Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy
|
|
|
- Hubert Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Correction of rotational deformity of the tibia in cerebral palsy by percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy M. Inan, F. Ferri-de Baros, G. Chan, K. Dabney, F. Miller From The Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, USA A percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy with multiple drill holes and closed osteoclasis was used to correct rotational deformities of the tibia in patients with cerebral palsy. The technique is described and the results in 247 limbs (160 patients) are reported. The mean age at the time of surgery was 10.7 years (4 to 20). The radiographs were analysed for time to union, loss of correction, and angulation at the site of the osteotomy. Bone healing was obtained in all patients except one in a mean period of seven weeks (5 to 12). Malunion after loss of reduction at the site of the osteotomy developed in one tibia. Percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy of the tibia is a safe and simple surgical procedure. M. Inan, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon Orthopaedic Department Inonu University Medical Faculty, Malataya 44069, Turkey. F. Ferri-de Baros, MD, Research Fellow G. Chan, MD, Research Fellow K. Dabney, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon F. Miller, MD, Orthopaedic Surgeon Orthopaedic Department Alfred I. DuPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, Delaware 19899, USA. Correspondence should be sent to Dr M. Inan at Inonu University Medical Faculty, Turgut Özal Tip Merkezi, Ortopedi Bölümü, Elazig yolu 10.km, Malata, Turkey; minan@inonu.edu.tr 2005 British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery doi: / x.87b $2.00 J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2004;87-B: Received 5 May 2005; Accepted after revision 14 June 2005 Rotational deformity of the tibia is a common problem in patients with cerebral palsy and may result in an inefficient pattern of gait. 1,2 Derotation osteotomy of the tibia may be used to improve gait 3-8 when conservative treatment with splints or shoe modifications is ineffective Various surgical techniques have been described. These differ with regard to the level of the osteotomy, the method of fixation using a cast with or without a Kirschner (K-) wire, 5 Steinmann pin, 10 a staple, 7 plating, 8 an intramedullary nail 13 or external fixation, 14 and whether osteotomy of the fibula is performed. 15,16 Successful results have been reported with all of these techniques, but complications such as delayed union, nonunion, malunion, nerve palsy and compartment syndrome have been described. 17,18 The ideal technique would be one which provides union with a low rate of complications and minimal surgical trauma. The senior author (FM) therefore began to perform percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy using multiple percutaneous drill holes. Stabilisation of the site of the osteotomy and maintenance of correction were achieved by a proximal tibial pin incorporated in a short-leg cast. In this study we describe this technique and evaluate the results of 160 patients who underwent this procedure. Patients and Methods We performed a retrospective review of patients with cerebral palsy who underwent this procedure between January 1991 and December A total of 181 sets of notes were reviewed. There were 12 patients with insufficient data, seven with a follow-up of less than 12 months and two in whom fibular osteotomy had been performed intra-operatively because of an external rotation deformity of 60 which were excluded from the study. The remaining 160 (76 females and 84 males) with 247 derotation osteotomies (81 unilateral and 79 bilateral) were included. Inclusion criteria were an internal or external tibial rotation deformity causing functional disability and a distal tibial osteotomy performed without fibular osteotomy. Eight osteotomies in seven patients (six unilateral and one bilateral) had to be repeated and each was evaluated individually. The mean age at the time of operation was 10.7 years (4 to 20). All the patients were able to walk to a variable degree with or without an assistive device. Twenty were hemiplegic, 108 diplegic, and 32 were quadriplegic. The mean number of additional operations was 2.4 (0 to 6) for each leg including soft-tissue procedures, osteotomies in the foot, derotation osteotomies of the femur, and Dega pelvic osteotomies. Thirty-four limbs had a tibial derotation osteotomy alone, 36 had one additional operation, 56 two, 58 three, 43 four, 15 five, and four six. Clinical assessment. Rotational deformity was assessed clinically by measuring the thigh-foot angle. 19 The measurements were made using a goniometer with the patient prone and the hips VOL. 87-B, No. 10, OCTOBER
