Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Qi Zhang, Song Liu, Tao Zhang and Yingze Zhang *
|
|
|
- Clifton Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bony destructive injuries of the calcaneus: long-term results of a minimally invasive procedure followed by early functional exercise: a retrospective study Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Qi Zhang, Song Liu, Tao Zhang and Yingze Zhang * Abstract Background: Bony destructive injury of the calcaneus (BDIC) represents one of the most severe comminuted fractures of the calcaneus in which soft tissue coverage remains intact. The features of this injury include a collapsed articular surface, significant widening, severe loss of height and an unrecognisable outline of the calcaneus. This study aims to present the long-term outcomes of BDIC treated in a minimally invasive fashion followed by supervised early exercise. Methods: Twelve patients with unilateral BDICs were treated at our institution. The main surgical procedures included percutaneous traction and leverage reduction and internal compression fixation with anatomic plates and compression bolts. Early functional exercise was encouraged to mould the subtalar joint. The height, length and width of the calcaneus; Böhler s and Gissane s angles; reduction of the articular surfaces; and functional recovery of the affected feet were assessed. Results: The height, length and width of the calcaneus were substantially restored. The mean Böhler s and Gissane s angles of the affected calcaneus were 24.5 and degrees, respectively. Five patients regained anatomical or nearly anatomical reduction of their posterior facets. Residual articular displacement of more than 3 mm was noted in three patients. Patients were followed for a mean of 93.9 months. The mean American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score was Nine patients showed excellent or good results. Radiographic evidence of post-traumatic subtalar arthritis was observed in four cases. However, no subtalar arthrodesis was required. Conclusions: BDICs can be treated effectively with percutaneous reduction and internal compression fixation followed by early active exercise. This protocol resulted in satisfactory radiological and functional outcomes. Keywords: Calcaneal fracture, Bony destructive injury, Internal compression fixation, Percutaneous leverage, Early exercise * Correspondence: dryzzhang@126.com Equal contributors Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei , P.R. China 2014 Su et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 Page 2 of 8 Background Highly comminuted calcaneal fractures can lead to devastating long-term disability [1,2], which is often life-altering for patients [3]. Highly comminuted calcaneal fractures are complex injuries and remain a great challenge for orthopaedic surgeons. It is often difficult to fixate these injuries, and special technical skills are required to secure the reduction and stability of the fragments. Both conservative and operative treatments have been attempted to manage such injuries. The reasons for conservative management include the complex anatomy, soft tissue problems and complications related to open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) [4-7]. However, complications may also result from non-operative treatment, including incapacitating hindfoot malalignment (such as shortening, widening and varus angulation), subtalar arthrosis, peroneal tendon impingement, tibiotalar or fibulocalcaneal impingements and the technical difficulties of salvage surgery [3,8-11]. The widened heel can also be a cosmetic problem for women [12]. These reported complications support the selection of ORIF for highly comminuted intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Speck and Klaue treated 36 comminuted calcaneal fractures operatively and reported satisfactory clinical and radiological outcomes [13]. Their results suggest that anatomical reconstruction of calcaneal fractures is indicated even in highly comminuted fractures. However, several recent meta-analyses and prospective comparative trials have demonstrated that the evidence to support ORIF is weak compared with non-operative treatment [14-16]. In addition, soft tissue complications arising from ORIF still adversely affect the functional outcome, even when anatomical restoration of the subtalar congruency is achieved, which further limits the application of ORIF. Many authors have developed minimally invasive or percutaneous techniques for the reduction and fixation of calcaneal fractures hoping to prevent the welldocumented soft tissue complications related to ORIF techniques [17-20]. Although surgical techniques continue to evolve, the optimal treatment for highly comminuted fractures of the calcaneus continues to elude investigators. In efforts to manage these complex injuries with minimal soft tissue complications, we developed a minimally invasive technique with an emphasis on early joint exercise. The purpose of this study is to describe the features of highly comminuted calcaneal fractures and to report outcomes of such injuries treated with the proposed protocol. Methods From April 1, 2004, to October 31, 2006, 187 patients (215 feet) with displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures were treated at our institute. The study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University. Signed informed consent was obtained from each patient. The inclusion criteria were as follows: patients were adults (aged 18 years or over) with unilateral calcaneal fractures; evaluation was performed using radiography and CT scans; fractures were highly comminuted and intra-articular (Sanders type IV fractures) featuring a collapsed articular surface, more than five fracture fragments and the largest fragment diameter of less than 2.5 cm; significant shortening and widening (>25% of the normal width); more than 10% loss of height; and an unrecognisable outline of the calcaneus but with intact soft tissue coverage (Figure 1). To demonstrate the injury severity and to reflect the potentially devastating prognosis of the most serious part of Sanders type IV fractures of the calcaneus, we term such comminuted fractures bony destructive injuries of the calcaneus (BDICs). The exclusion criteria were as follows: open fractures; fractures treated using conventional Figure 1 A 53-year-old male patient suffered a left bony destructive injury of the calcaneus due to a fall from a height. Preoperative radiographs (A, lateral view; B, axial view) and computed tomography (CT) scans (C and D, the sagittal images) demonstrate significant widening and shortening, severe loss of height of the calcaneus and collapsed articular surfaces.
