Acromicric dysplasia: long term outcome and evidence of autosomal dominant inheritance
|
|
|
- Beverley Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Med Genet 2001;38: Département de Génétique, Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades, 149 rue de Sèvres, Paris, L Faivre M Le Merrer A Munnich P Maroteaux V Cormier-Daire Service de Génétique, Hôpital Robert Debré, Paris, C Baumann Service d Endocrinologie et Diabètologie, Hôpital Robert Debré, Paris, M Polak Endocrinologie Pédiatrique, Hôpital Debrousse, Lyon, P Chatelain Polyclinique Pédiatrique, American Memorial Hospital, Reims, V Sulmont Clinique Médicale Infantile, Hôpital Saint Antoine, Lille, J Cousin Médecine Infantile, CHRU La Tronche, Grenoble, M Bost Génétique Médicale, Hôpital Edouard Herriot, Lyon, M P Cordier Clinical Genetics Center, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia, PA, USA E Zackai K Russell Chirurgie Orthopédique Pédiatrique, Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades, Paris, G Finidori J C Pouliquen Correspondence to: Dr Cormier-Daire, cormier@necker.fr Revised version received 8 August 2001 Accepted for publication 22 August 2001 Acromicric dysplasia: long term outcome and evidence of autosomal dominant inheritance L Faivre, M Le Merrer, C Baumann, M Polak, P Chatelain, V Sulmont, J Cousin, M Bost, M P Cordier, E Zackai, K Russell, G Finidori, J C Pouliquen, A Munnich, P Maroteaux, V Cormier-Daire Abstract Acromicric dysplasia is a rare bone dysplasia characterised by short stature, short hands and feet, normal intelligence, mild facial dysmorphism, and characteristic x ray abnormalities of the hands. Only a very small number of children with this condition have been reported so far. Here we report on a series of 22 patients including 10 boys and 12 girls with acromicric dysplasia. Length was normal at birth and height fell progressively ov the centiles postnatally. The mean adult height was 130 cm (133 cm in males, 129 cm in females). The hands, feet, and limbs were short and OFC was normal. Intelligence was normal and mild dysmorphic features were noted. Other occasional features included well developed muscles, a hoarse voice, generalised joint limitation in some patients, frequent ear, tracheal, and respiratory complication, and spine abnormalities. Long term follow up showed that facial dysmorphism was less obvious in adults and that carpal tunnel syndrome was frequent in older patients. Apart from short metacarpals and phalanges, internal notch of the second metacarpal, external notch of the fifth metacarpal, and internal notch of the femoral heads, there were no major x ray abnormalities. No major complications, such as cardiac disease or major orthopaedic problems, occurred in the course of the disease. The condition appeared to be sporadic in 16 cases but the observation of vertical transmission in three families was consistent with an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. (J Med Genet 2001;38: ) Keywords: acromicric dysplasia; geleophysic dysplasia; long term outcome; autosomal dominant inheritance In 1986, Maroteaux et al 1 described a novel bone dysplasia in six unrelated children presenting with short stature, short hands and feet, normal intelligence, mild facial dysmorphic features, and characteristic x ray abnormalities of the hands. They called this condition acromicric dysplasia. 1 Only a few cases with features of acromicric dysplasia have been reported since then, but all children presented overlapping features with geleophysic dysplasia or Moore-Federman syndrome. 2 4 In the last 14 years, we have ascertained 18 additional cases of acromicric dysplasia in 15 families from five diverent countries and followed up four of the previously reported cases. Here we describe the clinical data and x ray features of these patients, with particular emphasis on the long term outcome in 10 adult patients, and provide further support for the autosomal dominant inheritance of this condition. Patients and methods Twenty-two patients (12 girls, 10 boys) from 15 families and five diverent countries were included in our study (table 1). Their ages ranged from 4.5 to 53 years with a mean age of 19 years. The diagnosis of acromicric dysplasia was based on the observation of short stature, short hands and feet, short and stubby metacarpals and phalanges with an external notch on the second metacarpal and an internal notch on the fifth metacarpal, and mild deformity of the femoral heads. Sixteen of our 22 patients were seen at least once in the medical genetics clinic of Necker-Enfants Malades Hospital. Questionnaires were sent to the referring physicians and patients were contacted directly for follow up information. Eight patients were identified through medical reports sent to our clinic for advice and questionnaires were sent to the referring physician for additional information. Results The mean length at birth was 48.6 cm (48.8 cm in boys, 48.5 cm in girls) and the mean adult height was 130 cm (133 cm in males, 129 cm in females), with a range from 115 to 140 cm. In all cases, the height fell progressively ov the centiles (fig 1). The limbs were short and OFC was normal. One case showed significant improvement after a limb lengthening procedure and one patient received growth hormone with no significant evect on final height. Short stature was generally well accepted by the patients and their quality of life was not avected. Adults did well in their professional lives and intelligence was normal. Facial dysmorphism was very similar in all cases (fig 2). It included a round face (17/22 cases), narrow palpebral fissures (17/22 cases), well defined eyebrows (14/22 cases), long eyelashes (14/22 cases), a bulbous nose with anteverted nostrils (19/22 cases), a long and prominent philtrum (16/22 cases), and thick lips (13/22 cases) with a small mouth (12/22 cases). Facial dysmorphism seemed less obvious in older patients. Occasional features included joint limitation (13/20 cases), kyphoscoliosis or lordosis (12/20 cases), recurrent ear, tracheal, and respiratory complications (otitis, tracheal infections, and
