Fig. I Facialfeatures of Case 1. * the inner canthal distance being 36 mm, the outer canthal distance 82 mm, and the interpupillary
|
|
|
- Julia McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Archtives of Disease in Childhood, 1980, 55, Aarskog's syndrome CAROLINE BERRY, JEAN CREE, AND TREVOR MANN Paediatric Research Unit, Prince Philip Research Laboratories, Guy's Hospital, London, and Royal Alexatndra Hospitalfor Sick Children, Brighton, Sussex SUMMARY Six children with Aarskog's facial-digital-genital syndrome are described, and the genetics of the condition discussed. We suggest that this anomaly may be fairly common and that a syndrome identification centre could lead to earlier diagnosis of children with this and other syndromes. In 1970 Aarskog,' in Norway, described a syndrome associating short stature with certain anomalies of the face, hands, feet, and genitalia in 7 males from two generations of the same family. He favoured transmission as an X-linked trait, noting that the carrier women in the pedigree tended to be short. All 7 were of normal intelligence. Since 1970 there have been several reports from transatlantic sources,2-7 describing similarly affected kindreds with full expression of features in males, and occasional minimal expression in the females. An account of the syndrome had already been given from the USA, for in 1967 Hanley et al.8 described 2 brothers with osteochondritis dissecans and associated malformations who undoubtedly had Aarskog's syndrome. It has been suggested that an alternative descriptive term might be the facial-digital-genital syndrome. We now report 6 boys with the syndrome, 3 of them brothers; this is the first description of this malformation from the UK. The eldest of the affected 3 brothers will first be described in detail. The anomalies he shows together with those found in his 2 brothers and the other 3 children are listed in the Table. Case reports Case 1 (Fig. 1), the second child born to unrelated parents, was delivered in 1967 at 33 weeks' gestation weighing 180 kg. At birth he was noted to have an odd facial appearance and abnormalities of the hands and feet. Further anomalies were noticed during his first 3 years, but the following observations were made when he was 10 years old. His height was then 131 cm (10-25th centile), weight 32-9 kg (75-90th centile), and head circumference 51 cm (10th centile). His forehead was broad with a prominent Fig. I Facialfeatures of Case 1. metopic suture, and his hairline showed a pronounced widow's peak. There was primary telecanthus, * the inner canthal distance being 36 mm, the outer canthal distance 82 mm, and the interpupillary distance 58 mm. The Mustarde indext5 was 62 %. He had slight right ptosis and was hypermetropic and astigmatic. His nose was short and * Increased distance between the inner canthi, affecting only the soft tissues. t The ratio of the inner canthal to interpupillary distance (normal less than 55 %). 706
2 Table Aarskog's syndrome 707 Features Case I Case 2 Case 3 Case 4 Case 5 Case 6 Birthweight (kg) ' Gestational age (weeks) Height centile < <3 Bone age Normal I year retarded Normal 1 year retarded Normal Not known Prominent forehead Metopic suture prominent + + Not known Widow's peak Telecanthus Ptosis + + Broad nasal bridge Short stubby nose Flared anteverted nostrils Long prominent philtrum Thin upper lip + + ± Pouting lower lip Linear groove below lower lip High narrow palate Prominent point to chin (not prognathism) Ears: thickened down-turned helices and fleshylobes Long neck and sloping shoulders Not known Long narrow chest Pectus excavatum Midline depression (xiphisternum to umbilicus) 'Button' umbilicus 'Shawl' scrotum Prominent median raphe Inguinal herniae Position of testes Both retractile Left retractile Right and left Both retractile Both retractile Both retractil! orchidopexy Clinodactyly 5th fingers with single or abnormal creases Simian crease + Broken Broken + + Interdigital webbing (mild syndactyly) Hyperextensible fingers Genu recurvatum Metatarsus varus Bulbous toes IQ or DQ IQ 83 Normal Normal Normal Normal Low normal stubby with anteverted nostrils, the nasal bridge being broad and prominent. The philtrum was long and the mouth wide, with a thin upper lip and a horizontal skin crease immediately below the lower lip. There was dental malocclusion with overbite. The palate was high and narrow. The ears had a thickened down-turned helix and a large fleshy lobe. He had a long neck with sloping shoulders and prominent sterno-clavicular joints. There was a minor degree of pectus excavatum in a long tubular chest, and a shallow midline depression continued from the xiphisternum to the umbilicus; the umbilicus was prominent and stood out like a button. The scrotum continued ventrally around the base of the penis giving a hooded appearance (shawl scrotum), and there was a pronounced median raphe simulating a bifid scrotum. Inguinal scars denoted previous repair of bilateral inguinal herniae (Fig. 2). Both testes were retractile. In the hands, the 5th digit showed clinodactyly and was short with a single ventral crease, although it had 3 interarticulating phalanges. There was webbing between the fingers, and abduction of the Fig. 2 Cases 1,3, and2 (left to right) showing midline depression of chest, prominent umbilicus, shawl scrotum, inguinal herniorrhaphy scars. thumb was limited by interdigital webbing (Fig. 3). Each palm had a single, broken simian crease. The feet were short, flat, and broad with a pronounced degree of metatarsus varus. There was
