, MD, PhD, Frank W. Roemer,
Original Research Can a Clinical Examination Demonstrate Intramuscular Tendon Involvement in Acute Hamstring Injuries? Michel D. Crema,* MD, Ali Guermazi, MD, PhD, Gustaaf Reurink, MD, PhD, Frank W. Roemer,
Surgical Management of Recurrent Musculotendinous Hamstring Injury in Professional Athletes
 Original Research Surgical Management of Recurrent Musculotendinous Hamstring Injury in Professional Athletes Bertrand Sonnery-Cottet,* MD, Matt Daggett, DO/MBA, Roland Gardon, MD, Barbara Pupim, MD, Julien
Original Research Surgical Management of Recurrent Musculotendinous Hamstring Injury in Professional Athletes Bertrand Sonnery-Cottet,* MD, Matt Daggett, DO/MBA, Roland Gardon, MD, Barbara Pupim, MD, Julien
Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons
 Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons Martin Hägglund, Markus Waldén and Jan Ekstrand Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When
Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons Martin Hägglund, Markus Waldén and Jan Ekstrand Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Thigh muscles injuries in professional soccer players: a one year longitudinal study. Original article.
 Thigh muscles injuries in professional soccer players: a one year longitudinal study Angelo Corazza 1 Davide Orlandi 1 Amedeo Baldari 2 Pietro Gatto 3,4 Marco Stellatelli 4 Claudio Mazzola 5 Roberto Galli
Thigh muscles injuries in professional soccer players: a one year longitudinal study Angelo Corazza 1 Davide Orlandi 1 Amedeo Baldari 2 Pietro Gatto 3,4 Marco Stellatelli 4 Claudio Mazzola 5 Roberto Galli
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
Imaging Diagnosis and Prognostication of Hamstring Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Rubin Hamstring Injuries Musculoskeletal Imaging Review David. Rubin 1 Rubin D FOCUS ON: Keywords: avulsion, hamstring, injury, muscle, strain DOI:10.2214/JR.12.8784 Received
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Rubin Hamstring Injuries Musculoskeletal Imaging Review David. Rubin 1 Rubin D FOCUS ON: Keywords: avulsion, hamstring, injury, muscle, strain DOI:10.2214/JR.12.8784 Received
Endoscopic Hamstring Repair and Ischial Bursectomy. Carlos A. Guanche, MD Southern California Orthopedic Institute
 Endoscopic Hamstring Repair and Ischial Bursectomy Carlos A. Guanche, MD Southern California Orthopedic Institute cguanche@scoi.com 1 Endoscopic Hamstring Repair and Ischial Bursectomy INTRODUCTION Hamstring
Endoscopic Hamstring Repair and Ischial Bursectomy Carlos A. Guanche, MD Southern California Orthopedic Institute cguanche@scoi.com 1 Endoscopic Hamstring Repair and Ischial Bursectomy INTRODUCTION Hamstring
A pilot randomised controlled trial of eccentric exercise to prevent hamstring injuries in community-level Australian Football
 Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport (2006) 9, 103 109 ORIGINAL PAPER A pilot randomised controlled trial of eccentric exercise to prevent hamstring injuries in community-level Australian Football
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport (2006) 9, 103 109 ORIGINAL PAPER A pilot randomised controlled trial of eccentric exercise to prevent hamstring injuries in community-level Australian Football
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bayer ML, Magnusson SP, Kjaer M. Early versus delayed rehabilitation
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bayer ML, Magnusson SP, Kjaer M. Early versus delayed rehabilitation
Hamstring Injury: When to Consider Surgical Treatment
 Hamstring Injury: When to Consider Surgical Treatment Prof. dr. Gino Kerkhoffs Orthopaedic Surgery www.acesamsterdam.nl Gino Kerkhoffs Hans Tol Guus Reurink Mario Maas Pau Golanó Rolf Peters Maarten Moen
Hamstring Injury: When to Consider Surgical Treatment Prof. dr. Gino Kerkhoffs Orthopaedic Surgery www.acesamsterdam.nl Gino Kerkhoffs Hans Tol Guus Reurink Mario Maas Pau Golanó Rolf Peters Maarten Moen
The hamstring muscle group consists of the biceps
 Technical Note Endoscopic Repair of Proximal Hamstring Avulsion Benjamin G. Domb, M.D., Dror Linder, M.D., Kinzie G. Sharp, M.S., P.A.-C., Adam Sadik, B.S., and Michael B. Gerhardt, M.D. Abstract: Hamstring