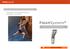
2 1412 M. INAN, F. FERRI-DE BAROS, G. CHAN, K. DABNEY, F. MILLER a Fig. 1 Photographs of a five-year-old patient showing a) internal tibial torsion, b) the determination of the level of osteotomy using fluoroscopy and c) a skin incision 0.5 cm in length made on the medial side of the tibia 1 to 2 cm proximal to the distal tibial epiphysis. extended, the knees flexed to 90 and the ankles in the neutral position. Ankle movement was recorded post-operatively and at the last follow-up. Radiological assessment. Radiographs were analysed for time to union, loss of correction, and maximum angulation at b c the site of the osteotomy in both the sagittal and coronal planes. Operative technique. The patient was placed supine on the operating table under general anaesthesia. After determination of the level of the osteotomy using fluoroscopy, a skin incision 0.5 to 1 cm in length was made on the medial side of the tibia 1 to 2 cm proximal to the distal tibial epiphysis (Fig. 1). The osteotomy was then performed by making multiple drill holes, typically six to ten, using a 3.2 mm drill bit (Fig. 2) and completed by angular bending of the bone in the anteroposterior (AP) direction (Fig. 2a). The osteotomy was then confirmed by fluoroscopy (Fig. 2b). Rotational bending was not performed in order to prevent the formation of an oblique osteotomy. A 1.5 or 2.0 mm K- wire was passed from lateral to medial at the level of the distal part of the tibial tuberosity, parallel to the tibial plateau to control rotation in the cast. Derotation was performed by slowly rotating the foot until a thigh-foot angle of 0 was achieved (Fig. 3). The measurement of the thighfoot angle intra-operatively was made with the patient in the supine position with the hip and knee in 90 of flexion, and the foot in neutral. To achieve a zero thigh-foot angle, rotational correction was made until the longitudinal axes of the foot and the thigh were identical. It was important to control derotation carefully by holding the heel and not the forefoot in order to obtain accurate rotation through the tibia. A short-leg cast was then applied with the proximal tibial K-wire incorporated in the cast to maintain correction. A radiograph was taken at the end of the operation to check the alignment of the tibia. The time of surgery from incision to closure of the wound was recorded for patients who had an isolated tibial derotation osteotomy. Post-operative management. Post-operative mobilisation mainly depended on the number and nature of the associated procedures performed. With an isolated distal tibial osteotomy the patient was allowed to walk bearing weight as tolerated on the first post-operative day. The K-wire was Fig. 2a Fig. 2b Photographs showing a) angular bending of the bone in the anteroposterior direction to complete the osteotomy and b) confirmation of the osteotomy by fluoroscopy. THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
3 CORRECTION OF ROTATIONAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA IN CEREBRAL PALSY BY PERCUTANEOUS SUPRAMALLEOLAR OSTEOTOMY 1413 Fig. 3 Diagrams showing a derotation done by slowly rotating the foot until a thigh foot angle of 0 is obtained. removed, without anaesthesia, in the clinic when formation of callus was seen on the radiographs at approximately three to four weeks after operation. The cast was removed when there was bone healing, defined as the presence of callus bridging three cortices in two radiographic planes (AP and lateral). The patients were then allowed to bear weight fully. Results The mean follow-up was 4.6 years (1 to 13) and the mean time to union was seven weeks (5 to 12). The mean duration of surgery recorded from 34 isolated procedures was eight minutes (5 to 15). A total of 103 external derotation osteotomies was performed for internal torsion (mean 24 ; 8 to 55 ) and 144 internal derotation osteotomies for external torsion (mean 33 ; 10 to 45 ). A neutral (0 ) thighfoot angle was obtained in all tibiae intra-operatively. At the last follow-up, the mean thigh-foot angle was 3 (30 internal to 28 external) in the externally-rotated group and 9 (20 internal to 45 external) in the internally-rotated group. Intra-operatively, extension of the osteotomy into the ankle joint occurred in one tibia in a patient aged 16 years. A short-leg cast was used to stabilise the fracture and the patient was not allowed to bear weight until fracture callus