2 746 Faivre, Le Merrer, Baumann, et al Table 1 Clinical features in acromicric dysplasia patients Familial cases Sporadic cases Ethnic origin Fr Fr Fr Fr A A Fr Fr Fr Fr Fr A Fr USA USA Sp Sp Fr It Fr Fr It Sex F M F M F M F M F F M F F F M F F M M F M M 10M/12F Familial case /22 Length at birth (cm) NA NA Follow up Age (years) Height (cm) * in adults Abnormal voice NA NA NA NA NA NA NA + 5/15 Well developed muscles NA NA NA + + NA /18 Joint limitation H,Fi All All E,Fi S Fi Fi E,Fi NA NA H,E E,F, E,Fi, H E,H, 13/20 H,K H Fi Facial dysmorphism /22 Heart malformations /22 Hepatomegaly /22 Eye abnormalities NA NA /20 Ear abnormalities NA NA - - 6/20 Tracheal, respiratory /22 Spine abnormalities NA NA /20 Carpal tunnel /22 Fr, ; A, Africa; Sp, Spain; It, Italy. F, female; M, male. H, hips; Fi, fingers; E, elbows; K, knees; S, shoulders. NA, not available. *+20 cm after limb lengthening procedure. asthma, 10/20 cases), well developed muscles (10/18 cases, fig 3), eye refraction defects (hypermetropia, myopia, and astigmatism, 8/20 cases), abnormally hoarse voice (5/15 cases), heart malformations (atrial septal defect and bicuspid aorta, 4/22 cases), and carpal tunnel syndrome in older patients (3/22 cases, table 1). No pain, thickened skin, or hepatomegaly was observed. Finally, irregular leg length (1/22 cases), osteoarthritis (1/22 cases), clenched fingers (1/22 cases), Brown syndrome (limitation of upward gaze) (1/22 cases), pulmonary hypertension (1/22 cases), autoimmune diabetes (1/22 cases), hepatitis (1/22 cases), delayed puberty (1/22 cases), and cm A Height n = 10 boys +2 M 2 Total precocious puberty (1/22 cases) were occasionally noted. Besides short metacarpals and phalanges, internal notch of the second metacarpal, and external notch of the fifth metacarpal, other consistent features were shortened fourth and fifth metacarpals and markedly delayed bone age. Mild pointing of the second to fifth metacarpals was observed in 15/22 cases and cone shaped epiphyses in 5/22 cases. X rays of the older patients showed that the notches of the hands disappeared in adulthood (fig 4). An internal notch of the femoral heads was consistently observed and persisted in adulthood (fig 5). There was neither osteopenia nor Years Years Figure 1 Maximum and minimum growth curve in 22 acromicric dysplasia patients. Birth length ranged from 45 to 51 cm. Adult height ranged from 115 to 140 cm. cm B Height n = 12 girls +2 M 2
3 Acromicric dysplasia 747 Figure 2 Facial dysmorphism in 12 patients with acromicric dysplasia. Note the round face, narrow palpebral fissures, well defined eyebrows and long eyelashes, a bulbous nose with anteverted nostrils, a long and prominent philtrum, and thick lips with a small mouth. The facial dysmorphism seems less obvious in adults. Figure 3 obvious vertebral, epiphyseal, or metaphyseal anomalies. Urinary oligo- and mucopolysaccharides showed no evidence of storage disorder. Histology of the skin performed in one case at the age of 53 years was normal as well as liver and tracheal histology in another patient. Similarly, there were no endocrine or cytogenetic abnormalities, except in one patient with partial growth hormone deficiency. Sixteen out of 22 cases were sporadic with parental age within normal limits (mean father s age at birth 29 years, mean mother s age at birth 27 years). Six of our 22 cases were familial with vertical transmission, suggesting an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance (fig 6). Discussion Here we report progressive dwarfism, short hands and feet, normal intelligence, and mild dysmorphic features in 22 patients with acromicric dysplasia. Additional clinical features of the syndrome were identified in this study, namely well developed muscles, hoarse voice, generalised joint limitations, frequent ear, tracheal, and respiratory complications, and spine abnormalities. Long term follow up showed that facial dysmorphism was less obvious in adults and that carpal tunnel syndrome was frequent in older patients. The severity of dwarfism was quite variable, but consistently below 3 SD, and OFC was consistently normal. Life expectancy was normal and no major complications, such as cardiac disease or major orthopaedic problems, occurred in the course of the disease. Only mild x ray abnormalities were noted and notches of the hands disappeared in adulthood. Several acromicric dysplasia patients with features of geleophysic dysplasia and Moore- Federman syndrome, namely stiv joints, thickened skin, and hepatomegaly, have been reported, raising the question of whether geleophysic dysplasia, Moore-Federman syndrome, and acromicric dysplasia could be the same entity. 2 4 Moreover, short stature with short hands and feet, normal birth length with reduced postnatal growth rate, and delayed bone age are common features in all three conditions. Table 2 summarises the diverences between the three entities. First, thickened skin Front views of five acromicric dysplasia patients. The limbs, hands, and feet were short and well developed muscles were noted in several patients.