Technical Note Endoscopic Repair of Proximal Hamstring Avulsion Benjamin G. Domb, M.D., Dror Linder, M.D., Kinzie G. Sharp, M.S., P.A.-C., Adam Sadik, B.S., and Michael B. Gerhardt, M.D. Abstract: Hamstring
IMAGING OF LOWER LIMB MUSCLE INJURY Written by Justin Lee and Jeremiah Healy, UK
 SPORTS RADIOLOGY IMAGING OF LOWER LIMB MUSCLE INJURY Written by Justin Lee and Jeremiah Healy, UK Sports-related skeletal muscle injuries are a common cause of loss of playing time in both the amateur
SPORTS RADIOLOGY IMAGING OF LOWER LIMB MUSCLE INJURY Written by Justin Lee and Jeremiah Healy, UK Sports-related skeletal muscle injuries are a common cause of loss of playing time in both the amateur
MR Imaging of the Distribution and Location of Acute Hamstring Injuries in Athletes
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.197.176 on 2/4/18 from IP address 46.3.197.176. Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Arthur A. De Smet 1 Thomas M. Best 2 Received May 3,
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.197.176 on 2/4/18 from IP address 46.3.197.176. Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Arthur A. De Smet 1 Thomas M. Best 2 Received May 3,
The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2018) 17, 650-655 http://www.jssm.org ` Research article The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running Gaku Tokutake 1, Rieko Kuramochi
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2018) 17, 650-655 http://www.jssm.org ` Research article The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running Gaku Tokutake 1, Rieko Kuramochi
Hospital NEO,Turku, Finland
 Hamstring syndrome from fibrous band to tendinosis Sakari Orava, Janne Sarimo, Lasse Lempainen, Jyrki Heinänen Hospital NEO,Turku, Finland 1 Hamstring muscles- ANATOMY over two big joints pelvic stabilizers
Hamstring syndrome from fibrous band to tendinosis Sakari Orava, Janne Sarimo, Lasse Lempainen, Jyrki Heinänen Hospital NEO,Turku, Finland 1 Hamstring muscles- ANATOMY over two big joints pelvic stabilizers
To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player
 To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player Hembre, A. 1 and Eriksrud, O. 2 1 Apex klinikken, Oslo, Norway 2 1080 Motion AB, Stockholm, Sweden
To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player Hembre, A. 1 and Eriksrud, O. 2 1 Apex klinikken, Oslo, Norway 2 1080 Motion AB, Stockholm, Sweden
Hamstring Strain. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
HIP CASESTUDY 3. Body Chart-Initial Hypothesis: Property of VOMPTI, LLC. For Use of Participants Only. No Use or Reproduction Without Consent 1
 Body Chart-Initial Hypothesis: HIP CASESTUDY 3 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT OCS FAAOMPT Hamstring Strain HS Tendinopathy Lumbar Radiculopathy Lumbar
Body Chart-Initial Hypothesis: HIP CASESTUDY 3 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT OCS FAAOMPT Hamstring Strain HS Tendinopathy Lumbar Radiculopathy Lumbar
Distal Musculotendinous T Junction Injuries of the Biceps Femoris
 Original Research Distal Musculotendinous T Junction Injuries of the Biceps Femoris An MRI Case Review Tom Entwisle,* BSc, MBBS, FRANZCR, Yuan Ling, MBBS, FRANZCR, Alex Splatt, MBBS, FRANZCR, Peter Brukner,
Original Research Distal Musculotendinous T Junction Injuries of the Biceps Femoris An MRI Case Review Tom Entwisle,* BSc, MBBS, FRANZCR, Yuan Ling, MBBS, FRANZCR, Alex Splatt, MBBS, FRANZCR, Peter Brukner,
1. Malliaropoulos N, Papacostas E, Kiritsi O, et al. Posterior thigh muscle injuries in elite track
 References: 1. Malliaropoulos N, Papacostas E, Kiritsi O, et al. Posterior thigh muscle injuries in elite track and field athletes.am J Sports Med. 2010; 38(9):1813-9. 2. Askling, CM, Tengvar, M, Saartok,
References: 1. Malliaropoulos N, Papacostas E, Kiritsi O, et al. Posterior thigh muscle injuries in elite track and field athletes.am J Sports Med. 2010; 38(9):1813-9. 2. Askling, CM, Tengvar, M, Saartok,
Surgical repair of complete proximal hamstring tendon ruptures in water- skiers. and bull riders: A report of four cases and review of the literature.