3 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 Page 3 of 8 plates and screws; polytraumatic injuries of the lower extremities at the time of hospital admission; and severe medical ailments. Twelve patients with unilateral BDIC were identified. These patients included 10 males and 2 females with an average age of 39 years (range, years); from these patients, the study involved 5 left feet and 7 right feet. Eleven patients were injured due to fall from a height, and one was involved in a traffic accident. According to the Sanders classification system [21], the BDICs were all type IV fractures. The patients underwent operative therapy at a mean of 7.6 days after injury (range, 6 to 11 days), when the swelling had subsided and positive wrinkles had appeared on the hind feet. The main surgical procedures included percutaneous traction and leverage reduction and internal compression fixation with anatomic plates and compression bolts (Shandong Wego Orthopedic Device Co., LTD). The aim was the restoration of height, length and width of the calcaneus; correction of Böhler s angle; and anatomical or nearly anatomical reconstruction of the articular surfaces. Surgical technique The surgical technique has been described in detail in our previous studies [22,23]. Under either epidural or spinal anaesthesia, the patients were placed in a lateral decubitus position. A C-arm fluoroscopic unit was employed to guide and assess the reduction and fixation of BDICs. During the operation, a 3.5 mm Steinmann pin was inserted into the calcaneus at the level of the calcaneal tuberosity. The pin was distracted posteroinferiorly along the long axis of the calcaneus to restore the length. Another one or two Steinmann pins were then introduced through the superoposterior portion of the calcaneus into the fragments for percutaneous leverage. Repeated leverage was recommended for a good reduction of the posterior articular surface and restoration of calcaneal height. Stress was applied to both walls of the calcaneus with clasped hands to reduce the width and height. If satisfactory reduction was achieved, the pins were advanced into the anterior part of the calcaneus for provisional fixation. A 3.5 cm longitudinal incision midway between the fibula and the Achilles tendon was made on the posterior aspect of the lateral hindfoot. An anatomical plate of the appropriate size (56.4, 60.4 or 64.4 mm in length) was selected and inserted into a subcutaneous tunnel created with a periosteal elevator. Two compression bolts (30 60 mm in length and 4 mm in diameter) were inserted into the posterior part of the hindfoot in a lateral-medial direction, and the third bolt was inserted directly into the sustentaculum tali. The patient was then placed in a supine position. Small incisions on the medial wall were made to expose the screws, and particular care was taken to avoid damaging the neurovascular bundles and tendons. The nuts (2.5 or 3.5 mm in thickness and 4 mm in inner diameter) were tightened on the screws, which were capable of generating considerable compressive force to restore the width of calcaneus to the utmost degree. Because the volume of the calcaneus is relatively constant, reducing the width can subsequently restore the height of the calcaneus (see Additional file 1). The compression bolt was broken off at the constricted area (Figure 2). Additional cancellous screws were sometimes used to secure the multi-fragmented fractures. Postoperative management Postoperative radiographs and CT scans were taken to assess the quality of reduction and fixation. Supervised functional exercise was conducted to mould the subtalar joint Figure 2 The instruction of the compression bolts. The compression bolts consist of nuts and screws with a constricted area (A; arrow). The nuts are used to fasten the screws (B). The part of the screw distal to the constricted area is broken off (C).
