DIFFERENTITATING BACK AND HIP PAIN
|
|
|
- Gabriel Arnold
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DIFFERENTITATING BACK AND HIP PAIN MANAGEING LATERAL HIP PAIN DR ANGIE FEARON PHD, M(PTHY), B(APP)SC(PHTY) Effective treatment of lateral hip pain relies on the correct diagnosis; understanding the aetiology and pathology; recognising, understanding and addressing the modifiable risk factors; identifying and evaluating the contribution of biomechanical deficiencies and the contribution of pain; and then prescribing, modifying and progressing the most appropriate
2 DIFFERENTIATING BACK AND HIP PAIN & MANAGING LATERAL HIP PAIN TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents... 2 Case study On examination:...4 What would hip OA look like?...5 Differentiation back and hip pain... 6 Visa G Development of the VISA G (13) Completing the VISA G VISA G Questionnaire UNDERSTANDING LATERAL HIP PAIN management of Lateral hip pain Principles: Address the risk factors Address the pain Address the muscle imbalances Exercise prescription 101 (29) Exercise therapy (mechanotherapy) ISOMetrics (30, 31) Exercise therapy (mechanotherapy) Muscle hypertrophy Exercise therapy (mechanotherapy) Effective treatment relies on What doesn t help Not improving? References... 25
3 Case study CASE STUDY Wendy is a 59 year old woman who works full time in job with significant responsibilities - she works long hours. She has a large family, and 12 grandchildren. She comes to see you because she has lateral hip pain. Prior to her attendance her GP arranged for her to have an MRI of her right and left hips. The report states that there is bilateral tendinopathy of the Gluteus medius and gluteus minimus tendons, with associated tears in both tendons bilaterally. Her GP has sent her in for Physio. If this fails, the GP wants her to have surgery. Phx: Intermittent pain over the R > L lateral hip over five + years. Wendy reports no obvious past or present trauma that has contributed to the current presentation. She had one cortico-steroid injection 18 months ago. This resulted in good pain relief for six months. She did not undertake any rehabilitation following the injection. The pain returned 12 months ago and she doesn t want to have another injection. She has had some physio already which hurt. Chx: No significant medical co-morbidities (diabetes, cancer, hypertension), BMI ~ 27 kg/m 2 Musculoskeletal co-morbidities: Wendy reports OA in the mid foot and great toe (R > L); patellofemoral pain (R > L); hand OA; low back pain (R), and SIJ pain (R). Medications: Intermittent NSAID, paracetamol. Nil else reported. 24/24 behaviour: Night: Difficulty sleeping at night - wakes 3 to 4 times. Is able to go back to sleep but is unable to lie on R side for any length of time. This can be a problem in L side lying also.
4 CASE STUDY AM: hip is OK, feet very sore. Day: Hip has near constant ache; feet increasingly sore as day progresses, knees - activity dependent. Wendy finds it difficult to articulate what makes the hip pain worse. She says they varies on a day to day basis for no reason. Aggs: Hips: walking, lying on side, stairs (ascend and descend) Knees: stairs (ascend and descend) Feet: pain through midfoot (tarso-metatarsal joints) with weight bearing Back: lying, sit to stand Ease: Hips: near constant ache, Pt reports nothing eases; Knees: not climbing stairs; Feet: Not weight bearing; Back: sitting, slight movement (not extremes) VISA-G score: 30/100 ON EXAMINATION: Gait: Positive Trendelenburg with R stance (trunk lean to R), prolonged stance on R. Lack of push off bilaterally. Reduced step length bilaterally. (Pain in hips R>L and feet) Sit to stand: Uses hands to push up with, when asked to refrain weight bears on L > R, MR/Add of hips bilaterally (reproduces lateral hip and knee pain) Lunge: MR/Add R>L, pronated feet (pain in hip, knee and feet R>L) Step up: MR/Add, (pain in hip, knee and feet R>L) SLS: Pain reproduced on R after 10 seconds, in hip adduction which she can correct with advice. L pain free for 20 seconds. R and L very poor control/balance Lx: Flexion: NAD; Extension: ½ pain on L4 L5 SIJ; Side Flexion R - 5 cm AK pain reproduced in back; L 5cm above knee, P 0, stretch on right; Rotation R ¾ slight L4 L5; L 4/4, P 0 SIJ: Stork negative, AP compression negative, ASLR negative Hip: ROM: MR, LR, Flex, Ext, Add, Abd, Faddir. All = NAD 4
5 CASE STUDY Faber: Reproduces lateral hip pain, R and L Resisted de-rotation from Flex/add: Reproduces lateral hip pain, R, not L Knee: ROM NAD; ligaments NAD; meniscus NAD; patellofemoral joint: medial glide R =1/3 VMO = concave, reduced in size and does not activate with static quads. Feet: Bony hyperplasia about mid foot = likely tarso-metatarsal OA; reduced active arch unable to control in w/b. Wt bearing pain eased with supportive taping Palpation: Lx ms sp through Lx R>>L, L5/S1 painful on R SIJ - R slightly painful, sacrotuberous ligament painful Hip Gluteal ms (mid buttock) painful and muscle spasm GT pain anterior>posterior, R>L WHAT WOULD HIP OA LOOK LIKE? - Hip joint can refer to buttock, GT, groin, anterior thigh (and foot) (2, 3) - Restricted ROM in hip joint (4) - Groin or anterior pain with MR (4) - Difficulty with shoes and socks (5) - Groin/anterior pain with Faber (5) 5
6 Differentiation back and hip pain DIFFERENTIATION BACK AND HIP PAIN
7 DIFFERENTIATION BACK AND HIP PAIN Adapted from Brukner and Khan, 2015, Sports Anatomy (1) 7
8 DIFFERENTIATION BACK AND HIP PAIN Adapted from Reiman, 2014 (6), with (7-11) 8
9 DIFFERENTIATION BACK AND HIP PAIN Confirmed on MRI Compared to Asymptomatic people(12) Clinically compared to people with OA(5) 9
