An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification. Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization
|
|
|
- Vincent Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization
3 What are the problems? When did they happen? How did they arise? Why did they occur? What is the diagnosis? Who else is at risk? Where can the patient/family get help?
4 Classification of Observable Differences Normal variations Minor anomalies Major anomalies
5 Model for Variation in Skin Color
6
7 Minor Anomaly Minor variations of normal morphological features of little of no known medical, surgical, or cosmetic significance Single minor anomalies are present in about 15% of newborns
8
9
10
11
12 Significance of minor anomalies Occurrence of single minor anomaly Occurrence of two minor anomalies Presence of 3 or more minor anomalies 42% of idiopathic MR have 3 or more anomalies External minor anomalies in the head and neck region and the hand 15% of all newborns 3% have an associated major anomaly Less common 11% have an associated major anomaly Unusual 1% 90% have an major associated anomaly 80% of which are minor anomalies Constitutes 71% of minor anomalies
13 Major Anomaly Abnormality that has medical, surgical, or cosmetic significance
14 Major anomalies are more common in early embryos (up to 15%) than they are in newborns (3%). Most severely malformed embryos are spontaneously aborted during first 6 to 8 weeks.
15 postaxial preaxial
16
17
18 Categorizing congenital anomalies/dysmorphic features 1. Malformation 2. Deformation 3. Disruption 4. Dysplasia
19
20 Pathogenesis of congenital abnormalities 1. Deformation an abnormal mechanical force which distorts an otherwise normal structure
21 Deformation :There is normal development, but this process is acted upon by an extrinsic or intrinsic mechanical force. Extrinsic forces include multiple gestations, abnormal uterus, or oligohydramnios. Intrinsic forces include neuromuscular abnormalities, amyoplasia, or skeletal anomalies. Deformations affect approximately 2% of newborns. These anomalies have a good prognosis and are typically easy to treat with physical therapy or external fixation devices (casts or braces). Examples include: club feet
22 club foot plagiocephaly
23 Deformations due to oligohydramnios
24 Pathogenesis of congenital abnormalities 2. Disruption an abnormal structure of an organ or tissue as a result of external factors disturbing the normal developmental process include ischemia, infection or trauma These are typically isolated non-genetic events that have a low recurrence risk Example: Amniotic band syndrome Intestinal atresia caused by vascular insufficiency
25
26 Disruption of lip formation due to amniotic bands
27
28 Congenital ring constrictions with amniotic bands
29 Pathogenesis of congenital abnormalities 3. Malformation primary structural defect of an organ which results from an inherent abnormality in development hypoplasia, incomplete closure, incomplete separation, usually occurring before 10 weeks of gestation.
30 Malformation : There is an intrinsically abnormal developmental process, with the early development of a tissue or organ being arrested, delayed, or misdirected. These anomalies can be caused by a teratogen or abnormalities in a gene, a group of genes, or a chromosome. Major malformations are those which have medical, surgical or cosmetic significance. Examples include: cleft lip/palate, cardiac defects, and abdominal wall defects. Minor malformations are insignificant variants. Examples include: pre-auricular ear pits, hair whorls, and clinodactyly.
31 Neural Tube Defects
32 Gastroschisis
33 Omphalocele
34 Ambiguous genitalia
35 Bladder exstrophy
36
37
38 Pathogenesis of congenital abnormalities 4. Dysplasia Error of morphogenesis due to the abnormal cellular organization of function in a specific type of tissue most often due to single gene defects, Example renal dysplasia, hemangioma, and skeletal dysplasia: Achondroplasia, ectodermal dysplasia, osteogenesis imperfecta
39 Ectodermal dysplasia
40 Achondroplasia
41 Clinical presentation of congenital Syndromes malformations Associations Sequences
42 A B Embryonic period Fetal period Death of the embryo is possible Susceptibility to abnormalities is increased Functional disorders are more likely
43 genetic etiology should be suspected Congenital anomalies (e.g major anomaly or > 2 minor anomalies) Growth deficit (e.g. short stature or failure to thrive) Developmental delay, mental deficit or developmental regression Failure to develop secondary sexual characteristics Ambiguous genitalia Funny looking kid
44 Causes of congenital anomalies
45
46 Diabet Poorly controlled diabetes has been associated with an increased rate of microcephaly fetal cardiovascular, renal, and neural tube and caudal regression syndrome are seen with higher frequency than expected.
