Rotator cuff tendinopathy: a model for the continuum of pathology and related management
|
|
|
- Peregrine Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Correspondence to Dr Jeremy S Lewis, Therapy Department, Chelsea and Westminster NHS Healthcare, 369 Fulham Road, London SW10 9NH, UK; jeremy. lewis@chelwest.nhs.uk Accepted 31 March 2009 Rotator cuff : a model for the continuum of pathology and related management Jeremy S Lewis ABSTRACT Background Pathology of the soft tissues of the shoulder including the musculotendinous rotator cuff and subacromial bursa are extremely common and are a principal cause of pain and suffering. Competing theories have been proposed to explain the pathoaetiology of rotator cuff pathology at specifi c stages and presentations of the condition. This review proposes a model to describe the continuum of the rotator cuff pathology from asymptomatic through full thickness rotator cuff tears. Conclusions The pathoaetiology of rotator cuff failure is multifactorial and results from a combination of intrinsic, extrinsic and environmental factors. Recently a new and generic model detailing the continuum of pathology has been proposed. This model is relevant for the rotator cuff and provides a framework to stage the continuity of rotator cuff pathology. Furthermore, it provides a structure to identify the substantial defi ciencies in our knowledge base and areas where research would improve our understanding of the pathological and repair process, together with assessment and management. The strength of this model adapted for the rotator cuff s and subacromial bursa will be tested in its ability to incorporate and adapt to emerging research. INTRODUCTION Certain sports place substantial demands on the shoulder. Elite swimmers execute approximately 2 million strokes per year, 1 2 and professional baseball pitchers generate ball speeds of up to 165 km/h with associated peak internal-rotation velocities up to 6940 /s. 3 4 These data elucidate why pathologies of the musculotendinous rotator cuff and subacromial bursa (SAB) are considered principal causes of shoulder pain. Various theories have been proposed to explain the pathogenesis of rotator cuff. These include compression from extrinsic and intrinsic causes, underuse and overuse, 5 11 genetics, 12 evolutionary adaptations 13 and nutrition To date, a defi nitive understanding of the pathoaetiology of rotator cuff has not been because of equivocal and insufficient research evidence. A review of anatomy, function and pathology of the rotator cuff has recently been published. 16 Cook and Purdam 17 recently presented a generic model to define the continuum of pathology. This new paradigm involves staging pathology chronologically within a clinical, histological and imaging framework. The continuum involves a transition from normal to currently irreversible pathology. Variations of the generic model may be required because of regional anatomical and/ or biomechanical considerations. The purpose of this review is to discuss the relevance of this new generic model with regard to rotator cuff and to propose management options for each of the stages described by Cook and Purdam. 17 ROTATOR CUFF TENDINOPATHY: A NEW MODEL The rotator cuff model (detailed in fig 1) is based on the generic model presented by Cook and Purdam 17 and involves placing normal rotator cuff as the optimal functional unit. This is defined as a structurally sound that is pain-free and capable of performing the normal functional tasks required by the individual. Within this model, the unit has the capacity to positively adapt to appropriate and graduated stress. Underloaded occurs when the rotator cuff does not receive appropriate physiological stress. Although this may occur throughout the, its presence will be disproportionate and may affect the region of the rotator crescent and the articular side of the supraspinatus With an appropriate stimulus, an underloaded may return to become a normal. Tendon underuse may result in an imbalance of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (tissue inhibitors of MMP (TIMPs)), which may eventuate in degradation. Imaging (ultrasound (US) and MRI) investigations may reveal age- and activity-related structural pathology, which in this stage of the continuum may remain asymptomatic. The normal rotator cuff and the underloaded, if subject to an activity level in excess of that normally placed on the, may subject the tissue to overload. If the overload is transient, which may be identified on MRI as in an increase in volume due to increased bound water content, the may return to its preloaded state. This state termed normal overload is painfree and is a normal response to loading rotator cuff tissue through activity and exercise. However, the increased volume under the coracoacromial arch may potentially increase the strain in the coracoacromial ligament. Because of its trapezoidal shape and the relatively smaller surface area on the acromial side, strain within the ligament may potentially lead to the development of acromial traction spurs. The development of these osteophytes may depend on load and the anatomy of the region. 20 Continuous loading in this state may have an either positive or negative effect on the. This will depend on 918 Br J Sports Med 2010;44: doi: /bjsm
2 Under loaded Normal Rotator cuff : a model for the continuum of pathology Under loaded/ normal overload the intensity, volume and frequency of the load applied to the. If applied in a graduated and controlled manner, the loading will lead to a capable of withstanding greater stress. If the applied load exceeds the physiological capacity of the rotator cuff, the effect may be upregulation. The first stage may be reactive and is predominantly seen in an acutely overloaded. This stage may involve the SAB tissue, where abnormal neuropeptide (substance P) and cytokine levels have been reported Although there may be no substantial areas of degeneration, there will be increased swelling within the, and it possibly involves bursal effusion. Cook and Purdam 17 have suggested that this stage occurs following a burst of unaccustomed activity and exists as a transition phase between normal and disrepair. This stage is probably driven by an increased activation of tenocytes, whose first response is driving a deposition of proteoglycans with larger molecular weight such as aggrecan. Pain may be present, and this may be constant or intermittent and probably position and activity dependent. Constant pain and/or night pain may further implicate the SAB. 23 In this stage, failure of the rotator cuff to control superior translation of the humeral head may lead to a secondary irritation of the superior fibres of the against the coracoacromial ligament and the undersurface of the acromion. 