Soccer Specifics. High Performance Therapy. Course Presented by Stuart Hinds NIEL ASHER EDUCATION
|
|
|
- August Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NIEL ASHER EDUCATION Soccer Specifics High Performance Therapy Course Presented by Stuart Hinds Stuart Hinds is a 4 x Olympic Therapist having worked wth the Australian Olympic Team at the 2000, 2004, 2008 and 2012 Games. Stuart lectures at Victoria University (Melbourne, Australia) and works regularly with elite soccer players. The notes contained herein are designed to accompany the Performance Therapy video classes available online.
2 Soccer Specifics High Performance Therapy Disclaimer & Warning Notice The techniques demonstrated in this course may only ever be performed by a suitably qualified healthcare professional. Taking this course does not grant you any form of license to practice manual therapy. Do not practice any form of manual therapy unless it falls within your professional scope of practice. Depending on where you practice, you may be required by law to meet certain criteria for practicing manual therapy, even if you are a qualified medical or healthcare practitioner. If you are not sure about the laws and regulations governing the practice of manual therapy in your area, you must make the necessary enquiries to ensure that you meet any and all requirements that may be in place. If you are unsure, please contact your professional organization or licensing board. Course Presented by: STUART HINDS Niel Asher Education, 2016 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 1
3 Introduction So to say that soccer is popular is an understatement. Soccer is now the leading participation sport in Europe, Asia, and the Americas. The world game has the dynamics of a skill based sport that also demands power, strength, speed and endurance. As the game continues to improve and develop at all levels, so the demands on player s bodies increase. Whilst these course notes provide an overview of some of the most common soccer injuries, the accompanying video classes show the practical techniques that should be employed to help keep players injury-free and improve their speed and agility on the field. Sports therapy has developed to the point where it is no longer acceptable to chase injuries around the body. Today s therapist focuses on the asymptomatic body-components that are most highly loaded and stressed, and works to help those muscles stay healthy and at their best. Soccer Injuries In order to determine the most common injuries in soccer and how they occur, researchers reviewed 15 years of injury surveillance data from the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). Over the 15 years of the study, 6,693 injuries from more than 22,000 games and 6,281 injuries from more than 62,000 practices were reported. Some of the general findings illustrate how practices and games pose different risks for players, as follows: - The injury rate during games was 4 times higher than during practices - Game injuries were often contact injuries between players, while practice injuries were often not. - In both games and practices, more than 60% of injuries were in the lower extremities. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 2
4 There were also clear trends for other types of injuries that soccer players are prone to. All of the following injuries rank in the top 5 of injuries that were experienced either in practice or games: - Muscle-tendon injuries to the thigh this included injuries to the quadriceps and hamstring muscles. - Muscle-tendon injuries to the hip or pelvis because of the complex anatomy of this part of the body, injuries to the soft tissues of the hip and pelvis. - Muscle-tendon injuries to the knee: these included tears in ligaments or oversuse syndromes of the patellofemoral Muscle-tendon - Injuries to the leg and foot: these include medial tibial stress syndrome, lateral ankle sprains. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 3
5 Course Contents This workbook is designed to accompany the video classes that are available online. Here we provide an overview of some of the most common soccer-related injuries together with details of how they can often be minimized if not avoided altogether. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 4
6 Soccer - Hip and Thigh The balance between the agonist and antagonist relationships is imperative. Soccer is a skillbased sport that depends highly on accurate passing and possession of the ball, which in turn requires dynamic strength and endurance, plus the ability to change directions at any given moment. With this in mind it is so important to take the time be sure that the dominant muscles of the hip are not being run on overload. When striking or passing the ball, soccer players normally kick the ball from the inside or medial portion of the foot, which requires the hip to be in external rotation. This puts the external rotators into a shortened position and places a significant load to the stabilizing gluteal muscles. This why we see so many soccer players with hip conditions relating to excessive load to the gluteus medius and minimus - two very important muscles in terms of biomechanics of the hip but also important to the function of the lower extremities. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 5
7 Hip Flexor Strain Hip flexors are located on the front of the hip and lift the thigh up or bend the waist forward or down when the limbs are fixed. These muscles are used a lot in soccer, cycling, running, kicking and jumping activities. When a new load is placed on the muscle or repetitive stresses are encountered without rest, the muscle may stretch or tear. Cause of Injury Repetitive stress on the hip flexor muscles without adequate time for recovery. Excessive stress placed on the muscles without appropriate strengthening and warm-up. Improper form when running. Forceful hyperextension of the leg at the hip. Signs and Symptoms Pain in the upper groin area over the anterior portion of the hip. Pain with movement of the leg at the hip. Inflammation and tenderness over the hip flexor. Complications if Left Unattended Hip flexor strains left untreated can become chronic and lead to inflexible muscles that could lead to other injuries. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 6
8 The muscle could also continue to tear, eventually leading to a complete rupture from the attachment. Immediate Treatment Cessation of activities that aggravate the hip flexors. Ice for the first hours. Anti- inflammatory medication. Then heat and massage to promote blood flow and healing. Rehabilitation and Prevention Conditioning is the key to rehabilitation and prevention of hip flexor strains. Muscles that are strong and flexible are much more resilient. Stretching the hip flexors, abdominals, lower back, quadriceps and hamstrings helps to lower the stress load placed on the hip flexors. Strengthening of iliopsoas and the other muscles of the hip, quadriceps, lower back and abdomen will help to prepare the hip flexors for unexpected stresses. Long-Term Prognosis Although the potential for chronic pain and inflexibility exists, hip flexor strains usually recover fully when given adequate rest and active recovery using stretching and strengthening exercises. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 7