4 748 Faivre, Le Merrer, Baumann, et al Figure 4 X rays of the hands in acromicric dysplasia. Note the short metacarpals and phalanges, the internal notch of the second metacarpal and the external notch of the fifth metacarpal, short fourth and fifth metacarpals, mild pointing of the second to fifth metacarpals, and markedly delayed bone age. Note that hand notches disappeared in adulthood. and hepatomegaly are features of both geleophysic dysplasia and Moore-Federman syndrome, but are never observed in acromicric dysplasia. Second, cardiac valve dysplasia is observed in geleophysic dysplasia only. 5 Third, while life expectancy and functional prognosis are good in acromicric dysplasia and Moore- Federman syndrome, they are poor in geleophysic dysplasia. 6 In addition, the internal notch of the femoral heads is specific to acromicric dysplasia. Also, histological signs of storage disorder have been found in geleophysic Figure 5 X rays of the pelvis in acromicric dysplasia. Note the internal notch of the femoral heads. This notch did not disappear with age.
5 Acromicric dysplasia 749 Family 1 Family 2 Family 3 Figure 6 Vertical transmission of the disease in the three familial cases of acromicric dysplasia. dysplasia Finally, the mode of inheritance is diverent in the three conditions: autosomal dominant in acromicric dysplasia and Moore- Federman syndrome 9 10 and autosomal recessive in geleophysic dysplasia We therefore believe that at least geleophysic dysplasia is a distinct entity from acromicric dysplasia. The diverences between acromicric dysplasia and Moore-Federman syndrome are minor and the existence of only two reports of Moore- Ferderman syndrome limits the knowledge of the disease. 3 9 However, the hypothesis of clinical variability of the same entity with hepatomegaly and thickened skin being more obvious with age is not supported by the long term follow up of four patients aged 33 years or more in our series. The pathogenesis of the disease is unknown. Cartilage histology was performed in two of the first six cases with acromicric dysplasia 1 and showed some disorganisation of the growth Table 2 Similarities and diverences between acromicric dysplasia, Moore-Federman syndrome, and geleophysic dysplasia Acromicric dysplasia Moore-Federman 10 Geleophysic dysplasia 5 Major distinctive features Thickened skin + + Cardiac valve disease + Prognosis Good Good Poor Femoral heads Notch Deformed Dysplastic Histology Normal NR Storage Inheritance AD AD AR Minor distinctive features Joint contractures Mild - 13/20 Moderate - 10/11 Severe - 21/23 Hepatomegaly 0/22 5/11 14/21 Height <3rd centile 22/22 11/11 16/21 Speech delay 0/22 NR 4/14 Voice Hoarse Hoarse High pitched Eye abnormalities 8/20 9/11 Possible Similarities Birth length Often normal Often normal Often normal Reduced postnatal growth speed Delayed bone age Consistent NR Frequent Susceptibility to ENT and respiratory infections + NR + NR: not reported. ENT: ear, nose, and throat. zone with islands of cells, some of them degenerated, an abnormal organisation of collagen forming thick rims around the cells, and wide fibres in the inter-territorial matrix, and a large accumulation of glycogen in most chondrocytes. These results do not suggest which are the candidate genes in this disorder. In conclusion, we believe that acromicric dysplasia is a genuine entity, distinct from geleophysic dysplasia and, here, we provide additional support for the autosomal dominant inheritance of acromicric dysplasia. It is hoped that further familial cases will help in the mapping and identifying of the disease gene. We would like to acknowledge Damien Bonnet for his heart ultrasound expertise, Francis Brunelle for helpful discussion on x rays, Sylvie Fraitag and Catherine Prost for histological studies and electron microscopy of the skin, and Y Deris for photographic assistance. 1 Maroteaux P, Stanescu R, Stanescu V, Rappaport R. Acromicric dysplasia. Am J Med Genet 1986;24: Hennekam RC, van Bever Y, Oorthuys JW. Acromicric dysplasia and geleophysic dysplasia: similarities and diverences. Eur J Pediatr 1996;155: Winter RM, Patton MA, Challener J, Mueller RF, Baraitser M. Moore-Federman syndrome and acromicric dysplasia: are they the same entity? J Med Genet 1989;26: Lipson AH, Kan AE, Kozlowski K. Geleophysic dysplasia B acromicric dysplasia with evidence of glycoprotein storage. Am J Med Genet Suppl 1987;3: Santolaya JM, Groninga LC, Delgado A, Monasterio JL, Camarero C, Bilbao FJ. Patients with geleophysic dysplasia are not always geleophysic. Am J Med Genet 1997;72: Wraith JE, Bankier A, Chow CW, Danks DM, Sardharwalla IB. Geleophysic dysplasia. Am J Med Genet 1990;35: Shohat M, Gruber HE, Pagon RA, WitcoV LJ, Lachman R, Ferry D, Flaum E, Rimoin D. Geleophysic dysplasia: a storage disorder avecting the skin, bone, liver, heart, and trachea. J Pediatr 1990;117: Pontz BF, Stöb H, Henschke F, Freisinger P, Karbowski A, Spranger J. Clinical and ultrasound findings in three patients with geleophysic dysplasia. Am J Med Genet 1996; 63: Moore WT, Federman DD. Familial dwarfism and stiv joints. Report of a kindred. Arch Intern Med 1965;115: Fell JME, Stanhope R. Reviving the Moore-Federman syndrome. JRSocMed1993;86: Spranger J, Gilbert EF, Arya S, Hoganson GMI, Opitz JM. Geleophysic dysplasia. Am J Med Genet 1984;19: Titomanlio L, Della Casa R, Lecora M, Farina V, Sebastio G, Andria G, Parenti G. Geleophysic dysplasia: 7-year follow-up study of a patient with an intermediate form. Am J Med Genet 1999;86:82-5.