47 The rate of malformation appears be directly related to the level of fasting hyperglycemia at diagnosis. Fasting Glucose (mg/dl) Rate of Malformation < % % > %
48
49 Common teratogens drugs Alcohol Anti-coagulants - Warfarin Anti-convulsants - Phynetoin, Valproic acid Antibiotics - Streptomycin/Tetracycline Psychiatric drugs - Lithium Illicit drugs - cocaine/ heroin Hormones -estrogens Isotretinoin
50 Chemical Carbon Monoxide Insecticides Mercury Organic Solvents Paint Polychlorin biphenyl Smoking
51 The evaluation of a dysmorphic child requires a systematic approach with a: detailed history careful physical examination
52 HISTORY Pregnancy history Birth history Past Medical History Developmental History Family History
53 Pregnancy history - Problems with infertility (medications [clomid], techniques [IVF - invitro fertilization, PGD - preimplantation genetic diagnosis, ICSI - intracytoplasmic sperm injection ( - Fetal Movement (active, decreased ( - Exposures (medications, tobacco, alcohol, drugs, chemicals( - Illnesses (fevers, exposures to infections ( - Problems (bleeding, pre-term labor, abnormal prenatal testing or ultrasound (
54 Presentation: breech? Birth history Delivery: vaginal, c-section (why?) Neonatal course (complications/problems and days hospitalized)
55 Past Medical History Similar to standard history (illnesses, hospitalizations, surgeries, immunizations, medications, allergies) including a detailed review of systems.
56 Developmental History Address parental concerns. Determine ages for milestones (gross motor, fine motor, personal/social, language, rolling over, sitting, walking, and talking). Determine current milestones (appropriate for age?)
57 Family History A detailed three-generation family pedigree should be obtained for all patients. The family pedigree is an essential tool that allows for the direct visualization of the relationship of physical features or conditions in order to determine inheritance patterns. The proband, who is the individual of interest, should be indicated with an arrow. Lastly, in addition to conditions or physical traits, a complete pedigree should include ages with ethnicities, and causes of death.
58 Evaluation of the dysmorphic child The evaluation of a dysmorphic child requires a systematic approach with a: detailed history careful physical examination
59 physical examination Every body part has to be examined with particular emphasis on size, shape, color, position, spacing, and symmetry. Below are some frequently used concepts and descriptions :
60
61
62
63 Digital Dysmorphology Digitall face analysis Machine learning Healthy Down
64
65
66
67
68
69 Growth Growth is a key and vital concept in the evaluation of all children. Measurements of the child's weight, length, and head circumference should be plotted on the standardized growth charts.
70 Head : shape pl from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly from bracalyhyceph ( fontanel size/shape (wide, large, small), sutures (ridges, agiocephaly prominent ) Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes : shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) Neck : length (short, long), webbed, excess skin Chest : symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (wide-spaced ) Heart : Abdomen : routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
71
72
73 Suture Growth Sutures allow growth perpendicular to them Growth at suture lines related to brain growth
74 Early Closure Causes Growth Parallel to the Suture
75 Sagittal Synostosis Boat-Head (Scaphocephaly)
76
77 .
78 Coronal Synostosis Bent-Head (Plagiocepahly)
79
80 Metopic Synostosis Triangle-Head (Trigonocephaly)
81
82
83
84 Microcephaly
85
86
87 Hydrocephalus 87
88 2 months old male, noted at birth to have a big head
89
90
91 Head : from brachycephaly ( shape from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly,capp from CAPP), fontanel size/shape plagiocephaly (wide, large, small), sutures (ridges, prominent ) Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes :,MyPACS shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : Neck : Chest : Heart : Abdomen : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) length (short, long), webbed, excess skin symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (wide-spaced ) routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
92
93
94
95
96
97
98 Receding anterior hair line with hair hypopigmentation Silver colored hair
99
100
101 Head : from brachycephaly ( shape from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly,capp from CAPP), fontanel size/shape plagiocephaly (wide, large, small), sutures (ridges, prominent ) Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes :,MyPACS shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : Neck : Chest : Heart : Abdomen : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) length (short, long), webbed, excess skin symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (wide-spaced ) routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
102 Hypertelorism Zellweger Syndrome
103
104 Hypotelorism distal duplication 14p
105
106 Palpebral slant Upslant downslant
107
108 Blephrophimosis Unilateral microphthalmia Unilateral anophthalmia Bilateral anophthalmia
109 Corneal opacity Heterochromia Squint Congenital glaucoma
110 Cataract Epibulbar dermoid Bilateral ptosis of eyelids Microphtalmia
111 Microphthalmia Coloboma
112 Head : from brachycephaly ( shape from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly,capp from CAPP), fontanel size/shape (wide, plagiocephaly large, small), sutures (ridges, prominent ),MyPACS Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes : shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : Neck : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) length (short, long), webbed, excess skin Chest : symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (wide-spaced ) Heart : Abdomen : routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
113
114 Preauricular skin tags
115 Hypoplastic ear
116
117 Microtia
118
119
120
121
122
123 Low Set
124
125
126
127
128 Angulation of the Auricle Vertical Plane of head Horizontal plane Longest Diameter Protrusion