24 Because of the upregulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor in the early stages of rotator cuff overuse, 16 neovascularity may be present. Cook and Purdam 17 defined the next stage in the continuum as disrepair. This will involve essentially the same spectrum of clinical symptoms as reactive. The symptoms may be more commonly associated with movement and activity. Tendon disrepair may be characterised by substantial areas of swelling, degeneration, hypoechoic areas on greyscale US imaging that correspond with disorganisation of the matrix, increases in ground substance and Reactive with bursal Tendon disrepair with bursal may also include element of reactive Degenerated with bursal may also include element of reactive Figure 1 Rotator cuff : a model for the continuum of pathology. Dotted arrows, potentially reversible; solid two-directional arrows, reversible; solid single-directional arrows, irreversible; dotted single-directional arrows, irreversible without going through an intermediate step. some separation of the collagen fibres. It will also be observed as swelling and increased signal on MRI. A bursal reaction characterised by effusion and areas of neovascularity within the and bursa may be present. The presence of neovascularity may be more evident if examined with the off stretch, following an activity or after heating. Cook and Purdam 17 have classified the final stage as degenerated, and for the rotator cuff, this will be associated with substantial structural failure in the form of large partial-thickness, full-thickness and massive rotator cuff tears. 25 In the late stages, there may also be radiological evidence of glenohumeral and acromial degenerative changes. STAGING TREATMENT WITHIN THIS MODEL Patient education, pain reduction, load management (unloading and reloading) and re-injury prevention form the basis of symptomatic rotator cuff rehabilitation. In addition to this, consideration should be given to the possibility of SAB associated with the presenting symptoms. To maintain optimal health and function, s require appropriate ongoing mechanical stimulation. Chronically underloaded in a sedentary population may result in asymptomatic degeneration and tears, which will increase with age. This may occur as a result of alterations in the concentrations of the MMPs and TIMPs. It is not currently understood why elite-level athletes develop asymptomatic rotator cuff pathology. 26 It may be due to overuse or fluctuating periods of activity and relative rest influencing MMP and TIMP concentrations. It may also be due to the relatively low innervation in s that do not produce a pain response in the presence of structural pathology until a specific threshold is reached. Treatment for an underloaded rotator cuff involves a -reloading programme in a controlled and graduated manner. The management for a structurally and functionally normal rotator cuff involves maintenance of physical activity with appropriate controlled and graduated increase in loading as required. To maximise the benefit of -loading Br J Sports Med 2010;44: doi: /bjsm
3 Table 1 Continuum of rotator cuff pathology, with imaging fi ndings, clinical presentations and management options State Underloaded Normal Underloaded/normal overload Reactive (acute phase) Tendon disrepair (subacute to chronic phase) Degenerated (chronic phase) Imaging Essentially normal Asymptomatic degeneration and tears may be present Increasing with age Cause Suboptimal mechanical stress (stress shielding) Increase in MMP1 and MMP13 Due to chronic suboptimal tenocyte stimulation Clinical Pain-free and suboptimal shoulder function Management Reload in controlled and graduated manner Normal Asymptomatic degeneration and tears may be present Increasing with age Appropriate mechanical stress Normal tensile and compressive properties Pain-free normal shoulder movement and function Maintain physical activity Increase loading in controlled and graduated manner Oedematous Asymptomatic degeneration and tears may be present Increasing with age Tendon mechanically overloaded May be benefi cial or may lead to reactive Pain-free shoulder function may be normal or suboptimal Reload in controlled and graduated manner Oedematous Neovascularity Bursal (evidenced by effusion) Hypoechoic areas may be present in grey scale (may or may not be cause of pain and symptoms) Tendon mechanically overloaded by surpassing physiological capacity of (1) normal or (2) chronically unloaded No certainty where pain is coming from Pain increases with activity Persistent pain and night pain suggest bursal Relative rest Decrease loading by controlling activity level to VAS pain 1 2/10(?) Biomechanical unloading interventions Exercise(?) Reduce pain Relative rest(?) Modalities(?) (Laser, magnetism) Manual therapy cervicothoracic spine/upper quadrant(?) Guided analgesic±cs injection(?) (primarily for pain control, CS may decrease cell proliferation and protein production) Response to shoulder symptom assessment procedure(?) Reduce swelling Produced by tenocyte activity leading to volume of ground substance. Aggrecan key protein responsible for swelling Ibuprofen inhibits aggrecan and downregulates cellular response. Has no detrimental effect on repair(?) Ice/cryotherapy(?) decrease in cell metabolism Oedematous Neovascularity Bursal (evidenced by effusion) Degeneration to small PTT present (may or may not be cause of pain and symptoms) Substantial overload and incomplete healing No certainty where pain is coming from Pain increased with activity Persistent pain and night pain suggest bursal Reduce pain Relative rest(?) Modalities(?) (US, laser, ESWT, magnetism) Manual therapy(?) Guided injection(?) Response to shoulder symptom assessment procedure(?) GTN patches(?) Reduce neovascularity Ice/cryotherapy(?) Heat/thermal modalities(?) Guided sclerosant injections(?) ESWT(?) Exercise (eccentric)(?) Exercise Reload using a supervised graduated exercise programme Control VAS pain to 1 2/10 Eccentric exercise therapy Include manual therapy Include exercise to depress humeral head(?) Nutritional supplements/dietary changes(?) Surgery Lavage(?) Bursectomy(?) Neovascularity less likely with an increase in size of tear Bursal (evidenced by effusion) Large PTT to FTT present involving the rotator cable (may or may not be a cause of pain if present) Fat infi ltration may be evident in muscle in CT/MRI Substantial overload and areas of partial- to full-thickness tears No certainty where pain (if present) is coming from Painful to pain-free shoulder movement Passive movement greater than active movement Reduce pain Relative rest(?) Modalities(?) (US, laser, ESWT, magnetism) Manual therapy(?) Guided injection(?) Response to shoulder symptom assessment procedure(?) GTN patches(?) Reduce neovascularity Ice/cryotherapy(?) Heat/thermal modalities(?) Guided sclerosant injections(?) ESWT(?) Exercise (eccentric)(?) Exercise Reload using a supervised graduated exercise programme Control VAS pain to 1 2/10 Eccentric exercise therapy Include manual therapy Include exercise to depress humeral head(?) Specialised exercise programme for large to massive RC tears(?) Stimulation of cellular activity US(?), heat/thermal therapy(?), laser(?), magnetic therapy(?) Continued 920 Br J Sports Med 2010;44: doi: /bjsm