3 708 Berry, Cree, anid Mann Fig. 3 Right hands of Cases 1, 3, and 2 (left to right) showing interdigital webbing. webbing of the toes, and the distal portions of the 1st and 2nd toes were bulbous, the 2nd toe inclining away from the first. IQ was 83 on the Wechsler scale. Chromosome studies using Giemsa banding showed a normal male pattern. A vertebral x-ray showed no abnormality, and the bone age was normal. His two brothers Case 2 (Fig. 4) and Case 3 (Fig. 5) have almost identical anomalies (Table). Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 September Downloaded from Fig. 4 Facialfeatures of Case 2. Fig. 5 Facial features of Case 3. The mother of these 3 children (Cases 1, 2, and 3) showed some of their features. Her height was 153 cm (3rd centile). Her eyes were prominent but there was no primary telecanthus. She had a broad thin upper lip and fleshy ear lobes. Her nose and palate were normal. There was clinodactyly of the 5th fingers and both these digits were short on 12 October 2018 by guest. Protected by
4 with single ventral creases; there was a fixed flexion deformity of the 5th metacarpo-phalangeal joints. Her 1st and 2nd toes were bulbous terminally. She has 3 brothers; one brother has hands and feet similar to hers, and looks very much like one of her affected sons. Her first child was found to have a widow's peak, fleshy ear lobes, clinodactyly of the 5th fingers, and slight bilateral metatarsus varus, but no other features of Aarskog's syndrome. His young sister also has a widow's peak and fleshy ear lobes, but none of the other striking features present in her 3 affected brothers. The father showed no features of the syndrome. Identification of Aarskog's syndrome in this family soon led to the recognition of the syndrome in the following 3 boys. They are not related to each other. Case 4 (Fig. 6) had been examined at birth by one of us (TM) and because of 'a strange facies' and other dysmorphic features, has been followed up Fig. 6 Facial features of Case 4. Fig. 7 Aarskog's syntdrome 709 Case 4. Feet showing metatarsus varus. ever since. His height and weight have remained at between the 3rd and 10th centiles. He has normal intelligence although his school reported that he has learning problems, especially with mathematics. This child is remarkable in showing almost all the components of Aarskog's syndrome so far described (Table). His mother is short (height cm). She shows a slight widow's peak, prominence of the chin, camptodactyly of the 5th fingers with a single crease on the right side, hyperextensibility of the metacarpo-phalangeal joints, short broad feet with metatarsus varus and bulbous ends to the toes similar to those of her son (Fig. 7). Her other child, a daughter, shows no sign of the condition. Case 5 was first seen at age 2 months in the orthopaedic clinic because of his metatarsus varus, and the syndrome was recognised at age 21 years. His features are listed in the Table. His mother is of normal height (167 cm) and shows no obvious features of Aarskog's syndrome. Case 6 was diagnosed when being investigated for short stature at age 16 months. His features are shown in the Table. His mother's height is only 155 cm, but she has no sign of the condition. An elder brother is normal but a maternal first cousin, a boy, unknown to us, may be affected. Genetics This condition appears to be controlled by a single gene, but whether this is autosomal or X-linked is not clear. As all the initial cases were boys and their mothers sometimes showed minor features, an X- linked gene seems likely to be responsible. In 1975 Berman et al.9 reviewed families with good pedigree data and found evidence for transmission through females and some, but not all, of these women showed features of the condition. Two women had affected sons by two different marriages. This
