A comparative radiographic investigation of femoroacetabular impingement in young patients with and without hip pain
|
|
|
- Prudence Tamsyn Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /clinics/2012(05)10 CLINICAL SCIENCE A comparative radiographic investigation of femoroacetabular impingement in young patients with and without hip pain Omar Ferreira Miguel, I Henrique Berwanger de Amorim Cabrita, II Marcelo Bordalo Rodrigues, III Alberto Tesconi Croci IV I Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Arthroplasty Service, São Paulo/SP, Brazil. II Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Emergency Group, São Paulo/SP, Brazil. III Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Head of the Radiology Service of the Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, São Paulo/SP, Brazil. IV Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Arthroplasty Service, São Paulo/SP, Brazil. OBJECTIVE: To compare the existence of radiographic abnormalities in two groups of patients, those with and without hip pain. METHODS: A total 222 patients were evaluated between March 2007 and April 2009; 122 complained of groin pain, and 100 had no symptoms. The individuals in both groups underwent radiographic examinations of the hip using the following views: anteroposterior, Lequesne false profile, Dunn, Dunn 45, and Ducroquet. RESULTS: A total of 1110 radiographs were evaluated. Female patients were prevalent in both groups (52% symptomatic, 58% asymptomatic). There were statistically significant differences between the groups in age (p,0.0001), weight (p = 0.002) and BMI (p = 0.006). The positive findings in the group with groin pain consisted of the presence of a bump on the femoral head in the anteroposterior view (p,0.0001) or in the Dunn 45 view (p = 0.008). The difference in the a angle in the anteroposterior, Dunn, Dunn 45, and Ducroquet views for all of the cases studied was p, The joint space measurement differed significantly between groups in the Lequesne view (p = 0.007). The Lequesne anteversion angle (r) and the femoral offset measurement also differed significantly (p = and p = , respectively). CONCLUSIONS: We conclude that the best views for diagnosing a femoroacetabular impingement are the anteroposterior pelvic orthostatic, the Dunn 45, and the Ducroquet views. The following findings correlated with hip pain: a decrease in the femoral offset, an increase in the a angle, an increase in the Lequesne r angle, a decrease in the CE angle of Wiberg, a thinner articular space and the presence of a bump on the femoral head-neck transition. KEYWORDS: Radiography; Articular Pain; Hip Joint; Femoral Head; Abnormalities; Femoroacetabular Impingement. Miguel OF, Cabrita HB, Rodrigues MB, Croci AT. A comparative radiographic investigation of femoroacetabular impingement in young patients with and without hip pain. Clinics. 2012;67(5): Received for publication on January 3, 2012; First review completed on January 27, 2012; Accepted for publication on January 27, omarfmiguel@gmail.com Tel.: INTRODUCTION Studies conducted on the pathogenesis of osteoarthrosis show a gradual loss of the components of the cartilaginous matrix. This loss initially occurs via a decrease in the level of proteoglycans and through changes in the integrity of the collagen structure (1). Focal areas of damage to the joint cartilage, with fibrillation and loss of volume, are one of the hallmarks of osteoarthrosis (OA). The localizations and Copyright ß 2012 CLINICS This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. No potential conflict of interest was reported. severity of those cartilaginous injuries are primarily defined by mechanical factors that are involved in the etiopathogenesis of OA (2). The loss of the biomechanical properties associated with the events that produce repetitive injuries, and the subsequent deterioration of the cartilage, cause erosion of the joint surface extending as far as the subchondral bone (3). The mechanisms related to axial overload alone cannot explain the full development of OA in individuals whose skeletal structures and intra-articular pressures are apparently normal. The study of the deformities that give rise to abnormal collisions between the bone structures of the femur and the acetabulum have demonstrated that one of the main causes of hip cartilage degeneration are the biomechanical and 463
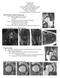
2 Radiographic evaluation of adult hips bone structural changes that affect the rotational movement of the joint, i.e., the femoroacetabular impact (FAI) (4-7). This field is an evolving area of research in hip OA. According to Peixoto et al. (8), OA is responsible for 7.7% of all hospital admissions within the Brazilian National Health System and 7.6% of the healthcare funds in this country. Between 1997 and 2001, according to these same authors, there was a 194.4% increase in hospital admissions due to OA. Hip OA is diagnosed based on the patient history and physical examination and is confirmed with plain radiographs that include anteroposterior (AP) panoramic radiography of the pelvis and AP and lateral views of the hip joint (4,8,9). No consensus exists regarding the series of radiographic views that might demonstrate factors that would predispose individuals to the development of hip OA. The early detection of anatomic and biomechanical abnormalities may result in early clinical or surgical interventions to prevent the degeneration of the joint (10). The objective of the present study was to evaluate the utility of a radiographic series for the early detection of factors that may predispose individuals to developing hip OA. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital das Clínicas, School of Medicine, University of São Paulo. A total of 222 patients were evaluated between March 2007 and April One hundred twenty-two patients complained of groin pain and were followed for treatment in the Hip Group of our institution. One hundred patients without symptoms formed the control group and were followed for treatment in the Shoulder and Elbow Group of our institution. Only one hip with a normal range of motion was studied per patient. In patients with groin pain on both sides, only the most symptomatic hip was studied. If the pain intensity was similar or the same on both sides, one side was randomly selected to be radiographed. If the patient had only one painful hip, the asymptomatic hip was not included in the control group to avoid possible bias from patients who were influenced by their own control. In the asymptomatic group, hips were randomly selected to ensure the randomization of sides. The inclusion criteria for both groups were the following: 1. Age between 20 and 50 years. 2. The absence of prior hip disease, lumbar pain, or any orthopedic treatment (exceptions included diseases of the shoulder and elbow). 