4 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 Page 4 of 8 as soon as pain was tolerable. Toe, ankle and subtalar motion was permitted on the first postoperative day. The patients began to roll the soles of their foot on a water bottle on the third postoperative day. Partial weight bearing was started at four weeks. The weight applied to the injured foot was gradually increased within the limits of patient discomfort, and the patients generally attained full weightbearing status at 6 to 12 weeks postoperatively. Postoperative complications were recorded. Patients were followed up at one to six month intervals. Radiographs and CT scans were taken to assess the reduction and union at one, two, three, and six months and at one year, and then at six month intervals thereafter. Functional evaluation was performed according to the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) scores [24]. To minimise observer bias, the questionnaires and physical examinations were all performed by one author. Radiological measurement The width and length of the calcaneus were measured preoperatively and postoperatively. A 10 cm calibrator (Beijing Granville Technologies, Beijing, China) was placedclosetoandparalleltothesoleofthefootasa measurement calibration standard when the axial and lateral radiographs of the calcaneus were taken. The images were transmitted to the PACS workstation. The width of the calcaneus was measured on the axial images with the use of the software SIENET MagicView 300 (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany), and the length of the calcaneus was measured on the lateral images. Statistical analysis The data were analyzed with the use of SPSS 13.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The one sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was applied to analyze the continuous variables. Continuous variables with normal distributions were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), and analyzed using the two sample t test. Continuous variables with non-normal distributions were recorded as the median and interquartile values, and analyzed using the Mann Whitney U test. A P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results The mean operative time, radiation exposure, and intraoperative blood loss plus postoperative drainage were 78 minutes (range, 56 to 93 minutes), 9.2 s (range, 6 to 15 s) and 122 ml (range, 95 to 148 ml), respectively. There were no intraoperative iatrogenic neurovascular injuries. Postoperative radiographs and CT scans demonstrated that gross anatomy of the calcaneus was restored in all patients (Figure 3). The postoperative Böhler s angle, height, width and length of the calcaneus were significantly different from those measured preoperatively (Table 1). However, there was no significant change in Gissane s angle. Anatomical or nearly anatomical reduction of the posterior articular surface was achieved in five patients. The posterior articular facet step ranged from 3 to 5 mm (mean, 3.9 mm) in the other seven patients according to the immediate postoperative CT scan. One patient (8.3%) developed a superficial wound infection that required a dressing change and seven days of oral cefamezin. The wound infection eventually resolved. Patients were followed up for an average of 93.9 ± 10.8 months (range, 79 to 115 months). Early functional exercise reduced the residual displacement of the posterior articular surface. Among the seven patients with residual articular displacement of more than 3 mm immediately after the operation, a residual displacement of greater than 3 mm remained in only three patients, and the other patients had a less than 3 mm step on the posterior facet at follow up. Radiographs and CT scans taken at the final review showed that four patients (33%) developed degenerative changes in their congruent subtalar joints (Figure 4). Among these four patients, two complained of mild pain after walking for long distances and had mild restriction when going up and down hills; one patient had moderate pain after walking two kilometres and complained of moderate restriction when he walked up or down an incline; one patient can walk normally without any pain (see Additional file 2, with signed consent obtained from this patient). Nine patients had no restriction during walking, either on flat terrain or on an incline. No patients required subtalar arthrodesis at the final follow up. The mean AOFAS score was 83.8 ± 8.0 (range, 69 to 94), and the results were graded as excellent in 4 cases, good in 5 cases, fair in 2 cases and poor in 1 case. Nine patients returned to their previous occupations within nine months after the operation. Three patients had changed to work requiring less heavy labour. Discussion BDICs are highly comminuted calcaneal fractures that constitute the most severe portion of Sanders type IV calcaneal fractures. This type of injury features a significant loss of height, shortening and widening of the calcaneus, and the collapse of the articular surfaces, especially the posterior articular surface. We proposed a management protocol for such injuries, including percutaneous traction and leverage, internal compression fixation with clasped hands and an anatomical platecompression bolt system followed by early functional exercise and weight bearing. Excellent or good functional recovery was achieved in most patients. Highly comminuted intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus are extremely difficult to treat, and many authors have reported particularly poor prognosis [25,26]. For all