4 Table 1 Continued Nutritional supplements/dietary changes(?) Surgery Lavage(?) Bursectomy(?) Bursectomy+acromioplasty(?) Repair(?) important to consider amount of muscular fat infi ltration prior to repair The future Pharmacological modifi cation of cytokines/mmp/timmp/adamts activity(?) Stem cells(?) Platelet-rich plasma injections(?) Tendon grafts(?) Bursectomy+acromioplasty(?) Repair(?) important to consider amount of muscular fat infi ltration prior to repair The future Pharmacological modifi cation of cytokines/mmp/timp/adamts activity(?) Stem cells(?) Platelet-rich plasma injections(?) Exercise No high-load elastic or eccentric exercise(?) No exercise that involves energy storage and release(?) Concentrate on rhythmical arm movements (?) (short lever if required) Nutritional supplements/dietary changes(?) The future Pharmacological modifi cation of cytokines/mmp/timp/adamts activity(?) ADAMTS, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs; CS, corticosteroid; ESWT, extracorporeal short-wave therapy; FTT, full-thickness tear; GTN, glyceryl trinitrate; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PTT, partial-thickness tear; RC, rotator cuff; TIMPs, tissue inhibitors of MMP; US, ultrasound; US, therapeutic ultrasound; VAS pain, visual analogue scale for pain;, decrease;, increase;?, uncertainty research required. activities, the load, duration and intensity of activity placed on the rotator cuff s must be carefully controlled, structured and monitored. Load reduction, together with pain management, is a key component in the management of reactive. Evidence-based guidance is not currently available. One suggestion requiring vigorous scientific enquiry would be to reduce activity level to control pain to a level of 1 to 2 out of 10 (worst imaginable pain) on a visual analogue scale of pain. Additionally, during this period of relative rest, modalities, taping and manual therapy may be considered to reduce pain and restore shoulder movement and function. The inclusion of these procedures, at this stage of management, is not substantiated by definitive research evidence, and ongoing scientific enquiry is essential. Other methods of assessing the shoulder in order to determine management options, including pain reduction and restoration of movement, have been suggested. 27 The presence of intratendinous swelling is a potential feature of this stage of pathology. Selective non-steroidal anti-infl ammatory drugs appear to inhibit cell proliferation and matrix glycosaminoglycan synthesis, 28 and the synthesis of aggrecan may be inhibited by the non-steroidal anti-infl ammatory drug, ibuprofen. 29 Guided SAB injections may help reduce pain and improve function. 30 Uncertainty exists as to whether injections should include analgesic or analgesic and steroid Although yet to be substantiated, cryotherapy may also reduce swelling. Exercises to reduce superior migration of the humeral head on the glenoid fossa may be beneficial. High-load eccentric exercises and fast concentric/eccentric regimes should probably be avoided. Dietary changes may be beneficial to improve health and symptoms Ongoing pain management and the other components of management for reactive remain important components for the treatment of disrepair. Graduated reloading including concentric, isometric and eccentric exercise is introduced during this stage. Evidence exists that glenohumeral external and internal rotations have opposing effects on subacromial pressure 34 with external rotation lowering pressure. Additionally, exercises to depress the humeral head may also be warranted. 27 Failure of an exercise programme to achieve the desired outcome may necessitate other management options such as glyceryl trinitrate patches, 35 injection therapy and possibly surgery. Conservative treatment should generally be considered before surgical intervention All interventions require vigorous scientific investigation. Evidence exists from other regions that reducing the expression of neovascularity is associated with a reduction in symptoms. 38 A number of therapeutic techniques such as cyrotherapy, thermal modalities and exercise may contribute to reducing neovascularity. The relationship between neovascularity and symptoms arising from rotator cuff pathology and the SAB is yet to be established, and if a defi nitive correlation exists, then research designed to investigate the best methods of reducing the expression of neovascularity in a timely manner without resulting in short- or long-term damage is required. Pain control and restoring normal movement are the principal aims of managing degenerated. 39 Clinical investigations have suggested that even in the presence of substantial structural pathology, range of movement and power may be improved when pain is reduced and management options described for disrepair are relevant for degeneration. Another key factor that may positively influence outcome is the presence of a functioning rotator cable. 19 The decision to Br J Sports Med 2010;44: doi: /bjsm
5 attempt a surgical repair of the tear should be informed on an assessment of the (1) individual patient s functional requirements, (2) size of the tear and (3) the amount of fat infiltration into the muscle because the presence of fatty streaks has been associated with negative surgical outcomes Future advances in pharmacology, stem cell research and grafts may lead to advances in the management of degenerated s and other aspects of the continuum of rotator cuff pathology. Table 1 summarises the continuum of rotator cuff pathology, with imaging findings, clinical presentations and management options. CONCLUSION Recently, a new and generic model detailing the continuum of pathology has been proposed. This model is relevant for the rotator cuff and provides a framework to stage the continuity of rotator cuff disease. Furthermore, it provides a structure to identify the substantial deficiencies in our knowledge base and areas, where research would improve our understanding of the pathological and repair process, together with assessment and management. Cook and Purdam 17 have suggested that the strength of their generic model will be tested in its ability to incorporate and adapt to emerging research. This also applies for the rotator cuff continuum model presented in this paper. Competing interests None. Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed. What is already known on this topic Rotator cuff is common and associated with substantial morbidity. Confl icting theories pertaining to the pathogenesis of rotator cuff and bursal pathology exist. What this study adds The review is presented attempting to describe a model for the continuum of rotator cuff. The continuum involves a transition from normal to currently irreversible pathology. The stages involve asymptomatic, normal overload, reactive, disrepair and degenerative. The model describes a corresponding aetiological, clinical, histological and imaging framework for the various stages, together with a framework for management. REFERENCES 1. Richardson AB, Jobe FW, Collins HR. The shoulder in competitive swimming. Am J Sports Med 1980;8: Ciullo JV, Stevens GG. The prevention and treatment of injuries to the shoulder in swimming. Sports Med 1989;7: Feltner M, Dapena J. Three-dimensional interactions in a two-segment kinetic chain. Part I: General model. Int J Sport Biomech 1989;5: Dillman CJ, Fleisig GS, Andrews JR. Biomechanics of pitching with emphasis upon shoulder kinematics. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 1993;18: Vogel KG. Tendon structure and response to changing mechanical load. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2003;3:323 5; discussion Bunata RE, Brown DS, Capelo R. Anatomic factors related to the cause of tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89: Lyman J, Weinhold PS, Almekinders LC. Strain behavior of the distal achilles : implications for insertional achilles. Am J Sports Med 2004;32: Thornton GM, Shao X, Chung M, et al. Changes in mechanical loading lead to -specifi c alterations in MMP and TIMP expression: infl uence of stressdeprivation and intermittent cyclic hydrostatic compression on rat supraspinatus and Achilles s. Br J Sports Med 2008;In Press. 9. Soslowsky LJ, Thomopoulos S, Esmail A, et al. Rotator cuff tendinosis in an animal model: role of extrinsic and overuse factors. Ann Biomed Eng 2002;30: Perry SM, McIlhenny SE, Hoffman MC, et al. Infl ammatory and angiogenic mrna levels are altered in a supraspinatus overuse animal model. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2005;14:79S 83S. 11. Riley GP, Curry V, DeGroot J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase activities and their relationship with collagen remodelling in pathology. Matrix Biol 2002;21: Harvie P, Ostlere SJ, Teh J, et al. Genetic infl uences in the aetiology of tears of the rotator cuff. Sibling risk of a full-thickness tear. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86: Lewis J, Green A, Yizhat Z, et al. Subacromial impingement syndrome: has evolution failed us? Physiotherapy 2001;87: Radák Z, Takahashi R, Kumiyama A, et al. Effect of aging and late onset dietary restriction on antioxidant enzymes and proteasome activities, and protein carbonylation of rat skeletal muscle and. Exp Gerontol 2002;37: Lewis JS, Sandford FM. Rotator cuff : is there a role for polyunsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants? J Hand Ther 2009;22:49 55; quiz Lewis JS. Rotator cuff. Br J Sports Med 2009;43: Cook JL, Purdam CR. Is pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain the clinical presentation of load-induced. Br J Sports Med 2009;43: Bey MJ, Song HK, Wehrli FW, et al. Intratendinous strain fi elds of the intact supraspinatus : the effect of glenohumeral joint position and region. J Orthop Res 2002;20: Burkhart SS, Esch JC, Jolson RS. The rotator crescent and rotator cable: an anatomic description of the shoulder s suspension bridge. Arthroscopy 1993;9: Edelson JG, Taitz C. Anatomy of the coraco-acromial arch. Relation to degeneration of the acromion. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1992;74: Gotoh M, Hamada K, Yamakawa H, et al. Increased substance P in subacromial bursa and shoulder pain in rotator cuff diseases. J Orthop Res 1998;16: Sakai H, Fujita K, Sakai Y, et al. Immunolocalization of cytokines and growth factors in subacromial bursa of rotator cuff tear patients. Kobe J Med Sci 2001;47: Santavirta S, Konttinen YT, Antti-Poika I, et al. Infl ammation of the subacromial bursa in chronic shoulder pain. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1992;111: Lazarus MD, Yung SW, Sidles JA, et al. Anterosuperior humeral head displacement: limitation by the coracoacromial arch. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 1996;5:S Jozsa L, Kannus P. Human s: anatomy, physiology and pathology. Champaign, Illinois, USA: Human Kinetics, Miniaci A, Mascia AT, Salonen DC, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder in asymptomatic professional baseball pitchers. Am J Sports Med 2002;30: Lewis JS. Rotator cuff /subacromial impingement syndrome: is it time for a new method of assessment? Br J Sports Med 2009;43: Riley GP, Cox M, Harrall RL, et al. Inhibition of cell proliferation and matrix glycosaminoglycan synthesis by non-steroidal anti-infl ammatory drugs in vitro. J Hand Surg Br 2001;26: Tsai WC, Tang FT, Hsu CC, et al. Ibuprofen inhibition of cell proliferation and upregulation of the cyclin kinase inhibitor p21cip1. J Orthop Res 2004;22: Henkus HE, Cobben LP, Coerkamp EG, et al. The accuracy of subacromial injections: a prospective randomized magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthroscopy 2006;22: Plafki C, Steffen R, Willburger RE, et al. Local anaesthetic injection with and without corticosteroids for subacromial impingement syndrome. Int Orthop 2000;24: Br J Sports Med 2010;44: doi: /bjsm
6 32. Alvarez CM, Litchfi eld R, Jackowski D, et al. A prospective, double-blind, randomized clinical trial comparing subacromial injection of betamethasone and xylocaine to xylocaine alone in chronic rotator cuff tendinosis. Am J Sports Med 2005;33: Ekeberg OM, Bautz-Holter E, Tveitå EK, et al. Subacromial ultrasound guided or systemic steroid injection for rotator cuff disease: randomised double blind study. BMJ 2009;338:a Werner CM, Blumenthal S, Curt A, et al. Subacromial pressures in vivo and effects of selective experimental suprascapular nerve block. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2006;15: Murrell GA. Using nitric oxide to treat. Br J Sports Med 2007;41: Haahr JP, Østergaard S, Dalsgaard J, et al. Exercises versus arthroscopic decompression in patients with subacromial impingement: a randomised, controlled study in 90 cases with a one year follow up. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64: Haahr JP, Andersen JH. Exercises may be as effi cient as subacromial decompression in patients with subacromial stage II impingement: 4-8- years follow-up in a prospective, randomized study. Scand J Rheumatol 2006;35: Alfredson H, Ohberg L. Sclerosing injections to areas of neo-vascularisation reduce pain in chronic Achilles : a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2005;13: Ainsworth R, Lewis JS. Exercise therapy for the conservative management of full thickness tears of the rotator cuff: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med 2007;41: Ben-Yishay A, Zuckerman JD, Gallagher M, et al. Pain inhibition of shoulder strength in patients with impingement syndrome. Orthopedics 1994;17: Brox JI, Røe C, Saugen E, et al. Isometric abduction muscle activation in patients with rotator tendinosis of the shoulder. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1997;78: Steenbrink F, de Groot JH, Veeger HE, et al. Pathological muscle activation patterns in patients with massive rotator cuff tears, with and without subacromial anaesthetics. Man Ther 2006;11: Goutallier D, Postel JM, Gleyze P, et al. Infl uence of cuff muscle fatty degeneration on anatomic and functional outcomes after simple suture of fullthickness tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2003;12: Liem D, Lichtenberg S, Magosch P, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of arthroscopic supraspinatus repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89: Br J Sports Med: first published as /bjsm on 12 April Downloaded from on 21 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright. Br J Sports Med 2010;44: doi: /bjsm
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of
 Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears
 Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
8/8/2017. Partial Rotator Cuff Tears. Disclosures. Prevalence. Geoffrey S. Van Thiel, MD/MBA OrthoIllinois
 Partial Rotator Cuff Tears Geoffrey S. Van Thiel, MD/MBA OrthoIllinois Associate Professor Rush University Medical Center Associate Professor University of Illinois Team Physician US National Soccer Team
Partial Rotator Cuff Tears Geoffrey S. Van Thiel, MD/MBA OrthoIllinois Associate Professor Rush University Medical Center Associate Professor University of Illinois Team Physician US National Soccer Team
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
New insights into the mechanisms of tendon injury
 New insights into the mechanisms of tendon injury What is normal tendon? A extracellular matrix tissue Type 1 collagen Small amounts of CRITICAL proteins Ground substance Proteoglycans, glycoproteins Structures
New insights into the mechanisms of tendon injury What is normal tendon? A extracellular matrix tissue Type 1 collagen Small amounts of CRITICAL proteins Ground substance Proteoglycans, glycoproteins Structures
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the
Acromioplasty. Surgical Indications and Considerations
 1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012
 Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
Considerations 3/9/2018. Asheesh Bedi, MD. I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest related to the content of this presentation.
 Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
Shoulder Impingement. Eden Raleigh Orthopaedic Surgeon Shoulder & Knee Surgery. Ph:
 Shoulder Impingement Eden Raleigh Orthopaedic Surgeon Shoulder & Knee Surgery Ph: 9421 1900 0402697115 dredenraleigh@gmail.com My Background Specialising in Shoulder and Knee Surgery Main focus on Arthroscopic/Sports
Shoulder Impingement Eden Raleigh Orthopaedic Surgeon Shoulder & Knee Surgery Ph: 9421 1900 0402697115 dredenraleigh@gmail.com My Background Specialising in Shoulder and Knee Surgery Main focus on Arthroscopic/Sports
Achilles tendon injury
 Achilles tendon injury Achilles tendinopathy is highly prevalent in athletes who participate in running-based sports but can also occur in racket sports and in sedentary people. Research suggests there
Achilles tendon injury Achilles tendinopathy is highly prevalent in athletes who participate in running-based sports but can also occur in racket sports and in sedentary people. Research suggests there
Management of common shoulder pathologies. Val Jones Physiotherapy Practitioner Sheffield Shoulder & Elbow Unit
 Management of common shoulder pathologies Val Jones Physiotherapy Practitioner Sheffield Shoulder & Elbow Unit Objectives Review evidence based assessment and management of common shoulder pathologies
Management of common shoulder pathologies Val Jones Physiotherapy Practitioner Sheffield Shoulder & Elbow Unit Objectives Review evidence based assessment and management of common shoulder pathologies
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
 SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Conservative management of subacromial pathology Mel Cusi MBBS, Cert Sp Med, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Presenting symptoms Shoulder
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Conservative management of subacromial pathology Mel Cusi MBBS, Cert Sp Med, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Presenting symptoms Shoulder
TIPS FOR SUCCESSFUL SHOULDER TREATMENT. In Service Training 16 th May 2014
 TIPS FOR SUCCESSFUL SHOULDER TREATMENT In Service Training 16 th May 2014 Training day aims to address: Controversies of impingement syndrome diagnosis Controversies of MRI/USS imaging Clinical diagnosis
TIPS FOR SUCCESSFUL SHOULDER TREATMENT In Service Training 16 th May 2014 Training day aims to address: Controversies of impingement syndrome diagnosis Controversies of MRI/USS imaging Clinical diagnosis
The challenges Tendinopathy a continuum The long and winding road A (very) brief history History - continued Tendon tissue model Collagen types
 The challenges Tendinopathy a continuum The journey and its utility Craig Purdam Head of Discipline Physical Therapies Tendinopathy is varied does not respond universally to a given intervention The clinical
The challenges Tendinopathy a continuum The journey and its utility Craig Purdam Head of Discipline Physical Therapies Tendinopathy is varied does not respond universally to a given intervention The clinical
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Principles of Treatment. Case Studies. Principles of Treatment. Clinical Perspectives for the GP
 Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Shoulder Disorders
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Shoulder Disorders NAOEM Oct 14 th, 2017 Michael Codsi, M.D. www.drcodsi.com Learning Objectives SLAP tears diagnosis, imaging and treatment How to diagnose rotator cuff
Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Shoulder Disorders NAOEM Oct 14 th, 2017 Michael Codsi, M.D. www.drcodsi.com Learning Objectives SLAP tears diagnosis, imaging and treatment How to diagnose rotator cuff
THE ROTATOR CUFF the science behind the disease
 THE ROTATOR CUFF the science behind the disease Jerome Goldberg www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick What do we know Many older people have RC tears Many people
THE ROTATOR CUFF the science behind the disease Jerome Goldberg www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick What do we know Many older people have RC tears Many people
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
 Differential Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Disease Director of Clinical Outcomes and Research Director University of Southern California; Los Angeles, CA lmichene@pt.usc.edu http://pt.usc.edu/coor/ Rotator
Differential Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Disease Director of Clinical Outcomes and Research Director University of Southern California; Los Angeles, CA lmichene@pt.usc.edu http://pt.usc.edu/coor/ Rotator
mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading
 Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Diclofenac And Triamcinolone Acetonide Impair Tenocytic Differentiation And Promote Adipocytic Differentiation Of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Diclofenac And Triamcinolone Acetonide Impair Tenocytic Differentiation And Promote Adipocytic Differentiation Of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Maritha Fredriksson, Yan Li, Anders Stråman, Lars-Arne Haldosen,
Diclofenac And Triamcinolone Acetonide Impair Tenocytic Differentiation And Promote Adipocytic Differentiation Of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Maritha Fredriksson, Yan Li, Anders Stråman, Lars-Arne Haldosen,
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
THE OLDER TENNIS AND GOLF ATHLETE: INJURY MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION
 THE OLDER TENNIS AND GOLF ATHLETE: INJURY MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION William Micheo, MD Professor and Chairman Physical Medicine, Rehabilitation, and Sports Medicine Department University of Puerto Rico
THE OLDER TENNIS AND GOLF ATHLETE: INJURY MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION William Micheo, MD Professor and Chairman Physical Medicine, Rehabilitation, and Sports Medicine Department University of Puerto Rico
Latest technology in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant tendinopathy
 Latest technology in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant tendinopathy Dr K Arjun Rao Consultant Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician FACSEP FFSEM(UK) Specialist Sportscare W.A. WA Institute of Sport School
