Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary?
|
|
|
- Eugene Bruce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14: DOI /s y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary? A. K. Singh K. Vinay Received: 27 October 2012 / Accepted: 18 April 2013 / Published online: 14 May 2013 The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Abstract Background The aim of this retrospective study was to determine the need for bone grafting in the surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. We reviewed 390 cases of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures treated with plate osteosynthesis with or without autologous iliac bone grafting, and compared outcomes and complications related to fracture stabilization. Materials and methods Three hundred ninety patients with displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures that were treated with plate osteosynthesis from December 2002 to December 2010 were reviewed. Two hundred two patients (group A) were treated by osteosynthesis with autologous bone grafting, and 188 patients (group B) were treated by osteosynthesis without bone grafting. One hundred eightyone patients with an AO type 73-C1 fracture (Sanders type II), 182 patients with an AO type 73-C2 fracture (Sanders type III), and 27 patients with an AO type 73-C3 fracture (Sanders type IV) were included in this study. Bohler s angle, the crucial angle of Gissane, and calcaneal height in the immediate postoperative period and at the 2-year follow-up were compared. Any change in the subtalar joint status was documented and analyzed. The final outcomes of all patients were evaluated by the AOFAS Ankle Hindfoot Scale and compared in both groups. A. K. Singh (&) Department of Orthopedics, Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences, C 1/157, Vishesh Khand, Gomti Nagar, Gadia, Barabanki, Uttar Pradesh , India ashu.ortho@gmail.com K. Vinay Department of Orthopedics, Institute of Medical Sciences BHU, Varanasi, India Results The mean full weight-bearing time in group A (with bone grafting) was significantly lower (median 6.2 months, range months) than that in group B (without bone grafting; median 9.8 months, range months). The immediate-postoperative Bohler s angle and that at the 2-year follow-up were significantly higher in group A. The loss of Bohler s angle after 2 years was significantly lower in group A (mean 3.5 ; 95%CI ) than in group B (mean 6.2 ; 95 % CI ). The average change in the crucial angle and the average change in calcaneal height were not statistically significant for either group. The infection rate in the bone grafting group was higher, though statistically insignificantly so, than in the nongrafting group (8.3 vs. 6.3 %). No significant difference was found between the groups in terms of the rates of good reduction, postoperative osteoarthritis, and subtalar fusion. Regarding the efficacy outcomes, the mean AOFAS score was lower (mean 76.4 points; 95 % CI points) in group A than in group B (mean, 81.6 points; 95 % CI, points), but this difference was not significant (p [ 0.05). Conclusions Bohler s angle showed improved restoration and the patients returned to full weight-bearing earlier when bone grafting was used in the treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fracture. However, the functional outcomes and complication rates of both groups were similar. Keywords Bone graft Introduction Calcaneus Displaced intra-articular fractures Calcaneal fractures account for approximately 2 % of all fractures, with displaced intra-articular fractures comprising
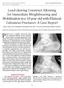
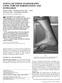
2 300 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14: % of these injuries [1, 2]. Displaced intra-articular fractures carry a high morbidity; % of patients return to work within 9 months, but approximately 20 % are not able to return to work within a year, rendering intra-articular calcaneal fractures costly from a socio-economic perspective [2, 3]. Axial load in falling is the most common mechanism of calcaneal fracture. In such injuries, the lateral talar process is forced downward and breaks through the posterior articular facet, reducing Bohler s angle [4]. Plate osteosynthesis of the intra-articular fracture is a standard treatment method. The first documented treatment of a series of calcaneal fractures with internal fixation was reported by Leriche [5] in Ever since Lenormant first described the use of bone grafting to fill the space created after open reduction of a calcaneal fracture in 1928, this technique has maintained its popularity. Choices of bone graft have included autogenous and allogenous cancellous bone grafts, polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), and bone substitutes. However, the need for bone grafts in the treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fracture is still controversial, and there is no strong evidence to support any functional benefits of using bone grafts [6]. Surgeons in favor of bone grafting believe that it could stimulate fracture healing, leading to early full weight-bearing; may prevent posttraumatic arthritis; and could increase mechanical strength, thus helping to prevent significant late collapse [7, 8]. Those not in favor of bone grafts have stated that the highly vascular calcaneus heals radiographically 4 8 weeks after surgery in the absence of bone grafting [9 11], that internal fixation can adequately support the articular surface, that bone grafting increases the infection rate, blood loss, and postoperative pain [12, 13], and that it is also important to consider donor site morbidity and complications involved with harvesting an autograft [14, 15]. The purpose of the current study was therefore to compare the outcomes and complications of two methods utilized for the surgical treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. We analyzed cases of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture treated by open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) with