5 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 Page 5 of 8 Figure 3 Postoperative radiographs (A, lateral view; B, axial view) and CT images (C, the sagittal image; D, the coronal image) of the same patient show that the gross anatomy of the calcaneus was restored and that the subtalar joint was significantly reduced. practical purposes, ORIF remains the treatment of choice for such injuries at many orthopaedic trauma centres [27]. The majority of orthopaedic surgeons emphasise anatomical reduction of the articular surfaces of the subtalar joint, especially the posterior articular surface. However, simply restoring the subtalar joint surfaces does not guarantee a symptom-free foot [28]. The role of the subtalar joint as a major source of disability may have been overestimated [4]. In addition to the collapse of the posterior articular facet, the major deformities of BDICs include a significant Table 1 The preoperative and postoperative radiographic measurement of the twelve calcaneal fractures Pre-operation Post-operation P value Böhler angle ( ) 19.6 ± ± Gissane angle ( ) ± ± Talocalcaneal 29.3 ± ± 5.1 <0.001 height (mm) Width of the 37.2 ± ± 2.7 <0.001 calcaneus (mm) Length of the calcaneus (mm) 63.4 ± ± loss of height and severe shortening and widening of the calcaneus. These deformities can lead to late sequelae. Anterior impingement may result from the loss of calcaneal height. Compression of the peroneal tendon sheath by widening the calcaneus can cause severe lateral hindfoot pain after fracture union [29]. In addition, the soft tissues also contribute significantly to residual symptoms [4]. Therefore, the reduction of the posterior articular surface is not the unique keystone to a good outcome; restoration of the calcaneal height, width and length, the mechanical axis of the hindfoot and soft tissue balance are also important prognostic factors [30-32]. In the current study, BDICs were treated with a minimally invasive surgical technique, which consists of percutaneous leverage, internal compression fixation with anatomical plates and compression bolts through small lateral incisions. Wang et al. [33] conducted a biomechanical study to compare the stability obtained using the anatomical plate and compression bolts versus that of a conventional plate and cancellous screws in the fixation of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. During N cyclic axial loading, the anatomical plate and compression
6 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 Page 6 of 8 Figure 4 The radiographs (A, anteroposterior view; B, lateral view) and CT images (C, sagittal view; D, axial view) taken at the latest follow up demonstrate the congruent subtalar joint and degenerative changes. bolts showed significantly lower irreversible deformation and a higher level of fixation failure than those of the conventional plate and cancellous screws. This minimally invasive technique was applied to treat displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures, which was demonstrated to be an effective alternative treatment, offering the combination of fewer soft tissue complications and good reduction [22,23]. In contrast to previous studies, the current study only recruited the most severe portion of Sanders type IV fractures without the inclusion of Sanders type II and type III fractures and the less severe type IV fractures. In addition to early exercise of the toe, ankle and subtalar joints, patients were instructed to roll the soles of their foot on a water bottle beginning on the third postoperative day. The twelve patients were followed up for an average of 93.9 months, which is significantly longer than the follow-up periods of the previous two studies. Percutaneous tractional reduction with the use of Steinmann pins can restore the calcaneal length to a great degree [22,24,34]. Percutaneous leverage can primarily reduce the fractured articular surface and the calcaneal height. Both manual and implantary compression can further recreate the width and height of the calcaneus [22,24]. When recreation of gross calcaneal anatomy is obtained during the operation, walking ankle motion is recreated as well [27]. In the current study, gross anatomical calcaneal structures were achieved in all patients, and a normal walking gait was regained for each patient at the follow ups. Restoration of the gross anatomy of the calcaneus can simplify later subtalar fusions if necessary [11]. We did not use plaster for provisional fixation after the operation. Immobilisation in plaster adversely affects the end result [35,36]. Essex-Lopresti has stressed that exercise therapy has advantages over immobilisation [2]. Early motion is helpful to restore function [37,38]. In the proposed protocol for BDIC, early active mobilisation, including rolling the soles of the feet on a water bottle and early partial and full weight bearing, is an essential part of the treatment algorithm. Early functional exercise can mould the calcaneal articular surfaces via repeated compression of the talus, which contributes to a congruous subtalar joint and the restoration of Böhler s angle [4]. For BDIC, percutaneous reduction and internal compression fixation cannot reduce all fractured fragments, especially the collapsed ones. The smaller fracture segments close to the articular surface, which were above the compression bolt inserted into the sustentaculum tali, cannot be reached and secured by a Kirschner wire or a screw, regardless of the internal fixator used during the operation. These small fracture