5 710 Berry, Cree, and Mann suggested either an X-linked gene with partial expression in carrier females, or an autosomal gene with sex limitation leading to much greater expression in males. To distinguish between these two possibilities, sons of affected males were studied. Four affected men had 7 unaffected sons, strongly supporting X-linked rather than autosomal control. However, since then Welsh (G Welsh, personal communication) and Harris10 have described an affected father and son, so that an autosomal dominant gene with sex limitation of expression has to be considered. The matter will become clearer when more families have been studied, although a later review1' again favours the X-linked hypothesis. Discussion The finding of this malformation syndrome in 4 unrelated families (6 cases) in the south of England suggests that the condition is not as rare as may appear from the scanty reports in the British journals. The problem for the paediatrician today is familiarisation with the ever increasing number of new syndromes. We believe that there is a good case for setting up a national reference centre ofsyndromes. Had such a centre existed 8 years ago, the syndrome in the original family might have been recognised, and almost certainly a diagnosis would have been made in Case 4 shortly after birth. His parents have had 8 years of anxiety about their son's condition. Furthermore, when they sought genetic advice some years ago before embarking on a further pregnancy, they were told, incorrectly as we now know, that the chance of recurrence of the syndrome in another child was small. Affected children not detected at birth are commonly referred to an orthopaedic surgeon because of metatarsus varus or other limb abnormalities; general surgeons may be consulted about inguinal herniae or cryptorchidism: eye problems are common and may lead to an ophthalmic consultation, or the child may be referred to a paediatrician because of shortness of stature. A national reference centre would surely heighten the awareness of all clinicians and lead to a speedier diagnosis of some of the more obscure syndromes, and to a greater understanding of their genetic implications. Case 4 was presented to the Paediatric Section of the Royal Society of Medicine on the 27 October We thank Mr David St Clair Roberts, Ophthalmic Surgeon, Sussex Eye Hospital, Brighton, Mr Austin Brown, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton, and Professor Paul Polani for invaluable assistance, Dr S J R Macoun and Dr C Chantler for permission to publish Case 6, and the staff of the Photographic Departments of the Royal Sussex County Hospital, Brighton, and Guy's Hospital, London, for their help. Financial support was provided by the Royal Alexandra Hospital Centenary Research Fund, the DHSS, and the Spastics Society. References Aarskog D. A familial syndrome of short stature associated with facial dysplasia and genital anomalies. JPediatr 1970; 77: Scott C I, Jr. Unusual facies, joint hypermobility, genital anomaly, and short stature. A new dysmorphic syndrome. Birth Defects 1971; 7: Pt 6, Furukawa C T, Hall B D, Smith D W. The Aarskog syndrome. J Pediatr 1972; 81: Sugarman G I, Rimoin D L, Lachman R S. The facialdigital-genital (Aarskog) syndrome. Am J Dis Child 1973; 126: Kirkham T H, Milot J, Berman P. Ophthalmic manifestations of Aarskog (facial-digital-genital) syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 1975; 79: Duncan P A, Klein R M, Wilmot P L, Shapiro L R. Additional features of the Aarskog syndrome. J Pediatr 1977; 91: Fryns J P, Macken J, Vinken L, Ogodt-Ameye L, van den Berghe H. The Aarskog syndrome. Hum Genet 1978; 42: Hanley W B, McKusick V A, Barranco F T. Osteochondritis dissecans with associated malformations in two brothers. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1967; 49A: Berman P, Desjardins C, Fraser F C. The inheritance of the Aarskog facial-digital-genital syndrome. J Pediatr 1975; 86: Harris D J. Male-to-male transmission of the Aarskog syndrome (abstract). In Littlefield J W, Ebling F J G, Henderson I W, eds. Fifth International Conference on Birth Defects, Montreal, Canada, Excerpta Medica, International Congress Series No 426. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica, 1977: 95. Escobar V, Weaver D D. Aarskog syndrome. New findings and genetic analysis. JAMA 1978; 240: Correspondence to Dr Jean Cree, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Dyke Road, Brighton, Sussex BN1 3JN. Received 7 August 1979,
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses
 J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia
 JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY
 Ypn. J. Human Genet. 33, 487-492, 1988 APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY Yoshinori [ZUMIKAWA, Kenji NARITOMI, Shoko [KEMA, Yoshinobu
Ypn. J. Human Genet. 33, 487-492, 1988 APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY Yoshinori [ZUMIKAWA, Kenji NARITOMI, Shoko [KEMA, Yoshinobu
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL. Denise LM Goh
 APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum?
 JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab
 Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Hirschsprung's disease
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 100-104 Interstitial deletion of distal 13q associated with Hirschsprung's disease M A LAMONT*, M FITCHETTt, AND N R DENNIS* From *the Department of Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 100-104 Interstitial deletion of distal 13q associated with Hirschsprung's disease M A LAMONT*, M FITCHETTt, AND N R DENNIS* From *the Department of Child Health,
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Symphalangism. Symphalangism usually involves the proximal, interphalangeal
 Case Reports 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 285. A Pedigree from South India GEMMA SAVARINATHAN and WILLARD R. CENTERWALL From the Department of Paediatrics, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore,
Case Reports 7. med. Genet. (I966). 3, 285. A Pedigree from South India GEMMA SAVARINATHAN and WILLARD R. CENTERWALL From the Department of Paediatrics, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore,
Introduction. Images supplied. SUBJECT IMAGES (Victor Vinnetou) TARGET IMAGES (Mbuyisa Makhubu)
 Victor Vinnetou and Mbuyisa Makhubu facial comparison case, compiled by Dr T Houlton, School of Anatomical Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand (3 June 2016) Introduction There currently exists an
Victor Vinnetou and Mbuyisa Makhubu facial comparison case, compiled by Dr T Houlton, School of Anatomical Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand (3 June 2016) Introduction There currently exists an
What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability?
 What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability? Aleksandra Jezela-Stanek, M.D., Ph. D. The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw
What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability? Aleksandra Jezela-Stanek, M.D., Ph. D. The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw
Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
ARTICLE. Keywords: Aarskog Scott syndrome; FGD1; X-linked; mutations; phenotype genotype correlation; mental retardation
 (2004) 12, 16 23 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1018-4813/04 $25.00 ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg Phenotypic and molecular characterisation of the Aarskog Scott syndrome: a survey of
(2004) 12, 16 23 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1018-4813/04 $25.00 ARTICLE www.nature.com/ejhg Phenotypic and molecular characterisation of the Aarskog Scott syndrome: a survey of
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions
 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
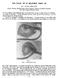 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Yunis-Varon syndrome
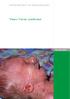 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
May Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Awareness Day
 May 2018- Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Awareness Day A note from the author Hello NCP friends! The NCP Health Ministry always aims to provide a variety of articles over the course of the year, from common
May 2018- Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Awareness Day A note from the author Hello NCP friends! The NCP Health Ministry always aims to provide a variety of articles over the course of the year, from common
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University
 Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
and duodenal atresia. Two other families reported may have had the same syndrome. Case reports CASE 1 (III.8, FAMILY 1)
 JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X
 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 46-50 Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality J. HARVEY, C. JUDGE, and S. WIENER From St. Nicholas Hospital, Carlton, Victoria, Auistralia
Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 46-50 Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality J. HARVEY, C. JUDGE, and S. WIENER From St. Nicholas Hospital, Carlton, Victoria, Auistralia
HAND ARTHROPATHY: A CLUE TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF THE KNIEST (SWISS CHEESE CARTILAGE) DYSPLASIA
 Rheumatology and Rehabilitation, 1980,19,167-169 HAND ARTHROPATHY: A CLUE TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF THE KNIEST (SWISS CHEESE CARTILAGE) DYSPLASIA BY RIDA A. FRAYHA 1, HUSN FRAYHA 2 AND RAFIC MELHEM 3 The Departments
Rheumatology and Rehabilitation, 1980,19,167-169 HAND ARTHROPATHY: A CLUE TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF THE KNIEST (SWISS CHEESE CARTILAGE) DYSPLASIA BY RIDA A. FRAYHA 1, HUSN FRAYHA 2 AND RAFIC MELHEM 3 The Departments
associated with coloboma, hypospadias, deafness, short stature, and radial synostosis
 76 A new syndrome of cleft palate associated with coloboma, hypospadias, deafness, short stature, and radial synostosis summary A new syndrome characterized by cleft palate, coloboma, hypospadias, deafness,
76 A new syndrome of cleft palate associated with coloboma, hypospadias, deafness, short stature, and radial synostosis summary A new syndrome characterized by cleft palate, coloboma, hypospadias, deafness,
De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 2, pp. E79-E84, 2010 De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies HADI AHMAD AHZAD 1, SITI FATIMAH RAMLI 1, TAN MAY LOONG 2, IMAN SALAHSHOURIFAR
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 2, pp. E79-E84, 2010 De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies HADI AHMAD AHZAD 1, SITI FATIMAH RAMLI 1, TAN MAY LOONG 2, IMAN SALAHSHOURIFAR
Abnormal Facies, Myopia, and Short Stature
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 787. Abnormal Facies, Myopia, and Short Stature C. G. KEITH, R. H. DOBBS, D. G. SHAW, and K. COTTRALL From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 787. Abnormal Facies, Myopia, and Short Stature C. G. KEITH, R. H. DOBBS, D. G. SHAW, and K. COTTRALL From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London
Puzzling Pedigrees. Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits?
