Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available evidence
|
|
|
- Jemimah McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI /s EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available evidence Received: 25 January 2007 Accepted: 10 February 2007 Published online: 5 March 2007 R. Bondì ( ) R. Padua A. Battaglia A. Campi Orthopaedics Department San Giacomo Hospital Rome, Italy bondi.r@libero.it R. Bondì R. Padua E. Romanini GLOBE Working Group for Evidence- Based Orthopaedics Rome, Italy L. Bondì Orthopaedics Department Tor Vergata University of Rome Rome, Italy Abstract Calcaneal fracture is the most common of the tarsal fractures and represents 1% 2% of all fractures. The fractures may be divided into extra-articular (not affecting the joint) and intra-articular (involving the talo-calcaneal and calcaneal cuboid joints) types. The management of heel fractures includes nonoperative and operative treatments, but no clear consensus has been reached. The choice of operative treatment is still controversial with many factors influencing the final clinical outcome. Many studies have assessed the outcome of treatment of calcaneal fractures, but there is a general disagreement on their management. The objective of this study was to collect and evaluate the scientific evidence reported in the literature supporting the different treatments for calcaneal fractures. Key words Evidence-based medicine Calcaneal fractures Heel fractures Os calcis fractures Treatment outcome Introduction Calcaneal fracture (os calcis or heel fracture) is a complex injury that represents 1% 2% of all fractures. It is the most common of the tarsal fractures and it plays a fundamental role in foot biomechanics, weight bearing, foot pain and foot wear. Men are more often affected than women and the incidence is higher in young and middleaged subjects [1]. The fracture generally occurs by highenergy trauma. A common fracture mechanism is an axial stress to the talo-calcaneal joint caused by a fall from a height of more than 1 meter or by a road accident. It can be bilateral and associated with other fractures, and it can be seriously disabling it can be the most severe cases [2]. Calcalneal fractures may be divided into extra-articular (not affecting the joint) and intra-articular (involving the talo-calcaneal and calcaneal cuboid joints) types [3]. Moreover, they can be classified according to the mechanism of injury, the anatomic characteristics, and the findings at plain x-rays and computed tomography (CT). The best evaluation of these fractures is traditional imaging, including plain x-rays in anteroposterior (AP), lateral and oblique views of the foot, Harris view of the heel and Broden s views of the hindfoot. CT scan best assesses heel fractures, provides a three-dimensional image and may be useful to understand fracture details and to plan a correct surgical approach [2]. The management for heel fractures is a real challenge for the orthopaedic surgeon: it varies widely and no clear consensus has been reached [2, 4, 5]. Conservative treatment is well accepted for extra-articular fractures and it is based on cryotherapy, cast immobilization, early range of motion, early compression of the plantar arch. The choice
2 37 of operative treatment is still controversial and many factors influence the final clinical outcome. Operative management includes closed reduction and internal fixation with pins, wires, screws or plates, with different medial or lateral incisions (or both), and arthrodesis [2]. Even if the outcomes of calcaneal fracture treatments have been assessed in several studies, there is a general disagreement on the most appropriate management of these injuries, in particular for displaced intra-articular fractures. The aim of this study was to collect and evaluate the scientific evidence supporting the different treatment in the management of calcaneal fractures. Materials and methods A bibliographic search was conducted to identify articles comparing different treatments for calcaneal fractures. We searched for meta-analyses, systematic reviews, guidelines and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared two or more devices in the management of calcaneal fractures. Our search strategy included the following databases: Cochrane Musculoskeletal Injuries Group specialised register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Health Technology Assessment (HTA), PEDro, MEDLINE (1966 to December 2006), EMBASE (1980 to December 2006), CINAHL (1982 to December 2006), AMED (1985 to 2006), DARE, TRIPdatabase, and the National Research Register (UK). The search was completed in December All RCTs and quasi RCTs included in the study regarded patients with calcaneal fractures evaluated by x-rays with or without CT or MRI with a follow-up at least of six months. We searched for any nonoperative or operative treatment, such as plaster cast immobilization, early mobilization, impulse compression to closed reduction with pin fixation, open reduction and internal fixation with K wires, screws or plates through different approaches, using or not bone graft, and arthrodesis. The outcome measures included assessment of pain, ability to wear shoes, return to work, quality of life, range of motion, walking ability, imaging evaluation and complications. The following terms, selected from the National Library of Medicine s medical subject headings (MESH) database, were searched: human; calcaneus; fractures, bone; heel; os calcis; and treatment outcome. Results Our research identified only 8 quasi RCTs and RCTs (Table 1), 1 systematic review, 