7 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 Page 7 of 8 segments cannot be reduced anatomically and fixed, and they may present as persistent displacement on the postoperative CT images. In the current study, seven patients had a displacement of greater than 3 mm on the posterior articular surface after initial operation. After the operation, supervised functional exercises were conducted to mould the subtalar joint and to further reduce any retained displaced fracture segments that were not fixed. At follow ups, improved fracture reduction was noted in four patients with a retained displacement of less than 3 mm. However, we did not consider it a significant secondary loss of reduction. Early active exercise was also useful in improving foot function and minimising the foot pain. In our study, walking with no or minimal pain was reported in nine patients. Extensive damage to the soft tissues surrounding the calcaneus during the operation may cause residual symptoms [4]. Precise soft tissue management can minimise the risk of soft tissue complications. In this study, we treated BDICs in a minimally invasive fashion, which can reduce the surgical damage to adjacent soft tissues and subsequently reduce the risk of complications, such as wound breakdown and deep infection. Early active mobilisation can provide effective treatment for problematic soft tissues. In this case series, no patients had severe soft tissue complications. Only one patient sustained a superficial infection, which was cured by dressing changes and oral antibiotics. The current study is limited by a small sample size. In addition, there is no control group. Controlled studies with a large sample size are needed to verify the efficiency of the proposed protocol for BDICs. Another limitation is the retrospective nature of the study. All operations were performed by one senior author, which not only minimised the bias of different surgical techniques among different surgeons but also contributed to the small sample size. In the future, when more surgeons are trained and instructed to apply this surgical technique, a randomized prospective cohort study containing a large patient population with BDICs will be possible. The minimally invasive surgical technique does not provide direct visualization of the articular facets, and can not guarantee acurate reduction of the posterior articular facet. However, this technique can achieve clinical outcome as good as, if not better than the traditional open techniques in treating displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures [23]. The relatively bulky size of the nuts may result in potential nerve injury, skin irritation or flexor hallucis longus tendeon restriction, although no such complications were reported in the current study. Conclusion BDIC is the most severe and highly comminuted type of intra-articular calcaneal fracture, and it can be treated with a minimally invasive procedure featuring percutaneous traction and leverage reduction and internal compression fixation using an anatomic plate and compression bolts. The restoration of width, height and length of the calcaneus is as important as the reconstruction of the articular congruency. Early functional exercise and weight bearing can help mould the subtalar joints, which can further reduce the retained displacement of the articular surfaces and improve the outcomes with an acceptable complication rate. Additional files Additional file 1: Surgical technique using anatomical plate and compression bolt. Additional file 2: Patient s walking. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions YZ, YS and WC designed the study; YS, WC and SL made substantial contributions to acquire X-ray films and CT images, and measured Böhler s angle, Gissane s angle and residual articular displacement; TZ organised the follow ups, and QZ evaluated the functional outcomes; TZ and QZ analyzed the data; YS, WC and SL drafted and designed the manuscript; YZ had primary responsibility for final content; All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements The authors wish to thank Dr. Zhiyong Hou and Dr. Qingxian Wang for their assistance and cooperation in this study. Received: 23 September 2013 Accepted: 8 April 2014 Published: 11 April 2014 References 1. Widen A: Fractures of the calcaneus: a clinical study with special reference to the technique and results of open reduction. Acta Chir Scand Suppl 1954, 188: Essex-Lopresti P: The mechanism, reduction technique, and results in fractures of the os calcis. Br J Surg 1952, 39: Kalsi R, Dempsey A, Bunney EB: Compartment syndrome of the foot after Calcaneal fracture. J Emerg Med 2012, 43(2):e101 e Pozo JL, Kirwan EO, Jackson AM: The long-term results of conservative management of severely displaced fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 1984, 66: Buckley RE, Meek RN: Comparison of open versus closed reduction of intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a matched cohort in workmen. J Orthop Trauma 1992, 6: Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T: Intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results of closed treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993, 290: Parmar HV, Triffitt PD, Gregg PJ: Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum treated operatively or conservatively. A prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 1993, 75: Benirschke SK, Sangeorzan BJ: Extensive intraarticular fractures of the foot. Surgical management of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993, 292: Laughlin RT, Carson JG, Calhoun JH: Displaced intra-articular calcaneus fractures treated with the Galveston plate. Foot Ankle Int 1996, 17: Thordarson DB, Krieger LE: Operative vs. nonoperative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus: a prospective randomized trial. Foot Ankle Int 1996, 17: Thermann H, Krettek C, Hüfner T, Schratt HE, Albrecht K, Tscherne H: Management of calcaneal fractures in adults. Conservative versus operative treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1998, 353:
8 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 Page 8 of Mittlmeier T, Machler G, Lob G, Mutschler W, Bauer G, Vogl T: Compartment syndrome of the foot after intraarticular calcaneal fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1991, 269: Speck M, Klaue K: Internal fixation of comminuted calcaneal fractures: clinical and radiological results. Foot Ankle Surg 1997, 3: Bajammal S, Tornetta P 3rd, Sanders D, Bhandari M: Displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2005, 19: Buckley R, Tough S, McCormack R, Pate G, Leighton R, Petrie D, Galpin R: Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2002, 84-A: Randle JA, Kreder HJ, Stephen D, Lliams J, Jaglal S, Hu R: Should calcaneal fractures be treated surgically? A meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2000, 377: Fernandez DL, Koella C: Combined percutaneous and minimal internal fixation for displaced articular fractures of the calcaneus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993, 290: Tornetta P 3rd: Percutaneous treatment of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2000, 375: Carr JB: Surgical treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a review of small incision approaches. J Orthop Trauma 2005, 19: Lawrence SJ, Loutzenhiser LE: Technical tip: percutaneous fixation of sustentacular fractures of the calcaneus. Foot Ankle Int 2007, 28: Sanders R: Displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000, 82: Wang Q, Chen W, Su Y, Pan J, Zhang Q, Peng A, Wu X, Wang P, Zhang Y: Minimally invasive treatment of calcaneal fracture by percutaneous leverage, anatomical plate, and compression bolts the clinical evaluation of cohort of 156 patients. J Trauma 2010, 69(6): Wu Z, Su Y, Chen W, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Li M, Wang H, Zhang Y: Functional outcome of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a comparison between open reduction/internal fixation and a minimally invasive approach featured an anatomical plate and compression bolts. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012, 73(3): Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M: Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 1994, 15: Myerson M, Quill GE Jr: Late complications of fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1993, 75: Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, Walling A: Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993, 290: Hetsroni I, Nyska M, Ben-Sira D, Arnson Y, Buksbaum C, Aliev E, Mann G, Massarwe S, Rozenfeld G, Ayalon M: Analysis of foot and ankle kinematics after operative reduction of high-grade intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Trauma 2011, 70: Hutchinson F 3rd, Huebner MK: Treatment of os calcis fractures by open reduction and internal fixation. Foot Ankle Int 1994, 15: Chen W, Li X, Su Y, Zhang Q, Smith WR, Zhang X, Zhang Y: Peroneal tenography to evaluate lateral hindfoot pain after calcaneal fracture. Foot Ankle Int 2011, 32: Dhillon MS, Bali K, Prabhakar S: Controversies in calcaneus fracture management: a systematic review of the literature. Musculoskelet Surg 2011, 95(3): Rammelt S, Zwipp H: Calcaneus fractures: facts, controversies and recent developments. Injury 2004, 35(5): Wang H, Yang Z, Wu Z, Chen W, Zhang Q, Li M, Li Z, Zhang Y: A biomechanical comparison of conventional versus an anatomic plate and compression bolts for fixation of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 2012, 32(4): Chan SC, Alexander IJ: Subtalar arthrodesis with interposition tricortical iliac crest graft for late pain and deformity after calcaneus fracture. Foot Ankle Int 1997, 18: Schepers T, Patka P: Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures by ligamentotaxis: current concepts review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009, 129: Bruce J, Sutherland A: Surgical versus conservative interventions for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013, 1:CD O Farrell DA, O Byrne JM, McCabe JP, Stephens MM: Fractures of the os calcis: improved results with internal fixation. Injury 1993, 24: McBride DJ, Rammamurthy C, Laing P: The hindfoot: calcaneal and talar fractures and dislocations Part I: fractures of the calcaneum. Curr Orthop 2005, 19: Zwipp H, Rammelt S, Barthel S: Calcaneal fractures open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). Injury 2004, 35: doi: / Cite this article as: Su et al.: Bony destructive injuries of the calcaneus: long-term results of a minimally invasive procedure followed by early functional exercise: a retrospective study. BMC Surgery :19. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available evidence
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Tao Zhang, Xingwang Wu, Zhanpo Wu and Yingze Zhang *
 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING. Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion
 AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile?