bone grafts and without bone grafts by comparing the outcomes and complications of the intra-articular calcaneal fractures in these two treatment groups. We compared the infection rates, times to full weight-bearing, reduction of the posterior facet, subtalar fusion rates, reduction of Bohler s angle, changes in the crucial angle, changes in calcaneal height, and efficacy outcomes between the two groups. Materials and methods This study was done to compare the outcomes and complications of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation either with or without bone grafting. The protocol of this study was approved by the research department of the Institute of Medical Sciences, BHU. The study was authorized by the local ethical committee and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki as revised in The need for informed consent was waived by the ethical committee since the rights and interests of the patients would not be violated and their privacy and anonymity was assured by the study design. During the 8 years from December 2002 to December 2010, 454 patients with displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures were admitted to the hospital. Medical records and X-ray films were retrieved for all of the patients who had undergone open reduction and internal fixation of the calcaneus. The inclusion criteria were as follows: Unilateral, displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures [posterior articular facet step-off more than 2 mm, significant shortening, loss of height, and widening of the calcaneus, i.e., decreased Bohler s and Gissane s angles (see Fig. 1a), valgus deviation [ 10, varus deviation [ 5 ] of Sanders type II, III, or IV Age C 18 years Records for a follow-up period of at least 2 years should be available for each case included in this study. Three hundred ninety patients with unilateral isolated displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture were included in this study as per the inclusion criteria. Bilateral calcaneal fractures, open fractures, and fractures in patients \18 years of age were not included in this study. Other than the demographic details, information concerning the duration of hospital stay, duration of leave, and time to full weight-bearing were collected. All the cases included in this study were divided into two groups: patients treated with bone grafting (group A) and those treated without bone grafting (group B). The average age in the bone grafting group was 40.0 (range 18 74) years and that in the nongrafting group was 41.2 (range 18 75) years. Gender proportions in the two groups were considered to be similar (p = 0.42). Both groups were similar in terms of the side fractured (p = 0.82) and the fracture type (p [ 0.05) (Table 1). In all cases selected, patients were operated on between the seventh and tenth day after injury (range 2 21 days, average 8.0 days), when the soft-tissue edema had decreased and the wrinkle sign was positive on hind-foot soft tissue. All of the operations were performed under general or spinal anesthesia, with the patient placed in the lateral decubitus position, using the extended lateral approach (Fig. 2). Locking plates and screws were used in
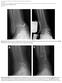
3 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14: Fig. 1 a Pre-op loss of Bohler s angle in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. b Restoration of Bohler s angle by plate osteosynthesis Table 1 Demographic profile of study Patient characteristics Open reduction and internal fixation with bone grafting (group A) Open reduction and internal fixation without bone grafting (group B) p value Sex Male:female 152:50 130: Side Right:left 120:82 110: Mean age (years) all cases requiring open reduction and internal fixation. In the patients receiving a bone graft, cancellous autograft was taken from the ipsilateral iliac crest. Posterior and anterior calcaneal facet reconstruction, including the bridging in Gissane s angle, Bohler s angle (see Fig. 1b) along with calcaneal height, width, and length restoration, and no varus valgus deviation were the main goals of open reduction. The standard postoperative protocol was followed. Nonweight-bearing walking was started after surgery, usually on the third postoperative day. Ankle and subtalar joint mobilization exercises were started when tolerated by the patient. Progressive weight-bearing was started after 6 weeks, initially with 25 % of their weight. Full weightbearing after 12 weeks was allowed provided that the reduced and stabilized fracture position remained unchanged and that clinicoradiological signs of bone healing (no pain, swelling, or tenderness at the fracture site clinically and no visible fracture lines in X-rays) were present at that time. The X-ray films were assessed to determine the type of fracture that had occurred. The preoperative computed tomography (CT) scans were reviewed to classify the Fig. 2 Standard L-shaped lateral approach and restoration of the posterior facet fractures according to the Sanders classification (Table 2). The Sanders CT-scan classification is based on the articular fracture lines of the posterior articular calcaneal facet (A, lateral; B, central; C, medial), and the severity of the fracture (Sanders types I IV) depends on the number of lines and their courses. The immediate postoperative X-rays were compared with the radiological findings at the 2-year follow-up visit. The immediate-postoperative film was taken on the second or third postoperative day. These X-rays included standard anteroposterior, true lateral, and axial views of the calcaneum. Bohler s angle, the crucial angle, and the height of the calcaneus were measured in radiographs as shown in Fig. 3. Any change in these parameters during follow-up was documented. Serial changes in Bohler s angle, the crucial angle, and the calcaneal height were calculated. Absolute values of the differences were used for statistical analysis. Statistical significance was taken as p \ The t test for equality was used to test for significant differences. In all cases, patient characteristics, mean follow-up time, fracture classification information based on the