 Surgical repair of complete proximal hamstring tendon ruptures in water- skiers and bull riders: A report of four cases and review of the literature. Key Words Proximal hamstring ruptures Surgical repair
Surgical repair of complete proximal hamstring tendon ruptures in water- skiers and bull riders: A report of four cases and review of the literature. Key Words Proximal hamstring ruptures Surgical repair
H amstring injuries are common in sprinting, dancing,
 106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for hamstring injuries in community level Australian football B J Gabbe, C F Finch, K L Bennell, H Wajswelner... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
106 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk factors for hamstring injuries in community level Australian football B J Gabbe, C F Finch, K L Bennell, H Wajswelner... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Clinical recovery of two hip adductor longus ruptures: a case-report of a soccer player
 Thorborg et al. BMC Research Notes 2013, 6:205 CASE REPORT Open Access Clinical recovery of two hip adductor longus ruptures: a case-report of a soccer player Kristian Thorborg 1,2*, Jesper Petersen 3,
Thorborg et al. BMC Research Notes 2013, 6:205 CASE REPORT Open Access Clinical recovery of two hip adductor longus ruptures: a case-report of a soccer player Kristian Thorborg 1,2*, Jesper Petersen 3,
Asymmetry after Hamstring Injury in English Premier League: Issue Resolved, Or Perhaps Not?
 Asymmetry after Hamstring Injury in English Premier League: Issue Resolved, Or Perhaps Not? Authors P. Barreira 1, B. Drust 2, M. A. Robinson 1, J. Vanrenterghem 3 Affiliations Key words horizontal force
Asymmetry after Hamstring Injury in English Premier League: Issue Resolved, Or Perhaps Not? Authors P. Barreira 1, B. Drust 2, M. A. Robinson 1, J. Vanrenterghem 3 Affiliations Key words horizontal force
Lower Limb. Hamstring Strains. Risk Factors. Dr. Peter Friis 27/04/15. 16% missed games AFL 6-15% injury in rugby 30% recurrent
 Lower Limb Dr. Peter Friis MB BS FACSP Sports Physician Hamstring Strains 16% missed games AFL 6-15% injury in rugby 30% recurrent Risk Factors Modifiable Warm up Fatigue Strength Flexibility L/Spine Pelvic
Lower Limb Dr. Peter Friis MB BS FACSP Sports Physician Hamstring Strains 16% missed games AFL 6-15% injury in rugby 30% recurrent Risk Factors Modifiable Warm up Fatigue Strength Flexibility L/Spine Pelvic
Dominic Carreira M.D. Matt Kruchten, B.S. Fort Lauderdale, FL
 Dominic Carreira M.D. Matt Kruchten, B.S Fort Lauderdale, FL Disclosures ConMed Linvatec: Consulting and Education Zimmer Biomet Consulting and Education Royalties for Product Development The hamstring
Dominic Carreira M.D. Matt Kruchten, B.S Fort Lauderdale, FL Disclosures ConMed Linvatec: Consulting and Education Zimmer Biomet Consulting and Education Royalties for Product Development The hamstring
Different thigh muscle activation distribution after two specific eccentric exercises: evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging
 Different thigh muscle activation distribution after two specific eccentric exercises: evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging Poster No.: C-2025 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: F.
Different thigh muscle activation distribution after two specific eccentric exercises: evaluation by magnetic resonance imaging Poster No.: C-2025 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: F.
The Effects of a Closed-Chain, Eccentric Training Program on Hamstring Injuries of a Professional Football Cheerleading Team
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Nursing Faculty Research and Publications Nursing, College of 3-1-2011 The Effects of a Closed-Chain, Eccentric Training Program on Hamstring Injuries of a
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Nursing Faculty Research and Publications Nursing, College of 3-1-2011 The Effects of a Closed-Chain, Eccentric Training Program on Hamstring Injuries of a
 p< e-mail: m.abbaszadeh@mubabol.ac.ir strain gauge (repeatability) (accuracy) SG110 EMG SENIAM ASIS Biodex Medical System, Inc., Shirley, New York, Drouin Biometrics (EMG) DataLog RMS Band pass filter:
p< e-mail: m.abbaszadeh@mubabol.ac.ir strain gauge (repeatability) (accuracy) SG110 EMG SENIAM ASIS Biodex Medical System, Inc., Shirley, New York, Drouin Biometrics (EMG) DataLog RMS Band pass filter:
