AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
|
|
|
- Clifford Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CORONAL ALIGNMENT AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT ROBERT S. JEFFERY, RICHARD W. MORRIS, ROBIN A. DENHAM From Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth Maquet s line passes from the centre of the femoral head to the cenfre of the body of the talus. The distance of this line from the centre of the knee on a long-leg radiograph provides the most accurate measure of coronal alignment. Malalignment causes abnormal forces which may lead to loosening after knee replacement. We report a series of 115 Denham knee replacements performed between 1976 and 1981 using the earliest design of components, inserted with intramedullary guide rods. Patients were assessed clinically and long-leg standing radiographs were taken before operation, soon after surgery and up to 12 years later. In two-thirds of the knees (68%) Maquet s line passed through the middle third of the prosthesis on postoperative films and the incidence of subsequent loosening was 3%. When Maquet s line was medial or lateral to this, an error of approximately ± 3#{176}, the incidence of loosening at a median period of eight years was 24%. This difference is highly significant (j =.1). Accurate coronal alignment appears to be an important factor in prevention of loosening. Means of improving the accuracy of alignment and of measuring it on long-leg radiographs are discussed. On an anteroposterior long-leg radiograph, a line from the centre of the femoral head to the centre of the body of the talus normally passes through the middle third of the knee (Maquet 1972). If this is not the case after total knee replacement, compression forces on the concave side and tensile forces on the convex side of the joint may lead to loosening (Denham and Bishop 1978). Bargren, Blaha and Freeman (1983) have demonstrated in cadaver studies that eccentric loading of the tibial component caused failure at between a third and a half of the force required to produce failure by central loading, depending on the type of prosthesis and the position of the load. In the clinical situation, malaligned prostheses are subjected to cyclical eccentric loading. At total knee replacement, it is difficult to obtain consistently acceptable tibiofemoral alignment by eye because of the tourniquet, drapes and subcutaneous fat. Externaijigs or intramedullary guide rods are required. R. S. Jeffery, FRCS, Orthopaedic Registrar R. A. Denham, FRCS, Emeritus Consultant Department of Orthopaedics, Queen Alexandra Hospital, Cosham, Portsmouth, Hampshire P6 3LY, England. R. W. Morris, MSc, Lecturer in Medical Statistics Department of Public Health Medicine, United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals, Guy s Hospital, London Bridge, London SE1 9RT, England. Correspondence should be sent to Mr R. Jeffery British Editorial Society ofbone and Joint Surgery 31-62X/91/5l85 $2. JBoneJoint Surg[Br] 1991 ; 73-8: We have studied 1 15 Denham knee replacements aligned with intramedullary guide rods, performed between 1976 and Full-length standing radiographs were taken before operation, postoperatively and on alternate years thereafter. Maquet s line was used to assess coronal alignment on all these films and the results have been related to the incidence of loosening after a median follow-up period of eight years. PATIENTS From 1976 to April 1981, a total of 139 Denham total knee replacements were performed at Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth under the care of the senior author (RAD) using the original pattern of components and a standard technique. Of these, one patient with bilateral prostheses emigrated and the radiographs of one patient (2 knees) have been lost. In 2 knees long-leg alignment radiographs were not taken before or after operation. For 13 knees pre-operative radiographs were not taken because the patients were unable to stand or had fixed knee flexion of more than 2#{176}. No postoperative standing radiographs were made of eight knees because of infection or poor general condition. There was one postoperative death due to pulmonary embolus. Excluding these 24 knees, the study included full prospective records for 12 patients with 115 prostheses. Details are given in Table I. All patients were followed VOL. 73-B, No. 5, SEPTEMBER