3. Normal range of motion of the hip (as measured with manual goniometric tools). 4. Agreeing to participate in the project by signing an informed consent form. The exclusion criteria included the following: 1. Technical difficulties or the inability of the patient to remain on the table during radiographic procedures. 2. An expressed desire by the patient to withdraw from the study. CLINICS 2012;67(5): The presence of osteoarthrosis up to a grade two on the Lawrence classification scale (34) and confirmed by the first radiographic image. 4. The presence of morphological and/or anatomical abnormalities compatible with childhood diseases, trauma sequelae, or tumoral disease. Anthropometric data were obtained to calculate the body mass index (BMI). This study and the accompanying informed consent statement were approved by the Ethics Committee for Research Project Analysis under protocol number 1342/06. Radiographic evaluation All of the radiographic procedures were performed with Phillips Medical Systems Duo Diagnost 800 ma equipment. The sequence of radiographic images included the following: an AP view of the hip while the patient was standing upright on two feet (11), a Lequesne false profile view, a Dunn view, a Dunn view with 45 degrees of flexion (Dunn 45 ), and a Ducroquet view (12,13). Data Analysis The sequence of evaluation for each view included the following: 1. AP: an orthostatic support was used to maintain the limbs at 20 of internal rotation, and the x-ray tube was centralized to the sacrum and parallel to the floor. The center-edge angle of Wiberg, the width of the joint space, the acetabular tilt (14), the acetabular retroversion or anteversion, the alpha angle (a) (6,7,13) (Figure 1A), and the presence or absence of a bump were evaluated. 2. Lequesne false profile: the patient was placed in the upright position with 65 of external rotation of the pelvis, and the tube was centered on the hip. We measured the vertical-central anterior Lequesne and Sèze angle (VCA) (25), the anterosuperior joint space, and the Lequesne femoral anteversion angle (r) (Figure 1B) (6,13,15). 3. Dunn: the patient was placed in the supine position with 90 flexion of the hip and knee and 20 abduction of the hip without any rotational deviation. We measured the alpha (a) angle (Figure 1C) and the presence or absence of a bump at the femoral head-neck junction (12). 4. Dunn 45 : the patient was placed in the supine position with 45 flexion and 20 abduction of the hip without any rotational deviation. The a angle (Figure 1D) and the presence or absence of a bump were measured (12). 5. Ducroquet: the patient was placed in the supine position with 90 flexion and 45 abduction of the hip without any rotational deviation. The femoral offset (the difference between the center of the femoral head and the axis of the neck), the a angle (Figure 1E), and the presence or absence of a bump were measured (12,13,15). In each case, the a angle was measured as follows: the first line follows the long axis of the femoral neck and passes through the femoral head center, and the second line passes through the femoral head center and through the femoral head and neck junction (7). The Lequesne femoral anteversion angle (r) is measured as follows: the first line passes through the femoral diaphysis 464
3 Radiographic evaluation of adult hips used for independent samples with a nonparametric distribution. A confidence level of 5% (a = 0.05) was used. RESULTS General Clinical Findings The group of symptomatic patients consisted primarily of female patients (52%) with a mean age of 41 years, a mean height of 1.7 m, a mean weight of 71.4 kg and a mean BMI of The group of asymptomatic patients consisted primarily of female patients (58%) with a mean age of 31 years, a mean height of 1.68 m, a mean weight of 66.2 kg and a mean BMI of Statistically significant differences were observed between the groups in terms of age (p,0.0001), weight (p = 0.002), and BMI (p = 0.006). In our study, we evaluated a total of 222 patients and 222 hips with 1110 radiographs. Our sample size was larger than those of prior studies according to our review of the literature (7,14,16-21). Figure 1 - Samples of the measurement of a and r angles: (A) a angle in the AP view, (B) Lequesne femoral anteversion angle (r) in the Lequesne false profile view, (C) a angle in the Dunn view, (D) a angle in the Dunn 45 view and (E) a angle in the Ducroquet view. center, and the second line passes through the major diameter of the femoral neck. The angle formed by the junction of these two lines is referred to as the r angle (12). Statistical analysis The normality of the distributions was assessed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for continuous variables. The distribution was accepted as parametric if the results of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test were not significant. Parametric tests were used only for the comparison between distributions that were considered to be normal (Gauss curves). The descriptive statistics and the results of the Kolmogorov- Smirnov (KS) test for each variable are presented in the statistical tables according to the groups (samples). The Student s t test was used for unrelated samples with a parametric distribution to infer the differences between the means of the variables, and the Mann-Whitney U test was Radiologic measurements of the hip joint A bump in the AP view was more frequently present in the symptomatic cases (p,0.0001). A bump was observed in 3% of the asymptomatic cases and in 24% of the symptomatic cases. In the Dunn 45 view, a bump was visualized in 24% of the asymptomatic cases and in 41% of the symptomatic cases (p = 0.008). For the Ducroquet and Dunn views, no statistically significant differences were present in terms of the visualization of a bump (p = 0.35 and p = 0.91, respectively). With regard to the acetabular version, there were no statistically significant findings in the AP view (p = 0.30). The evaluation of the a angle (Table 1) demonstrated statistical significance in all of the cases. For the AP view, the mean a angle was 53 (SD = 11.6) for the asymptomatic cases and 72.7 (p,0.0001) (SD = 9.1) for the symptomatic cases (Table 1). For the Dunn view, the mean a angle was 59.8 (SD = 10.9) for the asymptomatic cases and 71.6 (p,0.0001) (SD = 7.0) for the symptomatic cases (Table 1). For the Dunn 45 view, the mean a angle was 67.5 (SD = 8.1) for the asymptomatic cases was and 72.7 (p,0.0001) (SD = 6.4) for the symptomatic cases (Table 1). For the Ducroquet view, the mean a angle was 59.1 (SD = 8.2) for the asymptomatic cases and 71.2 (p,0.0001) (SD = 7.1) for the symptomatic cases (Table 1). The acetabular inclination data did not demonstrate any statistically significant differences in our study (p=0.28). The joint space, which was also evaluated from the AP and Lequesne views, only revealed a significant difference in the Lequesne view (p = 0.007) with a mean of 4.9 millimeters for the asymptomatic group (SD = 0.9) and 4.5 Table 1 - Comparison of the Radiographic Measurements. Measurements Radiographic View Assymptomatic Symptomatic p-value Anteroposterior 53 +/ /- 9.1 p, a angle Dunn / /- 7 p, Dunn / /- 6.4 p, Ducroquet / /- 7.1 p, r angle Lequesne 17 +/ / p =