 28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular. calcaneal fractures
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks
 Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures. Kali Luker, PGY-1
 Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments -
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture
 Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):9261-9269 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017905 Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):9261-9269 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017905 Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures
Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials
 British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture Dislocation Injuries
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Functional outcomes of different modalities of fixation in intra-articular calcaneus fractures
 2018; 2(4): 199-204 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 199-204 Received: 25-08-2018 Accepted: 27-09-2018 Rajesh V Chawda Associate Professor,
2018; 2(4): 199-204 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 199-204 Received: 25-08-2018 Accepted: 27-09-2018 Rajesh V Chawda Associate Professor,
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure
 Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome
 Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision
 Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures
 Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum
 Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum DEMOGRAPHICS AND TREATMENT A. P. Molloy, M. S. Myerson, P. Yoon From Institute for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, USA
Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum DEMOGRAPHICS AND TREATMENT A. P. Molloy, M. S. Myerson, P. Yoon From Institute for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, USA
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture: an anatomical specimen study
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a retrospective case analysis
 Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Introduction. Introduction 10/2/2009. Bryan Lapinski, MD
 Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 218-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures Mário Baptista, Rui Pinto, João Torres From Faculdade de Medicina
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 218-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures Mário Baptista, Rui Pinto, João Torres From Faculdade de Medicina
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure
 Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted Calcaneum Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Accepted: 3 April 2009
 Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
 PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures
 FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
The optimal management of displaced
 Review Article Advances in Surgical Management of Intra-articular Calcaneus Fractures Abstract Andrew R. Hsu, MD Robert B. Anderson, MD Bruce E. Cohen, MD JAAOS Plus Webinar Join Dr. Cohen for the interactive
Review Article Advances in Surgical Management of Intra-articular Calcaneus Fractures Abstract Andrew R. Hsu, MD Robert B. Anderson, MD Bruce E. Cohen, MD JAAOS Plus Webinar Join Dr. Cohen for the interactive
Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum
 JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
Prospective study of fracture calcaneus with Allan s procedure- bone grafting without implants
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Functional outcome of intra-articular tongue type of calcaneus fractures treated with percutaneous technique
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Dalal BY et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):371-376 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164171
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Dalal BY et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):371-376 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164171
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
Case. 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms. Your diagnosis?
 Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Surgical Technique. Calcaneal Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Calcaneal Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Calcaneal Locking Plate Surgical TechniqueCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Calcaneal Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Calcaneal Locking Plate Surgical TechniqueCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study
 CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Diabetics. Referred for management of complex pilon fracture? 5/10/2017. Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?)
 Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients
 Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
CALCANEAL FRACTURE. Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET. Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day:
 CALCANEAL FRACTURE Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day: It was the nightingale, and not the lark, That pierced the fearful hollow of
CALCANEAL FRACTURE Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day: It was the nightingale, and not the lark, That pierced the fearful hollow of
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Calcaneal Fractures in Children
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 18:469-474 1998 Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphi a Calcaneal Fractures in Children Suguru Inokuchi, M.D., Norio Usami, M.D., Eiichi Hiraishi, M.D., and Takeshi
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 18:469-474 1998 Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphi a Calcaneal Fractures in Children Suguru Inokuchi, M.D., Norio Usami, M.D., Eiichi Hiraishi, M.D., and Takeshi
Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion
 Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion W I L L I A M P. H U N T I N G T O N, M. D. W. H O D G E S D A V I S, M. D. R O B E R T B. A N D E R S O N,
Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion W I L L I A M P. H U N T I N G T O N, M. D. W. H O D G E S D A V I S, M. D. R O B E R T B. A N D E R S O N,
INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement
 016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
A new radiographic view of the hindfoot
 Ikoma et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2013, 6:48 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access A new radiographic view of the hindfoot Kazuya Ikoma 1*, Masahiko Noguchi 2, Koji Nagasawa
Ikoma et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2013, 6:48 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access A new radiographic view of the hindfoot Kazuya Ikoma 1*, Masahiko Noguchi 2, Koji Nagasawa
The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology
 The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology Treatment of Hindfoot Non-Union with DynaNail TTC Fusion System A CASE REPORT Dr. L. Daniel Latt, MD, PhD Background The DynaNail TTC Fusion System is intended
The Latest Breakthrough in TTC Fusion Technology Treatment of Hindfoot Non-Union with DynaNail TTC Fusion System A CASE REPORT Dr. L. Daniel Latt, MD, PhD Background The DynaNail TTC Fusion System is intended
The Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System
 Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
The subtalar distraction bone block arthrodesis following the late complications of. T. Schepers, MD PhD
 The subtalar distraction bone block arthrodesis following the late complications of calcaneal fractures: a systematic review T. Schepers, MD PhD Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands
The subtalar distraction bone block arthrodesis following the late complications of calcaneal fractures: a systematic review T. Schepers, MD PhD Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands
Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary?
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:299 305 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0246-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary? A. K. Singh K. Vinay
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:299 305 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0246-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary? A. K. Singh K. Vinay
Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:87 95 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0082-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach Mohamed F.
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:87 95 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0082-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach Mohamed F.
Pilon fractures. Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota
 Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
Minimally invasive, no hardware subtalar arthrodesis with autogenous posterior iliac bone graft
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:39 45 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0081-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimally invasive, no hardware subtalar arthrodesis with autogenous posterior iliac bone graft Mohamed A. M. Eid Maged
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:39 45 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0081-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimally invasive, no hardware subtalar arthrodesis with autogenous posterior iliac bone graft Mohamed A. M. Eid Maged
Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries
 Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries by Alaa Mansour DPM 1*, Lawrence Fallat DPM, FACFAS 2 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal 10 (1): 5 Severe traumatic injuries
Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries by Alaa Mansour DPM 1*, Lawrence Fallat DPM, FACFAS 2 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal 10 (1): 5 Severe traumatic injuries
Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Surgical Technique Guide
 Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate
 wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 04 Page April 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
The pilon tibiale fracture
 The pilon tibiale fracture Thomas Beck Spitalzentrum Oberwallis OTC Trauma course september 2017 xxx I have no financial relationships with commercial entities that produce healthcare related products.
The pilon tibiale fracture Thomas Beck Spitalzentrum Oberwallis OTC Trauma course september 2017 xxx I have no financial relationships with commercial entities that produce healthcare related products.
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY
 FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture
 214 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd BRIEF REPORT Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture Yun-tao Wang, MD, PhD, Xiao-tao Wu,
214 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd BRIEF REPORT Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture Yun-tao Wang, MD, PhD, Xiao-tao Wu,
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report
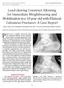 Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
 Xu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0655-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
Xu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0655-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
Open surgery vs minimal invasive methods for calcaneus fractures. Eur J Transl Myol 28 (2): , 2018
 Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Case Report Lateral Subtalar Dislocation with Tarsometatarsal Dislocation: A Case Report of a Rare Injury
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 8090721, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8090721 Case Report Lateral Subtalar Dislocation with Tarsometatarsal Dislocation: A Case Report
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 8090721, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8090721 Case Report Lateral Subtalar Dislocation with Tarsometatarsal Dislocation: A Case Report
