Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee
|
|
|
- Daniela Snow
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOCTYPE = ARTICLE Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee William I. Sterett, MD,* and J. Richard Steadman, MD From the Steadman Hawkins Sports Medicine Foundation, Vail, Colorado Background: Treatment of patients with degenerative knees and varus malalignment presents a difficult clinical problem. Hypothesis: Combining a medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with the microfracture chondral resurfacing procedure is a viable treatment option. Study Design: Retrospective review of prospectively collected data. Methods: A group of 38 consecutive patients (mean age, 51.3 years; range, 34 to 72 years; 29 men and 10 women) with varus malalignment and chondral lesions who were treated with chondral resurfacing (an abrasion and microfracture technique) combined with a medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. All patients had >5 of varus malalignment. Patients were evaluated preoperatively with the Lysholm and Western Ontario & McMasters Universities Osteoarthritis Index scoring systems and at a minimum of 2 years follow-up. Results: Thirty-three of 38 patients (87%) were available for 2-year follow-up (average, 45 months; range, 24 to 80 months). Lysholm scores improved from a preoperative score of 43.5 to 78.0 at follow-up; Western Ontario & McMasters Universities Osteoarthritis Index scores improved from 45.8 to The average Tegner score was 5.0. Conclusions: Combining a medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with the microfracture chondral resurfacing procedure in the varus knee is an effective method of decreasing pain and increasing function at a minimum of 2 years follow-up. Keywords: high tibial osteotomy; chondral resurfacing; microfracture; degenerative knee; varus malalignment *Address correspondence to William I. Sterett, MD, Steadman- Hawkins Clinic, 181 W. Meadow Drive, Suite 400, Vail, CO Presented at the annual meeting of the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine, Sun Valley, Idaho, June The American Journal of Sports Medicine, Vol. 32, No. 5 DOI: / American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine Beginning in 1981, chondral resurfacing procedures of articular cartilage defects have been performed extensively. Techniques currently used for chondral resurfacing of articular cartilage defects include abrasion with or without microfracture, 4,20,25,26 dowel-type plugs such as mosaicplasty or OATS, 12,15 and dowel plugs with allograft or autologous cell transfer. 23 These techniques are all used commonly and seem to be beneficial in the acutely damaged nonarthritic knee. In the past, an unloading osteotomy helped to decrease the pressure on the articular surface of degenerative knees with varus malalignment. 1,5,6,7,8,14,16,22 Procedures such as shortening an already shortened leg, problems with the proximal tibiofibular joint, operating in and around the peroneal nerve, 24 and the closing wedge osteotomy concerned us. We began performing an opening wedge osteotomy on the medial side of the proximal tibia in conjunction with a chondral resurfacing procedure in the degenerative varus knee in This combination produced more accurate realignment, extensile incisions that should not complicate total knee arthroplasty if necessary in the future, and restoration of the native height to the tibia. The purpose of this study was to determine the outcome of patients with varus malalignment who underwent a chondral resurfacing procedure and a high tibial osteotomy. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patient Population Between 1995 and 1997, 38 patients (28 men and 10 women; average age, 51.3 years; range, 34 to 79 years) underwent an open wedge high tibial osteotomy with a chondral resurfacing procedure by an abrasion technique and microfracture. Patients were candidates for the above procedure when (1) medial chondral degeneration was present; (2) varus malalignment was present, in which the patients weightbearing axis measured >5 of varus or their weightbearing line fell in the medial third of the tibial plateau, or the weightbearing axis was not fully in the medial third of the tibia but the entire meniscus had been previously excised; (3) the chief complaint was medial sided knee pain; and (4) the desired Tegner activity score was 4 or greater. A grade 4 Tegner score corresponds to moderate work or recreational sports. If the chief com- 1243
2 1244 Sterett and Steadman The American Journal of Sports Medicine TABLE 1 Patient Treatment History and Associated Pathologies Number of Patients Previous surgeries None 11 One 11 Two or greater 16 Pathologies at osteotomy ACL (no reconstructions) 4 Medial meniscal 23 Lateral meniscal 8 Chondral pathology Medial compartment 37 Lateral compartment 6 Patella/trochlear groove 5 plaint was medial side knee pain, the presence of patellofemoral arthrosis was not a factor in the algorithm for patient selection. Treatment history of the study patients is summarized in Table 1. Before the surgical procedure, all patients completed subjective self-administered evaluation forms to provide Lysholm 17 and Western Ontario & McMasters Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) 3 scores. Patients completed the same forms and reported their Tegner activity level at follow-up. Figure 1. Weightbearing axis connecting center of the hip to the center of the ankle. Alignment Measurements The weightbearing axis of the knee is defined by the angle subtended by a line from the center of the hip to the center of the knee and continued to the center of the ankle. Hsu 13 found that this angle was 1.2 of varus in 120 normal knees. Our way of drawing the lines is slightly different. We draw a line from the center of the hip to the center of the ankle 10 and mark where the line falls at the level of the tibial plateau (Figure 1). In performing an osteotomy, rather than correcting to a particular angle on the anatomic axis, we attempt to move this line to the base of the lateral tibial spine. This line correction shifts the weight to the lateral compartment of the knee. Roughly, it is a 4 correction from normal (typically, measuring 3 of valgus on the weightbearing axis). Surgical Technique The patient was placed supine on the operating room table. The head of the bed was reversed to the foot to allow for fluoroscopic visualization from the hip to the ankle. Diagnostic arthroscopy was performed including assessments of the patellofemoral joint and the medial and the lateral compartments. The lateral compartment was evaluated. If extensive grade 4 changes were seen in the lateral compartment, we did not perform the osteotomy. If Grade 4 changes were present but small, less than 2 cm, we still performed an osteotomy but did not overcorrect beyond neutral as we would for a knee