The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy (average 6 years follow-up)
|
|
|
- Kelly Hunt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2003) 11 : KNEE DOI /s Cengiz Sen Mehmet Kocaoglu Levent Eralp The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy (average 6 years follow-up) Received: 10 June 2002 Accepted: 16 December 2002 Published online: 29 March 2003 Springer-Verlag 2003 C. Sen ( ) Ortopedive Travmatoloji Anabilimdali, Medical Faculty, University of Gaziosmanpasa, Tokat, Turkey Tel.: , Fax: , senc64@yahoo.com M. Kocaoglu L. Eralp Medical Faculty of Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey Abstract We evaluated the midterm results of high tibial osteotomy in patients with medial compartment arthritis. This study included 53 patients treated with high tibial osteotomy accompanied by either internal fixation (group A, n=26) or Ilizarov-type external fixator (group B, n=27). Clinical assessment of patients was performed using Hospital of Special Surgery scoring. Radiography was based on orientation angles of the knee (medial proximal tibial angle, lateral distal femoral angle, posterior proximal tibial angle) and mechanic axis alignment test. We used the Insall-Salvati index to determine patellar height. The mean follow-up in group A was 77 months (range ) and that in group B 72 months (range ). The patients of group B demonstrated better results in terms of Hospital of Special Surgery score, alignment of lower extremity, and preventing of progression of arthritis. We believe that normal alignment and orientation of the knee could be precisely established with a circular external fixator, and that some disadvantages such as patella infera, failed correction, and loss of bone in proximal tibia as observed after classic high tibial osteotomy can be avoided. Furthermore, progression of arthritis can be prevented if the mechanical axis passes through the lateral compartment of the knee. Keywords Arthritis Osteotomy High tibial Circular fixator Introduction The original technique of high tibial osteotomy was first described by Jackson and Waugh [10] in Coventry et al. [4] later popularized it and presented longer term results on this method [4]. Maquet [13] described his dome osteotomy technique, and in 1992 Paley and Tetsworth [18] introduced new concepts into orthopedic surgery concerning the definition, detection, and treatment of femoral and tibial deformities. Paley et al. [19] then recommended a new method for the treatment of medial compartment arthritis. This dome osteotomy, with the concavity facing the knee joint, is performed below tibial tuberosity. Following osteotomy fixation can be achieved with an Ilizarov type circular external fixator [3, 22]. The purpose of this study was to assess the advantages of circular external fixation comparing to internal fixation utilized for high tibial osteotomy. Patients and method This study was carried out between January 1992 and December 1996 and included 53 patients (41 women, 12 men) with medial compartment arthritis. Group A consisted of 26 patients (median age 52.4, range 43 58) who underwent high tibial osteotomy with Coventry technique using internal fixation hardware: buttress plate in 7, Puddu plate in 3, Kirschner wires in 3, and staples in 13. To avoid some disadvantages of the Coventry technique we performed reverse dome osteotomy below the tuberositas tibia with circular external fixator. Group B consisted of 27 consecutive patients (median age 51.7, range 42 59) who underwent high tibial osteotomy
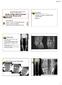
2 140 using Ilizarov-type circular external fixator. The same team (M.K., C.S., L.E.) performed surgery in group B. The our basic criteria for high tibial osteotomy were pain, confined to medial compartment, sufficient muscle strength, no flexion contracture greater than 15, good range of motion, and no instability [20]. All patients had unilateral involvement (36 left, 17 right). The patients were assessed by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) functional scoring, and their mechanical axis deviation of lower extremities and orientation were evaluated by the radiological criteria of Paley and Tetsworth [18]. In addition, The Insall-Salvati index was measured to evaluate pre- and postoperative patellar height. The degree of osteoarthritis was determined according to Ahlback s classification, and stages I, II, and III arthritis were detected in 14, 8, and 4 patients in group A; 12, 13, and 2 patients in group B, respectively. To confirm quality of lateral compartment cartilage diagnostic arthroscopy was performed before the osteotomy for all patients of group B. If a patient s cartilage had damage more than grade I [23], the patient was excluded from this study. Mean follow-up was 77 months (range ) in group A and 72 months (61 113) in group B. Differences in mean function and radiological measurements were evaluated statistically by Student s t test. P values less than 0.05 were accepted as statistically significant at a 95% confidence interval. Preoperative planning During pre- and postoperative examinations standing anteroposterior and lateral orthoroentgenographies of both hips, knees, and ankles were taken, and malalignment tests in the frontal and sagittal planes were drawn and measured. The fixator frame consists of three