Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip
|
|
|
- Amos Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip Ingmar Ipach 1,2*, Ina-Christine Rondak 3, Saskia Sachsenmaier 1, Elisabeth Buck 1, Roland Syha 4 and Falk Mittag 1 Abstract Background: During the last years, terms like acetabular retroversion, excessive overcoverage, and abnormal head-neck-junction with the so called pistol-grip-deformity has been added to the classical description of hip dysplasia. These anatomical changes could lead to a femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). Both kinds of FAI has been indentified as a main reason for hip pain and progressive degenerative changes leading to early osteoarthritis of the hip. A lot of radiographic criteria on pelvic views have been established to detect classical dysplasia and FAI. The present study was initiated to assess the hypothesis that age and severity of osteoarthritis affect measurements of different radiographic parameters. Methods: The pelvic radiographs of 1614 patients were measured for head-ratio, CE-angle, roof obliquity, extrusion-index, depth-to-width ratio, CCD-angle, sharp s angle. To evaluate the severity of osteoarthritis of the hip the classification by Kellgren and Lawrence was used. Associations between age and radiographic parameters or severity of osteoarthritis were assessed by Spearman s (ρ) or Kendall s (r) rank correlation coefficient, respectively. Results: 366 (22.7%) patients presented no sign of osteoarthritis, 367 (22.7%) patients presented I osteoarthritis, 460 (28.5%) patients presented II osteoarthritis, 307 (19%) III osteoarthritis and 114 (7.1%) IV osteoarthritis of the hip. The mean head-ratio of all patients was 1.13 ± 0.26 ( ), the mean CE-angle ± (0-70 ), the mean roof obliquity was ± 4.96 (10 55 ), the mean extrusion-index was ± 9.21 ( ), the mean depth-to-width ratio was ± 8.90 ( ), the mean CCD-angle was ± 7.22 ( ) and the mean sharp s angle was 9.75 ± 5.40 (1-34 ) There was a weak association between age and the severity of osteoarthritis of the hips (left: r = 0.291; right: r = 0.275; both P < 0.001) with higher osteoarthritis levels observable for elderly patients). Conclusion: Severity of osteoarthritis has a negative impact on measurements of different radiographic parameters. Therefore - in our opinion - epidemiological studies on prearthrotic deformities should only be performed in healthy adults with no signs of osteoarthritic changes. Keywords: Radiographic Signs, Impingement, Hip, Dysplasia, Osteoarthritis * Correspondence: IngmarIpach@gmx.de 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University Hospital of Tuebingen, Hoppe-Seyler-Straße 3, Tuebingen, Germany 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hospital of Ingolstadt, Krumenauerstraße 25, Ingolstadt, Germany Full list of author information is available at the end of the article 2014 Ipach et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 Page 2 of 7 Background During the last years, terms like acetabular retroversion, excessive overcoverage, and abnormal head-neck-junction with the so called pistol-grip-deformity [1-4] has been added to the classical description of hip dysplasia with a lateral CEA-angle of less then 25 and a roof obliquity angle of more than 10 [5]. These anatomical changes could lead to a femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). Two kinds of FAI have been described. In Cam impingement a repetitive contact between an abnormal head-neckjunction and the acetabular rim causes cartilage damage in the anterosuperior area of the acetabulum. In Pincer impingement a direct contact between the femoral neck and a local/generalized overcovered acetabulum leads also to repetitive damage of the cartilage at the acetabular rim [6-16]. Both kinds of FAI has been indentified as a main reason for hip pain and progressive degenerative changes leading to early osteoarthritis of the hip [1-4,6,7]. The diagnosis of FAI should be based on detailed physical examination and appropriate imaging studies. A lot of radiographic criteria on pelvic views have been established to detect classical dysplasia and FAI [17-21]. The head-ratio has already described as reliable for the detection of pistol-grip-deformity [7,8,22]. It has also been shown that radiographic FAI findings are very common in a population of healthy young adults [23]. Goodman et al. have shown that pistol-grip-deformity is due to a three-dimensional structural abnormality with no change in severity with age [24]. According to Kellgren and Lawrence [25] progressive degenerative changes lead to osteophytes, narrowing of the joint space, and deformity of the bone ends. These changes mayhaveanegativeimpactonradiographicparameters. Thepresentstudywasinitiatedtoassesstheinfluenceof severity of osteoarthritis on radiographic parameters. Methods Ethical approval has been received by the ethic committee of Tübingen (025/2014R). We analysed our data bank for all pelvic-views which has been performed in our institution in the period between 1 st January 2006 and 31 st December To exclude the negative influence of pelvic tilt and rotation on radiographic parameters, only standardized pelvic radiographs were included in this study. The distance between the tip of the coccyx and the middle of the symphysis was 32 mm for men and 47 mm for women and the teardrop sign appeared symmetrical [1]. The pelvic-views were measured for head-ratio, CEangle, roof obliquity, extrusion-index, depth-to-width ratio, CCD-angle, sharp s angle [8,17-20,22,26]. In cases with the presents of a THA, fracture or Dysplasia Crowne II/IV on one side, only the other was measured. To evaluate the severity of osteoarthritis of the hip the classification by Kellgren and Lawrence was used [25]. Statistical analysis Statistical analyses were conducted with the use of IBM SPSS Statistics 21 and R software, version (R Core Team). In order to account for repeated measurements of both hips on patient level, analysis was conducted separately for left and right hips or using summarized values for both sides (i.e. mean or maximum values of both hips). When analyzing the influence of age on severity of osteoarthritis different radiographic parameters, left and right hip were analyzed separately. When analyzing the influence of severity of osteoarthritis on the different radiographic parameters, the most severe hip and corresponding measurements or in case of equal severity on