10 VISA G VISA G DEVELOPMENT OF THE VISA G (13) The VISA-G was developed to evaluate the severity of impact of gluteal tendinopathy. The VISA G was constructed and tested with the intention that it should be used as a whole, although segments of it may provide clinicians with insight in to how their clients are progressing. The minimal significant difference is currently being calculated. We expect that changes would be seen over weeks, rather than days. The clinical diagnosis that this score is valid for is (14) : 1. Pain over the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter (GT) 2. Pain on palpation of the GT 3. Reproduction of GT pain with the FABER test 4. No difficulty with putting on shoes or socks The score is valid for those with concurrent low back pain. It has not been tested on those with concurrent hip osteoarthritis. If the FABER test reproduced groin pain the person probably has an intra-articular problem (14). COMPLETING THE VISA G When asking a client to complete this on the first occasion it is best to show them each question. In particular, clients may stumble on question 8. Question 8 has three sections, A, B and C. Clients should only respond to one of A, B or C. Which section they respond to depends on their pain level with weight bearing activities see the definition attached to each section. Question 8 is particularly important as it provides weighting for levels of activity. For example, someone with no pain with walking, shopping or weight bearing activities (Section C, score=6) but who only moves about the house, scores lower than someone who has pain with these activities but that pain doesn t prevent them from participating in 20 to 29 mins of these activities each day (Section B, score=15). Once all the questions are answered, calculate the score out of 100. If someone fails to answer a questions (try to avoid this), mark the score out of the total available scores this has not been tested for robustness, but it is a clinically reasonable thing to do. If the person answers all three sections of question 8 use the worst case activity scenario (Section C, score=6). 10
11 VISA G Down load the VISA G and the instructions from ResearchGate Go to the Contributions Tab. 11
12 VISA G Questionnaire VISA G QUESTIONNAIRE
13 VISA G QUESTIONNAIRE 13
14 VISA G QUESTIONNAIRE 14
15 UNDERSTANDING LATERAL HIP PAIN UNDERSTANDING LATERAL HIP PAIN Increased compression of the gluteal tendons on the GT, via the ITB. (15) Grimaldi and Fearon 2015, (16, 17)
16 MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN PRINCIPLES: 1. Address the modifiable risk factors 2. Address the pain (by managing the load 24/7) 3. Address the muscle imbalances and weakness 4. Address the neuromucsular control 5. Address the co-morbidities Stop the compression Address the risk factors Control the load Improve the strength Improve N/M patterns Treat the co-morbidities 16
17 MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN ADDRESS THE RISK FACTORS (1, 18, 19) Reduce the adduction and MR Increase the quadriceps strength 17
18 MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN ADDRESS THE PAIN Stop the compression (STOP these)(20) Do these Grimaldi and Fearon (2015) Add a pillow Limited evidence Rolled up blanket in a pillow case 18
19 MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN Manage the 24/7 load bearing (17, 21-23) Isometrics (24) Tape (anecdotal evidence) Massage ECSW therapy (controversial) (25) CSI (last option in my opinion) (26, 27) ADDRESS THE MUSCLE IMBALANCES Motor control? True strength? Pain inhibition? Trunk vs hip vs thigh (quads) Might be all of these (28) 19
20 MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION 101 (29) Frequency of exercises for a) Strengthening (3 x week) b) pain relief (3-4 x day) (dose not optimised) c) Ms activation (> 3 x day) d) Stretching Ms (daily) e) Stretching joints (daily) EXERCISE THERAPY (MECHANOTHERAPY) 1 ISOMETRICS (30, 31) Low intensity Long holds (as the patient can cope) (32, 33) Lifelonglegging Accessed 25 June 2016 Consider doing this as an isometric hold. 20
21 MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN EXERCISE THERAPY (MECHANOTHERAPY) 2 MUSCLE HYPERTROPHY Low speed, high load Weight bearing Better feedback (manage the load) EXERCISE THERAPY (MECHANOTHERAPY) 3 G med activation (34) 1. Side lying (with MR) (med and min) (32, 33) 2. Single leg squat 3. Lateral band walking 4. Single leg dead lift 5. Transverse hop 6. Forward hop 7. Forward lunge c.f. static lunge (35, 36) 8. Clam (30 ) (NOTE least effective for activation) You can vary how the stabilising leg is pushing with abduction, or stabilised In neutral (with more knee flexion). 21
22 MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL HIP PAIN Any lower limb pain issue (e.g. OA knee, foot). Back pain (37) Diabetes and adiposity (38) Address the co-morbidities EFFECTIVE TREATMENT RELIES ON Correct diagnosis Understanding the aetiology and pathology Recognising, understanding and addressing the modifiable risk factors Identifying and evaluating the contribution of biomechanical deficiencies Identifying and evaluating the contribution of pain And then Prescribing, modifying, progressing the most appropriate interventions WHAT DOESN T HELP High load drill Exercise without recover (3 days) Working people in to pain Isolated eccentric exercises US and frictions 22
23 Not improving? NOT IMPROVING? 1. Re-assess clinically Ms/joints/strength balance 2. Re-visit with the person a. What activities they are doing / not doing? b. Are they doing the exercises? i. At all? ii. Correctly (technique)? iii. Enough? iv. Too much? v. Have they added some extra ones in? 3. Monitoring the total tendon loading 4. Re-consider the diagnosis 5. Re-consider the treatment options 6. Consider referral
24 Look after your self be active, many times during the day, and eat well. Acknowledgements: Jill Cook, Jennie Scarvell, Teresa Neeman, Mike Reiman, Alison Grimaldi and Paul Smith. University of Canberra and The Australian National University The Trauma and Orthopaedic Research Unit at the Canberra Hospital. 24
