Superficial femoral popliteal vein: An anatomic study
|
|
|
- Hollie Fowler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Superficial femoral popliteal vein: An anatomic study Steven M. Santilli, MD, PhD, FACS, Eugene S. Lee, MD, Shane E. Wernsing, BA, Daniel A. Diedrich, BS, Michael A. Kuskowski, PhD, and Ronald L. Shew, PhD, Minneapolis, Minn Objective: The superficial femoral popliteal vein (SFPV) has been used as an alternative conduit for both arterial and venous reconstructive surgery. Its popularity continues to grow, despite concern about the potential for venous morbidity after harvest. The purpose of this study was to determine an anatomic safe length of SFPV for harvest, assuming that the preservation of at least one valve and one significant collateral vein in the remaining popliteal vein (PV) segment can minimize venous morbidity. Methods: Forty-four SFPVs were harvested from 39 cadaveric specimens. The length of both the superficial femoral vein (SFV) and PV was measured, and the number and location of valves and significant side branches (more than 2 mm in diameter) of the PV were measured. The Student two-tailed t test was used as a means of comparing vein lengths between the sexes. Correlation coefficients were determined for the effect of patient height on vein length, stratified by means of sex. Results: Vein length (SFV mean, 24.4 ± 4 cm; PV mean, 18.8 ± 4 cm) varied with sex (male SFV mean, 28.1 ± 5 cm; male PV mean, 21.5 ± 3 cm; female SFV mean, 22.6 ± 4 cm; female PV mean, 18.4 ± 3 cm; P =.01). Valve number (mean, 1.8 ± 0.5) and location and collateral vein number (mean, 5 ± 1.8) and location were variable and independent of height or sex. Conclusion: An anatomic safe length of SFPV for harvest to minimize venous morbidity would include all the SFV and 12 cm of PV in 95% of women and 15 cm of PV in 95% of men. We found that the male sex was a significant determinant for a longer safe length of vein that can be harvested. (J Vasc Surg 2000;31:450-5.) The superficial femoral popliteal vein (SFPV) has become well-established as an alternative conduit for infrainguinal, aortoiliac, and major venous reconstructions. 1-5 Fear that SFPV harvest will result in From the Vascular Surgery Section, Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Surgery, University of Minnesota (Drs Santilli and Lee); University of Minnesota Medical School (Messrs Wernsing and Diedrich); Geriatric Research, Education, and Clinical Center, Veterans Affairs Medical Center (Dr Kuskowski); and the Department of Cell Biology and Neuroanatomy, University of Minnesota (Dr Shew). Competition of interest: nil. Supported by a Department of Veterans Affairs Merit Review Grant and a Public Health Service, National Research Service Award (1F32HL ). Presented at the Fifty-third Annual Meeting of The Society for Vascular Surgery, Washington, DC, Jun 6 9, Reprint requests: Steven M. Santilli, MD, VAMC, 1 Veterans Dr, Vascular Surgery Section, Surgery 112, Minneapolis, MN Copyright 2000 by The Society for Vascular Surgery and International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery, North American Chapter /2000/$ /1/ doi: /mva significant morbidity because of acute and chronic venous hypertension persists, and most investigators report some degree of leg swelling immediately after harvest. 6-9 However, some investigators report harvest of the conduit with minimal or no long-term morbidity, whereas other investigators note significant early and late morbidity. 6-9 Intuitively, the key to preventing morbidity appears to be the status of the veins remaining after the harvest of the SFPV, particularly the popliteal vein (PV). Therefore, the length of vein harvested, the presence of venous competence (of the remaining deep veins after femoral popliteal vein harvest), and the collateral vessels between the PV and profunda femoris vein (PFV) are thought to be important in preventing significant postharvest morbidity. With these factors in mind, we performed a cadaver study to determine: (1) the average lengths of both the superficial femoral vein (SFV) and the PV; (2) the number and location of valves in the PV; (3) the number and location of significant (more than 2 mm in diameter) collateral veins in the PV; and (4) the average safe length of SFPVs that can be harvested, preserving at least one valve and one significant collateral vein 450
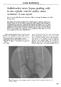
2 Volume 31, Number 3 Santilli et al 451 Fig 1. Cadaveric dissection of the popliteal vein demonstrating collateral veins (arrows). The groin is to the right, and the knee is to the left. proximal to the preserved valve in the remaining PV segment after SFPV harvest. METHODS Forty-four SFPVs harvested from 39 cadaveric specimens were used for data analysis. In five cases, the SFPVs were harvested bilaterally, whereas the remainder were harvested from the right leg. Excluded from the study were cases with previous leg or knee trauma (including operative procedures) or SFPV segments that had been damaged during preservation. The SFPV was carefully exposed through a medial leg incision from its junction with the PFV to the origin of the PV at the entry of the anterior tibial vein. After exposure, all significant collateral veins (more than 2 mm, confirmed by means of the outside diameter measurements) in the PV were identified, preserved, and photographed (Fig 1). The location of the collateral veins was measured in the PV as the distance from the inferior edge of the adductor hiatus to the collateral vein (Fig 2). SFV length was measured from the SFV/PFV confluence to the inferior edge of the adductor hiatus, and PV length was measured from the inferior edge of the adductor hiatus to the entry of the anterior tibial vein. The SFPV was then opened along its entire length, the luminal surface was washed with water, and valves within the PV were identified and photographed (Fig 3). Valve locations in the PV were recorded as distances from the inferior edge of the adductor hiatus. The Student two-tailed t test was used as a means of comparing anatomic safe vein lengths between the sexes, and nonparametric correlation coefficients were determined to compare the effect of cadaver height on vein lengths stratified by means of sex (SPSS 9.0, Chicago, Ill). RESULTS Forty-four SFPVs were harvested from 39 cadaveric specimens, 13 male (mean height, 170 cm) and 26 female (mean height, 150 cm; Fig 4). All measurements are recorded in Table I. A comparison of right and left vein lengths was performed by using a paired two-tailed t test in five cadavers (Table II), and no difference was found between the two limbs (P =.9). Both SFV and PV lengths and distances to valve and collateral branch locations in the PV