129 Head : from brachycephaly ( shape from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly,capp from CAPP), fontanel size/shape plagiocephaly (wide, large, small), sutures (ridges, prominent ) Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes :,MyPACS shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : Neck : Chest : Heart : Abdomen : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) length (short, long), webbed, excess skin symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (wide-spaced ) routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
130
131
132
133 Nose Short or long nose (the nose is usually 2/3 3/4 the length of the distance between the nasal bridge and the upper lip) Long nose Short nose Heminasal aplasia
134
135 Head : from brachycephaly ( shape from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly,capp from CAPP), fontanel size/shape plagiocephaly (wide, large, small), sutures (ridges, prominent ) Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes :,MyPACS shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : Neck : Chest : Heart : Abdomen : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) length (short, long), webbed, excess skin symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (wide-spaced ) routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
136
137
138 Aarskog Syndrome (Faciogenital dysplasia) Widow s Peak Small nose Chin crease Hypertelorism Long philtrum carp mouth
139 Head : from brachycephaly ( shape from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly,capp from CAPP), fontanel size/shape plagiocephaly (wide, large, small), sutures (ridges, prominent ) Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes :,MyPACS shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : Neck : Chest : Heart : Abdomen : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) length (short, long), webbed, excess skin symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (wide-spaced ) routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
140 Score lip and philtrum separately Significant dysmorphology Normal
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154 Head : from brachycephaly ( shape from dolichocephaly/scapholocephaly,capp from CAPP), fontanel size/shape plagiocephaly (wide, large, small), sutures (ridges, prominent ) Hair : color, texture, distribution (low/high hairline, whorls ) Eyes :,MyPACS shape (almond); palpebral fissures (length, slant), spacing (hypotelorism, hypertelorisim ) Ears : shape (box, simple), position (low-set, posteriorly rotated ) Nose : root, bridge (prominent, flat, wide), tip (bulbous, wide ) Midface : Mouth : Chin : Neck : Chest : Heart : Abdomen : flat, hypoplastic size, shape (down-turned, up-turned), palate (intact, cleft), teeth (wide-spaced, crowded ) small (micrognathia), prominent (prognathia), recessed (retrognathia ) length (short, long), webbed, excess skin symmetry, size, nipples: shape (inverted), spacing (widespaced ) routine exam for rate, rhythm and murmurs hepatosplenomegaly, hernias
155
156
157
158 Skeletal Class III, concave profile Source: Dr. Wisanu Charoenkul
159
160
161 Micrognathia Retrognathia Hypoplasia of malar region
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL. Denise LM Goh
 APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Approach to a Child with Dysmorphism/ Congenital Malformation
 Definition Approach to a Child with Dysmorphism/ Congenital Malformation Dr Prajnya Ranganath Dysmorphology is a discipline of clinical genetics which deals with the study of abnormal patterns of human
Definition Approach to a Child with Dysmorphism/ Congenital Malformation Dr Prajnya Ranganath Dysmorphology is a discipline of clinical genetics which deals with the study of abnormal patterns of human
Objectives See course web page for full objectives Read : , (not Bayes theorem section)
 An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
History. History and Physical Exam of the Pediatric Patient. History of Present Illness. Chief Complaint. Past Medical History. Past Medical History
 History History and Physical Exam of the Pediatric Patient Colleen A. Kraft, M.D., FAAP Richmond Pediatric Associates, Inc. Source Who is giving the history? Is this the patient s primary caretaker? 1
History History and Physical Exam of the Pediatric Patient Colleen A. Kraft, M.D., FAAP Richmond Pediatric Associates, Inc. Source Who is giving the history? Is this the patient s primary caretaker? 1
HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM
 HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM 1.CRANIUM Is the size of head normal.?(measure ofc).is the skull shape abnormal( LOOK FROM ABOVE)? Are there any swellings on
HEAD TO FOOT EXAMINATION DR JP,ASST. PROF.ICH,GOVT MEDICAL COLLEGE KOTTAYAM 1.CRANIUM Is the size of head normal.?(measure ofc).is the skull shape abnormal( LOOK FROM ABOVE)? Are there any swellings on
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE
 CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab
 Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders
 Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Chapter 21 The Newborn At Risk: Congenital Disorders Congenital Anomalies or Malformations May be caused by genetic or environmental factors Approximately 2% to 3% of all infants born have a major malformation
Common Genetic syndromes. Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria
 Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions
 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Quick Reference Guide
 This index may help determine a clinical diagnosis. Fairly common dysmorphic features are listed with corresponding syndromes in which the characteristic is a frequent finding. The syndrome features are
This index may help determine a clinical diagnosis. Fairly common dysmorphic features are listed with corresponding syndromes in which the characteristic is a frequent finding. The syndrome features are
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University
 Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability?
