SECONDARY LENGTHENING OF THE SOFT PALATE USING MILLARD'S ISLAND FLAP TECHNIQUE. By R. DIJKSTRA. Zwolle, The Netherlands
|
|
|
- Rolf Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SECNDARY LENGTHENNG F THE SFT PALATE USNG MLLARD'S SLAND FLAP TECHNQUE By R. DJKSTRA Zwolle, The Netherlands MST investigators nowadays are inclined to the opinion that velo-pharyngeal closure during normal speech is brought about by a flap-like movement of the soft palate, rather than by sphincteric action. Thus the soft palate is raised by contraction of the levator muscles, fibres of which cross and ioin in the middle third of the palate. They form a muscular sling with both ends attached to the base of the skull. n contraction of this loop the palate is pulled up and backwards, drawn up in its middle third to touch the posterior pharyngeal wall at, or just above, the level of the first cervical vertebra. The posterior third of the palate generally remains flaccid and hangs down, screening the actual area of closure from the examining eye. f, for some reason, closure in this way cannot be easily effected, other muscles may come into play. The palato-pharyngeus muscles (Braithwaite, 62) and possibly the uppermost fibres of the superior constrictor of the pharynx (Whillis, 3 o) can pull the palate backwards, and at the same time narrow the pharynx in its lateral dimension. n this way they play a compensatory role where the valve mechanism, as operated by the levator muscle, is not competent. n the congenital cleft palate it is found that fusion of the paired muscles has not taken place. Apart from this abnormality, or perhaps secondary to it, there is a lack of development in the antero-posterior dimension. Normally the aponeurosis, formed by the tendinous fibres of the tensor palati muscles, forms about one-third of the antero-posterior length of the soft palate. n the cleft palate this aponeurosis has not developed to this extent, according to Veau (3), owing to lack of muscle pull during the foetal stage. As a consequence, the levator muscles, partly attached to this aponeurosis, partly inserting their fibres in the tissue of the free edges of the cleft, run in a more forward direction in the cleft palate (Ruding, 64) than they do in the normal palate. When a cleft of the palate is simply sutured, the position of the levator muscles is not altered and the active part of the palate, as a result, lies too far forward. The levator bundle is tethered to the hard palate on shorter rein than normally, as the underdeveloped aponeurosis allows less muscle movement. Lengthening of the anterior third of the palate by freeing the aponeurosis from the posterior rim of the hard palate is the aim of the lengthening operations, both of primary closure and of secondary procedures. To make the most of this lengthening, after detaching the aponeurosis from the posterior rim of the hard palate, the overlying nasal mucosa has to be divided and tissue has to be added to close the resulting defect in nasal mucosa. A number of procedures have been devised, making use of either grafts or flaps (Dorrance and Bransfield, 43; Sanvenero-Rosselli, 55 ; Cronin, 57; Millard, i62, 63 ; Honig, 63). Whether such methods, applied at the time of primary closure of the palate, give speech results superior to the simple methods such as the V-Y type of repair, in which nasal mucosa is not divided, is still not proven conclusively. f shortness of the palate plays a role in velo-pharyngeal incompetence after simple repair of a cleft palate, the same more radical methods can be used to produce secondary lengthening, in order to attain a normal closing mechanism in speech. 2B ~
2 ~4 BRTSH JURNAL F PLASTC SURGERY t is thus necessary to asccrtain that the palate is short with respect to the anteroposterior diameter of the pharynx, and that there is good muscle action. This is best done by lateral radiological examination as described by Calnan (56). We use four views :. The soft palate at rest, while the patient is breathing through the nose or saying "m ". Pronunciation of this nasal consonant does not involve complete relaxation of the soft palate, but comes near to it, and is easy to achieve in children. 2 and 3. Phonation, using the sustained vowels "u " and "i" These normally involve complete velo-pharyngeal closure and are diagnostically the most important. n cases of insufficiency, a gap is seen between the active part of the soft palate (levator ridge) and the posterior pharyngeal wall, and the diameter of this gap is measured. 4. Producing the consonant "s ". This, like blowing, often involves a more pronounced elevation of the soft palate, due to stronger muscle action and perhaps also higher intra-oral pressure. Closure can sometimes be seen in patients who display minor to moderate nasality in speech. Use of contrast media, at least in children, is not necessary and can even jeopardise the co-operation of the patient, which is so important. TABLE Number of ] mmobile No measurepatients / ncom ~etence in mm. palates ments possible Moderate to severe nasality Slight nasality,. 2 No nasality 5., t is appreciated that this only gives a two-dimensional impression of a threedimensional structure and that, for instance, the width of the pharynx is not taken into account. However, a positive correlation between the degree of nasality in speech and the lateral radiological findings on phonation was found by others (Bj6rk and Nylen, 63 ; Hagerty and Hofmeister) and could also be demonstrated by us, as will be shown. An unselected, consecutive series of 73 patients was reviewed, in whom closure of a cleft palate was carried out by Dr J. Hage between 54 and 6. n 63 patients the operation was performed before they were 8 months of age ; the remaining o were between 2 and 5 years. A minor degree of nasality, only discernable by the trained ear, was found in io patients (3 per cent) and a definite nasality, which could be classified as abnormal speech by the layman, was found in 7 patients (24 per cent). This makes a total of 27 patients with varying degrees of nasality in speech. n 24 of these patients lateral radiographs were obtained. The findings in these 24 patients are enumerated in the Table. Radiographs were also made in 5 random patients from this series, in whom no nasality in speech could be demonstrated. The Table gives the distance between the levator ridge and the posterior pharyngeal wall as measured on the radiographs made while phonating the vowel "i ". n the three cases in which no accurate measurements could be made, the soft palate had been tethered to the posterior pharyngeal wall by a pharyngeal flap.
