Fovea Alta on MR Images: Is It a Marker of Hip Dysplasia in Young Adults?
|
|
|
- Mitchell Bridges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Beltran et al. MRI of Fovea Alta Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Luis S. Beltran 1 Jason D. Mayo 2 Zehava S. Rosenberg 1 Maria Diaz De Tuesta 3 Olga Martin 3 Luis P. Neto, Sr. 4 Jenny T. Bencardino 1 Beltran LS, Mayo JD, Bencardino JT, et al. Keywords: developmental dysplasia of the hip, diagnostic marker, fovea alta, MRI DOI: /AJR Received November 6, 2011; accepted after revision January 10, Department of Radiology, New York University Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York University Langone Medical Center, 660 First Ave, Rm 218, New York, NY Address correspondence to L. S. Beltran (Luis.Beltran@nyumc.org). 2 New Britain Radiologic Associates, New Britain, CT. 3 Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal, Madrid, Spain. 4 Universidade Federal de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil. AJR 2012; 199: X/12/ American Roentgen Ray Society Fovea Alta on MR Images: Is It a Marker of Hip Dysplasia in Young Adults? OBJECTIVE. The objective of our study was to investigate the association between high fovea capitis (fovea alta) and hip dysplasia in young adults. MATERIALS AND METHODS. In a retrospective study, blinded observers reviewed 82 pelvic radiographic and hip MRI studies of three groups of patients: those with developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) (center-edge angle, 20 ), those with borderline DDH (center-edge angle, ), and control patients (center-edge angle, > 25 ). The center-edge angle and coxa valga (femoral neck-shaft angle, > 135 ) were assessed on pelvic radiographs, and fovea alta was assessed on MR images (delta angle, 10 ). The Mann-Whitney and Fisher exact tests were used to correlate fovea alta with DDH and with coxa valga, respectively. Interobserver agreement for center-edge and delta angles and the diagnostic performance of fovea alta as a marker of DDH were calculated. RESULTS. Thirty-one patients with DDH, 23 with borderline DDH, and 28 without DDH were included. Excellent interobserver agreement was found for center-edge angle (concordance correlation coefficient, 0.94) and for delta angle (concordance correlation coefficient, 0.91). Fovea alta had a significant association with DDH (p < 0.001) but no association with coxa valga (p > 0.57). A significant difference (p < 0.001) was found between patients with DDH (3.4 ) and those without DDH (21.7 ) with respect to mean delta angle measurements. Fovea alta had 69.4% sensitivity, 82.1% specificity, 67.2% positive predictive value, 81.0% negative predictive value, and 75.6% overall accuracy as an indicator of DDH. CONCLUSION. Fovea alta shows promise as a strong MRI marker of DDH. D evelopmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) can vary greatly in morphologic features, ranging from a mildly shallow acetabulum to a completely dislocated high-riding hip. Despite routine screening during infancy, DDH, particularly when mild, can remain undetected into young adulthood, predisposing patients to early osteoarthritis [1]. This condition can have serious clinical implications because unrecognized DDH with superimposed arthrosis has been found to account for a large number of hip arthroplasties. A recent study by Engesæter et al. [2] showed that 26% of 634 total hip replacements in patients younger than 44 years were performed for osteoarthritis secondary to hip dysplasia. The cause of osteoarthritis in mild hip dysplasia may be related to high asymmetric concentration of force across the hip joint due to relative lateralization of the hip center of rotation, poor acetabular coverage of the femo- ral head, and small contact area between the femoral head and dysplastic acetabulum. All of these factors can produce irreversible articular cartilage and labral damage [3 5] with a secondary detrimental effect on the longevity of the hip joint. Thus accurate and prompt diagnosis of DDH, before the premature onset of osteoarthritis, is paramount for determining the treatment regimen and for assessing the necessity of surgical intervention, such as periacetabular osteotomy and femoral varus derotation osteotomy. The imaging diagnosis of hip dysplasia in the young adult may be subtle and has traditionally been based on radiographic evaluation. Patients with mild hip dysplasia typically have subtle uncovering of the femoral head by the acetabulum rather than a highriding dislocated hip. The most commonly used measurement is the center-edge angle of Wiberg, which is used to assess acetabular coverage of the femoral head. Other com- AJR:199, October
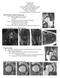