4 Radiographic evaluation of adult hips CLINICS 2012;67(5): Table 2 - Comparison between the data from Meyer et al and the data from our study. Radiographic view a angle (symptomatic), our study a angle (asymptomatic), our study a angle, Meyer et al AP 72.7+/ / Dunn 71.6+/ / Dunn / / Ducroquet 71.2+/ / millimeters for the symptomatic group (SD = 1.2). However, no significant differences were observed on the AP view (p = 0.30). Using the AP view, the mean center-edge (CE) angle of Wiberg was 30 (SD = 7.8) for the asymptomatic group and 27.5 (SD = 9.9) for the symptomatic group. These findings were statistically significant (p = 0.03). No statistically significant differences were found between the groups in the Lequesne view with regard to the criterion of the VCA angle (p = 0.30). The measurement of the Lequesne anteversion angle (r) (Table 1) was significantly different between the two groups (p = 0.005). The mean was 17 (SD = 3.2) for the asymptomatic group and 18 (SD = 10.2) for the symptomatic group. A statistically significant difference was also demonstrated in the measurement of the femoral offset (p = ). The patients in the asymptomatic group had a mean value of eight millimeters, whereas those in the symptomatic group had a mean value of seven millimeters. DISCUSSION A review of the literature reveals that many studies have analyzed the a angle, the femoral offset, the sphericity of the femoral head-neck, and the existence of a protuberance or bump (1,3,5,12,14,21,24-27). However, no prior studies analyzed and compared the radiographs of symptomatic and asymptomatic hips in reference to factors possibly associated with the development of osteoarthrosis in young adults. A large number of studies have noted that the presence of bumps promotes impingement (3,5,10,17,21,24,28-32), but no studies have evaluated the prevalence of cam impingement in radiographic examinations. In our study, the presence of bumps was evaluated using the AP, Dunn, Dunn 45, and Ducroquet views. The data obtained from the AP and Dunn 45 views in the symptomatic cases were statistically significant, with a 24% (p,0.0001) prevalence of bumps in the AP view and a 41% (p = 0.008) prevalence of bumps in the Dunn 45 view. No significant differences were present in the Dunn and Ducroquet views (p = 0.91 and p = 0.35, respectively). This analysis revealed the best views for diagnosing bumps to be the AP and Dunn 45 views (12). Other data obtained in this study showed the mean height of the bumps to be 4 mm. The a angle (Figure 1) was measured in accordance with the descriptions of Nötzli et al. (7) and Meyer et al. (12) using the AP (Figure 1 A), Dunn (Figure 1C), Dunn 45 (Figure 1D), and Ducroquet (Figure 1E) views. Each of these views demonstrated statistically significant differences, all p, (Table 1). However, in our study, we found that the observed values of the a angle for normal (asymptomatic) hips using these views were greater than what was previously described by Nötzli et al. (7), Meyer et al. (12) (Table 2), and Rackhra et al. (32). The values reported by these studies are closer to those of our study, particularly the results for the femoroacetabular impingement cam type. The mean a angle in our study was 72.7, compared to 74.1 in the Rackhra et al. (32) study. In our study, the mean a angles for normal (asymptomatic) hips for each view were as follows: the AP view, 53 ; the Dunn view, 59.8 ; the Dunn 45 view, 67.5 ; and the Ducroquet view, For the symptomatic hips, the mean values for each view were as follows: the AP view, 72.7 ; the Dunn view, 71.6 ; the Dunn 45 view, 72.7 ; and the Ducroquet view, The measurements of the superolateral joint space in the AP view did not differ statistically between the groups (p = 0.3). However, for the superolateral joint space measurements obtained using the Lequesne view, the mean value was 4.5 mm in the symptomatic group and 4.9 mm in the asymptomatic group (p = 0.007). These values suggest the reduction in joint space to be a significant cause of hip pain. According to Meyer et al. (12), the mean r angle measured in the Lequesne view (Figure 1B) for normal patients was 21 with a range from 12 to 30. In our study, the mean value was 17 for the asymptomatic group and 17.8 for the symptomatic group, both values considered to be within the normal range. However, the difference between the groups was significant (p = 0.005), which led to the conclusion that diseased hips have an abnormal r angle when compared with the control group (Table 1). Despite the small differences between the means, the symptomatic group had r angle variations ranging from 6 to 52. The evaluation of the femoral offset using the Ducroquet view revealed a statistically significant difference between the symptomatic group, with a mean of 7 mm, and the asymptomatic group, with a mean of 8.1 mm (p = 0.02). Therefore, in painful hips, the space between the femoral head and the femoral neck is substantially smaller. The data in the literature suggest that the normal value should be 11 mm (21,33). However, Wenger et al. (1) suggested that normal values were as low as 7 mm. We identified the following points related to painful conditions of the hip: 1. A diminished femoral offset. 2. An increase in the a angle. 3. An increase in the Lequesne r angle. 4. A decrease in the CE angle of Wiberg. 5. A decrease of the joint space. 6. The presence of a bump at the femoral head-neck transition. The best views for diagnosing femoroacetabular impingement are the pelvic orthostatic AP, and the Dunn 45 and Ducroquet views. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Miguel OF contributed to the original idea, data collection, discussion and conclusions. Cabrita HB contributed to the original idea and project development. Rodrigues MB contributed to the orientation of the 466