SED-BRACHYDACTYLY AND DISTINCTIVE SPEECH: REPORT OF TWO NEW CASES
 GENETIC COUNSELING, Vol. 18, No 1, 2007, pp 85-97 D. García et al., Tattoo dysplasia SED-BRACHYDACTYLY AND DISTINCTIVE SPEECH: REPORT OF TWO NEW CASES BY D. GARCÍA-CRUZ 1, G.F. ZAFRA DE LA ROSA 2, J. SÁNCHEZ-CORONA
GENETIC COUNSELING, Vol. 18, No 1, 2007, pp 85-97 D. García et al., Tattoo dysplasia SED-BRACHYDACTYLY AND DISTINCTIVE SPEECH: REPORT OF TWO NEW CASES BY D. GARCÍA-CRUZ 1, G.F. ZAFRA DE LA ROSA 2, J. SÁNCHEZ-CORONA
HAND ARTHROPATHY: A CLUE TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF THE KNIEST (SWISS CHEESE CARTILAGE) DYSPLASIA
 Rheumatology and Rehabilitation, 1980,19,167-169 HAND ARTHROPATHY: A CLUE TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF THE KNIEST (SWISS CHEESE CARTILAGE) DYSPLASIA BY RIDA A. FRAYHA 1, HUSN FRAYHA 2 AND RAFIC MELHEM 3 The Departments
Rheumatology and Rehabilitation, 1980,19,167-169 HAND ARTHROPATHY: A CLUE TO THE DIAGNOSIS OF THE KNIEST (SWISS CHEESE CARTILAGE) DYSPLASIA BY RIDA A. FRAYHA 1, HUSN FRAYHA 2 AND RAFIC MELHEM 3 The Departments
MOLECULAR SCREENING OF ADAMTSL2 GENE IN 33 PATIENTS REVEALS THE GENETIC HETEROGENEITY OF GELEOPHYSIC DYSPLASIA
 MOLECULAR SCREENING OF ADAMTSL2 GENE IN 33 PATIENTS REVEALS THE GENETIC HETEROGENEITY OF GELEOPHYSIC DYSPLASIA Slimane Allali, Carine Le Goff, Isabelle Pressac-Diebold, Gwendolyne Pfenning, Clã mentine
MOLECULAR SCREENING OF ADAMTSL2 GENE IN 33 PATIENTS REVEALS THE GENETIC HETEROGENEITY OF GELEOPHYSIC DYSPLASIA Slimane Allali, Carine Le Goff, Isabelle Pressac-Diebold, Gwendolyne Pfenning, Clã mentine
Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
AAK* - KK - FG - * Corresponding author
 Open Access Case report Synophyrs, curly eyelashes and Ptyrigium colli in a girl with Desbuquois dysplasia: a case report and review of the literature Ali Al Kaissi 1,2 *, Klaus Klaushofer 1 and Franz
Open Access Case report Synophyrs, curly eyelashes and Ptyrigium colli in a girl with Desbuquois dysplasia: a case report and review of the literature Ali Al Kaissi 1,2 *, Klaus Klaushofer 1 and Franz
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia
 JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24,
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Dwarfism with gloomy face: a new syndrome with features of 3-M syndrome
 1861 Med Genet 1991; 28: 186-191 Dwarfism with gloomy face: a new syndrome with features of 3-M syndrome M Le Merrer, R Brauner, P Maroteaux Abstract Nine children with primordial dwarfism are described
1861 Med Genet 1991; 28: 186-191 Dwarfism with gloomy face: a new syndrome with features of 3-M syndrome M Le Merrer, R Brauner, P Maroteaux Abstract Nine children with primordial dwarfism are described
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
.. -. U. SPONDYLOMETAPHYSEAL DYSPL.ASIA
 Spondylometaphyseal Dysplasia A family is described in which the father, son, and daughter have spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, consistent with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. Radiologic changes
Spondylometaphyseal Dysplasia A family is described in which the father, son, and daughter have spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, consistent with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. Radiologic changes
G enetic disorders of the skeleton or skeletal dysplasias
 201 LETTER TO JMG Acrocapitofemoral dysplasia: an autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia with cone shaped epiphyses in the hands and hips G R Mortier, PPGKramer, A Giedion, F A Beemer... J Med Genet 2003;40:201
201 LETTER TO JMG Acrocapitofemoral dysplasia: an autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia with cone shaped epiphyses in the hands and hips G R Mortier, PPGKramer, A Giedion, F A Beemer... J Med Genet 2003;40:201
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
Fig. I Facialfeatures of Case 1. * the inner canthal distance being 36 mm, the outer canthal distance 82 mm, and the interpupillary
 Archtives of Disease in Childhood, 1980, 55, 706-710 Aarskog's syndrome CAROLINE BERRY, JEAN CREE, AND TREVOR MANN Paediatric Research Unit, Prince Philip Research Laboratories, Guy's Hospital, London,
Archtives of Disease in Childhood, 1980, 55, 706-710 Aarskog's syndrome CAROLINE BERRY, JEAN CREE, AND TREVOR MANN Paediatric Research Unit, Prince Philip Research Laboratories, Guy's Hospital, London,
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Approach to Pediatric Anemia and Pallor. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Yunis-Varon syndrome
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Perthes disease in a child with Silver-Russell syndrome
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 7 Number 1 Perthes disease in a child with Silver-Russell syndrome V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian Citation V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 7 Number 1 Perthes disease in a child with Silver-Russell syndrome V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian Citation V Kakar, R Botchu, M Katchburian.