25 REFERENCES REFERENCES References 1. Brukner, Bahr, Cook, Crossley, McConnell, McCrory, et al. Clinical sports medicine. 4th. ed. Sydney.: McGraw-Hill.; Arnold DR, Keene JS, Blankenbaker DG, Desmet AA. Hip pain referral patterns in patients with labral tears: analysis based on intra-articular anesthetic injections, hip arthroscopy, and a new pain "circle" diagram. The Physician and sportsmedicine. 2011;39(1): Lesher JM, Dreyfuss P, Hager N, Kaplan M, Furman M. Hip joint pain referral patterns: A descriptive study. Pain Medicine. 2008;9(1): Altman RD. Criteria for classification of clinical osteoarthritis. Journal of Rheumatology Supplement. 1991;27: Fearon A, Scarvell J, Neeman T, Cook J, Cormick W, Smith P. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome: defining the clinical syndrome. Br J Sports Med. 2012;47(10): Reiman MP, Thorborg K. CLINICAL EXAMINATION AND PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT OF HIP JOINT RELATED PAIN IN ATHLETES. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy. 2014;9(6): Coleman RE. Clinical Features of Metastatic Bone Disease and Risk of Skeletal Morbidity. Clinical Cancer Research. 2006;12(20):6243s-9s. 8. Hancock MJ, Maher CG, Latimer J, Spindler MF, McAuley JH, Laslett M, et al. Systematic review of tests to identify the disc, SIJ or facet joint as the source of low back pain. European Spine Journal. 2007;16(10): Poultsides LA, Bedi A, Kelly BT. An algorithmic approach to mechanical hip pain. HSS journal : the musculoskeletal journal of Hospital for Special Surgery. 2012;8(3): Renstrom AF. Mechanism, diagnosis, and treatment of running injuries. Instructional Course Lectures. 1993;42: Vleeming A, Albert HB, Ostgaard HC, Sturesson B, Stuge B. European guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pelvic girdle pain. European spine journal : official publication of the European Spine Society, the European Spinal Deformity Society, and the European Section of the Cervical Spine Research Society. 2008;17(6): Lequesne M, Mathieu P, Vuillemin-Bodaghi V, Bard H, Djian P. Gluteal tendinopathy in refractory greater trochanter pain syndrome: diagnostic value of two clinical tests. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(2):
26 REFERENCES 13. Fearon AM, Ganderton C, Scarvell JM, Smith PN, Neeman T, Nash C, et al. Development and validation of a VISA tendinopathy questionnaire for greater trochanteric pain syndrome, the VISA-G. Man Ther. 2015;20(6): Fearon AM, Scarvell JM, Neeman T, Cook JL, Cormick W, Smith PN. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome: defining the clinical syndrome. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(10): Grimaldi A, Fearon A. Gluteal Tendinopathy: Integrating Pathomechanics and Clinical Features in Its Management. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2015;45(11): Birnbaum K, Prescher A, Niethard FU. Hip centralizing forces of the iliotibial tract within various femoral neck angles. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics Part B.19(2): Cook JL, Purdam C. Is compressive load a factor in the development of tendinopathy? Br J Sports Med. 2012;46(3): Meeuwisse WH, Tyreman H, Hagel B, Emery C. A dynamic model of etiology in sport injury: the recursive nature of risk and causation. Clin J Sport Med. 2007;17(3): Gaida JE, Ashe MC, Bass SL, Cook JL. Is adiposity an under-recognized risk factor for tendinopathy? A systematic review. Arthritis Care and Research. 2009;61(6): Almekinders LC, Weinhold PS, Maffulli N. Compression etiology in tendinopathy. Clinics in Sports Medicine. 2003;22(4): Andarawis-Puri N, Sereysky JB, Sun HB, Jepsen KJ, Flatow EL. Molecular response of the patellar tendon to fatigue loading explained in the context of the initial induced damage and number of fatigue loading cycles. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 2012;30(8). 22. Backman LJ, Andersson G, Wennstig G, Forsgren S, Danielson P. Endogenous substance P production in the Achilles tendon increases with loading in an in vivo model of tendinopathy - peptidergic elevation preceding tendinosis-like tissue changes. Journal of Musculoskeletal & Neuronal Interactions. 2011;11(2): Backman LJ, Fong G, Andersson G, Scott A, Danielson P. Substance P Is a Mechanoresponsive, Autocrine Regulator of Human Tenocyte Proliferation. PLoS One. 2011;6(11). 24. Rio E, Kidgell D, Purdam C, Gaida J, Moseley GL, Pearce AJ, et al. Isometric exercise induces analgesia and reduces inhibition in patellar tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(19): Rompe J, Segal N, Cacchio A, Furia J, Morral A, Maffulli N. Home Training, Local Corticosteroid Injection, or Radial Shock Wave Therapy for Greater Trochanter Pain Syndrome. American Journal of Sports Medicine. 2009;37(10):
27 REFERENCES 26. Haraldsson BT, Langberg H, Aagaard P, Zuurmond AM, van El B, Degroot J, et al. Corticosteroids reduce the tensile strength of isolated collagen fascicles. American Journal of Sports Medicine. 2006;34(12): Brinks A, van Rijn RM, Willemsen SP, Bohnen AM, Verhaar JAN, Koes BW, et al. Corticosteroid Injections for Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Primary Care. Annals of Family Medicine. 2011;9(3): Rio E, Kidgell D, Moseley GL, Gaida J, Docking S, Purdam C, et al. Tendon neuroplastic training: changing the way we think about tendon rehabilitation: a narrative review. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(4): Hoogenboom BJ, Voight ML, Prentice WE. Musculoskeletal Interventions: McGraw- Hill Education; Kosek E, Ekholm J. Modulation of pressure pain thresholds during and following isometric contraction. Pain. 1995;61(3): Kosek E, Lundberg L. Segmental and plurisegmental modulation of pressure pain thresholds during static muscle contractions in healthy individuals. Eur J Pain. 2003;7(3): Semciw AI, Green RA, Murley GS, Pizzari T. Gluteus minimus: an intramuscular EMG investigation of anterior and posterior segments during gait. Gait Posture. 2014;39(2): Semciw AI, Pizzari T, Murley GS, Green RA. Gluteus medius: an intramuscular EMG investigation of anterior, middle and posterior segments during gait. Journal of electromyography and kinesiology : official journal of the International Society of Electrophysiological Kinesiology. 2013;23(4): Distefano L, Blackburn J, Marshall S, Padua D. Gluteal muscle activation during common therapeutic exercises. Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy. 2009;39(7): Stastny P, Lehnert M, Zaatar AM, Svoboda Z, Xaverova Z. Does the Dumbbell- Carrying Position Change the Muscle Activity in Split Squats and Walking Lunges? J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(11): Stastny P, Lehnert M, Zaatar A, Svoboda Z, Xaverova Z, Pietraszewski P. The Gluteus Medius Vs. Thigh Muscles Strength Ratio and Their Relation to Electromyography Amplitude During a Farmer's Walk Exercise. Journal of human kinetics. 2015;45: Sayegh F, Potoupnis M, Kapetanos G. Greater trochanter bursitis pain syndrome in females with chronic low back pain and sciatica. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 2004;70(5):