2 Beltran et al. Fig year-old man with normal left center-edge angle. Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph shows angle measuring 35 (normal, > 25 ). monly used radiographic markers of hip dysplasia are the acetabular index angle and the vertical-center-anterior margin angle. The femoral head has a smooth surface coated with articular cartilage, except over an ovoid depression, called the fovea capitis, which is normally situated slightly inferior and posterior to the center of the head and is the attachment site of the ligamentum teres. Nötzli et al. [6] reported that the abnormal superior position of the fovea capitis, the so-called fovea alta, is a potential additional radiographic diagnostic marker of adult hip dysplasia. They also suggested that fovea alta, assessed by measurement of the delta angle, may be a predisposing factor for early acetabular and perifoveal articular cartilage injury and for osteoarthritis by decreasing the contact area of the femoral head with the superior weight-bearing articular surface of the acetabulum. Unlike radiography, which lacks sensitivity for assessing early osteoarthritis, MRI can be used to simultaneously detect morphologic disease associated with DDH, such as center-edge angle abnormalities, and to predict the presence of predisposing factors in osteoarthritis, such as cartilage and labral injury. The utility of MRI in detecting DDH, however, may be further enhanced by assessment for additional markers of hip dysplasia, such as the fovea alta. The primary aim of our study was to confirm the association of fovea alta and hip dysplasia through the use of MRI measurement of the delta angle. A secondary aim was to assess whether fovea alta is a true morphologic abnormality in hip dysplasia or reflects apparent head abnormality related to the presence of coxa valga deformity associated with hip dysplasia. Materials and Methods Our study was assessed by the internal review board at our institution and deemed exempt from full internal review board review. We performed a retrospective search of our PACS (isite PACS, Philips Healthcare) database from July 2007 through July 2010 for all patients in the age range years who had a clinical history of hip pain in the radiology report. Inclusion criteria were availability of MR images of the hip and a wellcentered anteroposterior pelvic radiograph obtained within 12 months of each other. Exclusion criteria included previous surgery and inadequate imaging studies, including absence of a well-centered anteroposterior pelvic radiograph and MR images of the hip within 12 months of each other, suboptimal image quality, or a hip that was in external rotation. Two radiologists (a musculoskeletal fellow and an attending radiologist with 1 Fig year-old man with normal right femoral neck-shaft angle. Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph cropped to show measurements shows angle measuring 128 (normal, ). Fig year-old woman with left developmental hip dysplasia. Anteroposterior radiograph shows decreased center-edge angle measuring 11. year of experience in musculoskeletal radiology) blindly and independently measured radiographic center-edge and femoral neck-shaft angles and MRI delta angles. Hip dysplasia was defined as a center-edge angle of 20 or less and borderline hip dysplasia as a center-edge angle of A nondysplastic hip was defined as having a centeredge angle greater than 25. Coxa valga was defined as a femoral neck-shaft angle greater than 135 and coxa vara as a femoral head-neck-shaft angle less than 120 [7]. Fovea alta was defined as a delta angle of 10 or less. Imaging Technique The anteroposterior radiograph of the pelvis was obtained according to standard radiographic protocol with the patient supine and both lower extremities oriented in 15 of internal rotation [8]. Technical radiographic exclusion criteria were Fig year-old woman with coxa valga. Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph cropped to show measurements shows increased femoral neck-shaft angle measuring AJR:199, October 2012
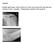
3 MRI of Fovea Alta Fig. 5 Illustration shows delta angle (δ) measured on midcoronal MR image where there is optimal visualization of fovea capitis and sourcil, determined by cross-referencing with scout lines on axial and coronal images. Angle is formed between two lines extending from medial edge of sourcil (point A) and superior edge of fovea capitis (point B) to center of femoral head. lack of obturator foramen symmetry, distance between the tip of the coccyx and symphysis pubis decreased less than 1 cm or increased more than 3 cm, and femoral external rotation. MR images were obtained according to standard MRI protocol with the patient supine and the hips in slight internal rotation, the latter achieved by taping the feet while maintaining contact of the great toes. Coronal proton density (with or without fat suppression) or T1-weighted images of the hip were selected for measurements. Imaging was performed with a 1.5-T MRI system (Magnetom Vision or Avanto, Siemens Healthcare) or a 3-T MRI system (Verio, Fig year-old man with normal delta angle. Coronal T1-weighted MR image shows angle greater than 10. Siemens Healthcare). The slice thickness ranged from 3 to 5 mm with no interslice gap. Fig year-old woman with fovea alta manifested by decreased delta angle. Coronal proton density weighted MR image shows angle of 10 (normal, > 10 ). Negative delta angle value indicates that medial edge of sourcil is medial to superior edge of fovea capitis, resulting in overlapping. Mild uncovering of femoral head