without chondral changes in the lateral compartment. The extent of Grade 4 changes in the medial compartment was evaluated. Any concomitant pathology, such as meniscal tear, was treated. Surgical findings at the time of osteotomy are detailed in Table 1. The chondral resurfacing was begun with trimming any loose flaps of unstable articular cartilage back to a stable rim. This area defined the extent of the lesion (Figure 2). A rough shave was performed in an attempt to generate punctate bleeding from the subchondral bone. A 45 arthroscopic (microfracture) awl (Linvatec, Largo, Fla) was used to make several 2-mm holes in the subchondral bone. These holes were placed as close together as possible without breaking into each other. When the fluid pressure was decreased and good bleeding was seen from each of the microfracture holes, the arthroscope was removed from the knee and the portals were closed. The leg was prepared again with Betadine, and another sterile extremity drape was applied. Following esmarch exsanguination, the tourniquet was inflated to 250 mm Hg. The external fixator pins (Dynafix, EBI, Warsaw, Ind) were placed approximately 1 cm below the level of the articular surface, parallel to the joint. Using the fixator as a guide, we placed distal pins in a bicortical fashion through the midtibia (Figure 3). Then, we removed the fixator so that the osteotomy could be performed. Beginning 2 cm below the pin sites, a small 2-cm incision was made in a longitudinal fashion beginning approx-
3 Vol. 32, No. 5, 2004 Chondral Resurfacing 1245 Figure 2. Grade 4 chondral degeneration of the medial femoral condyle and tibial plateau. Figure 4. A large borehole was drilled in the medial tibia, and a 3.2-mm drill bit was used to create multiple holes. Figure 3. The fixator was used as a guide to place distal pins. imately 3 cm medial to the tibial tubercle. To preserve the periosteal blood supply, no attempt was made to strip the soft tissues off of the anterior or posterior cortex of the tibia. Using a 4.8-mm drill bit, we made a large borehole in the medial tibia. A 3.2-mm drill bit was used from within the medullary canal where multiple holes were made anterior and posterior from the starting hole (Figure 4). An effort was made not to perforate the lateral cortex. A onequarter-inch stiletto osteotome was used to connect the dots of the multiple 3.2-mm drill holes. A closed osteoclasis was performed to open the osteotomy site. The lateral cortex was preserved. The fixator was applied, and the desired amount of correction was obtained intraoperatively (Figure 5). The amount of fixator opening required to achieve 1 mm of opening per day at the osteotomy site was calculated. The fixator was closed down at the end of the procedure (Figure 6). All patients used continuous passive motion for 6 hours per day for between 4 and 8 weeks depending on size and extent of the microfracture performed. Figure 5. Intraoperative radiograph demonstrating opening of the osteotomy before closure. Beginning postoperative day 5, the fixator began in divided increments to achieve a 1-mm opening per day at the osteotomy site. Radiographs were obtained 1 week into opening (Figure 7). Opening was continued until the desired amount of correction was achieved (Figure 8). Radiographs were obtained 6 weeks following the completion of distraction. The amount of consolidation was noted (Figure 9), and a decision was made on removal of the fixator. The fixator was removed in the operating room, and a second-look arthroscopy was performed. The amount of regenerate cartilage was documented (Figure 10). In this
4 1246 Sterett and Steadman The American Journal of Sports Medicine Figure 6. Intraoperative radiograph following osteotomy and placement of external fixator. Figure 8. Distraction completed. Figure 7. One week of distraction (1 mm per day) at osteotomy site. Figure 9. Partial consolidation, 6 weeks postoperatively.
5 Vol. 32, No. 5, 2004 Chondral Resurfacing 1247 TABLE 2 Scores for Study Patients (n = 33) Lysholm WOMAC a Tegner Preoperative Range Postoperative Range to 10 Change P value a WOMAC, Western Ontario & McMasters Universities Osteoarthritis Index. Figure 10. Second-look arthroscopy at 12 weeks following microfracture chondral resurfacing procedure. x-rays in varus and valgus. In this patient population, removal of the fixator ranged from 6 weeks to 15 weeks, based on the results of the above studies. Following the removal of the fixator, we allowed the patient to weight bear as tolerated as long as stable consolidation was achieved. Rarely, patients were kept nonweightbearing for up to 3 weeks after removal of the fixator when consolidation was questionable. Statistical Analysis Improvement in Lysholm score was determined using paired t tests. Comparison of Lysholm improvement for binary categorical variables was performed using the independent samples t-test and for multiple (>2) categorical variables was performed using one-way analysis of varience. Comparison of Lysholm improvement for continuous variables was performed using the Pearson correlation coefficient. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS (version 11, SPSS Inc, Chicago, Ill) software package. All reported P values are two-tailed with an alpha level of 0.05 indicating statistical significance. RESULTS Figure 11. Two years postoperatively. patient group, four patients required re-mircofracture of the chondral surfaces. When patients returned for followup, radiographs were obtained to monitor the consolidation (Figure 11). It is often difficult with regenerate bone to decide when there is enough consolidation for safe removal of the external fixator. A variety of methods were used during the course of this study to determine consolidation. These included AP x-rays, CT scans, and occasionally stress AP Two patients were lost to follow-up. Two patients knees were considered failures: one patient had a total knee replacement 35 months following high tibial osteotomy (HTO), and another patient had a repeat osteotomy 60 months following initial HTO. Of the remaining 38 patients, 33 (87%) were available for follow-up at an average of 45 months (range, months). The patients Lysholm, WOMAC, and Tegner activity scores appear in Table 2. One patient s Lysholm score decreased from preoperative to postoperative. Four patients had a slight improvement (increase by 1 to 15 points) in their Lysholm score. Twenty-eight patients showed an improvement in their Lysholm score of greater than 20 points (range, 22-85). There was no correlation between age at time of surgery and improvement in Lysholm. There was also no association between Lysholm improvement and lateral compartment pathology. Those patients with no previous surgeries had higher postoperative Lysholm and more improvement in Lysholm, although it was not significantly higher than patients with a history of previous knee surgery.