28 REFERENCES 38. Gaida JE, Cook JL, Bass SL. Adiposity and tendinopathy. Disability and rehabilitation. 2008;30(20-22):
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS): Assessment & Management
 Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS): Assessment & Management Rachael Mary McMillan Physiotherapist, Alphington Sports Medicine Clinic & FFA Australian Women s National Football Teams PhD Candidate
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS): Assessment & Management Rachael Mary McMillan Physiotherapist, Alphington Sports Medicine Clinic & FFA Australian Women s National Football Teams PhD Candidate
Clinical diagnosis of hip dysfunction
 Clinical diagnosis of hip dysfunction Trish Wisbey-Roth Specialist Sport Physiotherapist (FACP), Olympic Physio, Masters of Sport Physiotherapy ( AIS/UC) Active Rehabilitation Consultant. Case Study: Jane,
Clinical diagnosis of hip dysfunction Trish Wisbey-Roth Specialist Sport Physiotherapist (FACP), Olympic Physio, Masters of Sport Physiotherapy ( AIS/UC) Active Rehabilitation Consultant. Case Study: Jane,
Hip Region. PHTY2020: Lecture
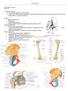 Region PHTY2020: Lecture 2.1 29.02.16 Functional Overview Transfer body weight form trunk to legs Allows leg to adopt numerous positions needed for standing, walking running, stairs, sitting and other
Region PHTY2020: Lecture 2.1 29.02.16 Functional Overview Transfer body weight form trunk to legs Allows leg to adopt numerous positions needed for standing, walking running, stairs, sitting and other
WHEN THE HIP IS NOT THE HIP
 WHEN THE HIP IS NOT THE HIP M Cusí MBBS, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar spine Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar
WHEN THE HIP IS NOT THE HIP M Cusí MBBS, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar spine Conditions that can be confused with hip pain 1. Referred pain lumbar
HIP_CASE 2_OA. Hip Forces. Function of the Hip. Property of VOMPTI, LLC. For Use of Participants Only. No Use or Reproduction Without Consent 1
 HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
GREATER TROCHANTERIC PAIN SYNDROME CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE
 GREATER TROCHANTERIC PAIN SYNDROME CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Disclaimer This guideline is intended as an aid for clinicians treating patients diagnosed with greater trochanteric pain syndrome, utilizing
GREATER TROCHANTERIC PAIN SYNDROME CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Disclaimer This guideline is intended as an aid for clinicians treating patients diagnosed with greater trochanteric pain syndrome, utilizing
Training the Joint Replacement Client
 KNEE PRE-OP SAMPLE EXERCISE PLAN Quadricep: Shuttle 1 leg and 2 legs (focus on 1 leg) Leg Press 1 and 2 legs (focus on 1 leg) Sit to Stand (if no pain or compensation) Supine Circle Foam knee extension
KNEE PRE-OP SAMPLE EXERCISE PLAN Quadricep: Shuttle 1 leg and 2 legs (focus on 1 leg) Leg Press 1 and 2 legs (focus on 1 leg) Sit to Stand (if no pain or compensation) Supine Circle Foam knee extension
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES
 APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS
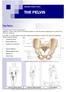 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
STAIRS. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care. I have no relevant disclosures. Top 5 (or 6) Pathologies. Big 3- Questions to Ask
 I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions
 Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R
 S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H L A B R A L R E P A I R P R O T O C O L This protocol provides appropriate guidelines
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H L A B R A L R E P A I R P R O T O C O L This protocol provides appropriate guidelines
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain
 Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
The evaluation and management of patients with
 Greater Trochanteric Hip Pain 1.5 ANCC Contact Hours Diane M. Kimpel Chadwick C. Garner Kevin M. Magone Jedediah H. May Matthew W. Lawless In the patient with lateral hip pain, there is a broad differential
Greater Trochanteric Hip Pain 1.5 ANCC Contact Hours Diane M. Kimpel Chadwick C. Garner Kevin M. Magone Jedediah H. May Matthew W. Lawless In the patient with lateral hip pain, there is a broad differential
Standard of Care: Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFS)
 Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (719.46) Patellofemoral Pain syndrome A general category of anterior knee pain from patella malalignment.
Department of Rehabilitation Services Physical Therapy Case Type / Diagnosis: Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (719.46) Patellofemoral Pain syndrome A general category of anterior knee pain from patella malalignment.
Pain, Practice and Performance: The Knee. Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred MDT, APA Prinicipal Physiotherapist Director
 Pain, Practice and Performance: The Knee Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred MDT, APA Prinicipal Physiotherapist Director 17.04.2009 Functional Anatomy Knee & Patellofemoral Joint Mechanism Ligaments Meniscus, Fat
Pain, Practice and Performance: The Knee Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred MDT, APA Prinicipal Physiotherapist Director 17.04.2009 Functional Anatomy Knee & Patellofemoral Joint Mechanism Ligaments Meniscus, Fat
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain. History
 A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
A Syndrome (Pattern) Approach to Low Back Pain Hamilton Hall MD FRCSC Professor, Department of Surgery, University of Toronto Medical Director, CBI Health Group Executive Director, Canadian Spine Society
Young Adult Hip problems. Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth)
 Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
Today s session. Common Problems in Rehab. Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist. physiofitness.com.au facebook.
 Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist physiofitness.com.au facebook.com/physiofitness Today s session Essential list for the lower body Rehab starting point Focussing on activation,
Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APA Principal Physiotherapist physiofitness.com.au facebook.com/physiofitness Today s session Essential list for the lower body Rehab starting point Focussing on activation,
GREATER TROCHATERIC PAIN SYNDROME (GTPS) - Advice & Rehabilitation Leaflet
 Dr Patrick Wheeler Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Leicester General Hospital Gwendolen Road, Leicester, LE5 4PW Telephone: 0116 258 4365 Patient information and rehabilitation leaflet - Greater
Dr Patrick Wheeler Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Leicester General Hospital Gwendolen Road, Leicester, LE5 4PW Telephone: 0116 258 4365 Patient information and rehabilitation leaflet - Greater
BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD
 Physical Therapy Protocol Partial or full thickness gluteus medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is
Physical Therapy Protocol Partial or full thickness gluteus medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is
2/28/2017. Learning Objectives. Hip Joint: Anatomy and Kinesiology
 Regional Pain Syndromes: Hip and Knee Srinivas Nalamachu, MD Clinical Assistant Professor, KU School of Medicine President and Medical Director, Pain Management Institute Overland Park, KS Learning Objectives
Regional Pain Syndromes: Hip and Knee Srinivas Nalamachu, MD Clinical Assistant Professor, KU School of Medicine President and Medical Director, Pain Management Institute Overland Park, KS Learning Objectives
Lunge. Lunging. Single Leg Squat. Single Leg Squat 5/21/2011. Rehabilitation of the Injured Runner MN APTA
 Injury: the Big 6 Evidence-Based Exercise for the Injured Runner Jason Lunden, PT Board Certified Specialist in Sports Physical Therapy Excel Physical Therapy Bozeman, MT Rates 20-90% Knee injuries: 42%
Injury: the Big 6 Evidence-Based Exercise for the Injured Runner Jason Lunden, PT Board Certified Specialist in Sports Physical Therapy Excel Physical Therapy Bozeman, MT Rates 20-90% Knee injuries: 42%
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults
 What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
River City Running Symposium Jenelle Deatherage, PT, OCS Rock Valley Physical Therapy
 River City Running Symposium 2015 Jenelle Deatherage, PT, OCS Rock Valley Physical Therapy A Brief History of my Running Career Then and... Now Common Running Injuries- Prevention and Treatment Jenelle
River City Running Symposium 2015 Jenelle Deatherage, PT, OCS Rock Valley Physical Therapy A Brief History of my Running Career Then and... Now Common Running Injuries- Prevention and Treatment Jenelle
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol Dr. David Hergan Labral Repair with or without FAI Component
 Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol Dr. David Hergan Labral Repair with or without FAI Component Initial Joint Protection Guidelines- (P.O. Day 1-4 wks): Joint Protection Patient education
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol Dr. David Hergan Labral Repair with or without FAI Component Initial Joint Protection Guidelines- (P.O. Day 1-4 wks): Joint Protection Patient education
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
LOW BACK PAIN. Contents What causes Low Back Pain?... 3
 YOUR GUIDE TO LOW BACK PAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What causes Low Back Pain?....... 3 What treatment can I receive?..... 4 What about exercise?...............
YOUR GUIDE TO LOW BACK PAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What causes Low Back Pain?....... 3 What treatment can I receive?..... 4 What about exercise?...............
Solutions for. Patello-femoral knee pain. Today s session. physiofitness.com.au facebook.
 Solutions for Patello-femoral knee pain presented by Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APAM Principal Physiotherapist Physio Fitness Australia physiofitness.com.au facebook.com/physiofitness Today s session
Solutions for Patello-femoral knee pain presented by Tim Keeley B.Phty, Cred.MDT, APAM Principal Physiotherapist Physio Fitness Australia physiofitness.com.au facebook.com/physiofitness Today s session
Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dora Street, Hurstville
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville WHEN SCIATICA IS NOT SCIATICA, WHAT DO YOU LOOK FOR? What do you look for, where? Low Back pain
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville WHEN SCIATICA IS NOT SCIATICA, WHAT DO YOU LOOK FOR? What do you look for, where? Low Back pain
Obesity is associated with reduced joint range of motion (Park, 2010), which has been partially
 INTRODUCTION Obesity is associated with reduced joint range of motion (Park, 2010), which has been partially attributed to adipose tissues around joints limiting inter-segmental rotations (Gilleard, 2007).
INTRODUCTION Obesity is associated with reduced joint range of motion (Park, 2010), which has been partially attributed to adipose tissues around joints limiting inter-segmental rotations (Gilleard, 2007).
KNEE REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 Jessica Barrow BSc Physiotherapy, SPT1 www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za Cell: 083 256 0434 Room GF03 Waterfall Hospital Cnr. Magwa Crescent and Mac Mac Avenue Tel: 011 304-7829 Fax: 011 304-7941 KNEE REHABILITATION
Jessica Barrow BSc Physiotherapy, SPT1 www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za Cell: 083 256 0434 Room GF03 Waterfall Hospital Cnr. Magwa Crescent and Mac Mac Avenue Tel: 011 304-7829 Fax: 011 304-7941 KNEE REHABILITATION
DR. (PROF.) ANIL ARORA MS
 Hip Examination DR. (PROF.) ANIL ARORA MS (Ortho) DNB (Ortho) Dip SIROT (USA) FAPOA (Korea), FIGOF (Germany), FJOA (Japan) Commonwealth Fellow Joint Replacement (Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, London,
Hip Examination DR. (PROF.) ANIL ARORA MS (Ortho) DNB (Ortho) Dip SIROT (USA) FAPOA (Korea), FIGOF (Germany), FJOA (Japan) Commonwealth Fellow Joint Replacement (Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, London,
Hip Cases from Clinic: Refining your history and physical
 Hip Cases from Clinic: Refining your history and physical Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 11/20/2017 Case #1 Healthy 21 M College
Hip Cases from Clinic: Refining your history and physical Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 11/20/2017 Case #1 Healthy 21 M College
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome
 2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
Gluteal Tendinopathy: pathomechanics and implications for assessment and management
 Gluteal Tendinopathy: pathomechanics and implications for assessment and management Authors: Alison Grimaldi PhD 1,2 Angela Fearon, PhD 3,4,5 1 2 3 4 1. Physiotec Physiotherapy 23 Weller Road, Tarragindi,
Gluteal Tendinopathy: pathomechanics and implications for assessment and management Authors: Alison Grimaldi PhD 1,2 Angela Fearon, PhD 3,4,5 1 2 3 4 1. Physiotec Physiotherapy 23 Weller Road, Tarragindi,
Assessment Form Post Polio Syndrome and Late Effects of Polio
 FULL NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: PHONE NUMBER: CURRENT HOME ADDRESS: EMAIL ADDRESS: THERAPIST: REFERRAL SOURCE: CURRENT GP: NEXT OF KIN: ACC/NHI NUMBER: PATIENT GOALS OF TODAY S ASSESSMENT: MAIN PROBLEMS PATIENT
FULL NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: PHONE NUMBER: CURRENT HOME ADDRESS: EMAIL ADDRESS: THERAPIST: REFERRAL SOURCE: CURRENT GP: NEXT OF KIN: ACC/NHI NUMBER: PATIENT GOALS OF TODAY S ASSESSMENT: MAIN PROBLEMS PATIENT
A patient guide to Hip Impingement Non-Surgical Management. Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy
 A patient guide to Hip Impingement Non-Surgical Management Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy Contents Page: 1 Cover 2 Contents 3 Hip impingement information 4 Conservative rehabilitation
A patient guide to Hip Impingement Non-Surgical Management Mr Sanjeev Patil Miss Louise Duncan Mr Frank Gilroy Contents Page: 1 Cover 2 Contents 3 Hip impingement information 4 Conservative rehabilitation
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form
 Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form Femoracetabular Impingement (FAI) Femoral Osteochondroplasty Acetabular Rim Trimming Acetabular Labrum Repair Location: o clock to o clock Debridement Articular
Post Operative Hip Arthroscopy Procedure Form Femoracetabular Impingement (FAI) Femoral Osteochondroplasty Acetabular Rim Trimming Acetabular Labrum Repair Location: o clock to o clock Debridement Articular
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R
 S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H L A B R A L R E P A I R P R O T O C O L This protocol provides appropriate guidelines
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H L A B R A L R E P A I R P R O T O C O L This protocol provides appropriate guidelines
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT
 SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
JOHN M. REDMOND, M.D.
