University of South Florida
|
|
|
- Rose Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of South Florida Pediatric Orthopaedics PGY 4 Competency Based Goals & Objectives Competency 1- Patient Care: Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment of health problems and the promotion of health. The expectation of the senior resident is that they meet all of the criteria of the junior resident as well as independently develop and implement a surgical and perioperative plan for the management of these patients. At the completion of training, the senior resident should be adept enough to supervise more junior level trainees in the appropriate management of pediatric patients. 1. Hone skills in identifying key history and exam needed to evaluate children presenting with conditions involving the musculoskeletal systems. 2. Understand the scope and use of diagnostic studies typically used by pediatric orthopedists. 3. Discuss and identify how the pediatric orthopedist and his/her care team involves the patient and family in decision making about complex diagnoses and highly sophisticated medical care issues. 4. Screen for developmental dysplasia for the hip in the newborn nursery and at appropriate health maintenance visits: a. Use competent physical examination techniques. b. Use radiographs and ultrasonography appropriately. c. Educate parents about the rationale for screening and referral. d. Refer when indicated. e. Introduce parents to the management options that the orthopedist may offer. 5. Screen for scoliosis on routine examinations (by exam and scoliometer) and refer as needed. 6. Screen for occult dysraphism. 7. Counsel families regarding risks and prevention of orthopedic injuries sustained from play near motor vehicles, lawn mowers, snow blowers, farm equipment, bicycles, snowmobiles, motorbikes and all-terrain vehicles. 8. Advise family about optimal weight and style of backpacks in order to prevent back injury. 9. Order and interpret (with the assistance of the radiologist) common diagnostic imaging procedures when evaluating and managing patients with orthopaedic conditions: plain radiographs, body MRI, CT scan, radionuclide bone scans. 10. Acute Pediatric Orthopaedic Conditions a. Residents will be proficient in evaluating the limping child. This includes the ability to discuss the etiology, pathoanatomy, treatment options, and surgical indications, as well as show proficiency in noncomplex surgical techniques, of the following conditions: i. Osteomyelitis ii. Septic arthritis iii. Transient synovitis iv. Leukemia v. Chronic recurrent multi-focal osteomyelitis vi. Discitis vii. Juvenile inflammatory arthritis b. The polytraumatized child Residents will be able to evaluate and prioritize treatment involved in polytrauma including general resuscitation as well as temporary and definitive treatment of fractures of the pelvis, spine and long bones. c. Isolated trauma Residents will be proficient in the evaluation and management of: i. Elbow fractures
2 1. Supracondylar humerus 2. Lateral condyle fractures 3. Radial head fractures 4. Nurse maid's elbow ii. Isolated fractures of the long bones iii. Physeal fractures: Residents will be familiar with the classification of physeal injuries as well as the treatment and potential complications of fractures involving the physis, with particular attention to: 1. Salter-Harris classification 2. Fractures of the distal radial physis 3. Fractures of the distal femoral physis 4. Fractures of the distal tibial physis 5. Fractures involving the proximal femoral physis d. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis Residents will be proficient in the evaluation, classification and management of slipped capital femoral epiphysis. This includes acute management with an emphasis on avoidance of complications, as well as management of complications and their late sequale. 11. Non-Acute Pediatric Orthopaedics: a. A. Benign rotational abnormalities Residents will be proficient in differentiating the following: i. Intoeing, including the diagnosis of: 1. Metatarsus abductus 2. Internal tibia torsion 3. Femoral anteversion ii. Out toeing, including the diagnosis of: 1. External tibial torsion 2. Femoral retro version b. Hip Residents should be proficient in discussing the natural history, etiology, pathoanatomy, nonsurgical i. Developmental dysplasia of the hip 1. Idiopathic 2. Teratologic, including neuromuscular and "syndrome related" ii. Legg-Calve Perthes disease iii. Idiopathic Coxa Vara iv. Idiopathic chondrolysis v. Potrussio acetabulum c. C. Knee Residents should be proficient in discussing the natural history, etiology, pathoanatomy, nonsurgical i. Osgood-Schlatter's ii. Osteochondritis dessicans iii. Discoid meniscus iv. Physiologic genu valgum v. Physiologic genu varum vi. Infantile and adolescent Blount's d. Foot Residents should be proficient in discussing the natural history, etiology, pathoanatomy, nonsurgical i. Club feet ii. Metatarsus adductus iii. Calcaneal valgus iv. Vertical talus v. Flexible flat feet vi. Tarsal coalition
3 vii. Accessory navicular viii. Adolescent bunions e. Spine Residents should be proficient in discussing the natural history, etiology, pathoanatomy, nonsurgical i. Scoliosis 1. Congenital 2. Neuromuscular, including cerebral palsy, spina bifida, muscular dystrophy, and "syndromic" 3. Idiopathic a. Infantile b. Juvenile c. Adolescent ii. Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis 12. Residents will be proficient in discussing the natural history, etiology, medical and orthopaedic manifestations, including non-surgical and surgical treatment, for the following conditions: a. Cerebral Palsy b. Spina Bifida c. Muscular dystrophy i. Duchenne's muscular dystrophy ii. Becker's muscular dystrophy iii. Congenital myotonic dystrophy d. Down's syndrome e. Arthrogryposis f. Osteogenesis imperfecta 13. Pathology Residents will be able to formulate a differential diagnosis and implement an evaluation plan for the following conditions: a. Unicameral bone cyst b. Aneurysmal bone cyst c. Nonossifying fibroma d. Fibrous dysplasia e. Eosinophilic granuloma f. Giant cell tumor g. Osteomyelitis h. Chondroblastoma i. Enchondromatosis j. Osteochondromatosis k. Ewing's sarcoma l. Osteogenic sarcoma Competency 2 Medical Knowledge: Understand the scope of established and evolving biomedical, clinical, epidemiological and social-behavioral knowledge needed by a pediatrician; demonstrate the ability to acquire, critically interpret and apply this knowledge needed by a pediatrician; demonstrate the ability to acquire, critically interpret and apply this knowledge in patient care. 1. Demonstrate knowledge of normal variations in foot, knee and leg development. 2. Know normal variations in gait and posture. 3. Demonstrate if the following presenting signs and symptoms are caused by an orthopaedic condition, and if so, treat appropriately: a. Limp b. Musculoskeletal pain
4 c. Refusal to walk or gain disturbance d. Refusal to use a limb e. Swollen or painful joint f. Bowed legs or knock-knees g. In-toeing or out-toeing 4. Identify the role and general scope of practice of pediatric orthopedists; recognize situations where children benefit from the skills of specialists training in care of children; and work effectively with these professionals in the care of children with orthopedic conditions. 5. Develop an efficient approach to finding information resources related to the musculoskeletal system (e.g. information on the web, in the literature, text books, or PDA s) to obtain rapid information that is relevant to a presenting patient problem. 6. At the beginning and end of a rotation or clinical experience, clarify your learning needs related to this subspecialty. Competency 3 Communication Skills: Demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in information exchange and partnering with patients, their families and professional associates. 1. Talk to family members about sensitive issues that relate to a patient s illness, e.g. coping with the child s altered needs in his/her home setting. 2. Write an effective and timely consultation note that summarizes the findings and recommendations of the pediatric orthopedist and clarifies the continued role and responsibility of the consultant. 3. Describe the role of all members of a multi-disciplinary team and show respect for the contributions of each. 4. Maintain comprehensive, timely and legible medical records. Competency 4 Practice Based Learning and Improvement: Demonstrate knowledge, skills and attitudes needed for continuous self-assessment, using scientific methods and evidence to investigate, evaluate and improve one s patient care practice. 1. Identify standardized guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of complex problems of the musculoskeletal system and learn the rationale for adaptations that optimize treatment. 2. Identify personal learning needs, systematically organize relevant information resources for future references, and plan for continuing data acquisition if appropriate. 3. Seek and incorporate feedback and self-assessment into a plan for professional growth and practice improvement (e.g. use evaluations provided by patients, peers, superiors and subordinates to improve patient care. Competency 5 Professionalism: Demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles and sensitivity to diversity. 1. Be honest and use integrity in your professional duties. 2. Reflect on your own biases toward particular illnesses or patient groups, and take steps to assure that these biases don t interfere with the care you deliver. 3. Appreciate the psychosocial impact of diseases commonly seen by the subspecialist (e.g. on the child, family, parents work, school). 4. Respect your patients /parents privacy, autonomy and need to maintain a positive self-concept, irrespective of age, gender or health belief system, and regardless of acuity of diseases.
5 5. Be sensitive to the ethical and legal dilemmas faced by providers working with patients with orthopedic problems. Strive to understand how the orthopedist and care team deals with these dilemmas and use such experiences to enhance your own understanding. Competency 6 System-Based Practice: Understand how to practice quality health care and advocate for patients within the context of the healthcare system. 1. Describe school-based scoliosis screening programs and the benefits and inherent limitations of such strategies. 2. Clarify how documentation and billing charges differ for consultations vs. referrals vs. on-going management of children treated on the pediatric orthopedic service. 3. Explore the difference between fee-for-service referrals and managed care referrals and the office systems needed to support both. 4. Describe patient and system factors that contribute to escalating costs of care in the subspecialty setting, and consider the impact of these costs on families and on the health care system. 5. Recognize and advocate for families who need assistance to deal with systems complexities, such as lack of insurance, multiple medication refills, multiple appointments with long transport times or inconvenient hours of service. 6. Support community prevention efforts related to pediatric orthopaedics by working with a local professional organization or organizing a project to do with colleagues. 7. Consider potential sources of medical error in this subspecialty setting (e.g. drug interactions, complex care plans, provider fatigue).
Orthopedics. 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Orthopedics 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for orthopedic injury, disease and dysfunction.
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Orthopedics 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for orthopedic injury, disease and dysfunction.
DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS WALTER REED NATIONAL MILITARY MEDICAL CENTER NATIONAL CAPITAL CONSORTIUM PEDIATRIC RESIDENCY PROGRAM.
 DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS WALTER REED NATIONAL MILITARY MEDICAL CENTER NATIONAL CAPITAL CONSORTIUM PEDIATRIC RESIDENCY PROGRAM February 2016 PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDIC AND SPORTS MEDICINE ROTATION 1. DURATION:
DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS WALTER REED NATIONAL MILITARY MEDICAL CENTER NATIONAL CAPITAL CONSORTIUM PEDIATRIC RESIDENCY PROGRAM February 2016 PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDIC AND SPORTS MEDICINE ROTATION 1. DURATION:
Topics and Cases in Pediatric Orthopaedics (Tuesday 6:30am 4 th Floor Orthopaedic Conference Room at Hamot)
 2015-2016 Topics and Cases in Pediatric Orthopaedics (Tuesday 6:30am 4 th Floor Orthopaedic Conference Room at Hamot) 1. Considerations in the Management of Pediatric Patients Kerry Armet 7 July 2015 Fluid
2015-2016 Topics and Cases in Pediatric Orthopaedics (Tuesday 6:30am 4 th Floor Orthopaedic Conference Room at Hamot) 1. Considerations in the Management of Pediatric Patients Kerry Armet 7 July 2015 Fluid
The Child With a Limp
 KID WITH A LIMP Common in ED, common in Exams Differential diagnosis is very wide Most causes benign, but mustn't miss Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Fractures / NAI SUFE (older, heavier children) The
KID WITH A LIMP Common in ED, common in Exams Differential diagnosis is very wide Most causes benign, but mustn't miss Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Fractures / NAI SUFE (older, heavier children) The
1. Review specialty services and programs available through Shriners Hospitals for Children
 Outreach Clinics: Creating Accessibility to Specialty Healthcare for Rural Families Presented By: Erin Jurkovich Director of Professional Relations Shriners Hospitals for Children Twin Cities June 15,
Outreach Clinics: Creating Accessibility to Specialty Healthcare for Rural Families Presented By: Erin Jurkovich Director of Professional Relations Shriners Hospitals for Children Twin Cities June 15,
4. Counsel patients and families regarding athletic participation, including:
 Sports Medicine Primary Goals for this Rotation GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening. Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing sports-related injuries, disorders and dysfunction in children
Sports Medicine Primary Goals for this Rotation GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening. Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing sports-related injuries, disorders and dysfunction in children
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation University of Toronto Rotation Specific Goals and Objectives Pediatrics
 General Requirements: Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation University of Toronto Rotation Specific Goals and Objectives Pediatrics To develop the necessary clinical skills and knowledge required in pediatric
General Requirements: Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation University of Toronto Rotation Specific Goals and Objectives Pediatrics To develop the necessary clinical skills and knowledge required in pediatric
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
1. Discuss some common pediatric problems seen in the clinic. Diagnosis Clinical examination (at birth and subsequent well-baby examinations)
 1 Pediatric Orthopaedics for Primary Care Providers 2 Disclosure Statement No conflicts related to this presentation 3 4 Goals 1. Discuss some common pediatric problems seen in the clinic 2. Examination
1 Pediatric Orthopaedics for Primary Care Providers 2 Disclosure Statement No conflicts related to this presentation 3 4 Goals 1. Discuss some common pediatric problems seen in the clinic 2. Examination
Pediatric Orthopaedic Fellowship Curriculum
 Pediatric Orthopaedic Fellowship Curriculum The Fellowship Pediatric Orthopaedic Curriculum is designed for the fellow to spend three months each in four content areas. There are five content areas comprising
Pediatric Orthopaedic Fellowship Curriculum The Fellowship Pediatric Orthopaedic Curriculum is designed for the fellow to spend three months each in four content areas. There are five content areas comprising
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI
 UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
University of South Florida
 University of South Florida Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics PGY 4 Competency Based Goals & Objectives Competency 1- Patient Care: Provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate and effective for the
University of South Florida Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics PGY 4 Competency Based Goals & Objectives Competency 1- Patient Care: Provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate and effective for the
Pediatric Rounds Topics and Objectives
 Pediatric Rounds Topics and Objectives Development Dysplasia Hip... 4... 4... 4... 5 Communicator... 5 Scholar... 5 Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis... 5... 5... 5... 6 Communicator... 6 Health Advocate...
Pediatric Rounds Topics and Objectives Development Dysplasia Hip... 4... 4... 4... 5 Communicator... 5 Scholar... 5 Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis... 5... 5... 5... 6 Communicator... 6 Health Advocate...