3 452 Santilli et al March 2000 Table I. Summary of superficial femoral vein and popliteal vein lengths and distances to valves and branches Average anatomic Anatomic safe safe length length of PV SFV length PV length PV branch total Men 50 cm* 15 cm* 28.1 ± 5.0 cm* 21.5 ± 3.0 cm* 5.7 ± 3.0 N = 13, average height, 170 cm Women 40 cm* 12 cm* 22.6 ± 4.0 cm* 18.4 ± 3.0 cm* 4.6 ± 1.0 N = 26, average height, 150 cm Total 24.4 ± 4.0 cm 18.8 ± 4.0 cm 5.0 ± 1.8 N = 39 cadavers N = 44 SFPVs *P <.01 with a two-tailed t test when comparing men with women. SFV, Superficial femoral vein; PV, popliteal vein; SFPVs, superficial femoral popliteal veins. Table II. A comparison of right and left popliteal vein lengths (in centimeters) in five cadavers (P =.9) Patient Right Left Difference were dependent on patient sex and independent of patient height. SFV and PV lengths were found to be significantly different between men and women (P <.01). Men had an average SFV length of 28.1 ± 5 cm and a PV length of 21.5 ± 3 cm, whereas women had an average SFV length of 21.5 ± 3 cm and a PV length of 18.4 ± 3 cm (Table I). Nonparametric correlations were performed to determine the effect of height on vein length. No significant correlations were found between height and vein lengths when analyzed by means of sex (women R, 0.128; P =.53; men R, 0.40; P =.20). Overall, the average anatomic safe vein length of the SFPV in men is 50 cm, and the average anatomic safe vein length of the SFPV in women is 40 cm. The anatomic safe length of the PV at a 95% CI level is 15 cm in men and 12 cm in women (Table I). The 95% CI level is the vein length at which the longest length can be harvested in 95% of the population while still leaving one valve and one collateral branch intact. DISCUSSION The SFPV has been used as a conduit for in situ reconstruction after removal of infected prosthetic aortic grafts, lower-extremity bypass grafting, and major venous reconstruction. 1-5 Excellent patency rates for reconstructions with the SFPV are reported, 1-5 but a hesitancy about its use remains because of the potential for significant venous morbidity after its harvest. Significant variation in venous morbidity, from minimal to debilitating pain and swelling, after SFPV harvest has been reported. 6-9 Further examination of these reports reveals that there is no accepted standard of care for the length of vein harvested, preoperative venous evaluation (including evaluation for valvular competence and functional venous testing), or standard perioperative care. Differences in care may account for the variation in reported morbidity after SFPV harvest, and therefore, a clinically safe length of SFPV for harvest has yet to be determined. Other interventions or pathologic conditions of the SFPV may shed light on a safe length for harvest. SFV ligation has been used to prevent pulmonary emboli from the lower extremity. The procedure fell into disfavor because of several reasons, including reports that SFPV ligation causes elevated venous foot pressures and the demonstration of a high rate venous ulceration by some investigators However, Masuda et al 13 reported a 13-year follow-up study in which SFV obstruction was demonstrated to be well tolerated with minimal morbidity, provided the PFV was patent. These findings suggest that earlier reports of significant morbidity after SFV ligation may be attributed to other factors, including incomplete diagnosis of the extent of venous disease (either PFV or proximal vein occlusion). Raju et al 14 reported on obstruction of the SFPV and demonstrated that there is no correlation between the anatomic locale, the extent of venous obstruction, or the venographic occurrence of collaterals and significant venous morbidity. They suggested there was an association
4 Volume 31, Number 3 Santilli et al 453 Distance to first Distance to last PV branch PV branch PV valve total Distance to first PV valve Distance to last PV valve 3.9 ± 3.0 cm 15.4 ± 4.0 cm 1.8 ± ± 4.0 cm 16.8 ± 3.0 cm 2.7 ± 3.0 cm 13.0 ± 4.0 cm 1.8 ± ± 5.0 cm 13.8 ± 4.0 cm 3.1 ± 3.0 cm 14.0 ± 4.0 cm 1.8 ± ± 5.0 cm 14.1 ± 3.0 cm Fig 2. Cadaveric dissection of the popliteal artery and popliteal vein as they emerge from the adductor hiatus. The groin is to the right, and the knee is to the left. between venous morbidity and the degree of venous reflux. These observations suggest that venous morbidity associated with ligation/obstruction of the SFPV is multifactorial in origin and may be related to both obstruction and reflux, and that harvest of the SFV alone without proximal obstruction and with a patent PFV is free of significant venous morbidity. We assume that an important factor in reducing venous morbidity after obstruction is the presence of significant collateral veins between the PV and the
5 454 Santilli et al March 2000 Fig 3. Close-up of cadaveric dissection of a valve (arrow) in the popliteal vein. The groin is to the right, and the knee is to the left. Fig 4. Cadaveric specimen of deep veins of the legs: the common femoral vein, profunda femoris vein, superficial femoral vein, popliteal vein, and anterior tibial vein. PFV. 15 Mavor and Galloway described the venous anatomy of the lower extremity, with particular attention to collateral venous channels. 16 They found that in more than 90% of specimens they could demonstrate a communication between the PV or venae comitantes of the popliteal artery and the common femoral or PFV. The role of collateral veins in preventing venous morbidity after SFPV harvest was further supported by Wells et al, who reported minimal clinical morbidity after SFPV harvest. 6 In this study, patients were examined with lower-extremity duplex scanning after SFPV harvest, and a constant finding was the presence of collateral veins between the PV stump and the PFV, which the authors felt were important in the prevention of significant venous morbidity. These data suggest that a patent PV with a collateral network to the PFV or common femoral vein is important in preventing venous morbidity after SFPV harvest. Given the conflicting reports of minimal or significant venous morbidity and the variety of reporting methods, it is difficult to determine a safe length of