1 meta-analysis and no guidelines. Of the 8 RCTs, 4 were reported in the 1990s. The remaining 4 more recent studies described different outcomes from the same large multicenter trial. RCTs In 1992, Erdmann and colleagues [6] reported a randomized controlled trial that compared conservative treatment with intermittent compression of the foot as therapy for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures in 23 patients. Intermittent compression of the plantar venous plexus was performed through a pneumatic plantar impulse device for 1 week. They were randomized as follows: 12 patients to the impulse compression group and 11 to the control group. After 1 week, all patients were discharged with a plaster cast for 1 month with no weight-bearing. Patients were evaluated at 1, 2, 3, 6 and 12 months for pain, measured on a visual analogue scale (VAS, 0 10), subtalar movement, walking distance, return to work and weight bearing. The authors reported a significant improvement in subtalar movement in the pumped group, but no difference in walking distance or weight bearing between the groups. One year later O Farrel et al. [7] reported a quasi-randomized controlled trial of 24 patients with displaced intra-articular calcanear fractures, and compared operative versus nonoperative treatment. Conservative treatment consisted of elevation, compression of the foot, physiotherapy at 7 days and gradual weight bearing as tolerated. Operative treatment consisted of open reduction and internal fixation with plate and early mobilization. Average follow-up was 15 months for the operative group and 14 months for the nonoperative group. The authors reported better results in the operative treatment group, in terms of footwear problems, longer pain-free walking distance, return to work, subtalar range of movement, and Bohler s angle. Conservative and operative treatments for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus were also compared by Parma et al. in a quasi-randomized controlled trial also published in 1993 [8]. Overall, 31 patients were randomized to the conservative treatment group, and received foot elevation, ice packs, physiotherapy and early foot movement, while 25 patients were treated with open reduction and internal fixation with Kirschner wire followed by cast immobilization for 6 weeks. Weight bearing was allowed at 6 8 weeks. The patients were evaluated for pain, ankle joint range of movement (ROM), subtalar joint movement, function, walking ability, return to work, return to normal recreation, shoe wear, and use of analgesics. No significant differences in outcomes were found between the operative and nonoperative groups at 1-year follow-up. Thordarson and Krieger also carried out a randomized controlled trial of operative versus nonoperative management in 30 patients with displaced intra-articular cal-
3 38 Table 1 Selected clinical trials comparing treatments for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Reference Year Patients Treatments Outcome measures Results Erdmann Impulse compression Pain (VAS), subtalar Significant improvement in subtalar et al. [6] (24 fractures) vs. no impulse movement,walking movement in the pumped group; no compression distance, return to work, difference in walking distance and weight bearing weight bearing between the 2 groups O Farrel Operative vs. Footwear problems, Better results from operative et al. [7] nonoperative pain-free walking treatment compared with nonoperative treatment distance, return to work, treatment (in particular, return to subtalar range of work and ability to wear shoes) movement, Bohler s angle Parmar Operative vs. Pain, ankle joint ROM, No significant difference in outcome et al. [8] nonoperative subtalar joint movement, between operative and nonoperative treatment function, walking ability, treatment groups return to work, return to normal recreation, shoe wear, use of analgesics Thordarson Operative vs. Outcome assessment Better results of operative treatment et al. [9] nonoperative questionnaire (pain, daily compared with nonoperative treatment treatment activity, walking (in particular, return to work and ability limitations, shoe wear, to wear shoes) exercise, work); Bohler s angle Buckley Operative vs. SF-36, VAS, Bohler s Not statistically significant differences et al. [10] (471 fractures) nonoperative angle, complications in functional results between operative treatment and nonoperative treatment. Patients between 20 and 29 years, patients who were not receiving Worker s compensation, women, patients with a light workload, with a higher Bohler s angle, with a single fracture, with a simple displaced intra-articular fracture had better results with operative treatment than with nonoperative treatment Howard Operative vs. Complications Patients treated surgically were moreet et al. [11] (459 fractures) nonoperative treatment likely to develop complications Barla women Operative vs. SF-36, VAS, Bohler s Better results from operative treatment et al. [12] (43 fractures) nonoperative angle compared to nonoperative treatment treatment O Brien Operative vs. SF-36, VAS, personal Not statistically significant differences et al. [13] (351 fractures) nonoperative treatment gait satisfaction score in personal gait satisfaction scores between groups VAS, analogue score; ROM, range of motion caneal fractures [9]. Nonoperative treatment consisted of ice packs, foot elevation and a bulky Jones dressing, followed by a removable posterior splint and early foot motion. Weight bearing was allowed at 8 weeks as tolerated. Operative treatment included a standardized lateral approach with reduction and internal fixation with screws