also is evident. Measurements The radiographic center-edge angle was determined by constructing a best-fit circle on each femoral head and connecting a horizontal line through the centers of both circles. The angle formed by a line drawn perpendicular to the horizontal line at the midpoint of each femoral head and a second line from the center of the femoral head to the outer margin of the acetabular roof was then measured [9] (Figs. 1 and 2). The femoral neck-shaft angle was measured on anteroposterior pelvic radiographs at the intersection of the femoral neck axis and the long axis of the femur (Figs. 3 and 4). MRI measurements of the delta angle were performed on midcoronal proton density weighted (with or without fat suppression) or T1-weighted images on which there was optimal visualization of both the fovea capitis and the acetabular sourcil, as determined by cross-referencing with the scout lines on sagittal and axial images (Figs. 5 7). The angle formed by lines drawn from the medial edge of the sourcil and the superior edge of the fovea capitis to A Fig year-old man without developmental dysplasia of hip. A, Axial proton density weighted MR image shows externally rotated hip with anterior location of fovea capitis. Dotted line indicates axis of femoral neck. B, Coronal proton density weighted MR image shows decreased delta angle of 7 (normal, > 10 ) and anterior location of fovea capitis relative to medial edge of sourcil. C, Anteroposterior pelvic radiograph shows normal center-edge angle of greater than 25, indicating absence of hip dysplasia. Presence of external rotation of femur can simulate fovea alta deformity. B C AJR:199, October
4 Beltran et al. the center of the femoral head was measured. The delta angle was defined as positive when the medial edge of the sourcil was lateral to the superior edge of the fovea capitis. The delta angle was defined as negative when the medial edge of the sourcil was medial to the superior edge of the fovea capitis. Fovea alta was defined as a delta angle of 10 or less. The femoral head was in neutral or mild internal rotation position. Images on which the femur was externally rotated as determined by anterior orientation of the axis of the femoral neck and anterior location of the fovea capitis on axial MR images (which can simulate fovea alta deformity) were excluded from the study (Fig. 8). Statistical Analysis The Mann-Whitney exact test was used to correlate dysplastic (center-edge angle, 20 ) and nondysplastic (center-edge angle, > 25 ) hips with the delta angle. The Fisher exact test was used to correlate fovea alta and coxa valga. Concordance correlation coefficient was used to assess interobserver agreement for center-edge angle and delta angle measurements. A concordance correlation coefficient greater than 0.7 was interpreted as excellent agreement. The diagnostic performance of fovea alta as a marker of hip dysplasia was assessed. Results Twelve patients did not meet the inclusion criteria because of inadequate imaging. Eightytwo consecutively registered patients (23 men, 59 women; age range, years; mean age, 29 years) met the inclusion criteria. Thirty-one of the patients had dysplastic hips, 23 patients had borderline dysplastic hips, and 28 patients had nondysplastic hips, according to radiographic center-edge angle measurements. For both readers, there was a significant association between fovea alta, measured by MRI delta angle, and hip dysplasia (p < 0.001). There was also a statistically significant difference in mean delta angle measurements between dysplastic (δ = 3.4 ) and nondysplastic (δ = 21.7 ) hips (p < 0.001). In the comparison of average delta angle measurements between normal, borderline dysplastic, and dysplastic hips (Table 1), the average delta angle was significantly different between nondysplastic hips and dysplastic hips and between borderline dysplastic and dysplastic hips for both readers (Table 2). Also for both readers, no significant difference was seen between average delta angle in nondysplastic hips and borderline dysplastic hips (Table 2). As an indicator of hip dysplasia, fovea alta had 69.4% sensitivity, 82.1% specificity, 67.2% positive predictive value, TABLE 1: Mean Delta Angle MRI Measurements Reader Normal Hip (n = 28) Borderline Dysplasia (n = 23) Dysplasia (n = 31) ± ± ± ± ± ± 12.7 Note Values are mean ± SD in degrees. Normal hip is a center-edge angle greater than 25 ; borderline dysplasia, greater than 20 and up to 25 ; dysplasia, 20 or less. TABLE 2: Results of Exact Mann-Whitney Test of MRI Delta Angle Measurements Reader Normal Hip Versus vs Borderline Dysplasia 81.0% negative predictive value, and 75.6% overall accuracy. There was no significant association between coxa valga and fovea alta evaluations for either reader (p > 0.57). Excellent agreement was seen between readers for radiographic center-edge angle (concordance correlation coefficient, 0.94) and MRI delta angle (concordance correlation coefficient, 0.91). Patient Group Normal Hip Versus Dysplasia Borderline Dysplasia Versus Dysplasia < < Note Values are p. Discussion The concept that young adults with DDH have an abnormally high position of the fovea capitis