2 71 R. S. JEFFERY, R. W. MORRIS, R. A. DENHAM up until revision, death or a minimum of eight years postoperatively. Forty-four patients died from causes unrelated to their knee replacement, the surviving 58 patients were contacted (68 knees). METHODS Operative technique. The Denham knee replacement uses intramedullary guide rods to achieve coronal alignment (Thacker and Fulford 1986). The femoral template has an 18 cm intramedullary stem and the femoral component has a similar intramedullary stem, tapering from a 3 mm x 1 mm oval to a 5 mm x 5 mm square section. The instruments used for preparation of the tibial plateau include an intramedullary guide rod : the tibial component has a central hole which admits a full-length 6 mm diameter intramedullary guide rod, which is removed when the cement has set (Fig. 1). Table I. Details of the series of 12 patients with 115 knee replacements Female : male 85:17 OA:RA 5:52 Age at operation (years) Median (range) 66 (21 to 85) Interquartile range 6 to 71 Previous reconstructive surgery Knee replacement 5 Tibial osteotomy 3 Benjamin osteotomy 4 Hip replacement 3 Hiparthrodesis I Fig. I The tibial component with a removable intramedullary guide rod, and two views ofthe femoral component. Abnormal femoral or tibial diaphyses Abnormal bowing 2 Previous fracture 2 Length of follow-up (years) Median (range) 8 ( to 12) Interquartile range 4 to 1 one patient also had a femoral osteotomy Follow-up. The patients had been assessed clinically and radiographically pre-operatively, postoperatively and on alternate years until they died or until the prosthesis was removed. All patients who were too old or frail to attend were contacted at the time of the review to establish whether the knee was pain free, and whether function and movement had remained the same or had deteriorated. ning of the tibial component was defined as occurring when there was pain associated with a fracture in the cement or an increasing radiolucent line. Alignment radiographs. The patient stands, trying to take weight equally on both feet, with the knees in maximal extension, and positioned to face the X-ray tube at a distance of 18 cm. A 1 ma,.5 second exposure is used at 1 to 115 kv, depending on leg thickness. The 15 cm X 35.5 cm Cronex film (DuPont) varies from Fig. 2 Measurements on an alignment radiograph. THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
3 CORONAL ALIGNMENT AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT 711 High Plus, through Standard, to High Definition so that a single exposure will produce optimal images of the hip, knee and ankle. Each long film is displayed on a large viewing screen Table II. Alignment data Variation of tibiofemoral angle from 7#{176} valgus (degrees) U Maquet s line passes within the middle third of the knee. Maquet s line passes through the knee. E Maquet s line passes outside the knee. Distance of Maquet s line from the centre of the knee (mm) Mean (SD) Mean (SD) Pre-operative (n = 1 1 5) 12.4 (8.9) 42 (32) Postoperative (n = 1 1 5) 2.6 (2. 1) 9 (9) 8-to 12yearfollowup(n52) 3.3(3.4) 11 (12) and the mid-medullary lines of the femur and of the tibia are drawn, passing through points which bisect the diameter of the bone at a quarter of its length from each end. Maquet s line is drawn from the centre of the femoral head to the centre of the body of the talus. Measurements are then made of the tibiofemoral angle and of the distance (D) from the centre of the tibia! plateau to Maquet s line (Fig. 2). The radiographic image of the tibia! prosthesis is 7 mm wide, so Maquet s line passes through the middle third of the knee when the distance D is 1 1 mm or less ; D is recorded as negative for varus angulation and positive for va!gus. An error of rotation of the limb of up to 2#{176} during radiography introduces a projectiona! error of less than 2#{176} in the tibiofemoral angle, provided that the knee is fully extended (RWM). The combination ofrotation and knee flexion may introduce much larger errors. All leg alignment films should therefore be taken in maxima! extension ; a lateral view was taken in this position in each case, to confirm that the alignment film was acceptable PREOPERATIVE (n115) of knees Table III. Pre-operative deformity related to postoperative angulation Postoperative tiblofemoral e (degrees) Pre-operative tibiofemoral angle(degrees) Mean (SD) > 3 varus valgus (3.7) 3 valgus to 3 varus valgus (3.2) 4to lvalgus(normal) valgus (3.1) 1 1 to 17 valgus valgus (3.4) > 17 valgus valgus (2.9) one way analysis of variance p = YEARS ( n 52) knees to to to to to to to to to to to to to to to to Varus TIBIAL COMPONENT Valgus h_ Fig. 3 D(mm) Alignment before and after operation and at a minimum of eight years postoperatively, related to the width of the tibial component. In order to calculate the error due to measurement of the same angle on different films, we recorded the angle between the femoral mid-medullary line and a line from the centre of the femoral head to the centre of the knee. This should remain constant if the shape and rotation of the femur is unchanged. RESULTS Alignment. Before operation, Maquet s line passed through the middle third of the knee in only 13% of the 1 15 radiographs. After operation, this was true of 68% of the early radiographs and 65% of those taken at more than eight years after knee replacement (Table II and Figure 3). In these cases the corresponding tibiofemoral angle was from about 4#{176} to about 1#{176} valgus. The standard deviation for the measurement of the same angle on different films ofthe same patient was.8#{176}. Table III shows that failure to achieve accurate VOL. 73-B, No. 5, SEPTEMBER 1991