4 302 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14: Table 2 Fracture distribution according to the Sanders classification system Sanders classification Group A Group B p value Type II A Type II B Type II C Type III AC Type III AB Type III BC Type IV Sanders system, time to full weight-bearing, patientreported outcome scores, infection, posterior facet incongruity, and subtalar joint fusion were reviewed. Sanders criteria was used to evaluate subtalar joint reduction, and Allmachers Arthrosis Rating Scale was employed for posttraumatic posterior facet degenerative changes (Table 3). The overall patient outcomes were summarized based on the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society Score (AOFAS) Ankle Hindfoot Scale, with excellent defined as points, good as points, fair as points, and poor as \50 points [16 18]. Results The average overall duration of follow-up was 2 years. The patients of group A (with bone grafting) had an average hospital stay of ± 5.2 days, and the group B patients (no bone grafting) had an average hospital stay of ± 4.8 days. There was no significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.68). Functional and radiological outcomes The mean time to full weight-bearing in group A (6.2 ± 1.7 months) was significantly lower (p = 0.02) than that in group B (9.8 ± 1.5 months). Bohler s angle at the 2-year follow-up was significantly higher in group A (p = 0.042). The loss of Bohler s angle after 2 years was significantly Fig. 3 Measurement of Bohler s angle, the crucial angle of Gissane, and the calcaneal height lower in group A (3.5 ± 1.4 ) than in group B (mean 6.2 ± 2.5, p = 0.014). The overall subtalar joint reduction was found to be satisfactory. No significant difference was found between the two groups on comparing the good reduction rate. Comparison of the immediate-postoperative radiological results and those at the 2-year follow-up showed changes in Bohler s angle, the crucial angle, and the height of the calcaneus (Tables 4 and 5). The average change in the crucial angle was 3.8 ± 1.8 for group A and 3.6 ± 2.1 for group B. This difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.48). The average change in calcaneal height was 2.8 ± 1.4 mm for group A and 2.5 ± 1.2 mm for group B. Again, this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.68). Regarding efficacy outcomes, the mean AOFAS score was lower (76.4 ± 5.4 points) in group A than in group B (81.6 ± 4.8 points) (Table 6), but this difference was not significant (p [ 0.82). In studies of group A, the result of treatment was excellent in 32 % of the patients, good in 39 %, fair in 24 %, and poor in 4 % of the patients. In group B, the outcome was excellent in 33 %, good in 43 %, fair in 19 %, and poor in 4 % cases. No significant difference was found on comparing both groups (p = 0.42). Table 3 Sanders criteria for subtalar joint reduction and Allmacher s criteria for subtalar joint osteoarthrosis Criteria for roentgenographic subtalar joint reduction [24] Anatomic, no articular incongruity whatsoever Near-anatomic, \3 mm of articular incongruity or gapping between fragments Approximate, 3 5 mm of articular incongruity or gapping between fragments Failure, [5 mm of articular incongruity or gapping between fragments Arthrosis rating scale 0 Normal I Osteophyte only II Osteophyte with subchondral cysts and normal joint space III Grade II? mild narrowing of the joint space IV Severe joint-space narrowing V Fused
5 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14: Table 4 Preoperative and postoperative radiological assessment of both groups Parameters Group A Group B Average value (standard deviation) Average value (standard deviation) Type II Type III Type IV Type II Type III Type IV Bohler s angle ( ) Post-op 28.2 (6.8) 25.4 (6.1) 21.1 (7.0) 25.6 (7.4) 26.9 (8.2) 21.2 (8.4) At 2-year follow-up 24.5 (6.9) 22.6 (6.8) 18.6 (7.2) 22.9 (7.9) 21.1 (7.8) 17.3 (7.2) Gissane s angle ( ) Post-op (8.5) (8.0) (8.9).4 (8.8) (10.9).0 (11.2) At 2-year follow-up (7.6) (7.9) (8.1) (9.0) (10.2).5 (9.2) Calcaneal height (mm) Post-op (3.96) 42.8 (4.12) 42.2 (4.14) 43.1 (4.14) 42.4 (4.04) 41.9 (4.12) At 2-year follow-up (4.10) 41.9 (4.24) 41.1 (4.28) 42.1 (4.26) 41.3 (4.24) 40.8 (4.33) Table 5 Comparison of the preoperative and postoperative radiological parameters of displaced calcaneal fractures treated with plate osteosynthesis with bone grafting (group A) or without bone grafting (group B) Radiological parameter Complications Group A Group B p value Average value ± standard deviation Average value ± standard deviation Mean Bohler s angle ( ) Immediate 28.2 ± ± post-op At 2-year 25.4 ± ± follow-up Bohler s angle loss 3.5 ± ± Mean Gissane angle ( ) Immediate ± ± post-op At 2-year ± ± follow-up Angle change 3.8 ± ± Mean calcaneal height (mm) Immediate 42.8 ± ± post-op At 2-year 40.0 ± ± follow-up Height loss 2.8 ± ± In this series of 390 patients, subtalar arthrosis occurred in 50 patients (12.8 %). Twenty-six patients had superficial wound dehiscence and 25 patients had wound infection. There were no donor-site wound complications (Table 7). Among the patients with subtalar arthrosis, 27 patients were in group A (13.36 %) and 23 patients were in group B (12.7 %). This difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.62). The postoperative subtalar fusion rate was 3.4 % in group B and 3.2 % in group A; no significant difference was found (p = 0.161). The infection rate in group A was higher (6.9 %) than that in group B (5.8 %), but no statistical significant difference was found (p = 0.562). Discussion The operative treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures with or without bone grafting is still a topic of debate. The practice of using a bone graft to fill the empty core of the calcaneus during surgery has become increasingly popular. Many authors have incorporated bone grafting into the fixation