and that this finding can be used as an additional radiographic marker of hip dysplasia was first introduced by Nötzli et al. in 2001 [6]. To the best of our knowledge, there have been no further reports on this topic since then. Nevertheless, hip dysplasia continues to be a serious health issue. In a recent study, Engesæter et al. [2] found that osteoarthritis secondary to hip dysplasia in patients younger than 44 years accounted for 26% of 634 hip replacements in their database. MRI has been found reliable for assessing morphologic abnormalities of DDH and for measuring acetabular coverage of the femoral head with the center-edge angle [10]. MRI has also been found to be an accurate technique for assessing associated injuries of the articular cartilage and labrum [11 13]. Furthermore, advanced biochemical MRI techniques, such as delayed gadolinium-enhanced MRI of cartilage (dgemric), have shown great potential for earlier detection of articular cartilage changes in osteoarthritis secondary to hip dysplasia [14]. The addition of fovea alta as a diagnostic MRI marker of hip dysplasia can further enhance the utility of MRI for detecting hip dysplasia, making the modality a comprehensive examination of both morphologic abnormalities and associated cartilage and labral injuries in the hip joint. Extrapolating the radiographic delta angle measurements of fovea alta developed by Nötzli et al. [6] to MRI measurements, we were able to confirm the association between fovea alta and hip dysplasia. We found a significant association between fovea alta and hip dysplasia for both readers (p < 0.001) and a statistically significant difference in mean delta angle measurements between dysplastic (d = 3.4 ) and nondysplastic (δ 21.7 ) hips (p < 0.001). We also found a statistically significant difference in mean delta angle measurements when comparing dysplastic and borderline dysplastic hips. However, no significant difference was seen between average delta angle in nondysplastic and borderline dysplastic hips (Table 2). These findings suggest that the delta angle may be a more reliable indicator of hip dysplasia in patients with a centeredge angle of 20 or less. Thus caution should be exercised in the use of delta angle to diagnose hip dysplasia in patients with a mildly decreased center-edge angle and borderline hip dysplasia (center-edge angle, ). Although, to our knowledge, there is no evidence in the literature to prove or disprove potential causes of the presence of fovea alta in hip dysplasia, we hypothesize that the abnormal contact pressure along the superior aspect of the femoral head and the lateralized center of hip rotation that occur in hip dysplasia likely contribute to the altered development of the shape of the femoral head during skeletal maturation, including the eventual position of the fovea capitis along a more superior aspect of 882 AJR:199, October 2012
5 MRI of Fovea Alta the femoral head. Nötzli et al. [6] also suggested that the position of the fovea capitis might be a predisposing factor in early acetabular and perifoveal articular cartilage injury leading to osteoarthritis by decreasing the contact area of the chondral tissue lined femoral head with the superior, weight-bearing chondral surface of the acetabulum. Our results show no significant association between coxa valga and fovea alta (p > 0.57). This evaluation was performed to exclude the possibility that the apparently high position of the fovea capitis along the femoral head in hip dysplasia is simply a manifestation of coxa valga (increased femoral neckshaft angle), which is frequently associated with hip dysplasia. In the assessment of interobserver variability, we found excellent agreement between readers for radiographic center-edge angle (concordance correlation coefficient, 0.94) and MRI delta angle (concordance correlation coefficient, 0.91). This finding is likely a reflection of the presence of discrete anatomic points in the measurements used to calculate the center-edge and delta angles, making them reliable diagnostic tools in assessment for hip dysplasia. Limitations of our study include the retrospective design and small patient sample. Furthermore, rather than using clinical or surgical confirmation of disease, we subdivided our patients into those with normal hips, those with borderline dysplastic hips, and those with definite hip dysplasia on the basis of radiographic center-edge angle measurements. Nevertheless, radiographic center-edge angle measurements are widely acceptable diagnostic parameters of hip dysplasia. In addition, the excellent interobserver agreement on our center-edge angle measurements suggests that our margin of error was small. Similarly, there is a potential for error in MRI measurement of the delta angle related to the position of the femur at the hip joint. Ideally, the femoral head should be in neutral position or in slight external or internal rotation to allow accurate measurement of the delta angle. Extreme internal or external rotation of the hip can lead to overestimation of the medial edge of the sourcil, which can result in a false-positive diagnosis of fovea alta (Fig. 8). Conclusion Using MRI