Pediatric Orthopedics: ``To Refer or Not to Refer``
 Pediatric Orthopedics: ``To Refer or Not to Refer`` Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS(C) McGill University Health Centre Intoeing Knock knees Bowlegs Flatfeet Toe walking Knee pain Hip click Intoeing Objectives
Pediatric Orthopedics: ``To Refer or Not to Refer`` Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS(C) McGill University Health Centre Intoeing Knock knees Bowlegs Flatfeet Toe walking Knee pain Hip click Intoeing Objectives
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Neurology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
Provide specific counseling to parents and patients with neurological disorders, addressing:
 Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
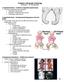 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident
 Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL3 level Prerequisites: Successful completion or waiver
Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL3 level Prerequisites: Successful completion or waiver
Effects of Immobilization. N24 Pedi Musculoskeletal Spring 2012, Week 14. Cabrillo ADN/C. Madsen RN, MSN 1. Physical effects on other systems
 Common Orthopedic Problems of Children Congenital Acquired Bones Neuromuscular Physical effects on other systems Pulmonary Cardiac Skin integrity Elimination GI GU 1 4 General Nursing Considerations any
Common Orthopedic Problems of Children Congenital Acquired Bones Neuromuscular Physical effects on other systems Pulmonary Cardiac Skin integrity Elimination GI GU 1 4 General Nursing Considerations any
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level
 Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM
 ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
An understanding of the components of the normal gait cycle will aid in describing abnormalities of gait.
 Approach to the Child with a Limp: Student writer: Brian Mayson Resident editor: Elmine Statham Background The child with a limp is a common problem seen in pediatrics. A limp is defined as any deviation
Approach to the Child with a Limp: Student writer: Brian Mayson Resident editor: Elmine Statham Background The child with a limp is a common problem seen in pediatrics. A limp is defined as any deviation
Normal lower limb variants in children
 Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits The Royal London & Barts and The London Children s Hospitals, Barts Health NHS Trust, London E1 1BB, UK Correspondence to: A Yeo andreayeo@doctors.org.uk
Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits The Royal London & Barts and The London Children s Hospitals, Barts Health NHS Trust, London E1 1BB, UK Correspondence to: A Yeo andreayeo@doctors.org.uk
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018
 Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
Intoeing: When to Worry? Sukhdeep K. Dulai SPORC 2018 What is it? Intoeing: When to worry? Why isn t it always cause for worry? What are the benign causes of intoeing? What are the pathologic causes of
PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS BRENT WEATHERHEAD, MD, FRCSC PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON MEDICAL DIRECTOR, REBALANCE
 PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS BRENT WEATHERHEAD, MD, FRCSC PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON MEDICAL DIRECTOR, REBALANCE DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO INDUSTRY CONFLICTS TO DECLARE I AM AN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON TRAINED IN
PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS BRENT WEATHERHEAD, MD, FRCSC PAEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON MEDICAL DIRECTOR, REBALANCE DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO INDUSTRY CONFLICTS TO DECLARE I AM AN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEON TRAINED IN
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Musculoskeletal Management of A Limping Child
 Musculoskeletal Management of A Limping Child Julieanne P. Sees, DO, FAOAO Pediatric Neuro-Orthopaedic Surgeon Medical Director, Neuro-Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Unit Wilmington, DE Objectives Identify
Musculoskeletal Management of A Limping Child Julieanne P. Sees, DO, FAOAO Pediatric Neuro-Orthopaedic Surgeon Medical Director, Neuro-Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Unit Wilmington, DE Objectives Identify
ABOS Part I Certification Examination Blueprint
 2017 ABOS Part I Certification Examination Blueprint www.abos.org Table of Contents General Principles 12-14% Biostatistics/epidemiology 1-3% Legal/ethical 0.5-1% Basic Science Principles 9-11% Spine 13-15%
2017 ABOS Part I Certification Examination Blueprint www.abos.org Table of Contents General Principles 12-14% Biostatistics/epidemiology 1-3% Legal/ethical 0.5-1% Basic Science Principles 9-11% Spine 13-15%
ROTATIONAL & ANGULAR VARIATIONS IN CHILDREN:
 ROTATIONAL & ANGULAR VARIATIONS IN CHILDREN: IN-TOEING, OUT-TOEING, BOWED LEGS, AND KNOCK-KNEES Leigh Ann Lather MD FAAP 29 September, 2018 MSK Bootcamp I have no relevant financial relationships with
ROTATIONAL & ANGULAR VARIATIONS IN CHILDREN: IN-TOEING, OUT-TOEING, BOWED LEGS, AND KNOCK-KNEES Leigh Ann Lather MD FAAP 29 September, 2018 MSK Bootcamp I have no relevant financial relationships with
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS UG Teaching Schedule. (October 2016 February 2017)
 DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS UG Teaching Schedule (October 2016 February 2017) THEORY (3 PM 4 PM) 07.10.2016 CTEV and flat foot 14.10.2016 CDH 21.10.2016 Torticollis, congenital pseudoarthrosis of tibia and
DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS UG Teaching Schedule (October 2016 February 2017) THEORY (3 PM 4 PM) 07.10.2016 CTEV and flat foot 14.10.2016 CDH 21.10.2016 Torticollis, congenital pseudoarthrosis of tibia and