 Physical Therapy Protocol Gluteus Medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is not intended to serve as
Physical Therapy Protocol Gluteus Medius repair with or without labral repair The intent of this protocol is to provide guidelines for your patient s therapy progression. It is not intended to serve as
Hip Arthroscopy. Labral Repair/Debridement with Femoroplasty
 Precautions for weeks 1 4 post-op: Hip Arthroscopy Labral Repair/Debridement with Femoroplasty Patient Education o For 1 week, Assist the involved LE during all transfers o For 2 weeks, Do not sit with
Precautions for weeks 1 4 post-op: Hip Arthroscopy Labral Repair/Debridement with Femoroplasty Patient Education o For 1 week, Assist the involved LE during all transfers o For 2 weeks, Do not sit with
Disclosures. Objectives. Overview. Patellofemoral Syndrome. Etiology. Management of Patellofemoral Pain
 Management of Patellofemoral Pain Implications of Top Down Mechanics Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this presentation David Nolan, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, SCS,
Management of Patellofemoral Pain Implications of Top Down Mechanics Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this presentation David Nolan, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, SCS,
Postoperative Days 1-7
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
ACL RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Postoperative Days 1-7 *IT IS EXTREMELY IMPORTANT THAT YOU WORK ON EXTENSION IMMEDIATELY Goals: * Control pain and swelling * Care for the knee and dressing *
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
7/20/14. Patella Instability. Alignment. PF contact areas. Tissue Restraints. Pain. Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint
 Patella Instability Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint Evan G. Meeks, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgery Sports Medicine The University of Texas - Houston Pivoting action Large effusion
Patella Instability Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint Evan G. Meeks, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgery Sports Medicine The University of Texas - Houston Pivoting action Large effusion
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
Phase 1- Immediate Rehabilitation (1-3 weeks): Goals Precautions:
 Phase 1- Immediate Rehabilitation (1-3 weeks): Goals: Protection of the repaired tissue Prevent muscular inhibition and gait abnormalities Diminish pain and inflammation Precautions: 20 lb. flat-foot weight-bearing
Phase 1- Immediate Rehabilitation (1-3 weeks): Goals: Protection of the repaired tissue Prevent muscular inhibition and gait abnormalities Diminish pain and inflammation Precautions: 20 lb. flat-foot weight-bearing
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Anterior knee pain.
 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee
 Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome Ø The ITB is fascia, a connective tissue that gives structure to the body. Its function is to protect the knee from sideways movement
Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome Ø The ITB is fascia, a connective tissue that gives structure to the body. Its function is to protect the knee from sideways movement
Protocol G Arthroscopic Surgery: Therapist Information
 Protocol G Arthroscopic Surgery: Therapist Information Please read entire protocol prior to initiating therapy Please do not hesitate to contact Dr. Wolff with questions or concerns. Rest is a vital component
Protocol G Arthroscopic Surgery: Therapist Information Please read entire protocol prior to initiating therapy Please do not hesitate to contact Dr. Wolff with questions or concerns. Rest is a vital component
The Painful Hip. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Hip Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Hip A 64 yo F presents to clinic complaining of a sore hip What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential diagnosis?
The Painful Hip Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Hip A 64 yo F presents to clinic complaining of a sore hip What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential diagnosis?
Dr Hamish Osborne. Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin
 Dr Hamish Osborne Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin New Approaches to Handling Tendinopathies By Hamish Osborne Definition Tendinopathy Absence of tightly packed collagen bundles Large amount
Dr Hamish Osborne Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin New Approaches to Handling Tendinopathies By Hamish Osborne Definition Tendinopathy Absence of tightly packed collagen bundles Large amount
Lower Body. Exercise intensity moderate to high.