procedure, and have achieved satisfactory results [19, 20]. Some surgeons always use bone grafts [7, 16], whereas other surgeons do not use them at all [21, 22]. A nationwide survey of the Netherlands reported that, among the surgeons who operated on the ORIF group, 20 % definitely used bone grafts, 42 % used grafting when deemed necessary, and 38 % did not use bone grafts at all [23]. The objective of the present study was to compare the outcomes and complication rates of both groups (A and B) and to determine the differences between the groups in terms of final outcomes and complications. The practice of bone grafting was not favored in early works [24 26]. Letournel [25] did not recommend the use of bone grafting, and said that although a gap is caused by cancellous crushing at the time of injury, the thalamic fragment and overall body reduction are supported by the lag screws and plate; in addition, because the medial wall is also fractured, proper filling of the space is impossible, and the speed of healing did not warrant the extra risk associated with a graft. Sanders et al. [24], Stephenson [26], and Zwipp et al. [27] achieved good results without the use of a
6 304 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14: Table 6 Comparison of AOFAS Ankle-Hindfoot Scores for displaced calcaneal fractures treated with plate osteosynthesis with bone grafting (group A) or without bone grafting (group B) Sanders fracture type Group A Group B Excellent Good Fair Poor Total Excellent Good Fair Poor Total Type II Type III Type IV (32.17 %) 79 (39.1 %) 50 (24.75 %) 8 (3.96 %) 63 (33.5 %) 82 (43.6 %) 36 (19.1 %) 7 (3.72 %) Table 7 Complications of displaced calcaneal fractures treated with plate osteosynthesis with bone grafting (group A) or without bone grafting (group B) Complications Group A Group B p value Superficial defect 12 (6.2 %) 14 (7.4 %) Infection 14 (6.9 %) 11 (5.8 %) Post-op osteoarthritis 27 (13.3 %) 23 (12.7) % Subtalar fusion 7 (3.4 %) 6 (3.2 %) bone graft. Lowery and Calhoun [28], in their recent extensive review of the treatment of calcaneal fracture, did not recommend the use of bone grafting. Longino [29] compared postoperative radiological and clinical results of LCP osteosynthesis with and without bone grafting and did not find any significant difference in the results obtained with or without grafting. Leung et al. [19, 20] recommended open reduction with rigid internal fixation with primary bone grafting as the preferred treatment method for calcaneal fracture. Our results showed that both groups of patients presented similar clinical and radiological progress. Bone grafting did not hasten their return to work. The group receiving a bone graft had a slightly longer duration of hospital stay, although this was not statistically significant. This may have been due to the extra surgical wound in the iliac area and the associated pain, which may have impeded their progress in relation to mobility [7]. This systematic review showed that patients treated with bone grafts were able to return to full weight-bearing earlier. However, no significant difference was observed in the other indicators. Many studies have reported higher infection rates when treating intra-articular calcaneal fractures with bone grafts, which is one of the reasons that authors propose that bone grafts should not be used [12]. According to the results of the present study, there was no significant difference in infection rate between patients with bone grafts and those without bone grafts. Restoration of Bohler s angle has also been associated with a better outcome [6, 30 32]. In the present work, the postoperative and 2-year follow-up radiographs were reviewed and the loss of Bohler s angle was compared between the two groups. It was found that the mean postoperative Bohler s angle was significantly higher and the mean loss of reduction of the angle was significantly lower in the bone-grafting group. The efficacy outcomes for the two groups were not significantly different when all of the categories were compared. In terms of the reported scores, the patients in the bone-grafting group yielded a lower mean AOFAS score. The subtalar joint reduction achieved during surgery was maintained during the long-term follow-up in both groups. This reflects the hypothesis of Loucks and Buckley [6] that surgical reduction of the subtalar joint is more important and that bone grafting does not provide any extra benefit. The morbidity associated with bone-graft harvesting from the iliac crest has been extensively studied and reviewed. The procedure of bone-graft harvesting increases the operative time and blood loss [30]. According to Silber et al., the complication rates associated with harvesting iliac bone grafts can be as high as 40 %, and encompass acute or chronic pain, hematoma formation, scarring, nerve injury, and wound problems. Given the extra surgical morbidity and the lack of any demonstrable extra benefit associated with bone grafting, we suggest that it should not be performed during surgery for calcaneal fracture. The primary limitation of the present study is that it is a retrospective investigation, and not all of the patient details relating to operative time, blood loss, and pain severity were available. Despite these limitations, this study provides evidence that the use of bone grafting along with internal fixation in the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures leads to better restoration of Bohler s angle and the prevention of late collapse. Thus, in intra-articular calcaneal fractures, if the space created after open reduction is large, bone grafts may be considered as a treatment option. Also, in this study, patients with bone grafts were able to return to full weight-bearing earlier. However, the intermediate and long-term efficacy outcomes in the two groups were similar, which means that patients with intraarticular calcaneal fractures that are treated without bone grafting have functional outcomes as good as patients with such fractures that are treated with bone grafting.
