COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN USE OF STAINLESS STEEL ENDERS NAILS AND TITANIUM ELASTIC NAILS FOR TREATMENT OF FRACTURES OF SHAFT FEMUR IN CHILDREN
|
|
|
- Zoe Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 12 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 09/05/14 Revised on: 26/05/14 Accepted on: 12/06/14 COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN USE OF STAINLESS STEEL ENDERS NAILS AND TITANIUM ELASTIC NAILS FOR TREATMENT OF FRACTURES OF SHAFT FEMUR IN CHILDREN Ulhas Sonar, Milind Ingle, M. R. Koichade, AvinashYelne Department of Orthopaedics, Indira Gandhi Government Medical College, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India of Corresponding Author: ABSTRACT Objectives: To compare results of Enders and titanium elastic intramedullary nailing for treatment of fractures of shaft femur in children between 5-15 years. Method: Twenty patients between age group of 5-15 years were treated with stainless steel Enders nailing and twenty patients of same age group were treated with titanium elastic nailing. Results were compared using Flynn etal 2001 criteria. Results: Average operative time was 36.2 minutes for Enders and 34.6minutes for titanium nailing. Average hospital stay was 6.21 days for Enders and 7.4 days titanium nailing. Average union time was 9.44 weeks in Enders and 9.52 weeks in titanium group. Average full weight bearing was achieved after weeks in Enders and after weeks in titanium group. Average full range of motion was achieved after 9.97weeks in Enders and after 9.50weeks in titanium group. Nail exterioration, nail irritation, superficial infection and asymptomatic lengthening were complications. Sixteen patients of Enders and fifteen of titanium group had excellent result as per Flynn etal2001 criteria. Rest had satisfactory results. There were no poor results. It indicated similar results in both groups. Conclusion: We found no statistically significant difference in outcomes of fractures treated with either method in clinical setting. Both methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. Keywords: Enders nails, Titanium elastic nails, fractures of shaft femur in children INTRODUCTION Shaft or diaphyseal fractures of the femur are uncommon but significant injuries in children. They constitute less than 2% of all skeletal injuries in children. The commonest causes of femoral shaft fractures are falls and road traffic accidents. For children under walking age, abuse needs to be considered. (1) For generations traction and casting were standard treatment for all femoral shaft fractures in children and femoral fractures ranked high in duration of hospitalization for single diagnosis. Advantages of spica cast include low cost, excellent safety profile and very high rate of good results with acceptable leg length equality, healing time and motion. (2) Operative management is becoming a preferred option because of fact that there is decrease in incidence of malunion, shorter hospital stay, lesser surgical cost, better nursing care and early ambulation. (3) There has been growing trend to widen the indications for surgical treatment as attention has been focused on the difficulty of caring for children in body cast for 2-3 months. (4) The methods included external fixation, compression plating and intramedullary nailing with either rigid or flexible nails. (5) Page 56
2 Intramedullary nail fixation has advantages as it is a percutaneous technique which does not damage growth cartilage. It keeps intact the fracture hematoma, maintains stability in three planes and provides opportunity to an early weight bearing giving an early rehabilitation at low cost with a minimal rate of complications. (6) It allows early weight bearing and walking.it aims to develop early bridging callus which contributes to rapid restoration of bone continuity. (7) In addition it requires much less operative time and fluoroscopy time. (8) MATERIAL AND METHODS This prospective study is an institutional based comparative study conducted at Indira Gandhi Government Medical College, Nagpur. All surgeries were performed by same surgical team.all patients between 5-15 years age group with closed or uncontaminated grade I compound fracture were included in study.thorough history taking and clinical examination was done at first visit and patients were admitted after radiological investigations were done. Patients were divided in two groups, one group to be treated with stainless steel Enders nailingand other with titanium elastic nailing. All patients were operated in supine position.after proper preparation medial and lateral incisions were taken. Using awl, centimeters proximal to physis, entry point was made. Nails were chosen so that each nail should fill at least 40% of canal by thickness. Nail lengths were predetermined on C-arm for Enders nailing. Two nails of similar thickness were bent approximately 25 at 1.5 centimeters from blunt ends. Both nails were passed up to fracture site. Closed reduction was done and whenever required open reduction was done and either of nail was passed in proximal fragment followed by second nail. Nails hammered to their final position. Thorough wound wash was given. Wounds closed in layers. Sterile dressing applied.sutures were removed on outpatient basis between 10-14th day. Patients were allowed partial weight bearing to full weight bearing at first follow up between 4-8 weeks as per pain tolerance of patients.x-rays were taken at every follow up.clinically wound related complications and limb length discrepancy was