Title: Hamstring strength and flexibility after hamstring strain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Title: Hamstring strength and flexibility after hamstring strain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Title: Hamstring strength and flexibility after hamstring strain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Clinical risk factors for hamstring muscle strain injury: a prospective study with correlation of injury by magnetic resonance imaging
 Br J Sports Med 2001;35:435 440 435 SPORTSMED.SA Sports Medicine Clinic, Adelaide, Australia G M Verrall P G Barnes A J Spriggins Department of Medical Imaging, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide J P Slavotinek
Br J Sports Med 2001;35:435 440 435 SPORTSMED.SA Sports Medicine Clinic, Adelaide, Australia G M Verrall P G Barnes A J Spriggins Department of Medical Imaging, Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide J P Slavotinek
What have we learnt? Direct trauma is common in contact sports such as soccer, rugby, football and martial arts SPORTS MEDICINE
 SPORTS MEDICINE DEFINITION OF ACUTE MUSCLE INJURY What have we learnt? Written by Angelo Del Buono, Chiara Sernia and Nicola Maffulli, Italy Muscle strains occur most often at the musculotendinous junction
SPORTS MEDICINE DEFINITION OF ACUTE MUSCLE INJURY What have we learnt? Written by Angelo Del Buono, Chiara Sernia and Nicola Maffulli, Italy Muscle strains occur most often at the musculotendinous junction
Muscle Injuries Clinical Guide 3.0
 January 2015 1 CONTENTS: CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION (p. 4) CHAPTER 2: EPIDEMIOLOGY (p.5) 2.1. Injury Definition and Severity 2.2. Epidemiology of Muscle Injuries in Football 2.2.1. Incidence and Prevalence
January 2015 1 CONTENTS: CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION (p. 4) CHAPTER 2: EPIDEMIOLOGY (p.5) 2.1. Injury Definition and Severity 2.2. Epidemiology of Muscle Injuries in Football 2.2.1. Incidence and Prevalence
Eccentric Knee-flexor Strength and Risk of Hamstring Injuries in Rugby Union: A
 1 TITLE 2 3 Eccentric Knee-flexor Strength and Risk of Hamstring Injuries in Rugby Union: A Prospective Study 4 5 6 Authors 7 Matthew N. Bourne 1, David A. Opar 2, Morgan D. Williams 3, Anthony J. Shield
1 TITLE 2 3 Eccentric Knee-flexor Strength and Risk of Hamstring Injuries in Rugby Union: A Prospective Study 4 5 6 Authors 7 Matthew N. Bourne 1, David A. Opar 2, Morgan D. Williams 3, Anthony J. Shield
Acute proximal hamstring rupture
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery June 2007 Acute proximal hamstring rupture Steven B. Cohen Thomas
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery June 2007 Acute proximal hamstring rupture Steven B. Cohen Thomas
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Engebretsen, A. H., Myklebust, G., Holme, I., Engebretsen, L., Bahr, R. (2010). Intrinsic risk factors for hamstring
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Engebretsen, A. H., Myklebust, G., Holme, I., Engebretsen, L., Bahr, R. (2010). Intrinsic risk factors for hamstring
The effect of hamstring flexibility on peak hamstring muscle strain in sprinting
 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Sport and Health Science 6 (2017) 283 289 Original article The effect of hamstring flexibility on peak hamstring muscle strain
HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Sport and Health Science 6 (2017) 283 289 Original article The effect of hamstring flexibility on peak hamstring muscle strain
Prior et al Mar Apr An Evidence-Based Approach to Hamstring Strain Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature
 [ Athletic Training ] An Evidence-Based Approach to Hamstring Strain Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature Mathew Prior, B Physiotherapy (Hons),* Michelle Guerin, B Physiotherapy (Hons), and Karen
[ Athletic Training ] An Evidence-Based Approach to Hamstring Strain Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature Mathew Prior, B Physiotherapy (Hons),* Michelle Guerin, B Physiotherapy (Hons), and Karen
Objectives. Sprains, Strains, and Musculoskeletal Maladies. Sprains. Sprains. Sprains. Physical Exam 5/5/2010
 Objectives, Strains, and Musculoskeletal Maladies Robert Hosey, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine Define sprains and strains Systematically evaluate and manage joint / muscle injuries When to refer
Objectives, Strains, and Musculoskeletal Maladies Robert Hosey, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine Define sprains and strains Systematically evaluate and manage joint / muscle injuries When to refer
What we ll cover... Two types of hamstring injury! What type of athletes tear hamstrings!