9 Groin Strain As with any strain, groin strain is a stretch or tear of any or all of the adductor muscles of the inner thigh or their tendons. Soccer, hockey and other sports that require pivoting and quick direction changes are the most common activities for groin pulls. These injuries range from simple stretching of the muscles to more severe tearing of the fibres. As with other strains it is graded 1 through to 3 with 3 being the most severe tear. Due to this location and function, athletes involved in sports where the leg is moved forcefully inward or outward are more susceptible to this injury. Damage is usually to the musculo-tendinous junction, about 5 cm from the pubis. Cause of Injury Forceful stretching of the adductor muscles of the hip. Forceful contraction of the adductor muscles. Signs and Symptoms Grade 1: Mild pain. Stiffness in the adductor muscles but little or no effect on athletic performance. Grade 2: More painful. Some swelling, tenderness, limited range of motion, pain when walking or jogging. Grade 3: Very painful. Significant swelling, pain with weight bearing, sometimes pain at rest or at night. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 8
10 Complications If Left Unattended Untreated groin strains can lead to an awkward gait and chronic pain that could lead to injuries in other areas. A minor muscle tear could become more severe and eventually tear completely. Immediate Treatment RICER. Anti-inflammatory medication. For a Grade 3 strain it may be necessary to seek a medical evaluation. Rehabilitation and Prevention After initial treatment, minor strains will respond to a gradual stretching and strengthening programme. More serious strains will require additional rest and a slow entry back into activities with extra warm-up activities before each session. Prevention of groin strains requires warming- up properly before activities, stretching for good flexibility in the adductors and strengthening of the abductor muscles, adductor muscles, abdominals and hip flexors for good muscular balance. Long-Term Prognosis Most groin strains will heal with no lasting effects. Only the most severe strains, with complete tears, require surgical correction. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 9
11 Tendinitis of the Adductor Muscles Inflammation in the adductor muscle tendons or tendon sheaths due to overuse can cause pain in the groin area. Soccer, hurdling and horse riding can all cause overuse in these muscles. Unresolved injuries such as groin strain can also lead to tendinitis. The adductor muscles include the pectineus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, gracilis and adductor magnus and the tendons any of these may become inflamed. The pain is similar to a groin strain but onset is gradual and chronic in nature. Cause of Injury Repetitive stress to the adductor muscles. Previous injury such as groin strain. Tight gluteal muscles. Signs and Symptoms Pain in the groin area. Pain when bringing the legs together against resistance. Pain when running, especially sprinting. Complications If Left Unattended If left unattended, tendinitis of the adductor muscles can lead to imbalance and injury to the other muscles of the hip joint. It can also result in a tear of one or more of the adductor muscles. Immediate Treatment Ice and rest from activities that cause pain. Anti-inflammatory medication. Then heat and massage to promote blood flow and healing. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 10
12 Rehabilitation and Prevention Rehabilitation for tendinitis of the adductors starts with gradual reintroduction into activity with stretching and strengthening exercises for the affected muscles. Use heat packs on the affected area before exercise at first, then continue with good warm-up activities to make sure the muscles are ready for activity. Strengthening the adductors and stretching the opposing abductors will help prevent this injury from recurring. Rehabilitating all groin pulls and other hip injuries completely will also prevent problems with the adductors. Long-Term Prognosis Long-term problems are seldom seen with tendinitis of the adductor muscles after treatment. If pain and limited mobility in the hip persists, additional help may be required from a sports medicine specialist. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 11
13 Hamstring Strain A hamstring strain or pull is a stretch or tear of the hamstring muscles or tendons. This is a very common injury, especially in activities that involve sprinting or explosive accelerations. A common cause of a hamstring strain is muscle imbalance between the hamstring and quadriceps, with the quadriceps being much stronger. Any of the hamstring muscles can be strained. Commonly minor tears happen in the belly of the biceps femoris muscle closest to the knee. Complete tears or ruptures usually pull away from this attachment as well. Excessive force against the muscles, especially during eccentric contraction (when the muscle is contracting and lengthening against force) can cause stretching, minor tears or even complete rupture. Cause of Injury Strength imbalance between the hamstrings and quadriceps. Forceful stretching of the muscle, especially during contraction. Excessive overload on the muscle. Signs and Symptoms Grade 1: Mildly tender and painful. Little or no swelling. Full muscular strength. Grade 2: More marked pain and tenderness. Moderate swelling and possible bruising. Gait affected - limping. Grade 3 (full tear): Extreme pain. Marked swelling and bruising. Inability to bear weight. Complications If Left Unattended Pain and tightness in the hamstring muscles will get worse without treatment. Tightness in the hamstrings can lead to lower back and hip problems. Untreated strains can progress to a full rupture. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 12
14 Immediate Treatment Grade 1: Ice. Anti-inflammatory medication. Grades 2 and 3: RICER. Anti-inflammatory medication. Seek medical help if a complete rupture is suspected or if the patient is unable to walk unaided. Then heat and massage to promote blood flow and healing. Rehabilitation and Prevention Stretching after the initial pain subsides will help speed recovery and prevent future recurrences. Strengthening the hamstrings to balance them with the quadriceps is also important. When re-entering activity, proper warm-up must be stressed and a gradual increase in intensity is important. Long-Term Prognosis Hamstring strains that are rehabilitated fully seldom leave any lingering effects. Complete ruptures may require surgery to repair and long-term rehabilitation. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 13