 Name: Puzzling Pedigrees Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits? Studying inheritance in humans is more difficult than studying inheritance in fruit flies
Name: Puzzling Pedigrees Essential Question: How can pedigrees be used to study the inheritance of human traits? Studying inheritance in humans is more difficult than studying inheritance in fruit flies
a guide to understanding craniosynostosis a publication of children s craniofacial association
 a guide to understanding craniosynostosis a publication of children s craniofacial association 1 a guide to understanding craniosynostosis this parent s guide to craniosynostosis is designed to answer
a guide to understanding craniosynostosis a publication of children s craniofacial association 1 a guide to understanding craniosynostosis this parent s guide to craniosynostosis is designed to answer
Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 469476. Hereditary index finger polydactyly: phenotypic, radiological, dermatoglyphic, and genetic findings in a large family* METN ATASU From the Departments of
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference?
 Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference? There has been a major revision in the approach to joint hypermobility (JH) as a whole. To recognize
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference? There has been a major revision in the approach to joint hypermobility (JH) as a whole. To recognize
Chromosomes and Karyotypes
 Chromosomes and Karyotypes Review of Chromosomes Super coiled DNA Structure: It may be A single coiled DNA molecule Chromosomes Or after replication, it may be two coiled DNA molecules held together at
Chromosomes and Karyotypes Review of Chromosomes Super coiled DNA Structure: It may be A single coiled DNA molecule Chromosomes Or after replication, it may be two coiled DNA molecules held together at
Educational Items Section
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Embryology, Semiology, Dysmorphology Jean-Loup Huret Genetics, Dept Medical Information,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Embryology, Semiology, Dysmorphology Jean-Loup Huret Genetics, Dept Medical Information,
Chromosome Disease. The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental
 Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
The clinical phenotype of PIGN deficiency and consequences of defective GPI biogenesis
 The clinical phenotype of PIGN deficiency and consequences of defective GPI biogenesis Jeshira Reynoso MD World Glycobiology Congress Philadelphia, PA Introduction Congenital (genetic) disorders of glycosylation
The clinical phenotype of PIGN deficiency and consequences of defective GPI biogenesis Jeshira Reynoso MD World Glycobiology Congress Philadelphia, PA Introduction Congenital (genetic) disorders of glycosylation
Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 488-492 Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome I D YOUNG AND J R MOORE From the Department of Child Health, University of Leicester, Leicester LE2 7LX. SUMMARY
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 488-492 Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome I D YOUNG AND J R MOORE From the Department of Child Health, University of Leicester, Leicester LE2 7LX. SUMMARY
Information booklet for parents
 PREFACE: ALBRIGHT HEREDITARY OSTEODYSTROPHY (AHO) OR PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PHP) AND PSEUDO-PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PPHP) Information booklet for parents Dr. Savitha D Shenoy, Dr. Peter Swift Children
PREFACE: ALBRIGHT HEREDITARY OSTEODYSTROPHY (AHO) OR PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PHP) AND PSEUDO-PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PPHP) Information booklet for parents Dr. Savitha D Shenoy, Dr. Peter Swift Children
Genetics Questions: There are 15 questions in total. The answers can be found on the accompanying document
 Page 1 Genetics Questions: These questions are aimed at medical and allied health professionals and they are designed to show where genetics has a role in clinical practice. There are 15 questions in total
Page 1 Genetics Questions: These questions are aimed at medical and allied health professionals and they are designed to show where genetics has a role in clinical practice. There are 15 questions in total
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
Klippel Trenaunay and Proteus Syndrome overlap--a diagnostic dilemma
 Klippel Trenaunay and Proteus Syndrome overlap--a diagnostic dilemma Puri K.J.P.S. (MD)*, Malhotra S.K. (MD)**, Akanksha Jain (MBBS)*** Professor& Head* Professor& Head** Resident*** Department of Dermatology,
Klippel Trenaunay and Proteus Syndrome overlap--a diagnostic dilemma Puri K.J.P.S. (MD)*, Malhotra S.K. (MD)**, Akanksha Jain (MBBS)*** Professor& Head* Professor& Head** Resident*** Department of Dermatology,
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE
 CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
Marfan Syndrome. Read the information below and construct a pedigree for the family described herein.