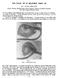
3 SECNDARY LENGTHENNG F THE SFT PALATE 115 When a radiologically appreciable gap is found, speech training alone will not be sufficient to overcome the abnormality. According to Van Gelder (165) this is the case with gaps of 4 mm. or over on phonation of" i ". Thus far in this department, surgical treatment for residual nasality after palate repair had consisted of a pharyngeal flap operation. The flap was usually raised on a superior base and attached at the posterior part of the soft palate, without concomitant push-back of the soft palate (Sercer, 135). This simple flap makes the naso-pharyngeal orifice smaller, partly by sheer bulk of the flap and partly by contraction of the donor defect on the posterior pharyngeal wall. Thus the compensatory sphincter mechanism FG. FG. 2 To show dissection of island flaps with neurovascular bundles. gets a better chance of closing the naso-pharyngeal leak. n due time the flap contracts to a short narrow band, and ultimately it is impossible to say whether it was originally based superiorly or inferiorly (Blackfield et al., 63 ; Skoog, 165). Speech results are not always found to be satisfactory with this procedure. Lengthening of the palate, aiming to restore the flap-like movement, seems to be a more logical approach to treatment for post-operative nasality. t was decided to adapt Millard's island flap procedure to this end. This operation was carried out in 17 patients, who had nasality following primary closure of a cleft palate. Twelve of these were patients from the above-mentioned series of reviewed cleft palate patients, while five had been operated on elsewhere. Their age ranged from 5 to 18 years. The technical details of the procedure are described
4 6 BRTSH JURNAL F PLASTC SURGERY by Millard. A few points, however, ought to be mentioned. n four early cases the island flap was cut from the anterior part of the muco-periostcum of the hard palate, and bascd on two neurovascular bundles, which as a consequence had to be dissected backwards from the undersurface of the remaining muco-periosteum (Fig. 2). n two cases, post-operative loss of gained length occurred, probably duc to contraction of the flap. This was attributed to ischacmia due to vascular trauma, sustained during the dissection. ne of these cases also developed a fistula in the denuded anterior part of the cleft. n the remaining cases a unilateral island flap was always used, overlying the whole length of the palatine vessels (Fig. ). Contraction of these flaps did not occur. TABLE Age at operation PRE-PERATVE Nasality Velophar. distance in mm. on X-ray Nasality Velophar. distance in mm. on X-ray i $ PST-PERATVE Mm. width of [ Fate of flap island flap as judged used by clips x r " i; 4 o b o r + o ' ( ( contraction contraction Nasality : + -- moderate ; + + = severe. To follow up the fate of the flap and its contribution to length gained, the island flap was marked with silver clips just within its anterior and posterior border, as described by Hage (66). These clips could be traced in cases on post-operative radiographs. n all cases measurements were made of the distance between the levator ridge and the posterior pharyngeal wall, on radiographs taken during phonation. The results of pre- and post-operative radiological examinations and speech assessment are shown in Table. n patients io and 12 a contracted pharyngeal flap tethered the posterior part of the soft palate to the posterior pharyngeal wall and this made pre-operative radiological measurements impossible. n patient, no elevation of the velum was obtained on vowel sounds. However, as mobility was good on " s ", lengthening was carried out. Subsequently a Hynes' pharyngoplasty (Hynes, 5 o) was done to overcome the remaining defect. Although the formed ridge could not be seen on later radiographs, narrowing of the pharynx was obviously maintained and closure was effected on" s ". Speech was ultimately improved. t will be seen that in this last patient, although the insufficiency measured 15 mm., an island flap measuring only ram. across was used. There are two reasons for this :
5 SECNDARY LENGTHENNG F THE SFT PALATE 117. Mucoperiosteum is in limited supply. When also some collapse of the palate exists, it is often not possible to obtain an island flap wider than to Z mm. particularly as it is also advisable to leave the scar tissue overlying the cleft in situ. Two flaps can then be raised on each side of this area. The island flap is formed from one, the other used by transposing it through to cover the island flap on its oral side. x. The second consideration applies to all lengthening procedures2and requires some elaboration. The soft palate is detached from the posterior rim of the hard palate by cutting through the aponeurosis and nasal mucosa after elevation of the mucoperiosteal flaps. t then retracts until the cutting knife has reached the lateral pharyngeal wall. This retraction must be largely caused by the muscles of the soft palate. The mechanism is probably that they, particularly the levator muscles, now take up a normal transverse course instead of the abnormal forward position seen in the cleft palate patient. This is in agreement with observations in three cases of congenital short palates, where we performed a lengthening operation. Retraction was much less than in those cases where a cleft previously existed and where the retraction averages mm. t stands to reason that pushing the palate further back than it will go spontaneously, will not improve active velo-pharyngeal closure, because on contraction the levator bundle will tend to attain its predetermined shortest transverse course. t appears that a" pushback" of more than mm. does not add any effective lengthening. This limitation of effective lengthening has been found by others as well (Trauner, 156 ). Writers who claimed to obtain lengthening of 15 mm. or more in some cases, always refer to the distance between the posterior rim of the hard palate and the anterior rim of the retroposed soft palate (Brauer, 165 ; Dorrance, 125). t is very unlikely that the length obtained in this way is all effective length. The term " pushback" would be better abandoned as well as the effort of " pushing" The lengthening operation should be regarded as a release operation. For the same reason lengthening procedures do not achieve the desired effect in cases of short palate without cleft, as Calnan (161) found in an X-ray study. We tried