4 712 R. S. JEFFERY, R. W. MORRIS, R. A. DENHAM alignment in this early series occurred mostly in patients with pre-operative varus deformity. Twenty patients had bowing or malunited fractures of the tibia! or femoral shaft or had had previous reconstructive operations (Table I). In ten of these (5%), Maquet s line passed outside the middle third of the knee postoperatively and in four it was over 23 mm from the centre of the tibia! plateau. Subsequent loosening. Eleven of the 1 15 knees (1%) had either been revised for loosening or showed definite clinical and radiological signs of loosening at follow-up. Only two of the 1 1 knees which loosened had been correctly aligned postoperatively (Fig. 4). We found no overallassociation between subsequent loosening and pre-operative malalignment, but there was a strong association with poor postoperative alignment (p =.1, Tables IV and V). When divided according to diagnosis and varus or valgus malalignment (Tables VI and VII), there was a difference between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis but this was not significant (p =.9). Knees with varus deformity pre-operatively were more likely to loosen than those with valgus Table IV. Pre-operative alignment related to subsequent loosening Maquet s line ning the middle third 15 1 (7%) Valgus or varus 1 1(1%) Total p = 1. (Fisher s exact test) Table V. Postoperative alignment related to subsequent loosening Maquet s line ning middle third 78 2(3%) Valgusorvarus 37 9(24%) Total p =.1 (Fisher s exact test) of knees U Prostheses which loosened Prostheses which did not loosen Table VI. Pre-operative alignment related to diagnosis and loosening Maquet s line Osteoarthritls Rheumatoid Nwnber Varus middlethird Valgus arthritis ning : varus versus valgus, p =.5 ; osteoarthritis versus rheumatoid arthritis, p =.9 (Fisher s exact test). < >35 to to to to to to Varus Valgus I TIBIAL Postoperative D (mm) Fig. 4 _ COMPONENT Postoperative alignment related to subsequent loosening. (p =.5), but postoperatively the difference was not significant. The association of loosening with postoperative malalignment was independent of pre-operative deformity (stratified chi-squared = 9.43, 2 df; p <.1, Table VIII). Conversely, when corrected for postoperative alignment, the effect of pre-operative deformity was not significant (stratified chi-squared = , 2 df; p >.5). Clinical review. Forty-one patients with 49 prostheses were reviewed clinically and radiographically eight to 12 years postoperatively (RSJ). Scores for pain, function and the findings on examination were added to give the BASK score (Aichroth et a! 1978). We found no independent relationship between either the early postoperative or the present alignment and the BASK score, although the two loose, unrevised prostheses were painful and had the lowest marks (Fig. 5). A low score for function often reflected general disability rather than an unsuccessful operation. Complications. The only major complications other than THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
5 CORONAL ALIGNMENT AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT 713 Table VII. Postoperative alignment related to diagnosis and loosening Osteoarthrith Rheumatoid arthritis (3) and poor postoperative alignment : Maquet s line was outside the middle third of the prosthesis in five of the 11 available postoperative ifims. Maquet s line Nwnber Varus middle third Valgus ning : varus versus valgus, p =.28 ; varus versus middle third, p=o.4; valgusversusmiddlethird, p =.26 (Fisher s exact test) Table VIII. Pre-operative and postoperative deformity related to loosening Postoperative Pre-operative Vanis middle third Nwnber Varus middlethird Valgus in >- Cl) Cl) #{149}#{149} #{149}:#{149},s Postoperative : Varus Fig. 5 D (mm) BASK knee score at eight- to 12-year follow-up related to postoperative alignment. loosening were one case of infection and one of severe translocation. One knee showed loosening ofthe femoral as well as the tibial component. In the 24 knee replacements performed during the same period and excluded from the main study for the reasons given previously, there were three cases of loosening, three of infection and one of translocation. Since 13 of these cases were excluded because of severe pre-operative deformities, it is of interest to note that they had a disproportionately high rate of both loosening Valgus DISCUSSION Measurement of alignment. Short-arm goniometers (Tew and Waugh 1985) and short radiographs (Bonnici and Allen 1991) are accurate only to 5#{176}. When the patient is carefully positioned and the knee is in full extension, fulllength standing radiographs can be used to measure tibiofemoral angles to within 2#{176}. Measuring this angle to 5#{176} accuracy would not appear to be sufficiently precise to detect the moderate degree of malalignment which can affect the result. ning and postoperative alignment. Some previous studies have included moderately malaligned knees within the range regarded as acceptable. This obscures the