 What s'new'in'hamstring'strain' injury'prevention'&'rehabilitation? Craig Ranson PhD Programme Director MSc Sports & Exercise Medicine Cardiff Metropolitan University Wales Rugby Team Physiotherapist @craigarxl
What s'new'in'hamstring'strain' injury'prevention'&'rehabilitation? Craig Ranson PhD Programme Director MSc Sports & Exercise Medicine Cardiff Metropolitan University Wales Rugby Team Physiotherapist @craigarxl
The effectiveness of different exercises protocols to prevent the incidence of hamstring injury in athletes
 Page 1 of 6 Training, Performance & Rehabilitation The effectiveness of different exercises protocols to prevent the incidence of hamstring injury in athletes F Naclerio*, M Goss-Sampson Abstract Introduction
Page 1 of 6 Training, Performance & Rehabilitation The effectiveness of different exercises protocols to prevent the incidence of hamstring injury in athletes F Naclerio*, M Goss-Sampson Abstract Introduction
HAMSTRING STRAIN INJURY
 HAMSTRING STRAIN INJURY The role of strength & voluntary activation Matthew N. Bourne B. App Sci. HMS. (Hons) 2016 Doctor of Philosophy (Thesis by publication) School of Exercise and Nutrition Sciences
HAMSTRING STRAIN INJURY The role of strength & voluntary activation Matthew N. Bourne B. App Sci. HMS. (Hons) 2016 Doctor of Philosophy (Thesis by publication) School of Exercise and Nutrition Sciences
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 May 11.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010 February ; 40(2): 67 81. doi:10.2519/jospt.2010.3047. Hamstring Strain Injuries: Recommendations for
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010 February ; 40(2): 67 81. doi:10.2519/jospt.2010.3047. Hamstring Strain Injuries: Recommendations for
Acute muscle strain injuries: a proposed new classification system
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-012-2118-z SPORTS MEDICINE Acute muscle strain injuries: a proposed new classification system Otto Chan Angelo Del Buono Thomas M. Best Nicola Maffulli Received: 29 March 2012 / Accepted:
DOI 10.1007/s00167-012-2118-z SPORTS MEDICINE Acute muscle strain injuries: a proposed new classification system Otto Chan Angelo Del Buono Thomas M. Best Nicola Maffulli Received: 29 March 2012 / Accepted:
Time for a paradigm shift in the classification of muscle injuries
 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Sport and Health Science 6 (2017) 255 261 Review Time for a paradigm shift in the classification of muscle injuries Bruce Hamilton
HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Sport and Health Science 6 (2017) 255 261 Review Time for a paradigm shift in the classification of muscle injuries Bruce Hamilton
Criteria for progressing rehabilitation and determining return to play clearance following hamstring strain injury
 1 2 3 Title: Criteria for progressing rehabilitation and determining return to play clearance following hamstring strain injury: A systematic review 4 5 6 7 8 Authors: Jack T. Hickey 1, Ryan G. Timmins
1 2 3 Title: Criteria for progressing rehabilitation and determining return to play clearance following hamstring strain injury: A systematic review 4 5 6 7 8 Authors: Jack T. Hickey 1, Ryan G. Timmins
Ultrasound and MRI Findings of Tennis Leg with Differential Diagnosis.
 Ultrasound and MRI Findings of Tennis Leg with Differential Diagnosis. Poster No.: R-0057 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. George, A. Thomas, R. Dutta, K. Gummalla; Singapore/SG
Ultrasound and MRI Findings of Tennis Leg with Differential Diagnosis. Poster No.: R-0057 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. George, A. Thomas, R. Dutta, K. Gummalla; Singapore/SG
Hamstring Injuries and Avulsions. Charles A. Bush-Joseph, MD Rush University Medical Center Team Physician, Chicago White Sox Chicago, IL
 Hamstring Injuries and Avulsions Charles A. Bush-Joseph, MD Rush University Medical Center Team Physician, Chicago White Sox Chicago, IL Disclosures No personal disclosures on this topic Institutional
Hamstring Injuries and Avulsions Charles A. Bush-Joseph, MD Rush University Medical Center Team Physician, Chicago White Sox Chicago, IL Disclosures No personal disclosures on this topic Institutional
Accuracy of Three Clinical Tests to Diagnose Hamstring Syndrome in Pa:ents with Posterior Hip Pain.
 Accuracy of Three Clinical Tests to Diagnose Hamstring Syndrome in Pa:ents with Posterior Hip Pain. Ricardo G. Schröder, PT 1 ; RobRoy L Mar8n, PT PhD 2 ; Juan Gomez-Hoyos, MD 1,3 ; Anthony Khoury M.Sc.
Accuracy of Three Clinical Tests to Diagnose Hamstring Syndrome in Pa:ents with Posterior Hip Pain. Ricardo G. Schröder, PT 1 ; RobRoy L Mar8n, PT PhD 2 ; Juan Gomez-Hoyos, MD 1,3 ; Anthony Khoury M.Sc.