rings and is reconstructed preoperatively (Fig. 1). Since the center of rotation angulation (CORA) is at the level of the knee joint, the hinge is placed on the proximal side of the proximal ring at a juxtaarticular position. The two hinges are applied on one or two holes lateral to the central bolt to create an open-up osteotomy. The distraction rod (motor unit) is positioned medially at equal distances from the two hinges. Technique The patients of group A underwent high tibial osteotomy using the Coventry technique. In the patients of group B a middiaphyseal fibular osteotomy was initially performed. The first wire is inserted perpendicular to the mechanical axis of the tibia and fixed to the proximal ring. Afterwards, a second wire is inserted parallel to the ankle joint and fixed to the distal ring, thus the frame is fixed to the leg. At this stage the hinges must be fluoroscopically controlled to be at the level of the CORA. Then 6-mim Schanz pins are inserted through the proximal and middle rings. An olived wire is pierced through fibula and fixed to distal ring. Finally, a percutaneous, reverse dome shaped osteotomy is performed with the help of a template. The distraction rod and both hinges are removed before osteotomy. Lateral translation is achieved by reversing fragments in clock or anticlockwise direction with an osteotome. In this way the axis of both proximal and distal fragments align, hence preventing malrotation of the ankle. Afterwards the distraction rod and hinges are remounted. The fixed angle in the hinges are the same as the x angle determined preoperatively. Results The mean preoperative and postoperative proximal tibial angle (MPTA), lateral distal femoral angle (LDFA), and posterior proximal tibial angle (PPTA) are presented demonstrated in Table 1 for both groups (Fig. 2). While the mechanical axis passed through the medial compartment of the knee in all patients except 7 in group A, it passed through the lateral compartment of the knee in 22 patients, through the center in 3, and medially in only 2 in group B. The relationship between postoperative mechanical axis and arthritis according to Ahlback is presented Table 2 (Fig. 3). In addition, we observed that preoperatively diagnosed stage III arthrosis in four patients of group A and Table 1 Functional and radiological mean values in groups A and B (HSS Hospital of Special Surgery score, MPTA proximal tibial angle, LDFA lateral distal femoral angle, PPTA posterior proximal tibial angle) Group A Group B Preop Postop Preop Postop HSS score (points) MPTA (degrees) LDFA (degrees) PPTA (degrees) MAD (mm) 30 a 2 a 32 a 12 b Insall-Salvati index Fig. 1 The view of a prereconstructed frame a Medial b Lateral
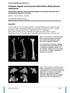
3 141 Fig. 2 a Preoperative radiographic view of a patient with severe varus. b Postoperative clinical view with maximal flexion after removal of frame. c Postoperative standing view after removal of frame. d, e Good realignment and no sign of arthritis after 88 months two patients of group B progressed to stage IV during follow-up. These patients had a medial mechanical axis postoperatively. We put in cast all patients of group A for 6 weeks. Full weight bearing was permitted after 3 months. None of the Table 2 Relationship between postoperative mechanical axis and stage of arthritis according to Ahlback Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV Group A Lateral compartment 3 Center 2 2 Medial compartment Group B Lateral compartment 22 Center 3 Medial compartment 2 patients of group B needed an external brace postoperatively. Knee and ankle exercises were initiated on the first postoperative day. Partial weight bearing was permitted with the aid of a crutch on the third postoperative day. The Ilizarov external fixator was removed at a median of 3 months (range 2 4) postoperatively. All osteotomy were healed. Patients in group B were examined more often until osteotomy was healed (on average six times in group B, three in group A). On the other hand, the circular external fixator was more expensive than Kirschner wires, buttress plate, staples, and Puddu plate. Temporary peroneal nerve palsy was observed in three patients of group A. Deep wound infection requiring débridement and antibiotherapy was detected in two patients and trombophlebitis in two. Thrombophlebitis occurred in 3 patients and pin tract infections in 11 patients of group B. All the complications healed without any sequelae by medical treatment. As a late complication, arthritis progressed to stage IV in four patients of group A and