effect of minor degrees of malalignment, though clearly showing major errors. Bargren et a! (1983) found an 1 1% failure rate in 18 knees between 1#{176} and 15#{176} valgus and an 86% rate in 14 knees outside this range. Our study has shown a clear association between minor degrees of postoperative malalignment and subsequent loosening. Intramedullary guide rods. Our study has shown that intramedullary guide rods can restore the tibiofemoral angle with reasonable accuracy in otherwise normal limbs. Whiteside (1989) reported achieving a tibiofemoral angle of between 4#{176} and 1#{176} valgus in 87% of 226 prostheses using an intramedullary system. Manning,.,. Elloy and Johnson (1988) reported 73% within 3#{176} of the mechanical axis, also using intramedullary guide rods... In our series, before the modified tibia! components were introduced, Maquet s line was within the middle third of the prosthesis in 68% of postoperative films. For patients who have had previous surgery or have bony deformity, special precautions are needed, including careful study oflong-leg radiographs. Improvementsto the prosthesis and technique. At operation it is important to locate accurately the surface marking Valgus of the mid-medullary canal on the articular surface. Better alignment would be possible with a longer intramedullary guide rod and a wider tip for the femoral stem ; but greater length might compromise a future hip replacement. The post-1981 design of the femoral stem has a wider tip and might be further improved by a centring device. The largest size of prosthesis which can be accommodated should be used ; this increases the width ofthe middle third. We feel that the added complexity of using femoral stems with varied angles is not justified ; the angle between the line ofthe femoral shaft and the line between the centres of the hip and knee was between 6#{176} and 8#{176} valgus in 87% of our pre-operative radiographs. Because of the poor correction of severe preoperative deformity in some early cases, modified tibia! components were introduced. These had a 1 5#{176} or 3#{176} VOL. 73-B, No. 5, SEPTEMBER 1991
6 714 R. S. JEFFERY, R. W. MORRIS, R. A. DENHAM polyethylene wedge on the undersurface to reduce the need for a wedge of cement on an eroded tibia! condyle. This wedge ofcement may fracture and lead to loosening. A 2#{176} or 4#{176} inclination of the surface of the plateau was later added to these special prostheses to overcompensate for severe pre-operative deformity. A permanent tibia! intramedullary stem is now used for cases with major instability. Who needs alignment radiographs? Alignment radiographs are expensive, bulky to store and time-consuming to measure, but they are essential in the development and assessment of prosthetic design. In clinical practice, these radiographs are necessary for patients with bony deformity or a previous operation. In all cases, a single postoperative alignment radiograph is valuable for audit and prognosis. CONCLUSIONS The theoretical need for Maquet s line to pass through the middle third of the knee is recognised. This corresponds to an error of up to 3#{176} from the normal tibiofemoral angle of 7#{176} valgus. In practice, a much wider range of angles has been regarded as acceptable. Our results for the Denham prosthesis confirm that there is a highly significant increase in loosening of the tibia! component when Maquet s line does not pass through the middle third of the knee. Intramedullary guide rods are one of the best available methods of alignment, and enabled us to achieve this higher standard in over two-thirds of postoperative radiographs. Since the reported series, modifications to the prosthesis and technique have improved accuracy in difficult cases. Careful study of long-leg radiographs and the selective use of special components are necessary for patients with previous injuries, operations or deformities of the lower limb. We thank Mr Wai Ng for his assistance with statistical presentation, Mrs L Blackwell and Mrs C McBride for clerical help, the photography and radiology departments at Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth and the medical illustration department at Southampton General Hospital. One or more of the authors have received or will receive benefits for personal or professional use from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. In addition benefits have also been or will be directed to a research fund, foundation, educational institution, or other non-profit institution with which one or more of the authors is associated. REFERENCES Aichroth P, Freeman MAR, Smillie IS, Souter WA. A knee function assessment chart. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1978 ; 6-B :38-9. Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MAR. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty : correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. ClinOrthop 1983; 173: Bonnici AV, Allen PR. Comparison of long leg and simple knee radiographs in assessment of knees prior to surgery. J Bone Joint Surg[Br] 1991 ; 73-B Supp 1:65. Denham RA, Bishop RED. Mechanics of the knee and problems in reconstructive surgery. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1978 ; 6-B : Manning M, Elloy M, Johnson R. The accuracy of intramedullary alignment in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1988; 7-B :852. Maquet P. Biom#{233}canique de la gonarthrose. Ada Orthop Beig 1972; 38 :Suppl.I :S33-S54. Tew M, Waugh W. Tibiofemoral alignment and results of knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1985 ; 67-B : Thacker C, Fulford P. Assessment of the Denham knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1986; 68-B :6-7. Whiteside LA. Intramedullary alignment of total knee replacement : a clinical and laboratory study. Orthop Rev Suppi 1989; 18:9-12. THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements:
 Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Preoperative Planning. The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to:
 Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
THE P.F.C. SIGMA FEMORAL ADAPTER. Surgical Technique
 THE P.F.C. SIGMA FEMORAL ADAPTER Surgical Technique Contents P.F.C. Sigma Femoral Adapter and Revision Knee Surgery Introduction 2 Preoperative Planning 2 Overview 3 Surgical Technique Preparation of the
THE P.F.C. SIGMA FEMORAL ADAPTER Surgical Technique Contents P.F.C. Sigma Femoral Adapter and Revision Knee Surgery Introduction 2 Preoperative Planning 2 Overview 3 Surgical Technique Preparation of the
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE SKS Total Knee Replacement
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE SKS Total Knee Replacement Femoral preparation A40577 1 2 5 1: Alignment rod A30049 + A30124 2: Centromedullary rod A40224 4: T-handle A40232 6: Femoral measuring device A40411 + A40414
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE SKS Total Knee Replacement Femoral preparation A40577 1 2 5 1: Alignment rod A30049 + A30124 2: Centromedullary rod A40224 4: T-handle A40232 6: Femoral measuring device A40411 + A40414
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Proximal Tibia Vara
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:458-464 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458 Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:458-464 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458 Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee
Masterclass. Tips and tricks for a successful outcome. E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter. September 15th, 2012, Brussels
 Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
VerSys 6 Beaded FullCoat Plus Hip Prosthesis
 VerSys 6 Beaded FullCoat Plus Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Stability without compromise VerSys 6 Beaded FullCoat Plus Hip Prosthesis 1 Surgical Technique For VerSys 6 Beaded FullCoat Plus Hip Prosthesis
VerSys 6 Beaded FullCoat Plus Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Stability without compromise VerSys 6 Beaded FullCoat Plus Hip Prosthesis 1 Surgical Technique For VerSys 6 Beaded FullCoat Plus Hip Prosthesis
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Knee Revision. Portfolio
 Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular Femoral Deformity and/or Retained Hardware
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
U2 PSA. Revision Knee. Surgical Protocol
 U2 PSA TM Revision Knee Surgical Protocol Table of Contents 1 Component Removal... 1 2 Tibial Preparation... 1 2.1 Tibial Canal Preparation... 1 2.2 Proximal Tibial Resection... 2 2.3 Non Offset Tibial
U2 PSA TM Revision Knee Surgical Protocol Table of Contents 1 Component Removal... 1 2 Tibial Preparation... 1 2.1 Tibial Canal Preparation... 1 2.2 Proximal Tibial Resection... 2 2.3 Non Offset Tibial
Important notice: the device(s) can be prescribed and implanted only by a doctor legally authorized to perform this type of surgery.
 rev.10 CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH - EVOLIS/GMK KNEE PROSTHESIS - INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can be prescribed
rev.10 CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH - EVOLIS/GMK KNEE PROSTHESIS - INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can be prescribed
Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and Varus Knee Deformity Based on Two-Dimensional Assessment of Side-to-Side Differences
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy
 Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy LATERAL RELEASE IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FOR A FIXED VALGUS DEFORMITY J. Brilhault, S. Lautman, L. Favard, P. Burdin From Trousseau University Hospital of Tours, France
Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy LATERAL RELEASE IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FOR A FIXED VALGUS DEFORMITY J. Brilhault, S. Lautman, L. Favard, P. Burdin From Trousseau University Hospital of Tours, France
Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates!