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue
 = Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
KNIEST DYSPLASIA NATURAL HISTORY
 KNIEST DYSPLASIA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations in Kniest Dysplasia
KNIEST DYSPLASIA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations in Kniest Dysplasia
A case with oto-spondylo-mega-epiphyseal-dysplasia (OSMED): the clinical recognition and differential diagnosis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2011; 53: 346351 Case A case with otospondylomegaepiphysealdysplasia (OSMED): the clinical recognition and differential diagnosis Kadri Karaer 1, Rasim Özgür Rosti 1,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2011; 53: 346351 Case A case with otospondylomegaepiphysealdysplasia (OSMED): the clinical recognition and differential diagnosis Kadri Karaer 1, Rasim Özgür Rosti 1,
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story
 To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story DDC Clinic mission: To enhance the quality of life for people with special needs caused by rare genetic disorders What Does It Take to Be Your Local
To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story DDC Clinic mission: To enhance the quality of life for people with special needs caused by rare genetic disorders What Does It Take to Be Your Local
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from. 3-M syndrome
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name 3M syndrome ICD 10: Q87.1 3-M syndrome Synonyms: Dolichospondylic dysplasia, 3Μ dwarfism, gloomy face syndrome, le Merrer
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Disease name 3M syndrome ICD 10: Q87.1 3-M syndrome Synonyms: Dolichospondylic dysplasia, 3Μ dwarfism, gloomy face syndrome, le Merrer
Case A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI.
 Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Limb/pelvis-hypoplasia/aplasia syndrome
 I Med Genet 1993; 30: 65-69 Centro di Genetica Umana, Ospedali Galliera, Mura Delle Cappuccine 14, 16128 Genoa, Italy. G Camera Ospedale Villa Malta, 84087 Sarno (Salerno). Italy. G Ferraiolo D Leo A Spaziale
I Med Genet 1993; 30: 65-69 Centro di Genetica Umana, Ospedali Galliera, Mura Delle Cappuccine 14, 16128 Genoa, Italy. G Camera Ospedale Villa Malta, 84087 Sarno (Salerno). Italy. G Ferraiolo D Leo A Spaziale
Mlicrospherophakia-metaphyseal dysplasia:
 I Med Genet 1990; 27: 467-471 Mlicrospherophakia-metaphyseal dysplasia: a 'new' dominantly inherited bone dysplasia with severe eye involvement Alain Verloes, Lionel Van Maldergem, Pierre de Marneffe,
I Med Genet 1990; 27: 467-471 Mlicrospherophakia-metaphyseal dysplasia: a 'new' dominantly inherited bone dysplasia with severe eye involvement Alain Verloes, Lionel Van Maldergem, Pierre de Marneffe,
Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (chondrodystrophic
 585 Med Genet 1992; 29: 58-62 SYNDROME OF THE MONTH Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (chondrodystrophic myotonia) Denis Viljoen, Peter Beighton Abstract Schwartz-Jampel syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder.
585 Med Genet 1992; 29: 58-62 SYNDROME OF THE MONTH Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (chondrodystrophic myotonia) Denis Viljoen, Peter Beighton Abstract Schwartz-Jampel syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder.
TERMINOLOGY. portion of a bone ossified from a primary center. portion of a bone ossified from a secondary center.
 Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University
 Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
The Genetics of Parenthood
 The Genetics of Parenthood Introduction Why do people, even closely related people, look slightly different from each other? The reason for these differences in physical characteristics (called phenotype)
The Genetics of Parenthood Introduction Why do people, even closely related people, look slightly different from each other? The reason for these differences in physical characteristics (called phenotype)
Case Report. Your Diagnosis
 Case Report 30-year-old gentleman, presented with bilateral dislocated radial head and with painful clunk in the knee [bilateral]. He is an active gentleman with good work history. He had a recent soft
Case Report 30-year-old gentleman, presented with bilateral dislocated radial head and with painful clunk in the knee [bilateral]. He is an active gentleman with good work history. He had a recent soft
Hths 2231 Laboratory 3 Genetics
 Watch Movie: Cystic Fibrosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-5 Activity #1: Under Lab 3 Click on activity 1 Click on Tour of the Basics Do all 6 What is exercises Activity
Watch Movie: Cystic Fibrosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-5 Activity #1: Under Lab 3 Click on activity 1 Click on Tour of the Basics Do all 6 What is exercises Activity
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION
 Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Dia 1. Dia 2 Turner syndrome. Dia 3 Turner syndrome. Turner syndrome. Henri Timmers internist-endocrinologist
 Dia 1 Turner syndrome Henri Timmers internist-endocrinologist Dept. of internal medicine Section of endocrinology Dia 2 Turner syndrome 1938 Henry Turner: description of clinical triad: - - short stature
Dia 1 Turner syndrome Henri Timmers internist-endocrinologist Dept. of internal medicine Section of endocrinology Dia 2 Turner syndrome 1938 Henry Turner: description of clinical triad: - - short stature
A growth disturbance and not a disorder with ligamentous laxity
 Marfan Syndrome A growth disturbance and not a disorder with ligamentous laxity 1 in 5,000-10,000 extensive phenotypic variability Fibrillin-1 abnormality Chromsome no. 15 Different forms of mutations
Marfan Syndrome A growth disturbance and not a disorder with ligamentous laxity 1 in 5,000-10,000 extensive phenotypic variability Fibrillin-1 abnormality Chromsome no. 15 Different forms of mutations
Trichorhinophalangeal Syndrome Type I : A Turkish Case
 Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 259-263 TÜB TAK SHORT REPORT Trichorhinophalangeal Syndrome Type I : A Turkish Case Mustafa KEND RC 1, Mehmet KESK N 1, Duran ARSLAN 1, Abdülhakim COfiKUN 2, Yusuf ÖZKUL 3 1 Department
Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 259-263 TÜB TAK SHORT REPORT Trichorhinophalangeal Syndrome Type I : A Turkish Case Mustafa KEND RC 1, Mehmet KESK N 1, Duran ARSLAN 1, Abdülhakim COfiKUN 2, Yusuf ÖZKUL 3 1 Department
ISSN CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR
 J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability?
 What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability? Aleksandra Jezela-Stanek, M.D., Ph. D. The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw
What dysmorphologists should keep in mind during evaluation of patients with blepharophimosis and mental disability? Aleksandra Jezela-Stanek, M.D., Ph. D. The Children s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw
Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, syndrome
 Severe Silver-Russell syndrome Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 447-451 D DONNAI*, E THOMPSONt, J ALLANSONt, AND M BARAITSERt From *the Regional Genetic Service, St Mary's Hospital, Manchester M13
Severe Silver-Russell syndrome Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 447-451 D DONNAI*, E THOMPSONt, J ALLANSONt, AND M BARAITSERt From *the Regional Genetic Service, St Mary's Hospital, Manchester M13
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
Names: Period: Punnett Square for Sex Chromosomes:
 Names: Period: Human Variations Activity Background A large variety of traits exist in the human population. The large number of combinations of these traits causes individuals to look unique, or different,
Names: Period: Human Variations Activity Background A large variety of traits exist in the human population. The large number of combinations of these traits causes individuals to look unique, or different,
Orofacial function of persons having. Report from questionnaires. Turner syndrome
 Orofacial function of persons having Turner syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Estimated occurrence: : girls born. Etiology: Girls with Turner syndrome are either
Orofacial function of persons having Turner syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises questionnaires. Estimated occurrence: : girls born. Etiology: Girls with Turner syndrome are either
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only)
 PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
Further delineation of Nevo syndrome
 v.. \. #/ 3666JMed Genet 1997;34:366-370 Further delineation of Nevo syndrome L I Al-Gazali, D Bakalinova, E Varady, J Scorer, M Nork Abstract A Nevo syndrome is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterised
v.. \. #/ 3666JMed Genet 1997;34:366-370 Further delineation of Nevo syndrome L I Al-Gazali, D Bakalinova, E Varady, J Scorer, M Nork Abstract A Nevo syndrome is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterised
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL. Denise LM Goh
 APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
Common Genetic syndromes. Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria
 Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
Common Genetic syndromes Dr. E.M. Honey Department Genetics Division Human Genetics University of Pretoria Definitions Deformation Malformation Disruption Dysplasia Syndrome Associations Complex Sequences
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
X-Linked Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda: Molecular Cause of a Heritable Platyspondyly
 X-Linked Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda: Molecular Cause of a Heritable Platyspondyly SPINE Volume 28, Number 22, pp E478 E482 2003, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Jörg Fiedler, PhD,* Anne-Marie
X-Linked Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda: Molecular Cause of a Heritable Platyspondyly SPINE Volume 28, Number 22, pp E478 E482 2003, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Jörg Fiedler, PhD,* Anne-Marie
Congenital heart malformation in Yunis-Varon syndrome
 788 77 Med Genet 1993 30: 788-792 Medical Genetics and Epidemiology, (The Centre for Medical Genetics), Adelaide, 72 King William Road, North Australia 5006, Australia. L C Ades E A Haan Organ Imaging,
788 77 Med Genet 1993 30: 788-792 Medical Genetics and Epidemiology, (The Centre for Medical Genetics), Adelaide, 72 King William Road, North Australia 5006, Australia. L C Ades E A Haan Organ Imaging,
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum?
 JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
Parvatasana. (Mountain pose)
 Parvatasana (Mountain pose) Parvatasana in Sanskrit means mountain. In this posture the body is stretched to look like a mountain. To relieve stress and revitalize your tired body and mind, parvatasana
Parvatasana (Mountain pose) Parvatasana in Sanskrit means mountain. In this posture the body is stretched to look like a mountain. To relieve stress and revitalize your tired body and mind, parvatasana
Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 488-492 Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome I D YOUNG AND J R MOORE From the Department of Child Health, University of Leicester, Leicester LE2 7LX. SUMMARY
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 488-492 Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome I D YOUNG AND J R MOORE From the Department of Child Health, University of Leicester, Leicester LE2 7LX. SUMMARY
Stickler syndrome. Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Genotype to Phenotype Simulation Booklet. Combining germ cells to create a new baby human
 Genotype to Phenotype Simulation Booklet Combining germ cells to create a new baby human 1 A Genetic Simulation Making A Face: Converting Genotype Into Phenotype by Simulating Meiosis and Fertilization
Genotype to Phenotype Simulation Booklet Combining germ cells to create a new baby human 1 A Genetic Simulation Making A Face: Converting Genotype Into Phenotype by Simulating Meiosis and Fertilization
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 2: 16, December Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma
 Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Reply to The question of heterogeneity in Marfan syndrome
 Reply to The question of heterogeneity in Marfan syndrome Catherine Boileau, Claudine Junien, Gwenaëlle Collod, Guillaume Jondeau, Olivier Dubourg, Jean-Pierre Bourdarias, Catherine Bonaïti-Pellié, Jean
Reply to The question of heterogeneity in Marfan syndrome Catherine Boileau, Claudine Junien, Gwenaëlle Collod, Guillaume Jondeau, Olivier Dubourg, Jean-Pierre Bourdarias, Catherine Bonaïti-Pellié, Jean
Mt. Vesuvius WORKOUT #9. 1 FUNK ROBERTS SPARTAN TRAINING SYSTEM // Workout 9 // Week 10 // week 10
 WORKOUT # week 10 MEDICAL DISCLAIMER This guide is for educational and informative purposes only and is not intended as medical or professional advice. Always consult your doctor before making any changes
WORKOUT # week 10 MEDICAL DISCLAIMER This guide is for educational and informative purposes only and is not intended as medical or professional advice. Always consult your doctor before making any changes
October. Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives
 October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
Abstract. Introduction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, September: 453-458, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Sanjad-Sakati Syndrome: A Rare Autosomal Recessive Disorder of Congenital Hypoparathyroidism-Microcephaly-Mental
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, September: 453-458, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Sanjad-Sakati Syndrome: A Rare Autosomal Recessive Disorder of Congenital Hypoparathyroidism-Microcephaly-Mental
May Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Awareness Day
 May 2018- Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Awareness Day A note from the author Hello NCP friends! The NCP Health Ministry always aims to provide a variety of articles over the course of the year, from common
May 2018- Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Awareness Day A note from the author Hello NCP friends! The NCP Health Ministry always aims to provide a variety of articles over the course of the year, from common
1 The bony framework along with car lage which gives shape to the body is called a: 2 A group of cells performing a similar ac on is a:
 CBSE Practice papers BODY MOVEMENTS class-6th-science Number of Questions: 65 For Answers and Solutions, Go to www.micromerits.com -> Select your grade -> Select Learn ->Select Subject Page link - http://www.micromerits.com
CBSE Practice papers BODY MOVEMENTS class-6th-science Number of Questions: 65 For Answers and Solutions, Go to www.micromerits.com -> Select your grade -> Select Learn ->Select Subject Page link - http://www.micromerits.com
STUDENT WORKSHEET. The Genetics of Parenthood Data Sheet. Parents and CHILD'S GENOTYPE ALLELE FROM DAD. H h I i J j K k.