5 radiographic examination and analysis of the images. Croci AT provided scientific advice and reviewed the manuscript. REFERENCES 1. Wenger DE, Kendell KR, Miner MR, Trousdale RT. Acetabular labral tears rarely occur in the absence of bony abnormalities. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(426):145-50, Brown CR. Arthritis and allied conditions. In: Callaghan JJ. Rosenberg AG. Rubash HE, editors. The adult hip. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p Correia AM. Estudo comparativo do posicionamento acetabular e sua relação com osteoartrite primária do quadril [dissertação]. São Paulo: Faculdade de Medicina. Universidade de São Paulo; Beall DP, Sweet CF, Martin HD, Lastine CL, Grayson DE, Ly JQ, et al. Skeletal Radiol. 2005;34(11): Goodman DA, Feighan JE, Smith AD, Latimer B, Buly RL. Cooperman DR. Subclinical slipped capital femoral epiphysis: Relation to osteoarthrosis of the Hip. J Bone joint Surg Am. 1997;79(10): Klaue K, Durnin CW, Ganz R. The Acetabular Rim Syndrome: A Clinical presentation of dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(3): Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Soecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J. The contour of the femoral head neck junction as a predictor for the risck of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(4):556-60, dx.doi.org/ / x.84b Peixoto SV, Giatti L, Afradique ME, Lima-Costa MF. Custo das internações hospitalares entre idosos brasileiros no âmbito do Sistema Único de Saúde. Epidem Serv Saúde. 2004;13(3): Harris WH. Etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(213): Siebenrock KA. Schoeniger R, Ganz R. Anterior femoro-acetabular impingement due to acetabular retroversion: treatment with periacetabular osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(2): Blankenbaker DG, Tuite MJ. The painful hip: new concepts. Skeletal Radiol. 2006;35(6):352-70, Meyer DC, Beck M, Ellis T, Ganz R, Leunig M. Comparison of six radiographic projections to assess femoral head/neck asphericity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;(445): Tönnis D, Heinecke A. Acetabular and femoral anteversion: Relationship with osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(12): Tannast M, Goricki D, Beck M, Murphy SB, Siebenrock KA. Hip damage occurs at the zone of femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;(466):273-80, Eijer H, Myers SR, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(7):475-81, dx.doi.org/ / Cooperman DR, Wallensten R, Stulberg SD. Acetabular dysplasia in the adult. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1983;(175): Dudda M, Mamisch TC, Beck C. Do normal radiographs exclude asphericity of the femoral head-neck junction? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;(467):651-9, Radiographic evaluation of adult hips 18. Labronici JP, Alves SD, Silva AF, Giuberti GR, Hoffmann R, Azevedo Neto JN, et al. Estudo anatômico do terço proximal do fêmur: impacto femoroacetabular e o efeito cam. Rev Bras Ortop. 2009;44(2): Lloyd-Roberts GC. Osteoarthritys of the hip: a study of the clinical pathology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1955;37(1): Murray RO. The aetiology of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. Br J Radiol. 1965;38(455):810-24, Peelle MW, Della Rocca GJ, Maloney WJ, Curry MC, Clohisy JC. Acetabular and femoral radiographic abnormalities associated with labral tears. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(441):327-33, /01.blo Solomon L. Patterns of osteoarthrytis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976;58(2): Tannast M, Siebenrock KA, Anderson SE. Femoroacetabular impingement: radiographic diagnosis what the radiologist should know. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(6): , AJR Clohisy JC, Knaus ER, Hunt DM, Lesher JM, Harris-Hayes M, Prathre H. Clinical presentation of patients with symptomatic anterior hip impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;(467):638-44, dx.doi.org/ /s y. 25. Delaunay S, Dussault RG, Kaplan PA, Alford BA. Radiographic measurements of dysplastic adult hips. Skeletal Radiol. 1997;26(2):75-81, Lequesne M, Malghem J, Dion E. The normal hip joint space: variations in width. shape. and architecture on 223 pelvic radiographs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63(9): Reynolds D, Lucas J, Klaue K. Retroversion of the acetabulum: a cause of hip pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(2):281-8, / X.81B Crestani MV, Telöken MA, Gusmão PA. Impacto femoroacetabular: uma das condições precursoras da osteoartrose do quadril. Rev Bras Ortop. 2006;41(8): Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Nötzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(417): Graves ML, Mast JW. Femoroacetabular impingement do outcomes reliably improve with surgical dislocations? Clin Orthop Rel Res. 2009;(467): Leunig M, Beulé PE, Ganz R. The concept of femoroacetabular impingement currente status and future perspectives. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;(467):616-22, Rackhra KS, Sheikh AM, Allen D, Beaulé PE. Comparsion of MRI alpha angle measurement planes in femoraoacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 2009;(467): Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7): Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4): ,
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION METHODS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pedro José Labronici 1, Sergio Delmonte Alves 2, Anselmo Fernandes da Silva 3, Gilberto Ribeiro Giuberti 3, Rolix Hoffmann 4, Justino Nóbrega de Azevedo Neto 4, Jorge Luiz Mezzalira Penedo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pedro José Labronici 1, Sergio Delmonte Alves 2, Anselmo Fernandes da Silva 3, Gilberto Ribeiro Giuberti 3, Rolix Hoffmann 4, Justino Nóbrega de Azevedo Neto 4, Jorge Luiz Mezzalira Penedo
Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
F.A.I. indications. E. Sabetta. Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta
 F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96S, S44 S52 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds L. Bellaïche a,, M. Lequesne b, J.-E. Gedouin
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96S, S44 S52 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds L. Bellaïche a,, M. Lequesne b, J.-E. Gedouin
Prevalence of Cam Deformity with Associated Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome in Hip Joint Computed Tomography of Asymptomatic Adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(1): 5-11, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.5 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Prevalence of Cam Deformity with Associated Femoroacetabular Impingement
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(1): 5-11, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.5 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Prevalence of Cam Deformity with Associated Femoroacetabular Impingement
Adolescent Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Gender Differences in Hip Morphology
 Adolescent Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Gender Differences in Hip Morphology Perry Hooper, DO Sameer Oak, MD Gehan Ibrahim, MD T. Sean Lynch, MD Ryan Goodwin, MD James Rosneck, MD International
Adolescent Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Gender Differences in Hip Morphology Perry Hooper, DO Sameer Oak, MD Gehan Ibrahim, MD T. Sean Lynch, MD Ryan Goodwin, MD James Rosneck, MD International
Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement?
 Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
PROPOSAL FOR STANDARDIZATION OF RADIOGRAPHIC STUDIES ON THE HIP AND PELVIS
 UPDATING ARTICLE PROPOSAL FOR STANDARDIZATION OF RADIOGRAPHIC STUDIES ON THE HIP AND PELVIS Giancarlo Cavalli Polesello 1, Tarsila Sato Nakao 2, Marcelo Cavalheiro de Queiroz 3, Daniel Daniachi 3, Walter
UPDATING ARTICLE PROPOSAL FOR STANDARDIZATION OF RADIOGRAPHIC STUDIES ON THE HIP AND PELVIS Giancarlo Cavalli Polesello 1, Tarsila Sato Nakao 2, Marcelo Cavalheiro de Queiroz 3, Daniel Daniachi 3, Walter
The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular rim during normal hip range of motion.
 RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) in adolescence
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Femoroacetabular Impingement After Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Does Slip Severity Predict Clinical Symptoms? Michael K. Dodds, MCh, MRCSI,* Damian McCormack, MCh, FRCSI,*w and Kevin
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Femoroacetabular Impingement After Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Does Slip Severity Predict Clinical Symptoms? Michael K. Dodds, MCh, MRCSI,* Damian McCormack, MCh, FRCSI,*w and Kevin
Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study
 Original Article Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study Cartilage 1(3) 188 193 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission:
Original Article Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study Cartilage 1(3) 188 193 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission:
We have observed damage to the labrum as a
 Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect A MRI-BASED QUANTITATIVE ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK OFFSET K. Ito, M.-A. Minka-II, M. Leunig, S. Werlen, R.Ganz From the AO ASIF Research
Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect A MRI-BASED QUANTITATIVE ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK OFFSET K. Ito, M.-A. Minka-II, M. Leunig, S. Werlen, R.Ganz From the AO ASIF Research
1/15/2012. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular impingement
 Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
1/15/ year old male. Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA
 29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI
 Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures
 Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Supine and Standing AP Pelvis Radiographs in the Evaluation of Pincer Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Radiology Corner. Femoroacetabular Impingement. Summary of Imaging Findings. Introduction. History
 Radiology Corner Femoroacetabular Impingement Guarantor: CPT Christa B. Blecher, USAF, MC 1 Contributors: MAJ Justin Q. Ly, USAF, MC 1 Note: This is the full text version of the radiology corner question
Radiology Corner Femoroacetabular Impingement Guarantor: CPT Christa B. Blecher, USAF, MC 1 Contributors: MAJ Justin Q. Ly, USAF, MC 1 Note: This is the full text version of the radiology corner question
Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement with Surgical Dislocation
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:146-154 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.146 Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement with Surgical Dislocation Ho-Hyun Yun, MD, Won-Yong Shon, MD, Ji-Yeol
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:146-154 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.146 Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement with Surgical Dislocation Ho-Hyun Yun, MD, Won-Yong Shon, MD, Ji-Yeol
Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip
 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients
Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients
Incidence of femoro-acetabular impingement in adult Indian population on the basis of specific radiological findings: A prospective study
 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
 Original citation: Turley, Glen A. (2012) Femoroacetabular impingement. Working Paper. Coventry: The University of Warwick.. (Unpublished) Permanent WRAP url: http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/53063 Copyright
Original citation: Turley, Glen A. (2012) Femoroacetabular impingement. Working Paper. Coventry: The University of Warwick.. (Unpublished) Permanent WRAP url: http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/53063 Copyright
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities
 Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities Iryna Havenko Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities Iryna Havenko Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD*
 Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD* *Orthopedic Medical Group,7910 Frost St. #200 San Diego, California 92123, USA **Riverside County Regional Medical
Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD* *Orthopedic Medical Group,7910 Frost St. #200 San Diego, California 92123, USA **Riverside County Regional Medical
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement
 Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI
 Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI Frank Kolo C. MD, Caecilia Charbonnier* PhD, Christian W.A. Pfirrmann ** MD, Sylvain R. Duc MD, Anne Lubbeke
Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI Frank Kolo C. MD, Caecilia Charbonnier* PhD, Christian W.A. Pfirrmann ** MD, Sylvain R. Duc MD, Anne Lubbeke
InTRoDucTIon. METHoDS. M. Jäger 1 *, b. bittersohl 1 *, c. Zilkens 1, H. S. Hosalkar 2, K. Stefanovska 1, S. Kurth 1, R. Krauspe 1
 May 12, 2011 Eu Ro PE an JouR nal of MED I cal RE SEaRcH 217 Eur J Med Res (2011) 16: 217-222 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2011 SuRgIcal HIP DISlocaTIon In SyMPToMaTIc cam FEMoRoacETabulaR IMPIngEMEnT: WHaT
May 12, 2011 Eu Ro PE an JouR nal of MED I cal RE SEaRcH 217 Eur J Med Res (2011) 16: 217-222 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2011 SuRgIcal HIP DISlocaTIon In SyMPToMaTIc cam FEMoRoacETabulaR IMPIngEMEnT: WHaT
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail?
 Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
Pathomorphologic Alterations Predict Presence or Absence of Hip Osteoarthrosis
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 465, pp. 46 52 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Pathomorphologic Alterations Predict Presence or Absence of Hip Osteoarthrosis Timo M. Ecker, MD * ;
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 465, pp. 46 52 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Pathomorphologic Alterations Predict Presence or Absence of Hip Osteoarthrosis Timo M. Ecker, MD * ;
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems?
 What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a recognized risk factor for
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2014; 20:271-276 Turkish Society of Radiology 2014 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE CT assessment of asymptomatic hip joints for the background of femoroacetabular impingement
Diagn Interv Radiol 2014; 20:271-276 Turkish Society of Radiology 2014 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE CT assessment of asymptomatic hip joints for the background of femoroacetabular impingement
Prevalence and characteristics of cam-type femoroacetabular deformity in 100 hips with symptomatic acetabular dysplasia: a case control study
 Ida et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:93 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence and characteristics of cam-type femoroacetabular deformity in 100 hips with symptomatic acetabular
Ida et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:93 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence and characteristics of cam-type femoroacetabular deformity in 100 hips with symptomatic acetabular
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes
 Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. 1 2 1
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. 1 2 1
Do Football Players Have a Greater Risk of Developing a Hip Impingement?
 Do Football Players Have a Greater Risk of Developing a Hip Impingement? Madeline Kay Johnson and Robert Stow, PhD Department of Kinesiology, University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire, Eau Claire, WI Acknowledgements
Do Football Players Have a Greater Risk of Developing a Hip Impingement? Madeline Kay Johnson and Robert Stow, PhD Department of Kinesiology, University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire, Eau Claire, WI Acknowledgements
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016
 Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes
 Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. Elsamaloty,
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. Elsamaloty,
What Is Normal Femoral Head/Neck Anatomy? An Analysis of Radial CT Reconstructions in Adolescents
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
The Young Adult Hip: FAI. Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California
 The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
Etiology and Severity of Impingement Injuries of the Acetabular Labrum: What Is the Role of Femoral Morphology?
 Etiology and Severity of Impingement Injuries of the Acetabular Labrum: What Is the Role of Femoral Morphology? Christopher J. Dy, MD, MSPH; Steven J. Schroder, MD; Matthew T. Thompson, MS; Jerry W. Alexander,
Etiology and Severity of Impingement Injuries of the Acetabular Labrum: What Is the Role of Femoral Morphology? Christopher J. Dy, MD, MSPH; Steven J. Schroder, MD; Matthew T. Thompson, MS; Jerry W. Alexander,
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete. Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute
 Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
Femoroacetabular Impingement in the Throwing Athlete Michael Banffy, MD Sports Medicine, Hip Preservation Kerlan Jobe Institute Disclosures None Baseball Hip Injuries - Background Abdominal/groin injuries
Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort
 Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this topic Objectives Evaluate and recognize common hip pathology
Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this topic Objectives Evaluate and recognize common hip pathology
Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults.
 Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults. Poster No.: C-0492 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arevalo, N. Santamaria, E. Diez, J. Gredilla Molinero, M. 1
Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults. Poster No.: C-0492 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arevalo, N. Santamaria, E. Diez, J. Gredilla Molinero, M. 1
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
25. PELVIC OSTEOTOMIES FOR THE TREATMENT OF HIP DYSPLASIA IN ADULTS
 Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology
 Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
HIP IMPINGEMENT. both musculoskeletal conditions and nonmusculoskeletal
 SPORTS SURGERY HIP IMPINGEMENT What do we know and what do we still need to find out? Written by Michael Leunig and Atul Kamath, Switzerland INTRODUCTION Groin pain is common in athletic populations. This
SPORTS SURGERY HIP IMPINGEMENT What do we know and what do we still need to find out? Written by Michael Leunig and Atul Kamath, Switzerland INTRODUCTION Groin pain is common in athletic populations. This
Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs
 Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs Moin Khan 1, Anil Ranawat 2, Dale Williams 1, Rajiv Gandhi 3, Hema Choudur
Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs Moin Khan 1, Anil Ranawat 2, Dale Williams 1, Rajiv Gandhi 3, Hema Choudur
21 year-old collegiate rower: R/O labral tear
 Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology
 Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology University of Rochester Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Raymond J. Kenney, MD P. Christopher Cook, MD Kelly
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology University of Rochester Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Raymond J. Kenney, MD P. Christopher Cook, MD Kelly
In the work-up for nonarthritic hip pain, the value