4 142 Fig. 3 a Preoperative radiographic view of a patient with severe loss of medial joint space. b Mechanical axis pass through 11 mm medially and normal MPTA. c Notice the widening of medial compartment and no sign arthritis after 84 months in two patients of group B; these were managed by total knee replacement 5 years after their index operations due to increasing pain. In contrast to functional results, MPTA and PPTA angles and mechanical axis were determined to be statistically different between groups A and B. Discussion Unlike inflammatory diseases, medial compartment arthrosis of the knee is thought to be caused primarily by a mechanical problem. Bony deformities of the tibia or femur and dynamic deformities resulting from lateral collateral ligament laxity may lead to malalignment and arthrosis [3, 19, 20, 22]. In preoperative radiographs of patients we detected malalignment in all cases. In group A the mean preoperative mechanical axis deviation was 30 mm medial, and mean MPTA, LDFA, and PPTA were 80, 90, 79, respectively; while the mean preoperative mechanical axis deviation was 32 mm medial and mean MPTA, LDFA, and PPTA were 82, 88, and 81 in group B, respectively. Two different techniques are utilized for high tibial osteotomy. The classic Coventry technique and high tibial osteotomy carried out with a circular external fixator. These two techniques have important biomechanical differences which may lead to functional and radiological results in the long term. In the classic Coventry technique the osteotomy is performed in form of a closing wedge above the tibial tuberosity [4]. It is still the most commonly preferred method due to its safety [2, 4, 16, 17, 20, 22]. However, complications such as loss of correction, paralysis of peroneal nerve, compartment syndrome, delayed union or nonunion, and intra-articular fractures are reported in 10 60% of cases [2, 8, 9, 13, 16, 19, 20, 28, 29]. Patella infera and patellofemoral malalignment may complicate a future total knee replacement. In addition, as a result of patellar eversion rotation of proximal fragment following osteotomies performed over tibial tuberosity, patellofemoral congruence can be deteriorated, and V-Y quadriceps plasty or osteotomy of tibial tuberosity may be required during the implantation of total knee prosthesis. On the other hand, removal of cancellous bone wedge may also lead to technical problems that can arise during a total knee replacement. Although some authors have stated that they observe no problems during total knee replacement in patients with previous Coventry osteotomies, obstacles in preparing the proximal tibia, the longevity of operation time, increase in bleeding, the requirement of bony graft or special type tibial component prosthesis, and technical difficulties regarding the extensor mechanism are to be accepted [7, 11, 14, 15, 19, 20, 21, 25, 26, 27, 28]. We found patella infera in 12 patients of group A and during knee replacement in 4 patients after Coventry osteotomy; we had to perform V-Y quadriceps plasty and Fulkerson osteotomy due to extensor apparatus problem. Therefore we agree that there is some difficulty during knee replacement after Coventry osteotomy. On the other hand, the Puddu plate technique is an alternative method using a medial open-up osteotomy, but currently there no longterm results are available. After redefiniton of the concept of lower extremity deformities, Paley et al. [19] introduced a new understand-
5 143 ing of the role and technique of high tibial osteotomy in the treatment of medial compartment arthritis. According to this new concept, CORA, which is the apex of deformity in medial compartment arthritis, is localized at the level of the joint line. Therefore the osteotomy should be dome shaped, and the center must overlap with the CORA. Thus the desired amount of correction can be achieved by performing an osteotomy and a normal mechanical axis can be established without creating a second deformity [3, 19, 22]. In addition, erosion of tibial bony plateau, patella infera, and problems related to extensor mechanism do not occur. Nonunion has not been reported as a complication of this technique. In our series there was no patella infera or nonunion. Moreover, we experienced no difficulty during knee replacement in two patients 5 years after high tibial osteotomy performed with circular external fixator. The Ilizarov circular external fixator has many advantages. The most important one is that precise correction may be adjusted during the postoperative period. Initiation of early weight bearing and range of motion exercises are other advantages. Overall elasticity of the fixator allows micromotions and facilitates union. The device can also correct additional deformities, such as procurvatum, recurvatum, and disproportional extremities [3, 19, 22]. In contrast, there are some disadvantages, including cost, more frequent clinical examination, less comfortable device, pin tract infection, and the need of more experienced hands to apply this fixator [3, 19, 21]. On the other hand, Dahl et al. [5] reported that there is a significant decrease in complications as experience is gained. Twenty-seven patients in our study were operated on by an osteotomy below the tibial tuberosity using an Ilizarov-type circular external fixator. Regarding clinical and radiological assessment we found a mean 12.2-point increase in HSS score and average corrections in mechanical axis and MPTA of 28 mm and 3, respectively, in group A, while on clinical assessment a mean 19.1-point increase in HSS score was observed. In addition, on radiographic evaluation average corrections in mechanical axis and MPTA were 44 mm and 8, respectively. HSS score, mechanical axis, and MPTA were significantly better in group B (P<0.05, Student s t test). Moreover, we encountered no instance of patella infera in the patients of group B. The better results and lower complication rate in group B may be related to our long experience with the Ilizarov technique, as we have been using this technique over 10 years. Successful results obtained after treatment for