MiUard's lengthening operation in three cases of congenital short palate, with very disappointing results. No effective lengthening was achieved, although during operation this seemed to be the case. CNCLUSN t is difficult to draw definite conclusions from our findings. The results of this trial with Millard's island flap procedure indicate that a permanent effective lengthening of up to mm. can be achieved, provided that neuro-vascular bundles are treated with respect. t is not possible to compare the speech results with those obtained by authors using other methods. n some cases, especially in patients with scarred palates, they were not spectacular. Any improvement gained could then be attributed, possibly, to the speech therapy which was often given post-operatively, and the extra attention paid to these patients. n the other hand, some cases showed rapid and spectacular improvement, often without speech therapy. The need for the latter is largely determined by established speech faults secondary to the nasal escape. n the whole, we thought results were better than those previously obtained with simple pharyngeal flaps. t must be acknowledged that the method is not universally applicable. Lengthening is obviously of no avail in the paralysed palate, and probably not in the congenitally short palate. Also island flaps are not advisable in the badly scarred and collapsed hard palate, for technical reasons. t is possible that the lengthening procedure in which use is made of a pharyngeal flap to close the nasal defect is preferable, in some cases, as the pharynx
6 18 BRTSH JURNAL F PLASTC SURGERY is also narrowed by contraction of the donor defect. Whichever operation is used in treating nasality, it seems that in cases of repaired cleft palate a lengthening procedure should be incorporated when radiological examination shows that the palate is actively mobile but short. SUMMARY A number of patients with nasality in speech after a cleft palate repair were treated by secondary lengthening of the palate with MiUard's island flap method. The lengthening achieved was found to be permanent in the majority of cases, but the effective lengthening was limited to a maximum of approximately mm. The cause of this phenomenon is discussed. t is thought that lengthening procedures ought to be included in the treatment of nasality in patients with a repaired cleft. The importance of preoperative radiographs of these patients, as being the only accurate and universally recordable assessment of the condition, is stressed. The data on which this paper is based were obtained in the St Elisabeth Ziekenhuis, Tilburg, from patients treated in the department of plastic surgery. would like to thank Dr J. Hage, Head of this department, for his encouragement and advice. Also am grateful to Mr R. W. Hiles for his help with this paper. REFERENCES BJ6RK, L, and NYLEtq, B. (63). Acta chir. scan& 126, 434. BLACKFELD, H. M., WSLEY, J. Q., MLLER, E. R. and LAWSN, L,. (63). Plastic reconstr. Surg. 3, 542. BRATHWATE, F. (162). n " Modern Trends in Plastic Surgery ", ed. Gibson, T. London : Butterworth. BRAUER, R.. (65). Plastic reconstr. Surg. 36. CALNAN, J. (56). Br. 3. plast. Surg. 8, (6). Br. J. plast. Surg. 3, 23. CRtoN, T. D. (157). Plastic reconstr. Surg. 2o, 474. DRRAXCE, G. M. (125). Ann. Surg. 82, 2o8. DgaANCE, G. M. and BRANSFELD (43). Ann. Surg. x7,. Haarlem. De erven F. BohnN. V. GELDER, L. VAN (65). " Het zachte gehemelte bij de spraak ". HAGE, J. (66). Br. J. plast. Surg., 317. HAGERTY and HFMESTER, cited by van Gelder in " Het zachte gehemeke bij de spraak " H~G, C. A. (163). " ver pharyngoplastiek". Thesis, Utrecht. HYNES, W. (5). Br. J. plast. Surg. 3, 2. MLLARD, D. R. (162). Plastic reconstr. Surg (163). Surgery Gynec. bstet. x6, 27. RUDNG, R. (164). Plastic reconstr. Surg. 33, 32. SANVENERo-RoSSELL, G. (55)- Fortschr. Kiefer- und Gesichts-Chir., 65. SERCER, A. (135). Revue Chir. struct. 5, 5. SKG, T. (65). Br. J. plast. Surg. x8, 265. TRAUNER, R. (156). Br. J. plast. Surg. 8, 21. VEAU, V. (131). " Division Palatine ". Paris : Masson. WHLLS, J. (13o). J. Anat. 65, 2.
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RHINOLALIA : A REVIEW OF 139 PHARYNGOPLASTIES. University Hospital, ~ Groningen, Holland
 OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RHINOLALIA : A REVIEW OF 139 PHARYNGOPLASTIES By A. J. C. HUFFSTADT, J. M. H. M. BORGHOUTS, and Mrs A. J. MOOLENAAR-BiJL University Hospital, ~ Groningen, Holland THE number of methods
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RHINOLALIA : A REVIEW OF 139 PHARYNGOPLASTIES By A. J. C. HUFFSTADT, J. M. H. M. BORGHOUTS, and Mrs A. J. MOOLENAAR-BiJL University Hospital, ~ Groningen, Holland THE number of methods
Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Stanford, California
 THE RESTRICTIVE PHARYNGEAL FLAP By JAROY WEBER, Jr., M.D., ROBERT A. CHASE, M.D. and RICHARD P. JOBE, M.D. Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Stanford, California THE historical
THE RESTRICTIVE PHARYNGEAL FLAP By JAROY WEBER, Jr., M.D., ROBERT A. CHASE, M.D. and RICHARD P. JOBE, M.D. Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Stanford, California THE historical
CINERADIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF COMBINED ISLAND FLAP PUSHBACK AND PHARYNGEAL FLAP IN THE SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF SUBMUCOUS CLEFT PALATE 1
 CINERADIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF COMBINED ISLAND FLAP PUSHBACK AND PHARYNGEAL FLAP IN THE SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF SUBMUCOUS CLEFT PALATE 1 By JOHN E. HOOPES, M.D., z A. LEE DELLON, 3 JACOB I. FABRIKANT, M.D.,
CINERADIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF COMBINED ISLAND FLAP PUSHBACK AND PHARYNGEAL FLAP IN THE SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF SUBMUCOUS CLEFT PALATE 1 By JOHN E. HOOPES, M.D., z A. LEE DELLON, 3 JACOB I. FABRIKANT, M.D.,
By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S. 1 Plastic Surgeon, University of Oxford
 BLOWING TESTS AND SPEECH By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S. 1 Plastic Surgeon, University of Oxford and CATHERINE E. RENFREW, F.C.S.T. Chief Speech Therapist, United Oxford Hospitals " Is the mechanism competent?
BLOWING TESTS AND SPEECH By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S. 1 Plastic Surgeon, University of Oxford and CATHERINE E. RENFREW, F.C.S.T. Chief Speech Therapist, United Oxford Hospitals " Is the mechanism competent?