Latest technology in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant tendinopathy Dr K Arjun Rao Consultant Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician FACSEP FFSEM(UK) Specialist Sportscare W.A. WA Institute of Sport School
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Pathophysiology and Treatment Options. Mike Walton Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Wrightington Hospital
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Pathophysiology and Treatment Options Mike Walton Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Wrightington Hospital Tendon Structure Tendons are mechanically responsible for the transmission
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Pathophysiology and Treatment Options Mike Walton Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Wrightington Hospital Tendon Structure Tendons are mechanically responsible for the transmission
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
Impingement syndrome. Clinical features. Management. Rotator cuff tear diagnosed. Go to rotator cuff tear
 Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC
 Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC International Convention of the Vietnamese Physicians, Dentists and Pharmacists of the Free World Melbourne 8 10 August 2014 Conflict of Interest None Subacromial
Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC International Convention of the Vietnamese Physicians, Dentists and Pharmacists of the Free World Melbourne 8 10 August 2014 Conflict of Interest None Subacromial
 www.simonmoyes.com+ www.shoulder-arthroscopy.co.uk Impingement)and)Rotator)Cuff) Tears) Presented+by+Mr+Simon+Moyes+ Shoulder)Experience) RNOH)shoulder)unit) Visi7ng)fellow)Royal)North)Shore,)Sydney) RNOH)shoulder)fellow)
www.simonmoyes.com+ www.shoulder-arthroscopy.co.uk Impingement)and)Rotator)Cuff) Tears) Presented+by+Mr+Simon+Moyes+ Shoulder)Experience) RNOH)shoulder)unit) Visi7ng)fellow)Royal)North)Shore,)Sydney) RNOH)shoulder)fellow)
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
Volume 17 Video Transcripts
 Volume 17 Video Transcripts Introduction This month s presentation is based on a paper published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine titled Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain
Volume 17 Video Transcripts Introduction This month s presentation is based on a paper published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine titled Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
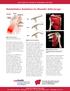 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
Platelet-Rich Plasma Can Be Used to Successfully Treat Elbow Ulnar Collateral Ligament Insufficiency in High- Level Throwers
 Platelet-Rich Plasma Can Be Used to Successfully Treat Elbow Ulnar Collateral Ligament Insufficiency in High- Level Throwers Am J Orthop. 2016 May;45(4):296-300 Authors: Dines JS Williams PN Elattrache
Platelet-Rich Plasma Can Be Used to Successfully Treat Elbow Ulnar Collateral Ligament Insufficiency in High- Level Throwers Am J Orthop. 2016 May;45(4):296-300 Authors: Dines JS Williams PN Elattrache
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
ORTHOPEDICS BONE Recalcitrant nonunions In total hip replacement total knee surgery increased callus volume
 ORTHOPEDICS Orthopedics has to do with a variety of tissue: bone, cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle. In this regard orthopedic and sports medicine share the same tissue targets. Orthopedics is mostly
ORTHOPEDICS Orthopedics has to do with a variety of tissue: bone, cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle. In this regard orthopedic and sports medicine share the same tissue targets. Orthopedics is mostly
Requested Topics for IST Redcar April 2012
 Requested Topics for IST Redcar April 2012 Rotator Cuff Tears Management Assessment & Management of ACJ Injuries Management of loss of ROM Hypermobile Adolescents Protocols & Classes at JCUH Distension
Requested Topics for IST Redcar April 2012 Rotator Cuff Tears Management Assessment & Management of ACJ Injuries Management of loss of ROM Hypermobile Adolescents Protocols & Classes at JCUH Distension
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention
 Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention Biomechanics Throwing a baseball is an unnatural movement Excessively high forces are generated at the elbow and shoulder Throwing requires
Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention Biomechanics Throwing a baseball is an unnatural movement Excessively high forces are generated at the elbow and shoulder Throwing requires
Rotator Cuff Tears Our approach
 Rotator Cuff Tears Our approach Terry R. Malone EdD., PT, ATC Professor of Physical Therapy University of Kentucky Nothing to disclose only wish Deep Musculature & Glenoid RC Insertion Data The RC insertion
Rotator Cuff Tears Our approach Terry R. Malone EdD., PT, ATC Professor of Physical Therapy University of Kentucky Nothing to disclose only wish Deep Musculature & Glenoid RC Insertion Data The RC insertion
The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs
 Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of
 Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Chronic Shoulder Disorders
 Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
Small Rotator Cuff Repair
 Small Rotator Cuff Repair 1. Defined a. Surgical repair of the rotator cuff (most commonly supraspinatus muscle) utilizing sutures b. May be done arthroscopically or open. c. May be done in conjunction
Small Rotator Cuff Repair 1. Defined a. Surgical repair of the rotator cuff (most commonly supraspinatus muscle) utilizing sutures b. May be done arthroscopically or open. c. May be done in conjunction
Biceps Tendon Rupture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about Biceps Tendon Rupture must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about Biceps Tendon Rupture must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a
Patient Presentation. Prevalence of Rotator Cu Tears. By Derek S. Shia, M.D.
 Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS. Rotator Cuff Tears
 Rotator Cuff Tears A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. A torn rotator cuff will weaken your shoulder. This means that many daily activities, like combing your hair
Rotator Cuff Tears A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. A torn rotator cuff will weaken your shoulder. This means that many daily activities, like combing your hair
Rotator Cuff Repair TRENDS OF REPAIRS. Evolution of Arthroscopic Repair. Shoulder Girdle. Rotator Cuff Repair 8/29/2013
 Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective randomized comparison study
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices
 Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices Aimee S. Klapach Orthopedic Surgeon; Knee, Shoulder, & Sports Medicine Sports & Orthopaedic Specialists, part of Allina Health Minnesota Department of Labor and
Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices Aimee S. Klapach Orthopedic Surgeon; Knee, Shoulder, & Sports Medicine Sports & Orthopaedic Specialists, part of Allina Health Minnesota Department of Labor and
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature
 Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
TOPAZ TM What you should know
 TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator cuff is a group of muscles
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator cuff is a group of muscles
Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder About your shoulder The shoulder is a ball and socket joint formed by a
Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder About your shoulder The shoulder is a ball and socket joint formed by a
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION
 NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION ACHILLES (Homer 800BC) When Achilles mother Thetis made her son invulnerable by submerging him in the Styx, the river
NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION ACHILLES (Homer 800BC) When Achilles mother Thetis made her son invulnerable by submerging him in the Styx, the river
A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement
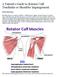 A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement Introduction Shoulder pain is a common condition whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. Shoulder pain and injuries
A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement Introduction Shoulder pain is a common condition whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. Shoulder pain and injuries
S3 EFFECTIVE FOR SHOULDER PATHOLOGIES -Dr. Steven Smith
 S3 EFFECTIVE FOR SHOULDER PATHOLOGIES -Dr. Steven Smith Introduction: Scapular function and its role in shoulder biomechanics has gained increased notoriety in the pathogenesis of shoulder dysfunction
S3 EFFECTIVE FOR SHOULDER PATHOLOGIES -Dr. Steven Smith Introduction: Scapular function and its role in shoulder biomechanics has gained increased notoriety in the pathogenesis of shoulder dysfunction
Shoulder Arthroscopy. Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij. NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions
 APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy. Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine
 Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
Impingement. Joe F de Beer, Karin S vanrooyen, Deepak N Bhatia. A shoulder condition found mostly in people in the year old age group.
 Impingement Joe F de Beer, Karin S vanrooyen, Deepak N Bhatia. A shoulder condition found mostly in people in the 40-60 year old age group. Anatomy: The rotator cuff is the tendon belonging to the muscles,
Impingement Joe F de Beer, Karin S vanrooyen, Deepak N Bhatia. A shoulder condition found mostly in people in the 40-60 year old age group. Anatomy: The rotator cuff is the tendon belonging to the muscles,
4/12/2016. Goals. Anatomy. Basic Anatomy. Biomechanics. Function. Traumatic Rupture of Proximal Biceps: In-season Rehabilitation and Management
 Goals Traumatic Rupture of Proximal Biceps: In-season Rehabilitation and Management Thomas F. LaPorta, MD To understand the anatomy of the biceps at the shoulder To present the mechanism, signs and symptoms,
Goals Traumatic Rupture of Proximal Biceps: In-season Rehabilitation and Management Thomas F. LaPorta, MD To understand the anatomy of the biceps at the shoulder To present the mechanism, signs and symptoms,
What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy?
 Specific Question: What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate evidence
Specific Question: What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate evidence
Evidence Based Approach to the Treatment of Lower Extremity Tendinopathy. Cage SA, Gallegos DM, Eilers MA, Warner BJ
 Evidence Based Approach to the Treatment of Lower Extremity Tendinopathy Cage SA, Gallegos DM, Eilers MA, Warner BJ Thank you PICO Question Patients Subjects suffering from lower extremity tendinopathy
Evidence Based Approach to the Treatment of Lower Extremity Tendinopathy Cage SA, Gallegos DM, Eilers MA, Warner BJ Thank you PICO Question Patients Subjects suffering from lower extremity tendinopathy
Medial Collateral Instability of the Elbow. CSES Residents Course Calgary AB February 1-3, 2017 WD Regan MD
 Medial Collateral Instability of the Elbow CSES Residents Course Calgary AB February 1-3, 2017 WD Regan MD Disclosures I have no disclosures to report Anatomy Medial Collateral Ligament Anterior Oblique
Medial Collateral Instability of the Elbow CSES Residents Course Calgary AB February 1-3, 2017 WD Regan MD Disclosures I have no disclosures to report Anatomy Medial Collateral Ligament Anterior Oblique
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods )
 Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
THE TENDONS OF THE supraspinatus, infraspinatus,
 1162 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Validity of the Lag Signs in Diagnosing Full-Thickness Tears of the Rotator Cuff: A Preliminary Investigation Caroline A. Miller, MSc, Gail A. Forrester, MSc, Jeremy S. Lewis,
1162 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Validity of the Lag Signs in Diagnosing Full-Thickness Tears of the Rotator Cuff: A Preliminary Investigation Caroline A. Miller, MSc, Gail A. Forrester, MSc, Jeremy S. Lewis,
Rotator Cuff Tears. Anatomy. Description
 Rotator Cuff Tears A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator cuff problem.
Rotator Cuff Tears A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of pain and disability among adults. In 2008, close to 2 million people in the United States went to their doctors because of a rotator cuff problem.