7 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14: Conflict of interest None. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited. References 1. Zwipp H, Rammelt S, Barthel S (2005) Fracture of the calcaneus. Unfallchirurg 108: Brauer CA, Manns BJ, Ko M, Donaldson C, Buckley R (2005) An economic evaluation of operative compared with nonoperative management of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Bone Joint Surg 87: Barei DP, Bellabarba C, Sangeorzan BJ, Benirschke SK (2002) Fractures of the calcaneus. Orthop Clin North Am 33: doi: /s (03) Canale ST, Beaty JH (2008) Campbell s operative orthopaedics, 11th edn. Mosby, Philadelphia, pp Leriche R (1922) Osteosynthese pour fracture par ecrasement du calcaneum a sept fragments. Lyon Chir 19: Loucks C, Buckley R (1999) Bohler s angle: correlation with outcome in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Orthop Trauma 13: Elsner A, Jubel A, Prokop A, Koebke J, Rehm KE, Andermahr J (2005) Augmentation of intraarticular calcaneal fractures with injectable calcium phosphate cement: densitometry, histology, and functional outcome of 18 patients. J Foot Ankle Surg 44: Jiang SD, Jiang LS, Dai LY (2008) Surgical treatment of calcaneal fractures with use of beta-tricalcium phosphate ceramic grafting. Foot Ankle Int 29: Eastwood DM, Langkamer VG, Atkins RM (1993) Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum. Part II: open reduction and internal fixation by the extended lateral transcalcaneal approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75: Ebraheim NA, Elgafy H, Sabry FF, Freih M, Abou-Chakra IS (2000) Sinus tarsi approach with trans-articular fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Foot Ankle Int 21: Grala P, Twardosz W, Tondel W, Olewicz-Gawlik A, Hrycaj P (2009) Large bone distractor for open reconstruction of articular fractures of the calcaneus. Int Orthop 33: Baumgaertel FR, Gotzen L (1993) Two-stage operative treatment of comminuted os calcis fractures. Primary indirect reduction with medial external fixation and delayed lateral plate fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290: Laurie SW, Kaban LB, Mulliken JB, Murray JE (1984) Donorsite morbidity after harvesting rib and iliac bone. Plast Reconstr Surg 73: Banwart JC, Asher MA, Hassanein RS (1995) Iliac crest bone graft harvest donor site morbidity. A statistical evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20: Goulet JA, Senunas LE, DeSilva GL, Greenfield ML (1997) Autogenous iliac crest bone graft. Complications and functional assessment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 339: Di Schino M, Bensaida M, Vandenbussche E, Augereau B, Nich C (2008) Results of open reduction and cortico-cancellous autograft of intra-articular calcaneal fractures according to Palmer. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 94: Kinner BJ, Best R, Falk K, Thon KP (2002) Is there a reliable outcome measurement for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures? J Trauma 53: Westphal T, Piatek S, Halm JP, Schubert S, Winckler S (2004) Outcome of surgically treated intraarticular calcaneus fractures- SF-36 compared with AOFAS and MFS. Acta Orthop Scand 75: Leung KS, Chan WS, Shen WY, Pak PL, So WS, Leung PC (1989) Operative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the os calcis the role of rigid internal fixation and primary bone grafting: preliminary results. J Orthop Trauma 3: Leung KS, Yuen KM, Chan WS (1993) Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Medium-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75: Huang PJ, Huang HT, Chen TB, Chen JC, Lin YK, Cheng YM et al (2002) Open reduction and internal fixation of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Trauma 52: Thornes BS, Collins AL, Timlin M, Corrigan J (2002) Outcome of calcaneal fractures treated operatively and non-operatively: the effect of litigation on outcomes. Ir J Med Sci 171: Schepers T, van Lieshout EM, van Ginhoven TM, Heetveld MJ, Patka P (2008) Current concepts in the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures: results of a nationwide survey. Int Orthop 32: Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, Walling A (1993) Operative treatment in 120 displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Clinical Orthop Relat Res 290: Letournel E (1993) Open treatment of acute calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290: Stephenson JR (1987) Treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus using medial and lateral approaches, internal fixation, and early motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69: Zwipp H, Tscherne H, Thermann H, Weber T (1993) Osteosynthesis of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus, results in cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290: Lowery RBW, Calhoun JH (1996) Fractures of the calcaneus (current topic review). Foot Ankle Int 17: Longino D, Buckley RE (2001) Bone graft in the operative treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: is it helpful? J Orthop Trauma 15: Schnee CL, Freese A, Weil RJ, Marcotte PJ (1997) Analysis of harvest morbidity and radiographic outcome using autograft for anterior cervical fusion. Spine 22: Paul M, Peter R, Hoffmeyer P (2004) Fractures of the calcaneum. A review of 70 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86: Shuler FD, Conti SF, Gruen GS, Abidi NA (2001) Woundhealing risk factors after open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneal fractures: does correction of Bohler s angle alter outcomes? Orthop Clin North Am 32:
Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture
 Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING. Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion
 AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular. calcaneal fractures
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile?