monitored. Results were classified as per criteria described by Flynn et al 2001 (11) as depicted in table no 1. Children exceeding the criteria in any category were assigned the worse results. (11) All cases were at least followed for minimum duration of six months.cases were further followed till the nail removal was done at varying periods. STATISTICAL METHODS The descriptive statistics for demographic variables like age, sex were obtained according to two nail types used in the surgery. The mean and standard deviations of diameters were obtained for the two nail types. The significance of difference in the mean nail diameter in both groups was evaluated using t-test for independent samples. Mean duration of surgery of two groups was evaluated for significance of difference using t-test for independent samples. Also, the difference between the mean stay at hospital for two groups of surgeries was determined using t-test for independent samples. The mean time for union, full weight bearing and full range motion between two surgery types was assessed for statistical significance using the above test. RESULTS In our study we derived the following results :- Minimum age in our series for Enders nailing group was six years, and for titanium elastic nailing group was also six years. And maximum age for Enders nailing group was thirteen years and for titanium elastic nailing group was fifteen years. An average mean age for Enders nailing group was 9.95years and for titanium elastic nailing group was 9.81years. Average age of male patient for Enders nailing was 10.6 years and for titanium elastic nailing was 9.5 years. Average age Page 57
3 of female patients for Enders nailing was 8.3 years and 10.5 years was for titanium elastic nailing. The difference between the mean ages of patients was found statistically insignificant (p > 0.05) between two selected groups of Enders and titanium elastic nailing. It indicates that there was no age bias while selecting patients for treatment as regards to age. In our study overall there was a male preponderance. In our series there were 70% males in Enders nailing group and in titanium elastic nailing group 75% were males and rest were the females. The proportion of males and females selected for the two types of surgeries was statistically insignificant with p > This indicated randomization as regards the gender distribution in two surgeries. In our series right side was involved in 42.5 % of patients and in 57.5% of patients left side was involved. In our study side distribution was almost similar in both surgical groups. This indicated randomization as regards the side distribution in two surgeries. In our study low energy injuries which includes fall were more common cause of fracture femur in children than high energy injuries including road traffic accidents. Distribution of mode of trauma was almost similar in two surgical groups indicating randomization regarding distribution of patients considering the mode of trauma. We had one grade I compound fracture which was treated with Enders nailing and rest were closed ones. We had two patients with associated injuries. Both hadipsilateral tibia fracture. One patient was treated with Enders nailing for femur and closed reduction and cast for tibia. Other patient was treated with titanium elastic nailing for fractures of femur as well as tibia. In our series transverse fractures were commonest overall. Oblique fractures were commoner than spiral fractures and comminuted fractures were least common. In our series middle third level fractures were commoner than upper third followed by lower thirdlevel fractures. In our series total operative time required was average 36.2 minutes for Enders nailing and for titanium elastic nailing it was 34.6 minutes. Maximum time required was 42 minutes and minimum was 30 minutes for Enders nail. For titanium elastic nailing maximum time required was 40 minutes and minimum time required was 30 minutes. There was no statistical significant difference in mean duration of surgery between two surgical groups indicating similar results. We had to open the fracture for getting reduction in four cases of Enders nailing and two cases of titanium elastic nailing. In most of the situation open reduction was required due to soft tissue interposition. Average stay at hospital was 6.21 days for patients treated with Enders nailing and 7.4 days for patients treated with titanium elastic nailing. The difference was found to be statistically insignificant with p > 0.05 using t-test for independent samples. On an average union was achieved in 9.44 weeks in Enders nailing group and in 9.52 weeks in titanium elastic nailing group. Union time was similar in both types of treatments. The difference was statistically insignificant (p > 0.05) for Union time. Our patients were able to bear full weight on an average after weeks in Enders nailing group and after weeks in titanium elastic nailing group. Out come in terms of time for full weight bearing was similar in both types of treatment. The difference was statistically insignificant (p > 0.05) for time for full weight bearing. Full range of motion was achieved in on an average after 9.97weeks in Enders nailing group and after 9.50weeks in titanium elastic nailing group. Outcome in terms of time for full range of motion was similar in both types of treatments. The difference was statistically insignificant (p > 0.05) for full range of motion. In our series there were no major complications. There was a single case of superficial infection in both groups which resolved with course of Page 58