was seen at the site of the osteotomy. Bony union occurred in ten weeks without further complications. The osteotomy extended proximally in two tibiae but bone healing was obtained without complications in both. Loss of reduction of > 5 was seen in eight tibiae postoperatively and was corrected by modification of the cast. Malunion following loss of reduction at the site of the osteotomy developed in one tibia. This patient, who was aged six years, developed a varus angulation of 12 and recurvatum of 16. Further surgery was not performed and at the time of the latest follow-up at three years there was still 7 of varus and 6 of recurvatum. Delayed union developed in four tibiae (two patients). One patient, aged 14 years, had a higher level of osteotomy, but union was obtained in 12 weeks without any surgical intervention. The second, aged 16 years, also had a higher level of osteotomy and spontaneous union developed with weight-bearing 12 weeks after surgery. In a third patient, aged 14 years, who also had a higher level of osteotomy, no signs of bone healing were noted on radiographs taken at ten weeks after operation. This patient was treated by a reamed intramedullary nail and union was obtained after eight weeks. During the early period of follow-up, temporary stiffness of the ankle was noted in nine joints. These patients had had a subtalar fusion and lengthening of the lateral column with or without a soft-tissue procedure in addition to the derotational osteotomy. None of the patients showed stiffness at the last follow-up. Complications. Complications recorded in the charts included pin-track infection, which was graded according to Paley s classification, 20 wound infection, displacement of the osteotomy, delayed union, nonunion, loss of reduction, malunion of > 5, refracture and early arrest of growth. Grade 3 infection occurred in one pin site and was treated by curettage and debridement, with oral antibiotics. There was no residual infection at follow-up. None of the patients developed infection at the site of the osteotomy, refracture, or early growth arrest. Discussion Rotational deformity of the tibia requiring surgical correction commonly occurs in patients with cerebral palsy. Recently, derotation osteotomy through the distal tibia has become the treatment of choice, but significant rates of complications (4.8% to 10%) have been reported. 17,18 Our study shows that a closed osteotomy after percutaneous drilling can be used to correct up to 45 of either external or internal rotation of the tibia in patients aged between four and 20 years. Maintenance of correction and stabilisation of the osteotomy are crucial for a successful result. Different methods have been advocated. Casting may result in loss of correction. Rattey and Hyndman 15 found that 17% of patients required repeat manipulation for excessive angulation after distal tibial osteotomy stabilised by a long-leg cast without internal fixation. Banks and Evans 17 developed a simple transverse osteotomy stabilised by a threaded pin incorporated in the cast and reported no cases of malunion. Dodgin et al 5 treated 63 limbs with distal tibial/fibular osteotomies which were stabilised by two crossed K-wires and a longleg cast. They did not report any loss of reduction but the total time of immobilisation was nine weeks. McNicol et al 7 used a single staple with a long-leg cast for three to four weeks to stabilise the supramalleolar osteotomy. Although they did not report any incidence of malunion, this was an open surgical procedure. Selber et al 8 preferred to use a T-plate and reported nonunion in two of 57 patients and an VOL. 87-B, No. 10, OCTOBER 2005
4 1414 M. INAN, F. FERRI-DE BAROS, G. CHAN, K. DABNEY, F. MILLER early arrest of growth in one. They concluded that their technique allowed early mobilisation and a high rate of bone healing. In our series, nonunion developed in one of 247 osteotomies and patients were allowed to bear weight early in a short-leg cast. Various levels have been used for derotation osteotomies in the tibia. Proximal osteotomies have been noted to have a higher risk of peroneal nerve injury and compartment syndrome. Diaphyseal osteotomies have the disadvantage of delayed or nonunion and often require the use of plates or intramedullary nails for stabilisation the site of the osteotomy. Recent reports suggest that an osteotomy at the supramalleolar level is the ideal for a derotation osteotomy of the tibia. 3-5,8,16 The need for an osteotomy of the fibula remains controversial. Some authors have reported that the intact fibula adds stability and prevents loss of fixation. 