varus gonarthrosis with high tibial osteotomy are time dependent. Many authors accept that success rates of 80 90% in the first 5 years. After 10 years postoperatively nearly one-half of patients require a total knee prosthesis [4, 8, 9, 16, 20, 28, 29]. These studies emphasize the importance of careful patient selection and surgical technique [4, 8, 9, 16, 20, 28, 29]. Billings et al. [2] recommend an arthroscopic guided high tibial osteotomy, rigid internal fixation, and early ambulation, while Sugita et al. [24] stress the importance of healthy cartilage on lateral tibial compartment. The finding of intact articular cartilage of lateral compartment during diagnostic arthroscopy performed prior to the osteotomy was of paramount importance in group B. We detected a higher success rate in group A after 5 years, while we found no difference between early and late functional results in group B. We believe that this continuing success of function is related to the rigid fixation provided by the Ilizarov fixator, permitting an earlier ambulation, and weight bearing. In addition, maintenance of correction during the postoperative period with the aid of external fixator and the possibility of adjusting precise correction during follow-up examinations is a key factor enabled by the circular external fixator. Moreover, we believe that mechanical axis should pass through the lateral compartment after correction to obtain good results. We determined the adequacy of the postoperative mechanical axis according to the criteria proposed by Fujisawa et al. [6]. This rating system divides the articular surface of the tibia virtually into 100 U in the horizontal plane; the ideal postoperative mechanical axis should pass through the lateral points. Many authors believe that slight overcorrection into valgus position leads to longterm favorable results [2, 3, 8, 9, 17, 19, 20, 21, 28, 29]. In these publications 2 4 of valgus is accepted as efficient. In their investigation Coventry et al. [4] observed satisfactory outcomes in only 63% of patients with varus or neutral alignment, compared to satisfactory function levels as high as 94% in knees with mechanical axes in 4 6 valgus position. Many studies report that a few degrees of overcorrection during high tibial osteotomy can prevent arthrosis. Hernigou et al. [8] reported that satisfactory results were achieved in knees corrected to 3 6 valgus without any progression in arthrosis, while results were not satisfactory in knees with less than 3 valgus accompanied by progression of arthrosis. Majima et al. [12] concluded that overcorrection slows the progression of medial compartment arthrosis and has no harmful effect on the lateral compartment. Antonescu [1] performed 250 high tibial osteotomies and reported 152 cases with excellent and good outcomes after a follow-up of 8 15 years. In this group the arthrosis did not progressed in 105 cases (69%) with a postoperative valgus of 3 6 ; in 47 cases (31%) with insufficient correction arthritis progressed. In our series only three patients in group A achieved a valgus correction of 3 6 while in group B all patients except did so. In both groups arthrosis progressed in the patients who had insufficient valgus correction. Thereafter six of them underwent total knee replacement. Therefore we agree that mechanical axis should pass through the lateral compartment of the knee to obtain good outcomes for the future. Moreover, we believe that valgus correction positively affected functional results in group B as well. In the treatment of medial compartment arthrosis the desired amount of correction can be precisely achieved with high tibial osteotomy by using an Ilizarov circular exter-
6 144 nal fixator in selective cases. Moreover, important complications observed in a classic osteotomy, such as depletion of bone stock, patella infera, and disorders of extensor mechanism, which can hazard a possible future total knee prosthesis, can be avoided. We concluded that this technique can be successfully applied in experienced hands for the treatment of varus gonarthrosis since it has a precise correction ability with a low complication rate. References 1. Antonescu DN (2000) Is knee osteotomy still indicated in knee osteoarthritis. Acta Orthop Belg 66: Billings A, Scott DF, Camorgo MP, Hoffman AA (2000) High tibial osteotomy with calibrated osteotomy guide, rigid internal fixation and early motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82: Catagni MA, Guerreshi F, Ahmad TS, Cattaneo R (1994) Treatment of genu varum in medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee using the Ilizarov method. Orthop Clin North Am 23: Coventry MB, Ilstrup DM, Walrichs SL (1993) Proximal tibial osteotomy. A critical long-term follow-up study of eighty-seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75: Dahl MT, Gulli B, Berg T (1994) Complications of limb lengthening: a learning curve. Clin Orthop 301: Fujisawa Y, Masahura K, Shiomini S (1973) The effect of high tibial osteotomy of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am 10: Haddad FS, Bentley G (2000) Total knee arthroplasty after high tibial osteotomy: a medium term review. J Arthroplasty 15: Hernigou PH, Medeivelle D, Debjre J, Goutallier D (1987) Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteen years follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69: Insall JN, Joseph DM, Msika C (1984) High tibial osteotomy for varus gonarthrosis. A long term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66: Jackson JP, Waugh W (1961) Tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br 43: Kaper BP, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Macdonald SJ (2001) Patella infera after high tibial osteotomy. J Arthroplasty 16: Majima T, Yasuda K, Katsuragi R, Kaneda K (2000) Progression of joint arthrosis 10 to 15 years after high tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop 381: Maquet P (1980) The biomechanics of the knee and surgical possibilities of healing osteoarthritic knee joints. Clin Orthop 146: Meding JB, Keating EM, Ritter MA, Faris PM (2000) Total knee arthroplasty after high tibial osteotomy. A comparison study in patients who had bilateral total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82: Mont MA, Antonardes S, Krachow KA, Hungerford DS (1994) Total knee arthroplasty after failed high tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop 299: Nagel A, Insall JN, Scuderi GR (1996) Proximal tibial osteotomy. A subjective outcome study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78: Naudi D, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Bourne TJ (1999) Survivorship of the high tibial valgus osteotomy. Clin Orthop 367: Paley D, Tetsworth K (1992) Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin Orthop 280: Paley D, Maar DC, Herzenberg JE (1994) New concepts in high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis. Orthop Clin North Am 25: Phillips MJ, Krachow KA (1998) High tibial osteotomy and distal femoral osteotomy for valgus or varus deformity around the knee. AAOS Instructional Course Lectures 47: Rinonapoli E, Mancini GB, Coruaglia A, Nusiello S (1998) Tibial osteotomy for varus gonarthrosis. Clin Orthop 353: Schwartsman V (1995) Circular external fixation in high tibial osteotomy. AAOS Instr Course Lectures 44: Sisk TD (1992) Knee injuries. In: Crenshaw AH (ed) Campbell s operative orthopaedics, 8th edn, vol 3. Mosby-Year Book, St Louis, pp Sugita T, Chiba T, Kawamatu T, Ohnuma M, Yoshizumi Y (2000) Assessment of articular cartilage of the lateral tibial plateau in varus osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee 7: Toksvig-Larsen S, Magyar G, Önsten I, Ryd L, Lindstrand A (1998) Fixation of the tibial component of total knee arthroplasty after high tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80: Trigani D, Ferrari Di Trentani P, Barbanti-Brodono G, Trentani F (2001) Patellar height after high tibial osteotomy. Int Orthop 246: Westrich GH, Peters LE, Haas SB, Buly RL, Windsor RE (1998) Patella height after high tibial osteotomy with internal fixation and early motion. Clin Orthop 354: Windsor RE, Insall JN, Vince KG (1998) Technical considerations of total knee arthroplasty after proximal tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70: Yasuda K, Majima T, Tscuhida T, Kaneda K (1992) A ten to 15 years follow-up observation of high tibial osteotomy in medial compartment osteoarthrosis. Clin Orthop 282:
High tibial osteotomy with Puddu plate for the treatment of varus gonarthrosis
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 948 954 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-006-0074-1 Mehmet Asik Cengiz Sen Bulent Kilic S. Bora Goksan Feyyaz Ciftci Omer F. Taser High tibial osteotomy with Puddu
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 948 954 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-006-0074-1 Mehmet Asik Cengiz Sen Bulent Kilic S. Bora Goksan Feyyaz Ciftci Omer F. Taser High tibial osteotomy with Puddu
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Mid Term Outcome of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
 Original Research Tarun Kumar Badam 1*, Muthukumar Balaji 2, Sathish Devadoss 3, A. Devadoss 4 1 Junior Resident, 2 Junior Consultant, 3 Senior Consultant, 4 Chief, Department of Orthopaedics, IORAS Devadoss
Original Research Tarun Kumar Badam 1*, Muthukumar Balaji 2, Sathish Devadoss 3, A. Devadoss 4 1 Junior Resident, 2 Junior Consultant, 3 Senior Consultant, 4 Chief, Department of Orthopaedics, IORAS Devadoss
21/01/10. Disclosures. Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature. Introduction. OW osteotomy and bone graft
 3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
There have been conflicting results reported in the
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity
 Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
International Journal of Orthopaedics Sciences 2018; 4(3): Apser Khan and Syed Ifthekar. DOI:
 2018; 4(3): 408-413 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 408-413 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-05-2018 Accepted: 15-06-2018 Apser Khan Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, SRMS IMS,
2018; 4(3): 408-413 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 408-413 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-05-2018 Accepted: 15-06-2018 Apser Khan Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, SRMS IMS,
Kocaoglu, Mehmet MD; Eralp, Levent MD; Sen, Cengiz MD; Cakmak, Mehmet MD; Dincyürek, Hakan MD; Göksan, S. Bora MD
 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity
 ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary?