6 Volume 31, Number 3 Santilli et al 455 SFPV for harvest. However, considering these data, we conclude that venous morbidity associated with SFPV harvest is probably not dependent on the harvest of the SFV, but more likely is caused by the harvest of the PV and is associated with two factors: significant reflux disease in the veins remaining after SFPV harvest and the absence of collateral veins from the PV to the PFV or common femoral vein. Therefore, we define an anatomic safe length of SFPV for harvest as a length that would leave one valve in the distal PV stump (to prevent reflux) and one significant collateral vein (more than 2 mm in diameter) in the PV stump superior to the valve. Although our study evaluates the anatomic safe vein length, the basis for which we perform SFV/PV harvest should be a thorough anatomic study. Clinical correlation studies are necessary to determine whether these anatomic safe vein lengths are functionally safe. Our data were analyzed in relation to height and sex. Height data were obtained from the medical records of the patients before death. In examining the data, we found that the anatomic safe vein length was independent of height and dependent on sex. In conclusion, the use of SFPV as an alternative conduit continues to expand. We have defined an anatomic safe vein length of SFPV for harvest to include one valve in the distal PV stump (to prevent reflux) and one significant collateral vein (more than 2 mm in diameter) in the PV stump superior to the valve. Given these criteria, 15 cm of PV in men and 12 cm of PV in women can be harvested distal to the inferior edge of the adductor hiatus with a 95% confidence of preserving at least one valve and one collateral vein. In our study, the average anatomic safe length of SFPV for harvest varied from 40 cm in women to 50 cm in men. We thank Ms Connie Lindberg for her editorial assistance in the preparation of the manuscript and Mr David Lee for his technical assistance during the cadaveric dissection. REFERENCES 1. Schulman ML, Badhey MR, Yatco R, Pillari G. An 11-year experience with deep leg veins as femoropopliteal bypass grafts. Arch Surg 1986;121: Schulman ML, Badhey MR, Yatco R. Superficial femoralpopliteal veins and reversed saphenous veins as primary femoropopliteal bypass grafts: a randomized comparative study. J Vasc Surg 1987;6: Clagett GP, Valentine RJ, Hagino RT. Autogenous aortoiliac/femoral reconstruction from superficial femoral-popliteal veins: feasibility and durability. J Vasc Surg 1997;25: Clagett GP, Bowers BL, Lopez-Viego MA, Rossi MB, Valentine RJ, Myers SI, et al. Creation of a neo-aortoiliac system from lower extremity deep and superficial veins. Ann Surg 1993;213: Hagino RT, Bengston TD, Fosdick DA, Valentine RJ, Clagett GP. Venous reconstructions using the superficial femoral-popliteal vein. J Vasc Surg 1997;26: Wells JK, Hagino RT, Bargmann KM, Jackson MR, Valentine RJ, Kakish HB. Venous morbidity after superficial femoral popliteal vein harvest. J Vasc Surg 1999;29: Sladen JG, Reid JDS, Maxwell TM, Downs AR. Superficial femoral vein: a useful autogenous harvest site. J Vasc Surg 1994;20: Downs AR, Guzman RP. Superficial femoral vein an alternate vascular conduit. In: Whittemore AD, editor. Advances in vascular surgery. Vol 4. St. Louis: CV Mosby; p Coburn M, Ashworth C, Francis W, Morin C, Broukhim M, Carney WI Jr. Venous stasis complications of the use of superficial femoral and popliteal veins for lower extremity bypass. J Vasc Surg 1993;17: Decamp PT, Ward JA, Ochsner A. Ambulatory venous pressure studies in post-phlebitic and other disease states. Surgery 1951;29: Allen AW, Linton RR, Donaldson GA. Thrombosis and embolism. Ann Surg 1943;118: Robinson JR, Moyer CA. Comparison of late sequelae of common and superficial femoral vein ligations. Surgery 1954;35: Masuda EM, Kistner RL, Ferris EB III. Long-term effects of superficial femoral vein ligation: thirteen year follow-up. J Vasc Surg 1992;16: Raju S, Fredericks R. Venous obstruction: an analysis of one hundred thirty-seven cases with hemodynamic, venographic, and clinical correlations. J Vasc Surg 1991;14: van Limborgh J. L anatomie du systeme veineux de l extremite infe rieure en relation avec la patholgie variqueuse. Folia Angiol (Pisa) 1961;VIII: Mavor K, Galloway JMD. Collaterals of the deep venous circulation of the lower limb. Surg Gyn Obstet 1967;9: Submitted Aug 3, 1999; accepted Oct 18, 1999.
J. G. Sladen, MD, J. D. S. Reid, MD, T. M. Maxwell, MD, and A. R. Downs, MD, Vancouver, British Columbia, and Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada
 Superficial femoral vein: harvest site A useful autogenous J. G. Sladen, MD, J. D. S. Reid, MD, T. M. Maxwell, MD, and A. R. Downs, MD, Vancouver, British Columbia, and Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Purpose:
Superficial femoral vein: harvest site A useful autogenous J. G. Sladen, MD, J. D. S. Reid, MD, T. M. Maxwell, MD, and A. R. Downs, MD, Vancouver, British Columbia, and Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Purpose:
Venous morbidity after superficial femoralpopliteal
 Venous morbidity after superficial femoralpopliteal vein harvest Joe K. Wells, MD, Ryan T. Hagino, MD, Kristina M. Bargmann, RN, BSN, Mark R. Jackson, MD, R. James Valentine, MD, Humam B. Kakish, MD, and
Venous morbidity after superficial femoralpopliteal vein harvest Joe K. Wells, MD, Ryan T. Hagino, MD, Kristina M. Bargmann, RN, BSN, Mark R. Jackson, MD, R. James Valentine, MD, Humam B. Kakish, MD, and
Influence of the profunda femoris vein on venous hemodynamics of the limb
 Influence of the profunda femoris vein on venous hemodynamics of the limb Experience from thirty-one deep vein valve reconstructions Ingvar Eriksson, M.D., and Bo Almgren, M.D., Uppsala, Sweden Venous
Influence of the profunda femoris vein on venous hemodynamics of the limb Experience from thirty-one deep vein valve reconstructions Ingvar Eriksson, M.D., and Bo Almgren, M.D., Uppsala, Sweden Venous
Symptomatic venous thromboembolism after femoral vein harvest
 From the Western Vascular Society Symptomatic venous thromboembolism after femoral vein harvest Ravi V. Dhanisetty, MD, a Timothy K. Liem, MD, a Gregory J. Landry, MD, a Brett C. Sheppard, MD, b Erica
From the Western Vascular Society Symptomatic venous thromboembolism after femoral vein harvest Ravi V. Dhanisetty, MD, a Timothy K. Liem, MD, a Gregory J. Landry, MD, a Brett C. Sheppard, MD, b Erica
Venous stasis complications of the use of the superficial femoral and popliteal veins for lower extremity bypass
 Venous stasis complications of the use of the superficial femoral and popliteal veins for lower extremity bypass Michael Coburn, MD, Charles Ashworth, MD, Warren Francis, MD, Christopher Morin, MD, Maryam
Venous stasis complications of the use of the superficial femoral and popliteal veins for lower extremity bypass Michael Coburn, MD, Charles Ashworth, MD, Warren Francis, MD, Christopher Morin, MD, Maryam
Arterial reconstruction with deep leg veins for the treatment of mycotic aneurysms
 Arterial reconstruction with deep leg veins for the treatment of mycotic aneurysms Marshall E. Benjamin, MD, E. Jerry Cohn, Jr, MD, William A. Purtill, MD, Dinah J. Hanna, MD, Michael P. Lilly, MD, and
Arterial reconstruction with deep leg veins for the treatment of mycotic aneurysms Marshall E. Benjamin, MD, E. Jerry Cohn, Jr, MD, William A. Purtill, MD, Dinah J. Hanna, MD, Michael P. Lilly, MD, and
Journal of American Science 2017;13(3) Neoaortoiliac system (NAIS) for treatment of infective aortic disease
 Neoaortoiliac system (NAIS) for treatment of infective aortic disease Hossam M. Saleh, MD Vascular Surgery Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Egypt. hosamsaleh2003@yahoo.com Abstract:
Neoaortoiliac system (NAIS) for treatment of infective aortic disease Hossam M. Saleh, MD Vascular Surgery Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Egypt. hosamsaleh2003@yahoo.com Abstract:
Exposure of the anterior tibial artery by medial popliteal extension
 Exposure of the anterior tibial artery by medial popliteal extension J. G. Sladen, FRCS(C), G. Kougeer, FRCS(C), and J. D. S. Reid, FRCS(C), Vancouver) British Columbia) Canada This report describes exploration
Exposure of the anterior tibial artery by medial popliteal extension J. G. Sladen, FRCS(C), G. Kougeer, FRCS(C), and J. D. S. Reid, FRCS(C), Vancouver) British Columbia) Canada This report describes exploration
Surgical disobliteration of postthrombotic deep veins endophlebectomy is feasible
 Surgical disobliteration of postthrombotic deep veins endophlebectomy is feasible Alessandra Puggioni, MD, a,c Robert L. Kistner, MD, a,b Bo Eklof, MD, PhD, a,b,c and Fedor Lurie, MD, PhD, a,b,c Honolulu,
Surgical disobliteration of postthrombotic deep veins endophlebectomy is feasible Alessandra Puggioni, MD, a,c Robert L. Kistner, MD, a,b Bo Eklof, MD, PhD, a,b,c and Fedor Lurie, MD, PhD, a,b,c Honolulu,
Venous drainage of the lower limb
 Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy
 Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
IS POLYTETRAFLUOROETHYLENE (PTFE) THE CORRECT CHOICE TO TREAT CONTAMINATED TRAUMATIC VASCULAR INJURIES?
 IS POLYTETRAFLUOROETHYLENE (PTFE) THE CORRECT CHOICE TO TREAT CONTAMINATED TRAUMATIC VASCULAR INJURIES? Nigel Denis MD Class of 2016 University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida, USA Disclosures
IS POLYTETRAFLUOROETHYLENE (PTFE) THE CORRECT CHOICE TO TREAT CONTAMINATED TRAUMATIC VASCULAR INJURIES? Nigel Denis MD Class of 2016 University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida, USA Disclosures
Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series. Lower Extremity Arteries
 Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series Lower Extremity Arteries 1 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches For the life of the flesh is in the blood. Leviticus 17:11 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches After
Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series Lower Extremity Arteries 1 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches For the life of the flesh is in the blood. Leviticus 17:11 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches After
INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL. Arya ashok 1, Swapna kumary 2
 INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 0 09) (November, 07) () UNILATERAL VARIATION OF GREAT SAPHENOUS VEIN- A CADAVERIC STUDY Arya ashok, Swapna kumary
INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 0 09) (November, 07) () UNILATERAL VARIATION OF GREAT SAPHENOUS VEIN- A CADAVERIC STUDY Arya ashok, Swapna kumary
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI?
 Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Venous Reflux Duplex Exam
 Venous Reflux Duplex Exam GWENDOLYN CARMEL, RVT PHYSIOLOGIST, DEPARTMENT OF VASCULAR SURGERY NEW JERSEY VETERANS HEALTHCARE CENTER EAST ORANGE, NJ PURPOSE: To identify patterns of incompetence and which
Venous Reflux Duplex Exam GWENDOLYN CARMEL, RVT PHYSIOLOGIST, DEPARTMENT OF VASCULAR SURGERY NEW JERSEY VETERANS HEALTHCARE CENTER EAST ORANGE, NJ PURPOSE: To identify patterns of incompetence and which
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Axial transformation of the profunda femoris vein
 Axial transformation of the profunda femoris vein Seshadri Raju, MD, Todd Fountain, BS, Peter Neglén, MD, and M. Devidas, PhD, Jackson, Miss. Purpose: To highlight a special subset of cases of venous stasis
Axial transformation of the profunda femoris vein Seshadri Raju, MD, Todd Fountain, BS, Peter Neglén, MD, and M. Devidas, PhD, Jackson, Miss. Purpose: To highlight a special subset of cases of venous stasis
Femoral Artery. Its entrance to the thigh Position Midway between ASIS and pubic symphysis
 Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M
 Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Protocols for the evaluation of lower extremity venous reflux: supine, sitting, or standing?
 Protocols for the evaluation of lower extremity venous reflux: supine, sitting, or standing? Susan Whitelaw RVT, RDMS PURPOSE Duplex imaging of the lower extremity veins is performed to assess the deep
Protocols for the evaluation of lower extremity venous reflux: supine, sitting, or standing? Susan Whitelaw RVT, RDMS PURPOSE Duplex imaging of the lower extremity veins is performed to assess the deep
Case Discussion. Disclosures. Critical Limb Ischemia: A Selective Approach to Revascularization Works Best 4/28/2012. None. 58 yo M, DM, CAD, HTN
 Critical Limb Ischemia: A Selective Approach to Revascularization Works Best None Disclosures Michael S. Conte MD, FACS Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Heart and Vascular Center
Critical Limb Ischemia: A Selective Approach to Revascularization Works Best None Disclosures Michael S. Conte MD, FACS Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Heart and Vascular Center
Schedule of Benefits. for Professional Fees Vascular Procedures
 Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
Rare Vascular Anomalies in the Femoral Triangle During Varicose Vein Surgery
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:99-104 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CLINICAL RESEARCH https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.99 Rare Vascular Anomalies in the Femoral Triangle
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:99-104 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CLINICAL RESEARCH https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.99 Rare Vascular Anomalies in the Femoral Triangle
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI
 Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Surgery is and Remains the Gold Standard for Limb-Threatening Ischemia
 Surgery is and Remains the Gold Standard for Limb-Threatening Ischemia Albeir Mousa, MD., FACS.,MPH., MBA Professor of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery West Virginia University Disclosure None What you
Surgery is and Remains the Gold Standard for Limb-Threatening Ischemia Albeir Mousa, MD., FACS.,MPH., MBA Professor of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery West Virginia University Disclosure None What you
Influence of vein size (diameter) on infrapopliteal reversed vein graft patency
 Influence of vein size (diameter) on infrapopliteal reversed vein graft patency Kurt R. Wengerter, MD, Frank J. Veith, MD, Sushil K. Gupta, MD, Enrico Ascer, MD, and Steven P. Rivers, MD, New York, N.Y.