15 Quadriceps Strain A forceful stretch or tear of the muscle or tendon in a weight-bearing muscle such as the quadriceps is painful and difficult to rest. The quadriceps are involved in supporting the hip and knee to hold the weight of the. A quadriceps strain can result from a forceful contraction of the quadriceps or unusual stress placed on the muscles. As with other strains it is graded 1 through 3, with 3 being the most severe tear. A strain may occur in any of the quadriceps muscles but the rectus femoris is most commonly injured. The force generated in activities such as playing soccer, sprinting, jumping and weight training may cause micro-tears in the muscle. When the muscle is stretched forcefully under a load as in high-impact sports like soccer and hockey it may also pull away from the muscle tendon junction or bony attachment or tear completely. Cause of Injury Forceful contraction or stretch of the quadriceps. Signs and Symptoms Grade 1: Mildly tender and painful. Little or no swelling. Full muscular strength. Grade 2: More marked pain and tenderness. Moderate swelling and possible bruising. Noticeable loss of strength. Grade 3 (full tear): Extreme pain. Deformity, swelling and bruising. Inability to contract the muscle. Complications If Left Unattended A grade 1 or 2 tear left unattended can continue to tear and become worse. A grade 3 tear left untreated can result in loss of mobility and a severe loss of flexibility in the muscle. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 14
16 Immediate Treatment RICER regimen. Anti-inflammatory medication. Immobilization in severe cases. Then heat and massage to promote blood flow and healing. Rehabilitation and Prevention After the required rest period, activities should be resumed cautiously. Avoid activities that cause pain. Stretching and strengthening of the quadriceps will be necessary. Ensuring a balance of strength between the quadriceps and hamstrings is important to prevent a strain. Proper warm-up techniques must be observed to prevent strains and gradually increasing intensity will help as well. Long-Term Prognosis Quadriceps strains seldom result in long-term pain or disability. Surgery is only needed in rare cases where a complete tear does not respond to immobilization and rest. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 15
17 Quadriceps Tendinitis Inflammation of the quadriceps tendon can be a result of repetitive stress to the quadriceps or excessive stress before the muscle is conditioned. Minor tears may occur in the tendon when it is stretched while subjected to loading. Pain just above the patella (kneecap), especially when extending (straightening) the knee, usually accompanies this injury. Cause of Injury Repetitive stress to the tendon, e.g. running or jumping. Repetitive acceleration and deceleration, e.g. soccer or hurdling. Untreated injury to the quadriceps. Signs and Symptoms Pain just above the patella. Jumping, running, kneeling or walking down stairs may aggravate the pain. Complications If Left Unattended The quadriceps muscles may become stiff and shortened and the tendon will become weak if left untreated. This could lead to a rupture of the tendon. A change in gait or landing form in the case of hurdlers can lead to other injuries as well. Immediate Treatment Rest and ice. Anti-inflammatory medication. Training modification. Rehabilitation and Prevention Rehabilitation should include stretching and strengthening exercises for the quadriceps. Activities such as swimming can be helpful to reduce the stress on the tendon during rehabilitation. Return to a normal activity schedule should be delayed until pain subsides completely and strength is restored. Keeping the quadriceps flexible and strong will help prevent this condition. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 16
18 Long-Term Prognosis A full recovery with no long-term disability or lingering effects can be expected in most cases of tendinitis, and surgery is only necessary in extremely rare cases. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 17
19 Soccer - Knee Like any running sport the knee is always vulnerable to injury. So we need to always be thinking about the stop-start and change of direction that soccer demands, and what that may mean for player s bodies. The strong powerful muscles of the thigh are always on high alert and are too often overlooked when asymptomatic. The battle between vastus medialis and lateralis should be high on the agenda. Hypertonicity to the short rectus femoris creates more compressive load to the patella; to the tibial condyles and grooves which it articulates. Always be on the lookout for resting knee discomfort in the sitting athlete. This is a sure indicator of increased hyper-tonicity in rectus femoris. The popliteus muscle is one of those muscles that can sneak under the radar. It is often a culprit for ongoing knee conditions. This is primarily due to its role in unlocking the knee when striding out into full extension, and the torque forces when changing direction. There is also its much debated attachment into the lateral meniscal line of the joint itself. Passing and striking the ball from the medial aspect of the foot adds that extra dimension of load to the muscles involved in this action - especially true for popliteus. Biceps femoris (short head) is a critical muscle in lateral knee dysfunction, notably with iliotibial band syndrome. Shortening via overload will create a torsional force at the distal attachment at the knee, placing excessive tendon load. The perilous overuse tendon injuries of the Achilles and deep toe flexors are also of concern once the load and endurance capabilities are exceeded. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 18
20 Anterior Collateral Ligament Sprain The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is commonly injured in sports where there are a lot of direction changes and possible impacts. Soccer, lacrosse and other fast-moving games often result in ACL sprains. The most common mechanism for this injury is when the knee rotates while the foot is planted. The stress can cause a tear in the ACL which can range from minor tearing of a few fibres to a complete rupture. It can also be torn as the result of a hard blow to the knee; usually other ligaments and the meniscus are involved. Sharp pain at the time of the injury accompanied by swelling in the knee joint may be a sign of an ACL tear. Cause of Injury Forceful twisting of the knee when the foot is planted. Occasionally a forceful blow to the knee, especially if the foot is fixed as well. Signs and Symptoms Pain immediately that may go away. Swelling in the knee joint. Instability in the knee, especially with the tibia. Complications If Left Unattended If left unattended this injury may not heal properly. Instability in the joint could lead to injury to other ligaments. Chronic pain and instability could lead to future limitations. Immediate Treatment RICER. Immobilization. Immediate referral to a sports medicine professional. rehabilitation and prevention Once stability and strength return and pain subsides, gradual introduction of activities such as stationary biking can be undertaken. Range of motion and strengthening exercises are an important part of rehabilitation. Swimming and other non-weight bearing exercise may be COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 19