4 39 or a plate with screws; a posterior splint was applied. Weight bearing was allowed at 10 weeks. Average follow-up was 17 months for the operative group and 14 months for the nonoperative group. The patients were evaluated through a new functional outcome assessment questionnaire (score, 0 100) on pain (30 points), daily activity limitations (10 points), shoe wear (10 points), walking (20 points), exercise (10 points), and work (20 points). Bohler s angle was also measured. The authors demonstrated significantly better results from operative treatment than from nonoperative treatment. In the period , four reports were published on the results of a large multicenter randomized clinical trial designed by the Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society and carried out between 1991 and The trial compared nonoperative management and operative treatment in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. In Buckley et al. [10], 424 patients (471 calcaneal fractures) were randomized to 2 groups: 218 patients (262 fractures) to the nonoperative treatment group, with elevation, ice, rest and early mobilization; 206 (249 fractures) to the operative group with open reduction and internal fixation with plate, screws or wires using a standard lateral approach. Bone graft was used according to the preference of the surgeon. All patients respected a period of 6 weeks of non-weight-bearing and none used a cast. After 6 weeks the physiotherapy protocol began. The patients were evaluated at 2, 4, 6, 12, 26, and 52 weeks and after 2 years. At 1- and 2-year follow-up, the patients were assessed through SF-36, a general health-outcome measure, and VAS. CT was performed pre-operatively, postoperatively and after 2 years to assess the reduction. The authors demonstrated that operative treatment provides no improvement in functional results compared to nonoperative treatment for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. However, statistical analysis demonstrated that patients who were not receiving Worker s Compensation, women, patients between 20 and 29 years of age, with a light workload, with a higher Bohler s angle, with a single fracture, with a simple displaced intra-articular fracture were more likely to have better results with operative treatment than with nonoperative treatment. More reduction is anatomic and better outcome can be predicted. Nonoperative treatment could be recommended to patients over 50 years of age, males, those who are receiving Worker s Compensation, and those with heavy workload occupation. The higher energy fractures, with a lower Bohler s angle, have worse results compared with those after a low energy trauma. Howard et al. [11] assessed complications following management of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures, which are a significant cause of morbidity. The population consisted of 424 patients (459 fractures). Two hundred and eighteen patients (233 fractures) were randomized to the nonoperative treatment group and 206 patients (226 fractures) were assigned to the operative group with open reduction and internal fixation using a standard lateral approach. All patients respected a period of 6 weeks of nonweightbearing and none used a cast. The patients treated with open reduction and internal fixation were more likely to develop complications. The long-term outcomes of treatments for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures were assessed specifically in women by Barla et al. [12]. The study considered 41 women (43 calcaneal fractures), of which 21 received nonoperative treatment and 20 had open reduction and internal fixation. The patients were evaluated at 2, 4, 6, 12, 26, and 52 weeks and at 2 years through the SF-36 and VAS, and Bohler s angle was measured as a prognostic factor of long-term outcome. The SF36 (p=0.04) and VAS (p=0.10) indicated significantly better results in the operative group compared to the nonoperative group. There also was a statistically significant improvement of Bohler s angles in the operative group (p=0.001). Finally, the patients personal satisfaction with gait over a 2- to 8-year follow-up was reported by O Brien et al. [13]. This study assessed how fracture type, treatment and patient demographics influenced gait satisfaction after displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Three hundred and nineteen patients (351 calcaneal fractures), randomized to either nonoperative treatment or operative treatment, were available for analysis. Personal gait satisfaction scores were not significantly different between the two treatment groups. Systematic review and meta-analysis The Cochrane Collaboration systematic review by Bridgman et al., published in 2006 [3], aimed to identify and evaluate the most appropriate treatments for intraarticular calcaneal fractures. The authors identified 6 randomized trials, of which 4 were included, 1 was excluded and 1 was ongoing. The selected trials regard 2 different comparisons: operative versus nonoperative treatment and impulse compression versus no impulse compression. The authors concluded that there is only limited evidence that open reduction and internal fixation with plate or K wires may be superior to nonoperative treatment. The clinical trials available in the literature are small and of poor methodology. The same conclusion was made for impulse compression management. Randle and colleagues [14] published a meta-analysis in 2000 on the issue of whether calcaneal fractures should be treated surgically. The authors selected 6 RCTs that