measurements, we found a significant association between fovea alta and hip dysplasia in our patient sample. Future studies with a larger patient group may help confirm the reliability of fovea alta as a marker of hip dysplasia on MR images. Awareness of the imaging appearance of fovea alta by radiologists and orthopedic surgeons coupled with recognition of other established diagnostic imaging markers may lead to improved diagnosis of mild hip dysplasia, which may facilitate treatment and prevent or delay the onset of osteoarthritis in this patient population. Future directions may include the use of advanced MRI (such as dgemric) of the articular cartilage to assess for characteristic patterns of biochemical cartilage alterations in patients with fovea alta and hip dysplasia, particularly involving the chondral surfaces in the perifoveal femoral head and the superomedial aspect of the acetabular roof. References 1. Mahan ST, Katz JN, Kim YJ. To screen or not to screen? A decision analysis of the utility of screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009; 91: Engesæter IØ, Lehmann T, Laborie LB, Lie SA, Rosendahl K, Engesæter LB. Total hip replacement in young adults with hip dysplasia: age at diagnosis, previous treatment, quality of life, and validation of diagnoses reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register between 1987 and Acta Orthop 2011; 82: Armand M, Lepistö J, Tallroth K, Elias J, Chao E. Outcome of periacetabular osteotomy: joint contact pressure calculation using standing AP radiographs 12 patients followed for average 2 years. Acta Orthop 2005; 76: Hipp JA, Sugano N, Millis MB, Murphy SB. Planning acetabular redirection osteotomies based on joint contact pressures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999; Jul: Michaeli DA, Murphy SB, Hipp JA. Comparison of predicted and measured contact pressures in normal and dysplastic hips. Med Eng Phys 1997; 19: Nötzli HP, Müller SM, Ganz R. The relationship between fovea capitis femoris and weight bearing area in the normal and dysplastic hip in adults: a radiologic study. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 2001; 139: Reikerås O, Høiseth A, Reigstad A, Fönstelien E. Femoral neck angles: a specimen study with special regard to bilateral differences. Acta Orthop Scand 1982; 53: Clohisy JC, Carlisle JC, Beaulé PE, et al. A systematic approach to the plain radiographic evaluation of the young adult hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008; 90(suppl 4): Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint, with special reference to the complication of osteoarthritis. Acta Chir Scand 1939; 83(suppl 58): Chen L, Boonthathip M, Cardoso F, Clopton P, Resnick D. Acetabulum protrusio and center edge angle: new MR-imaging measurement criteria a correlative study with measurement derived from conventional radiography. Skeletal Radiol 2009; 38: James S, Miocevic M, Malara F, Pike J, Young D, Connell D. MR imaging findings of acetabular dysplasia in adults. Skeletal Radiol 2006; 35: Nishii T, Sugano N, Tanaka H, Nakanishi K, Ohzono K, Yoshikawa H. Articular cartilage abnormalities in dysplastic hips without joint space narrowing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001; Feb: Nishii T, Tanaka H, Nakanishi K, Sugano N, Miki H, Yoshikawa H. Fat-suppressed 3D spoiled gradient-echo MRI and MDCT arthrography of articular cartilage in patients with hip dysplasia. AJR 2005; 185: Kim YJ, Jaramillo D, Millis MB, Gray ML, Burstein D. Assessment of early osteoarthritis in hip dysplasia with delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003; 85: AJR:199, October
Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults.
 Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults. Poster No.: C-0492 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arevalo, N. Santamaria, E. Diez, J. Gredilla Molinero, M. 1
Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults. Poster No.: C-0492 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arevalo, N. Santamaria, E. Diez, J. Gredilla Molinero, M. 1
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View
 Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Imaging Evaluation of Developmental Hip Dysplasia in the Young Adult
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review eltran et al. Imaging of Developmental Hip Dysplasia Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.201.115 on 12/20/17 from IP address 46.3.201.115.
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review eltran et al. Imaging of Developmental Hip Dysplasia Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.201.115 on 12/20/17 from IP address 46.3.201.115.
A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
What is a Hip Dysplasia?
 What is a Hip Dysplasia? Hip dysplasia, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)[1] or congenital dysplasia of the hip (CDH)[2] is a congenital or acquired deformation or misalignment of the hip joint.
What is a Hip Dysplasia? Hip dysplasia, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)[1] or congenital dysplasia of the hip (CDH)[2] is a congenital or acquired deformation or misalignment of the hip joint.
Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
1/15/ year old male. Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA
 29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Outcome of periacetabular osteotomy
 Acta Orthopaedica ISSN: 1745-3674 (Print) 1745-3682 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort20 Outcome of periacetabular osteotomy Mehran Armand, Jyri Lepistö, Kaj Tallroth, John
Acta Orthopaedica ISSN: 1745-3674 (Print) 1745-3682 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort20 Outcome of periacetabular osteotomy Mehran Armand, Jyri Lepistö, Kaj Tallroth, John
Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
21 year-old collegiate rower: R/O labral tear
 Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Supine and Standing AP Pelvis Radiographs in the Evaluation of Pincer Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule
 Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
 The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamwong Saisamorn MD*, Tanatip Sisuchinthara MS* Thunchanok Jittivilai PN*, Kamolporn Keawpornsawan
The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamwong Saisamorn MD*, Tanatip Sisuchinthara MS* Thunchanok Jittivilai PN*, Kamolporn Keawpornsawan
Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it?
 Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it? Poster No.: P-0049 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. De Roeck, F. M. H. M. Vanhoenacker ; Antwerpen/BE, 1 2 1 2 Antwerp/BE
Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it? Poster No.: P-0049 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. De Roeck, F. M. H. M. Vanhoenacker ; Antwerpen/BE, 1 2 1 2 Antwerp/BE
Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
Adult Hip Radiography: Lines and angles
 Adult Hip Radiography: Lines and angles Poster No.: P-0209 Congress: ESSR 2017 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. L. Proença, A. P. Caetano, L. Bogalho; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Education and training, Education,
Adult Hip Radiography: Lines and angles Poster No.: P-0209 Congress: ESSR 2017 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. L. Proença, A. P. Caetano, L. Bogalho; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Education and training, Education,
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
1/15/2012. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular impingement
 Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
Disclosure. FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software. Acceptance of Hip Arthroscopy & FAI. Public. Payors. Orthopaedic Community
 2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD
 Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Adult hip
Adult Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Adult hip
Hip Arthroscopy: Intra-articular Saucerization of the Acetabular Cotyloid Fossa
 Hip Arthroscopy: Intra-articular Saucerization of the Acetabular Cotyloid Fossa JAMES K. BRANNON, MD, FAAOS abstract Full article available online at ORTHOSuperSite.com. Search: 20120123-23 Hip arthroscopy
Hip Arthroscopy: Intra-articular Saucerization of the Acetabular Cotyloid Fossa JAMES K. BRANNON, MD, FAAOS abstract Full article available online at ORTHOSuperSite.com. Search: 20120123-23 Hip arthroscopy
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes
 The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review
 Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review Poster No.: P-0037 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. G. Flanagan, J. Sarkodieh, K. Mcdonald, M. Ramachandran,
Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review Poster No.: P-0037 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. G. Flanagan, J. Sarkodieh, K. Mcdonald, M. Ramachandran,
The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular rim during normal hip range of motion.
 RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide Toacetabular Component Anteversion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session. DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips
 Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips Michael A. DiPietro, M.D. John F. Holt Collegiate Professor of Radiology Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable
Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips Michael A. DiPietro, M.D. John F. Holt Collegiate Professor of Radiology Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2007) 15, 366e371 ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.10.005 Cartilage thickness
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2007) 15, 366e371 ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.10.005 Cartilage thickness
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies
 Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
ORIGINAL STUDY INTRODUCTION
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 38-43 ORIGINAL STUDY Influence of labral tears on the outcome of acetabular augmentation procedures in adult dysplastic hips Prospective assessment with a minimum follow-up
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 38-43 ORIGINAL STUDY Influence of labral tears on the outcome of acetabular augmentation procedures in adult dysplastic hips Prospective assessment with a minimum follow-up
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems?
 What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA. Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS
 CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
Ischiofemoral impingement: spectrum of findings
 Ischiofemoral impingement: spectrum of findings Poster No.: C-1005 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Thomas, R. Dominguez Oronoz, M. Vera Cartas, S. Roche, 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 X. Merino-Casabiel,
Ischiofemoral impingement: spectrum of findings Poster No.: C-1005 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Thomas, R. Dominguez Oronoz, M. Vera Cartas, S. Roche, 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 X. Merino-Casabiel,
A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur
 A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur Tadashi Tsukeoka, Yoshikazu Tsuneizumi, TaeHyun Lee. Chiba Rehabilitation Center, Chiba, Japan. Disclosures:
A Useful Reference Guide for the Stem Anteversion During Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Dysplastic Femur Tadashi Tsukeoka, Yoshikazu Tsuneizumi, TaeHyun Lee. Chiba Rehabilitation Center, Chiba, Japan. Disclosures:
Does Native Combined Anteversion Influence Pain Onset in Patients With Dysplastic Hips?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:3716 3722 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4373-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 INTERNATIONAL
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:3716 3722 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4373-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 INTERNATIONAL
Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine
 Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications. Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout
 Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail?
 Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
Measurement of lateral acetabular coverage: a comparison between CT and plain radiography
 Journal of Hip Preservation Surgery Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 392 400 doi: 10.1093/jhps/hnv063 Advance Access Publication 22 October 2015 Research article Measurement of lateral acetabular coverage: a comparison
Journal of Hip Preservation Surgery Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 392 400 doi: 10.1093/jhps/hnv063 Advance Access Publication 22 October 2015 Research article Measurement of lateral acetabular coverage: a comparison
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult
 Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Shunsaku Nishihara 1, Nobuhiko Sugano 1, Takashi Nishii 1, Hisashi Tanaka 2, Hideki Yoshikawa 1, and Takahiro Ochi 1
 J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD*
 Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD* *Orthopedic Medical Group,7910 Frost St. #200 San Diego, California 92123, USA **Riverside County Regional Medical
Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD* *Orthopedic Medical Group,7910 Frost St. #200 San Diego, California 92123, USA **Riverside County Regional Medical
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Evaluation of three ultrasound techniques used for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
 Evaluation of three ultrasound techniques used for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) Poster No.: C-2049 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. M. D. B. Pacheco,
Evaluation of three ultrasound techniques used for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) Poster No.: C-2049 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. M. D. B. Pacheco,
Evaluation of three ultrasound techniques used for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
 Evaluation of three ultrasound techniques used for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) Poster No.: C-2049 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. M. D. B. Pacheco,
Evaluation of three ultrasound techniques used for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) Poster No.: C-2049 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. M. D. B. Pacheco,
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Ultrasound and radiography findings in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a pictorial review
 Ultrasound and radiography findings in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a pictorial review Poster No.: C-2542 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords:
Ultrasound and radiography findings in developmental dysplasia of the hip: a pictorial review Poster No.: C-2542 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords:
Sports Medicine and Radiology
 Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R, M.D. 1), Richolt JA, M.D. 3)
 Three-dimensional analysis of the proximal femur in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on computed tomography. Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R,
Three-dimensional analysis of the proximal femur in patients with slipped capital femoral epiphysis based on computed tomography. Kordelle J, M.D. 1), Millis M, M.D. 2), Jolesz FA, M.D. 1), Kikinis R,
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures
 Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Does Radiographic Coxa Profunda Indicate Increased Acetabular Coverage or Depth in Hip Dysplasia?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:2056 2066 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4084-x Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Radiographic
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:2056 2066 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4084-x Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Radiographic
Successful Pavlik treatment in late-diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:1661 1668 DOI 10.1007/s00264-012-1587-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Successful Pavlik treatment in late-diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip Michiel A. J. van de
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2012) 36:1661 1668 DOI 10.1007/s00264-012-1587-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Successful Pavlik treatment in late-diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip Michiel A. J. van de
Case Developmental dysplasia of hip
 Case 13303 Developmental dysplasia of hip Hidayatullah Hamidi, Sahar Maroof French medical institute for children, Kabul, Afghanistan Email: Hedayatullah.hamidi@gmail.com Maroofsahar1@gmail.com French
Case 13303 Developmental dysplasia of hip Hidayatullah Hamidi, Sahar Maroof French medical institute for children, Kabul, Afghanistan Email: Hedayatullah.hamidi@gmail.com Maroofsahar1@gmail.com French
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies
 Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
Peggers Super Summaries: Paediatric Hip
 EMBRYOLOGY Development o Mesenchymal stem cells cartilage blood supply bone Dates o 6/40 Limb development o 8-11/40 hip development (acetabulum and hip formed from one bone splitting by apoptosis) o 16/40
EMBRYOLOGY Development o Mesenchymal stem cells cartilage blood supply bone Dates o 6/40 Limb development o 8-11/40 hip development (acetabulum and hip formed from one bone splitting by apoptosis) o 16/40
The Pavlik harness is a positioning device commonly
 RESEARCH PAPERS Ultrasound Evaluation of Hip Position in the Pavlik Harness Leslie E. Grissom, MD*, H. Theodore Harcke, MD*, S. Jay Kumar, MOt, George S. Bassett, MOt, G. Dean MacEwen, MOt Fifty infants
RESEARCH PAPERS Ultrasound Evaluation of Hip Position in the Pavlik Harness Leslie E. Grissom, MD*, H. Theodore Harcke, MD*, S. Jay Kumar, MOt, George S. Bassett, MOt, G. Dean MacEwen, MOt Fifty infants
Case 61. Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative.
 Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
Hindfoot Alignment Measurements: Rotation-Stability of Measurement Techniques on Hindfoot Alignment View and Long Axial View Radiographs
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Buck et al. Measurements Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Florian M. Buck 1 Adrienne Hoffmann 1 Nadja Mamisch-Saupe 1 Norman Espinosa 2 Donald
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Buck et al. Measurements Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Florian M. Buck 1 Adrienne Hoffmann 1 Nadja Mamisch-Saupe 1 Norman Espinosa 2 Donald
The Young Adult Hip: FAI. Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California
 The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD
 Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Hip dysplasia
Hip Dysplasia David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of Orthopedic Surgery & Pediatrics NYU Langone Medical Center & NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Overview Hip dysplasia
)371( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE. Research performed at Dr. Sheikh Children Hospital, Mashhad, Iran
 )371( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of Diagnostic Value of Single View Static & Dynamic Technique in Diagnosis of Developmental Dysplasia of Hip:
)371( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Assessment of Diagnostic Value of Single View Static & Dynamic Technique in Diagnosis of Developmental Dysplasia of Hip:
Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96S, S44 S52 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds L. Bellaïche a,, M. Lequesne b, J.-E. Gedouin
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96S, S44 S52 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds L. Bellaïche a,, M. Lequesne b, J.-E. Gedouin
Computer-Assisted Rotational Acetabular Osteotomy for Patients with Acetabular Dysplasia
 Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:99-105 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.99 Computer-ssisted Rotational cetabular Osteotomy for Patients with cetabular Dysplasia Yutaka Inaba,
Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:99-105 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.99 Computer-ssisted Rotational cetabular Osteotomy for Patients with cetabular Dysplasia Yutaka Inaba,
First practical session. Bones of the gluteal region
 First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
A comparison of ultrasonography and radiography in the management of infants with suspected developmental dysplasia of the hip
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 524-529 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of ultrasonography and radiography in the management of infants with suspected developmental dysplasia of the hip Hakan Atalar, Halil Dogruel,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 524-529 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of ultrasonography and radiography in the management of infants with suspected developmental dysplasia of the hip Hakan Atalar, Halil Dogruel,
F.A.I. indications. E. Sabetta. Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta
 F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
L side 65% Torticollis, Plagiocephaly, Metatarsus varus Flat foot.
 DEVELOPMENTAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP [DDH] Older terminology was Congenital dislocation of the hip. DDH means developmental dysplasia of the hip. DDH is better than CDH as dislocation is not always congenital.
DEVELOPMENTAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP [DDH] Older terminology was Congenital dislocation of the hip. DDH means developmental dysplasia of the hip. DDH is better than CDH as dislocation is not always congenital.
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
Joints of the lower limb
 Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI
 Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
Mohamed El-Sayed Tarek Ahmed Sameh Fathy Hosam Zyton. Introduction
 J Child Orthop (2012) 6:471 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0451-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The effect of Dega acetabuloplasty and Salter innominate on acetabular remodeling monitored by the acetabular index
J Child Orthop (2012) 6:471 477 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0451-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The effect of Dega acetabuloplasty and Salter innominate on acetabular remodeling monitored by the acetabular index
Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement?
 Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
25. PELVIC OSTEOTOMIES FOR THE TREATMENT OF HIP DYSPLASIA IN ADULTS
 Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Kassarjian et al. MRI of the Quadratus Femoris Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Ara Kassarjian 1 Xavier Tomas 2 Luis Cerezal 3 Ana Canga 4,5 Eva Llopis 6 Kassarjian A, Tomas
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Kassarjian et al. MRI of the Quadratus Femoris Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Ara Kassarjian 1 Xavier Tomas 2 Luis Cerezal 3 Ana Canga 4,5 Eva Llopis 6 Kassarjian A, Tomas
Analysis of Nonunion of the Superior Pubic Ramus Osteotomy Site After Curved Periacetabular Osteotomy
 福岡大医紀 (Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ.):42(1),95 101,2015 Analysis of Nonunion of the Superior Pubic Ramus Osteotomy Site After Curved Periacetabular Osteotomy Tetsuya SAKAMOTO, Masatoshi NAITO Department of
福岡大医紀 (Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ.):42(1),95 101,2015 Analysis of Nonunion of the Superior Pubic Ramus Osteotomy Site After Curved Periacetabular Osteotomy Tetsuya SAKAMOTO, Masatoshi NAITO Department of
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes
 Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. Elsamaloty,
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. Elsamaloty,
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology
 Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module
 1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia
 Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