Things People Report that the School Nurse Said to Them. J. Jay Crawford, M.D. Knoxville Orthopaedic Clinic
 Things People Report that the School Nurse Said to Them J. Jay Crawford, M.D. Knoxville Orthopaedic Clinic Knoxville Orthopaedic Clinic www.kocortho.com Use our App Text kocnow to 61234. You will immediately
Things People Report that the School Nurse Said to Them J. Jay Crawford, M.D. Knoxville Orthopaedic Clinic Knoxville Orthopaedic Clinic www.kocortho.com Use our App Text kocnow to 61234. You will immediately
Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
LECTURE 8: DEVELOPMENTAL ORTHOPAEDICS. Paediatric MS History o Reason for referral o Past history
 LECTURE 8: DEVELOPMENTAL ORTHOPAEDICS Paediatric MS History o Reason for referral o Past history Antenatal history Birth history (term? Premmy? Breech? Complications?). Medical history/investigations/tests
LECTURE 8: DEVELOPMENTAL ORTHOPAEDICS Paediatric MS History o Reason for referral o Past history Antenatal history Birth history (term? Premmy? Breech? Complications?). Medical history/investigations/tests
OMISSION BE CHILLY in PÆDIATRIC ORTHOPÆDICS
 OMISSION BE CHILLY in PÆDIATRIC ORTHOPÆDICS Mohammad Diab, M.D. Chief, Pædiatric Orthopædics UCSF limping knee - acute - chronic foot - metatarsus adductus - flat torsion - knock knees - bow legs scoliosis
OMISSION BE CHILLY in PÆDIATRIC ORTHOPÆDICS Mohammad Diab, M.D. Chief, Pædiatric Orthopædics UCSF limping knee - acute - chronic foot - metatarsus adductus - flat torsion - knock knees - bow legs scoliosis
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor hallucis tendon procedures, for hallux varus, 536 537 Acetabular disorders, intoeing in, 551 553 Akron dome osteotomy, for cavus deformities,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor hallucis tendon procedures, for hallux varus, 536 537 Acetabular disorders, intoeing in, 551 553 Akron dome osteotomy, for cavus deformities,
Longitudinal Sports Medicine Experience Family Medicine Faculty Liaison: Peter Lundblad, MD, FAAFP, CAQSM Last review/update: 2/2017
 Longitudinal Sports Medicine Experience Family Medicine Faculty Liaison: Peter Lundblad, MD, FAAFP, CAQSM The Sports Medicine experience includes a required 1-week block experience completed in the 1 st
Longitudinal Sports Medicine Experience Family Medicine Faculty Liaison: Peter Lundblad, MD, FAAFP, CAQSM The Sports Medicine experience includes a required 1-week block experience completed in the 1 st
Lower Extremity Malalignment: When to Refer and When to Reassure?
 Lower Extremity Malalignment: When to Refer and When to Reassure? Mary Aschenbrener, PA-C Minnesota Academy of Physician Assistants 03/18/16 Cary H. Mielke, MD Chief of Staff Orthopaedic Burn Spinal cord
Lower Extremity Malalignment: When to Refer and When to Reassure? Mary Aschenbrener, PA-C Minnesota Academy of Physician Assistants 03/18/16 Cary H. Mielke, MD Chief of Staff Orthopaedic Burn Spinal cord
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis
 The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Foot and Ankle Natalie Stork, MD
 Foot and Ankle Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics Children s Mercy Kansas City,
Foot and Ankle Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics Children s Mercy Kansas City,
7/1/2012. Repetitive valgus stresses cause microfractures in the apophyseal cartilage (weak link) Common in year olds
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
How Many Referrals to a Pediatric Orthopaedic Hospital Specialty Clinic Are Primary Care Problems?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE How Many Referrals to a Pediatric Orthopaedic Hospital Specialty Clinic Are Primary Care Problems? Eric Y. Hsu, MD,* Richard M. Schwend, MD,w and Leamon Julia, RNz Purpose: Many primary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE How Many Referrals to a Pediatric Orthopaedic Hospital Specialty Clinic Are Primary Care Problems? Eric Y. Hsu, MD,* Richard M. Schwend, MD,w and Leamon Julia, RNz Purpose: Many primary
Crowd-sourcing the identification of rehabilitation-relevant review
 Crowd-sourcing the identification of rehabilitation-relevant review A Cochrane Rehabilitation initiative William Levack, 1 Stefano Negrini, 2,3 Farooq Rathore, 4 Joel Pollet 3 1 University of Otago, New
Crowd-sourcing the identification of rehabilitation-relevant review A Cochrane Rehabilitation initiative William Levack, 1 Stefano Negrini, 2,3 Farooq Rathore, 4 Joel Pollet 3 1 University of Otago, New
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Genetics
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
In-toeing and Out-toeing
 In-toeing and Out-toeing What is all the fuss about? Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
In-toeing and Out-toeing What is all the fuss about? Natalie Stork, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
1. Adequate diet and iron intake to prevent iron deficiency 2. Signs and symptoms of malignant disease
 Hematology/Oncology Description: The pediatric hematology-oncology division sees a wide spectrum of pediatric disease including but not limited to leukemia, hemophilia, solid tumors, ITP, and other blood
Hematology/Oncology Description: The pediatric hematology-oncology division sees a wide spectrum of pediatric disease including but not limited to leukemia, hemophilia, solid tumors, ITP, and other blood
In-toeing, Out-toeing, Growing Pains, Bowlegs, Knock-Knees and Flat Feet
 Jeffrey B. Neustadt, M.D. Scott W. Beck, M.D. Gregory V. Hahn, M.D. Drew E. Warnick, M.D. Paul L. Benfanti, M.D. Lee G. Phillips, M.D. Daniel C. Bland, M.D. Common Benign Orthopaedic Conditions In-toeing,
Jeffrey B. Neustadt, M.D. Scott W. Beck, M.D. Gregory V. Hahn, M.D. Drew E. Warnick, M.D. Paul L. Benfanti, M.D. Lee G. Phillips, M.D. Daniel C. Bland, M.D. Common Benign Orthopaedic Conditions In-toeing,
A free online interactive information resource for clinicians.