5 40 compared operative versus nonoperative treatment for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with follow-up of at least 12 months reporting functional and clinical outcomes. The surgical technique was different across the six studies: from Kirschner wires only to a single bone screw, a lag screw and plate, plate and screws with or without bone graft. The length of immobilization of operated patients varied from 5 days to 6 weeks. The weight bearing as tolerated began at 6 weeks in three studies and by 8 weeks in the others. The conservative treatment groups did not differ much: rest, ice packs, no immobilization or immobilization with compression bandage or removable splint, early mobilization and weight-bearing at 6 10 weeks. The authors concluded that there was a trend to better results in the operative groups regarding pain, return to work, gait abnormalities and radiographic findings. However, they could not make any treatment recommendations for displaced calcaneal fractures on the basis of the studies included in the meta-analysis. Discussion Controversy over the better treatment for displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures has been described throughout history. Many retrospective and a few small prospective studies reported better results from operative treatment than from conservative management [10]. The metaanalysis of Randle et al. [14] reported a trend for a better outcome from surgical management of calcaneal fractures, but the authors underlined the weak strength of the evidence for deciding on the optimal treatment for this type of fracture. However, the ideal meta-analysis is obtained analyzing randomized controlled trials (RCTs), while these 6 studies consisted in prospective trials not correctly randomized and retrospective comparative studies. Non-randomized trials could have potential bias, so they cannot provide statistically significant data. Our research strategy identified a few randomized trials evaluating treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Most of these trials have poor quality, small sample, short follow-up, several types of bias, different outcome measures (often not validated), and are often methodologically not correct. The 2006 systematic review of the Cochrane Database [3] underlined there is no strong evidence regarding the optimal treatment for displaced intra-articular fractures. The evidence summarized in this review [3, 7, 9] suggests that surgical treatment with internal fixation with a plate and early movement may lead to better results than conservative treatment. Better results were seen in particular for return to work, ability to wear shoes and return to normal activities; Bohler s angle was also improved in the operative groups. The clinical trials had a follow-up no longer than 2 years, so no data on joint degeneration in the 2 groups were provided. The authors concluded that the small number of patients included in these trials only permits suggesting preliminary findings. This review noted the existence of an ongoing randomized clinical trial of Buckley [10], but there is no reference to the overall results. It is surprising that a review published in 2006 in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews seems updated not before 2002 (a note claims update in 2003). From this multicenter prospective randomized controlled trial many other studies derived, each of them regarding a particular aspect of the studied problem. We report each of them, underlying the good quality of the multicenter trial, for its design, sample size and follow-up. The authors demonstrated there is no statistically significant improvement from operative treatment compared with nonoperative treatment. However, patients between 20 and 29 years of age, patients who were not receiving Worker s Compensation, women, patients with a light workload, with a higher Bohler s angle, with a single fracture, with a simple displaced intra-articular fracture had better results with operative treatment than with nonoperative treatment. Although the 4 RCTs [10 13] deriving from the large multicenter study gave important data on the operative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures, they provide no definitive evidence on the best management of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures, in particular for the varying severity of the fractures. These studies considered all types of fractures in the same group. It could be useful to study the same type of fracture, classified through the same classification system, to better understand the real outcome derived from different treatments. Moreover, no randomized controlled trials comparing different surgical treatments or different forms of conservative management are available. So, particular attention should be given to these comparisons. In summary, methodologically correct trials are necessary to confirm whether the trends and conclusions from previous trials are valid. Long-term follow-up is necessary to study the degenerative effects on joint of the different treatments even if a large multicenter clinical trial, well designed and conducted, suggests important evidence, it is not possible at the moment to provide a definitive conclusion regarding the better results of operative management of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures, compared with conservative treatment. There is a real need for well designed studies to obtain strong evidence for the management of these fractures, to define timing, selection and role of different surgical techniques.