 STUDENT WORKSHEET The Genetics of Parenthood Data Sheet Parents and Child's gender Child's name Fill in data table as you determine each trait described in the Guidebook. Do not simply flip the coin for
STUDENT WORKSHEET The Genetics of Parenthood Data Sheet Parents and Child's gender Child's name Fill in data table as you determine each trait described in the Guidebook. Do not simply flip the coin for
Information booklet for parents
 PREFACE: ALBRIGHT HEREDITARY OSTEODYSTROPHY (AHO) OR PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PHP) AND PSEUDO-PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PPHP) Information booklet for parents Dr. Savitha D Shenoy, Dr. Peter Swift Children
PREFACE: ALBRIGHT HEREDITARY OSTEODYSTROPHY (AHO) OR PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PHP) AND PSEUDO-PSEUDOHYPOPARATHYROIDISM (PPHP) Information booklet for parents Dr. Savitha D Shenoy, Dr. Peter Swift Children
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency
 Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Sotos syndrome. Nazneen Rahman Institute of Cancer Research
 Sotos syndrome Nazneen Rahman Institute of Cancer Research Sotos syndrome- background Sporadic condition Distinctive facial appearance Overgrowth (tall with big heads) Learning difficulties Other variably
Sotos syndrome Nazneen Rahman Institute of Cancer Research Sotos syndrome- background Sporadic condition Distinctive facial appearance Overgrowth (tall with big heads) Learning difficulties Other variably
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation Vol. 7, Issue 4, October - December 2015
 ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia with joint
 Syndrome of the month MRC Research Unit for Medical Genetics, Department of Human Genetics, Medical School, University of Cape Town, Observatory 7925, South Africa P Beighton Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia
Syndrome of the month MRC Research Unit for Medical Genetics, Department of Human Genetics, Medical School, University of Cape Town, Observatory 7925, South Africa P Beighton Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia
PROTOCOLS. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Principal investigator. Co-investigators. Background
 Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Transplantable Organs
 Transplantable Organs Liver Kidneys Pancreas Intestine Organ Information Heart The body s hardest working muscle, the heart beats 70 times each minute as it pumps blood throughout the body. Some conditions
Transplantable Organs Liver Kidneys Pancreas Intestine Organ Information Heart The body s hardest working muscle, the heart beats 70 times each minute as it pumps blood throughout the body. Some conditions
treacher collins syndrome
 a guide to understanding treacher collins syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding treacher collins syndrome this parent s guide to Treacher Collins syndrome
a guide to understanding treacher collins syndrome a publication of children s craniofacial association a guide to understanding treacher collins syndrome this parent s guide to Treacher Collins syndrome
Familial infantile scoliosis associated with bilateral paralysis of conjugate gaze
 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1979, 16, 448452 Familial infantile scoliosis associated with bilateral paralysis of conjugate gaze MENACHEM GRANAT1, ZVI FRIEDMAN, AND TAMAR ALONI From the Genetic Unit and
Journal of Medical Genetics, 1979, 16, 448452 Familial infantile scoliosis associated with bilateral paralysis of conjugate gaze MENACHEM GRANAT1, ZVI FRIEDMAN, AND TAMAR ALONI From the Genetic Unit and
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features
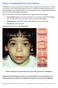 Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features Fetal exposure to alcohol during the first trimester affects development of facial features. The areas most affected are the orbital region (eyes) and mid-face.
Section C: Assessing Sentinel Facial Features Fetal exposure to alcohol during the first trimester affects development of facial features. The areas most affected are the orbital region (eyes) and mid-face.
Hyper IgE Syndrome. IDF US Information: Hyper IgE Syndrome. Definition of Hyper IgE Syndrome
 Hyper IgE Syndrome Definition of Hyper IgE Syndrome Hyper-IgE syndrome (HIES) is a complex primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a spectrum of abnormalities related to the immune system, bones,
Hyper IgE Syndrome Definition of Hyper IgE Syndrome Hyper-IgE syndrome (HIES) is a complex primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by a spectrum of abnormalities related to the immune system, bones,
Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses
 J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
J7 Med Genet 1991; 28: 117-121 Pitfalls in counselling: the craniosynostoses Romana Marini, Karen Temple, Lyn Chitty, Sally Genet, Michael Baraitser Abstract We describe three families to highlight the
Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis. Rodney J. Scott
 Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis Rodney J. Scott Ability to interrogate Genomic Material ~1930 Crude analyses 2012 Highly precise analyses A (very) brief history
Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis Rodney J. Scott Ability to interrogate Genomic Material ~1930 Crude analyses 2012 Highly precise analyses A (very) brief history
New Patient Questionnaire Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery
 Page 1 of 5 New Patient Questionnaire Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery First Name: Last Name: Middle: DOB: Height: Weight: Primary Care Physician/Pediatrician Name: Address: Phone Number: Chief Compliant
Page 1 of 5 New Patient Questionnaire Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery First Name: Last Name: Middle: DOB: Height: Weight: Primary Care Physician/Pediatrician Name: Address: Phone Number: Chief Compliant
The Genetics of Parenthood Data Sheet
 The Genetics of Parenthood Data Sheet Parents and Child's gender Child's name Fill in data table as you determine each trait described in the Guidebook. Do not simply flip the coin for all traits before
The Genetics of Parenthood Data Sheet Parents and Child's gender Child's name Fill in data table as you determine each trait described in the Guidebook. Do not simply flip the coin for all traits before
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures. Rena Heathcote
 Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
Warm-Up Activity. Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram.
 Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Orofacial function of persons having. Report from questionnaires. Silver-Russell syndrome
 Orofacial function of persons having Silver-Russell syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises 7 questionnaires. Synonyms: Russell-Silver syndrome, Silver syndrome. Estimated occurrence:
Orofacial function of persons having Silver-Russell syndrome Report from questionnaires The survey comprises 7 questionnaires. Synonyms: Russell-Silver syndrome, Silver syndrome. Estimated occurrence:
A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH)
 Case Reports A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH) M N Lucas 1, Savithri Dias 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2006; 35:141-3 (Key words: hereditary hypophosphataemic
Case Reports A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH) M N Lucas 1, Savithri Dias 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2006; 35:141-3 (Key words: hereditary hypophosphataemic
For the people of West Cork and surrounding areas. Information for patients and their families. Bantry Urgent Care Centre
 Bantry Urgent Care Centre For the people of West Cork and surrounding areas Information for patients and their families The Bantry Urgent Care Centre is made up of a Local Injury Unit and a Medical Assessment
Bantry Urgent Care Centre For the people of West Cork and surrounding areas Information for patients and their families The Bantry Urgent Care Centre is made up of a Local Injury Unit and a Medical Assessment