 Marfan Syndrome Read the information below and construct a pedigree for the family described herein. The genetics counseling community ascribes to a belief in non-directive counseling. That is, they feel
Marfan Syndrome Read the information below and construct a pedigree for the family described herein. The genetics counseling community ascribes to a belief in non-directive counseling. That is, they feel
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, syndrome
 Severe Silver-Russell syndrome Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 447-451 D DONNAI*, E THOMPSONt, J ALLANSONt, AND M BARAITSERt From *the Regional Genetic Service, St Mary's Hospital, Manchester M13
Severe Silver-Russell syndrome Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 447-451 D DONNAI*, E THOMPSONt, J ALLANSONt, AND M BARAITSERt From *the Regional Genetic Service, St Mary's Hospital, Manchester M13
Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features
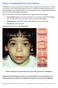 Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features Fetal exposure to alcohol during the first trimester affects development of facial features. The areas most affected are the orbital region (eyes) and mid-face.
Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features Fetal exposure to alcohol during the first trimester affects development of facial features. The areas most affected are the orbital region (eyes) and mid-face.
Case Report Lower Lid Ectropion in Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
 Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 952834, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/952834 Case Report Lower Lid Ectropion in Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Xiaoyun Zhang,
Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 952834, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/952834 Case Report Lower Lid Ectropion in Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Xiaoyun Zhang,
In human populations where prognathism is not the norm, it may be a malformation,
 PROGNATHISME ALVEOLAIRE ou du MAXILLAIRE SUPERIEUR Maxillary prognathism is often associated with Cornelia de Lange Syndrome; however, so-called false prognathism or false projection of the upper jaw.
PROGNATHISME ALVEOLAIRE ou du MAXILLAIRE SUPERIEUR Maxillary prognathism is often associated with Cornelia de Lange Syndrome; however, so-called false prognathism or false projection of the upper jaw.
Mesoaxial complete syndactyly and synostosis
 8686 Med Genet 1998;35:868-874 Department of Medical Biology and Genetics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical Faculty, Sivas, Turkey E F Percin I Sezgin Department of Orthopaedics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical
8686 Med Genet 1998;35:868-874 Department of Medical Biology and Genetics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical Faculty, Sivas, Turkey E F Percin I Sezgin Department of Orthopaedics, Cumhuriyet University, Medical
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Pedigree Analysis. A = the trait (a genetic disease or abnormality, dominant) a = normal (recessive)
 Pedigree Analysis Introduction A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships. These diagrams make it easier to visualize
Pedigree Analysis Introduction A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships. These diagrams make it easier to visualize
Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal
 Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies
 Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies This leaflet provides a brief summary of the genetics of the muscular dystrophies. An understanding of their inheritance patterns makes it possible for families
Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies This leaflet provides a brief summary of the genetics of the muscular dystrophies. An understanding of their inheritance patterns makes it possible for families
What is Craniosynostosis?
 What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
Statutory Approvals Committee minutes
 Statutory Approvals Committee minutes Item 2 Centre 0102 (Guys Hospital) Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) application for Blepharophimosis, Ptosis and Epicanthus Inversus Syndrome types 1 & 2 (BPES
Statutory Approvals Committee minutes Item 2 Centre 0102 (Guys Hospital) Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) application for Blepharophimosis, Ptosis and Epicanthus Inversus Syndrome types 1 & 2 (BPES
characteristic facies and brachyphalangy
 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 430-437 A 'new' syndrome of mental retardation with characteristic facies and brachyphalangy ALASDAIR G. W. HUNTER, PHYLLIS J. McALPINE, NOREEN L. RUDD, AND F. CLARKE
Journal of Medical Genetics, 1977, 14, 430-437 A 'new' syndrome of mental retardation with characteristic facies and brachyphalangy ALASDAIR G. W. HUNTER, PHYLLIS J. McALPINE, NOREEN L. RUDD, AND F. CLARKE
This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing.