 Lower Body Lower Body Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goals of strengthening the lower body. Along with increasing strength of the leg muscles this workout will
Lower Body Lower Body Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women with the goals of strengthening the lower body. Along with increasing strength of the leg muscles this workout will
5/14/2013. Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury:
 Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
Exercise Therapy for Patients with Knee OA Knee Exercise Protocol Knee Home Exercise Programme
 Chapter FOUR Exercise Therapy for Patients with Knee OA Knee Exercise Protocol Knee Home Exercise Programme Chris Higgs Cathy Chapple Daniel Pinto J. Haxby Abbott 99 n n 100 General Guidelines Knee Exercise
Chapter FOUR Exercise Therapy for Patients with Knee OA Knee Exercise Protocol Knee Home Exercise Programme Chris Higgs Cathy Chapple Daniel Pinto J. Haxby Abbott 99 n n 100 General Guidelines Knee Exercise
EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX
 EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX Finding Comfortable Positions Sex and Back Pain When your back hurts, simple actions such as getting undressed or giving a hug may cause pain. If just the thought of having
EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX Finding Comfortable Positions Sex and Back Pain When your back hurts, simple actions such as getting undressed or giving a hug may cause pain. If just the thought of having
ACL REHABILITATION PROGRAMME
 Jessica Barrow BSc Physiotherapy (WITS) 083 256 0434 Room GF03 Waterfall Hospital Cnr. Magwa Crescent and Mac Mac Avenue Tel: 011 304-7829 Fax: 011 304-7941 ACL REHABILITATION PROGRAMME Rehabilitation
Jessica Barrow BSc Physiotherapy (WITS) 083 256 0434 Room GF03 Waterfall Hospital Cnr. Magwa Crescent and Mac Mac Avenue Tel: 011 304-7829 Fax: 011 304-7941 ACL REHABILITATION PROGRAMME Rehabilitation
Running Athlete: Part C. Case Analysis Materials
 Running Athlete: Part C Case Analysis Materials Case 1 Subjective Examination (performed offcamera) Runs very sporadically, but generally 2-3 x per week around 2-4 miles Play recreational soccer Denies
Running Athlete: Part C Case Analysis Materials Case 1 Subjective Examination (performed offcamera) Runs very sporadically, but generally 2-3 x per week around 2-4 miles Play recreational soccer Denies
Common Lower Limb Pathology Related to Running. Catherine Irwin, PT, OCS January 10, 2012
 Common Lower Limb Pathology Related to Running Catherine Irwin, PT, OCS January 10, 2012 Objectives Pathology Treatment Shoe guidelines Pathology Shin Splints Posterior Tibialis Tendonitis Achilles Tendonopathy/Sever
Common Lower Limb Pathology Related to Running Catherine Irwin, PT, OCS January 10, 2012 Objectives Pathology Treatment Shoe guidelines Pathology Shin Splints Posterior Tibialis Tendonitis Achilles Tendonopathy/Sever
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R
 S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H This protocol provides appropriate guidelines for the rehabilitation of patients following
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R H I P A R T H R O S C O P Y W I T H This protocol provides appropriate guidelines for the rehabilitation of patients following
right Initial examination established that you have 'flat feet'. Additional information left Left foot is more supinated possibly due to LLD
 Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
REHABILITATION FOLLOWING ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION (using Hamstring Graft)
 REHABILITATION FOLLOWING ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION (using Hamstring Graft) PHASE 1: (0-3 WEEKS) Goal: Protect graft, manage pain, decrease swelling and improve range of movement. To optimise
REHABILITATION FOLLOWING ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION (using Hamstring Graft) PHASE 1: (0-3 WEEKS) Goal: Protect graft, manage pain, decrease swelling and improve range of movement. To optimise
Diagnosis: Gluteus Medius Tear, Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer
 Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Gluteus Medius Tear, Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Gluteus Medius Repair, CAM / Pincer Decompression, Labral refixation / Capsular Shift
Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Gluteus Medius Tear, Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Gluteus Medius Repair, CAM / Pincer Decompression, Labral refixation / Capsular Shift
Prevention of common running injuries
 Prevention of common running injuries Lower limb and hip joint pain, along with soft tissue structures of the lower leg, can be extremely painful and frustrating injuries. Some of the most common running
Prevention of common running injuries Lower limb and hip joint pain, along with soft tissue structures of the lower leg, can be extremely painful and frustrating injuries. Some of the most common running
Female Athlete Knee Injury
 Female Athlete Knee Injury Kelly C. McInnis, DO Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Massachusetts General Hospital Sports Medicine Center Outline Historical Perspective Gender-specific movement patterns
Female Athlete Knee Injury Kelly C. McInnis, DO Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Massachusetts General Hospital Sports Medicine Center Outline Historical Perspective Gender-specific movement patterns
What we ll cover... Two types of hamstring injury! What type of athletes tear hamstrings!
 What s'new'in'hamstring'strain' injury'prevention'&'rehabilitation? Craig Ranson PhD Programme Director MSc Sports & Exercise Medicine Cardiff Metropolitan University Wales Rugby Team Physiotherapist @craigarxl
What s'new'in'hamstring'strain' injury'prevention'&'rehabilitation? Craig Ranson PhD Programme Director MSc Sports & Exercise Medicine Cardiff Metropolitan University Wales Rugby Team Physiotherapist @craigarxl
Precautions following Hip Arthroscopy/FAI: (Refixation/Osteochondroplasty)
 Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Labral Repair / Capsular Shift, CAM / Pincer Decompression RX: Evaluate / Treat, and follow attached protocol
Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Labral Repair / Capsular Shift, CAM / Pincer Decompression RX: Evaluate / Treat, and follow attached protocol
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement. Normalize gait pattern with brace (if indicated) and crutches
 General Guidelines: Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement Normalize gait pattern with brace (if indicated) and crutches Weight-bearing: 20 lbs foot flat
General Guidelines: Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Gluteus Medius Repair with or without Labral Debridement Normalize gait pattern with brace (if indicated) and crutches Weight-bearing: 20 lbs foot flat
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
LUMBAR SPINE CASE 3. Property of VOMPTI, LLC. For Use of Participants Only. No Use or Reproduction Without Consent 1. L4-5, 5-S1 disc, facet (somatic)
 LUMBAR SPINE CASE 3 A.J. Lievre, PT, DPT, OCS, CMPT Aaron Hartstein, PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Richmond 2018-2019 L4-5, 5-S1 disc, facet (somatic) L5/S1 Radiculopathy
LUMBAR SPINE CASE 3 A.J. Lievre, PT, DPT, OCS, CMPT Aaron Hartstein, PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Richmond 2018-2019 L4-5, 5-S1 disc, facet (somatic) L5/S1 Radiculopathy
A.J. Lievre, PT, DPT, OCS, CMPT Aaron Hartstein, PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT
 LUMBAR SPINE CASE #3 A.J. Lievre, PT, DPT, OCS, CMPT Aaron Hartstein, PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 L4-5, 5-S1 disc, facet (somatic) L5/S1 Radiculopathy
LUMBAR SPINE CASE #3 A.J. Lievre, PT, DPT, OCS, CMPT Aaron Hartstein, PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 L4-5, 5-S1 disc, facet (somatic) L5/S1 Radiculopathy
FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT
 THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
Achilles Tendinopathy (Mid-portion)
 Achilles Tendinopathy (Mid-portion) What is Achilles tendinopathy? Achilles tendinopathy or tendinitis is a term that has been used for many years to describe pain, swelling and thickening around the Achilles
Achilles Tendinopathy (Mid-portion) What is Achilles tendinopathy? Achilles tendinopathy or tendinitis is a term that has been used for many years to describe pain, swelling and thickening around the Achilles
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries. The Hip.