6 1248 Sterett and Steadman The American Journal of Sports Medicine TABLE 3 Survival Data a Cumulative Standard Cumulative Number Time (months) Status Survival Error Events Remaining 24 Censored b (2) Censored (7) Censored (3) Failed Censored (2) Censored (6) Censored (2) Censored (3) Failed Censored (5) Censored (1) Censored (1) 2 1 a Number of cases: 34; censored: 32 (94.12%); events: 2. Mean survival time = 75.5 months; standard error = 2.9; 95% confidence interval (69.9, 81.1) (limited to 80). b Censored cases are cases for which follow-up is not available past the given time period, therefore are not included in the survivorship analysis past that time period. Of the 38 patients who underwent the procedure, 15 had infections associated with the external fixator, which required medication. Three patients required intravenous antibiotic treatment, and 12 patients were treated with oral antibiotics. One patient, following premature removal of the fixator, lost correction. There was no association between decreased Lysholm score at follow-up and complications. Correction of 0 to 4 valgus was obtained in 28 patients, 5 patients had 5 to 10o of valgus, and 5 patients had 1 to 6 of varus. In the 2 patients who failed, the correction was 7 and 10 of valgus. Kaplan-Meir survivorship analysis showed a 96% survivorship at 3 years and an 84% survivorship at 5 years (Table 3). The endpoint for survivorship analysis was defined as a revision HTO or total knee replacement following initial HTO. DISCUSSION When performing a chondral resurfacing procedure in conjunction with a high tibial osteotomy in the varus knee, we have found improvement to be predictable and meaningful as evidenced by the Lysholm, WOMAC, and Tegner scores at a minimum of 2-year follow-up (Table 2). A proximal tibial osteotomy, medial opening or lateral closing, will unload the medial joint, 19 decrease the medial tibial sclerosis,1 and improve the adduction moment about the knee during gait. 11,28 Resurfacing the degenerative knee by using a chondral resurfacing procedure, such as microfracture, 4,25,26 will improve results obtained with an osteotomy alone. 2 Medial opening wedge osteotomy has several advantages over a lateral closing wedge osteotomy; specifically, it is more controllable than the one-shot accuracy of a closing wedge osteotomy. Using a distraction technique allows fine-tuning of the alignment postoperatively during followup clinic visits. The incision should not complicate knee replacement in the future, if such is necessary, because the incision is small and almost directly midline and extensile. A lateral closing wedge osteotomy shortens a leg. The varus knee is typically already short due to medial collapse. An opening wedge osteotomy will restore the height of this deficient knee. By not having to operate on the lateral side of the proximal tibia, one minimizes complications to either the proximal tibiofibular joint or the peroneal nerve. Regardless of the amount of correction required in a medial opening wedge osteotomy, we have not found it necessary to either release the proximal tibiofibular joint or perform a fibular osteotomy. In fact, the stability created by leaving the tibiofibular joint intact has been beneficial in our hands. There are other reports 18 of opening wedge tibial osteotomy by callous distraction. At 1-year follow-up, Magyar et al 18 found an increase in Lysholm scores of 35 points with mean Lysholm scores of 91. We saw similar changes in Lysholm scores in our patients; however, our study population started at lower Lysholm scores. In 1996, Nagel et al 21 looked at patients (average age, 49 years) who were undergoing a lateral closing wedge osteotomy of the proximal tibial. Their Tegner activity score at follow-up was 4.8. This was not a significant change from the preoperative score. Thus, the patients were able to maintain their level of activity; 82% were willing to have the procedure again. In patients younger than 55 years of age and undergoing total knee arthroplasty, authors found the Hospital of Special Surgery score increased 37 points at follow-up, roughly equal to the 37.5 increase on the Lysholm score in our study. 27 The Tegner activity score in their patients at follow-up was a mean of 3.5, which was an increase from 1.3 preoperatively. This demonstrated that total knee
7 Vol. 32, No. 5, 2004 Chondral Resurfacing 1249 arthroplasty could markedly increase the patient s Tegner activity level from a sedentary level to an active productive level of work and sport. Total knee arthroplasty in patients younger than 55 years old had a much lower Tegner activity level both preoperatively and at follow-up than patients undergoing high tibial osteotomy in studies by Diduch et al 9 and Stern et al 27 One limitation of the current study is the need for longer follow-up. We need to determine if a combined medial open wedge osteotomy and microfracture chondral resurfacing procedure will provide greater longevity in its ability to delay or eliminate the need for arthroplasty as compared to the longevity of patients treated with a closing wedge osteotomy in isolation. An additional limitation is the lack of a control group with medial open wedge osteotomy without microfracture. Although most patients improved, we cannot conclude how much of the improvement was due to the combined procedure versus just an osteotomy. The results of patients with varus malalignment and lesions requiring chondral resurfacing are extremely promising when they are treated with the combined procedure microfracture for the chondral resurfacing and high tibial osteotomy. We face a difficult problem with these patients. In conclusion, our evidence indicates that, at follow-up a minimum of 2 years after the surgical procedure, patients with varus malalignment and chondral surface lesions of the knee can be treated effectively with chondral resurfacing by microfracture and high tibial osteotomy. REFERENCES 1. Akamatsu Y, Koshino T, Saito T, et al: Changes in osteosclerosis of the osteoarthritic knee after high tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop 334: , Akizuki S, Yasukawa Y, Takizawa T: Does arthroscopic abrasion arthroplasty promote cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritic knees with eburnation? A prospective study of high tibial osteotomy with abrasion arthroplasty versus high tibial osteotomy alone. Arthroscopy 13: 9 17, Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, et al: Validation study of WOMAC: A health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Rheumatology 15: , Blevins FT, Steadman JR, Rodrigo JJ, et al: Treatment of articular cartilage defects in athletes: An analysis of functional outcome and lesion appearance. Orthopedics 21: , Coventry MB: Upper tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop 182: 46 52, Coventry MB: Upper tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg 67A: , Coventry MB: Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee: A preliminary report. [The Classic.] Clin Orthop 248: 4 8, Coventry MB, Bowman PW: Long-term results of upper tibial osteotomy for degenerative arthritis of the knee. Acta Orthop Belg 48: , Diduch DR, Insall JN, Scott WN, et al: Total knee replacement in young active patients: Long-term follow-up and functional outcome. J Bone Joint Surg 79A: , Dugdale TW, Noyes FR, Styer D: Preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomy: The effect of lateral tibiofemoral separation and tibiofemoral length. Clin Orthop 274: , Goh JCH, Bose K, Khoo BC: Gait analysis study on patients with varus osteoarthrosis of the knee. Clin Orthop 294: , Hangody L, Kish G, Karpati Z, et al: Mosaicplasty for the treatment of articular cartilage defects: Application in clinical practice. Orthopedics 21: , Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, et al: Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop 266: , Ivarsson I, Myrnerts R, Gillquist J: High tibial osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis of the knee: A 5 to 7 and 11 year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg 72B: , Kish G, Modis L, Hangody L: Osteochondral mosaicplasty for the treatment of focal chondral and osteochondral lesions of the knee and talus in the athlete: Rational, indications, techniques and results. Clin Sports Med 18: 45 66, Korovessis P, Katsoudaas G, Salonikides P, et al: Medium- and longterm results of high tibial osteotomy in an agricultural population. Orthopedics 22: , Lysholm J, Gillquist J: Evaluation of knee ligament surgery with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale. Am J Sports Med 10: , Magyar G, Toksvig-Larsen S, Lindstrand A: Open wedge tibial osteotomy by callus distraction in gonoarthrosis: Operative technique and early results in 36 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 69: , McKellop HA, Sigholm G, Redfern FG, et al: The effect of simulated fracture-angulations of the tibia on cartilage pressures in the knee joint. J Bone Joint Surg 73A: , Menche DS, Frenkel SR, Blair B, et al: A comparison of abrasion burr arthroplasty and subchondral drilling in the treatment of full-thickness cartilage lesions in the rabbit. Arthroscopy 12: , Nagel A, Insall JN, Scuderi GR: Proximal tibial osteotomy: A subjective outcome study. J Bone Joint Surg 78A: , Naudie D, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH: Survivorship of the high tibial osteotomy: A 10- to 22-year followup study. Clin Orthop 367: 18 27, Schneider U, Breusch S, von der Mark K: Current status of autologous chondrocyte transplantation. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 137: , Soejima O, Ogata K, Ishinishi T, et al: Anatomic considerations of the peroneal nerve for division of the fibula during high tibial osteotomy. Orthop Rev 23: , Steadman JR, Briggs KK, Rodrigo JJ, et al: Outcomes of patients treated arthroscopically by microfracture for traumatic chondral defects of the knee: Average 11-year follow-up. Arthroscopy 19: , Steadman JR, Karas SG, Miller BS, et al: The microfracture technique in the treatment of full-thickness chondral lesions of the knee in National Football League players. J Knee Surg 16: 83 86, Stern SH, Bowen MK, Insall JN, et al: Cemented total knee arthroplasty for gonarthrosis in patients 55 years old and younger. Clin Orthop 260: , Wada M, Imura S, Nagatani K, et al: Relationship between gait and clinical results after high tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop 354: , 1998
Factors Affecting the Union of Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Titanium Wedge Plate
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Ochsner Journal 16:464 470, 2016 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Factors Affecting the Union of Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Titanium Wedge Plate Husam
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Ochsner Journal 16:464 470, 2016 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Factors Affecting the Union of Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Using a Titanium Wedge Plate Husam
Meniscal Tears/Deficiency in Athletes
 Meniscal Tears/Deficiency in Athletes A. Amendola MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Sports Medicine Duke University 1 2 Meniscal tears Introduction Meniscal tears are one of the most frequent
Meniscal Tears/Deficiency in Athletes A. Amendola MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Sports Medicine Duke University 1 2 Meniscal tears Introduction Meniscal tears are one of the most frequent
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Ideal Candidate for Cartilage Restoration. Large or Complex Lesions
 Complex Biological Knee Reconstruction: Bipolar, Multifocal Lesions and Osteoarthritis William Bugbee, MD Attending Physician, Scripps Clinic 18 th International Sports Medicine Fellow s Conference Ideal
Complex Biological Knee Reconstruction: Bipolar, Multifocal Lesions and Osteoarthritis William Bugbee, MD Attending Physician, Scripps Clinic 18 th International Sports Medicine Fellow s Conference Ideal
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries. Cartilage Surgery. The Knee.