 A Review Paper Paul B. Lewis, MD, MS, Alexander E. Weber, MD, and Shane J. Nho, MD, MS Abstract Diagnostic imaging is an essential aspect of the work-up for nonarthritic hip pain. This review, a comprehensive
A Review Paper Paul B. Lewis, MD, MS, Alexander E. Weber, MD, and Shane J. Nho, MD, MS Abstract Diagnostic imaging is an essential aspect of the work-up for nonarthritic hip pain. This review, a comprehensive
Range of motion in femoroacetabular impingement
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 327-332 ORIGINAL STUDY Range of motion in femoroacetabular impingement Emmanuel AUDEnAERT, Jan VAn HOUCkE, Bastiaan MAES, Luc VAnDEn BOSSCHE, Jan ViCTOR, Christophe PATTyn
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 327-332 ORIGINAL STUDY Range of motion in femoroacetabular impingement Emmanuel AUDEnAERT, Jan VAn HOUCkE, Bastiaan MAES, Luc VAnDEn BOSSCHE, Jan ViCTOR, Christophe PATTyn
CommonKnowledge. Pacific University. Rory J. Hansen Pacific University. Fall
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Fall 8-13-2016 Dunn Lateral View is the Most Predictable Plain Film Radiograph for Demonstrating
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Fall 8-13-2016 Dunn Lateral View is the Most Predictable Plain Film Radiograph for Demonstrating
Hip Arthroscopy. Christopher J. Utz, MD. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati
 Hip Arthroscopy Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. Brief History 2. Review of
Hip Arthroscopy Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. Brief History 2. Review of
Efficacy of Intra-articular Steroid Injection in Patients with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Case Report Korean J Pain 1 April; Vol. 6, No. : 1-19 pissn 0-919 eissn 9-069 http://dx.doi.org/10./kjp.1.6..1 Efficacy of Intra-articular Steroid Injection in Patients with Femoroacetabular Impingement
Case Report Korean J Pain 1 April; Vol. 6, No. : 1-19 pissn 0-919 eissn 9-069 http://dx.doi.org/10./kjp.1.6..1 Efficacy of Intra-articular Steroid Injection in Patients with Femoroacetabular Impingement
SPORTS HEALTH. The Etiology of Femoroacetabular Impingement: What We Know and What We Don t. Methods
 521576SPHXXX10.1177/1941738114521576Chaudhry and Ayeni research-article2014 vol. 6 no. 2 [ Orthopaedic Surgery ] The Etiology of Femoroacetabular Impingement: What We Know and What We Don t Harman Chaudhry,
521576SPHXXX10.1177/1941738114521576Chaudhry and Ayeni research-article2014 vol. 6 no. 2 [ Orthopaedic Surgery ] The Etiology of Femoroacetabular Impingement: What We Know and What We Don t Harman Chaudhry,
10/15/17. Acknowledgements. The Sporting Hip & Groin. TheSporting. SportingHip. The Sporting. The Sporting. The Sporting.
 Michael O Brien Physiotherapist Acknowledgements The TheSporting SportingHip Hip & Groin Impingement or instability? Andrew Wallis Alesha Coonan (Gledhill-Tunks) Melbourne Orthopaedic Group Mr. Jit Balakumar
Michael O Brien Physiotherapist Acknowledgements The TheSporting SportingHip Hip & Groin Impingement or instability? Andrew Wallis Alesha Coonan (Gledhill-Tunks) Melbourne Orthopaedic Group Mr. Jit Balakumar
Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View
 Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement
 Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
[ RESIDENT S CASE PROBLEM ]
![[ RESIDENT S CASE PROBLEM ] [ RESIDENT S CASE PROBLEM ]](/thumbs/82/86190184.jpg) [ RESIDENT S CASE PROBLEM ] ANDREA B. AUSTIN, DPT¹ PT² DPT³ PT, PhD 4 Identification of Abnormal Hip Motion Associated With Acetabular Labral Pathology ip pain can disrupt functional mobility regardless
[ RESIDENT S CASE PROBLEM ] ANDREA B. AUSTIN, DPT¹ PT² DPT³ PT, PhD 4 Identification of Abnormal Hip Motion Associated With Acetabular Labral Pathology ip pain can disrupt functional mobility regardless
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy
 Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
Does Radiographic Coxa Profunda Indicate Increased Acetabular Coverage or Depth in Hip Dysplasia?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:2056 2066 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4084-x Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Radiographic
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:2056 2066 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4084-x Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Radiographic
The causes of hip pain range from intra-articular
 Current Concepts Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Carlos A. Guanche, M.D., and Aaron A. Bare, M.D. Abstract: The etiology of degenerative joint disease of the hip remains unsolved.
Current Concepts Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Carlos A. Guanche, M.D., and Aaron A. Bare, M.D. Abstract: The etiology of degenerative joint disease of the hip remains unsolved.
What Is the Impingement-free Range of Motion of the Asymptomatic Hip in Young Adult Males?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:1284 1288 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4072-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:1284 1288 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4072-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 6-2011 Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint Ronald Huang
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 6-2011 Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint Ronald Huang
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications. Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout
 Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Disclosures. Objectives 11/18/2015. Hip Preservation in the Adolescent and Young Adult. Financial - None I do not perform total joint arthroplasty
 Hip Preservation in the Adolescent and Young Adult Alfred A. Mansour, III, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation UT-Ortho 59th Annual Edward T. Smith Orthopaedic Lectureship November 5-6, 2015
Hip Preservation in the Adolescent and Young Adult Alfred A. Mansour, III, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation UT-Ortho 59th Annual Edward T. Smith Orthopaedic Lectureship November 5-6, 2015
Title; Periacetabular Osteotomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Acetabular Dysplasia in. Patients with and without Labral Tears.