 What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability? Aleksandra Jezela-Stanek, M.D., Ph. D. The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw
What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability? Aleksandra Jezela-Stanek, M.D., Ph. D. The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
A1a. Dysmorphology Assessment. Session Summary. Session Objectives. References. Session Outline
 A1a Dysmorphology Assessment Karlene Coleman, RN, MN, CGC Clinical Instructor Nell Hodgson Woodruff School of Nursing, Emory University, Atlanta, GA Certified Genetics Counselor Children s Healthcare of
A1a Dysmorphology Assessment Karlene Coleman, RN, MN, CGC Clinical Instructor Nell Hodgson Woodruff School of Nursing, Emory University, Atlanta, GA Certified Genetics Counselor Children s Healthcare of
Craniosynostosis. Diagnosis and Treatment
 Craniosynostosis Diagnosis and Treatment 2015 For more information about the Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program ABOUT The Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program takes a multidisciplinary approach to treating
Craniosynostosis Diagnosis and Treatment 2015 For more information about the Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program ABOUT The Weill Cornell Craniofacial Program takes a multidisciplinary approach to treating
Cleft Lip and Palate: The Effects on Speech and Resonance
 Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Ann W. Kummer, PhD, CCC-SLP Cincinnati Children s Cleft lip and/or palate can have a negative impact on both speech and resonance. The following is a summary of normal anatomy, the types and causes of
Physical examination of Newborn By Dr behzad barekatain MD Assistant professor of pediatrics, neonatologist Academic member of isfahan university of
 Physical examination of Newborn By Dr behzad barekatain MD Assistant professor of pediatrics, neonatologist Academic member of isfahan university of medical sciences 1 Swelling of the eyelids is common
Physical examination of Newborn By Dr behzad barekatain MD Assistant professor of pediatrics, neonatologist Academic member of isfahan university of medical sciences 1 Swelling of the eyelids is common
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010
 Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Yunis-Varon syndrome
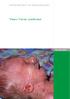 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
Department of Neurosurgery. Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly
 Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies
 Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
Chromosome 13. Introduction
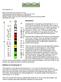 Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Chromosome 13 Chromosome Disorder Outreach Inc. (CDO) Technical genetic content provided by Dr. Iosif Lurie, M.D. Ph.D Medical Geneticist and CDO Medical Consultant/Advisor. Ideogram courtesy of the University
Approach to the Genetic Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders
 Approach to the Genetic Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders Dr Wendy Jones MBBS MRCP Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery What is a genetic diagnosis?
Approach to the Genetic Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders Dr Wendy Jones MBBS MRCP Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery What is a genetic diagnosis?
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Dr.ALI AL BAZZAZ PLASTIC SURGON CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Cleft lip (cheiloschisis) and cleft palate (palatoschisis), which can also occur together as cleft lip and palate, are variations of a type of clefting
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
NEW PATIENT FORM. Please print in ink and fill in all blanks Please fill out front and back. Patient s Full Name
 NEW PATIENT FORM Please print in ink and fill in all blanks Please fill out front and back Patient s Full Name Date of Birth Age Sex Social Security Number Referring Doctor or Family Physician Phone #
NEW PATIENT FORM Please print in ink and fill in all blanks Please fill out front and back Patient s Full Name Date of Birth Age Sex Social Security Number Referring Doctor or Family Physician Phone #
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly
 Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly Andrew Jea MD MHA FAAP Professor and Chief Section of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Department of Neurosurgery Indiana University School of Medicine
Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly Andrew Jea MD MHA FAAP Professor and Chief Section of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Department of Neurosurgery Indiana University School of Medicine
a Genetics Unit, Department of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Received 29 June 2004 Accepted 3 November 2004
 Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
Abstract. Introduction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, September: 453-458, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Sanjad-Sakati Syndrome: A Rare Autosomal Recessive Disorder of Congenital Hypoparathyroidism-Microcephaly-Mental
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, September: 453-458, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Sanjad-Sakati Syndrome: A Rare Autosomal Recessive Disorder of Congenital Hypoparathyroidism-Microcephaly-Mental
Meet Libby. Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies Definitions. Dr. Victor Malinovsky
 Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
1/27/2017. Nursing Care of the Pediatric Neurosurgical Patient. Assessment is the key...