4 antibiotics for few days. There was one case of nail exterioration in titanium elastic nailing group which was asymptomatic and was found incidentally when a patient was called for implant removal. There were three patients in titanium elastic nailing group and two in Enders nailing group who suffered irritation at entry site of nail. All were resolved with course of few days of analgesics. There were four cases of lengthening in Enders nailing group and five cases of lengthening in titanium elastic nailing group. Lengthening was less than one centimeter in all cases and was clinically asymptomatic. In our series in Enders nailing group sixteen patients had excellent results and four patients had satisfactory results. There were no poor results. In titanium elastic nailing group fifteen patients had excellent results and five patients had satisfactory results. There were no poor results. Flynn et al 2001 scoring was almost similar in both surgical groups indicating similar results in both groups. The results of our study are also depicted in the X- ray photographs provided. DISCUSSION Goals of treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children and adolescent are achieving bone union with length, alignment and limb s functional restoration, without losing movements of adjacent joints. (12) Enders and titanium elastic nails are the two types of flexible intramedullary nails used over the years; and both of them are consistently producing good results. (13) Small incision is required for these procedures. They usually require less time and minimal blood loss occur without damaging (14) epiphyseal area. Retrograde fixation is preferred. It has demonstrated significantly less axial range of motion and greater torsional stiffness than antegrade fixation in transverse as well as communited fracture patterns. (15) Normally recommendation for distal third femur fractures is antegrade nail insertion. But study done by Mehlman et al in synthetic models demonstrated that given satisfactory cortical starting points in the distal fragment, retrograde insertion provides greater stability. (16) Even about rotational stability, the study done by Gwyn et al has proved that this method of fixation provides a consistent mean of rotational stability for variety of fracture pattern in a synthetic model. (17) Most of the complications are caused by use of too thin nails, asymmetry of the frame, and malorientation of the implants. (18) Many studies have proven efficacy of both methods in treatment of femoral shaft fractures but very few have discussed about comparison of both methods of fixation. According to Wall EJ et al 2008 the in vitro mechanical studies comparing the two types of nails have demonstrated superior or equal stability in association with the use of titanium nails as compared with stainless steel nail. Biomechanical properties of titanium are often considered to be better than those of stainless steel with regard to biocompatibility, modulus of elasticity, osseointegration, corrosion resistance, and magnetic resonance imaging compatibility.but in clinical setting he has found superior results with use Enders nails as compared with titanium elastic nails in terms of rate of malunion. He hypothesized that the increased flexibility of titanium as compared with stainless steel nails may be responsible for the outcome. He stated that stainless steel nails are stiffer than titanium nails, which may be beneficial for preventing angular malunions following pediatric femoral fractures. (19) But there are some recent studies which have found no difference between clinical outcomes of both procedures. According to study performed by Lohiya et al 2011, there was no difference in results with type of nail used in his series (p = 0.12). Furthermore, he concluded that stainless steel nails produce results similar to titanium nails at considerably lesser price. (20) In another study performed by Kumar et al 2011 in sixty two fractures treated with flexible intramedullary nailing, he did not find any mismatch in the results of fractures stabilized with Page 59
5 titanium elastic nails or with that of Enders nails. (21) CONCLUSION We found that flexible intramedullary nailing is effective method of treatment for fractures of shaft of femur in pediatric age group between five to fifteen years with good outcomes and reasonably less complications. Enders nailing and titanium elastic nailing both are effective in treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children. We found no statistically significant difference in outcomes of fractures treated with either method in clinical setting. Both methods have their own advantages. Using titanium elastic nail the insertion of nail and negotiation of fracture was much easier as compared with Enders Nails. But implant removal was difficult compared to Enders nail. On the other hand Enders nail are much cheaper as compared to titanium elastic nail which is important aspect in Indian scenario. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Authors acknowledge the immense help received from scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals, books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. REFERENCES 1. Madhuri V, Gahukamble AD, Dutt V, Tharyan P. Interventions for treating femoral shaft fractures in children and adolescents (Protocol). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 4. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD Flynn JM, Skaggs DL. Femoral shaft fractures. In :Beaty JH, Kasser JR, editors. Rockwood and Wilkin s Fractures in children volume four.7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, a Wolter Kluwer business ; P Singh P, Sharma V, Singh H, Wani IH, Gupta R, Gupta N. Treatment of Fractures Of the shaft of the femur in children by Ender`s nails: A prospective study. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2009;11:1. 4. Khurram B, Humayun BEG. Flexible intramedullary nailing versus external fixation of paediatric femoral fractures. Actaorthop. Bel 2006;72: Vidyadhara S, Rao SK. Global reconstruction of type IIIA open comminuted femoral shaft fracture with segmental bone loss in an 11- year-old girl. Singapore Med J. 2006;47(9): Ramírez JA, NafarrateEBlNúñez JA, Vallejo J, Campbell O, Peña JC. Arturo Aguirre Madrid Clavoscentromedularesflexibles en el tratamiento de fracturaspediátricas. Revista Mexicana de orthopaediapaediatrica 2004;6: Ligier JN, Metaizeau JP, Prévot J, Lascombes P. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1988, 70(1): Gregory P, Sullivan JA, Hernodon WA. Adolescent femoral shaft fractures: rigid versus flexible nails. Orthopedics 1995; 18: Anglen JO, Choi L. Treatment Options in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures. journal of orthop trauma 2005;19: Oztürkmen Y, Doğrul C, Balioğlu MB, Karli M. Intramedullary stabilization of pediatric diaphyseal femur fractures with elastic Ender nails. ActaOrthopTraumatolTurc. 2002;36(3): Shekhar L, Mayanger JC. A clinical study of Ender nails fixation in femoral shaft fractures in children. Indian J Orthop 2006; 40: Cunha FM, Figueiredo LA, Coelho LFA, Malheiros DS, Terra DL, Lima CLFA. Femoral shaft fracture in children and adolescent. ActaOrthop Bras.2007; 15(2): Page 60
6 13. Hasan Al-Sayed. Titanium Elastic Nail Fixation for Paediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures.Pan Arab J. Orth. Trauma- 2006; 10 (1): Shiha A, Rifae HH, El-Deen MA. Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fractures in Children. Pan Arab J. Orth. Trauma ;8: Fricka KB, Mahar AT, Lee SS, Newton PO. Biomechanical analysis of antegrade and retrograde flexible intramedullary nail fixation of pediatric femoral fractures using a synthetic bone model. J PediatrOrthop Mar- Apr;24(2): Mehlman CT, Nemeth NM, Glos DL. Antegrade versus retrograde titanium elastic nail fixation of pediatric distal-third femoralshaft fractures: a mechanical study. J Orthop Trauma Oct; 20(9): Gwyn DT, Olney BW, Dart BR, Czuwala PJ. Rotational control of various pediatric femur fractures stabilized with titanium elastic intramedullary nails. J PediatrOrthop Mar-Apr;24(2): Lascombes P, Haumont T, Journeau P. Use and abuse of flexible intramedullary nailing in children and adolescents. J PediatrOrthop Nov-Dec;26(6): Wall EJ, Jain V, Vora V, Mehlman CT, Crawford AH. Complications of titanium and stainless steel elastic nail fixation of pediatric femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(6): Lohiya R, Bachhal V, Khan U, Kumar D, Vijayvargiya V, Sankhala SS. Flexible intramedullary nailing in paediatric femoral fractures. A report of 73 cases. J OrthopSurg Res. 2011;22: Kumar S, Roy SK, Jha AK, Chatterjee D, Banerjee D, Garg AK. An evaluation of flexible intramedullary nail fixation in femoral shaft fractures in paediatric age group. J Indian Med Assoc.2011;109: Criteria described by Flynn et al for evaluation of final outcome in fixation of fracture shaft femur (2001) Parameters Excellent Satisfactory Poor Limb length inequality Less than 1 centimeter Less than 2 centimeters More than 2 centimeters Malalignment Up to 5⁰ 5-10⁰ More than 10⁰ Pain None None Present Other complications None Minor Major complication and/or lasting morbidity Page 61
7 Photographs of X rays Titanium Elastic Nailing Group X-Rays 1) Case 1 a) Pre-operative X ray b) Immediate post operative X ray c) Union seen on X ray at 9 weeks Page 62
8 Enders Nailing Group X-Rays Case no. 1 :-a) Preoperative X ray b) Immediate post operative X ray c) Union seen on X ray at 9 weeks Page 63
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4
 Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Introduction. Mohammad Ruhullah 1*, Sanjay Shah 1, Hare Ram Singh 1, Dipak Shrestha 2. Bagmati, Nepal. Abstract
 This article has been published in whole in Maced J Med Sci. 2013 Dec 15; 6(4):350-355. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013 Dec 15; 1(1):12-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2013.003
This article has been published in whole in Maced J Med Sci. 2013 Dec 15; 6(4):350-355. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2013 Dec 15; 1(1):12-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2013.003
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures
 TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
PAEDIATRIC FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES MANAGED WITH TENS
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 7(1) : 119-124, 2016 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) PAEDIATRIC FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES MANAGED WITH TENS AMIT BATRA, ADITYA JAIN, MOHIT KHANNA, DHARVIN LAMBA, SURESH
Indian J.Sci.Res. 7(1) : 119-124, 2016 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) PAEDIATRIC FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES MANAGED WITH TENS AMIT BATRA, ADITYA JAIN, MOHIT KHANNA, DHARVIN LAMBA, SURESH
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Original Research Article Treatment of Paediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture with Titanium Elastic Nails Dr. Neeraj Mahajan 1, Dr.