6 41 References 1. Matherne TH, Tivorsak T, Monu JU (2007) Calcaneal fractures: what the surgeon needs to know. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 36: Lowery RBW, Calhoun JH (1996) Fractures of the calcaneus part I: anatomy, injury mechanism and classification. Foot Ankle Int 17: Bridgman SA, Dunn KM, McBride DJ, Richards PJ (2006) Interventions for treating calcaneal fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD Kenwright J (1993) Fractures of the calcaneum. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75: Lowery RBW, Calhoun JH (1996) Fractures of the calcaneus part II: treatment. Foot Ankle Int 17: Erdmann MW, Richardson J, Templeton J (1992) Os calcis fractures: a randomized trial comparing conservative treatment with impulse compression of the foot. Injury 23: O Farrel DA, O Byrne JM, McCabe JP, Stephens MM (1993) Fractures of the os calcis: improved results with internal fixation. Injury 24: Parmar HV, Triffitt PD, Gregg PJ (1993) Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum treated operatively or conservatively. A prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75: Thordarson DB, Krieger LE (1996) Operative versus non operative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus: a prospective randomized trial. Foot Ankle Int 17: Buckley R, Tough S, McCormack R et al (2002) Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84: Howard JL, Buckley R, McCormack R et al (2003) Complications following management of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective randomized trial comparing open reduction internal fixation with nonoperative management. J Orthop Trauma 17: Barla J, Buckley R, McCormack R et al (2004) Displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: long-term outcome in women. Foot Ankle Int 25: O Brien J, Buckley R, McCormack R et al (2004). Personal gait satisfaction after displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a 2 8 year follow up. Foot Ankle Int 25: Randle JA, Kreder HJ, Stephen D et al (2000) Should calcaneal fractures be treated surgically? A meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 377:
Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials
 British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome
 Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile?
 28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture
 Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures. Kali Luker, PGY-1
 Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
HOW TO DEVELOP A RESEARCH PROTOCOL
 Research and Evidence Based Medicine Committee 2010-2011 HOW TO DEVELOP A RESEARCH PROTOCOL Evidence-Based Medicine The conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions
Research and Evidence Based Medicine Committee 2010-2011 HOW TO DEVELOP A RESEARCH PROTOCOL Evidence-Based Medicine The conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks
 Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Surgical versus conservative treatment for acute first-time anterior shoulder dislocation: the evidence
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:207 213 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0095-7 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Padua R. Bondì L. Bondì A. Campi Surgical versus conservative treatment for acute first-time anterior
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:207 213 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0095-7 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Padua R. Bondì L. Bondì A. Campi Surgical versus conservative treatment for acute first-time anterior
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients
 Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
Calcaneal Fracture. Phase 1 Maximum Protection Phase (0-8 weeks)
 Phase 1 Maximum Protection Phase (0-8 ) Goals for Phase 1 Education of injury and surgical precautions Decrease edema Pain reduction Scar tissue mobility Increase ankle ROM Prevent muscular inhibition
Phase 1 Maximum Protection Phase (0-8 ) Goals for Phase 1 Education of injury and surgical precautions Decrease edema Pain reduction Scar tissue mobility Increase ankle ROM Prevent muscular inhibition
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision
 Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Prospective study of fracture calcaneus with Allan s procedure- bone grafting without implants
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING. Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion
 AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
Evidenced-Based Medicine: Where Does it Fit in Foot and Ankle Surgery?