21 used until the strength returns to normal. Strengthening the muscles of the quadriceps, hamstrings and calves will help to protect the ACL. Proper conditioning before beginning high-impact activities will also provide protection. Long-Term Prognosis ACL sprains that involve a complete tear often require surgery to reattach the ligament. Minor sprains can often be healed completely without surgery. Return to full activity may be a prolonged process and some activities may be limited. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 20
22 Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Pain in the patella (kneecap), especially after sitting for a long time or running downhill, may result from incorrect movement of the patella over the femur or tight tendons. The articular cartilage under the patella may become inflamed as well, leading to another condition called chondromalacia patellae which is found more commonly in women. The angle formed between the two lines of pull of the quadriceps muscle and the patellar (tendon) ligament is known as the Q-angle. If the patella moves out of its normal path, even slightly, it can cause irritation and pain. Tight tendons also place pressure on the patella causing inflammation. Cause of Injury Incorrect running form or improper shoes. Weak or tight quadriceps. Chronic patella dislocations. Signs and Symptoms Pain on and under the patella which worsens after sitting for extended periods or walking down stairs. Clicking or grinding may be felt when flexing the knee. Dull, aching pain in the centre of the knee. Complications If Left Unattended The inflammation from this condition if left unattended can worsen and cause more permanent damage to the surrounding structures. If the tendon becomes inflamed it could eventually rupture. The cartilage under the patella may also become inflamed. Immediate Treatment Rest and reducing exercise intensity and duration. Ice and anti-inflammatory medication. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 21
23 Rehabilitation and Prevention Rehabilitation starts with restoring the strength and flexibility of the quadriceps. When returning to activity after pain has subsided, gradual increases in intensity, limiting repetitive stresses on the knee and proper warm-up techniques will ensure that the pain does not return. Strong, flexible quadriceps and hamstrings and avoiding overuse will help prevent patellofemoral pain syndrome. A good warm- up before training will also help. Long-Term Prognosis With complete treatment there are seldom any long-lasting effects. If the condition does not respond to treatment surgical intervention may sometimes be required. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 22
24 Patellar Tendinitis Soccer and other activities that require repetitive jumping can lead to tendinitis in the patellar (tendon) ligament, also referred to as jumper s knee. The force placed on the tendon over time can lead to inflammation and pain. The pain is generally felt just below the patella (kneecap). Patellar tendinitis affects the teno-osseous junction of the quadriceps tendon as it attaches to the superior pole of the patella and the patellar (tendon) ligament as it attaches to the inferior pole of the patella and the tibial tuberosity. Pain is concentrated on the patellar (tendon) ligament but can also occur at the insertion of the patellar (tendon) ligament into the tibial tuberosity. The patellar (tendon) ligament is involved in straightening the knee. It is also the first area to experience shock when landing from a jump. It is forced to stretch as the quadriceps contracts to slow down the flexion of the knee. This repetitive stress can lead to minor trauma to the tendon which will lead to inflammation. Repetitive flexion and extension of the knee also place stress on this tendon if the tendon does not travel in the required path. Cause of Injury Repetitive jumping and landing activities. Running and kicking activities. Untreated minor injury to the patellar tendon. Signs and Symptoms Pain and inflammation of the patellar tendon, especially from repetitive or eccentric knee extension activity or kneeling. Swelling and tenderness around the tendon. Complications If Left Unattended As with most tendinitis, inflammation that is left untreated will cause additional irritation, setting up a vicious cycle. This can eventually lead to a rupture of the tendon. Damage to surrounding tissue may also occur. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 23
25 Immediate Treatment RICER. Anti-inflammatory medication. Rehabilitation and Prevention Stretching the quadriceps, hamstrings and calves will help relieve pressure on the patellar tendon. During rehabilitation it is important to identify the conditions that caused the injury in the first place. Thorough warm-up and proper conditioning can help prevent the onset of this condition. A support strap placed below the knee may be needed at first to support the tendon during the initial return to activity. Prevention of this condition requires strong quadriceps and a good balance of strength between the muscles that surround the knee. Long-Term Prognosis Complete recovery without lingering effects can be expected with rehabilitation and treatment. Occasionally it may return due to a weakened tendon, especially in older athletes. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 24
26 Soccer - Lower Limb Treating soccer players takes time and persistence. We have to look carefully at all the muscles of the leg that are intrinsically important to the function of the foot. Load issues of the prime plantar flexors, the explosive gastrocnemius, the never ending endurance required of the soleus muscles, then the deep toe flexors which are imperative to the foot function and load. Addressing load issues for the soleus and gastrocenemius muscles is vital. Once these muscles have become excessively loaded we start to see neuroplasticity changes as these prime dorsiflexors start to fatigue. This is were we start to see the beginnings of such conditions as medial tibial stress syndrome and, add as these deep toe flexors control foot position, this can also have dramatic effects for other key structures such as the achilles tendon. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 25
27 Calf Strain Failure to warm-up properly can lead to calf strains. The calf muscles are used when taking off during a sprint, jumping, changing directions or standing up from a deep squat. These are usually explosive movements requiring forceful contractions of the calf muscles. Strains can result from incorrect foot positioning during activity or an eccentric contraction beyond the strength level of the muscle. When taking off and changing direction the calf muscles are particularly vulnerable to tearing at their junction with the tendon. An eccentric contraction, a contraction while the muscle stretches such as when landing from a jump, can also cause a tear if the muscle is fatigued or not strong enough to bear the load placed on it. Cause of Injury Forceful contraction of gastrocnemius or soleus. Forceful eccentric contraction. Improper foot position when pushing off or landing. Signs and Symptoms Pain in the calf muscle, usually mid-calf. Pain when standing on tiptoes and sometimes pain when bending the knee. Swelling or bruising in the calf. Complications If Left Unattended Any strain left unattended can lead to a complete rupture. The calf muscles are used when standing and walking so pain can become disabling. A limp or change in gait due to this injury could lead to injury in other areas. Immediate Treatment RICER. Anti-inflammatory medication. Then heat and massage to promote blood flow and healing. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 26