 11111 Fact Sheet 54 FRAGILE X SYNDROME This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing. In summary Fragile X is a condition caused
11111 Fact Sheet 54 FRAGILE X SYNDROME This fact sheet describes the condition Fragile X and includes a discussion of the symptoms, causes and available testing. In summary Fragile X is a condition caused
An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification. Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization
 An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization What are the problems? When did they happen? How did they arise? Why
An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization What are the problems? When did they happen? How did they arise? Why
THE COSTELLO SYNDROME: A BOY WITH THICK MITRAL VALVES AND ARRHYTHMIAS
 Jpn J Human Genet 38, 329-334, 1993 Case Report THE COSTELLO SYNDROME: A BOY WITH THICK MITRAL VALVES AND ARRHYTHMIAS Yoshinori IZUMIKAWA,* Kenji NARITOMI, Takaya TOHMA, Noboru SHIROMA, and Kiyotake HIRAYAMA
Jpn J Human Genet 38, 329-334, 1993 Case Report THE COSTELLO SYNDROME: A BOY WITH THICK MITRAL VALVES AND ARRHYTHMIAS Yoshinori IZUMIKAWA,* Kenji NARITOMI, Takaya TOHMA, Noboru SHIROMA, and Kiyotake HIRAYAMA
The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1968, 43, 94. The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome C. J. PADFIELD, M. W. PARTINGTON*, and N. E. SIMPSON* From the Departments of Paediatrics and Biology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario,
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1968, 43, 94. The Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome C. J. PADFIELD, M. W. PARTINGTON*, and N. E. SIMPSON* From the Departments of Paediatrics and Biology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario,
William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the roof of the
 John B. Pietsch, M.D. William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. Cleft Lip and Palate What are Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate? In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the
John B. Pietsch, M.D. William F. Walsh, M.D. Katharine D. Wenstrom, M.D. Cleft Lip and Palate What are Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate? In the early weeks of fetal development, parts of the lip or palate (the
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 2: 16, December Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma
 Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
Section Objectives: Pedigrees illustrate inheritance. Pedigrees illustrate inheritance
 What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
What You ll Learn You will compare the inheritance of recessive and dominant traits in humans. You will analyze the inheritance patterns of traits with incomplete dominance and codominance. You will determine
Information for fathers invited for a screening test for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia major
 Information for fathers invited for a screening test for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia major Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for fathers invited to have a screening test for haemoglobin
Information for fathers invited for a screening test for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia major Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for fathers invited to have a screening test for haemoglobin
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE. Dr Rasime Kalkan
 SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM
 HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM 1.CRANIUM Is the size of head normal.?(measure ofc).is the skull shape abnormal( LOOK FROM ABOVE)? Are there any swellings on
HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM 1.CRANIUM Is the size of head normal.?(measure ofc).is the skull shape abnormal( LOOK FROM ABOVE)? Are there any swellings on
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24,
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Syndactyly. What is syndactyly? Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
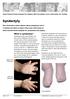 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
Case Report. Your Diagnosis
 Case Report 30-year-old gentleman, presented with bilateral dislocated radial head and with painful clunk in the knee [bilateral]. He is an active gentleman with good work history. He had a recent soft
Case Report 30-year-old gentleman, presented with bilateral dislocated radial head and with painful clunk in the knee [bilateral]. He is an active gentleman with good work history. He had a recent soft
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
Duplications of proximal 16q
 Duplications of proximal 16q rarechromo.org Sources and References The information in this leaflet is drawn partly from the published medical literature. The first-named author and publication date are
Duplications of proximal 16q rarechromo.org Sources and References The information in this leaflet is drawn partly from the published medical literature. The first-named author and publication date are
Stickler syndrome. Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Names: Period: Punnett Square for Sex Chromosomes:
 Names: Period: Human Variations Activity Background A large variety of traits exist in the human population. The large number of combinations of these traits causes individuals to look unique, or different,
Names: Period: Human Variations Activity Background A large variety of traits exist in the human population. The large number of combinations of these traits causes individuals to look unique, or different,
Disclosure Statement
 Disclosure Statement I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. I do not intend
Disclosure Statement I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. I do not intend
Congenital Athelia and Cleft Palate: A Case Report of Two Generations
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2009;14:46-50 Congenital Athelia and Cleft Palate: A Case Report of Two Generations CP WONG, KK NG Abstract Key words Athelia is a rare condition and is almost always associated
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2009;14:46-50 Congenital Athelia and Cleft Palate: A Case Report of Two Generations CP WONG, KK NG Abstract Key words Athelia is a rare condition and is almost always associated
Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
Bladder exstrophy and epispadias
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Bladder exstrophy and epispadias This leaflet explains about bladder exstrophy and epispadias and what to expect
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Bladder exstrophy and epispadias This leaflet explains about bladder exstrophy and epispadias and what to expect
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010
 Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Chapter 15 Chromosomes
 Chapter 15 Chromosomes Chromosome theory of inheritance Genes located on chromosomes = gene locus Thomas Hunt Morgan, Columbia Univ. Fly room Drosophila 100s of offspring 2n = 8 3 prs autosomes X and Y
Chapter 15 Chromosomes Chromosome theory of inheritance Genes located on chromosomes = gene locus Thomas Hunt Morgan, Columbia Univ. Fly room Drosophila 100s of offspring 2n = 8 3 prs autosomes X and Y
ISSN CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR
 J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
Lab Activity 36. Principles of Heredity. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Lab Activity 36 Principles of Heredity Portland Community College BI 233 Terminology of Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes: A pair, of which you get one from mom, and one from dad. Example: the pair of
Supplementary Clinical Information
 Supplementary Clinical Information Patient 1 This female was born as the second child of a twin after a pregnancy duration of 32 weeks. The birth was otherwise uncomplicated and her twin brother was healthy.