Semimembranosus Muscle Injuries In Sport. A Practical MRI use for Prognosis
 Semimembranosus Muscle Injuries In Sport. A Practical MRI use for Prognosis Authors Ramon Balius 1, Mireia Bossy 2, Carles Pedret 1, Lluís Capdevila 3, Xavier Alomar 4, Bryan Heiderscheit 5, Gil Rodas
Semimembranosus Muscle Injuries In Sport. A Practical MRI use for Prognosis Authors Ramon Balius 1, Mireia Bossy 2, Carles Pedret 1, Lluís Capdevila 3, Xavier Alomar 4, Bryan Heiderscheit 5, Gil Rodas
Hams t r ing s t r ain injur ie s: ar e we heading in the right direction?
 Hams t r ing s t r ain injur ie s: ar e we heading in the right direction? Jurd an M endiguchia, 1 Edu ard A len tor n - G eli, 2 M a t t B r ughelli 3 Acute hamstring injuries are the most prevalent muscle
Hams t r ing s t r ain injur ie s: ar e we heading in the right direction? Jurd an M endiguchia, 1 Edu ard A len tor n - G eli, 2 M a t t B r ughelli 3 Acute hamstring injuries are the most prevalent muscle
Apophysis. Apophyseal Avulsion. Apophyseal avulsion injuries 3/2/2017
 Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
Can therapeutic ultrasound accurately detect bone stress injuries in athletes?
 Can therapeutic ultrasound accurately detect bone stress injuries in athletes? Author Beck, Belinda Ruth Published 2013 Journal Title Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine DOI https://doi.org/10.1097/jsm.0b013e3182926bda
Can therapeutic ultrasound accurately detect bone stress injuries in athletes? Author Beck, Belinda Ruth Published 2013 Journal Title Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine DOI https://doi.org/10.1097/jsm.0b013e3182926bda
MR DIAGNOSTICS OF MUSCLE TRAUMA. Ivo Nikolov, M.D., Radiologist - Spectar Imaging Centre, Sofia
 MR DIAGNOSTICS OF MUSCLE TRAUMA Ivo Nikolov, M.D., Radiologist - Spectar Imaging Centre, Sofia Мyofibrils Сonnective tissue Fibers - Endomysium Fascicle - Permysium Мuscle - Еpimysium Question of the
MR DIAGNOSTICS OF MUSCLE TRAUMA Ivo Nikolov, M.D., Radiologist - Spectar Imaging Centre, Sofia Мyofibrils Сonnective tissue Fibers - Endomysium Fascicle - Permysium Мuscle - Еpimysium Question of the
Case Studies: Low Back Pain in the Athlete. Jim Messerly DO
 Case Studies: Low Back Pain in the Athlete Jim Messerly DO Nothing to disclose Case #1 History 15 y/o male presents for evaluation of his low back pain. His pain has been present for several months. The
Case Studies: Low Back Pain in the Athlete Jim Messerly DO Nothing to disclose Case #1 History 15 y/o male presents for evaluation of his low back pain. His pain has been present for several months. The
Musculoskeletal problems in soccer players: current concepts
 Musculoskeletal problems in soccer players: current concepts Original article Umile Giuseppe Longo 1,2 Mattia Loppini 1,2 Roberta Cavagnino 1,2 Nicola Maffulli 3 Vincenzo Denaro 1,2 1 Specialization School
Musculoskeletal problems in soccer players: current concepts Original article Umile Giuseppe Longo 1,2 Mattia Loppini 1,2 Roberta Cavagnino 1,2 Nicola Maffulli 3 Vincenzo Denaro 1,2 1 Specialization School
Thoracolumbar Spine Conditions: Treatment and Return to Play
 Thoracolumbar Spine Conditions: Treatment and Return to Play C H R I S T O P H E R B U R K S, MD B I E N V I L L E O R T H O P A E D I C S P E C I A L I S T S O C E A N S P R I N G S, MS Thoracolumbar
Thoracolumbar Spine Conditions: Treatment and Return to Play C H R I S T O P H E R B U R K S, MD B I E N V I L L E O R T H O P A E D I C S P E C I A L I S T S O C E A N S P R I N G S, MS Thoracolumbar
Proximal Hamstring Tendon Repair
 Dr. Mark Price MGH Sports Medicine Center 175 Cambridge Street, 4th floor Boston, MA 02114 www.massgeneral.org/ortho-sports-medicine/dr-price Proximal Hamstring Tendon Repair The hamstrings are a group
Dr. Mark Price MGH Sports Medicine Center 175 Cambridge Street, 4th floor Boston, MA 02114 www.massgeneral.org/ortho-sports-medicine/dr-price Proximal Hamstring Tendon Repair The hamstrings are a group
Henderson, G. (Gary); Barnes, C. A. (Christopher); Portas, M. D. (Matthew)
 TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository Factors associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury in English Premier League soccer players Item type Authors Article Henderson, G. (Gary); Barnes,
TeesRep - Teesside's Research Repository Factors associated with increased propensity for hamstring injury in English Premier League soccer players Item type Authors Article Henderson, G. (Gary); Barnes,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know
 Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
Return to Play After Hamstring Injuries: A Qualitative Systematic Review of Definitions and Criteria
 Sports Med (2016) 46:899 912 DOI 10.1007/s40279-015-0468-7 SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Return to Play After Hamstring Injuries: A Qualitative Systematic Review of Definitions and Criteria Nick van der Horst 1 Sander
Sports Med (2016) 46:899 912 DOI 10.1007/s40279-015-0468-7 SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Return to Play After Hamstring Injuries: A Qualitative Systematic Review of Definitions and Criteria Nick van der Horst 1 Sander
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih
 This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bahr, R., Thorborg, K., Ekstrand, J. (2015). Evidence-based hamstring injury prevention is not adopted by the majority
This file was dowloaded from the institutional repository Brage NIH - brage.bibsys.no/nih Bahr, R., Thorborg, K., Ekstrand, J. (2015). Evidence-based hamstring injury prevention is not adopted by the majority
Rehabilitation After Hamstring-Strain Injury Emphasizing Eccentric Strengthening at Long Muscle Lengths: Results of Long-Term Follow-Up
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2017, 26, 131-140 http://dx.doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2015-0099 2017 Human Kinetics, Inc. ORIGINAL RESEARCH REPORT Rehabilitation After Hamstring-Strain Injury Emphasizing Eccentric
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2017, 26, 131-140 http://dx.doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2015-0099 2017 Human Kinetics, Inc. ORIGINAL RESEARCH REPORT Rehabilitation After Hamstring-Strain Injury Emphasizing Eccentric
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults
 What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
Injury profile among elite male youth soccer players in a Swedish first league
 Original Article 2005; Timpka et al., 2008). Van der Sluis et al. (2014) suggest that growth and maturation are potential risk factors for sport injury in talented soccer players. The period of maximal
Original Article 2005; Timpka et al., 2008). Van der Sluis et al. (2014) suggest that growth and maturation are potential risk factors for sport injury in talented soccer players. The period of maximal
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Rehabilitation of an ACL injury in a 29 year old male with closed kinetic chain exercises: A case study
 Abstract Objective: This paper will examine a rehabilitation program for a healthy 29 year old male who sustained an incomplete tear of the left ACL. Results: Following a 9 week treatment plan focusing
Abstract Objective: This paper will examine a rehabilitation program for a healthy 29 year old male who sustained an incomplete tear of the left ACL. Results: Following a 9 week treatment plan focusing
Development of a Functional Movement Screening Tool for Football
 Development of a Functional Movement Screening Tool for Football By Erin Morehead MSc Medicine and Science in Sport and Exercise BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment for the
Development of a Functional Movement Screening Tool for Football By Erin Morehead MSc Medicine and Science in Sport and Exercise BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment for the
D.O.I: http: doi.org/ /jbe ATHANASIOU HADJIMICHAEL MICHALIS 1 & STERGIOULAS APOSTOLOS 2
 VOLUME 12.1, 2016 D.O.I: http: doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2016.0104 Hamstring Strains in Football. Prevention and Rehabilitation Rules. Systematic Review. ATHANASIOU HADJIMICHAEL MICHALIS 1 & STERGIOULAS APOSTOLOS
VOLUME 12.1, 2016 D.O.I: http: doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2016.0104 Hamstring Strains in Football. Prevention and Rehabilitation Rules. Systematic Review. ATHANASIOU HADJIMICHAEL MICHALIS 1 & STERGIOULAS APOSTOLOS
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF A SOCCER PLAYER Oluseun A. Olufade, MD 4/22/16 OUTLINE Epidemiology Injury prevention Hamstring FIFA 11+ Athletic development program Sports science BORN TO PLAY SOCCER SECRET
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF A SOCCER PLAYER Oluseun A. Olufade, MD 4/22/16 OUTLINE Epidemiology Injury prevention Hamstring FIFA 11+ Athletic development program Sports science BORN TO PLAY SOCCER SECRET