 Nursing Care of the Pediatric Neurosurgical Patient Julie Deibel, APN, NP-C, CNE Pediatric Neurosurgery Illinois Neurological Institute Assessment is the key..... Overview Consideration of development
Nursing Care of the Pediatric Neurosurgical Patient Julie Deibel, APN, NP-C, CNE Pediatric Neurosurgery Illinois Neurological Institute Assessment is the key..... Overview Consideration of development
Chapter 13. DiGeorge Syndrome
 Chapter 13 DiGeorge Syndrome DiGeorge Syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disease caused by abnormal migration and development of certain cells and tissues during fetal development. As part of the developmental
Chapter 13 DiGeorge Syndrome DiGeorge Syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disease caused by abnormal migration and development of certain cells and tissues during fetal development. As part of the developmental
Objectives. VACTERL Association. Vertebral Anomalies Anal Atresia Cardiac anomalies TE Fistula Renal Limb Anomalies Hydrocephalus
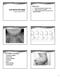 Courtney Grassham, NNP BC Objectives 1. Identify abnormal physical findings on exam 2. Identify abnormal x ray findings 3. Identify common characteristics associated with different Syndromes. VACTERL Association
Courtney Grassham, NNP BC Objectives 1. Identify abnormal physical findings on exam 2. Identify abnormal x ray findings 3. Identify common characteristics associated with different Syndromes. VACTERL Association
Craniofacial Microsomia
 Patient and Family Education Craniofacial Microsomia Children with craniofacial microsomia (CFM) have a small or underdeveloped part of the face, usually the ear and jaw. The eye, cheek and neck may also
Patient and Family Education Craniofacial Microsomia Children with craniofacial microsomia (CFM) have a small or underdeveloped part of the face, usually the ear and jaw. The eye, cheek and neck may also
Dysmorphology terminology and genetic syndromes
 Dysmorphology terminology and genetic syndromes Ayman El-Hattab, MD, FAAP, FACMG Consultant, Genetics and Metabolic The Division of Clinical Genetics and Metabolic Disorders Pediatric Department, Tawam
Dysmorphology terminology and genetic syndromes Ayman El-Hattab, MD, FAAP, FACMG Consultant, Genetics and Metabolic The Division of Clinical Genetics and Metabolic Disorders Pediatric Department, Tawam
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL
 What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
What is Hemifacial Microsomia? By Pravin K. Patel, MD and Bruce S. Bauer, MD Children s Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL 773-880-4094 Early in the child s embryonic development the structures destined to
Normal fetal face and neck
 Normal fetal face and neck Maria A. Calvo-Garcia, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Cincinnati, Ohio Disclosure I have no disclosures Goals & objectives
Normal fetal face and neck Maria A. Calvo-Garcia, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Cincinnati, Ohio Disclosure I have no disclosures Goals & objectives
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
HEARING LOSS IN UNILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
 Jadranka Handzic M.D., Ph.D., Professor of Otolaryngology, Audiology and Vestibulology Department for Otolaryngology and Audiology University Hospital Center Rebro Kispaticeva 12 Croatia HEARING LOSS IN
Jadranka Handzic M.D., Ph.D., Professor of Otolaryngology, Audiology and Vestibulology Department for Otolaryngology and Audiology University Hospital Center Rebro Kispaticeva 12 Croatia HEARING LOSS IN
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis. Rodney J. Scott
 Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis Rodney J. Scott Ability to interrogate Genomic Material ~1930 Crude analyses 2012 Highly precise analyses A (very) brief history
Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis Rodney J. Scott Ability to interrogate Genomic Material ~1930 Crude analyses 2012 Highly precise analyses A (very) brief history
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features
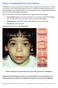 Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features Fetal exposure to alcohol during the first trimester affects development of facial features. The areas most affected are the orbital region (eyes) and mid-face.
Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features Fetal exposure to alcohol during the first trimester affects development of facial features. The areas most affected are the orbital region (eyes) and mid-face.
What is Craniosynostosis?
 What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Tan TY, Dillon OJ, Stark Z, et al. Diagnostic effect and cost-effectiveness of whole-exome sequencing of ambulant children with suspected monogenic conditions. JAMA Pediatr.
Supplementary Online Content Tan TY, Dillon OJ, Stark Z, et al. Diagnostic effect and cost-effectiveness of whole-exome sequencing of ambulant children with suspected monogenic conditions. JAMA Pediatr.
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities. Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD. Pediatric Genetics Team
 Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
Genetics and Developmental Disabilities Stuart K. Shapira, MD, PhD Pediatric Genetics Team National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention The
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses
 J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Phenotypic characterization of derivative 22 syndrome: case series and review
 Journal of Genetics, Vol. 97, No. 1, March 2018, pp. 205 211 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-018-0905-0 Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Phenotypic characterization of derivative 22 syndrome:
Journal of Genetics, Vol. 97, No. 1, March 2018, pp. 205 211 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-018-0905-0 Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Phenotypic characterization of derivative 22 syndrome:
To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story
 To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story DDC Clinic mission: To enhance the quality of life for people with special needs caused by rare genetic disorders What Does It Take to Be Your Local
To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story DDC Clinic mission: To enhance the quality of life for people with special needs caused by rare genetic disorders What Does It Take to Be Your Local
And Then There Were Two. Renae Buehner RNC, BSN Avera McKennan Labor and Delivery Unit Supervisor, Lead OB Flight RN
 And Then There Were Two Renae Buehner RNC, BSN Avera McKennan Labor and Delivery Unit Supervisor, Lead OB Flight RN Disclosures I have none She s coming in hot Assisting the maternal patient in a safe
And Then There Were Two Renae Buehner RNC, BSN Avera McKennan Labor and Delivery Unit Supervisor, Lead OB Flight RN Disclosures I have none She s coming in hot Assisting the maternal patient in a safe
TERMINOLOGY. portion of a bone ossified from a primary center. portion of a bone ossified from a secondary center.
 Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
28/04/2016. I have nothing to declare and no financial. interest or relationship to disclose
 I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
ار ناج هکنآ مان هب تخومآ
 فکرت را جان آنکه به نام آموخت صرع در حاملگی بیش از 90 درصد مادران مصروع می توانند فرزندان طبیعی داشته باشند Are antiepileptic drugs necessary? What effect do antiepileptic drugs have on the fetus? What
فکرت را جان آنکه به نام آموخت صرع در حاملگی بیش از 90 درصد مادران مصروع می توانند فرزندان طبیعی داشته باشند Are antiepileptic drugs necessary? What effect do antiepileptic drugs have on the fetus? What
Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 704 708 CASE REPORT Proboscis lateralis: report of two cases Lütfi Eroğlu a, *, Osman Ata Uysal b a Faculty of Medicine, Department of Plastic and
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Genetics
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
A case with oto-spondylo-mega-epiphyseal-dysplasia (OSMED): the clinical recognition and differential diagnosis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2011; 53: 346351 Case A case with otospondylomegaepiphysealdysplasia (OSMED): the clinical recognition and differential diagnosis Kadri Karaer 1, Rasim Özgür Rosti 1,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2011; 53: 346351 Case A case with otospondylomegaepiphysealdysplasia (OSMED): the clinical recognition and differential diagnosis Kadri Karaer 1, Rasim Özgür Rosti 1,
Neonatal Hypotonia. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy. Neurology Chapter of IAP
 The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
FERTILITY SERVICES PERSONAL HISTORY
 FERTILITY SERVICES PERSONAL HISTORY ONE FERTILITY KITCHENER WATERLOO 4271 King St E., Suite 200 KITCHENER, Ontario N2P 2X7 P 519-650-0011 F 519-650-0033 www.onefertilitykw.com Date: Age: Height: Weight:
FERTILITY SERVICES PERSONAL HISTORY ONE FERTILITY KITCHENER WATERLOO 4271 King St E., Suite 200 KITCHENER, Ontario N2P 2X7 P 519-650-0011 F 519-650-0033 www.onefertilitykw.com Date: Age: Height: Weight:
Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years?
 Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years? Kenneth Lyons Jones, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of California, San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA Generalizations About Phenotype
Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years? Kenneth Lyons Jones, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of California, San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA Generalizations About Phenotype
Figure 1. Basic anatomy of the palate
 CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
CHAPTER 10 CLEFT LIP AND PALATE Chen Yan, MD and Sanjay Naran, MD I. ANATOMY AND DEFINITIONS A. Cleft Lip (CL) alone, Cleft Lip with Cleft Palate (CLP), and Cleft Palate (CP) alone 1. CL alone and CLP
Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism Cases Studies Angela Sun, M.D. University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Case 1 5 day old with poor feeding Exclusively breastfeeding Decreased urine
Genetics and Inborn Errors of Metabolism Cases Studies Angela Sun, M.D. University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Case 1 5 day old with poor feeding Exclusively breastfeeding Decreased urine
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF)
 CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF) NNFF International NF1 Genetic Mutation Analysis Consortium Submission Form FORM USE Name of investigator (required field): Institution (required field):
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF) NNFF International NF1 Genetic Mutation Analysis Consortium Submission Form FORM USE Name of investigator (required field): Institution (required field):
New Patient Information Form
 New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
TERMS: Neonatal Period: Birth --> 28 days of life. Term Infant: weeks of gestation
 Normal newborn objectives Quickly identify any danger signs Assess the normal adaptations of a newborn after birth Identify conditions requiring special care or follow-up observation. Identify any birth
Normal newborn objectives Quickly identify any danger signs Assess the normal adaptations of a newborn after birth Identify conditions requiring special care or follow-up observation. Identify any birth
Preconception/prenatal family history questionnaire
 1 of 5 Today s date: Person completing questionnaire: Patient Partner/spouse Name Date of birth Occupation Marital status (married, divorced, widowed, single) Last grade completed Height Weight Adopted
1 of 5 Today s date: Person completing questionnaire: Patient Partner/spouse Name Date of birth Occupation Marital status (married, divorced, widowed, single) Last grade completed Height Weight Adopted
APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY
 Ypn. J. Human Genet. 33, 487-492, 1988 APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY Yoshinori [ZUMIKAWA, Kenji NARITOMI, Shoko [KEMA, Yoshinobu
Ypn. J. Human Genet. 33, 487-492, 1988 APERT SYNDROME WITH PARTIAL POLYSYNDACTYLY: A PROPOSAL ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF ACROCEPHALOSYNDACTYLY Yoshinori [ZUMIKAWA, Kenji NARITOMI, Shoko [KEMA, Yoshinobu
PEDIATRICS. Module Topic/Content Student Learning Outcomes Resources Clinical Assessment Activities Course/Clinical Outcomes
 PEDIATRICS N332 Outline 1 Welcome back: Instructor Role and Student Role Discuss course requirements. Explain personal learning style and study patterns. Explain critical thinking and clinical judgment
PEDIATRICS N332 Outline 1 Welcome back: Instructor Role and Student Role Discuss course requirements. Explain personal learning style and study patterns. Explain critical thinking and clinical judgment
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1)
 Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Intersex Genital Mutilations in ICD-10 Zwischengeschlecht.org / StopIGM.org 2014 (v2.1) ICD-10 Codes and Descriptions: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en 1. Reference: 17 Most Common
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Apraxia/Mute FACTS: Some children do not speak due to stress in their lives. Other children may have hearing loss or a tongue deformity.