Supplementary Clinical Information Patient 1 This female was born as the second child of a twin after a pregnancy duration of 32 weeks. The birth was otherwise uncomplicated and her twin brother was healthy.
Family Studies and Aetiology of Club Foot
 J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, 227. Family Studies and Aetiology of Club Foot RUTH WYNNE-DAVIES From the Medical Research Council, Research Group on Genetic Problems in Orthopaedic Disease, Department of Orthopaedic
J. med. Genet. (I965). 2, 227. Family Studies and Aetiology of Club Foot RUTH WYNNE-DAVIES From the Medical Research Council, Research Group on Genetic Problems in Orthopaedic Disease, Department of Orthopaedic
Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
OSA in children. About this information. What is obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA)?
 About this information This information explains all about sleep-related breathing problems in children, focusing on the condition obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA). It tells you what the risk factors are
About this information This information explains all about sleep-related breathing problems in children, focusing on the condition obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA). It tells you what the risk factors are
Saint Mary s Hospital. Turner Syndrome. Information for parents and families
 Saint Mary s Hospital Turner Syndrome Information for parents and families Introduction Humans are usually born with 46 chromosomes which are arranged in 23 pairs. One of these pairs determines whether
Saint Mary s Hospital Turner Syndrome Information for parents and families Introduction Humans are usually born with 46 chromosomes which are arranged in 23 pairs. One of these pairs determines whether
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders. Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital
 Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
Unifactorial or Single Gene Disorders Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Hospital Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2011 Single
Limb/pelvis-hypoplasia/aplasia syndrome
 I Med Genet 1993; 30: 65-69 Centro di Genetica Umana, Ospedali Galliera, Mura Delle Cappuccine 14, 16128 Genoa, Italy. G Camera Ospedale Villa Malta, 84087 Sarno (Salerno). Italy. G Ferraiolo D Leo A Spaziale
I Med Genet 1993; 30: 65-69 Centro di Genetica Umana, Ospedali Galliera, Mura Delle Cappuccine 14, 16128 Genoa, Italy. G Camera Ospedale Villa Malta, 84087 Sarno (Salerno). Italy. G Ferraiolo D Leo A Spaziale
Common Genetic syndromes. Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria
 Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera
 PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
Acromicric dysplasia: long term outcome and evidence of autosomal dominant inheritance
 J Med Genet 2001;38:745 749 745 Département de Génétique, Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades, 149 rue de Sèvres, 75015 Paris, L Faivre M Le Merrer A Munnich P Maroteaux V Cormier-Daire Service de Génétique,
J Med Genet 2001;38:745 749 745 Département de Génétique, Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades, 149 rue de Sèvres, 75015 Paris, L Faivre M Le Merrer A Munnich P Maroteaux V Cormier-Daire Service de Génétique,
Table P-l. Summary of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects
 Table P-l of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects e) Table Reference: 8-21[bJ Interaction: Specific Delays in Development (Categ. DIOXIN by P-AGE, Categ. DIOXIN by C-TIHE) Exposure
Table P-l of Dioxin-by-Covariate Interactions for. Selected Birth Defects e) Table Reference: 8-21[bJ Interaction: Specific Delays in Development (Categ. DIOXIN by P-AGE, Categ. DIOXIN by C-TIHE) Exposure
Familial Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1055 CASE REPORT Familial Cleidocranial Dysplasia 1 Radhika Verma, 2 MK Jindal, 3 Sandhya Maheshwari IJCPD Familial Cleidocranial Dysplasia 1 Tutor, Department of Pedodontics,
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1055 CASE REPORT Familial Cleidocranial Dysplasia 1 Radhika Verma, 2 MK Jindal, 3 Sandhya Maheshwari IJCPD Familial Cleidocranial Dysplasia 1 Tutor, Department of Pedodontics,
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies
 Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