 A free online interactive information resource for clinicians www.pmmonline.org The limping child Helen Foster Professor of Paediatric Rheumatology Newcastle University Honorary Consultant Great North
A free online interactive information resource for clinicians www.pmmonline.org The limping child Helen Foster Professor of Paediatric Rheumatology Newcastle University Honorary Consultant Great North
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
EPOS REGIONAL CORE CURRICULUM COURSES
 Prishtina Kosovo on February 13-14, 2013 and in Tirana Albania on February 15-16, 2013 EPOS REGIONAL CORE CURRICULUM COURSES Prishtina Kosovo on February 13-14, 2013 and in Tirana Albania on February 15-16,
Prishtina Kosovo on February 13-14, 2013 and in Tirana Albania on February 15-16, 2013 EPOS REGIONAL CORE CURRICULUM COURSES Prishtina Kosovo on February 13-14, 2013 and in Tirana Albania on February 15-16,
Child Neurology Elective PL1 Rotation
 PL1 Rotation The neurology elective is available to first year residents in either a 2 or 4 week block rotation. The experience will include performing inpatient consultations, attending outpatient clinics
PL1 Rotation The neurology elective is available to first year residents in either a 2 or 4 week block rotation. The experience will include performing inpatient consultations, attending outpatient clinics
586 INDEX. Bone age, 21 Bowing of the leg, 153 Braces, 149, 500
 Index A Accessory navicular, 194 Achondroplasia, 51 Acromioclavicular (AC) sprain, 278, 280 Acromioclavicular separation, 478 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, 561 Acute slipped capital femoral epiphysis,
Index A Accessory navicular, 194 Achondroplasia, 51 Acromioclavicular (AC) sprain, 278, 280 Acromioclavicular separation, 478 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, 561 Acute slipped capital femoral epiphysis,
Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Fellowship Information. Addendum to University of Minnesota Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Part B Manual
 2013-2014 Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Fellowship Information Addendum to University of Minnesota Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Part B Manual Table of Contents Introduction Page 3 Goals/Objectives
2013-2014 Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Fellowship Information Addendum to University of Minnesota Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Part B Manual Table of Contents Introduction Page 3 Goals/Objectives
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents
 Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents The following document is intended to guide you in
Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents The following document is intended to guide you in
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Otolaryngology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
I have no financial relationships related to disclose
 Evaluation of a child with a limp / Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) Lee S. Segal, MD Chief, Division of Pediatric Orthopedics American Family Children s Hospital Department of Orthopedics and
Evaluation of a child with a limp / Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) Lee S. Segal, MD Chief, Division of Pediatric Orthopedics American Family Children s Hospital Department of Orthopedics and
UCSD DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY
 UCSD DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR ADVANCED PAIN MEDICINE ROTATION, UCSD MEDICAL CENTER Competencies Objective Learning Environment Instructional Method Assessment Tool Patient Care:
UCSD DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR ADVANCED PAIN MEDICINE ROTATION, UCSD MEDICAL CENTER Competencies Objective Learning Environment Instructional Method Assessment Tool Patient Care:
COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL PROBLEMS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT PATHOLOGIC VS. NORMAL
 COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL PROBLEMS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT PATHOLOGIC VS. NORMAL Clifford L. Craig, M.D. M2 Musculoskeletal Fall 2008 I. ANGULAR AND TORSIONAL DEFORMITIES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Examination Relaxed,
COMMON MUSCULOSKELETAL PROBLEMS GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT PATHOLOGIC VS. NORMAL Clifford L. Craig, M.D. M2 Musculoskeletal Fall 2008 I. ANGULAR AND TORSIONAL DEFORMITIES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Examination Relaxed,
Recognize the broad impact of hearing impairment on child and family, including social, psychological, educational and financial consequences.
 Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정
 Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정 Metatarsus adductus Epidemiology and Etiology 0.1-12% with higher number for multiple birth Deformation and compression from intrauterine crowding
Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정 Metatarsus adductus Epidemiology and Etiology 0.1-12% with higher number for multiple birth Deformation and compression from intrauterine crowding
The Limping Child. Todd Milbrandt, MD Division Chair Pediatric Orthopaedics Mayo Clinic Rochester
 The Limping Child Todd Milbrandt, MD Division Chair Pediatric Orthopaedics Mayo Clinic Rochester Faculty Disclosure No disclosures relevant to this talk Practice Gap Primary Care Providers are faced with
The Limping Child Todd Milbrandt, MD Division Chair Pediatric Orthopaedics Mayo Clinic Rochester Faculty Disclosure No disclosures relevant to this talk Practice Gap Primary Care Providers are faced with
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease. Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center
 Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
Other Congenital & Developmental Knee & Leg Disease Jong Sup Shim,M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Rotational Deformity Intoeing Outtoeing
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
Contents. copyrighted material by PRO-ED, Inc. Chapter 1. Chapter 2. Chapter 3. Chapter 4. Chapter 5. Conditions in Athletic Injuries
 Acknowledgments xiii Introduction to the First Edition xv Introduction to the Second Edition xvii Chapter 1 Conditions in Athletic Injuries Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear 2 Biceps Tendon Strain
Acknowledgments xiii Introduction to the First Edition xv Introduction to the Second Edition xvii Chapter 1 Conditions in Athletic Injuries Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear 2 Biceps Tendon Strain
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Hematology/Oncology/BMT
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Hematology/Oncology/BMT 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing hematologic or oncologic conditions,
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Hematology/Oncology/BMT 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing hematologic or oncologic conditions,
EXAMPLE OF STRONG APPLICATION Includes Entries from COTA Awarded Programs
 EXAMPLE OF STRONG APPLICATION Includes Entries from COTA Awarded Programs (NOTE only blinded submissions will be accepted and distributed for COTA review) Orthopaedic Trauma Fellowship Program Goals and
EXAMPLE OF STRONG APPLICATION Includes Entries from COTA Awarded Programs (NOTE only blinded submissions will be accepted and distributed for COTA review) Orthopaedic Trauma Fellowship Program Goals and
Limping in childhood
 CURRENT CONCEPTS REVIEW Limping in childhood Hugo DE BOECK, Peter VORLAT Limp is an abnormal gait which can be caused by pain, muscular dysfunction or deformity. Limp is never normal and the cause should
CURRENT CONCEPTS REVIEW Limping in childhood Hugo DE BOECK, Peter VORLAT Limp is an abnormal gait which can be caused by pain, muscular dysfunction or deformity. Limp is never normal and the cause should
PEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY THE SPECTRUM
 PEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY THE SPECTRUM A child's musculoskeletal problems are different from those of an adult. As children are still growing, the body's response to injuries, infections, and deformities
PEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY THE SPECTRUM A child's musculoskeletal problems are different from those of an adult. As children are still growing, the body's response to injuries, infections, and deformities
The Royal Children s Hospital. Registrar Orthopaedic Training Program. Curriculum
 The Royal Children s Hospital Registrar Orthopaedic Training Program Curriculum 8 August 2011 3 February 2012 Document history Version Date Prepared by Comments Draft 1 25 May 2011 Jit Balakumar, Leo Donnan
The Royal Children s Hospital Registrar Orthopaedic Training Program Curriculum 8 August 2011 3 February 2012 Document history Version Date Prepared by Comments Draft 1 25 May 2011 Jit Balakumar, Leo Donnan
Provide preventive counseling to parents and patients with specific endocrine conditions about:
 Endocrinology Description: The resident will become familiar with the diagnosis, management, and treatment of endocrine problems. The resident will evaluate patients with a multitude of endocrine problems,
Endocrinology Description: The resident will become familiar with the diagnosis, management, and treatment of endocrine problems. The resident will evaluate patients with a multitude of endocrine problems,
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES. Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM Academic
 WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Academic AM OC OC day CAM CAM PM with Dr. Lindley Wall Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Academic AM OC OC day CAM CAM PM with Dr. Lindley Wall Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Endocrinology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
 Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip *This guideline was developed from the American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline: Early Detection of Developmental
Clinical Practice & Referral Guideline - Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip *This guideline was developed from the American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline: Early Detection of Developmental
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES. Martin Boyer (hand surgery) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM AM PM VA OR Wohl
 WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) VA OR Wohl Dr. Goldfarb CAM OC OC OR CAM CAM OR Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
WEEKLY CLINICAL SCHEDULES Martin Boyer (hand surgery) VA OR Wohl Dr. Goldfarb CAM OC OC OR CAM CAM OR Carpal tunnel syndrome PIP dislocation CMC arthritis Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Distal Radius Fracture
Orthopedic Surgery Goals and Objectives FOOT AND ANKLE ROTATION. Preamble
 Orthopedic Surgery Goals and Objectives FOOT AND ANKLE ROTATION Preamble Residents will complete a junior and a senior foot & ankle rotation during their training. The expectations, goals and objectives
Orthopedic Surgery Goals and Objectives FOOT AND ANKLE ROTATION Preamble Residents will complete a junior and a senior foot & ankle rotation during their training. The expectations, goals and objectives
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Queen s Family Medicine PGY3 CARE OF THE ELDERLY PROGRAM
 PROGRAM Goals and Objectives Family practice residents in this PGY3 Care of the Elderly program will learn special skills, knowledge and attitudes to support their future focus practice in Care of the
PROGRAM Goals and Objectives Family practice residents in this PGY3 Care of the Elderly program will learn special skills, knowledge and attitudes to support their future focus practice in Care of the
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Nephrology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Nephrology 1. GOAL: Understand the general pediatrician's role in diagnosis and management of hypertension in children.