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries The Hip INTRODUCTION THE HIP The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. The socket is formed by the acetabulum, which is part
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries The Hip INTRODUCTION THE HIP The hip is a ball-and-socket joint. The socket is formed by the acetabulum, which is part
Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty. Faculty Disclosures. Objectives 11/17/2017
 Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty Jonathan R. Schiller, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Director, Adolescent
Hip Impingement and Arthritis: Preservation vs. Total Hip Arthroplasty Jonathan R. Schiller, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Director, Adolescent
Mastering the Musculoskeletal Exam UCSF Essentials of Women s Health July 7, 2016 Carlin Senter, M.D. Henry Crevensten, M.D.
 Mastering the Musculoskeletal Exam UCSF Essentials of Women s Health July 7, 2016 Carlin Senter, M.D. Henry Crevensten, M.D. I have nothing to disclose Outline Knee exam Shoulder exam Knee Anatomy The
Mastering the Musculoskeletal Exam UCSF Essentials of Women s Health July 7, 2016 Carlin Senter, M.D. Henry Crevensten, M.D. I have nothing to disclose Outline Knee exam Shoulder exam Knee Anatomy The
QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture.
 The Hip Andrew Pearse Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedics Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Introduction Brief anatomy and topography History & examination Osteoarthritis Investigations Referral
The Hip Andrew Pearse Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedics Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Introduction Brief anatomy and topography History & examination Osteoarthritis Investigations Referral
Diagnosis: Labral Tear, Internal Snapping Hip, CAM / Pincer. Procedure: Partial Psoas Release with CAM / Pincer Decompression and Labral Debridement
 Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, Internal Snapping Hip, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Partial Psoas Release with CAM / Pincer Decompression and Labral Debridement RX: Evaluate
Physical Therapy Prescription: Hip Arthroscopy Diagnosis: Labral Tear, Internal Snapping Hip, CAM / Pincer Procedure: Partial Psoas Release with CAM / Pincer Decompression and Labral Debridement RX: Evaluate
Bryan T. Kelly, MD Center for Hip Pain and Preservation Hospital for Special Surgery
 Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Labral refixation with or without FAI Component General Guidelines: Limited external rotation to 20 degrees (2 weeks) No hyperextension (4 weeks) Normalize gait pattern with
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Labral refixation with or without FAI Component General Guidelines: Limited external rotation to 20 degrees (2 weeks) No hyperextension (4 weeks) Normalize gait pattern with
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee)
 Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
LOW BACK PAIN. what you can do
 LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL
 ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use
ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use
Hip Pain. Anatomy of the hip
 Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses?
 Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses? Basics of Gait Analysis Gait cycle: heel strike to subsequent heel strike,
Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses? Basics of Gait Analysis Gait cycle: heel strike to subsequent heel strike,
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Hamstring Rehabilitation Protocol
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Hamstring Rehabilitation Protocol Focus on exercise quality avoid overstressing the donor area while it heals. Typically, isolated hamstring strengthening begins after the 6
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Hamstring Rehabilitation Protocol Focus on exercise quality avoid overstressing the donor area while it heals. Typically, isolated hamstring strengthening begins after the 6
Development and validation of a VISA tendinopathy questionnaire for Greater Trochanteric Pain
 Development and validation of a VISA tendinopathy questionnaire for Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome, the VISA-G Fearon AM 1, 2, Ganderton C 3, Scarvell JM 2,5, Smith PN 1,2,, Nash C 4, Cook JL 4 1 ANU
Development and validation of a VISA tendinopathy questionnaire for Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome, the VISA-G Fearon AM 1, 2, Ganderton C 3, Scarvell JM 2,5, Smith PN 1,2,, Nash C 4, Cook JL 4 1 ANU
Anterior Knee Pain in Children. Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine
 Anterior Knee Pain in Children Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Goals and Objectives To learn how to care for patients with chronic knee pain To be able to
Anterior Knee Pain in Children Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Goals and Objectives To learn how to care for patients with chronic knee pain To be able to
Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation 67th Annual McGill Refresher Course for Family Physicians Dec6/2016
 Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation 67th Annual McGill Refresher Course for Family Physicians Dec6/2016 David J Zukor MD FRCSC Chief Department of Orthopedic Surgery SMBD-Jewish General Hospital Associate Professor
Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation 67th Annual McGill Refresher Course for Family Physicians Dec6/2016 David J Zukor MD FRCSC Chief Department of Orthopedic Surgery SMBD-Jewish General Hospital Associate Professor
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING. dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K)
 SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
During the initial repair and inflammatory phase, focus should be on placing the lower limbs in a position to ensure that:
 The Anatomy Dimensions series of tutorials and workbooks is aimed at improving anatomical and pathological understanding for body movement professionals. It is ideal for teachers in disciplines such as
The Anatomy Dimensions series of tutorials and workbooks is aimed at improving anatomical and pathological understanding for body movement professionals. It is ideal for teachers in disciplines such as
The hip: Built for endurance and mobility
 The hip: Built for endurance and mobility The hip joint Some anatomical landmarks Innominate Ilium, pubis, ischium Sacrum Iliac crests Asis Psis Pubic tubercle Acetabulum Femur Head of femur Neck of femur
The hip: Built for endurance and mobility The hip joint Some anatomical landmarks Innominate Ilium, pubis, ischium Sacrum Iliac crests Asis Psis Pubic tubercle Acetabulum Femur Head of femur Neck of femur
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner
 Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Injury Recovery and Prevention. ~Joshua Bowen
 Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