Influence of vein size (diameter) on infrapopliteal reversed vein graft patency Kurt R. Wengerter, MD, Frank J. Veith, MD, Sushil K. Gupta, MD, Enrico Ascer, MD, and Steven P. Rivers, MD, New York, N.Y.
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division
 John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open techniques.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 14 Number 2 Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open A Rodriguez-Rivera,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 14 Number 2 Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open A Rodriguez-Rivera,
Remote Endarterectomy Update
 Remote Endarterectomy Update An endovascular alternative to bypass? BY JOHN D. MARTIN, MD Treating the superficial femoral artery (SFA) is still one of the most highly debated topics among vascular specialists.
Remote Endarterectomy Update An endovascular alternative to bypass? BY JOHN D. MARTIN, MD Treating the superficial femoral artery (SFA) is still one of the most highly debated topics among vascular specialists.
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization:
 Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
High Level Overview: Venous Anatomy of Lower Extremities. Anatomy of a Vein 5/11/2015. Barbara Deusterman, RN
 High Level Overview: Venous Anatomy of Lower Extremities Barbara Deusterman, RN What does this anatomy lecture have to do with visually guided sclerotherapy (VGS)? May 11, 2015 2 Anatomy of a Vein Almeida,
High Level Overview: Venous Anatomy of Lower Extremities Barbara Deusterman, RN What does this anatomy lecture have to do with visually guided sclerotherapy (VGS)? May 11, 2015 2 Anatomy of a Vein Almeida,
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD
 PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
Venous reflux in patients with previous venous thrombosis: Correlation with ulceration and other symptoms
 Venous reflux in patients with previous venous thrombosis: Correlation with ulceration and other symptoms deep N. Labropoulos, BSc, M. Leon, MD, A. N. Nicolaides, MS, FRCS, O. Sowade, MSc, MB, BS, N. Volteas,
Venous reflux in patients with previous venous thrombosis: Correlation with ulceration and other symptoms deep N. Labropoulos, BSc, M. Leon, MD, A. N. Nicolaides, MS, FRCS, O. Sowade, MSc, MB, BS, N. Volteas,
Tsunehisa Sakurai, MD, Masahiro Matsushita, MD, Naomichi Nishikimi, MD, and Yuji Nimura, MD, Nagoya, Japan
 Hemodynamic assessment of femoropopliteal venous reflux in with primary varicose veins patients Tsunehisa Sakurai, MD, Masahiro Matsushita, MD, Naomichi Nishikimi, MD, and Yuji Nimura, MD, Nagoya, Japan
Hemodynamic assessment of femoropopliteal venous reflux in with primary varicose veins patients Tsunehisa Sakurai, MD, Masahiro Matsushita, MD, Naomichi Nishikimi, MD, and Yuji Nimura, MD, Nagoya, Japan
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
Reproducibility of ultrasound scan in the assessment of volume flow in the veins of the lower extremities
 Reproducibility of ultrasound scan in the assessment of volume flow in the veins of the lower extremities Tomohiro Ogawa, MD, PhD, Fedor Lurie, MD, PhD, RVT, Robert L. Kistner, MD, Bo Eklof, MD, PhD, and
Reproducibility of ultrasound scan in the assessment of volume flow in the veins of the lower extremities Tomohiro Ogawa, MD, PhD, Fedor Lurie, MD, PhD, RVT, Robert L. Kistner, MD, Bo Eklof, MD, PhD, and
Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll.
 Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll. For the Department of Vascular Surgery and Kidney Transplantation University Hospital of Strasbourg, FRANCE Popliteal artery entrapment: misdiagnosed Epidemiology Prevalence:
Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll. For the Department of Vascular Surgery and Kidney Transplantation University Hospital of Strasbourg, FRANCE Popliteal artery entrapment: misdiagnosed Epidemiology Prevalence:
Imaging Strategy For Claudication
 Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Case Report Surgical Treatment for Profunda Femoris Artery Aneurysms: Five Case Reports
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 375278, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375278 Case Report Surgical Treatment for Profunda Femoris Artery Aneurysms: Five Case Reports Kimihiro
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 375278, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375278 Case Report Surgical Treatment for Profunda Femoris Artery Aneurysms: Five Case Reports Kimihiro
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS
 HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
Surgical approach for DVT. Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
2 Aortic Arch Debranching UCSF Vascular Symposium /14/16. J Endovasc Ther 2002;9:suppl 2; II98 105
 How I Do It: Aortic Arch Debranching Exposures, Tunnels and Techniques Warren Gasper MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Vascular Surgery No disclosures 2 Aortic Arch Debranching UCSF Vascular Symposium
How I Do It: Aortic Arch Debranching Exposures, Tunnels and Techniques Warren Gasper MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Vascular Surgery No disclosures 2 Aortic Arch Debranching UCSF Vascular Symposium
Deep axial reflux, an important contributor to skin changes or ulcer in chronic venous disease
 Deep axial reflux, an important contributor to skin changes or ulcer in chronic venous disease Gudmundur Danielsson, MD, PhD, a Bo Eklof, MD, PhD, b Andrew Grandinetti, PhD, c Fedor Lurie, MD, PhD, a and
Deep axial reflux, an important contributor to skin changes or ulcer in chronic venous disease Gudmundur Danielsson, MD, PhD, a Bo Eklof, MD, PhD, b Andrew Grandinetti, PhD, c Fedor Lurie, MD, PhD, a and
Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options
 Deepak N. Deshmukh DO April 27, 2018 Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options No Disclosures Popliteal Artery Aneurysms (PAAs) Male Predominanace Most common peripheral Aneurysm (70%) 30-50%
Deepak N. Deshmukh DO April 27, 2018 Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options No Disclosures Popliteal Artery Aneurysms (PAAs) Male Predominanace Most common peripheral Aneurysm (70%) 30-50%
Popliteal Aneurysm: When is surgical therapy indicated? PROF. GRZEGORZ OSZKINIS