 Sean T. Grambart, DPM, FACFAS Ankle and Foot Surgery Carle Clinic Association Evidenced-Based Medicine: Where Does it Fit in Foot and Ankle Surgery? MODULE: Calcaneal Fracture Evidence-Based Medicine The
Sean T. Grambart, DPM, FACFAS Ankle and Foot Surgery Carle Clinic Association Evidenced-Based Medicine: Where Does it Fit in Foot and Ankle Surgery? MODULE: Calcaneal Fracture Evidence-Based Medicine The
My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
 PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Tao Zhang, Xingwang Wu, Zhanpo Wu and Yingze Zhang *
 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments -
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report
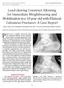 Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular. calcaneal fractures
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure
 Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture Dislocation Injuries
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement
 016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
Case. 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms. Your diagnosis?
 Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
Accepted: 3 April 2009
 Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a retrospective case analysis
 Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS. Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2
 NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
Indications and Non-Union Rate in Isolated Subtalar Arthrodesis
 Indications and Non-Union Rate in Isolated Subtalar Arthrodesis Verschae G, Bastías G, Miralles A, Barahona M, Bergeret JP, Gutierrez R, Layseca A Foot and Ankle Unit Hospital del Trabajador Santiago,
Indications and Non-Union Rate in Isolated Subtalar Arthrodesis Verschae G, Bastías G, Miralles A, Barahona M, Bergeret JP, Gutierrez R, Layseca A Foot and Ankle Unit Hospital del Trabajador Santiago,
Pilon Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Pilon Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Pilon Fractures Pilon fractures affect the bottom of the shinbone (tibia) at the ankle joint. In most cases, both bones in the lower leg, the tibia
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Pilon Fractures Pilon fractures affect the bottom of the shinbone (tibia) at the ankle joint. In most cases, both bones in the lower leg, the tibia
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures
 Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study
 CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v4i12.78 A Study to Find out the Effectiveness of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v4i12.78 A Study to Find out the Effectiveness of
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure
 Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Foot and ankle update
 Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
CALCANEAL FRACTURE. Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET. Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day:
 CALCANEAL FRACTURE Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day: It was the nightingale, and not the lark, That pierced the fearful hollow of
CALCANEAL FRACTURE Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day: It was the nightingale, and not the lark, That pierced the fearful hollow of
Lesser toe sequential repair
 Lesser toe sequential repair For the correction of lesser toe deformity Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is lesser toe deformity? The lesser toes are those other than your
Lesser toe sequential repair For the correction of lesser toe deformity Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is lesser toe deformity? The lesser toes are those other than your
Foot & Ankle. Mr Peter Black, FRCSEd. Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Anglesea Clinic Orthopaedics
 Foot & Ankle Mr Peter Black, FRCSEd Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Anglesea Clinic Orthopaedics Foot & Ankle Problems - Myths and Leg-ends All foot and ankle surgery is cripplingly painful There s no point
Foot & Ankle Mr Peter Black, FRCSEd Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Anglesea Clinic Orthopaedics Foot & Ankle Problems - Myths and Leg-ends All foot and ankle surgery is cripplingly painful There s no point
Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic, 501 N. 10th Street, Manitowoc, WI Procedure. Subtalar arthrodesis
 OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Calcaneal Fractures in Children
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 18:469-474 1998 Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphi a Calcaneal Fractures in Children Suguru Inokuchi, M.D., Norio Usami, M.D., Eiichi Hiraishi, M.D., and Takeshi
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 18:469-474 1998 Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphi a Calcaneal Fractures in Children Suguru Inokuchi, M.D., Norio Usami, M.D., Eiichi Hiraishi, M.D., and Takeshi
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology
 The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology Treatment of Hindfoot Non-Union with DynaNail TTC Fusion System A CASE REPORT Dr. L. Daniel Latt, MD, PhD Background The DynaNail TTC Fusion System is intended
The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology Treatment of Hindfoot Non-Union with DynaNail TTC Fusion System A CASE REPORT Dr. L. Daniel Latt, MD, PhD Background The DynaNail TTC Fusion System is intended
Section 4: Tarsal Coalitions
 Case H (Figure 2): PedCat CBCT transverse plane reconstruction of right Lisfranc midfoot dislocation compared to normal left foot. Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: The weight bearing CBCT study
Case H (Figure 2): PedCat CBCT transverse plane reconstruction of right Lisfranc midfoot dislocation compared to normal left foot. Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: The weight bearing CBCT study
Open surgery vs minimal invasive methods for calcaneus fractures. Eur J Transl Myol 28 (2): , 2018
 Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What?
 Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
Isolated Subtalar or Talonavicular Fusion Has Failed. Now What? Anish R. Kadakia MD Associate Professor Northwestern University: Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern Memorial Hospital Department of
The Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System
 Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates Ko Ishida 1), Yoichi Aota 2), Naoto Mitsugi 1),
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Spondylolysis repair using a pedicle screw hook or claw-hook system. a comparison of bone fusion rates Ko Ishida 1), Yoichi Aota 2), Naoto Mitsugi 1),
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
DEPARTMENT OF TRAUMATOLOGY AND HAND SURGERY INSTITUTE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SURGERY ANKLE AND FOOT INJURIES
 DEPARTMENT OF TRAUMATOLOGY AND HAND SURGERY INSTITUTE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SURGERY ANKLE AND FOOT INJURIES Presenter: Dr George Ayerh ENGLISH PROGRAM LECTURES EN_11/A - 2018 TOPICS I. Part: Ankle & Foot
DEPARTMENT OF TRAUMATOLOGY AND HAND SURGERY INSTITUTE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SURGERY ANKLE AND FOOT INJURIES Presenter: Dr George Ayerh ENGLISH PROGRAM LECTURES EN_11/A - 2018 TOPICS I. Part: Ankle & Foot
Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
 Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY
 1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:87 95 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0082-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach Mohamed F.
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:87 95 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0082-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach Mohamed F.
H: Orthopedic Nursing
 H: Orthopedic Nursing Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 87 Competency: H-1 Knowledge of H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge of human anatomy and physiology, specifically
H: Orthopedic Nursing Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 87 Competency: H-1 Knowledge of H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge of human anatomy and physiology, specifically
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
Trainers. Anne-Marie O Connor Musculoskeletal Podiatrist
 Trainers Anne-Marie O Connor Musculoskeletal Podiatrist Agenda Background Tarso-navicular stress fractures Case Study Interventions and research Further Research Anatomy Anatomically, wedged between the
Trainers Anne-Marie O Connor Musculoskeletal Podiatrist Agenda Background Tarso-navicular stress fractures Case Study Interventions and research Further Research Anatomy Anatomically, wedged between the
Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures
 FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
Medial circumflex artery Lateral circumflex artery
 Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Evaluation and Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures. Benjamin Maxson, DO Florida Orthopaedic Institute Orthopaedic Trauma Service
 Evaluation and Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures Benjamin Maxson, DO Florida Orthopaedic Institute Orthopaedic Trauma Service Disclosures Nothing to disclose Articular Fractures: Overview Require
Evaluation and Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures Benjamin Maxson, DO Florida Orthopaedic Institute Orthopaedic Trauma Service Disclosures Nothing to disclose Articular Fractures: Overview Require
Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries
 Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries by Alaa Mansour DPM 1*, Lawrence Fallat DPM, FACFAS 2 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal 10 (1): 5 Severe traumatic injuries
Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries by Alaa Mansour DPM 1*, Lawrence Fallat DPM, FACFAS 2 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal 10 (1): 5 Severe traumatic injuries
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Session II 11:30 11:45 am. Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio. Disclosure: (n)
 Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
FRCS orth course Important papers in Orthopaedics
 FRCS orth course Important papers in Orthopaedics Scaphoid, Distal radius Scaphoid fracture JBJS Am 2005 oct Should acute scaphoid fractures be fixed? A randomized controlled trial. Dias JJ, Wildin CJ,
FRCS orth course Important papers in Orthopaedics Scaphoid, Distal radius Scaphoid fracture JBJS Am 2005 oct Should acute scaphoid fractures be fixed? A randomized controlled trial. Dias JJ, Wildin CJ,
The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular
 The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures Berdine Bakker MSc, Jens A. Halm MD PhD, Esther M.M. Van Lieshout PhD, Tim Schepers MD PhD Erasmus MC,
The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures Berdine Bakker MSc, Jens A. Halm MD PhD, Esther M.M. Van Lieshout PhD, Tim Schepers MD PhD Erasmus MC,
Selected Fractures of the Foot: Diagnosis and Treatment.