 7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year
 Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury
 Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis*
 Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
Metal block augmentation for bone defects of the medial tibia during primary total knee arthroplasty
 Tsukada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:36 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Metal block augmentation for bone defects of the medial tibia during primary total knee arthroplasty Sachiyuki
Tsukada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:36 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Metal block augmentation for bone defects of the medial tibia during primary total knee arthroplasty Sachiyuki
Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA)
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22 (1 Suppl): 83-89 Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) F. TIAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22 (1 Suppl): 83-89 Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) F. TIAN
Intramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane
 KNEE Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane A COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL AND COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY IN AN ASIAN POPULATION T.-W. Huang, W.-H. Hsu, K.-T.
KNEE Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane A COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL AND COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY IN AN ASIAN POPULATION T.-W. Huang, W.-H. Hsu, K.-T.
Massive Varus- Overview. Massive Varus- Classification. Massive Varus- Definition 07/02/14. Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR
 07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Assessment of radiolucent lines around the Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement
 KNEE Assessment of radiolucent lines around the Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY FOR LOOSENING S. Kalra, T. O. Smith, B. Berko, N. P. Walton From Norfolk and Norwich
KNEE Assessment of radiolucent lines around the Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY FOR LOOSENING S. Kalra, T. O. Smith, B. Berko, N. P. Walton From Norfolk and Norwich
ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. 5 in 1. Conventional instrumentation 07/11/2013
 ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5 in 1 Conventional instrumentation PRO.GB.933/1.0 Octobre 2013 2 Tibial step 3 Intramedullary technique - Based on the preoperative plan, drill the medullary canal with the
ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5 in 1 Conventional instrumentation PRO.GB.933/1.0 Octobre 2013 2 Tibial step 3 Intramedullary technique - Based on the preoperative plan, drill the medullary canal with the
Alignment Rod. For intraoperatively confirming correction of the mechanical leg axis.
 Alignment Rod. For intraoperatively confirming correction of the mechanical leg axis. Easy to use Accuracy of surgery Reduces X-ray exposure Table of Contents Introduction Alignment Rod 2 Handling Technique
Alignment Rod. For intraoperatively confirming correction of the mechanical leg axis. Easy to use Accuracy of surgery Reduces X-ray exposure Table of Contents Introduction Alignment Rod 2 Handling Technique
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity
 ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY
 1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
Instructional Course Lecture 2011
 Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
Total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted navigation in patients with deformities of the femur and tibia: A report of 5 cases
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery July 2005 Total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted navigation
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery July 2005 Total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted navigation
Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment
 119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE
 DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis. Surgical Technique
 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique 1 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative
VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique 1 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative
Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
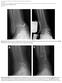 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
THE NATURAL FIT. Surgical Technique. Hip Knee Spine Navigation
 THE NATURAL FIT Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation MiniMAX Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation INTRODUCTION The MiniMAX TM is a cementless anatomic stem available in 9 right sizes and
THE NATURAL FIT Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation MiniMAX Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation INTRODUCTION The MiniMAX TM is a cementless anatomic stem available in 9 right sizes and
Overview. Acceptance criteria for all protocols
 X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
AML Hip System. Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique
 AML Hip System Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique Design Rationale Evolution In 1977, DePuy Synthes Companies introduced the original cementless total hip. The AML Hip launched in order to solve one
AML Hip System Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique Design Rationale Evolution In 1977, DePuy Synthes Companies introduced the original cementless total hip. The AML Hip launched in order to solve one
Ye-Ran Li, Yu-Hang Gao, Xin Qi *, Jian-Guo Liu, Lu Ding, Chen Yang, Zheng Zhang and Shu-Qiang Li
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
Surgical Technique. Hip System
 Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
The Leg Length Discrepancy in The Entire Lower Limbs after Total Hip Arthroplasty Influences The Coronal Alignment of Pelvis and Spine.