 Popliteal Aneurysm: When is surgical therapy indicated? PROF. GRZEGORZ OSZKINIS Asymptomatic mass - 38-40%will develop symptoms at a rate of 14%/yr Intermittent claudic ation (chronic ischemia) - 25%-40%
Popliteal Aneurysm: When is surgical therapy indicated? PROF. GRZEGORZ OSZKINIS Asymptomatic mass - 38-40%will develop symptoms at a rate of 14%/yr Intermittent claudic ation (chronic ischemia) - 25%-40%
Comparing patency rates between external iliac and common iliac artery stents
 Comparing patency rates between external iliac and common iliac artery stents Eugene S. Lee, MD, Carol Coleman Steenson, MD, FACR, FSCVIR, Kristina E. Trimble, Michael P. Caldwell, BS, Michael A. Kuskowski,
Comparing patency rates between external iliac and common iliac artery stents Eugene S. Lee, MD, Carol Coleman Steenson, MD, FACR, FSCVIR, Kristina E. Trimble, Michael P. Caldwell, BS, Michael A. Kuskowski,
Deep Venous Pathology. Eberhard Rabe Department of Dermatology University of Bonn Germany
 Deep Venous Pathology Eberhard Rabe Department of Dermatology University of Bonn Germany Disclosures None for this presentation Consultant: Sigvaris, EUROCOM Speakers bureau: Bayer Vital, Aspen, Boehringer,
Deep Venous Pathology Eberhard Rabe Department of Dermatology University of Bonn Germany Disclosures None for this presentation Consultant: Sigvaris, EUROCOM Speakers bureau: Bayer Vital, Aspen, Boehringer,
4/23/2009. Vein Bypass Remains the Gold Standard AND We Can Improve Outcomes. Lower Extremity Revascularization Options: Key Factors to Consider
 Vein Bypass Remains the Gold Standard AND We Can Improve Outcomes Lower Extremity Revascularization Options: Key Factors to Consider General health of the patient Michael S. Conte MD Division of Vascular
Vein Bypass Remains the Gold Standard AND We Can Improve Outcomes Lower Extremity Revascularization Options: Key Factors to Consider General health of the patient Michael S. Conte MD Division of Vascular
Disclosures. Talking Points. An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are
 An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are Fadi Saab, MD, FASE, FACC, FSCAI Metro Heart & Vascular Metro Health Hospital, Wyoming, MI Assistant Clinical
An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are Fadi Saab, MD, FASE, FACC, FSCAI Metro Heart & Vascular Metro Health Hospital, Wyoming, MI Assistant Clinical
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures SVS Practice Guidelines
 Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
The femoral artery and its branches in the baboon Papio anubis
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 291 295 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The femoral artery and its branches in the baboon Papio anubis Dyl
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 291 295 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The femoral artery and its branches in the baboon Papio anubis Dyl
Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report
 CASE REPORTS Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report Evan S. Cohen,/VII), Robert B. Holtzman, MD, and George W. Johnson, Jr., MD, Houston,
CASE REPORTS Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report Evan S. Cohen,/VII), Robert B. Holtzman, MD, and George W. Johnson, Jr., MD, Houston,
Anatomy. Patterns of reflux. Technique. Testing Reflux time Patient position. Difficult! Learning. NOT system optimisation. Clinical Assesment
 Anatomy Patterns of reflux Awareness Technique Testing Reflux time Patient position Difficult! Learning NOT system optimisation Enlarged Clinical Assesment Twisted Where are the symptoms? Why they are
Anatomy Patterns of reflux Awareness Technique Testing Reflux time Patient position Difficult! Learning NOT system optimisation Enlarged Clinical Assesment Twisted Where are the symptoms? Why they are
Intervention for Lower Extremity PAD: When, why and what?! Robert F Cuff, MD FACS RVT RPVI
 Intervention for Lower Extremity PAD: When, why and what?! Robert F Cuff, MD FACS RVT RPVI 1 Disclosures I have no financial disclosures related to this talk Objectives 1. Discuss indications for intervention
Intervention for Lower Extremity PAD: When, why and what?! Robert F Cuff, MD FACS RVT RPVI 1 Disclosures I have no financial disclosures related to this talk Objectives 1. Discuss indications for intervention
Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Peripheral artery disease (PAD) results from the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the arteries of the legs. For people with PAD, symptoms may be mild, requiring no treatment except modification of
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) results from the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the arteries of the legs. For people with PAD, symptoms may be mild, requiring no treatment except modification of
Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the. femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures John Y Kwon 1*, Catherine E Johnson 1, Paul Appleton 2, Edward K Rodriguez
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures John Y Kwon 1*, Catherine E Johnson 1, Paul Appleton 2, Edward K Rodriguez
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND. CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center
 LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center Learning Objectives Setup and patient positioning for optimizing success
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center Learning Objectives Setup and patient positioning for optimizing success
Clinical case. Symptomatic anterior accessory great saphenous vein (AAGSV) reflux
 Clinical case Symptomatic anterior accessory great saphenous vein (AAGSV) reflux A 70 year-old female presents with symptomatic varicose veins on left leg for more than 10 years. She complains of heaviness,
Clinical case Symptomatic anterior accessory great saphenous vein (AAGSV) reflux A 70 year-old female presents with symptomatic varicose veins on left leg for more than 10 years. She complains of heaviness,
17 FibulA FlAP Tor Chiu fibula flap 153
 17 Fibula Flap Tor Chiu Fibula Flap 153 Fibula Flap FLAP TERRITORY This flap includes a segment of the fibular bone with or without the overlying skin island on the peroneal/ lateral aspect of the calf.
17 Fibula Flap Tor Chiu Fibula Flap 153 Fibula Flap FLAP TERRITORY This flap includes a segment of the fibular bone with or without the overlying skin island on the peroneal/ lateral aspect of the calf.