both sides, averaged measurements over both hips were considered for each patient. Categorical variables are presented as frequencies, percentages, and continuous variables as means and standard deviations, or medians and interquartile ranges (Boxplots) for variables with skewed distributions. Associations between age and radiographic parameters or severity of osteoarthritis were assessed by Spearman s (ρ) or Kendall s (τ) rank correlation coefficient, respectively. Group comparisons based on severity of osteoarthritis of continuous measurements were conducted using either the one-way analysis of variances (ANOVA) or the Kruskall-Wallis test, as appropriate. All reported P values are two-tailed, with a P value of 0.05 indicating statistical significance and have not been adjusted for multiple testing. Results The pelvic radiographs of 1614 Patients were included into this study. In 1052 of all cases both sides were measured in 562 cases only the left (n = 311) or right side (n = 251) were measured for radiographic signs of FAI and dysplasia. Table 1 Measurement values for the different radiographic parameters of both hips n= Sharps-angle ± 5.40 (1-34 ) Head-ratio 1.13 ± 0.26 ( ) CE-angle ± (0-70 ) Roof obliquity ± 4.96 (10 55) The results are presented as means and standard deviations (Minimum Maximum). Extrusion-index (in %) ± 9.21 ( ) Depth-to-width ratio (in %) ± 8.90 ( ) CCD-angle ± 7.22 ( )
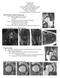
3 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 Page 3 of 7 Figure 1 Association between severity of osteoarthritis and age. Y-axis: age in years, X-axis: severity of osteoarthritis according to Kellgren-Lawrence (Kendall s correlation coefficient for left hips: r = 0.291; and right hips: r = 0.275; both p < 0.001). The mean age of all patients was 60.2 years ± % of all patients were male, 55.6% were female. 366 (22.7%) patients presented no sign of osteoarthritis, 367 (22.7%) patients presented I osteoarthritis, 460 (28.5%) patients presented II osteoarthritis, 307 (19%) III osteoarthritis and 114 (7.1%) patients presented IV osteoarthritis of the hip. The mean values of all different radiographic parameters are demonstrated in Table 1. There was a weak association between age and the severity of osteoarthritis of the hips (left: τ = 0.291; right: τ = 0.275; both P < 0.001) with higher osteoarthritis levels observable for elderly patients (Figure 1). The correlation between age and head-ratio, CE-angle, roof obliquity, extrusion-index, depth-to-width ratio, CCDangle, sharp s angle is demonstrated in Figures 2 and 3. Weak monotone associations were also observed between age and mean CE-angle (ρ = 0.334) (p < 0.001), mean sharps angle (ρ = ) (p < 0.001), mean extrusion-index (ρ = ) (p < 0.001), and mean CCD-angle (ρ =-0.205) (p < 0.001). On the other hand no correlations were seen between age and depth-to-width ratio (ρ =0.033) (p < 0.181), roof obliquity (ρ = 0.133) (p < 0.001) and headratio (ρ = 0.135) (p < 0.001). These results imply that age Figure 2 Correlation between CE-angle, roof-obliquity, depth-to-width-ratio, extrusion-index and age. a: Correlation between age and CE-angle. X-axis: age in years, Y-axis: CE-angle in degree. There was a weak monotone correlation between age and CE-angle (ρ = 0.334). b: Correlation between age and roof-obiquity. X-axis: age in years, Y-axis: roof obliquity in degree. There no correlation between age and roof obliquity (ρ = ). c: Correlation between age and depth-to-width-ratio. X-axis: age in years, Y-axis: depth-to-width-ratio in %. There was no correlation between age and depth-to-width-ratio (ρ = 0.033) d: Correlation between age and extrusion-index. X-axis: age in years, Y-axis: extrusion-index in %. There was weak negative correlation between age and extrusion-index (ρ = ).
4 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 Page 4 of 7 Figure 3 Correlation between sharps-angle, CCD-angle, head-ratio and age. a: Correlation between age and sharps-angle. X-axis: age in years, Y-axis: sharps-angle in degree. There was weak negative correlation between age and sharps-angle (ρ = ) b: Correlation between age and CCD-angle. X-axis: age in years, Y-axis: CCD-angle in degree. There was weak negative correlation between age and CCD-angle (ρ = ) c: Correlation between age and head-ratio. X-axis: age in years, Y-axis: head-ratio There was no correlation between age and head-ratio (ρ = 0.135). has only a weak or no impact on the different radiographic parameters for FAI and dysplasia. One-way ANOVA revealed statistical significant differences between patient groups based on severity (Kellgren-Lawrence 1-4 ) of osteoarthritis for the following measurements: CE-angle (p < 0.001), sharps-angle (p < 0.001), Extrusion-index (p < 0.001), and CCD-angle (p < 0.001). No statistical significant difference between patient groups based on severity (Kellgren-Lawrence 1-4 ) and depth-to-width ratio was seen (p = 0.535). Assuming a skewed distribution of head-ratio and roof-obliquity measurements, the nonparametric Kruskall-Wallis-test revealed a statistical significant difference between osteoarthritis groups headratio (P < 0.001) but none for roof-obliquity (Figure 4) (P = 0.18). These results imply that there is an association between the different radiographic parameters (excluded roof-obliquity and depth-to-width ratio) and the severity of osteoarthritis of the hip. Discussion During the last years a lot of studies have shown changes in the acetabular geometry and the head neck region as a main reason for an early osteoarthritis of the hip. Terms like femoroacetabular impingement have become more and more important in the explanation for hip pain and the early development of OA. These morphologic changes in the acetabular geometry such as an excessive overcoverage or an acetabular retroversion or changes in the head-neck-region lead to the so-called Pincer- or Cam-impingement [6-18]. However, the classic definition of hip-dysplasia with an undercoverage of the femoral head (reduced CE-angle) or a steep acetabular roof (increased roof obliquity) is still playing an important role in the indication of total hip arthroplasty in young adults [26-30]. While watching different epidemiological studies, an abnormal hip morphology with acetabular dysplasia has been reported in about 51-80% of all cases with OA of the hip [23]. Including radiographic findings for an excessive overcoverage of the femoral head, acetabular retroversion or an abnormal head-neck-junction, as a dysplastic change, hip-dysplasia was seen in nearly 97% of all patients [26]. The prevalence of acetabular dysplasia has been reported to be about 3.8% in the British population [28] and 4.5% in Chinese men [29]. An abnormal head-neckjunction seems to be present in about 40%-50% of all hips with OA [26,30]. A recent study has shown a high prevalence of radiographic finding for FAI in a cohort of 2081 healthy adults. The prevalence of CAM-impingement was up to 40%, the prevalence of Pincer-impingement up to 50% [23]. The present study was performed to assess the impact of severity of osteoarthritis on different radiographic