28 Rehabilitation and Prevention As the pain subsides, a programme of light stretching may help facilitate healing. When the pain has subsided, strengthening and stretching will help to prevent future injury. Proper warm-up before activities will help protect the muscle from tears. Strong, flexible muscles resist strains better and recover more quickly. Long-Term Prognosis Muscle strains, when treated properly with rest and therapy, seldom have lingering effects. In very rare cases where the muscle detaches completely, surgery may be required to re-attach the muscle. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 27
29 Achilles Tendon Strain Achilles tendon strains can be very painful and require significant healing time. An injury to this tendon can be debilitating because of its involvement in walking and even balance during weight-bearing. Explosive activities such as sprinting and jumping, and activities that involve pushing against resistance such as weight training, contribute greatly to this injury. The strain can be graded on a scale from 1 to 3: Grade 1 strain: Stretching or minor tear of less than 25% of the tendon. Grade 2 strain: 25 75% tearing of the tendon fibres. Grade 3 strain: % rupture of the tendon fibres. Cause of Injury Abrupt, forceful contraction of the calf muscles, especially when the muscle and tendon are either cold or inflexible. Excessive force applied to the foot forcing the ankle upward into dorsiflexion. Signs and Symptoms Pain in the Achilles tendon, from mild discomfort in grade 1 strains to severe, debilitating pain in grade 3 strains. Swelling and tenderness. Pain when rising on the toes. Inability to bend the ankle. Stiffness in the calf and heel area after resting. Complications If Left Unattended A minor tear may become a complete rupture if left unattended. Bursitis and tendinitis may develop from the inflamed tendon rubbing over the heel. Immediate treatment COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 28
30 RICER. Anti-inflammatory medication. Then heat and massage to promote blood flow and healing. Immobilization and medical help for grade 3 strains. Rehabilitation and Prevention Rest is important and a gradual return to activity must be undertaken. Stretching and strengthening the calf muscles is important to rehabilitation and to prevent recurrence. Warming-up the calf muscles properly before all activities, especially those involving forceful contractions such as sprinting, is essential to prevent strains. Long-Term Prognosis Due to the lower blood supply in tendons, they take longer to heal than the muscle, but with rest and rehabilitation the Achilles tendon can return to normal function. Severe ruptures usually require surgical repair. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 29
31 Achilles Tendinitis The Achilles tendon crosses the back of the heel, which means it rides over the bone as the muscle contracts and stretches. Inflammation of the Achilles tendon can be very painful; all of the body s weight is supported by this structure and footwear often presses against this area. Repetitive stress to the tendon can lead to inflammation that causes additional irritation and further inflammation. Activities such as soccer, basketball, running, volleyball and other running and jumping sports can lead to Achilles tendinitis. Repetitive contraction of the muscles in the calf and improper footwear or excessive pronation of the feet can lead to inflammation in the tendon. Cause of Injury Repetitive stress from running and jumping activities. Improper footwear or awkward landing pattern of the foot during running. Untreated injuries to the calf or Achilles tendon. Signs and Symptoms Pain and tenderness in the tendon. Swelling may be present. Contraction of the calf muscle causes pain; running and jumping may be difficult. Complications If Left Unattended Inflammation in the tendon can lead to deterioration of the tendon and eventual rupture if left untreated. Inflammation may lead to tightening of the tendon and attached muscle which could lead to tearing. Immediate Treatment Rest, reducing or discontinuing the offending activity. Ice. Anti-inflammatory medication. Then heat and massage to promote blood flow and healing. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 30
32 Rehabilitation and Prevention After a period of rest, usually lasting 5 10 days, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can be initiated. Heat may be used on the tendon before activity to warm the tendon properly. Adequate warm-up, along with strengthening and stretching exercises for the calves, will help prevent tendinitis of the Achilles tendon. Long-Term Prognosis Tendinitis seldom has lingering effects if treated properly. Tendinitis may take from five days to several weeks to heal but rarely needs surgery to repair it. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 31
33 Ankle Sprain Anyone who plays soccer is susceptible to an ankle sprain, an acute injury to any or all of the ligaments that support the ankle structure. Tearing or stretching of the ligaments can occur when the foot is rolled or twisted forcefully. High-impact sports involving jumping, sprinting or running on changing or uneven surfaces often lead to ankle sprains. Basketball, football, cross country and hockey are a few of the other sports commonly associated with ankle sprains. Lateral ankle or inversion sprains commonly occur when stress is applied to the ankle during plantar flexion. The anterior talofibular ligament is most commonly injured. The medial malleolus may act as a fulcrum to further injure the calcaneofibular ligament if the strain continues. The peroneal tendons may absorb some of this strain. Medial ankle sprains are less common because of the strong deltoid ligament and bony structure of the ankle. When ligaments are stretched beyond their normal range some tearing of the fibres may occur. Cause of Injury Sudden twisting of the foot. Rolling or force to the foot, most commonly laterally. Signs and Symptoms First-degree sprains: Little or no swelling; mild pain and stiffness in the joint. Second-degree sprains: Moderate swelling and stiffness; moderate to severe pain; difficulty weight-bearing and some instability in the joint. Third-degree sprains: Severe swelling and pain; inability to weight-bear; instability and loss of function in the joint. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 32