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline
 Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Prospective evaluation of chronic venous insufficiency based on foot venous pressure measurements and air plethysmography findings
 Prospective evaluation of chronic venous insufficiency based on foot venous pressure measurements and air plethysmography findings Masato Fukuoka, MD, Takaki Sugimoto, MD, and Yutaka Okita, MD, Kobe, Japan
Prospective evaluation of chronic venous insufficiency based on foot venous pressure measurements and air plethysmography findings Masato Fukuoka, MD, Takaki Sugimoto, MD, and Yutaka Okita, MD, Kobe, Japan
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Determine the patients relative risk of thrombosis. Be confident that you have had a meaningful discussion with the patient.
 Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
BC Vascular Day. Contents. November 3, Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3. Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6. Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8
 BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST I have constructed this lecture based on publications by leading cardiothoracic American surgeons: Timothy
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST I have constructed this lecture based on publications by leading cardiothoracic American surgeons: Timothy
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2)
 Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
A A U
 PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
A Successful External Valvuloplasty By Banding Application
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 13 Number 2 A Successful External Valvuloplasty By Banding Application U Yetkin, C Özbek, M Akyüz, S Bayrak,? Yürekli, A Gürbüz
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 13 Number 2 A Successful External Valvuloplasty By Banding Application U Yetkin, C Özbek, M Akyüz, S Bayrak,? Yürekli, A Gürbüz
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 287 291 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The topography of the superficial veins of the hind leg in the baboon
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 287 291 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The topography of the superficial veins of the hind leg in the baboon
N.S. Theivacumar, R.J. Darwood, M.J. Gough*
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg (2009) 37, 477e481 Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) of the Anterior Accessory Great Saphenous Vein (): Abolition of Sapheno-Femoral Reflux with Preservation of the Great Saphenous
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg (2009) 37, 477e481 Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) of the Anterior Accessory Great Saphenous Vein (): Abolition of Sapheno-Femoral Reflux with Preservation of the Great Saphenous
THE popliteal artery is the second most common site of aneurysm. The
 POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
Hemodynamic and clinical impact of ultrasoundderived venous reflux parameters
 From the American Venous Forum Hemodynamic and clinical impact of ultrasoundderived venous reflux parameters Peter Neglén, MD, PhD, a John F. Egger III, BA, a Jake Olivier, PhD, b and Seshadri Raju, MD,
From the American Venous Forum Hemodynamic and clinical impact of ultrasoundderived venous reflux parameters Peter Neglén, MD, PhD, a John F. Egger III, BA, a Jake Olivier, PhD, b and Seshadri Raju, MD,
Long-term results of infragenicular bypasses with autogenous vein originating from the distal superficial femoral and popliteal arteries
 Long-term results of infragenicular bypasses with autogenous vein originating from the distal superficial femoral and popliteal arteries Mark S. Rosenbloom, M.D., James J. Walsh, M.D., James J. Schuler,
Long-term results of infragenicular bypasses with autogenous vein originating from the distal superficial femoral and popliteal arteries Mark S. Rosenbloom, M.D., James J. Walsh, M.D., James J. Schuler,
Endovascular treatment (EVT) has markedly advanced,
 Ann Vasc Dis Vol. 6, No. 3; 2013; pp 573 577 Online August 12, 2013 2013 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.13-00055 Original Article A Review of Surgically Treated Patients with Obstruction
Ann Vasc Dis Vol. 6, No. 3; 2013; pp 573 577 Online August 12, 2013 2013 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.13-00055 Original Article A Review of Surgically Treated Patients with Obstruction
Valvular reflux after deep vein thrombosis: Incidence and time of occurrence
 Valvular reflux after deep vein thrombosis: Incidence and time of occurrence Arie Markel, MD, Richard A. Manzo, BS, CCVT, Robert O. Bergelin, MS, and D. Eugene Strandness, Jr., MD, Seattle, Wash. From
Valvular reflux after deep vein thrombosis: Incidence and time of occurrence Arie Markel, MD, Richard A. Manzo, BS, CCVT, Robert O. Bergelin, MS, and D. Eugene Strandness, Jr., MD, Seattle, Wash. From
Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems
 Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems Jacques Menetrey & Victoria B. Duthon Centre de médecine de l appareil locomoteur et du sport Swiss Olympic medical Center Unité d Orthopédie
Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems Jacques Menetrey & Victoria B. Duthon Centre de médecine de l appareil locomoteur et du sport Swiss Olympic medical Center Unité d Orthopédie
doi: /j.jvs
 doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.02.010 Muneaki Matsubara 1 Congenital-idiopathic superficial femoral artery aneurysm in a 7-year-old child Running Head: Femoral artery aneurysm in a child Muneaki Matsubara MD,
doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.02.010 Muneaki Matsubara 1 Congenital-idiopathic superficial femoral artery aneurysm in a 7-year-old child Running Head: Femoral artery aneurysm in a child Muneaki Matsubara MD,
Clinico-Anatomical and Radiological Correlation of Varicose Veins of Lower Limb A Cross-sectional Study
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Clinico-Anatomical and Radiological Correlation of Varicose Veins of Lower Limb A Cross-sectional Study Lalatendu Swain 1, Mamata Singh 2, Prabhat Nalini Rautray 3 ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Clinico-Anatomical and Radiological Correlation of Varicose Veins of Lower Limb A Cross-sectional Study Lalatendu Swain 1, Mamata Singh 2, Prabhat Nalini Rautray 3 ABSTRACT