 The Leg Length Discrepancy in The Entire Lower Limbs after Total Hip Arthroplasty Influences The Coronal Alignment of Pelvis and Spine. Hiroshi Fujimaki, MD 1, Yutaka Inaba, MD, PhD 2, Naomi Kobayashi,
The Leg Length Discrepancy in The Entire Lower Limbs after Total Hip Arthroplasty Influences The Coronal Alignment of Pelvis and Spine. Hiroshi Fujimaki, MD 1, Yutaka Inaba, MD, PhD 2, Naomi Kobayashi,
Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique
 Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique Table of Contents EMPERION Specifications 3 EMPERION Surgical Technique 9 EMPERION Catalog 18 Nota Bene: This technique description herein is made available to the
Clinical Evaluation Surgical Technique Table of Contents EMPERION Specifications 3 EMPERION Surgical Technique 9 EMPERION Catalog 18 Nota Bene: This technique description herein is made available to the
Overview. Acceptance criteria for all protocols
 X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION. Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique
 ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees INTRODUCTION
ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees INTRODUCTION
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an increasingly. Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(3): 214-218 REVIEW Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review Serban DRAGOSLOVEANU a,
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(3): 214-218 REVIEW Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review Serban DRAGOSLOVEANU a,
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF DYSPLASIA
 PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD Return to Menu
 S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD TOTAL KNEE INSTRUMENTS Wichita Fusion Nail Introduction...1 Preoperative Planning...2 Surgical Technique...3-8 Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E David A. McQueen, MD TOTAL KNEE INSTRUMENTS Wichita Fusion Nail Introduction...1 Preoperative Planning...2 Surgical Technique...3-8 Wichita Fusion Nail Surgical Technique
Continuing the Tradition. VerSys Heritage Hip System
 Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Biomechanics of. Knee Replacement. Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm
 Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
BIOTECH FUTURE KNEE Minimal Invasive (and classic) Surgical Technique
 BIOTECH FUTURE KNEE Minimal Invasive (and classic) Surgical Technique Page No. Product description 2. Pre-operational planning 3. 1st step Femoral resection 4. P/S Femoral component 7. 2nd step Proximal
BIOTECH FUTURE KNEE Minimal Invasive (and classic) Surgical Technique Page No. Product description 2. Pre-operational planning 3. 1st step Femoral resection 4. P/S Femoral component 7. 2nd step Proximal
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
HELIOS h i p s y s t e m
 HELIOS h i p s y s t e m Design The Helios stem is a highly polished, High Nitrogen Stainless Steel (ISO5832-9) dual tapered cemented stem. The design of the stem is based on the clinically lly successful
HELIOS h i p s y s t e m Design The Helios stem is a highly polished, High Nitrogen Stainless Steel (ISO5832-9) dual tapered cemented stem. The design of the stem is based on the clinically lly successful
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN
 V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH 44514-3250 (800) 837-3888 www.anatomicalconceptsinc.com Page 1 of 5 The
V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH 44514-3250 (800) 837-3888 www.anatomicalconceptsinc.com Page 1 of 5 The
NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION S A. Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical. ATechnique
 NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION ATechnique Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical INTRODUCTION The NexGen Complete Knee Solution Intramedullary Tibial Instruments have been designed to provide an
NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION ATechnique Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical INTRODUCTION The NexGen Complete Knee Solution Intramedullary Tibial Instruments have been designed to provide an
Optimizing function Maximizing survivorship Accelerating recovery
 Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement
 016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails
 Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Demonstrated Greater Accuracy to Plan Compared to Manual Technique
 EPiC Series in Health Sciences Volume 1, 2017, Pages 283 287 CAOS 2017. 17th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery Health Sciences Robotic-Arm Assisted Total
EPiC Series in Health Sciences Volume 1, 2017, Pages 283 287 CAOS 2017. 17th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery Health Sciences Robotic-Arm Assisted Total
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION. Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique
 POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees
POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees
Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation. Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME. Stem Extensions and Augments
 Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Stem Extensions and Augments Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer NexGen Tibial
Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Stem Extensions and Augments Zimmer NexGen Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer NexGen Tibial
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Alignment in total knee arthroplasty
 Alignment in total knee arthroplasty A COMPARISON OF COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY WITH THE CONVENTIONAL TECHNIQUE H. Bäthis, L. Perlick, M. Tingart, C. Lüring, D. Zurakowski, J. Grifka From the University
Alignment in total knee arthroplasty A COMPARISON OF COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY WITH THE CONVENTIONAL TECHNIQUE H. Bäthis, L. Perlick, M. Tingart, C. Lüring, D. Zurakowski, J. Grifka From the University