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(3E):981-985 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(3E):981-985 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture Management By Titanium Elastic Nailing; A Prospective Study Of 112 Patients
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 19 Number 3 Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture Management By Titanium Elastic Nailing; A Prospective Study Of 112 P Singh, R Kumar Citation P Singh,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 19 Number 3 Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture Management By Titanium Elastic Nailing; A Prospective Study Of 112 P Singh, R Kumar Citation P Singh,
Titanium elastic intramedullary nailing : closed or mini-open reduction?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 406-410 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic intramedullary nailing : closed or mini-open reduction? Bekir Yavuz Uçar, Mehmet Gem, Mehmet Bulut, Ibrahim Azboy, Abdullah Demirtaş,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 406-410 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic intramedullary nailing : closed or mini-open reduction? Bekir Yavuz Uçar, Mehmet Gem, Mehmet Bulut, Ibrahim Azboy, Abdullah Demirtaş,
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Complications Cast Treatment Psychosocial effect on children Economoic effects on their families [Hughes 1995] ORIF with Plate Ex Fix Antegrade Nail L
![Complications Cast Treatment Psychosocial effect on children Economoic effects on their families [Hughes 1995] ORIF with Plate Ex Fix Antegrade Nail L Complications Cast Treatment Psychosocial effect on children Economoic effects on their families [Hughes 1995] ORIF with Plate Ex Fix Antegrade Nail L](/thumbs/78/78093115.jpg) Introduction Cast or Traction + cast Nicol [2000] ORIF Kregor [ 93], Ward [92] Ex Fix Aronson [ 92], Tolo [93] Antegrade Nail Beaty [94], Buford [98], Galpin [ 94], Herndon [ 89] Flexible IM Pinning [00],
Introduction Cast or Traction + cast Nicol [2000] ORIF Kregor [ 93], Ward [92] Ex Fix Aronson [ 92], Tolo [93] Antegrade Nail Beaty [94], Buford [98], Galpin [ 94], Herndon [ 89] Flexible IM Pinning [00],
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures
 대한정형외과학회지 : 제 43 권제 1 호 2008 J Korean Orthop Assoc 2008; 43: 30-35 Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures Do-Young Kim, M.D., Sung-Ryong
대한정형외과학회지 : 제 43 권제 1 호 2008 J Korean Orthop Assoc 2008; 43: 30-35 Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures Do-Young Kim, M.D., Sung-Ryong
Original Article. * Received for Publication: August 20, 2007 * Revision Received: September 12, 2007 * Revision Accepted: September 15, 2007
 Original Article SHORT TERM OUTCOME OF TREATMENT OF FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN BY TWO METHODS: TRACTION PLUS CASTING, VERSUS INTRAMEDULLARY PIN FIXATION A COMPARATIVE STUDY Seyed Abdolhossein
Original Article SHORT TERM OUTCOME OF TREATMENT OF FEMORAL SHAFT FRACTURES IN CHILDREN BY TWO METHODS: TRACTION PLUS CASTING, VERSUS INTRAMEDULLARY PIN FIXATION A COMPARATIVE STUDY Seyed Abdolhossein
Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus Fractures with Tens - A Retrospective Analysis.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Management and outcome of diaphyseal femur fracture in Children: A tertiary care Experience
 Original article: Management and outcome of diaphyseal femur fracture in Children: A tertiary care Experience Ravi Kant Jain 1, Chirag Sethi 1, Pranav Mahajan 1, Ravindra Kumar 2 1Department of Orthopaedics,
Original article: Management and outcome of diaphyseal femur fracture in Children: A tertiary care Experience Ravi Kant Jain 1, Chirag Sethi 1, Pranav Mahajan 1, Ravindra Kumar 2 1Department of Orthopaedics,
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace
 18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHYSEAL FEMUR FRACTURE WITH INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL AND K. NAIL
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences October 2015; 2(10) ISSN: ISSN: Impact Factor (PIF): 2.