 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:199 204 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0099-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary? Mark Eidelman
J Child Orthop (2008) 2:199 204 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0099-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE The use of the Taylor spatial frame in adolescent Blount s disease: is fibular osteotomy necessary? Mark Eidelman
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
High tibial valgus osteotomy using the Tomofix plate Medium-term results in young patients
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 360-367 ORIGINAL STUDY High tibial valgus osteotomy using the Tomofix plate Medium-term results in young patients Saeed H. ZAKI, Paul J. RAE From the Wrightington Hospital
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 360-367 ORIGINAL STUDY High tibial valgus osteotomy using the Tomofix plate Medium-term results in young patients Saeed H. ZAKI, Paul J. RAE From the Wrightington Hospital
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Assessment of the Treatment Outcomes of Dome-shaped Proximal Tibial Osteotomy in Patients with Genu Varum Referred to Razi Hospital
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of the Treatment Outcomes of Dome-shaped Proximal Tibial Osteotomy in Patients with Genu Varum Referred to Razi Hospital Saeid Tabatabaei 1, Aboozar Narimani 1, Samira Mehramiri
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of the Treatment Outcomes of Dome-shaped Proximal Tibial Osteotomy in Patients with Genu Varum Referred to Razi Hospital Saeid Tabatabaei 1, Aboozar Narimani 1, Samira Mehramiri
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities
 Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
Calculation and Correction of Secondary Translation Deformities and Secondary Length Deformities BRUNO GLADBACH, DMED*; ETIENNE HEIJENS, DMED*; JOACHIM PFEIL, PROFDMED*; DROR PALEY, MD abstract External
Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust
 Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust Douglas D.R. Naudie,* MD, FRCSC, Annunziato Amendola, MD, FRCSC, and Peter J. Fowler, MD, FRCSC From the Division of Orthopaedic
Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust Douglas D.R. Naudie,* MD, FRCSC, Annunziato Amendola, MD, FRCSC, and Peter J. Fowler, MD, FRCSC From the Division of Orthopaedic
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016
 SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
Factors Affecting the Union of Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Titanium Wedge Plate
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Ochsner Journal 16:464 470, 2016 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Factors Affecting the Union of Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Titanium Wedge Plate Husam
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Ochsner Journal 16:464 470, 2016 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Factors Affecting the Union of Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Titanium Wedge Plate Husam
Lengthening & Deformity correction with. Fixator Assisted Nailing
 Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Extra-articular deformities in TKA
 Extra-articular deformities in TKA NOV Najaarscongres Donderdag 12 oktober 2017 Veldhoven G.G. van Hellemondt, MD Sint Maartenskliniek Nijmegen The Netherlands Disclosures Consultancy ZimmerBiomet Smith&Nephew
Extra-articular deformities in TKA NOV Najaarscongres Donderdag 12 oktober 2017 Veldhoven G.G. van Hellemondt, MD Sint Maartenskliniek Nijmegen The Netherlands Disclosures Consultancy ZimmerBiomet Smith&Nephew
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease
 Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Comparing dome high tibial osteotomy for patients more than sixty years old with patients less than sixty years old
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 2 No. 5 October 2008;381-388 Original article Comparing dome high tibial osteotomy for patients more than sixty years old with patients less than sixty years old Prakit Tienboon
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 2 No. 5 October 2008;381-388 Original article Comparing dome high tibial osteotomy for patients more than sixty years old with patients less than sixty years old Prakit Tienboon
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy
 Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy LATERAL RELEASE IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FOR A FIXED VALGUS DEFORMITY J. Brilhault, S. Lautman, L. Favard, P. Burdin From Trousseau University Hospital of Tours, France
Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy LATERAL RELEASE IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FOR A FIXED VALGUS DEFORMITY J. Brilhault, S. Lautman, L. Favard, P. Burdin From Trousseau University Hospital of Tours, France
Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Results of arthroscopic surgery, with or without high Tibial osteotomy, in osteoarthritis of knee
 2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
The effect of closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope
 The effect of closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope A RETROSPECTIVE RADIOLOGICAL REVIEW OF 120 CASES H. El-Azab, A. Halawa, H. Anetzberger, A. B. Imhoff, S. Hinterwimmer From Abteilung
The effect of closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope A RETROSPECTIVE RADIOLOGICAL REVIEW OF 120 CASES H. El-Azab, A. Halawa, H. Anetzberger, A. B. Imhoff, S. Hinterwimmer From Abteilung
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
Small-wire circular fixators and hybrid external fixation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique
 Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique W-Dahl, Annette; Toksvig-Larsen, Sören Published in: Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica
Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique W-Dahl, Annette; Toksvig-Larsen, Sören Published in: Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella Treated with a Different Method in Each Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890315, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890315 Case Report Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Bilateral Congenital Dislocation of the Patella