Endovascular and Hybrid Treatment of TASC C & D Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease
 Endovascular and Hybrid Treatment of TASC C & D Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease Arash Bornak, MD FACS Vascular & Endovascular Surgery University of Miami Miller School of Medicine No disclosure BACKGROUND
Endovascular and Hybrid Treatment of TASC C & D Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease Arash Bornak, MD FACS Vascular & Endovascular Surgery University of Miami Miller School of Medicine No disclosure BACKGROUND
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR
 How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Durability of venous valve reconstruction techniques for "primary" and postthrombotic reflux
 Durability of venous valve reconstruction techniques for "primary" and postthrombotic reflux Seshadri Raju, MD, Ruth K. Fredericks, MD, Peter N. Negl~n, MD, and J. David Bass, PhD, Jackson, Miss. Purpose:
Durability of venous valve reconstruction techniques for "primary" and postthrombotic reflux Seshadri Raju, MD, Ruth K. Fredericks, MD, Peter N. Negl~n, MD, and J. David Bass, PhD, Jackson, Miss. Purpose:
Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic
 Lung Segmentectomy for Patients with Peripheral T1 Lesions Bryan A. Whitson, MD, Rafael S. Andrade, MD, and Michael A. Maddaus, MD Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic option
Lung Segmentectomy for Patients with Peripheral T1 Lesions Bryan A. Whitson, MD, Rafael S. Andrade, MD, and Michael A. Maddaus, MD Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic option
POINT OF CARE ULTRASOUND - Venous US for DVT
 POINT OF CARE ULTRASOUND - Venous US for DVT The diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) using ultrasound in the emergency department. DVT US is easy to perform and can be usually be completed in less
POINT OF CARE ULTRASOUND - Venous US for DVT The diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) using ultrasound in the emergency department. DVT US is easy to perform and can be usually be completed in less
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks
 Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
RECOGNITION AND ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VENOUS INSUFFICIENCY
 RECOGNITION AND ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VENOUS INSUFFICIENCY Paul Kramer, MD, FACC, FSCAI Liberty Cardiovascular Specialists Liberty Regional Heart and Vascular Center DISCLOSURES NONE Venous
RECOGNITION AND ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VENOUS INSUFFICIENCY Paul Kramer, MD, FACC, FSCAI Liberty Cardiovascular Specialists Liberty Regional Heart and Vascular Center DISCLOSURES NONE Venous
The surface anatomy of the anterior leg compartment
 Surgical Anatomy of the Saphenous Nerve Victor Dayan, MD, Leandro Cura, MD, Santiago Cubas, MD, and Guillermo Carriquiry, MD Cardiovascular Surgery Department of the National Institute of Cardiac Surgery,
Surgical Anatomy of the Saphenous Nerve Victor Dayan, MD, Leandro Cura, MD, Santiago Cubas, MD, and Guillermo Carriquiry, MD Cardiovascular Surgery Department of the National Institute of Cardiac Surgery,
with the Spiral Composite Vein Graft
 Redacement of Superior Vena Cava with the Spiral Composite Vein Graft A Versatile Technique C. J. Chiu, M.D., J. Terzis, M.D., and M. L. MacRae, B.S. ABSTRACT A technique to construct a spiral vein graft
Redacement of Superior Vena Cava with the Spiral Composite Vein Graft A Versatile Technique C. J. Chiu, M.D., J. Terzis, M.D., and M. L. MacRae, B.S. ABSTRACT A technique to construct a spiral vein graft
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy
 Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
Femorocaval bypass with femoral crossover bypass for iliofemoral and caval occlusion
 Femorocaval bypass with femoral crossover bypass for iliofemoral and caval occlusion Kumar IL Patel, MD, David Rabinowitz, MD, Barry Hastings, MD, and Herbert Dardik, MD, Englewood, N.J. Progress in the
Femorocaval bypass with femoral crossover bypass for iliofemoral and caval occlusion Kumar IL Patel, MD, David Rabinowitz, MD, Barry Hastings, MD, and Herbert Dardik, MD, Englewood, N.J. Progress in the
A rational approach to detection of significant reflux with duplex Doppler scanning and air plethysmography
 A rational approach to detection of significant reflux with duplex Doppler scanning and air plethysmography Peter Negl6n, MD, PhD,* and Seshadri Raju, MD, Al-Ain, United Arab Emirates, and Jackson, Miss.
A rational approach to detection of significant reflux with duplex Doppler scanning and air plethysmography Peter Negl6n, MD, PhD,* and Seshadri Raju, MD, Al-Ain, United Arab Emirates, and Jackson, Miss.
Fig MHz cm/s. Table 1 Fig. 2. Fig. 3, 4. Fig. 5
 GE Fig. 1 3. 5 MHz 7 10 MHz 3. 5 5. 0 MHz B 10 20 cm/s Table 1 Fig. 2 Fig. 1 1 2 3 3 3 : 1 2 3 Fig. 3, 4 Fig. 5 Table 1 a b c Fig. 2 a B b B c Fig. 6 Table 1 Fig. 7 a b c Fig. 3 a AV b A VV c 1 cm 2 1
GE Fig. 1 3. 5 MHz 7 10 MHz 3. 5 5. 0 MHz B 10 20 cm/s Table 1 Fig. 2 Fig. 1 1 2 3 3 3 : 1 2 3 Fig. 3, 4 Fig. 5 Table 1 a b c Fig. 2 a B b B c Fig. 6 Table 1 Fig. 7 a b c Fig. 3 a AV b A VV c 1 cm 2 1
The role of ultrasound duplex in endovenous procedures
 The role of ultrasound duplex in endovenous procedures Neophytos A. Zambas MD, PhD Vascular Surgeon Polyclinic Ygia, Limassol, Cyprus ΚΕΑΕΧ ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΑΓΓΕΙΑΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΝΔΑΓΓΕΙΑΚΗΣ ΧΕΙΡΟΥΡΓΙΚΗΣ Pre
The role of ultrasound duplex in endovenous procedures Neophytos A. Zambas MD, PhD Vascular Surgeon Polyclinic Ygia, Limassol, Cyprus ΚΕΑΕΧ ΚΥΠΡΙΑΚΗ ΕΤΑΙΡΕΙΑ ΑΓΓΕΙΑΚΗΣ ΚΑΙ ΕΝΔΑΓΓΕΙΑΚΗΣ ΧΕΙΡΟΥΡΓΙΚΗΣ Pre
DIFFICULT ACCESS REMAINS A CONTRAINDICATION FOR EVAR APOSTOLOS K. TASSIOPOULOS, MD, FACS PROFESSOR AND CHIEF DIVISION OF VASCULAR SURGERY
 DIFFICULT ACCESS REMAINS A CONTRAINDICATION FOR EVAR APOSTOLOS K. TASSIOPOULOS, MD, FACS PROFESSOR AND CHIEF DIVISION OF VASCULAR SURGERY Disclosures Speaker Bureau: - Medtronic - Cook Medical - Bolton
DIFFICULT ACCESS REMAINS A CONTRAINDICATION FOR EVAR APOSTOLOS K. TASSIOPOULOS, MD, FACS PROFESSOR AND CHIEF DIVISION OF VASCULAR SURGERY Disclosures Speaker Bureau: - Medtronic - Cook Medical - Bolton
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