Postgraduate Medical School, University of London
 THE COMPARATIVE ANATOMY OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Part I Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate in Dogs By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S., M.R.C.P. Postgraduate Medical School, University of London IN the veterinary
THE COMPARATIVE ANATOMY OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Part I Classification of Cleft Lip and Palate in Dogs By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S., M.R.C.P. Postgraduate Medical School, University of London IN the veterinary
A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT
 A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Iftikhar Ahmad, M. Rafiq Khan, Abdullah Jan, Abdur Rasheed ( Department of E.N.T. and Head and Neck
A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Iftikhar Ahmad, M. Rafiq Khan, Abdullah Jan, Abdur Rasheed ( Department of E.N.T. and Head and Neck
Plastic and Jaw Department, United Sheffield Hospitals
 THE EXAMINATION OF IMPERFECT SPEECH FOLLOWING CLEFT-PALATE OPERATIONS By WILFRED HYNES, F.R.C.S Plastic and Jaw Department, United Sheffield Hospitals THE results of cleft-palate operations can be difficult
THE EXAMINATION OF IMPERFECT SPEECH FOLLOWING CLEFT-PALATE OPERATIONS By WILFRED HYNES, F.R.C.S Plastic and Jaw Department, United Sheffield Hospitals THE results of cleft-palate operations can be difficult
BONE GRAFTING IN TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 337
 PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
Longitudinal outcome of pharyngoplasty
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences (2009), 4(1): 17-21 CASE REPORT Longitudinal outcome of pharyngoplasty Peter J. Anderson*, Roslynn K. Sells, David. J. David Australian Craniofacial Unit, Women s and Children
Archives of Orofacial Sciences (2009), 4(1): 17-21 CASE REPORT Longitudinal outcome of pharyngoplasty Peter J. Anderson*, Roslynn K. Sells, David. J. David Australian Craniofacial Unit, Women s and Children
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
Cleft Lip and Palate: The Effects on Speech and Resonance
 Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
TREATMENT OF CLEFT PALATE ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA. By RANDELL CHAMPION, F.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Duchess of York Hospital for Babies, Manchester
 TREATMENT OF CLEFT PALATE ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA By RANDELL CHAMPION, F.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Duchess of York Hospital for Babies, Manchester IN spite of the present-day technique and medical research
TREATMENT OF CLEFT PALATE ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA By RANDELL CHAMPION, F.R.C.S.(Ed.) From the Duchess of York Hospital for Babies, Manchester IN spite of the present-day technique and medical research
OF THE LIP AND PALATE. By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham
 MAXILLARY DEFORMITIES IN REPAIRED CLEFTS OF THE LIP AND PALATE By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham IN patients with repaired clefts of the
MAXILLARY DEFORMITIES IN REPAIRED CLEFTS OF THE LIP AND PALATE By T. D. FOSTER, M.D.S., F.D.S., D.Orth.R.C.S. School of Dental Surgery, University of Birmingham IN patients with repaired clefts of the
Place and Manner of Articulation Sounds in English. Dr. Bushra Ni ma
 Place and Manner of Articulation Sounds in English Dr. Bushra Ni ma Organs of Speech Respiratory System Phonatory System Articulatory System Lungs Muscles of the chest Trachea Larynx Pharynx Lips Teeth
Place and Manner of Articulation Sounds in English Dr. Bushra Ni ma Organs of Speech Respiratory System Phonatory System Articulatory System Lungs Muscles of the chest Trachea Larynx Pharynx Lips Teeth
Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
study. The subject was chosen as typical of a group of six soprano voices methods. METHOD
 254 J. Physiol. (I937) 9I, 254-258 6I2.784 THE MECHANISM OF PITCH CHANGE IN THE VOICE BY R. CURRY Phonetics Laboratory, King's College, Neweastle-on-Tyne (Received 9 August 1937) THE object of the work
254 J. Physiol. (I937) 9I, 254-258 6I2.784 THE MECHANISM OF PITCH CHANGE IN THE VOICE BY R. CURRY Phonetics Laboratory, King's College, Neweastle-on-Tyne (Received 9 August 1937) THE object of the work
Pharyngeal Flap. Gregory C. Allen, MD
 Pharyngeal Flap Gregory C. Allen, MD Department of Pediatric Otolaryngology Associate Medical Director, Cleft Palate Team Children's Hospital Colorado Associate Professor Departments of Otolaryngology
Pharyngeal Flap Gregory C. Allen, MD Department of Pediatric Otolaryngology Associate Medical Director, Cleft Palate Team Children's Hospital Colorado Associate Professor Departments of Otolaryngology
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects. O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery
 Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
Mucoperiosteal Flap Necrosis after Primary Palatoplasty in Patients with Cleft Palate
 Mucoperiosteal Flap Necrosis after Primary Palatoplasty in Patients with Cleft Palate Percy Rossell-Perry 1, Omar Cotrina-Rabanal 2, Luis Barrenechea-Tarazona 3, Roberto Vargas-Chanduvi 3, Luis Paredes-Aponte
Mucoperiosteal Flap Necrosis after Primary Palatoplasty in Patients with Cleft Palate Percy Rossell-Perry 1, Omar Cotrina-Rabanal 2, Luis Barrenechea-Tarazona 3, Roberto Vargas-Chanduvi 3, Luis Paredes-Aponte
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY
 OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
Figure 1. Basic anatomy of the palate
 CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Does the Type of Cleft Palate Contribute to the Need for Secondary Surgery? A National Perspective
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Does the Type of Cleft Palate Contribute to the Need for Secondary Surgery? A National Perspective James
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Does the Type of Cleft Palate Contribute to the Need for Secondary Surgery? A National Perspective James
Comparative Study between Superiorly Based Pharyngeal Flap and Sphincteroplasty in Treatment of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency after Cleft Palate Repair