5 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 Page 5 of 7 Figure 4 Association between severity of osteoarthritis and radiographic parameters. a-g: Patient based measurement values of CE-angle, sharps-angle, Extrusion-index, depth-to-width ration, CCD-angle, head-ratio and roof-oblique by severity of osteoarthritis of the hip (Kellgren-Lawrence 0-4) [most severe hip and corresponding measurements or in case of equal severity on both sides, averaged measurements over both hips were considered]. a: X-axis: group 0-4 according to severity of osteoarthritis, Y-axis: CE-angle in degree. There was a statistical significant difference in the CE-angle between the groups (p < 0.001). b: X-axis: group 0-4 according to severity of osteoarthritis Y-axis: sharp s angle in degree. There was a statistical significant difference in the sharp s angle between the groups (p < 0.001) c: X-axis: group 0-4 according to severity of osteoarthritis Y-axis: depth-to-width-ratio in%. No statistical significant difference between the groups was seen (p = 0.535). d: X-axis: group 0-4 according to severity of osteoarthritis Y-axis: extrusion-index in%. There was a statistical significant difference in the extrusion-index between the groups (p < 0.001) e: X-axis: group 0-4 according to severity of osteoarthritis, Y-axis: roof-obliquity in degree. No statistical significant difference between the groups was seen (p = 0.18). f: X-axis: group 0-4 according to severity of osteoarthritis Y-axis: CCD-angle in degree. There was a statistical significant difference in the CCD-angle between the groups (p < 0.001). g: X-axis: group 0-4 according to severity of osteoarthritis Y-axis: head-ratio. There was a statistical significant difference in the head-ratio between the groups (p < 0.001). measurement values. We were able to show that degenerative changes has an negative impact on radiographic parameters for FAI and hip dysplasia. To our knowledge this was the first study focusing on this topic. The posterior head tilt in osteoarthritic hips has been discussed as being an acquired deformity created by the formation of osteophytes [8]. The present study support these findings, as the head-ratio demonstrated an increase with the severity of osteoarthritis. On the other hand it was shown that this deformity did not change with age and therefore it could be seen as a prearthrotic deformity and not as secondary to degeneration [24]. We not several limitations in this study. A testing on intra- and interobserver reliability hasn t be performed in this study, but previous studies already focussed on this topic [31]. Clohisy et al. [32] and Gosving et al. [33]
6 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 Page 6 of 7 reported about poor results for inter- and intra-observer reliability of measurements of radiographic signs for acetabular dysplasia, head-neck offset and pelvic tilt. Other studies were able to show a high inter- and intraobserver reliability for different radiographic parameters by using the Balnd-Altman-method [26,31,34,35]. The discrepancy between these studies could be explained by the using of different statistical methods. The kappa-coefficient by Cohen [34] is the first choice for testing inter- and intraobserver quality of categorical variables, it should not be used for data on a continuous level [34,35]. Correlation coefficients for testing reliability between two observers should not be used at all [34]. Therefore the Bland- Altman-method is a better choice for assessing agreement of continuous data [34,35]. Nevertheless the inter- and intrabserver quality of radiographic findings in the diagnostic of dysplasia, FAI and excessive overcoverage is one of the main problem in the clinical routine. Therefore the use of a threedimensional imaging might be helpful in unclear cases. Conclusion There seems to be a negative impact of severity of osteoarthritis on different radiographic parameters for the detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia. Therefore - in our opinion - epidemiological studies on prearthrotic deformities and radiographic paramters for FAI and hip dysplasia should only be performed in adults with no signs of osteoarthritic changes. Abbreviations CE-angle: Centre-edge-angle; CCD-angle: Caput-collum-diaphysis-angle; FAI: Femoroacetabular impingement; OA: Osteoarthritis; THA: Total hip arthroplasty. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions II: Drafting the manuscript IR: statistical analysis SS: graphical design, recruiting x-rays EB: performing measurements RS: controlling accuracy of measurements and quality of x-rays FM: Study design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Author details 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University Hospital of Tuebingen, Hoppe-Seyler-Straße 3, Tuebingen, Germany. 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hospital of Ingolstadt, Krumenauerstraße 25, Ingolstadt, Germany. 3 Department of Medical Statistics and Epidemiology, Technische Universität München, Ismaninger Str. 22, Munich 81675, Germany. 4 Department of Radiology, University Hospital of Tuebingen, Hoppe-Seyler-Straße 3, Tuebingen, Germany. Received: 10 January 2014 Accepted: 30 April 2014 Published: 8 May 2014 References 1. Beall DP, Sweet CF, Martin HD: Imaging findings of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome. Skeletal Radiol 2005, 34: James SL, Ali K, Malara F, Young D, O Donnell J, Connell DA: MRI findings of femoroacetabular impingement. AJR 2006, 187: Tannast M, Kubiak-Langer M, Langlotz F, Puls M, Murphy SB, Siebenrock KA: Non invasive threedimensional assessment of femoroacetabular impingement. J Orthop Res 2007, 25: Siebenrock KA, Schoeninger R, Ganz R: Anterior femoro-acetabular impingement due to acetabular retroversion: treatment with periacetabular osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003, 5(A): Miller MD: Review of Orthopaedics 5 th edition. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Nötzli H, Siebenrock KA: Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2003, 417: Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J: The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2002, 84: Murray RO: The aetiology of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. Br J Radiol 1965, 38: Jäger M, Wild A, Westhoff B: Femoroacetabular impingement caused by a femoral osseous head-neck bump deformity: clinical, radiological, and experimental results. J Orthop Sci 2004, 9: Koegh MJ, Batt ME: A review of femoroacetabular impingement in athletes. Sports Med 2008, 38: Stafford G, Witt J: The anatomy, diagnosis and pathology of femoroacetabular impingement. Br J Hosp Med 2009, 70: Anda S, Terjesen T, Kvistad KA, Svenningsen S: Acetabular angles and femoral anteversion in dysplastic hips in adults: CT-investigation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1991, 15(1): Anderson LA, Peters CL, Park BB, Stoddard GJ, Erickson JA, Crim JR: Acetabular cartilage delamination in femoroacetabular impingement. Risk factors and Magnetic Resonance imaging diagnosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009, 91: Fadul DA, Carrino JA: Imaging of femoroacetabular impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009, 91: Murphy SB, Ganz R, Müller ME: The prognosis in untreated dysplasia of the hip. A study of radiographic factors that predict the outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995, 77(7): Laude F, Boyer T, Nogier A: Anterior femoroacetabular impingement. Joint Bone Spine 2007, 74: Lequesne M: Coxometry measurement of the basic angles of the adult radiographic hip by a combined protractor. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic 1963, 30: Tannast M, Siebenrock KA, Anderson SE: Femoroacetabular Impingement: radiographic diagnosis what the radiologist should know. Am J Roentgenol 2007, 188(6): Steppacher SD, Tannast M, Werlen S, Siebenrock KA: Femoral morphology differs between deficient and excessive acetabular coverage. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2008, 466(4): Tönnis D, Heinecke A: Acetabular and femoral anteversion: relationship with osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999, 81(12): Wiberg G: Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint: With special reference to the complications of osteoarthritis. Acta Chir Scan 1939, 58: Ipach I, Mittag F, Sachsenmaier S, Heinrich P, Kluba T: A new classification for pistol grip deformity - correlation between the severity of the deformity and the grade of osteoarthritis of the hip. Fortschr Röntgenstrahl 2010, 183(4): Laborie LB, Lehmann TG, Engeæter I, Eastwood DM, Engeæter LB, Rosendahl K: Prevalence or radiographic findings thought to be associated with femoroacetabular impingement in a population-based cohort of 2081 healthy young adults. Radiology 2011, 260: Goodman DA, Feighan JE, Smith AD, Latimer B, Buly RL, Cooperman DR: Subclinical slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Relationship to osteoarthrosis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1997, 79(10): Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS: Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957, 16: Ipach I, Mittag F, Syha R, Kunze B, Wolf P, Kluba T: Indications for total hip arthroplasty in young adults - idiopathic osteoarthritis seems to be overestimated. Röfo 2012, 184(3): Harris WH: Etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop 1986, 213: Cooperman DR, Wallensten R, Stulberg SD: Post-reduction avascular necrosis in congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1980, 62(2):
7 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 Page 7 of Lau EM, Lin F, Lam D, Silman A, Croft P: Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men. Ann Rheum Dis 1995, 54(12): Stulberg SD, Cordell LD, MacEwen GD: Unrecognized childhood hip disease: a major cause of idiopathic osteoarthritis of the hip. In The Hip Procs Third Open Scientific Meeting of the Hip Society St Louis. Edited by Amstutz HC. St. Louis: C V Mosby; 2010: Ipach I, Arlt EM, Mittag F, Kunze B, Wolf P, Kluba T: A classification-system improves the intra- and interobserver reliability of radiographic diagnosis of pistol-grip-deformity. Hip Int 2011, 21(6): Clohisy JC, Carlisle JC, Trousdale R, Kim YJ, Beaule PE, Morgan P, Steger-May K, Schoenecker PL, Millis M: Radiographic evaluation of the hip has limited reliability. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009, 467(3): Gosvig KK, Jacobsen S, Sonne-Holm S, Palm H, Troelsen A: Prevalence of malformations of the hip joint and their relationship to sex, groin pain, and risk of osteoarthritis: a population-based survey. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010, 92(5): Bland JM, Altman DG: Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res 1999, 8: Bland JM, Altman DG: A note on the use of the intracalss correlation coefficient in the evaluation of agreement between two methods of measurement. Comput Biol Med 1990, 20: doi: / Cite this article as: Ipach et al.: Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders :150. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
Incidence of femoro-acetabular impingement in adult Indian population on the basis of specific radiological findings: A prospective study
 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION METHODS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pedro José Labronici 1, Sergio Delmonte Alves 2, Anselmo Fernandes da Silva 3, Gilberto Ribeiro Giuberti 3, Rolix Hoffmann 4, Justino Nóbrega de Azevedo Neto 4, Jorge Luiz Mezzalira Penedo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pedro José Labronici 1, Sergio Delmonte Alves 2, Anselmo Fernandes da Silva 3, Gilberto Ribeiro Giuberti 3, Rolix Hoffmann 4, Justino Nóbrega de Azevedo Neto 4, Jorge Luiz Mezzalira Penedo
Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI
 Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
Reliability of Simple Radiographic Parameters for Pincer FAI Sung Hoon Yang MD., Dong Hwi Kim, MD., Yong Chul Jeon, MD., Sang Hong Lee MD. PhD., Suenghwan Jo MD. PhD, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju,
All authors declare no potential conflict of interest related to this article.