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Nephrology 1. GOAL: Understand the general pediatrician's role in diagnosis and management of hypertension in children.
Index. orthopedic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM)
 BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Curriculum: Goals and Objectives Department of Medicine Harbor-UCLA Medical Center
 MEDICAL ONCOLOGY AND HEMATOLOGY (R2, R3) A. The PURPOSE of this rotation is to afford medical residents a broad clinical and training experience in the clinical diagnosis and management of common adult
MEDICAL ONCOLOGY AND HEMATOLOGY (R2, R3) A. The PURPOSE of this rotation is to afford medical residents a broad clinical and training experience in the clinical diagnosis and management of common adult
: Provide cardiovascular preventive counseling to parents and patients with specific cardiac diseases about:
 Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY PROFILE
 ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY PROFILE Orthopedic surgery focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation and prevention of diseases of the bones, joints, ligament, muscles, tendons and nerves. These specialists
ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY PROFILE Orthopedic surgery focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation and prevention of diseases of the bones, joints, ligament, muscles, tendons and nerves. These specialists
Common Injuries in the Young Athlete
 Common Injuries in the Young Athlete CHRISTOPHER RIAL, DO LECOM SPORTS MEDICINE PEEK N PEAK 03/04/18 Objectives 1.Recognize that overuse dominates injuries of the young athlete 2. Identify the benefits
Common Injuries in the Young Athlete CHRISTOPHER RIAL, DO LECOM SPORTS MEDICINE PEEK N PEAK 03/04/18 Objectives 1.Recognize that overuse dominates injuries of the young athlete 2. Identify the benefits
The resident will be assigned to be on call with the Oral and Maxillofacial service. Call will be set according to PARO guidelines.
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Lower Extremity Disorders in Children and Adolescents Brian G. Smith. DOI: /pir
 Lower Extremity Disorders in Children and Adolescents Brian G. Smith Pediatrics in Review 2009;30;287 DOI: 10.1542/pir.30-8-287 The online version of this article, along with updated information and services,
Lower Extremity Disorders in Children and Adolescents Brian G. Smith Pediatrics in Review 2009;30;287 DOI: 10.1542/pir.30-8-287 The online version of this article, along with updated information and services,
Columbia/NYOH Department of Orthopaedics Shoulder, Elbow, and Sports Medicine Service Competency Requirements
 Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH Department of Orthopaedics Shoulder, Elbow, and Sports Medicine Service Competency Requirements Patient Care Faculty will evaluate the resident s ability to obtain History,
Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH Department of Orthopaedics Shoulder, Elbow, and Sports Medicine Service Competency Requirements Patient Care Faculty will evaluate the resident s ability to obtain History,
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_057-4 Last Revised Date: August 2014 Responsible Department: Implementation Date: August 2014 Clinical Operations
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines LOWER EXTREMITY MRI (Foot, Ankle, Knee, Leg or Hip MRI) CPT Codes: 73718, 73719, 73720, 73721, 73722, 73723 Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines LOWER EXTREMITY MRI (Foot, Ankle, Knee, Leg or Hip MRI) CPT Codes: 73718, 73719, 73720, 73721, 73722, 73723 Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of
Your Orthopaedic Experience: Bones, Muscles and Joints. Getting you back into motion
 Your Orthopaedic Experience: Bones, Muscles and Joints Getting you back into motion Taking on your aches and pains You want to enjoy all life has to offer. And it s when you re mobile and active, and your
Your Orthopaedic Experience: Bones, Muscles and Joints Getting you back into motion Taking on your aches and pains You want to enjoy all life has to offer. And it s when you re mobile and active, and your
Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries. Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018
 Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018 Text I have no disclosures Overview Etiology, Physiology &Anatomy Common Physeal Overuse Injuries Stress Fractures Concussion
Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018 Text I have no disclosures Overview Etiology, Physiology &Anatomy Common Physeal Overuse Injuries Stress Fractures Concussion
Scientific Programme
 CCPOT Current Concepts in Paediatric Orthopaedics & Trauma Organised under the aegis of Pediatric Orthopaedic Foundation Academic Partners th th 7 & 8 April 2018 WelcomHotel Sheraton Saket, New Delhi Scientific
CCPOT Current Concepts in Paediatric Orthopaedics & Trauma Organised under the aegis of Pediatric Orthopaedic Foundation Academic Partners th th 7 & 8 April 2018 WelcomHotel Sheraton Saket, New Delhi Scientific
PEDIATRIC AND CONGENITAL IMAGING GUIDELINES MUSCULOSKELETAL 2009 MedSolutions, Inc
 MedSolutions, Inc. This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical Clinical Decision Support Tool symptoms or clinical presentations that are not
MedSolutions, Inc. This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical Clinical Decision Support Tool symptoms or clinical presentations that are not