 Egypt, J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg., Vol. 29, No. 2, July: 149-156, 2005 Comparative Study between Superiorly Based Pharyngeal Flap and Sphincteroplasty in Treatment of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency after
Egypt, J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg., Vol. 29, No. 2, July: 149-156, 2005 Comparative Study between Superiorly Based Pharyngeal Flap and Sphincteroplasty in Treatment of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency after
Osteotomy of the Premaxilla
 182 J. max.-fac. Surg. 8 (1980) 182-186 Osteotomy of the Premaxilla John BROUNS, Peter EGYEDI Department of Maxillo-Facial Surgery (Head: Prof. P. Egyedi, M.D., D.M.D.) State University of Utrecht, The
182 J. max.-fac. Surg. 8 (1980) 182-186 Osteotomy of the Premaxilla John BROUNS, Peter EGYEDI Department of Maxillo-Facial Surgery (Head: Prof. P. Egyedi, M.D., D.M.D.) State University of Utrecht, The
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction
 UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
A REVIEW OF THE RESULTS OF OPERATIONS ON CLEFT PALATES WITH REFERENCE TO MAXILLARY GROWTH AND SPEECH FUNCTION
 A REVIEW OF THE RESULTS OF OPERATIONS ON CLEFT PALATES WITH REFERENCE TO MAXILLARY GROWTH AND SPEECH FUNCTION By AMBROSE JOLLEYS, M.D., F.R.C.S. Surgeon, Royal Manchester Children's and Booth Hall Hospitals
A REVIEW OF THE RESULTS OF OPERATIONS ON CLEFT PALATES WITH REFERENCE TO MAXILLARY GROWTH AND SPEECH FUNCTION By AMBROSE JOLLEYS, M.D., F.R.C.S. Surgeon, Royal Manchester Children's and Booth Hall Hospitals
frontalis muscle while the patient makes an attempt to open the eye. With the first and third classes I am not now concerned, except
 OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
Closure of Palatal Fistula with Bucco-labial Myomucosal Pedicled Flap
 Annals of Pediatric Surgery, Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 104-108 Original Article Closure of Palatal Fistula with Bucco-labial Myomucosal Pedicled Flap Mohamed M. EL-Leathy* and Mohamed F. Attia** Pediatric
Annals of Pediatric Surgery, Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 104-108 Original Article Closure of Palatal Fistula with Bucco-labial Myomucosal Pedicled Flap Mohamed M. EL-Leathy* and Mohamed F. Attia** Pediatric
8 A SIMPLE FISTULA REPAIR, STEP BY STEP
 8 A SIMPLE FISTULA REPAIR, STEP BY STEP The first step is to suture the labia to the thighs and cover the anus with a swab (Figure 31). Figure 31 The labia are sutured to the thighs and the anus is covered
8 A SIMPLE FISTULA REPAIR, STEP BY STEP The first step is to suture the labia to the thighs and cover the anus with a swab (Figure 31). Figure 31 The labia are sutured to the thighs and the anus is covered
CLEFT LIP and PALATE. Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden. Information about Cleft Lip and Palate. English version
 CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
CLEFT LIP and PALATE Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg, Sweden Information about Cleft Lip and Palate English version 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS page What are cleft lip and palate? 3 Which children can
Cleft Palate Speech-Components and Assessment Voice and Resonance Disorders-ASLS-563. Key Components of Cleft Palate Speech.
 Cleft Palate Speech-Components and Assessment Voice and Resonance Disorders-ASLS-563 Key Components of Cleft Palate Speech Disorder Type of Disorder/ Causes Hypernasality Resonance Disorder insufficiency
Cleft Palate Speech-Components and Assessment Voice and Resonance Disorders-ASLS-563 Key Components of Cleft Palate Speech Disorder Type of Disorder/ Causes Hypernasality Resonance Disorder insufficiency
Scientific Forum. Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the Alar Rim
 Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Longitudinal Evaluation of Articulation and Velopharyngeal
 _ Longitudinal Evaluation of Articulation and Velopharyngeal Competence of Patients with Pharyngeal Flaps D. R. Van Demark, PH.D. M. A. Harpin, PH.D. In this study, 129 patients with cleft palate who had
_ Longitudinal Evaluation of Articulation and Velopharyngeal Competence of Patients with Pharyngeal Flaps D. R. Van Demark, PH.D. M. A. Harpin, PH.D. In this study, 129 patients with cleft palate who had
Class Voice: Review of Chapter 10 Voice Quality and Resonance
 Class Voice: Review of Chapter 10 Voice Quality and Resonance Tenor Luciana Pavarotti demonstrating ideal head position, alignment, inner smile, and feeling of up to achieve optimal resonance! Millersville
Class Voice: Review of Chapter 10 Voice Quality and Resonance Tenor Luciana Pavarotti demonstrating ideal head position, alignment, inner smile, and feeling of up to achieve optimal resonance! Millersville
Title of Mucoperiosteal Flap on the Cleft. Citation 音声科学研究 = Studia phonologica (1991),
 Title Velopharyngeal Function after Palat of Mucoperiosteal Flap on the Cleft Matsumoto, K Akiko; Isshiki, Nobuhi Author(s) Kimura, Tadashi; Nose, Kensuke; Kaw Tomoko Citation 音声科学研究 = Studia phonologica
Title Velopharyngeal Function after Palat of Mucoperiosteal Flap on the Cleft Matsumoto, K Akiko; Isshiki, Nobuhi Author(s) Kimura, Tadashi; Nose, Kensuke; Kaw Tomoko Citation 音声科学研究 = Studia phonologica
The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure. in Cleft Lip Repair*
 The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure in Cleft Lip Repair* RALPH HAMILTON, M.D. WILLIAM P. GRAHAM, III, M.D. PETER RANDALL, M.D. Philadelphia, Pa. 19104 Introduction A lip adhesion procedure utilizing
The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure in Cleft Lip Repair* RALPH HAMILTON, M.D. WILLIAM P. GRAHAM, III, M.D. PETER RANDALL, M.D. Philadelphia, Pa. 19104 Introduction A lip adhesion procedure utilizing
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX. By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
The Seated Nodding Test for O-A Atlas TPs
 Anterior is at the top of the illustrations. Putting the occiput on the atlas would be like closing facing pages of a book. Atlas superior facets converge anteriorly; their surfaces slope superiorly going
Anterior is at the top of the illustrations. Putting the occiput on the atlas would be like closing facing pages of a book. Atlas superior facets converge anteriorly; their surfaces slope superiorly going
From the Plastic and Jaw Department, United She3~eM Hospitals.