CLINICAL REASONING TOOLS
 CLINICAL REASONING TOOLS FRANK TUDINI PT, DSC,OCS,FAAOMPT MATT WALK PT, DPT,OCS, FAAOMPT Rothstein, Echternach and Riddle 2003 Hypothesis-Oriented Algorithm for Clinicians Patient-centered conceptual framework
CLINICAL REASONING TOOLS FRANK TUDINI PT, DSC,OCS,FAAOMPT MATT WALK PT, DPT,OCS, FAAOMPT Rothstein, Echternach and Riddle 2003 Hypothesis-Oriented Algorithm for Clinicians Patient-centered conceptual framework
This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source:
 This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source: Fyfe, Jackson, Opar, David, Williams, Morgan, & Shield, Anthony (2012) The role of neuromuscular
This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source: Fyfe, Jackson, Opar, David, Williams, Morgan, & Shield, Anthony (2012) The role of neuromuscular
MCL Tears: They all heal..or Do They? ERIK D. PETERSON, MD ORTHOPEDIC SPORTS MEDICINE SURGEON CORE ORTHOPEDICS
 MCL Tears: They all heal..or Do They? ERIK D. PETERSON, MD ORTHOPEDIC SPORTS MEDICINE SURGEON CORE ORTHOPEDICS Incidence Most Commonly Injured Ligament in the knee Mechanism Valgus applied stress to fixed/planted
MCL Tears: They all heal..or Do They? ERIK D. PETERSON, MD ORTHOPEDIC SPORTS MEDICINE SURGEON CORE ORTHOPEDICS Incidence Most Commonly Injured Ligament in the knee Mechanism Valgus applied stress to fixed/planted
SOCCER INJURY PREVENTION KEY FACTS SOLUTIONS CASE PRESENTATIONS MICHAEL BILLER, PT & KYLE HAMMOND, MD
 SOCCER INJURY PREVENTION KEY FACTS SOLUTIONS CASE PRESENTATIONS MICHAEL BILLER, PT & KYLE HAMMOND, MD Rationale for injury prevention programs Rate of injuries is increasing in many sports and injury types
SOCCER INJURY PREVENTION KEY FACTS SOLUTIONS CASE PRESENTATIONS MICHAEL BILLER, PT & KYLE HAMMOND, MD Rationale for injury prevention programs Rate of injuries is increasing in many sports and injury types
Hamstring strain injuries comprise a substantial percentage
 [ clinical commentary ] Bryan C. Heiderscheit, PT, PhD1 Marc A. Sherry, PT, DPT, LAT, CSCS2 Amy Silder, PhD3 Elizabeth S. Chumanov, PhD 4 Darryl G. Thelen, PhD 5 Hamstring Strain Injuries: Recommendations
[ clinical commentary ] Bryan C. Heiderscheit, PT, PhD1 Marc A. Sherry, PT, DPT, LAT, CSCS2 Amy Silder, PhD3 Elizabeth S. Chumanov, PhD 4 Darryl G. Thelen, PhD 5 Hamstring Strain Injuries: Recommendations
Why choose Ottauquechee PT
 Why does your back hurt? Low back pain is one of the most common patient complaints affecting 80% of adults at some point in their lives. Generally the source of pain is in the spine and/or its supporting
Why does your back hurt? Low back pain is one of the most common patient complaints affecting 80% of adults at some point in their lives. Generally the source of pain is in the spine and/or its supporting
Imaging lower limb injuries of the myotendinous junction in elite athletes
 Imaging lower limb injuries of the myotendinous junction in elite athletes Poster No.: P-0121 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Chowdhury, G. Rajeswaran, J. Lee, J.
Imaging lower limb injuries of the myotendinous junction in elite athletes Poster No.: P-0121 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Chowdhury, G. Rajeswaran, J. Lee, J.
The effects of bracing and knee flexion angle on hamstring activity during crutch walking: A preliminary study for post-operative care
 Baptist Health South Florida Scholarly Commons @ Baptist Health South Florida All Publications 2018 The effects of bracing and knee flexion angle on hamstring activity during crutch walking: A preliminary
Baptist Health South Florida Scholarly Commons @ Baptist Health South Florida All Publications 2018 The effects of bracing and knee flexion angle on hamstring activity during crutch walking: A preliminary
IMAGING OF THE HAMSTRING MUSCLE COMPLEX IN ELITE ATHLETES
 SPORTS RADIOLOGY IMAGING OF THE HAMSTRING MUSCLE COMPLEX IN ELITE ATHLETES Written by Paul Marovic and George Koulouris, Australia Hamstring injury is one of the most common acute musculoskeletal injuries
SPORTS RADIOLOGY IMAGING OF THE HAMSTRING MUSCLE COMPLEX IN ELITE ATHLETES Written by Paul Marovic and George Koulouris, Australia Hamstring injury is one of the most common acute musculoskeletal injuries
The value of weight-bearing functional CT scans
 The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