16,21 In our study, loss of reduction was noted in eight osteotomies (3.2%) after full weight-bearing. However, all the patients were treated successfully by modification of the cast and did not need further surgery. On the other hand, Manouel and Johnson 16 stated that leaving the fibula intact may cause recurrence of the rotational deformity. The reason for this is still unclear. It is clearly multifactorial, and may include muscle spasticity and foot deformity. 15,17,22 Theoretically, excessive derotation of the distal tibia in the presence of an intact fibula can lead to incongruity of the ankle. 23 In our study, stiffness of the ankle occurred after osteotomies of the foot performed at the same time as derotational osteotomy of the tibia. We have not seen any incidence of stiffness and performed correction of up to 45 of external and 55 of internal rotation. The maximum amount of derotation which can be achieved without a fibular osteotomy has not been clearly described. Lloyd-Roberts, Swann and Catterall 24 carried out a derotation on a child with club foot who had an internal rotation deformity of 45 without doing a fibular osteotomy. Asirvatham et al 21 performed derotation in 51 patients with poliomyelitis using O Donoghue s technique of mid-diaphyseal tibial osteotomy with an intact fibula. Their patents had internal rotation deformities which ranged from 30 to 90 (mean 57 ). Full correction was achieved in all patients. Two patients who had external rotation of 60 were excluded from our series. They required fibular osteotomy in addition to the supramalleolar osteotomy in order to achieve full correction. In all other patients who had an external rotation deformity of < 45 or an internal rotation deformity of < 55, full correction was achieved without an osteotomy of the fibula. Nonunion in the tibial metaphysis is rare. Delayed union and nonunion after supramalleolar osteotomy have been described infrequently regardless of the technique. 8,18 In our series, older age and a higher level of osteotomy appear to be important risk factors for delayed union. All the patients with delayed union were older than 14 years and the level of osteotomy was higher than in other patients. Open techniques are more invasive and may carry an increased risk of local infection. 8,16,18 In our study there was no superficial or deep infection at the site of the osteotomy. Pin-site infection can occur in the proximal tibia, but only one site required surgical treatment and all healed without sequelae. Arrest of growth after distal derotational osteotomy has been reported rarely. 7,15 Early arrest of growth was related to damage to the growth plate during osteotomy or application of the fixation device. There have been no cases in our series at the latest follow-up. An intra-articular fracture occurred in a 16-year-old girl while performing the supramalleolar osteotomy. After this complication, we used more drill holes in older patients to avoid this complication. Our results demonstrate that percutaneous supramalleolar osteotomy with multiple drill holes is a safe and simple surgical procedure. Using this technique, external rotation of the tibia of 45 or internal rotation of 55 can be corrected without a fibular osteotomy. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. References 1. Dunteman RC, Vankoski SJ, Dias LS. Internal derotation osteotomy of the tibia: pre- and postoperative gait analysis in persons with high sacral myelomeningocele. J Pediatr Orthop 2000;20: Stefko RM, de Swart RJ, Dodgin DA, et al. Kinematic and kinetic analysis of distal derotational osteotomy of the leg in children with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop 1998;18: Bennett JT, Bunnell WP, MacEwen GD. Rotational osteotomy of the distal tibia and fibula. J Pediatr Orthop 1985;5: Charki E, Pilliard D, Taussig G. Supramalleolar derotation osteotomy for torsion of the leg in children and adolescents: techniques and results. Ann Chir 1992;46:501-6 (in French). 5. Dodgin DA, De Swart RJ, Stefko RM, Wenger DR, Ko JY. Distal tibial/fibular derotation osteotomy for correction of tibial torsion: review of technique and results in 63 cases. J Pediatr Orthop 1998;18: King HA, Staheli LT. Torsional problems in cerebral palsy. Foot Ankle 1984;4: McNicol D, Leong JC, Hsu LC. Supramalleolar derotation osteotomy for lateral tibial torsion and associated equinovarus deformity of the foot. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1983;65-B: Selber P, Filho ER, Dallalana R, et al. Supramalleolar derotation osteotomy of the tibia, with T plate fixation: technique and results in patients with neuromuscular disease. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2004;86-B: Knittel G, Staheli LT. The effectiveness of shoe modifications for intoeing. Orthop Clin North Am 1976;7: Staheli LT. Torsion: treatment indications. Clin Orthop 1989;247: El-Said NS. Osteotomy of the tibia for correction of complex deformity. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1999;81-B: Steel HH SR, Sullivan PD. Complications of tibial osteotomy in children for genu varum or valgum. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1971;53-A: Kempf I, Dagrenat D, Kloos M. Correction osteotomy and stabilization with the interlocking nail. Unfallchirurg 1990;93: (in German). 14. Mylle J, Lammens J, Fabry G. Derotation osteotomy to correct rotational deformities of the lower extremities in children: a comparison of three methods. Acta Orthop Belg 1993;59: Rattey T, Hyndman J. Rotational osteotomies of the leg: tibia alone versus both tibia and fibula. J Pediatr Orthop 1994;14: Manouel M, Johnson LO. The role of fibular osteotomy in rotational osteotomy of the distal tibia. J Pediatr Orthop 1994;14: Banks SW, Evans EA. Simple transverse osteotomy and threaded-pin fixation for controlled correction of torsion deformities of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1955; 37-A: Payman KR, Patenall V, Borden P, Green T, Otsuka NY. Complications of tibial osteotomies in children with comorbidities. J Pediatr Orthop 2002;22: THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
5 CORRECTION OF ROTATIONAL DEFORMITY OF THE TIBIA IN CEREBRAL PALSY BY PERCUTANEOUS SUPRAMALLEOLAR OSTEOTOMY Staheli LT, Corbett M, Wyss C, King H. Lower-extremity rotational problems in children: normal values to guide management. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1985;67-A: Paley D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop 1990;250: Asirvatham R, Watts HG, Rooney RJ. Rotation osteotomy of the tibia after poliomyelitis: a review of 51 patients. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1990;72-B: Staheli LT. Rotational problems in children. Instr Course Lect 1994;43: Magnusson R. Rotational osteotomy: a method employed in cases of congenital club-foot. J Bone Joint Surg 1946;28: Lloyd-Roberts GC, Swann M, Catterall A. Medial rotation osteotomy for severe residual deformity in club foot: a preliminary report on a new method of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1974;56-B: VOL. 87-B, No. 10, OCTOBER 2005
Supramalleolar derotation osteotomy of the tibia, with T plate fixation
 Supramalleolar derotation osteotomy of the tibia, with T plate fixation TECHNIQUE AND RESULTS IN PATIENTS WITH NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASE P. Selber, E. R. Filho, R. Dallalana, M. Pirpiris, G. R. Nattrass, H.
Supramalleolar derotation osteotomy of the tibia, with T plate fixation TECHNIQUE AND RESULTS IN PATIENTS WITH NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASE P. Selber, E. R. Filho, R. Dallalana, M. Pirpiris, G. R. Nattrass, H.
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Modified dome shaped proximal tibial osteotomy for treatment of infantile tibia vara
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Geith MAA. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):394-399 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164175
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018
 Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
10/26/2017. Comprehensive & Coordinated Orthopaedic Management of Children with CP. Objectives. It s all about function. Robert Bruce, MD Sayan De, MD
 Comprehensive & Coordinated Orthopaedic Management of Children with CP Robert Bruce, MD Sayan De, MD Objectives Understand varying levels of intervention are available to optimize function of children
Comprehensive & Coordinated Orthopaedic Management of Children with CP Robert Bruce, MD Sayan De, MD Objectives Understand varying levels of intervention are available to optimize function of children
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Torsional Deformity (Rotational
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
management of sports injuries
 Br J Sp Med 1991; 25(4) Internal fixation of closed tibial fractures for the management of sports injuries A. Abdel-Salam FRCS, K. S. Eyres* FRCS and J. Cleary FRCS Department of Orthopaedics, Huddersfield
Br J Sp Med 1991; 25(4) Internal fixation of closed tibial fractures for the management of sports injuries A. Abdel-Salam FRCS, K. S. Eyres* FRCS and J. Cleary FRCS Department of Orthopaedics, Huddersfield
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Neurologic Damage. The most common neurologic injury following intramedullary tibial nailing is injury to the peroneal nerve.
 COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Theuseofgaitanalysisin orthopaedic surgical treatment in children with cerebral palsy
 Theuseofgaitanalysisin orthopaedic surgical treatment in children with cerebral palsy Aim of treatment Correction of functional disorder Requires analysis of function Basis for decision making Basis for
Theuseofgaitanalysisin orthopaedic surgical treatment in children with cerebral palsy Aim of treatment Correction of functional disorder Requires analysis of function Basis for decision making Basis for
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
Instructional Course Lecture 2011
 Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
PediLoc Tibia Surgical Technique
 PediLoc Tibia PediLoc Tibia Surgical Technique The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the author s suggested treatment for an uncomplicated procedure.
PediLoc Tibia PediLoc Tibia Surgical Technique The technique description herein is made available to the healthcare professional to illustrate the author s suggested treatment for an uncomplicated procedure.
Distal tibial physeal arrest after meningococcal septicaemia
 CHILDREN S ORTHOPAEDICS Distal tibial physeal arrest after meningococcal septicaemia MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME IN SEVEN ANKLES F. P. Monsell, J. R. Barnes, R. Kirubanandan, A. M. B. McBride From Bristol Royal
CHILDREN S ORTHOPAEDICS Distal tibial physeal arrest after meningococcal septicaemia MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME IN SEVEN ANKLES F. P. Monsell, J. R. Barnes, R. Kirubanandan, A. M. B. McBride From Bristol Royal
Supramalleolar wedge osteotomy: a method of correcting fixed equinus and associated deformities in children
 The Foot 15 (2005) 33 39 Supramalleolar wedge osteotomy: a method of correcting fixed equinus and associated deformities in children John E. Handelsman, Jacob Weinberg Schneider Children s Hospital, Division
The Foot 15 (2005) 33 39 Supramalleolar wedge osteotomy: a method of correcting fixed equinus and associated deformities in children John E. Handelsman, Jacob Weinberg Schneider Children s Hospital, Division
GREENS SURGICALS. Redefining Excellence INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR
 GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Tibia fractures are the third most common long bone
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elastic Intramedullary Nailing Versus Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Andrew T. Pennock, MD,*w Tracey P. Bastrom, MA,w and Vidyadhar V. Upasani, MD*w
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elastic Intramedullary Nailing Versus Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Pediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Andrew T. Pennock, MD,*w Tracey P. Bastrom, MA,w and Vidyadhar V. Upasani, MD*w
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Small-wire circular fixators and hybrid external fixation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
In-toeing and Out-toeing
 In-toeing and Out-toeing What is all the fuss about? Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
In-toeing and Out-toeing What is all the fuss about? Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Treatment of Diaphysio-Metaphyseal Fracture of Tibia by Intramedullary Nail in Combination with Poller Screw
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2469-6684.10001 Treatment of Diaphysio-Metaphyseal Fracture of Tibia by Intramedullary Nail in Combination with Poller Screw Ram Kewal
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2469-6684.10001 Treatment of Diaphysio-Metaphyseal Fracture of Tibia by Intramedullary Nail in Combination with Poller Screw Ram Kewal
Surgical Technique. Fibula Rod System
 Surgical Technique Fibula Rod System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve patient
Surgical Technique Fibula Rod System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve patient
Toe walking gives rise to parental concern. Therefore, toe-walkers are often referred at the 3 years of age.
 IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
Modern Rx of Polio. with Ilizarov & new techniques
 Modern Rx of Polio with Ilizarov & new techniques Poliomyelitis Best Teacher of Orthopaedics Teaches Thorough clinical examination Muscle charting Gait Analysis Analysis of Joint Instability Precision
Modern Rx of Polio with Ilizarov & new techniques Poliomyelitis Best Teacher of Orthopaedics Teaches Thorough clinical examination Muscle charting Gait Analysis Analysis of Joint Instability Precision
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Flexitsystem. - Description Flexitsystem solution - Ancillaries, instruments. Surgical technique for HTO lateral external closing wedge
 Surgical technique for HTO lateral external closing wedge - Description solution - Ancillaries, instruments Solution for closing high tibial osteotomy Genu varum: pathology Genu varum is a deformation
Surgical technique for HTO lateral external closing wedge - Description solution - Ancillaries, instruments Solution for closing high tibial osteotomy Genu varum: pathology Genu varum is a deformation
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS
 TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing
 Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity
 REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (3): 271 275 271 Fibula-related complications during bilateral tibial lengthening 60 patients followed for mean 5 years Seung-Ju Kim, Mandar Vikas Agashe, Sang-Heon Song, and
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE CHILDREN
 DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
DISPLACED FRACTURES OF THE LATERAL HUMERAL CONDYLE IN CHILDREN ALAN N. CONNER and M. G. H. SMITH, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Royal Hospital for Sick Chikl,-e,i, Glasgow Fracture of the lateral humeral
The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent Genu Varum
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:92-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.92 The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:92-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.92 The Efficacy of Percutaneous Lateral Hemiepiphysiodesis on Angular Correction in Idiopathic Adolescent
Orthotic Correction of Blount's Disease
 Orthotic Correction of Blount's Disease by Terry J. Supan, C.P.O. John M. Mazur, M.D. INTRODUCTION Infantile tibia vara is the result of abnormal growth in the proximal tibial epiphyseal late of the tibial
Orthotic Correction of Blount's Disease by Terry J. Supan, C.P.O. John M. Mazur, M.D. INTRODUCTION Infantile tibia vara is the result of abnormal growth in the proximal tibial epiphyseal late of the tibial
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity
 Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity F. E. Bilen, M. Kocaoglu, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul Medical School, Istanbul
Lengthening & Deformity correction with. Fixator Assisted Nailing
 Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D.,
 Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D., Director of the Paley Advanced Limb Lengthening Institute at St. Mary s Hospital in West Palm Beach, Florida. Located
Multiple Exostoses / Multiple Osteochondroma of the Lower Limb Guide By Dror Paley M.D., Director of the Paley Advanced Limb Lengthening Institute at St. Mary s Hospital in West Palm Beach, Florida. Located
MiniRail System. Part B: Foot Applications. By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito
 Q U I C K R E F E R E N C E G U I D E 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ORDERING INFORMATION MiniRail System Kit, M190C Contents: M 101 Standard
Q U I C K R E F E R E N C E G U I D E 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ORDERING INFORMATION MiniRail System Kit, M190C Contents: M 101 Standard
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
A New Benchmark in Tibial Fixation
 PediLoc T I B I A S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E A New Benchmark in Tibial Fixation Multiple plate designs for more options in osteotomies and fracture fixation Engineered from exclusive data resulting
PediLoc T I B I A S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E A New Benchmark in Tibial Fixation Multiple plate designs for more options in osteotomies and fracture fixation Engineered from exclusive data resulting
V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate
 Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Case Study: Christopher
 Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Changes in lower limb rotation after soft tissue surgery in spastic diplegia
 Acta Orthopaedica 2010; 81 (2): 245 249 245 Changes in lower limb rotation after soft tissue surgery in spastic diplegia 3-dimensional gait analysis in 28 children Bjørn Lofterød 1 and Terje Terjesen 2
Acta Orthopaedica 2010; 81 (2): 245 249 245 Changes in lower limb rotation after soft tissue surgery in spastic diplegia 3-dimensional gait analysis in 28 children Bjørn Lofterød 1 and Terje Terjesen 2
A comparative study of locking plate by MIPO versus closed interlocking intramedullary nail in extraarticular distal tibia fractures
 2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy
 Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL
 C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace
 18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease
 Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Combined technique for the correction of lower-limb deformities resulting from metabolic bone disease M. Kocaoglu, F. E. Bilen, C. Sen, L. Eralp, H. I. Balci From Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia. Case Report and Review of the Literature
 The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 23:387 391 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Correction of Tibia Vara With Six-Axis Deformity Analysis and the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman,
Fibula Rod System. Lateral Malleolus Fracture Indications:
 Fibula Rod System Fibula Rod System Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions for the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Fibula Rod System Fibula Rod System Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions for the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Original Research Article
 TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures
 Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Trauma Factors affecting fracture healing after intramedullary nailing of the tibial diaphysis for closed and grade I open fractures G. I. Drosos, M. Bishay, I. A. Karnezis, A. K. Alegakis From Royal United
Technique Guide. 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