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain
 DOI 10.1007/s11420-019-09670-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain Rachael J. Da Cunha, MD,
DOI 10.1007/s11420-019-09670-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain Rachael J. Da Cunha, MD,
Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy
 Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy M. Inan, F. Ferri-de Baros, G. Chan, K. Dabney, F. Miller From The Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for
Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy M. Inan, F. Ferri-de Baros, G. Chan, K. Dabney, F. Miller From The Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for
The coronal hypomochlion
 KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after High Tibial Osteotomy
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Modified dome shaped proximal tibial osteotomy for treatment of infantile tibia vara
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements:
 Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Modern High Tibial Osteotomy. Medial Compartment OsteoArthritis of Knee
 Modern High Tibial Osteotomy Medial Compartment OsteoArthritis of Knee Dr. Milind Chaudhary Director Int. Deformity & Lengthening Inst. Akola Consultant, Jaslok Hospital, Mumbai Imm.Past President ASAMI
Modern High Tibial Osteotomy Medial Compartment OsteoArthritis of Knee Dr. Milind Chaudhary Director Int. Deformity & Lengthening Inst. Akola Consultant, Jaslok Hospital, Mumbai Imm.Past President ASAMI
Section: Orthopaedics. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 DOI: 1.21276/aimdr.218.4.2.OR1 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Comparison Of Results Of High Tibial Osteotomy Using en Wedge Versus Close Wedge In Medial Uni- Compartmental Osteoarthritis
DOI: 1.21276/aimdr.218.4.2.OR1 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Comparison Of Results Of High Tibial Osteotomy Using en Wedge Versus Close Wedge In Medial Uni- Compartmental Osteoarthritis
Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee
 DOCTYPE = ARTICLE Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee William I. Sterett, MD,* and J. Richard Steadman, MD From the Steadman Hawkins Sports Medicine Foundation, Vail, Colorado
DOCTYPE = ARTICLE Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee William I. Sterett, MD,* and J. Richard Steadman, MD From the Steadman Hawkins Sports Medicine Foundation, Vail, Colorado
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS
 Original Article HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS Roger Avakian 1, Nilson Roberto Severino 2, Ricardo de Paula Leite Cury 3, Victor Marques de Oliveira 1, Tatsuo Aihara 4, Osmar Pedro
Original Article HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS Roger Avakian 1, Nilson Roberto Severino 2, Ricardo de Paula Leite Cury 3, Victor Marques de Oliveira 1, Tatsuo Aihara 4, Osmar Pedro
Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.019 Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up, MD Institute of Orthopaedics, Lerdsin Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.019 Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up, MD Institute of Orthopaedics, Lerdsin Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar
 Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar High Tibial Osteotomy: HTO! Valgisation HTO Intended to transfer the mechanical
Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar High Tibial Osteotomy: HTO! Valgisation HTO Intended to transfer the mechanical
Despite the expanding indications for knee arthroplasty,
 Prospective Outcomes of Young and Middle-Aged Adults With Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis Treated With a Proximal Tibial Opening Wedge Osteotomy Robert F. LaPrade, M.D., Ph.D., Stanislav I. Spiridonov,
Prospective Outcomes of Young and Middle-Aged Adults With Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis Treated With a Proximal Tibial Opening Wedge Osteotomy Robert F. LaPrade, M.D., Ph.D., Stanislav I. Spiridonov,
Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis
 Clinical Report Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(1)
Clinical Report Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(1)
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Why does it matter? Patellar Instability 7/23/2018. What is the current operation de jour? Common. Poorly taught. Poorly treated
 Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS
 STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures
 Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Su Chan Lee, MD, Kwang Am Jung, MD, Chang Hyun Nam, MD, Soong Hyun Jung, MD, Seung Hyun Hwang, MD
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:47-54 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.47 The Short-term Follow-up Results of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Using an Aescula Open Wedge Plate and
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:47-54 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.47 The Short-term Follow-up Results of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Using an Aescula Open Wedge Plate and
Malalignment can affect any of the three
 ch05_anbari:layout 1 8/20/2009 2:12 PM Page 47 C H A P T E R 5 Osteotomies: High Tibial, Distal Femoral, and Tibial Tubercle Ammar Anbari, MD Malalignment can affect any of the three compartments of the
ch05_anbari:layout 1 8/20/2009 2:12 PM Page 47 C H A P T E R 5 Osteotomies: High Tibial, Distal Femoral, and Tibial Tubercle Ammar Anbari, MD Malalignment can affect any of the three compartments of the
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Disclosures. Why Osteotomy? Osteotomies of the Knee Indications, Techniques and Outcomes
 Osteotomies of the Knee Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Tom Minas MD MS Director, Cartilage Repair Center BWH Associate Professor HMS, Boston Ma www.cartilagerepaircenter.org Disclosures Vericel (
Osteotomies of the Knee Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Tom Minas MD MS Director, Cartilage Repair Center BWH Associate Professor HMS, Boston Ma www.cartilagerepaircenter.org Disclosures Vericel (
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.13, No.3, July, 2000