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Cartilage Surgery The Knee CARTILAGE INJURY Treatment of cartilage injury remains one of the most significant challenges
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries Cartilage Surgery The Knee CARTILAGE INJURY Treatment of cartilage injury remains one of the most significant challenges
Surgical Considerations:
 Knee Osteoarthritis / Defects of the Articular Cartilage Articular cartilage defects are variable in their presentation, in terms of location as well as severity. Several surgical procedures have been
Knee Osteoarthritis / Defects of the Articular Cartilage Articular cartilage defects are variable in their presentation, in terms of location as well as severity. Several surgical procedures have been
21/01/10. Disclosures. Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature. Introduction. OW osteotomy and bone graft
 3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity
 ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust
 Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust Douglas D.R. Naudie,* MD, FRCSC, Annunziato Amendola, MD, FRCSC, and Peter J. Fowler, MD, FRCSC From the Division of Orthopaedic
Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust Douglas D.R. Naudie,* MD, FRCSC, Annunziato Amendola, MD, FRCSC, and Peter J. Fowler, MD, FRCSC From the Division of Orthopaedic
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury
 Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Osteotomies for Cartilage Protections. Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD San Francisco, Ca
 Osteotomies for Cartilage Protections Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD San Francisco, Ca ACI/Osteotomy Osteotomy: Optimal Patient Selection Mechanical axis falls within involved compartment Mild joint space narrowing
Osteotomies for Cartilage Protections Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD San Francisco, Ca ACI/Osteotomy Osteotomy: Optimal Patient Selection Mechanical axis falls within involved compartment Mild joint space narrowing
Meniscus Reconstruction: Trough Surgical Technique
 Meniscus Reconstruction: Trough Surgical Technique Technique Consultant Jeffrey L. Halbrecht, M.D. San Francisco, CA ABOUT THE TROUGH TECHNIQUE The trough technique for meniscal allograft reconstruction
Meniscus Reconstruction: Trough Surgical Technique Technique Consultant Jeffrey L. Halbrecht, M.D. San Francisco, CA ABOUT THE TROUGH TECHNIQUE The trough technique for meniscal allograft reconstruction
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Disclosures. Why Osteotomy? Osteotomies of the Knee Indications, Techniques and Outcomes
 Osteotomies of the Knee Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Tom Minas MD MS Director, Cartilage Repair Center BWH Associate Professor HMS, Boston Ma www.cartilagerepaircenter.org Disclosures Vericel (
Osteotomies of the Knee Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Tom Minas MD MS Director, Cartilage Repair Center BWH Associate Professor HMS, Boston Ma www.cartilagerepaircenter.org Disclosures Vericel (
Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates!
 7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis Classification of Knee Arthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis of Knee
 1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
arthritis of the knee.
 1351 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Current Concepts Review Unicompartmental Arthritis of the Knee BY RICHARD IORIO, MD, AND WILLIAM L. HEALY, MD Investigation performed
1351 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Current Concepts Review Unicompartmental Arthritis of the Knee BY RICHARD IORIO, MD, AND WILLIAM L. HEALY, MD Investigation performed
Figure 3 Figure 4 Figure 5
 Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
Joint Preservation Clinical Case
 Joint Preservation Clinical Case Jason M. Scopp, M.D. Director of Joint Preservation Peninsula Orthopaedic Associates, 1/19/19 Rational Rationale There are no absolutes. There is no dogma. Organize thoughts,
Joint Preservation Clinical Case Jason M. Scopp, M.D. Director of Joint Preservation Peninsula Orthopaedic Associates, 1/19/19 Rational Rationale There are no absolutes. There is no dogma. Organize thoughts,
Tibial Cartilage Defects
 Tibial Cartilage Defects Kevin C. Wang 1 Rachel M. Frank 2 Brian J. Cole 3 Email brian.cole@rushortho.com 1 2 3 Department of Orthopedics, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA Department
Tibial Cartilage Defects Kevin C. Wang 1 Rachel M. Frank 2 Brian J. Cole 3 Email brian.cole@rushortho.com 1 2 3 Department of Orthopedics, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA Department
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Case Report Arthroscopic Microfracture Technique for Cartilage Damage to the Lateral Condyle of the Tibia
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 795759, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/795759 Case Report Arthroscopic Microfracture Technique for Cartilage Damage to the Lateral Condyle of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 795759, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/795759 Case Report Arthroscopic Microfracture Technique for Cartilage Damage to the Lateral Condyle of
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
There have been conflicting results reported in the
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System. Surgical Technique
 Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System Surgical Technique Opening Wedge Osteotomy Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy 2 Prior to the osteotomy, a diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to verify
Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy System Surgical Technique Opening Wedge Osteotomy Tibial & Femoral Opening Wedge Osteotomy 2 Prior to the osteotomy, a diagnostic arthroscopy is performed to verify
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research
 New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
OSTEOCHONDRAL ALLOGRAFTS AND AUTOGRAFTS IN THE TREATMENT OF FOCAL ARTICULAR CARTILAGE LESIONS
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Surgery Policy Number: IV-115 Effective Date: 10/22/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Surgery Policy Number: IV-115 Effective Date: 10/22/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Comparing dome high tibial osteotomy for patients more than sixty years old with patients less than sixty years old
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 2 No. 5 October 2008;381-388 Original article Comparing dome high tibial osteotomy for patients more than sixty years old with patients less than sixty years old Prakit Tienboon
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 2 No. 5 October 2008;381-388 Original article Comparing dome high tibial osteotomy for patients more than sixty years old with patients less than sixty years old Prakit Tienboon
Mid Term Outcome of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
 Original Research Tarun Kumar Badam 1*, Muthukumar Balaji 2, Sathish Devadoss 3, A. Devadoss 4 1 Junior Resident, 2 Junior Consultant, 3 Senior Consultant, 4 Chief, Department of Orthopaedics, IORAS Devadoss
Original Research Tarun Kumar Badam 1*, Muthukumar Balaji 2, Sathish Devadoss 3, A. Devadoss 4 1 Junior Resident, 2 Junior Consultant, 3 Senior Consultant, 4 Chief, Department of Orthopaedics, IORAS Devadoss
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy (average 6 years follow-up)
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2003) 11 : 139 144 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-003-0344-0 Cengiz Sen Mehmet Kocaoglu Levent Eralp The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2003) 11 : 139 144 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-003-0344-0 Cengiz Sen Mehmet Kocaoglu Levent Eralp The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy
No Disclosures. Topics. Pediatric ACL Tears
 Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Meniscus cartilage replacement with cadaveric
 Technical Note Meniscal Allografting: The Three-Tunnel Technique Kevin R. Stone, M.D., and Ann W. Walgenbach, R.N.N.P., M.S.N. Abstract: This technical note describes an improved arthroscopic technique
Technical Note Meniscal Allografting: The Three-Tunnel Technique Kevin R. Stone, M.D., and Ann W. Walgenbach, R.N.N.P., M.S.N. Abstract: This technical note describes an improved arthroscopic technique
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis
 Clinical Report Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(1)
Clinical Report Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(1)
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Rakesh Patel, MD 4/9/09
 Rakesh Patel, MD 4/9/09 Chondral Injuries Very common Present in 63-66% patients undergoing arthroscopy 11-19% full-thickness lesions Up to 79% patients with ACL deficient knee have some form of chondral
Rakesh Patel, MD 4/9/09 Chondral Injuries Very common Present in 63-66% patients undergoing arthroscopy 11-19% full-thickness lesions Up to 79% patients with ACL deficient knee have some form of chondral
1 Introduction. 2 Data and method
 Open Med. 2015; 10: 457 461 Research Article Open Access Si Yulou, Xue Yanqin, Xing Yongjun* Method and effect of total knee arthroplasty osteotomy and soft tissue release for serious knee joint space
Open Med. 2015; 10: 457 461 Research Article Open Access Si Yulou, Xue Yanqin, Xing Yongjun* Method and effect of total knee arthroplasty osteotomy and soft tissue release for serious knee joint space
Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.019 Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up, MD Institute of Orthopaedics, Lerdsin Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.019 Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up, MD Institute of Orthopaedics, Lerdsin Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Results of arthroscopic surgery, with or without high Tibial osteotomy, in osteoarthritis of knee
 2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of partial replacement of the meniscus of the knee using a biodegradable scaffold
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of partial replacement of the meniscus of the knee using a biodegradable scaffold
OSTEOCHONDRAL ALLOGRAFT RECONSTRUCTION FOR MASSIVE BONE DEFECT
 OSTEOCHONDRAL ALLOGRAFT RECONSTRUCTION FOR MASSIVE BONE DEFECT Angelo J. Colosimo, MD -Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics -Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati
OSTEOCHONDRAL ALLOGRAFT RECONSTRUCTION FOR MASSIVE BONE DEFECT Angelo J. Colosimo, MD -Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics -Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati
Unstable Focally Arthritic Knee DeBerardino 8/18/2016. Current Management Options for the Unstable Focally Arthritic Middle-aged Knee.