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/.1590/1413-785217173951 Original Article INFLUENCE OF AGE ON PARAMETERS FOR FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT AND HIP DYSPLASIA IN X-RAYS INFLUÊNCIA DA IDADE SOBRE OS PARÂMETROS PARA
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/.1590/1413-785217173951 Original Article INFLUENCE OF AGE ON PARAMETERS FOR FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT AND HIP DYSPLASIA IN X-RAYS INFLUÊNCIA DA IDADE SOBRE OS PARÂMETROS PARA
Supine and Standing AP Pelvis Radiographs in the Evaluation of Pincer Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:1692 1696 DOI 10.1007/s11999-016-4766-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Supine
F.A.I. indications. E. Sabetta. Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta
 F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
F.A.I. indications E. Sabetta Arcispedale S. Maria Nuova Struttura Complessa Ortopedia e Traumatologia Direttore: Ettore Sabetta !.FAI treatment might become a mainstay in joint-preserving treatment of
Periacetabular osteotomy: sporting, social and sexual activity 9-12 years post surgery
 Hip Int 2014; 24 ( 1) : 27-31 DOI: 10.5301/hipint.5000077 Original Article Periacetabular osteotomy: sporting, social and sexual activity 9-12 years post surgery Jakob Klit 1, Charlotte Hartig-Andreasen
Hip Int 2014; 24 ( 1) : 27-31 DOI: 10.5301/hipint.5000077 Original Article Periacetabular osteotomy: sporting, social and sexual activity 9-12 years post surgery Jakob Klit 1, Charlotte Hartig-Andreasen
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement
 Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
Three-dimensional CT analysis to determine acetabular retroversion and the implications for the management of femoro-acetabular impingement W. Dandachli, S. Ul Islam, M. Liu, R. Richards, M. Hall-Craggs,
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Pathomorphologic Alterations Predict Presence or Absence of Hip Osteoarthrosis
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 465, pp. 46 52 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Pathomorphologic Alterations Predict Presence or Absence of Hip Osteoarthrosis Timo M. Ecker, MD * ;
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 465, pp. 46 52 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Pathomorphologic Alterations Predict Presence or Absence of Hip Osteoarthrosis Timo M. Ecker, MD * ;
 Original citation: Turley, Glen A. (2012) Femoroacetabular impingement. Working Paper. Coventry: The University of Warwick.. (Unpublished) Permanent WRAP url: http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/53063 Copyright
Original citation: Turley, Glen A. (2012) Femoroacetabular impingement. Working Paper. Coventry: The University of Warwick.. (Unpublished) Permanent WRAP url: http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/53063 Copyright
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures
 Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
InTRoDucTIon. METHoDS. M. Jäger 1 *, b. bittersohl 1 *, c. Zilkens 1, H. S. Hosalkar 2, K. Stefanovska 1, S. Kurth 1, R. Krauspe 1
 May 12, 2011 Eu Ro PE an JouR nal of MED I cal RE SEaRcH 217 Eur J Med Res (2011) 16: 217-222 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2011 SuRgIcal HIP DISlocaTIon In SyMPToMaTIc cam FEMoRoacETabulaR IMPIngEMEnT: WHaT
May 12, 2011 Eu Ro PE an JouR nal of MED I cal RE SEaRcH 217 Eur J Med Res (2011) 16: 217-222 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2011 SuRgIcal HIP DISlocaTIon In SyMPToMaTIc cam FEMoRoacETabulaR IMPIngEMEnT: WHaT
1/15/2012. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular impingement
 Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD*
 Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD* *Orthopedic Medical Group,7910 Frost St. #200 San Diego, California 92123, USA **Riverside County Regional Medical
Mitchell McDowell, DO**, Daljeet Sagoo, DO*, Michael P. Muldoon, MD*, Richard Santore, MD* *Orthopedic Medical Group,7910 Frost St. #200 San Diego, California 92123, USA **Riverside County Regional Medical
The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular rim during normal hip range of motion.
 RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs
 Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs Moin Khan 1, Anil Ranawat 2, Dale Williams 1, Rajiv Gandhi 3, Hema Choudur
Relationship Between the Alpha and Beta Angle in Diagnosing CAM type Femoroacetabular Impingement on Frog-leg Lateral Radiographs Moin Khan 1, Anil Ranawat 2, Dale Williams 1, Rajiv Gandhi 3, Hema Choudur
Does Radiographic Coxa Profunda Indicate Increased Acetabular Coverage or Depth in Hip Dysplasia?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:2056 2066 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4084-x Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Radiographic
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:2056 2066 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4084-x Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Radiographic
Adolescent Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Gender Differences in Hip Morphology
 Adolescent Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Gender Differences in Hip Morphology Perry Hooper, DO Sameer Oak, MD Gehan Ibrahim, MD T. Sean Lynch, MD Ryan Goodwin, MD James Rosneck, MD International
Adolescent Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): Gender Differences in Hip Morphology Perry Hooper, DO Sameer Oak, MD Gehan Ibrahim, MD T. Sean Lynch, MD Ryan Goodwin, MD James Rosneck, MD International
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology, Occupation & Environmental Medicine INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology, Occupation & Environmental Medicine https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.581 J Korean Med Sci 2017; 32: 581-586 Descriptive Epidemiology of Patients Undergoing Total Hip
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology, Occupation & Environmental Medicine https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.581 J Korean Med Sci 2017; 32: 581-586 Descriptive Epidemiology of Patients Undergoing Total Hip
What Is Normal Femoral Head/Neck Anatomy? An Analysis of Radial CT Reconstructions in Adolescents
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement?
 Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Cite this article as: Cooke WR, Gill HS, Murray DW, Ostlere SJ. Discrete mineralisation of the acetabular labrum: a novel marker of femoroacetabular impingement? Br J Radiol 2013;86:20120182. SHORT COMMUNICATION
Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study
 Original Article Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study Cartilage 1(3) 188 193 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission:
Original Article Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study Cartilage 1(3) 188 193 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission:
10/15/17. Acknowledgements. The Sporting Hip & Groin. TheSporting. SportingHip. The Sporting. The Sporting. The Sporting.