 Apraxia/Mute Mutism is a lack of speech in children It can be due to hearing loss, mouth or tongue deformities, difficulty forming sounds or extreme stress as a result of trauma or anxiety. A child who
Apraxia/Mute Mutism is a lack of speech in children It can be due to hearing loss, mouth or tongue deformities, difficulty forming sounds or extreme stress as a result of trauma or anxiety. A child who
Teratology and. Early Pregnancy
 Teratology and Early Pregnancy Wolfgang E. Paulus Institute for Reproductive Toxicology Institute of Reproductive Toxicology St. Elisabeth Hospital Ravensburg, Germany Academic Teaching Hospital of the
Teratology and Early Pregnancy Wolfgang E. Paulus Institute for Reproductive Toxicology Institute of Reproductive Toxicology St. Elisabeth Hospital Ravensburg, Germany Academic Teaching Hospital of the
PEDIATRIC MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 Division of Otolaryngology Main Phone: 847 504-3300 Main Fax: 847 504-3305 Mihir Bhayani, MD Judy L. Chen, MD Mark E. Gerber, MD, FACS, FAAP Joseph Raviv, MD Ilana Seligman, MD, FACS, FAAP Michael J. Shinners,
Division of Otolaryngology Main Phone: 847 504-3300 Main Fax: 847 504-3305 Mihir Bhayani, MD Judy L. Chen, MD Mark E. Gerber, MD, FACS, FAAP Joseph Raviv, MD Ilana Seligman, MD, FACS, FAAP Michael J. Shinners,
A. Definitions... CD-157. B. General Information... CD-158
 CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
OTOLARYNGOLOGY ONLINE. Preauricular sinus. Management. Dr. T. Balasubramanian 6/17/2010
 1 OTOLARYNGOLOGY ONLINE Preauricular sinus Management Dr. T. Balasubramanian 6/17/2010 This e book discusses the Etiopathogenesis of preauricular sinus. Even though it is commonly encountered surgical
1 OTOLARYNGOLOGY ONLINE Preauricular sinus Management Dr. T. Balasubramanian 6/17/2010 This e book discusses the Etiopathogenesis of preauricular sinus. Even though it is commonly encountered surgical
U.S. Naval Hospital Naples, Italy Infertility Questionnaire
 U.S. Naval Hospital Naples, Italy Infertility Questionnaire The following questions make up a screening questionnaire that will help us in caring for you during your pregnancy. Your answers may indicate
U.S. Naval Hospital Naples, Italy Infertility Questionnaire The following questions make up a screening questionnaire that will help us in caring for you during your pregnancy. Your answers may indicate
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Liz Kacew, MScN, NP-PHC & Terry Broda, NP-PHC January 28, 2015 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder "" is an umbrella term describing the range of effects that can occur with
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Liz Kacew, MScN, NP-PHC & Terry Broda, NP-PHC January 28, 2015 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder "" is an umbrella term describing the range of effects that can occur with
TURNERS SYNDROME. Mike Chan Alex Sproul Casey Sully 11/24/08
 TURNERS SYNDROME Mike Chan Alex Sproul Casey Sully 11/24/08 Turner s Syndrome A female is missing part or all of an X chromosome. Turner s Syndrome It is a chromosomal disorder affecting females in which
TURNERS SYNDROME Mike Chan Alex Sproul Casey Sully 11/24/08 Turner s Syndrome A female is missing part or all of an X chromosome. Turner s Syndrome It is a chromosomal disorder affecting females in which
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ)
 Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
Skeletal Dysplasias. Let me Count the Whys. Normal Skeletal Development. Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias 3/6/2017
 Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager
Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager
Supplementary Clinical Information
 Supplementary Clinical Information Patient 1 This female was born as the second child of a twin after a pregnancy duration of 32 weeks. The birth was otherwise uncomplicated and her twin brother was healthy.
Supplementary Clinical Information Patient 1 This female was born as the second child of a twin after a pregnancy duration of 32 weeks. The birth was otherwise uncomplicated and her twin brother was healthy.
The Mystery of Risk. Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child. Ira J. Chasnoff, MD
 The Mystery of Risk Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child Ira J. Chasnoff, MD irachasnoff@gmail.com Attachment: Basic Concepts n Attachment is the interconnectedness between human beings.
The Mystery of Risk Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child Ira J. Chasnoff, MD irachasnoff@gmail.com Attachment: Basic Concepts n Attachment is the interconnectedness between human beings.
Congenital heart malformation in Yunis-Varon syndrome
 788 77 Med Genet 1993 30: 788-792 Medical Genetics and Epidemiology, (The Centre for Medical Genetics), Adelaide, 72 King William Road, North Australia 5006, Australia. L C Ades E A Haan Organ Imaging,
788 77 Med Genet 1993 30: 788-792 Medical Genetics and Epidemiology, (The Centre for Medical Genetics), Adelaide, 72 King William Road, North Australia 5006, Australia. L C Ades E A Haan Organ Imaging,
CLUBFOOT QUESTIONNAIRE. NAME (Person with clubfoot) Date of Birth / / M
 Date / / CLUBFOOT QUESTIONNAIRE Genetic Analysis of Limb Malformations NAME (Person with clubfoot) Date of Birth / / M F Mother's name Date of birth / / Ethnic origin Father's name Date of birth / / Ethnic
Date / / CLUBFOOT QUESTIONNAIRE Genetic Analysis of Limb Malformations NAME (Person with clubfoot) Date of Birth / / M F Mother's name Date of birth / / Ethnic origin Father's name Date of birth / / Ethnic