 Current Management Options for the Unstable Focally Arthritic Middle-aged Knee With focus on HTOs and UKAs +/- ACL reconstruction Disclosures Research support: Arthrex, MTF, Histogenics Consultant: Aesculap/B.Braun,
Current Management Options for the Unstable Focally Arthritic Middle-aged Knee With focus on HTOs and UKAs +/- ACL reconstruction Disclosures Research support: Arthrex, MTF, Histogenics Consultant: Aesculap/B.Braun,
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Why does it matter? Patellar Instability 7/23/2018. What is the current operation de jour? Common. Poorly taught. Poorly treated
 Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement
 016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
Osteochondral allografting for all other joints is not covered as the evidence is insufficient to determine the
 Medical Coverage Policy Osteochondral Autologous Chrondrocyte Implantation for Focal Articular Cartilage Lesions EFFECTIVE DATE: 05 20 2008 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 10 16 2018 OVERVIEW A variety of procedures
Medical Coverage Policy Osteochondral Autologous Chrondrocyte Implantation for Focal Articular Cartilage Lesions EFFECTIVE DATE: 05 20 2008 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 10 16 2018 OVERVIEW A variety of procedures
Case Report. Byung Ill Lee, MD and Byoung Min Kim, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(4):263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.4.263 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Concomitant Osteochondral utograft Transplantation
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(4):263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.4.263 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Concomitant Osteochondral utograft Transplantation
evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization
 evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* Updated 1/30/2018 *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology
evicore MSK joint surgery procedures requiring prior authorization Moda Health Commercial Group and Individual Members* Updated 1/30/2018 *Check EBT to verify member enrollment in evicore program Radiology
High Tibial Osteotomy
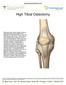 High Tibial Osteotomy With each step, forces equal to three to eight times your body weight travel between the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia) in your knee. These forces are dampened by a meniscus
High Tibial Osteotomy With each step, forces equal to three to eight times your body weight travel between the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia) in your knee. These forces are dampened by a meniscus
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Osteochondral Allograft Transplantation and Autograft Transfer System (OATS/mosaicplasty) in the Treatment of Articular
 Osteochondral Allograft Transplantation and Autograft Transfer System (OATS/mosaicplasty) in the Treatment of Articular Cartilage Lesions Corporate Medical Policy File name: Osteochondral Allograft Transplantation
Osteochondral Allograft Transplantation and Autograft Transfer System (OATS/mosaicplasty) in the Treatment of Articular Cartilage Lesions Corporate Medical Policy File name: Osteochondral Allograft Transplantation
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
AUTOLOGOUS CHONDROCYTE IMPLANTATION FOR CHONDRAL KNEE DAMAGE B.A. Jalba 1, C.S. Jalba 2, F. Gherghina 3, M. Cruce 3
 AUTOLOGOUS CHONDROCYTE IMPLANTATION FOR CHONDRAL KNEE DAMAGE B.A. Jalba 1, C.S. Jalba 2, F. Gherghina 3, M. Cruce 3 1-EMERGENCY CLINICAL HOSPITAL FLOREASCA BUCHAREST 2-EMERGENCY CLINICAL HOSPITAL SFANTUL
AUTOLOGOUS CHONDROCYTE IMPLANTATION FOR CHONDRAL KNEE DAMAGE B.A. Jalba 1, C.S. Jalba 2, F. Gherghina 3, M. Cruce 3 1-EMERGENCY CLINICAL HOSPITAL FLOREASCA BUCHAREST 2-EMERGENCY CLINICAL HOSPITAL SFANTUL
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field
 Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Combined intra-articular and varus opening wedge osteotomy for lateral depression and valgus malunion of the proximal part of the tibia. Surgical technique Kerkhoffs,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Combined intra-articular and varus opening wedge osteotomy for lateral depression and valgus malunion of the proximal part of the tibia. Surgical technique Kerkhoffs,
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Treatment Options for Articular Cartilage Defects of the Knee
 Innovations Treatment Options for Articular Cartilage Defects of the Knee Alvin J. Detterline Steven Goldberg ernard R. ach, Jr. rian J. Cole The treatment of symptomatic articular cartilage defects of
Innovations Treatment Options for Articular Cartilage Defects of the Knee Alvin J. Detterline Steven Goldberg ernard R. ach, Jr. rian J. Cole The treatment of symptomatic articular cartilage defects of
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
REVIEW ARTICLE. Malalignment: A Requirement for Cartilage and Organ Restoration
 REVIEW ARTICLE Malalignment: A Requirement for Cartilage and Organ Restoration Alexander E. Weber, MD, Matthew E. Gitelis, BS, Mark A. McCarthy, MD, Adam B. Yanke, MD, and Brian J. Cole, MD, MBA Abstract:
REVIEW ARTICLE Malalignment: A Requirement for Cartilage and Organ Restoration Alexander E. Weber, MD, Matthew E. Gitelis, BS, Mark A. McCarthy, MD, Adam B. Yanke, MD, and Brian J. Cole, MD, MBA Abstract:
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Cartilage Repair Options
 Imaging of Cartilage Repair Carl S. Winalski, MD Imaging Institute Department of Biomedical Engineering Cleveland Clinic Cartilage Repair Options Direct repair Marrow stimulation Autologous transplantation
Imaging of Cartilage Repair Carl S. Winalski, MD Imaging Institute Department of Biomedical Engineering Cleveland Clinic Cartilage Repair Options Direct repair Marrow stimulation Autologous transplantation
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate. 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique
 Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning HTO Body weight < 100 kg, Non smoker. For preoperative planning be aware of potential femoral
Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning HTO Body weight < 100 kg, Non smoker. For preoperative planning be aware of potential femoral
Cartilage Repair Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Safety, feasibility, and radiographic outcomes of the anterior meniscal takedown technique to approach chondral defects on the tibia and posterior femoral
Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Safety, feasibility, and radiographic outcomes of the anterior meniscal takedown technique to approach chondral defects on the tibia and posterior femoral
HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS
 Original Article HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS Roger Avakian 1, Nilson Roberto Severino 2, Ricardo de Paula Leite Cury 3, Victor Marques de Oliveira 1, Tatsuo Aihara 4, Osmar Pedro
Original Article HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS Roger Avakian 1, Nilson Roberto Severino 2, Ricardo de Paula Leite Cury 3, Victor Marques de Oliveira 1, Tatsuo Aihara 4, Osmar Pedro
Orthopaedic Advances. Abstract
 Orthopaedic Advances Cartilage Restoration Techniques for the Patellofemoral Joint Robert H. Brophy, MD Robert D. Wojahn, MD Joseph D. Lamplot, MD From Washington University Orthopedics, Chesterfield,
Orthopaedic Advances Cartilage Restoration Techniques for the Patellofemoral Joint Robert H. Brophy, MD Robert D. Wojahn, MD Joseph D. Lamplot, MD From Washington University Orthopedics, Chesterfield,
TREATMENT OF CARTILAGE LESIONS
 TREATMENT OF CARTILAGE LESIONS Angelo J. Colosimo, MD -Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics -Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center -Associate Professor
TREATMENT OF CARTILAGE LESIONS Angelo J. Colosimo, MD -Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics -Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center -Associate Professor
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Oh My Aching Knee. Oh My Aching Knee WHO AM I? 10/15/2012. Jan Pieter Hommen, MD Orthopedic Surgeon Sports Medicine Arthroscopy Joint Replacements
 Oh My Aching Knee Jan Pieter Hommen, MD Orthopedic Surgeon Sports Medicine Arthroscopy Joint Replacements Oh My Aching Knee Jan Pieter Hommen, MD Orthopedic Surgeon Sports Medicine Arthroscopy Joint Replacements
Oh My Aching Knee Jan Pieter Hommen, MD Orthopedic Surgeon Sports Medicine Arthroscopy Joint Replacements Oh My Aching Knee Jan Pieter Hommen, MD Orthopedic Surgeon Sports Medicine Arthroscopy Joint Replacements
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study
 Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery
 Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery KOCO EATON, M.D. T A M P A B A Y R A Y S ( 1 9 9 5 P R E S E N T ) T A M P A B A Y B U C C A N E E R S ( 2 0 1 5 2 0 1 6 ) T A M P A B A Y R O W D I E S ( 2 0 1 4 2 0 1 7
Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery KOCO EATON, M.D. T A M P A B A Y R A Y S ( 1 9 9 5 P R E S E N T ) T A M P A B A Y B U C C A N E E R S ( 2 0 1 5 2 0 1 6 ) T A M P A B A Y R O W D I E S ( 2 0 1 4 2 0 1 7
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Ankle Arthritis PATIENT INFORMATION. The ankle joint. What is ankle arthritis?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi?
 Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi? #$%&' ()"*+!," Philippe Neyret E Servien S Lustig P Verdonk One or more of the authors of the next presentation have identified no potential conflicts of interest 2 Consequences
Save the meniscus Mais pourquoi? #$%&' ()"*+!," Philippe Neyret E Servien S Lustig P Verdonk One or more of the authors of the next presentation have identified no potential conflicts of interest 2 Consequences
Table of Contents. Step One: Locate Medullary Canal 4 Step Two: Prepare Femur 4. Step Three: Size Femur 5. Step Four: Prepare Tibia 5
 Zimmer Natural-Knee Unicompartmental MIS Intramedullary Surgical Technique Zimmer MIS Surgical Technique for Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Developed in conjunction with Aaron A. Hofmann, MD Professor
Zimmer Natural-Knee Unicompartmental MIS Intramedullary Surgical Technique Zimmer MIS Surgical Technique for Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Developed in conjunction with Aaron A. Hofmann, MD Professor
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments
 TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Anterior Tibial Subluxation with ACL Deficient Knees influences the Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction.
 Anterior Tibial Subluxation with ACL Deficient Knees influences the Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction. RYOTA TAKASE 1), KAZUHISA HATAYAMA 1), MASANORI TERAUCHI 1) KENICHI SAITO 2), HIROTAKA CHIKUDA
Anterior Tibial Subluxation with ACL Deficient Knees influences the Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction. RYOTA TAKASE 1), KAZUHISA HATAYAMA 1), MASANORI TERAUCHI 1) KENICHI SAITO 2), HIROTAKA CHIKUDA
Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation
 Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation Victor M. Ilizaliturri Jr., MD, Bernal Gonzalez-Gutierrez, MD, Humberto Gonzalez-Ugalde, MD, Javier Camacho-Galindo, MD Adult Joint Reconstruction Service
Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation Victor M. Ilizaliturri Jr., MD, Bernal Gonzalez-Gutierrez, MD, Humberto Gonzalez-Ugalde, MD, Javier Camacho-Galindo, MD Adult Joint Reconstruction Service
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
IKDC DEMOGRAPHIC FORM
 IKDC DEMOGRAPHIC FORM Your Full Name Your Date of Birth / / Your Social Security Number - - Your Gender: Male Female Occupation Today s Date / / The following is a list of common health problems. Please
IKDC DEMOGRAPHIC FORM Your Full Name Your Date of Birth / / Your Social Security Number - - Your Gender: Male Female Occupation Today s Date / / The following is a list of common health problems. Please
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