 28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients
 Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks
 Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Tao Zhang, Xingwang Wu, Zhanpo Wu and Yingze Zhang *
 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 04 Page April 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
Session II 11:30 11:45 am. Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio. Disclosure: (n)
 Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1223-9 REVIEW The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review Tim Schepers Received: 1 December 2010 / Accepted: 20 January 2011 #
DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1223-9 REVIEW The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review Tim Schepers Received: 1 December 2010 / Accepted: 20 January 2011 #
Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available evidence
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures. Kali Luker, PGY-1
 Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome
 Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture Dislocation Injuries
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular
 The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures Berdine Bakker MSc, Jens A. Halm MD PhD, Esther M.M. Van Lieshout PhD, Tim Schepers MD PhD Erasmus MC,
The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures Berdine Bakker MSc, Jens A. Halm MD PhD, Esther M.M. Van Lieshout PhD, Tim Schepers MD PhD Erasmus MC,
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure
 Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Functional outcomes of different modalities of fixation in intra-articular calcaneus fractures
 2018; 2(4): 199-204 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 199-204 Received: 25-08-2018 Accepted: 27-09-2018 Rajesh V Chawda Associate Professor,
2018; 2(4): 199-204 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 199-204 Received: 25-08-2018 Accepted: 27-09-2018 Rajesh V Chawda Associate Professor,
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure
 Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision
 Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 218-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures Mário Baptista, Rui Pinto, João Torres From Faculdade de Medicina
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 218-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures Mário Baptista, Rui Pinto, João Torres From Faculdade de Medicina
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum
 Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum DEMOGRAPHICS AND TREATMENT A. P. Molloy, M. S. Myerson, P. Yoon From Institute for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, USA
Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum DEMOGRAPHICS AND TREATMENT A. P. Molloy, M. S. Myerson, P. Yoon From Institute for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, USA
Accepted: 3 April 2009
 Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
 PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments -
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a retrospective case analysis
 Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
Functional outcome of intra-articular tongue type of calcaneus fractures treated with percutaneous technique
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Dalal BY et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):371-376 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164171
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Dalal BY et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):371-376 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164171
Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials
 British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Clinical Research on Foot & Ankle
 Clinical Research on Foot & Ankle Roll et al., Clin Res Foot Ankle 2018, 6:3 DOI: 10.4172/2329-910X.1000278 Research Article Open Access Calcaneocuboid Joint Involvement in Calcaneal Fractures-CT Based
Clinical Research on Foot & Ankle Roll et al., Clin Res Foot Ankle 2018, 6:3 DOI: 10.4172/2329-910X.1000278 Research Article Open Access Calcaneocuboid Joint Involvement in Calcaneal Fractures-CT Based
Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study
 CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):9261-9269 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017905 Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):9261-9269 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017905 Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
The optimal management of displaced
 Review Article Advances in Surgical Management of Intra-articular Calcaneus Fractures Abstract Andrew R. Hsu, MD Robert B. Anderson, MD Bruce E. Cohen, MD JAAOS Plus Webinar Join Dr. Cohen for the interactive
Review Article Advances in Surgical Management of Intra-articular Calcaneus Fractures Abstract Andrew R. Hsu, MD Robert B. Anderson, MD Bruce E. Cohen, MD JAAOS Plus Webinar Join Dr. Cohen for the interactive
,
 , 49, 2013, 2 5 REVIEWS.,.,.,.,.,..,.. FRACTURES OF THE TALUS: COMPLICATIONS AND PROGNOSIS S. Asyov, V. Tzanov, K. Tzonkov, L. Zahariev, H. Stoychev, D. Pachev and M. Iliev Second Clinic of Orthopedic
, 49, 2013, 2 5 REVIEWS.,.,.,.,.,..,.. FRACTURES OF THE TALUS: COMPLICATIONS AND PROGNOSIS S. Asyov, V. Tzanov, K. Tzonkov, L. Zahariev, H. Stoychev, D. Pachev and M. Iliev Second Clinic of Orthopedic
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Prospective study of fracture calcaneus with Allan s procedure- bone grafting without implants
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic, 501 N. 10th Street, Manitowoc, WI Procedure. Subtalar arthrodesis
 OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
SINUS TARSI APPROACH FOR TREATMENT OF DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2018 vol. 122, no. 2 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS SINUS TARSI APPROACH FOR TREATMENT OF DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES B. Veliceasa 1, B. Puha 1*, D. Popescu
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2018 vol. 122, no. 2 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS SINUS TARSI APPROACH FOR TREATMENT OF DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES B. Veliceasa 1, B. Puha 1*, D. Popescu
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum
 JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
Diabetics. Referred for management of complex pilon fracture? 5/10/2017. Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?)
 Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
NEW FIXATION STRATEGIES FOR OSTEOPOROTIC BONE
 NEW FIXATION STRATEGIES FOR OSTEOPOROTIC BONE THE PROBLEMS Fixation failure Malunion F 83 yrs 2 Months 6 Months F 81 yrs 3 Months FIXATION AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES (FATs) Surgical procedures aimed at increasing
NEW FIXATION STRATEGIES FOR OSTEOPOROTIC BONE THE PROBLEMS Fixation failure Malunion F 83 yrs 2 Months 6 Months F 81 yrs 3 Months FIXATION AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES (FATs) Surgical procedures aimed at increasing
Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Qi Zhang, Song Liu, Tao Zhang and Yingze Zhang *
 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bony destructive injuries of the calcaneus: long-term results of a minimally invasive procedure followed by early functional exercise: a retrospective
Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bony destructive injuries of the calcaneus: long-term results of a minimally invasive procedure followed by early functional exercise: a retrospective
The extended lateral approach for intra-articular calcaneal fractures: An inverse relation between surgeon's experience and wound complications
 The extended lateral approach for intra-articular calcaneal fractures: An inverse relation between surgeon's experience and wound complications Tim Schepers MD PhD, Dennis Den Hartog MD PhD, Lucas M.M.
The extended lateral approach for intra-articular calcaneal fractures: An inverse relation between surgeon's experience and wound complications Tim Schepers MD PhD, Dennis Den Hartog MD PhD, Lucas M.M.
Pilon Fractures Pearls of Treatment Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSOT November 2017, Tampa
 Pilon Fractures Pearls of Treatment Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSOT November 2017, Tampa Disclosures No relevant disclosures There is more literature
Pilon Fractures Pearls of Treatment Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSOT November 2017, Tampa Disclosures No relevant disclosures There is more literature
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What?
 Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
Lisfranc injuries. Mikko Kirjavainen, MD, PhD. Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki Finland
 Lisfranc injuries Mikko Kirjavainen, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki Finland Lisfranc injuries are midfoot fracture dislocations. The
Lisfranc injuries Mikko Kirjavainen, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki Finland Lisfranc injuries are midfoot fracture dislocations. The
Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures
 FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
/ 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66
 1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
Calcaneal fractures: Where are we now?
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2018) 13:1 11 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-017-0297-3 REVIEW Calcaneal fractures: Where are we now? Aisha Razik 1 Mark Harris 1 Alex Trompeter 1 Received: 21 August 2015 / Accepted:
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2018) 13:1 11 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-017-0297-3 REVIEW Calcaneal fractures: Where are we now? Aisha Razik 1 Mark Harris 1 Alex Trompeter 1 Received: 21 August 2015 / Accepted:
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures
 Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture using intra-acetabular bended plates
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, 93-97 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture using intra-acetabular bended plates Valentinas Uvarovas, Igoris Šatkauskas, Giedrius Petryla,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, 93-97 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture using intra-acetabular bended plates Valentinas Uvarovas, Igoris Šatkauskas, Giedrius Petryla,
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Introduction. Introduction 10/2/2009. Bryan Lapinski, MD
 Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Tibial plateau fractures: four years review at B&B Hospital
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2004) Vol. 2, No. 4, Issue 8, 315-323 Original Article Tibial plateau fractures: four years review at B&B Hospital Shrestha BK 1, Bijukachhe B 2, Rajbhandary T 2,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2004) Vol. 2, No. 4, Issue 8, 315-323 Original Article Tibial plateau fractures: four years review at B&B Hospital Shrestha BK 1, Bijukachhe B 2, Rajbhandary T 2,
Open surgery vs minimal invasive methods for calcaneus fractures. Eur J Transl Myol 28 (2): , 2018
 Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
Spine A Preliminary Study of the Efficacy of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate as a Bone Graft Expander for Instrumented Posterolateral Fusions
 Bibliography Spine Epstein, N.E., A Preliminary Study of the Efficacy of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate as a Bone Graft Expander for Instrumented Posterolateral Fusions. Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques,
Bibliography Spine Epstein, N.E., A Preliminary Study of the Efficacy of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate as a Bone Graft Expander for Instrumented Posterolateral Fusions. Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques,
Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal Fixation in Tibial Plateau Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2015), PP 50-54 www.iosrjournals.org Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2015), PP 50-54 www.iosrjournals.org Study on the Functional Outcome of Internal
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach
 Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach W. Bret Smith, DO Steve Steinlauf, MD Greg E. Gaski, MD Disclosure
Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach W. Bret Smith, DO Steve Steinlauf, MD Greg E. Gaski, MD Disclosure
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar
 Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar High Tibial Osteotomy: HTO! Valgisation HTO Intended to transfer the mechanical
Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar High Tibial Osteotomy: HTO! Valgisation HTO Intended to transfer the mechanical
REVISIONAL SUBTALAR JOINT FUSIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW
 C H A P T E R 9 REVISIONAL SUBTALAR JOINT FUSIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Mitzi L. Williams, DPM INTRODUCTION An isolated subtalar joint arthrodesis has proven over the years to be a successful procedure
C H A P T E R 9 REVISIONAL SUBTALAR JOINT FUSIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Mitzi L. Williams, DPM INTRODUCTION An isolated subtalar joint arthrodesis has proven over the years to be a successful procedure
Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
AUGMENT. Bone Graft. Tibiotalar Fusion. rhpdgf-bb/β-tcp THE FIRST AND ONLY PROVEN ALTERNATIVE TO AUTOGRAFT IN ANKLE AND HINDFOOT ARTHRODESIS
 rhpdgf-bb/β-tcp AUGMENT Bone Graft THE FIRST AND ONLY PROVEN ALTERNATIVE TO AUTOGRAFT IN ANKLE AND HINDFOOT ARTHRODESIS CASE REPORT Tibiotalar Fusion as presented by Mark Glazebrook, MD Assoc Professor
rhpdgf-bb/β-tcp AUGMENT Bone Graft THE FIRST AND ONLY PROVEN ALTERNATIVE TO AUTOGRAFT IN ANKLE AND HINDFOOT ARTHRODESIS CASE REPORT Tibiotalar Fusion as presented by Mark Glazebrook, MD Assoc Professor
Jail Technique for the Fixation of Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Jail Technique for the Fixation of Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures Operative Management of Split Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Jail Technique for the Fixation of Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures Operative Management of Split Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture
Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted Calcaneum Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted
Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report
 Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
We investigated a new method of stress
 SUBTALAR STRESS RADIOGRAPHY USING FORCED DORSIFLEXION AND SUPINATION TOMOO ISHII, SHUMPEI MIYAGAWA, TORU FUKUBAYASHI, KOICHIRO HAYASHI From the University of Tsukuba, Japan We investigated a new method
SUBTALAR STRESS RADIOGRAPHY USING FORCED DORSIFLEXION AND SUPINATION TOMOO ISHII, SHUMPEI MIYAGAWA, TORU FUKUBAYASHI, KOICHIRO HAYASHI From the University of Tsukuba, Japan We investigated a new method
Section: Orthopaedics. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4.3.OR2 Original Article ISSN (O):239-2822; ISSN (P):239-284 A Comparative Study of Operative Management of Internal Fixation of Closed Tibial Plateau Fracture by Plates with Screws
DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4.3.OR2 Original Article ISSN (O):239-2822; ISSN (P):239-284 A Comparative Study of Operative Management of Internal Fixation of Closed Tibial Plateau Fracture by Plates with Screws
Meniscal Injuries with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Role of Arthroscopy
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Meniscal Injuries with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Role of Arthroscopy Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid 3, Munir
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Meniscal Injuries with Tibial Plateau Fractures: Role of Arthroscopy Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid 3, Munir
Sinus Tarsi Volume Changes with Hindfoot Positioning on Weight-Bearing CT Scan
 Sinus Tarsi Volume Changes with Hindfoot Positioning on Weight-Bearing CT Scan Michael Hull, M.D. Tyler Rutherford, M.S. Rebecca A. Cerrato, M.D. John T. Campbell, M.D. Clifford L. Jeng, M.D. Measuring
Sinus Tarsi Volume Changes with Hindfoot Positioning on Weight-Bearing CT Scan Michael Hull, M.D. Tyler Rutherford, M.S. Rebecca A. Cerrato, M.D. John T. Campbell, M.D. Clifford L. Jeng, M.D. Measuring
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture: an anatomical specimen study
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Preface: Contemporary Management of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
 Current Perspectives on Management of Calcaneal Fractures Foreword Thomas J. Chang xiii Preface: Contemporary Management of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures xv Clinical Management of Acute,
Current Perspectives on Management of Calcaneal Fractures Foreword Thomas J. Chang xiii Preface: Contemporary Management of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures xv Clinical Management of Acute,
The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology
 The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology Treatment of Hindfoot Non-Union with DynaNail TTC Fusion System A CASE REPORT Dr. L. Daniel Latt, MD, PhD Background The DynaNail TTC Fusion System is intended
The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology Treatment of Hindfoot Non-Union with DynaNail TTC Fusion System A CASE REPORT Dr. L. Daniel Latt, MD, PhD Background The DynaNail TTC Fusion System is intended
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Influence of intraoperative conventional fluoroscopy versus cone beam CT on longterm clinical outcome in isolated displaced talar fractures
 Vetter et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1043-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Influence of intraoperative conventional fluoroscopy versus
Vetter et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1043-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Influence of intraoperative conventional fluoroscopy versus
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