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC LONG BONE FRACTURES OF LOWER LIMB BY TITANIUM ELASTIC NAILS *Dr.K.Venkataswamy, Dr.J.Venkateshwarulu, Dr.TandraVenkateshwararao, Dr.Shivanshu Mittal, Dr.J.Sreenath Rao
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF PAEDIATRIC LONG BONE FRACTURES OF LOWER LIMB BY TITANIUM ELASTIC NAILS *Dr.K.Venkataswamy, Dr.J.Venkateshwarulu, Dr.TandraVenkateshwararao, Dr.Shivanshu Mittal, Dr.J.Sreenath Rao
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 104: , 2014
 529275SJS104010.1177/1457496914529275A. Salonen, T. Lahdes-Vasama, V. M. Mattila, J. Välipakka, O. PajuloScandinavian Journal of Surgery research-article2014 Original Article Scandinavian Journal of Surgery
529275SJS104010.1177/1457496914529275A. Salonen, T. Lahdes-Vasama, V. M. Mattila, J. Välipakka, O. PajuloScandinavian Journal of Surgery research-article2014 Original Article Scandinavian Journal of Surgery
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Journal of American Science 2017;13(11) Submuscular Plating in Spiral Unstable Pediatric Femur Fractures
 Submuscular Plating in Spiral Unstable Pediatric Femur Fractures M. Salah Abdel hafiz, MD, Ibrahim Elsebaey, MD, Ahmed Elshorbagy MBBCH Department of Orthopedic Surgery Al-Azhar Faculty of Medicine ah_shorbagy@yahoo.com
Submuscular Plating in Spiral Unstable Pediatric Femur Fractures M. Salah Abdel hafiz, MD, Ibrahim Elsebaey, MD, Ahmed Elshorbagy MBBCH Department of Orthopedic Surgery Al-Azhar Faculty of Medicine ah_shorbagy@yahoo.com
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on Surgical Management of Distal Tibial Fractures by Using Minimally Invasive Technique
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on Surgical Management of Distal Tibial Fractures by Using Minimally Invasive Technique
Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures
 Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Paul Thompson, PhD Biomedical
Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Paul Thompson, PhD Biomedical
Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: A treatment concept
 Original Article Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: A treatment concept Ramji Lal Sahu* *Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics SMS and RI, Sharda University, Greater Noida,
Original Article Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: A treatment concept Ramji Lal Sahu* *Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics SMS and RI, Sharda University, Greater Noida,
M.S (orthopedics), FRAS (Germany) Chairman and chief Orthopedic consultant Surgeon, Q1 Hospital, Vizag. AP.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.1.OR3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Management of Diaphyseal Fractures of Long Bones in Children with Titanium Elastic Nails A Prospective Study of
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.1.OR3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Management of Diaphyseal Fractures of Long Bones in Children with Titanium Elastic Nails A Prospective Study of
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
InternationalJournalofAgricultural
 www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya
 Original Article Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya O.O. Soren, MBChB (Moi), MMed (Orthopaedics) (Makerere), Consultant Orthopaedic
Original Article Outcome of surgical implant generation network nail initiative in treatment of long bone shaft fractures in Kenya O.O. Soren, MBChB (Moi), MMed (Orthopaedics) (Makerere), Consultant Orthopaedic
Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 512-520 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures Gamal EL-ADL, Mohamed F. MOSTAFA, Mohamed A. KHALIL, Ahmed ENAN From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 512-520 ORIGINAL STUDY Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures Gamal EL-ADL, Mohamed F. MOSTAFA, Mohamed A. KHALIL, Ahmed ENAN From Mansoura
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Closed diaphyseal fractures of femur in children treated by hip spica: early result of a clinical study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Ansari MAQ et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):22-26 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175113
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Ansari MAQ et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):22-26 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175113
In paediatric femoral shaft fractures implementation of elastic stable intramedullary nail (ESIN) - A retrospective study
 Original Article In paediatric femoral shaft fractures implementation of elastic stable intramedullary nail (ESIN) - A retrospective study Jimmy Joseph Meleppuram 1*, Syed Ibrahim 2 1 PG Student, 2 Sr.
Original Article In paediatric femoral shaft fractures implementation of elastic stable intramedullary nail (ESIN) - A retrospective study Jimmy Joseph Meleppuram 1*, Syed Ibrahim 2 1 PG Student, 2 Sr.
A comparative study of locking plate by MIPO versus closed interlocking intramedullary nail in extraarticular distal tibia fractures
 2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Treatment of open tibial shaft fractures using intra medullary interlocking
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Reddy GR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 17 May;():66-7 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.18/issn.455-451.intjresorthop171574
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Fracture fixation. Types. Mechanical considerations. Biomechanics of fracture fixation. External fixation. Internal fixation
 Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
UNCORRECTED PROOF. Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution. V.S. Pai a, *, P. David Gwynne-Jones a, Jean Claude Theis b
 Injury Extra (2004) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext 2 3 Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 V.S. Pai a,
Injury Extra (2004) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext 2 3 Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 V.S. Pai a,
Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution
 Injury Extra (2005) 36, 185 189 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution V.S. Pai a, *, P. David Gwynne-Jones a, Jean Claude Theis b a Dunedin Hospital,
Injury Extra (2005) 36, 185 189 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext Femoral elastic nailing in the older child: proceed with caution V.S. Pai a, *, P. David Gwynne-Jones a, Jean Claude Theis b a Dunedin Hospital,
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
Type I : At the level of lesser trochanter Type II : Less than 2.5 cm below lesser trochanter. Type III : cm below lesser trochanter
 Type II : Major fracture line along the intertrochanteric line with communition in coronal plain. Type III : Fracture at the level of lesser trochanter with variable communition and extension in subtrochanteric
Type II : Major fracture line along the intertrochanteric line with communition in coronal plain. Type III : Fracture at the level of lesser trochanter with variable communition and extension in subtrochanteric
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee): A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Surgical Management Of Fractures Of The Femur Shaft In Children And Adolescents Using Flexible Nails - A Prospective Study
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 23 Number 1 Surgical Management Of Fractures Of The Femur Shaft In Children And Adolescents Using Flexible Nails - A Prospective Study V Sidhu,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 23 Number 1 Surgical Management Of Fractures Of The Femur Shaft In Children And Adolescents Using Flexible Nails - A Prospective Study V Sidhu,
Outcome of Titanium Elastic Intramedullary Nail in the Treatment of Shaft of Femur Fracture in Children. Khan JA, 1 Singh GP, 2 Pandey A 2
 Outcome of Titanium Elastic Intramedullary Nail in the Treatment of Shaft of Femur Fracture in Children. Khan JA, 1 Singh GP, 2 Pandey A 2 ABSTRACT Background 1 Karnali Academy of Health Sciences Jumla,
Outcome of Titanium Elastic Intramedullary Nail in the Treatment of Shaft of Femur Fracture in Children. Khan JA, 1 Singh GP, 2 Pandey A 2 ABSTRACT Background 1 Karnali Academy of Health Sciences Jumla,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Surgical Technique. Intramedullary locked Nailing With Screws for Humerus Fractures Solid/Cannulated. Humeral Interlocking Nail.
 Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
A prospective study of treatment of distal femur fractures with locking condylar plate
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rekha YB et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1117-1121 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174699
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rekha YB et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1117-1121 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174699
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons.
 Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
THE NANCY NAIL. The End Caps ADVANTAGES OF NANCY NAIL
 NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
Titanium elastic nail in femur fractures as an alternative to spica cast in preschoolers
 J Child Orthop (2012) 6:505 511 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0448-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Titanium elastic nail in femur fractures as an alternative to spica cast in preschoolers Yasser M. Assaghir Received:
J Child Orthop (2012) 6:505 511 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0448-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Titanium elastic nail in femur fractures as an alternative to spica cast in preschoolers Yasser M. Assaghir Received:
COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS
 COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS D.M. Kamau, MBChB, MMed (Ortho Surg), L.N. Gakuu, MBChB, MMed (Surg), FCS (ECSA), Professor, E.M. Gakuya,
COMPARISON OF CLOSED FEMUR FRACTURE: SKELETAL TRACTION AND INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING COST-EFFECTIVENESS D.M. Kamau, MBChB, MMed (Ortho Surg), L.N. Gakuu, MBChB, MMed (Surg), FCS (ECSA), Professor, E.M. Gakuya,
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of Both Bone Leg In Patients Attending Assam Medical College Hospital, Dibrugarh. Partha Pratim Das 5
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. V(Aug. 2017), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Study of Compound Fractures of
MJ-FLEX The New Metaizeau Nail TM. Operative Technique
 MJ-FLEX The New Metaizeau Nail TM Operative Technique General Description 3 Intended Use 3 Indication For Use 3 Features And Benefits 4 Equipment Required 5 Implant Principles 6 Nail Selection 6 Prior
MJ-FLEX The New Metaizeau Nail TM Operative Technique General Description 3 Intended Use 3 Indication For Use 3 Features And Benefits 4 Equipment Required 5 Implant Principles 6 Nail Selection 6 Prior
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing
 Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring Fixator
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
Reconstruction plate fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 200,, -90 ORIGINAL STUDY Reconstruction plate fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in children oustafa EL-SAYED, azen ABULSAAD, ahmoud EL- HADIDI, Wael EL-ADL, agdy EL-BATOUTY
Acta Orthop. Belg., 200,, -90 ORIGINAL STUDY Reconstruction plate fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in children oustafa EL-SAYED, azen ABULSAAD, ahmoud EL- HADIDI, Wael EL-ADL, agdy EL-BATOUTY
Original Research Article
 TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Apply this knowledge into proper management strategies and referrals
 1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
TREATMENT OF SUBTROCHANTERIC FEMUR FRACTURES WITH PROXIMAL FEMORAL NAILS: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Original Article Orthopaedics TREATMENT OF SUBTROCHANTERIC FEMUR FRACTURES WITH PROXIMAL FEMORAL NAILS: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Ravindra S. Patil 1, Dhanish V. Mehendiratta 2, Sahil Bhagat 2, Rishi Doshi 2,
Original Article Orthopaedics TREATMENT OF SUBTROCHANTERIC FEMUR FRACTURES WITH PROXIMAL FEMORAL NAILS: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Ravindra S. Patil 1, Dhanish V. Mehendiratta 2, Sahil Bhagat 2, Rishi Doshi 2,
Comparative Study of Fixation Devices for Intertrochanteric Fractures
 Comparative Study of Fixation Devices for Intertrochanteric Fractures C. Sticlaru * A. Davidescu Politehnica University of Timişoara Politehnica University of Timişoara Timişoara, România Timişoara, România
Comparative Study of Fixation Devices for Intertrochanteric Fractures C. Sticlaru * A. Davidescu Politehnica University of Timişoara Politehnica University of Timişoara Timişoara, România Timişoara, România
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails
 Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Tibial plateau fractures: four years review at B&B Hospital
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2004) Vol. 2, No. 4, Issue 8, 315-323 Original Article Tibial plateau fractures: four years review at B&B Hospital Shrestha BK 1, Bijukachhe B 2, Rajbhandary T 2,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2004) Vol. 2, No. 4, Issue 8, 315-323 Original Article Tibial plateau fractures: four years review at B&B Hospital Shrestha BK 1, Bijukachhe B 2, Rajbhandary T 2,
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
The change in energy absorbed post removal of metalwork in a simulated paediatric long bone fracture
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:443 447 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0606-z BASIC SCIENCE The change in energy absorbed post removal of metalwork in a simulated paediatric long bone fracture Alan J. Howieson Michael
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:443 447 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0606-z BASIC SCIENCE The change in energy absorbed post removal of metalwork in a simulated paediatric long bone fracture Alan J. Howieson Michael
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure?