 Selected Fractures of the Foot: Diagnosis and Treatment www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview Forefoot Fractures Lisfranc MT 5 th MT Hindfoot Fractures Calcaneus Talus Tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc s) Fracture
Selected Fractures of the Foot: Diagnosis and Treatment www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview Forefoot Fractures Lisfranc MT 5 th MT Hindfoot Fractures Calcaneus Talus Tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc s) Fracture
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Tibiotalocalcaneal fusion over retrograde SIGN Nail
 Tibiotalocalcaneal fusion over retrograde SIGN Nail PROF (DR.) SYED ANWARUZZAMAN Professor and Head Department of Orthopedic &trauma Comilla Medical college & Hospital Comilla, Bangladesh Introduction
Tibiotalocalcaneal fusion over retrograde SIGN Nail PROF (DR.) SYED ANWARUZZAMAN Professor and Head Department of Orthopedic &trauma Comilla Medical college & Hospital Comilla, Bangladesh Introduction
Sagittal Subtalar and Ankle Joint Assessment with Weight-bearing Fluoroscopy during Shod Ambulation
 Sagittal Subtalar and Ankle Joint Assessment with Weight-bearing Fluoroscopy during Shod Ambulation 1 Emily L. Exten, M.D. 2 Benjamin McHenry, Ph.D. 1,2 Gerald Harris, Ph.D., P.E. 1 Medical College of
Sagittal Subtalar and Ankle Joint Assessment with Weight-bearing Fluoroscopy during Shod Ambulation 1 Emily L. Exten, M.D. 2 Benjamin McHenry, Ph.D. 1,2 Gerald Harris, Ph.D., P.E. 1 Medical College of
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture: an anatomical specimen study
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate
 wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery
 PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle.
 X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Complex hinge joint Articulations among: Fibula Tibia Talus Tibial plafond Distal tibial articular surface
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Complex hinge joint Articulations among: Fibula Tibia Talus Tibial plafond Distal tibial articular surface
CHARLOTTE. 7.0 Multi-Use Compression Screw System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 CHARLOTTE 7.0 Multi-Use Compression Screw System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 1 Chapter 2 2 Chapter 3 3-9 Chapter 4 10-12 Appendix A 13-14 Design Rationale Screw Behavior Surgical Technique Procedure
CHARLOTTE 7.0 Multi-Use Compression Screw System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 1 Chapter 2 2 Chapter 3 3-9 Chapter 4 10-12 Appendix A 13-14 Design Rationale Screw Behavior Surgical Technique Procedure
Satisfaction analysis of Figure 8 (open heel) short leg cast
 Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
Financial Disclosure. The authors have not received any financial support for the preparation of this work.
 Persistent Clubfoot Deformity Following Treatment by the Ponseti Method W.B. Lehman, M.D. Alice Chu, M.D. New York Ponseti Clubfoot Center Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Financial Disclosure
Persistent Clubfoot Deformity Following Treatment by the Ponseti Method W.B. Lehman, M.D. Alice Chu, M.D. New York Ponseti Clubfoot Center Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Financial Disclosure