 THE " BLUE FLAP ": A METHOD OF TREATMENT By WILFRED HYNES, F.R.C.S. From the Plastic and Jaw Department, United She3~eM Hospitals. THE " blue flap," one of the most difficult problems in surgery, is apt
THE " BLUE FLAP ": A METHOD OF TREATMENT By WILFRED HYNES, F.R.C.S. From the Plastic and Jaw Department, United She3~eM Hospitals. THE " blue flap," one of the most difficult problems in surgery, is apt
Clinical experience from primary palatoplasty and studies of velopharyngeal
 The Effect of Intravelar Veloplasty on Velopharyngeal Competence Following Pharyngeal Flap Surgery Bennie L. Jarvis, M.D. Wicuiam C. Trier, M.D. Clinical experience from primary palatoplasty and studies
The Effect of Intravelar Veloplasty on Velopharyngeal Competence Following Pharyngeal Flap Surgery Bennie L. Jarvis, M.D. Wicuiam C. Trier, M.D. Clinical experience from primary palatoplasty and studies
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Surgical Treatment of Short Nose
 Surgical Treatment of Short Nose Dr. Otto YT Au MD (JEFFERSON, USA) 1957, MCPS (MANITOBA) 1963, FHKAM (SURGERY) 1995 Diplomate American Board Plastic Surgery Plastic Surgery Specialist Dr.OttoYTAu A nice
Surgical Treatment of Short Nose Dr. Otto YT Au MD (JEFFERSON, USA) 1957, MCPS (MANITOBA) 1963, FHKAM (SURGERY) 1995 Diplomate American Board Plastic Surgery Plastic Surgery Specialist Dr.OttoYTAu A nice
Study models of 5 year old children as predictors of surgical outcome in unilateral cleft lip and palate
 European Journal of Orthodontics 19 (1997) 165-170 1997 European Orthodontic Society Study models of 5 year old children as predictors of surgical outcome in unilateral cleft lip and palate Nikki Atack,
European Journal of Orthodontics 19 (1997) 165-170 1997 European Orthodontic Society Study models of 5 year old children as predictors of surgical outcome in unilateral cleft lip and palate Nikki Atack,
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SEVENTH NERVE PARALYSIS. By B. GRUNDT, M.D. Oslo, Norway
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SEVENTH NERVE PARALYSIS By B. GRUNDT, M.D. Oslo, Norway WE are all familiar with the patient who has paralysis of the facial nerve. The oblique mouth and the corresponding oblique
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SEVENTH NERVE PARALYSIS By B. GRUNDT, M.D. Oslo, Norway WE are all familiar with the patient who has paralysis of the facial nerve. The oblique mouth and the corresponding oblique
Vancouver, B.C., Canada
 THE "ALAR SHIFT" REVISITED By THEODORE F. WILKIE, B.A., M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), F.A.C.S. Vancouver, B.C., Canada IN the hands of many plastic surgeons certain procedures have an evanescent history. Usually
THE "ALAR SHIFT" REVISITED By THEODORE F. WILKIE, B.A., M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), F.A.C.S. Vancouver, B.C., Canada IN the hands of many plastic surgeons certain procedures have an evanescent history. Usually
King's College Hospital Dental School, London, S.E. 5.
 OSTECTOMY AT THE MANDIBULAR SYMPHYSIS J. H. SOWRAY, B.D.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.), L.R.C.P., M.R.C.S. and R. HASKELL, M.B., B.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.). King's College Hospital Dental School, London, S.E.
OSTECTOMY AT THE MANDIBULAR SYMPHYSIS J. H. SOWRAY, B.D.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.), L.R.C.P., M.R.C.S. and R. HASKELL, M.B., B.S., F.D.S.R.C.S. (Eng.). King's College Hospital Dental School, London, S.E.
From Stoke Mandeville Hospital, Aylesbury, Bucks.
 STENOSIS OF THE NOSTRILS: A REPORT OF THREE CASES By P. S. BAjAJ, M.S., F.R.C.S.(Ed.), F.R.C.S. and B. N. BAILEY, F.R.C.S. From Stoke Mandeville Hospital, Aylesbury, Bucks. ACQUIRED stenosis of the anterior
STENOSIS OF THE NOSTRILS: A REPORT OF THREE CASES By P. S. BAjAJ, M.S., F.R.C.S.(Ed.), F.R.C.S. and B. N. BAILEY, F.R.C.S. From Stoke Mandeville Hospital, Aylesbury, Bucks. ACQUIRED stenosis of the anterior
McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Morphological variations of soft palate and influence of age on it: A digital cephalometric study
 Original Research Article Morphological variations of soft palate and influence of age on it: A digital cephalometric study C. Vani 1*, T. Vinila Lakshmi 2, V. Dheeraj Roy 3 1 Professor, 2 Post graduate
Original Research Article Morphological variations of soft palate and influence of age on it: A digital cephalometric study C. Vani 1*, T. Vinila Lakshmi 2, V. Dheeraj Roy 3 1 Professor, 2 Post graduate
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Outcome of Velopharyngoplasty in Patients With Velocardiofacial Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Velopharyngoplasty in Patients With Velocardiofacial Syndrome Josine C. C. Widdershoven, MD; Bart M. Stubenitsky, MD, PhD; Corstiaan C. Breugem, MD, PhD; Aebele B. MinkvanderMolen,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Velopharyngoplasty in Patients With Velocardiofacial Syndrome Josine C. C. Widdershoven, MD; Bart M. Stubenitsky, MD, PhD; Corstiaan C. Breugem, MD, PhD; Aebele B. MinkvanderMolen,
CLEFT PALATE & MISARTICULATION
 CLEFT PALATE & MISARTICULATION INTRODUCTION o Between the 6th and 12th weeks of fetal gestation,the left and right sides of the face and facial skeleton fuse in the midddle. When they do fail to do so,
CLEFT PALATE & MISARTICULATION INTRODUCTION o Between the 6th and 12th weeks of fetal gestation,the left and right sides of the face and facial skeleton fuse in the midddle. When they do fail to do so,
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Ear lobe reconstruction Techniques revisited ANANTHARAJAN NATARAJAN Department of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery,
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Ear lobe reconstruction Techniques revisited ANANTHARAJAN NATARAJAN Department of Plastic Reconstructive Surgery,
Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients. Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects
 HEAD AND NECK SURGERY Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects Kyung S. Koh, MD, PhD,* Tae Suk Oh, MD,* and Jin Woo Song,
HEAD AND NECK SURGERY Upper Triangular Flap Method for Primary Repairs of Incomplete Unilateral Cleft Lip Patients Minor to Two-Thirds Way Defects Kyung S. Koh, MD, PhD,* Tae Suk Oh, MD,* and Jin Woo Song,
G l o s s a r y. The lack of closure of a normal body orifice or. passage
 A P P E N D I XE G l o s s a r y Allergic rhinitis Swelling of the membrane in the nasal chamber due to allergic reactions; the condition may obstruct breathing Alveolar ridge The bony arches of the maxilla
A P P E N D I XE G l o s s a r y Allergic rhinitis Swelling of the membrane in the nasal chamber due to allergic reactions; the condition may obstruct breathing Alveolar ridge The bony arches of the maxilla
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
Large full-thickness nasal tip defects after Mohs
 RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with
 REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
REPAIR OF THE CLEFT LIP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery ONE out of every eight hundred children in the United States is born with a cleft lip, a cleft palate, or both. Within this group
23 LENGTHENING OF THE
 III 23 LENGTHENING OF THE CLEFT DGES OF AND SOFT AATE THE UVULA THE SOPHISTICATION OF CLEFT PALATE SURGERY HAD ADVANCED BEYOND MERELY CLOSING THE CLEFT HOLE ATTENTION TURNED TOWARD CLOSURE OF THE VELOPHARYNGEAL
III 23 LENGTHENING OF THE CLEFT DGES OF AND SOFT AATE THE UVULA THE SOPHISTICATION OF CLEFT PALATE SURGERY HAD ADVANCED BEYOND MERELY CLOSING THE CLEFT HOLE ATTENTION TURNED TOWARD CLOSURE OF THE VELOPHARYNGEAL
First Assistant, Professional Unit, Nuffield Department of Plastic Surgery, University of Oxford
 DIAGNOSIS, PROGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT OF " PALATO- PHARYNGEAL INCOMPETENCE," WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO RADIOGRAPHIC INVESTIGATIONS I By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S. First Assistant, Professional Unit, Nuffield
DIAGNOSIS, PROGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT OF " PALATO- PHARYNGEAL INCOMPETENCE," WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO RADIOGRAPHIC INVESTIGATIONS I By JAMES CALNAN, F.R.C.S. First Assistant, Professional Unit, Nuffield
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Horizontal Jaw Relation
 Horizontal Jaw Relation Horizontal Jaw Relation It is the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla in a horizontal plane. It can also be described as the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla
Horizontal Jaw Relation Horizontal Jaw Relation It is the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla in a horizontal plane. It can also be described as the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla
Colorectal procedure guide
 Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
There are numerous suture techniques described for nasal. Septocolumellar Suture in Closed Rhinoplasty ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Erdem Tezel, MD, and Ayhan Numanoğlu, MD Abstract: Several surgeons advise a variety of tip sutures and describe their own techniques in open approach. Septocolumellar suture is one of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Erdem Tezel, MD, and Ayhan Numanoğlu, MD Abstract: Several surgeons advise a variety of tip sutures and describe their own techniques in open approach. Septocolumellar suture is one of
Johannesburg, South Africa
 NEUROVASCULAR ISLAND FLAP IN THE TREATMENT OF TROPHIC ULCERATION OF THE HEEL By ISIDORE KAPLAN, F.R.C.S., F.R.C.S.(Ed.) Johannesburg, South Africa THE transfer of skin and subcutaneous tissue on a neurovascular
NEUROVASCULAR ISLAND FLAP IN THE TREATMENT OF TROPHIC ULCERATION OF THE HEEL By ISIDORE KAPLAN, F.R.C.S., F.R.C.S.(Ed.) Johannesburg, South Africa THE transfer of skin and subcutaneous tissue on a neurovascular
The primary goals of cleft palate repair are to PEDIATRIC/CRANIOFACIAL
 PEDIATRIC/CRANIOFACIAL Evaluation of Two Palate Repair Techniques for the Surgical Management of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency Albert S. Woo, M.D. Gary B. Skolnick, B.S. Neil S. Sachanandani, M.D. Lynn
PEDIATRIC/CRANIOFACIAL Evaluation of Two Palate Repair Techniques for the Surgical Management of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency Albert S. Woo, M.D. Gary B. Skolnick, B.S. Neil S. Sachanandani, M.D. Lynn
LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
Cleft palate repair: art and issues
 Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 231 241 Cleft palate repair: art and issues A. Michael Sadove, MD, FACS, FAAP*, John A. van Aalst, MD, John Andrew Culp, BA Division of Plastic Surgery, Indiana University Medical
Clin Plastic Surg 31 (2004) 231 241 Cleft palate repair: art and issues A. Michael Sadove, MD, FACS, FAAP*, John A. van Aalst, MD, John Andrew Culp, BA Division of Plastic Surgery, Indiana University Medical
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
LINGUISTICS 130 LECTURE #4 ARTICULATORS IN THE ORAL CAVITY
 LINGUISTICS 130 LECTURE #4 ARTICULATORS IN THE ORAL CAVITY LIPS (Latin labia ) labial sounds bilabial labiodental e.g. bee, my e.g. fly, veal TEETH (Latin dentes) dental sounds e.g. think, they ALVEOLAR
LINGUISTICS 130 LECTURE #4 ARTICULATORS IN THE ORAL CAVITY LIPS (Latin labia ) labial sounds bilabial labiodental e.g. bee, my e.g. fly, veal TEETH (Latin dentes) dental sounds e.g. think, they ALVEOLAR
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery
 Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Associate Professor of Plastic Surgery, University of Upsala, Sweden