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol13, No3, July, 2000 2, 3 ) : 40-12, Tel : (02) 966-1616 Fax : (02) 968-2394 E-mail : adkajs@thrunetcom 471 8, 1 2 ) (Table 1) 1 6 14, 2 1 2 1 Ender 29
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol13, No3, July, 2000 2, 3 ) : 40-12, Tel : (02) 966-1616 Fax : (02) 968-2394 E-mail : adkajs@thrunetcom 471 8, 1 2 ) (Table 1) 1 6 14, 2 1 2 1 Ender 29
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System. Surgical Technique
 Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System Surgical Technique Opening Wedge Osteotomy Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy 2 Prior to the osteotomy, a diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to verify
Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System Surgical Technique Opening Wedge Osteotomy Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy 2 Prior to the osteotomy, a diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to verify
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint: Comparison between the Aescula and TomoFix Plate
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:185-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.185 Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:185-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.185 Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Distal Femoral Osteotomy to Treat Patellar Instability with Valgus Lower Extremity Alignment in Adolescents
 Distal Femoral Osteotomy to Treat Patellar Instability with Valgus Lower Extremity Alignment in Adolescents Sheena R. Black, MD, Henry B. Ellis, MD, Philip L. Wilson, MD, David A. Podeszwa, MD LLRS Annual
Distal Femoral Osteotomy to Treat Patellar Instability with Valgus Lower Extremity Alignment in Adolescents Sheena R. Black, MD, Henry B. Ellis, MD, Philip L. Wilson, MD, David A. Podeszwa, MD LLRS Annual
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE. Limb Reconstruction System. Part B: Correction of Deformities. By Dr. S. Nayagam
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 11 Limb Reconstruction System Part B: Correction of Deformities By Dr. S. Nayagam CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE... Page
Operative Technique. by PROF. NAYAGAM. LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities
 Operative Technique by PROF. NAYAGAM LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities 11 Quick Reference Guide CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part A: General Principles Page N o I Introduction
Operative Technique by PROF. NAYAGAM LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part B: Correction of Deformities 11 Quick Reference Guide CONTENTS LIMB RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM Part A: General Principles Page N o I Introduction
Osteotomy at the distal third of tibial tuberosity with LCP L-buttress plate for correction of tibia vara
 Huang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Osteotomy at the distal third of tibial tuberosity with LCP L-buttress plate for correction of tibia vara
Huang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Osteotomy at the distal third of tibial tuberosity with LCP L-buttress plate for correction of tibia vara
Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee
 Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee BY MARK B. COVENTRY, M.D.", ROCHESTER, MINNESOTA From the Section of Orthopedic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation,
Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee BY MARK B. COVENTRY, M.D.", ROCHESTER, MINNESOTA From the Section of Orthopedic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation,
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1): pissn eissn Knee Surgery & Related Research
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Osteotomies for Cartilage Protections. Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD San Francisco, Ca
 Osteotomies for Cartilage Protections Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD San Francisco, Ca ACI/Osteotomy Osteotomy: Optimal Patient Selection Mechanical axis falls within involved compartment Mild joint space narrowing
Osteotomies for Cartilage Protections Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD San Francisco, Ca ACI/Osteotomy Osteotomy: Optimal Patient Selection Mechanical axis falls within involved compartment Mild joint space narrowing
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
Principles Starting Point Trajectory L/A/R Stable Construct. DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS 5/16/2017
 DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS Medical/Orthopaedic Publications Editorial/Governing Board OTA Newsletter Editor OsteoSynthesis, The JOT Online Discussion Forum Editor JOT Associate Editor JAAOS
DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS Medical/Orthopaedic Publications Editorial/Governing Board OTA Newsletter Editor OsteoSynthesis, The JOT Online Discussion Forum Editor JOT Associate Editor JAAOS
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Large segmental defects of the tibia caused by highenergy. Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children
 PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
PATIENT INFORMATION Gentle Guided Growth to Correct Knock Knees and Bowed Legs in Children The Guided Growth System eight-plate quad-plate INTRODUCTION Children need gentle guidance and correction in many
Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip
 Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip DG Nabi, MS, TS Rashid, MS, KK Ahmed, MS Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College, Srinagar, India ABSTRACT
Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip DG Nabi, MS, TS Rashid, MS, KK Ahmed, MS Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College, Srinagar, India ABSTRACT
Chronic patellar dislocation in adults
 CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate. 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique
 Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning HTO Body weight < 100 kg, Non smoker. For preoperative planning be aware of potential femoral
Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning HTO Body weight < 100 kg, Non smoker. For preoperative planning be aware of potential femoral