 Michael O Brien Physiotherapist Acknowledgements The TheSporting SportingHip Hip & Groin Impingement or instability? Andrew Wallis Alesha Coonan (Gledhill-Tunks) Melbourne Orthopaedic Group Mr. Jit Balakumar
Michael O Brien Physiotherapist Acknowledgements The TheSporting SportingHip Hip & Groin Impingement or instability? Andrew Wallis Alesha Coonan (Gledhill-Tunks) Melbourne Orthopaedic Group Mr. Jit Balakumar
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a recognized risk factor for
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2014; 20:271-276 Turkish Society of Radiology 2014 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE CT assessment of asymptomatic hip joints for the background of femoroacetabular impingement
Diagn Interv Radiol 2014; 20:271-276 Turkish Society of Radiology 2014 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE CT assessment of asymptomatic hip joints for the background of femoroacetabular impingement
Prevalence and characteristics of cam-type femoroacetabular deformity in 100 hips with symptomatic acetabular dysplasia: a case control study
 Ida et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:93 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence and characteristics of cam-type femoroacetabular deformity in 100 hips with symptomatic acetabular
Ida et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:93 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence and characteristics of cam-type femoroacetabular deformity in 100 hips with symptomatic acetabular
A comparative radiographic investigation of femoroacetabular impingement in young patients with and without hip pain
 DOI:10.6061/clinics/2012(05)10 CLINICAL SCIENCE A comparative radiographic investigation of femoroacetabular impingement in young patients with and without hip pain Omar Ferreira Miguel, I Henrique Berwanger
DOI:10.6061/clinics/2012(05)10 CLINICAL SCIENCE A comparative radiographic investigation of femoroacetabular impingement in young patients with and without hip pain Omar Ferreira Miguel, I Henrique Berwanger
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) in adolescence
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Femoroacetabular Impingement After Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Does Slip Severity Predict Clinical Symptoms? Michael K. Dodds, MCh, MRCSI,* Damian McCormack, MCh, FRCSI,*w and Kevin
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Femoroacetabular Impingement After Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: Does Slip Severity Predict Clinical Symptoms? Michael K. Dodds, MCh, MRCSI,* Damian McCormack, MCh, FRCSI,*w and Kevin
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology
 Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology University of Rochester Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Raymond J. Kenney, MD P. Christopher Cook, MD Kelly
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology University of Rochester Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Raymond J. Kenney, MD P. Christopher Cook, MD Kelly
Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96S, S44 S52 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds L. Bellaïche a,, M. Lequesne b, J.-E. Gedouin
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96S, S44 S52 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging data in a prospective series of adult hip pain in under-50 year-olds L. Bellaïche a,, M. Lequesne b, J.-E. Gedouin
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it?
 Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it? Poster No.: P-0049 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. De Roeck, F. M. H. M. Vanhoenacker ; Antwerpen/BE, 1 2 1 2 Antwerp/BE
Measurements in Femoro-Acetabular Impingement : How to do it? Poster No.: P-0049 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. De Roeck, F. M. H. M. Vanhoenacker ; Antwerpen/BE, 1 2 1 2 Antwerp/BE
Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 166-173 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiographic markers of acetabular retroversion : Correlation of the cross-over sign, ischial spine sign and posterior wall sign Clément M.L. WERNER,
We have observed damage to the labrum as a
 Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect A MRI-BASED QUANTITATIVE ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK OFFSET K. Ito, M.-A. Minka-II, M. Leunig, S. Werlen, R.Ganz From the AO ASIF Research
Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect A MRI-BASED QUANTITATIVE ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK OFFSET K. Ito, M.-A. Minka-II, M. Leunig, S. Werlen, R.Ganz From the AO ASIF Research
Periacetabular Osteotomy Restores the Typically Excessive Range of Motion in Dysplastic Hips With a Spherical Head
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4089-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP SYMPOSIUM Periacetabular
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4089-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP SYMPOSIUM Periacetabular
Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Femoroacetabular impingement: normal values of the quantitative morphometric parameters in asymptomatic hips
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:1707 1714 DOI 10.1007/s00330-014-3171-4 MUSCULOSKELETAL Femoroacetabular impingement: normal values of the quantitative morphometric parameters in asymptomatic hips Marianne Lepage-Saucier
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:1707 1714 DOI 10.1007/s00330-014-3171-4 MUSCULOSKELETAL Femoroacetabular impingement: normal values of the quantitative morphometric parameters in asymptomatic hips Marianne Lepage-Saucier
Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Cam and Pincer Femoroacetabular Impingement: CT Findings of Features Resembling Femoroacetabular Impingement in a Young Population Without Symptoms
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Chakraverty et al. CT of Femoroacetabular Impingement Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Julian K. Chakraverty 1 Carl Sullivan Chee Gan Srikanth Narayanaswamy
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Chakraverty et al. CT of Femoroacetabular Impingement Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Julian K. Chakraverty 1 Carl Sullivan Chee Gan Srikanth Narayanaswamy
Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities
 Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities Iryna Havenko Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
Comparative study of the contact pressures in hip joint models with femoroacetabular impingment with different cephalic deformities Iryna Havenko Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
Does Salter Innominate Osteotomy Predispose the Patient to Acetabular Retroversion in Adulthood?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:1755 1762 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4053-4 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Salter
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:1755 1762 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4053-4 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Does Salter
Disclosures. Objectives 11/18/2015. Hip Preservation in the Adolescent and Young Adult. Financial - None I do not perform total joint arthroplasty
 Hip Preservation in the Adolescent and Young Adult Alfred A. Mansour, III, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation UT-Ortho 59th Annual Edward T. Smith Orthopaedic Lectureship November 5-6, 2015
Hip Preservation in the Adolescent and Young Adult Alfred A. Mansour, III, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation UT-Ortho 59th Annual Edward T. Smith Orthopaedic Lectureship November 5-6, 2015
Prevalence of Cam Deformity with Associated Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome in Hip Joint Computed Tomography of Asymptomatic Adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(1): 5-11, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.5 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Prevalence of Cam Deformity with Associated Femoroacetabular Impingement
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(1): 5-11, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.1.5 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Prevalence of Cam Deformity with Associated Femoroacetabular Impingement
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement
 Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Downloaded from:
 Nicholls, AS; Kiran, A; Pollard, TC; Hart, DJ; Arden, CP; Spector, T; Gill, HS; Murray, DW; Carr, AJ; Arden, NK (2011) The association between hip morphology parameters and nineteen-year risk of end-stage
Nicholls, AS; Kiran, A; Pollard, TC; Hart, DJ; Arden, CP; Spector, T; Gill, HS; Murray, DW; Carr, AJ; Arden, NK (2011) The association between hip morphology parameters and nineteen-year risk of end-stage
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail?
 Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
SPORTS HEALTH. The Etiology of Femoroacetabular Impingement: What We Know and What We Don t. Methods
 521576SPHXXX10.1177/1941738114521576Chaudhry and Ayeni research-article2014 vol. 6 no. 2 [ Orthopaedic Surgery ] The Etiology of Femoroacetabular Impingement: What We Know and What We Don t Harman Chaudhry,
521576SPHXXX10.1177/1941738114521576Chaudhry and Ayeni research-article2014 vol. 6 no. 2 [ Orthopaedic Surgery ] The Etiology of Femoroacetabular Impingement: What We Know and What We Don t Harman Chaudhry,
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems?
 What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement with Surgical Dislocation
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:146-154 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.146 Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement with Surgical Dislocation Ho-Hyun Yun, MD, Won-Yong Shon, MD, Ji-Yeol
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:146-154 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.146 Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement with Surgical Dislocation Ho-Hyun Yun, MD, Won-Yong Shon, MD, Ji-Yeol
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions. Claudio Mella, MD
 Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Impingement Adversely Affects 10-year Survivorship After Periacetabular Osteotomy for DDH
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:1602 1614 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-2799-8 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Impingement
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:1602 1614 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-2799-8 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Impingement
Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
What Are the Radiographic Reference Values for Acetabular Under- and Overcoverage?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4038-3 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research Publication of The ssociation of one and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 ERNESE HIP SYMPOSIUM What re the Radiographic
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4038-3 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research Publication of The ssociation of one and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 ERNESE HIP SYMPOSIUM What re the Radiographic
The causes of hip pain range from intra-articular
 Current Concepts Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Carlos A. Guanche, M.D., and Aaron A. Bare, M.D. Abstract: The etiology of degenerative joint disease of the hip remains unsolved.
Current Concepts Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Carlos A. Guanche, M.D., and Aaron A. Bare, M.D. Abstract: The etiology of degenerative joint disease of the hip remains unsolved.
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016
 Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Rapidly Progressive Osteoarthritis after Arthroscopic Labral Repair for Dysplasia. Dean K. Matsuda, MD Monti Khatod, MD Los Angeles, California, USA
 Rapidly Progressive Osteoarthritis after Arthroscopic Labral Repair for Dysplasia Dean K. Matsuda, MD Monti Khatod, MD Los Angeles, California, USA Recent reports of poor clinical outcomes after arthroscopic
Rapidly Progressive Osteoarthritis after Arthroscopic Labral Repair for Dysplasia Dean K. Matsuda, MD Monti Khatod, MD Los Angeles, California, USA Recent reports of poor clinical outcomes after arthroscopic
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult
 Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Fovea Alta on MR Images: Is It a Marker of Hip Dysplasia in Young Adults?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Beltran et al. MRI of Fovea Alta Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Luis S. Beltran 1 Jason D. Mayo 2 Zehava S. Rosenberg 1 Maria Diaz De Tuesta 3 Olga
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Beltran et al. MRI of Fovea Alta Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Luis S. Beltran 1 Jason D. Mayo 2 Zehava S. Rosenberg 1 Maria Diaz De Tuesta 3 Olga
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
25. PELVIC OSTEOTOMIES FOR THE TREATMENT OF HIP DYSPLASIA IN ADULTS
 Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
1/15/ year old male. Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA
 29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
29 year old male Hip Preservation Surgery for Acetabular Dysplasia in Adolescents and Young Adults Eduardo Novais, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedic Surgery PATHOMECHANICS OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Static
Radiology Corner. Femoroacetabular Impingement. Summary of Imaging Findings. Introduction. History
 Radiology Corner Femoroacetabular Impingement Guarantor: CPT Christa B. Blecher, USAF, MC 1 Contributors: MAJ Justin Q. Ly, USAF, MC 1 Note: This is the full text version of the radiology corner question
Radiology Corner Femoroacetabular Impingement Guarantor: CPT Christa B. Blecher, USAF, MC 1 Contributors: MAJ Justin Q. Ly, USAF, MC 1 Note: This is the full text version of the radiology corner question
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA. Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS
 CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Title; Periacetabular Osteotomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Acetabular Dysplasia in. Patients with and without Labral Tears.