 Title; Periacetabular Osteotomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Acetabular Dysplasia in Patients with and without Labral Tears Authors; Tomonobu Hagio, MD 1 ; Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD 1 ; Yoshinari Nakamura,
Title; Periacetabular Osteotomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Acetabular Dysplasia in Patients with and without Labral Tears Authors; Tomonobu Hagio, MD 1 ; Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD 1 ; Yoshinari Nakamura,
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) occurs when the
 The Biomechanics of Femoroacetabular Impingement Daniel E. Martin, MD, and Scott Tashman, PhD Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is proposed as a possible biomechanical etiology of early, idiopathic hip
The Biomechanics of Femoroacetabular Impingement Daniel E. Martin, MD, and Scott Tashman, PhD Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is proposed as a possible biomechanical etiology of early, idiopathic hip
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult
 Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Stephanie W. Mayer, MD. Director of Child and Young Adult Hip Preservation Sports Medicine Center Children s Hospital Colorado
 Stephanie W. Mayer, MD Director of Child and Young Adult Hip Preservation Sports Medicine Center Children s Hospital Colorado University of Colorado Sports Medicine Assistant Team Physician, Colorado Avalanche
Stephanie W. Mayer, MD Director of Child and Young Adult Hip Preservation Sports Medicine Center Children s Hospital Colorado University of Colorado Sports Medicine Assistant Team Physician, Colorado Avalanche
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes
 The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
Treatment of reduced femoral antetorsion by subtrochanteric rotational osteotomy
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 490-496 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of reduced femoral antetorsion by subtrochanteric rotational osteotomy Hanspeter HUBER, Mathias HAEFELI, Stefan DIERAUER, Leonhard E. RAMSEIER
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 490-496 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of reduced femoral antetorsion by subtrochanteric rotational osteotomy Hanspeter HUBER, Mathias HAEFELI, Stefan DIERAUER, Leonhard E. RAMSEIER
Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it?
 Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it? Poster No.: P-0049 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. De Roeck, F. M. H. M. Vanhoenacker ; Antwerpen/BE, 1 2 1 2 Antwerp/BE
Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it? Poster No.: P-0049 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. De Roeck, F. M. H. M. Vanhoenacker ; Antwerpen/BE, 1 2 1 2 Antwerp/BE
Adult Hip Radiography: Lines and angles
 Adult Hip Radiography: Lines and angles Poster No.: P-0209 Congress: ESSR 2017 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. L. Proença, A. P. Caetano, L. Bogalho; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Education and training, Education,
Adult Hip Radiography: Lines and angles Poster No.: P-0209 Congress: ESSR 2017 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. L. Proença, A. P. Caetano, L. Bogalho; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Education and training, Education,
Labral Tears / Femoro- Acetabular Impingement / Hip Arthroscopy/THA. Dr Allen Turnbull Hip and Knee Surgery
 Labral Tears / Femoro- Acetabular Impingement / Hip Arthroscopy/THA Hip Anatomy Labrum Fovea Femoral Head Articular Cartilage Ligamentum Teres Labral Tears Function of Labrum Deepens acetabulum by 20%
Labral Tears / Femoro- Acetabular Impingement / Hip Arthroscopy/THA Hip Anatomy Labrum Fovea Femoral Head Articular Cartilage Ligamentum Teres Labral Tears Function of Labrum Deepens acetabulum by 20%
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. 78 Int J Res Med. 2013; 2(1);78-82 e ISSN: p ISSN: Morphological aspect of acetabulum of hip bone
 AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. 98 Int J Res Med. 2013; 2(1); e ISSN: p ISSN: Non-metric variation of the neck of the femur
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF NON-METRIC VARIATION OF THE NECK OF THE FEMUR Kintu Vyas 1*,Vipul Patel 2,Abhijeet Joshi 3,Bhavesh Shroff 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF NON-METRIC VARIATION OF THE NECK OF THE FEMUR Kintu Vyas 1*,Vipul Patel 2,Abhijeet Joshi 3,Bhavesh Shroff 4 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Hip arthroscopy. Anatomy The hip is functionally a ball and socket joint.
 Hip arthroscopy The term arthroscopy (or keyhole surgery) refers to the viewing of the inside of a joint through a small operating telescope. First described in the 1970s, arthroscopic techniques have
Hip arthroscopy The term arthroscopy (or keyhole surgery) refers to the viewing of the inside of a joint through a small operating telescope. First described in the 1970s, arthroscopic techniques have
Groin pain secondary to Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome - A case of mistaken identity
 Groin pain secondary to Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome - A case of mistaken identity Elizabeth Tan 1, Pramod Durgakeri 2 1,2. Box Hill Hospital, Victoria, Australia CASE STUDY Please cite this
Groin pain secondary to Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome - A case of mistaken identity Elizabeth Tan 1, Pramod Durgakeri 2 1,2. Box Hill Hospital, Victoria, Australia CASE STUDY Please cite this
Periacetabular Osteotomy Restores the Typically Excessive Range of Motion in Dysplastic Hips With a Spherical Head
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4089-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP SYMPOSIUM Periacetabular
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4089-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP SYMPOSIUM Periacetabular
CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT
 SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
SPORTS REHABILITATION CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT A case study and rationale for treatment Written by Joanne Kemp and Kay Crossley, Australia BACKGROUND The hip joint and FAI
UCC Library and UCC researchers have made this item openly available. Please let us know how this has helped you. Thanks!
 UCC Library and UCC researchers have made this item openly available. Please let us know how this has helped you. Thanks! Title Author(s) Diagnosis and management of femoroacetabular impingement: a review
UCC Library and UCC researchers have made this item openly available. Please let us know how this has helped you. Thanks! Title Author(s) Diagnosis and management of femoroacetabular impingement: a review
Sports Medicine and Radiology
 Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