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Functional outcome of both bone fracture forearm managed with titanium elastic intramedullary nail system in pediatric age group
 2018; 2(1): 37-41 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 37-41 Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 24-12-2017 Harish K Assistant Professor, Mandya,
2018; 2(1): 37-41 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 37-41 Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 24-12-2017 Harish K Assistant Professor, Mandya,
KEYWORDS: Tibial fracture, Diaphyseal fracture, closed interlocking intramedullary nailing,
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 4 Pages 2529-2534 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Closed Intra-Medullary Interlocking Nail Improves Surgical
Surgical outcome of fracture shaft femur in children using flexible intramedullary nailing
 2017; 3(3): 1137-1151 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 1137-1151 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-05-2017 Accepted: 06-06-2017 Vishwanath C Department of Orthopaedics, Adichunchanagiri Institute
2017; 3(3): 1137-1151 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 1137-1151 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-05-2017 Accepted: 06-06-2017 Vishwanath C Department of Orthopaedics, Adichunchanagiri Institute
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct
 Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent
 Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski, Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker, Lida Acuña-Huete Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Wan-Ju Li, PhD Biomedical
Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski, Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker, Lida Acuña-Huete Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Wan-Ju Li, PhD Biomedical
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient
 Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 76/ Sept. 21, 2015 Page 13162
 A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
Malunion in floating knee injuries An analysis in 30 patients presenting to a tertiary care facility and are surgically treated
 2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
PROXIMAL TIBIAL PLATE
 SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures. Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams
 Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of El Minoufiya, Egypt
Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of El Minoufiya, Egypt
Unreamed Solid Locked Nailing In The Treatment Of Compound Diaphyseal Fractures Of The Tibia.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 Unreamed Solid Locked Nailing In The Treatment Of Compound Diaphyseal Fractures Of The Tibia. R Singh, T Motten, N Kalsotra, R Gupta,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 Unreamed Solid Locked Nailing In The Treatment Of Compound Diaphyseal Fractures Of The Tibia. R Singh, T Motten, N Kalsotra, R Gupta,
Use Of Ender's Nailing in Treatment of Pediatric Fracture Shaft Femur
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 33-40 www.iosrjournals.org Use Of Ender's Nailing in Treatment
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 33-40 www.iosrjournals.org Use Of Ender's Nailing in Treatment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ABSTRACT: Orthopaedic surgeons often encounter diaphyseal femur fractures, because these
 A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE SHAFT FEMUR WITH CLOSED INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL. Mahendranath Reddy D 1, Muralidhar B.M 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mahendranath Reddy D,
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE SHAFT FEMUR WITH CLOSED INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL. Mahendranath Reddy D 1, Muralidhar B.M 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mahendranath Reddy D,
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old
 1 Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City MO, USA rmschwend@cmh.edu 5 th Annual SLAOTI
1 Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City MO, USA rmschwend@cmh.edu 5 th Annual SLAOTI
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
Intramedullary Nailing for Femur Fracture Management
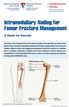 514-412-4400, ext. 23310 thechildren.com/trauma Intramedullary Nailing for Femur Fracture Management A Guide for Parents The femur is the longest bone in the body. It begins at the hip joint and ends at
514-412-4400, ext. 23310 thechildren.com/trauma Intramedullary Nailing for Femur Fracture Management A Guide for Parents The femur is the longest bone in the body. It begins at the hip joint and ends at
Segmental tibial fractures treated with unreamed interlocking nail A prospective study
 2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