34 Complications If Left Unattended Chronic pain and instability in the ankle joint may result if left unattended. Loss of strength and flexibility and possible loss of function may also result. Increased risk of re-injury. Immediate Treatment RICER. Second and third-degree sprains may require immobilization and immediate medical attention should be sought. Rehabilitation and Prevention Strengthening the muscles of the lower leg is important to prevent future sprains. Balance training will help to improve proprioception (the body s awareness of movement and joint position sense) and strengthen the weakened ligaments. Flexibility exercises to reduce stiffness and improve mobility are needed also. Bracing during the initial return to activity may be needed but should not replace strengthening and flexibility development. Long-Term Prognosis With proper rehabilitation and strengthening the athlete should not experience any limitations. A slight increase in the probability of injuring that ankle may occur. Athletes who continue to experience difficulty with the ankle may need additional medical interventions including, in rare cases, possible surgery to tighten the ligaments. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 33
35 Peroneal Tendinitis The tendons of peroneus longus and peroneus brevis run from the perineal muscles in the lateral calf to the foot. The perineal muscles are involved in stabilizing the foot and providing support to the ankle to prevent lateral rolling of the joint. Perineal tendinitis is most commonly a result of overuse of the perineal muscles or of inversion sprains which stretch the perineal tendons. It can be caused by excessive pronation of the foot as the perineal muscles have to work harder to stabilize the foot when it is pronated. Running and jumping involve repeated contraction of the perineal muscles and can lead to inflammation of their tendons. Soccer players who play often on uneven surfaces or have excessive pronation often develop perineal tendinitis. Cause of Injury Over-pronation of the foot during running or jumping. Prior ankle injury leading to an incorrect path of travel for the tendons. Signs and Symptoms Pain and tenderness along the tendons. Pain is most severe at the beginning of the activity and diminishes as the activity continues. Gradual increase in pain over time. Complications If Left Unattended Unattended tendinitis can lead to a complete rupture of the tendons. Perineal tendinitis can lead to subluxations. The chronic inflammation can also lead to damage to the ligaments surrounding the tendons. Immediate Treatment Rest, especially from running or jumping activities. Ice. Anti-inflammatory medication. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 34
36 Rehabilitation and Prevention Stretching of the calf muscles and a gradual reintroduction into activity is important for rehabilitation. During the recovery period it is important to identify and correct any foot or gait abnormalities that may be contributing to the problem. Prevention of this condition requires strong, flexible muscles of the lower leg to support the foot and ankle. Long-Term Prognosis With proper treatment, perineal tendinitis will usually heal completely with no lingering effects. In rare cases the tendinitis may not respond to traditional treatment and may require surgical intervention to relieve the pressure causing the inflammation. Orthotics to support the medial arch may be required in some cases. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 35
37 Soccer - Performance Therapy True high performance therapy starts with the premise that we can use our hands-on ability to help athletes perform better. This is all about us playing our part to allow our athletes to train and compete more efficiently. Flexibility screening is the most important part of this work. This is how we scrutinize for injury prevention; how we see ahead and help to avoid those injuries. We need to be the predictors of injury and we can usually do this by observing the smallest of changes in the athletes critical range of movement. A research study into hamstring injuries in Australian Rules Football (AFL) showed that the most common predictors for hamstring injury are: - 1. Age - 2. History of Injury - 3. Reduced dorsiflexion We regularly apply a regime of testing of our AFL athletes for dorsiflexion and then applying soft tissue protocols to help maintain a functional range of movement for both performance enhancement and injury prevention. Similarly, for soccer players, who have a high incidence of groin injuries due to the action of kicking across the body, we will regularly assess the balance between the hip adductors and abductors. Simply put, it s about being aware of how the athletes train and play, and testing and assessing continually for asymptomatic overload issues. Most of these can be addressed. COMMON SOCCER INJURIES 36
38 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES NIEL ASHER EDUCATION 37
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella)
 Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
What causes it? Sports experts believe that groin strains can be caused by a variety of different factors, including:
 Groin Strains A strain is often a bruise, stretching, or tearing of muscle fibres, which run from the front of the hip bone to the inside of the thigh. These 'hip-adductor' muscles, namely the adductor
Groin Strains A strain is often a bruise, stretching, or tearing of muscle fibres, which run from the front of the hip bone to the inside of the thigh. These 'hip-adductor' muscles, namely the adductor
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
Hamstring Strain. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints)
 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
(Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage)
 Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
Introduction. Anatomy
 the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome can be defined as a Retro-patellar (behind the
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome can be defined as a Retro-patellar (behind the
A Patient s Guide to Patellar Tendonitis
 A Patient s Guide to Patellar Tendonitis 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Patellar Tendonitis 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears
 Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Copyright Vanderbilt Sports Medicine. Table of Contents. The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2. What is Patellofemoral Pain?...4
 Table of Contents The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2 What is Patellofemoral Pain?....4 What to Expect From a Medical Evaluation....6 What to Expect After Therapy....7 1 The Kneecap and Knee Joint The knee
Table of Contents The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2 What is Patellofemoral Pain?....4 What to Expect From a Medical Evaluation....6 What to Expect After Therapy....7 1 The Kneecap and Knee Joint The knee
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents
 Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents Description Patella Instability is an injury to the kneecap (patella) affecting the joint it forms with the thigh bone (femur) Patella Instability can occur
Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents Description Patella Instability is an injury to the kneecap (patella) affecting the joint it forms with the thigh bone (femur) Patella Instability can occur
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee)
 Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Tibia: the second longest bone in the body
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
Anterior knee pain.