John J Christoforetti, MD Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
 ARTHROSCOPIC ASSISTED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR WITH HUMAN ACELLULAR DERMAL ALLOGRAFT PATCH AUGMENTATION FOR REVISION OF FAILED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR: SHORT TERM CLINICAL AND MRI RESULT John J Christoforetti,
ARTHROSCOPIC ASSISTED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR WITH HUMAN ACELLULAR DERMAL ALLOGRAFT PATCH AUGMENTATION FOR REVISION OF FAILED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR: SHORT TERM CLINICAL AND MRI RESULT John J Christoforetti,
1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the:
 1 1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the: a. Carrying angle of the arm b. Scapulohumeral rhythm c. Glenohumeral capsular pattern d. Abduction resistance
1 1. The coordinated action of a scapular upward rotation and humeral abduction is known as the: a. Carrying angle of the arm b. Scapulohumeral rhythm c. Glenohumeral capsular pattern d. Abduction resistance
How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 500 505 ORIGINAL ARTICLE How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring D. Goutallier a,, J.-M. Postel a, C. Radier b, J. Bernageau
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 500 505 ORIGINAL ARTICLE How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring D. Goutallier a,, J.-M. Postel a, C. Radier b, J. Bernageau
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Shoulder Subacromial Pain. Issued by Physiotherapy Department
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Shoulder Subacromial Pain Issued by Physiotherapy Department This leaflet provides information about shoulder subacromial pain. About your Shoulder The shoulder
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Shoulder Subacromial Pain Issued by Physiotherapy Department This leaflet provides information about shoulder subacromial pain. About your Shoulder The shoulder
P.O. Box Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine
 P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS OF ULTRASOUND GUIDED INTRATENDINOUS PROLOTHERAPY INJECTION WITH CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT TO TREAT
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS OF ULTRASOUND GUIDED INTRATENDINOUS PROLOTHERAPY INJECTION WITH CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT TO TREAT FOCAL SUPRASPINATUS TENDINOSIS : RANDOMISED CONTROL STUDY 1,2
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS OF ULTRASOUND GUIDED INTRATENDINOUS PROLOTHERAPY INJECTION WITH CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT TO TREAT FOCAL SUPRASPINATUS TENDINOSIS : RANDOMISED CONTROL STUDY 1,2
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus
 Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
Rehab Considerations: Meniscus Steve Cox, PT, DPT Department of Orthopaedics School of Medicine University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 -Anatomy/ Function/ Injuries -Treatment Options
Review Article The Role of Acromioplasty for Management of Rotator Cuff Problems: Where Is the Evidence?
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 467571, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467571 Review Article The Role of Acromioplasty for Management of Rotator Cuff Problems:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 467571, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/467571 Review Article The Role of Acromioplasty for Management of Rotator Cuff Problems:
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment
 SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
Large/Massive Rotator Cuff Repair
 Large/Massive Rotator Cuff Repair 1. Defined a. Suturing of tears within the rotator cuff (most commonly supraspinatus muscle). Massive RCR usually involve more than the supraspinatus. b. May be done arthroscopically
Large/Massive Rotator Cuff Repair 1. Defined a. Suturing of tears within the rotator cuff (most commonly supraspinatus muscle). Massive RCR usually involve more than the supraspinatus. b. May be done arthroscopically
A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Repair Surgery
 NewYork-Presbyterian Columbia ORTHOPAEDICS A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Repair Surgery NewYork-Presbyterian Columbia ORTHOPAEDICS The Rotator Cuff At Columbia Orthopaedics, patients find nationally
NewYork-Presbyterian Columbia ORTHOPAEDICS A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Repair Surgery NewYork-Presbyterian Columbia ORTHOPAEDICS The Rotator Cuff At Columbia Orthopaedics, patients find nationally
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders
Rotator Cuff Tears: New Understandings
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/medical-breakthroughs-from-penn-medicine/rotator-cuff-tears-newunderstandings/2073/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/medical-breakthroughs-from-penn-medicine/rotator-cuff-tears-newunderstandings/2073/
Analysis of Results of Platelet-rich Plasma with Arthroscopic Acromioplasty and Arthroscopic Acromioplasty: A Comparative Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/381 Analysis of Results of Platelet-rich Plasma with Arthroscopic Acromioplasty and Arthroscopic Acromioplasty: A Comparative
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/381 Analysis of Results of Platelet-rich Plasma with Arthroscopic Acromioplasty and Arthroscopic Acromioplasty: A Comparative
Shoulder Labral Tear and Shoulder Dislocation
 Shoulder Labral Tear and Shoulder Dislocation The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint with tremendous flexibility and range of motion. The ball is the humeral head while the socket is the glenoid.
Shoulder Labral Tear and Shoulder Dislocation The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint with tremendous flexibility and range of motion. The ball is the humeral head while the socket is the glenoid.
Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY
 Diagnosis Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY Degenerative muscular changes associated with rotator cuff tears include fatty infiltration and atrophy. Increased
Diagnosis Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY Degenerative muscular changes associated with rotator cuff tears include fatty infiltration and atrophy. Increased
Bilateral Shoulder Pain
 HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019
 AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
Dr Jane Fitzpatrick Sports Medicine Professionals 21 Erin Street Richmond VIC
 Dr Jane Fitzpatrick Sports Medicine Professionals 21 Erin Street Richmond VIC Dr Jane Fitzpatrick Private Practice Consulting Sports Medicine Medical Director for Biathlon Australia Team Physician Australian
Dr Jane Fitzpatrick Sports Medicine Professionals 21 Erin Street Richmond VIC Dr Jane Fitzpatrick Private Practice Consulting Sports Medicine Medical Director for Biathlon Australia Team Physician Australian
Natural History of RTC Disease Is Non Op Treatment OK in a Young Person? Leesa M. Galatz, MD COI Disclosure Information Leesa M.
 Natural History of RTC Disease Is Non Op Treatment OK in a Young Person? Leesa M. Galatz, MD Mount Sinai Professor of Orthopedics Leni and Peter May Department of Orthopedic Surgery Icahn School of Medicine
Natural History of RTC Disease Is Non Op Treatment OK in a Young Person? Leesa M. Galatz, MD Mount Sinai Professor of Orthopedics Leni and Peter May Department of Orthopedic Surgery Icahn School of Medicine
Icd 10 rotator cuff repair
 Search Search pages & people Search Search Search pages & people Search Icd 10 rotator cuff repair UPDATED. February 4, 2016. Question: Patient has been seen in office during the global period after a
Search Search pages & people Search Search Search pages & people Search Icd 10 rotator cuff repair UPDATED. February 4, 2016. Question: Patient has been seen in office during the global period after a