 Title; Periacetabular Osteotomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Acetabular Dysplasia in Patients with and without Labral Tears Authors; Tomonobu Hagio, MD 1 ; Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD 1 ; Yoshinari Nakamura,
Title; Periacetabular Osteotomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Acetabular Dysplasia in Patients with and without Labral Tears Authors; Tomonobu Hagio, MD 1 ; Masatoshi Naito, MD, PhD 1 ; Yoshinari Nakamura,
Range of motion in femoroacetabular impingement
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 327-332 ORIGINAL STUDY Range of motion in femoroacetabular impingement Emmanuel AUDEnAERT, Jan VAn HOUCkE, Bastiaan MAES, Luc VAnDEn BOSSCHE, Jan ViCTOR, Christophe PATTyn
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2012, 78, 327-332 ORIGINAL STUDY Range of motion in femoroacetabular impingement Emmanuel AUDEnAERT, Jan VAn HOUCkE, Bastiaan MAES, Luc VAnDEn BOSSCHE, Jan ViCTOR, Christophe PATTyn
Topic: Femoroacetabular Impingement Surgery Date of Origin: July 1, Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: January 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Femoroacetabular Impingement Surgery Date of Origin: July 1, 2008 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: January 2014 Policy No: 160 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Femoroacetabular Impingement Surgery Date of Origin: July 1, 2008 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: January 2014 Policy No: 160 Effective Date: April 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER
Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage
 Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT AS A CAUSE OF EARLY OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HIP M. Beck, M. Kalhor, M. Leunig, R. Ganz From the University
Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage FEMOROACETABULAR IMPINGEMENT AS A CAUSE OF EARLY OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HIP M. Beck, M. Kalhor, M. Leunig, R. Ganz From the University
What Is the Impingement-free Range of Motion of the Asymptomatic Hip in Young Adult Males?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:1284 1288 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4072-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2015) 473:1284 1288 DOI 10.1007/s11999-014-4072-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons SYMPOSIUM: 2014 BERNESE HIP
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Hip Arthroscopy. Christopher J. Utz, MD. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati
 Hip Arthroscopy Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. Brief History 2. Review of
Hip Arthroscopy Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. Brief History 2. Review of
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
21 year-old collegiate rower: R/O labral tear
 Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Labral Tears/FAI. Andrew Parker, MD
 Labral Tears/FAI Andrew Parker, MD Athletic Hip Injuries Incidence of hip injuries has increased dramatically over the last decade In part due to better recognition with improved imaging and arthroscopy,
Labral Tears/FAI Andrew Parker, MD Athletic Hip Injuries Incidence of hip injuries has increased dramatically over the last decade In part due to better recognition with improved imaging and arthroscopy,
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes
 The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: Interventions of interest are: are: Observation. Interventions of interest.
 Protocol Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement (701118) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/13 Next Review Date: 07/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/09, 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 07/13,
Protocol Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement (701118) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/13 Next Review Date: 07/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/09, 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 07/13,
Radial dgemric in developmental dysplasia of the hip and in femoroacetabular impingement: preliminary results
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1421e1428 Radial dgemric in developmental dysplasia of the hip and in femoroacetabular impingement: preliminary results S.E. Domayer yz, T.C. Mamisch x, I. Kress
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1421e1428 Radial dgemric in developmental dysplasia of the hip and in femoroacetabular impingement: preliminary results S.E. Domayer yz, T.C. Mamisch x, I. Kress
Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.014 10/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 06/22/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s)
Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.014 10/01/2010 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 06/22/2012 Section: Surgery Place(s)
Metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing has become a
 154 Quantifying Degree of Difficulty in Hip Resurfacing of Pistol-Grip Deformity Burton Ma, Ph.D., Stephane G. Bergeron, M.D., Heather J. Grant, M.Sc., John Rudan, M.D., and John Antoniou, M.D., Ph.D.
154 Quantifying Degree of Difficulty in Hip Resurfacing of Pistol-Grip Deformity Burton Ma, Ph.D., Stephane G. Bergeron, M.D., Heather J. Grant, M.Sc., John Rudan, M.D., and John Antoniou, M.D., Ph.D.
Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults.
 Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults. Poster No.: C-0492 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arevalo, N. Santamaria, E. Diez, J. Gredilla Molinero, M. 1
Imaging findings of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults. Poster No.: C-0492 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arevalo, N. Santamaria, E. Diez, J. Gredilla Molinero, M. 1
Groin pain secondary to Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome - A case of mistaken identity
 Groin pain secondary to Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome - A case of mistaken identity Elizabeth Tan 1, Pramod Durgakeri 2 1,2. Box Hill Hospital, Victoria, Australia CASE STUDY Please cite this
Groin pain secondary to Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome - A case of mistaken identity Elizabeth Tan 1, Pramod Durgakeri 2 1,2. Box Hill Hospital, Victoria, Australia CASE STUDY Please cite this
Page: 1 of 21. Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Page: 1 of 21 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Description Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) results from localized compression in the joint due to an anatomical mismatch between the head of the
Page: 1 of 21 Last Review Status/Date: September 2015 Description Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) results from localized compression in the joint due to an anatomical mismatch between the head of the
Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.98 Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return
MP 7.01.98 Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. 78 Int J Res Med. 2013; 2(1);78-82 e ISSN: p ISSN: Morphological aspect of acetabulum of hip bone
 AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
AN OSSEOUS STUDY OF MORPHOLOGICAL ASPECT OF ACETABULUM OF HIP BONE Kintu Vyas 1*,Bhavesh Shroff 2,Kalpesh Zanzrukiya 3 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy, Medical College, Baroda. 2 Assistant
Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Policy Number: 7.01.118 Last Review: 11/2013 Origination: 11/2009 Next Review: 11/2014 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will
Surgical Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Policy Number: 7.01.118 Last Review: 11/2013 Origination: 11/2009 Next Review: 11/2014 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications. Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout
 Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes
 Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. Elsamaloty,
Current Concepts in the Imaging of Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndromes Poster No.: C-1840 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. ABDULLAH, J. Zeiss, H. Semaan, H. Semaan, H. Elsamaloty,
Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI
 Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI Frank Kolo C. MD, Caecilia Charbonnier* PhD, Christian W.A. Pfirrmann ** MD, Sylvain R. Duc MD, Anne Lubbeke
Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI Frank Kolo C. MD, Caecilia Charbonnier* PhD, Christian W.A. Pfirrmann ** MD, Sylvain R. Duc MD, Anne Lubbeke
Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 6-2011 Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint Ronald Huang
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 6-2011 Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint Ronald Huang