 AN OPERATION FOR INVERTED NIPPLES By TORD SKOOG, M.D. Associate Professor of Plastic Surgery, University of Upsala, Sweden THE human embryology and anatomy of deformed nipples was thoroughly studied by
AN OPERATION FOR INVERTED NIPPLES By TORD SKOOG, M.D. Associate Professor of Plastic Surgery, University of Upsala, Sweden THE human embryology and anatomy of deformed nipples was thoroughly studied by
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Frenuloplasty with A Splitthicknes Skin Graft
 Original Article Frenuloplasty with A Splitthicknes Skin Graft Ghodrat Mohammadi, Masoud Nnaderpour From Department of Otolaryngology, Tabriz University of Medical Science, Tabriz, Iran. Correspondence:
Original Article Frenuloplasty with A Splitthicknes Skin Graft Ghodrat Mohammadi, Masoud Nnaderpour From Department of Otolaryngology, Tabriz University of Medical Science, Tabriz, Iran. Correspondence:
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
The Advantages of Two Stages in Repair. of Bilateral Cleft Lip. VICTOR SPINA, M.D. Sado Paulo, Brazil
 The Advantages of Two Stages in Repair of Bilateral Cleft Lip VICTOR SPINA, M.D. Sado Paulo, Brazil The suggestion of using two stages for the surgical correction of complete bilateral clefts of the lip
The Advantages of Two Stages in Repair of Bilateral Cleft Lip VICTOR SPINA, M.D. Sado Paulo, Brazil The suggestion of using two stages for the surgical correction of complete bilateral clefts of the lip
The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead
 IRRADIATION INJURIES OF THE PERINEUM By R. L. B. BEARE, F.R.C.S. The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead MISGUIDED radiotherapy has in the past caused much misery, and continues to do so, although
IRRADIATION INJURIES OF THE PERINEUM By R. L. B. BEARE, F.R.C.S. The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead MISGUIDED radiotherapy has in the past caused much misery, and continues to do so, although
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
MeELisa D. Moore, M.D. W. THomas Lawrence, M.D. JEFFREY J. PTAK, M.D. WILLIAM C. TRIER, M.D.
 _ Complications of Primary Palatoplasty: A Twenty-One-Year Review MeELisa D. Moore, M.D. W. THomas Lawrence, M.D. JEFFREY J. PTAK, M.D. WILLIAM C. TRIER, M.D. The complications of 196 patients who underwent
_ Complications of Primary Palatoplasty: A Twenty-One-Year Review MeELisa D. Moore, M.D. W. THomas Lawrence, M.D. JEFFREY J. PTAK, M.D. WILLIAM C. TRIER, M.D. The complications of 196 patients who underwent
THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction
 THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
A NEW OPERATION FOR CONGENITAL AND PARALYTIC PTOSIS. By M. SARWAR, M.B., B.S., D.O.M.S. Ophthalmologist, United Oxford Hospitals
 A NEW OPERATION FOR CONGENITAL AND PARALYTIC PTOSIS By M. SARWAR, M.B., B.S., D.O.M.S. Ophthalmologist, United Oxford Hospitals THE various remedies for ptosis have never been really satisfactory, as is
A NEW OPERATION FOR CONGENITAL AND PARALYTIC PTOSIS By M. SARWAR, M.B., B.S., D.O.M.S. Ophthalmologist, United Oxford Hospitals THE various remedies for ptosis have never been really satisfactory, as is
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
ISOLATED CLEFT PALATE IS AMONG
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JOURNAL CLUB Impact of Cleft Width in Clefts of Secondary Palate on the Risk of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency Scan for Author Audio Interview Derek J. Lam, MD, MPH; Lynn L. Chiu, MD; Kathleen
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JOURNAL CLUB Impact of Cleft Width in Clefts of Secondary Palate on the Risk of Velopharyngeal Insufficiency Scan for Author Audio Interview Derek J. Lam, MD, MPH; Lynn L. Chiu, MD; Kathleen
Pharyngoplasty. The Welsh Centre for Cleft Lip and Palate. Speech and Language Therapy. Morriston Hospital. Swansea.
 Pharyngoplasty The Welsh Centre for Cleft Lip and Palate Speech and Language Therapy Morriston Hospital Swansea www.wales.nhs.uk/cleft-team Pharyngoplasty surgery This leaflet has been designed to help
Pharyngoplasty The Welsh Centre for Cleft Lip and Palate Speech and Language Therapy Morriston Hospital Swansea www.wales.nhs.uk/cleft-team Pharyngoplasty surgery This leaflet has been designed to help
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 69-74 www.iosrjournals.org Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 69-74 www.iosrjournals.org Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
WILLIAM B. BOHANNAN DDS, MD PROFESSIONAL CORPORATION
 7.12.18 WILLIAM B. BOHANNAN DDS, MD RE: Samuel Bower Site #6 To whom it may concern: Mr. Bower and his parents wish to seek additionally opinions for site #6. They are trying to decide if further surgery
7.12.18 WILLIAM B. BOHANNAN DDS, MD RE: Samuel Bower Site #6 To whom it may concern: Mr. Bower and his parents wish to seek additionally opinions for site #6. They are trying to decide if further surgery
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF MANDIBULAR ASYMMETRY By MARIAN GORSKI, M.D., 1 and IRENA HALINA TARCZYNSKA, M.D. Maxillo-Facial Clinic, Warsaw Medical Academy
 SURGICL TRETMENT OF MNDIULR SYMMETRY y MRIN GORSKI, M.D., 1 and IREN HLIN TRCZYNSK, M.D. Maxillo-Facial Clinic, Warsaw Medical cademy UNILTERL mandibular deformities may be due to either overgrowth or
SURGICL TRETMENT OF MNDIULR SYMMETRY y MRIN GORSKI, M.D., 1 and IREN HLIN TRCZYNSK, M.D. Maxillo-Facial Clinic, Warsaw Medical cademy UNILTERL mandibular deformities may be due to either overgrowth or
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Rotation-Advancement Principle. in Cleft Lip Closure. D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida
 Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
Rotation-Advancement Principle in Cleft Lip Closure D. RALPH MILLARD, JR., M.D., F.A.C.S. Miami, Florida Correction of prealveolar, alveolar, and postalveolar clefts poses a fivefold project: natural appearance,