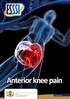 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Badminton. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Badminton Badminton's origin may be traced as far back as fifth century China when players would volley a
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Badminton Badminton's origin may be traced as far back as fifth century China when players would volley a
Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee
 Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome Ø The ITB is fascia, a connective tissue that gives structure to the body. Its function is to protect the knee from sideways movement
Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome Ø The ITB is fascia, a connective tissue that gives structure to the body. Its function is to protect the knee from sideways movement
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Injury Recovery and Prevention. ~Joshua Bowen
 Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
Dr. Gene Desepoli Anterolateral Shin Splints Summary Treatment Sheet
 Dr. Gene Desepoli Anterolateral Shin Splints Summary Treatment Sheet Pathology: Anterolateral shin splints results from strain to the tibialis anterior muscle from eccentric overuse, running on hard ground
Dr. Gene Desepoli Anterolateral Shin Splints Summary Treatment Sheet Pathology: Anterolateral shin splints results from strain to the tibialis anterior muscle from eccentric overuse, running on hard ground
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING. dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K)
 SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY
 Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Make sure you have properly fitting running shoes and break these in gradually. Never wear new running shoes for a race or a long run.
 Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
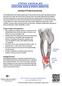 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION
 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
Common Knee Injuries
 Common Knee Injuries In 2010, there were roughly 10.4 million patient visits to doctors' offices because of common knee injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and ligament tears. Knee injury
Common Knee Injuries In 2010, there were roughly 10.4 million patient visits to doctors' offices because of common knee injuries such as fractures, dislocations, sprains, and ligament tears. Knee injury
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
 ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
Patellar Instability. OrthoInfo Patella Instability Page 1 of 5
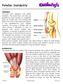 Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Knee Pain. Pain in the pressure on. the kneecap. well as being supported (retinaculum) quadricep. Abnormal. to the knee. or dislocate.
 Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
A Patient s Guide to Patellar Tendonitis
 A Patient s Guide to Patellar Tendonitis Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can better understand
A Patient s Guide to Patellar Tendonitis Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can better understand
SPORTSSOCIETY Developing attractive and dynamic societies via sports Project Nr: CB67. Preventative and rehabilitation exercises of sports injures
 Preventative and rehabilitation exercises of sports injures Diagnosis: Plantar Facitis What is Plantar Facitis? Plantar fascitis(pf) is a painful inflammatory process of the plantar fascia, the connective
Preventative and rehabilitation exercises of sports injures Diagnosis: Plantar Facitis What is Plantar Facitis? Plantar fascitis(pf) is a painful inflammatory process of the plantar fascia, the connective
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These
Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
What is an ACL Tear?...2. Treatment Options...3. Surgical Techniques...4. Preoperative Care...5. Preoperative Requirements...6
 Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
A Patient s Guide to Quadriceps Tendonitis
 A Patient s Guide to Quadriceps Tendonitis 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Quadriceps Tendonitis 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
ANKLE SPRAINS. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
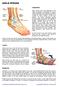 ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. The Femur. Quadriceps 12/11/2017
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Thigh, Hip, Groin, and Pelvis Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas The Femur Is the longest and the second strongest bone in the body and is designed to permit maximum
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Thigh, Hip, Groin, and Pelvis Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas The Femur Is the longest and the second strongest bone in the body and is designed to permit maximum
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS
 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
Everything. You Should Know. About Your Ankles
 Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
 UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS
 SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
Human anatomy reference:
 Human anatomy reference: Ankle Restriction: Ankle restriction usually occurs due to poor mechanics which may have developed from a trauma or excessive use into compression such as running or being overweight.
Human anatomy reference: Ankle Restriction: Ankle restriction usually occurs due to poor mechanics which may have developed from a trauma or excessive use into compression such as running or being overweight.
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE
 POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Expected Outcome. Causes
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome This article is also available in Spanish: El síndrome de dolor patelofemoral (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome) (topic.cfm?topic=a00763). Patellofemoral pain syndrome is a broad
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome This article is also available in Spanish: El síndrome de dolor patelofemoral (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome) (topic.cfm?topic=a00763). Patellofemoral pain syndrome is a broad
Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, MD
 ACHILLES TENDINITIS Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, MD ANATOMY The Achilles tendon is a strong tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel. When the calf muscles contract, they pull on the Achilles tendon
ACHILLES TENDINITIS Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, MD ANATOMY The Achilles tendon is a strong tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel. When the calf muscles contract, they pull on the Achilles tendon
Post-Operative Physical Therapy Protocol for Autograft ACL Reconstruction
 Adam J. Farber, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Board Certified; Fellowship-trained in Sports Medicine & Arthroscopic Surgery P: 480-219-3342; F: 480-219-3271 Post-Operative Physical Therapy
Adam J. Farber, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Board Certified; Fellowship-trained in Sports Medicine & Arthroscopic Surgery P: 480-219-3342; F: 480-219-3271 Post-Operative Physical Therapy
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome The foot is subjected to forces hundreds of times the bodyweight, thousands of times
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome The foot is subjected to forces hundreds of times the bodyweight, thousands of times
A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems
 A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE
 TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
Hip Strains. Anyone can experience a hip strain just doing everyday tasks, but strains most often occur during sports activities.
 Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Pilates for an Endurance Triathlete
 Pilates for an Endurance Triathlete with special focus on Achilles Tendonitis and Posterior Tibialis Tendonitis Danielina Snyman June 7, 2014 CTTC 2014 Chicago, Il Abstract Triathlon is a physical demanding
Pilates for an Endurance Triathlete with special focus on Achilles Tendonitis and Posterior Tibialis Tendonitis Danielina Snyman June 7, 2014 CTTC 2014 Chicago, Il Abstract Triathlon is a physical demanding
Knee Conditioning Program
 Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears
 WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY ORTHOPEDICS Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears Knowing what to expect for ACL surgery is key for a healthy surgery and recovery. Our sports medicine specialists are committed
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY ORTHOPEDICS Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears Knowing what to expect for ACL surgery is key for a healthy surgery and recovery. Our sports medicine specialists are committed
A Patient s Guide to Collateral Ligament Injuries
 A Patient s Guide to Collateral Ligament Injuries 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
A Patient s Guide to Collateral Ligament Injuries 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
Knee Pain Solutions. Assess Your Pain. Make a Plan. Take Action
 Knee Pain Solutions Assess Your Pain Make a Plan Take Action By Jared Evans Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist Giammalva Fitness Director There are many different causes of knee pain and understanding
Knee Pain Solutions Assess Your Pain Make a Plan Take Action By Jared Evans Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist Giammalva Fitness Director There are many different causes of knee pain and understanding
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Human anatomy reference:
 Human anatomy reference: Weak Glut Activation Weak gluteal activation comes from poor biomechanics, poor awareness when training or prolonged exposure in deactivated positions such as sitting. Weak Glut
Human anatomy reference: Weak Glut Activation Weak gluteal activation comes from poor biomechanics, poor awareness when training or prolonged exposure in deactivated positions such as sitting. Weak Glut
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis
 Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM
 KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
 GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
right Initial examination established that you have 'flat feet'. Additional information left Left foot is more supinated possibly due to LLD
 Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
Marathon Running & Knee Injuries
 Marathon Running & Knee Injuries Mr Sanjiv Jari Consultant Knee, Lower Limb & Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Surgeon Honorary Clinical Lecturer, University of Manchester. www.thekneedoc.co.uk www.sportmedclinic.com
Marathon Running & Knee Injuries Mr Sanjiv Jari Consultant Knee, Lower Limb & Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Surgeon Honorary Clinical Lecturer, University of Manchester. www.thekneedoc.co.uk www.sportmedclinic.com
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Meniscal Repair The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Trigger Point Management
 Trigger Point Management What is a Trigger Point (TrP)? Ø A trigger point is a hyperirritable spot located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. They may form following a sudden trauma or may develop on a
Trigger Point Management What is a Trigger Point (TrP)? Ø A trigger point is a hyperirritable spot located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. They may form following a sudden trauma or may develop on a
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
Dynamic Flexibility and Mobility
 Dynamic Flexibility and Mobility Below is the standard dynamic flexibility series. Your workout should have a prescribed warm-up, but if it doesn't a three minute total body warm-up, (i.e., jogging, rope
Dynamic Flexibility and Mobility Below is the standard dynamic flexibility series. Your workout should have a prescribed warm-up, but if it doesn't a three minute total body warm-up, (i.e., jogging, rope
Common Sports Injuries 1. Ankle Sprain Prevention:
 Common Sports Injuries This guide is intended to help coaches treat, prevent, and speed recovery in their athletes. The most common 10 injuries are covered below. They include ankle sprain, groin pull,
Common Sports Injuries This guide is intended to help coaches treat, prevent, and speed recovery in their athletes. The most common 10 injuries are covered below. They include ankle sprain, groin pull,
Property of Latmedical, LLC.
 Dedicate to providing a strong product mix, Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine,
Dedicate to providing a strong product mix, Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine,
ACTIVITIES AND EXERCISES AFTER INJURY TO THE MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT (MCL) OF THE KNEE
 ACTIVITIES AND EXERCISES AFTER INJURY TO THE MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT (MCL) OF THE KNEE PHASE 1: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY (grade 2 and 3) THREE WEEKS AFTER INJURY (grade 1) The knee should be
ACTIVITIES AND EXERCISES AFTER INJURY TO THE MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT (MCL) OF THE KNEE PHASE 1: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY (grade 2 and 3) THREE WEEKS AFTER INJURY (grade 1) The knee should be
Guide to Prevention of Sports Injuries
 Guide to Prevention of Sports Injuries Maintaining an active lifestyle offers a number of benefits for your physical and mental health. While exercise and sports-related activities often have a positive
Guide to Prevention of Sports Injuries Maintaining an active lifestyle offers a number of benefits for your physical and mental health. While exercise and sports-related activities often have a positive
ACHILLES TENDON DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO ACHILLES TENDON DISORDERS An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What is the Achilles Tendon?.....................................
MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO ACHILLES TENDON DISORDERS An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What is the Achilles Tendon?.....................................
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
How do you do exercises for patellar tracking disorder?
 To print: Use your web browser's print feature. Close this window after printing. Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Table of Contents Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Patellar Tracking Disorder:
To print: Use your web browser's print feature. Close this window after printing. Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Table of Contents Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises Patellar Tracking Disorder:
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
