Lecture Objectives: Lecture Objectives: (cont.) GASTROINTESTINAL DYSFUNCTION LauriAnne Martin. 1. Discuss nutritional disturbances during childhood.
|
|
|
- Octavia Ford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GASTROINTESTINAL DYSFUNCTION LauriAnne Martin Lecture Objectives: 1. Discuss nutritional disturbances during childhood. 2. Describe the various types of dehydration and nursing care indicated. 3. Discuss gastrointestinal dysfunctions during childhood and their treatment. 4. Formulate a plan of care for the child with a disorder of motility. 5. Describe the clinical manifestations and nursing management of children with intestinal parasitic diseases. Lecture Objectives: (cont.) 6. Review the pathophysiology, therapeutic and nursing care management for children with inflammatory disorders. 7. Analyze the nursing process in the care of a child with hepatic disorders. 8. Describe the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, therapeutic, and nursing care for children with structural and obstructive disorders. 9. Formulate a plan of care for the child with a malabsorption syndrome. 10. Describe the nursing management for the child who has ingested an injurious agent. 1
2 Reading Assignment: Wong, Perry, & Hockenberry (2006). Maternal Child Nursing Care. Chapter 47, pp Nutritional Disturbances Vitamin Disturbances Mineral Disturbances Vegetarian Diets Protein and energy malnutrition Food sensitivity Vitamin Disturbances True deficiencies rare in US High fat diet with low vegetable/fruit intake responsible for most deficiencies Vitamin D Vitamin B6 Vitamin A Folic Acid 2
3 Mineral Disturbances Macrominerals-daily requirements>100mg Microminerals-daily requirements<100 mg Mineral deficiencies Phytates/oxalates Vegetarian Diets Lacto-ovovegetarians- exclude meat, consume dairy and fish Lactovegetarians- exclude meat and eggs, but drink milk Pure vegetarians- exclude any food of animal origin Zen macrobiotics Semi-vegetarians Vegetarian Diets and Nursing Care Management Identify nutritional deficits Dietary assessment Implement teaching based on food guide pyramid Educate family about vitamin toxicity and planning healthy vegetarian diet 3
4 Vegetarian Diet and Nursing Care Management (cont.) Lactoovovegetarian diet nutritionally adequate Vegan require supplementation with vit. D and B12 for child 2-12 years Breastfeeding infants Combining incomplete proteins Protein and Energy Malnutrition (PEM) Kwashiorkor Marasmus Kwashiorkor Deficiency of protein with adequate supply of calories Appearance- thin, wasted extremities, prominent abdomen, muscular atrophy, dry, scaly skin, alopecia Permanent blindness from Vit. A deficiency Diarrhea produces electrolyte imbalances 4
5 Marasmus Deficiency of both calories and protein Appearance- gradual wasting, severe atrophy, of body tissues, appears old with flabby, wrinkled skin Found in third world countries Usually syndrome of physical and emotional deprivation Child so lethargic that prostration occurs Therapeutic Management High quality protein, increased carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals Control diarrhea Rehydration with appropriate route Protect from infection Tailoring activity to allow for adequate rest Food Sensitivity Any type of adverse reaction to food or additives- common food sources Two types Food intolerances Food allergies 5
6 Food Intolerance Involves non-immunologic mechanisms Food Allergy Caused by exposure to allergens- usually proteins- that are capable of inducing sensitization when ingested Occurs after food ingested one or more times More common in infancy because of the immature intestinal tract S/S can mimic acute asthma attack- CAN BE FATAL May outgrow Foods causing severe anaphylaxis avoided for life Atopy Hereditary link One parent with allergies- child has 50% chance of developing allergies Two parents with allergies- child has 100% chance of developing allergies Education Parents, teachers, all caregivers informed of allergy and tx. Medical ID bracelet and epi-pen available 6
7 Preventing Atopy in Children Identify children at risk Prenatal precautions Postnatal precautions Environmental control Cow s Milk Allergy Adverse reaction to cow s milk protein S/S- diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, wheezing, coughing, asthma, nasal discharge, bronchitis, excessive crying, eczema Diagnosis- allergy testing and/or removal of cow s milk from diet Cow s Milk Allergy (cont.) Management- substitute a formula which has predigested proteins, avoid soy based formulas and goat s milk Nursing considerations- identifying potential milk allergies 7
8 Lactose Intolerance Deficiency of the enzyme lactase Three types Congenital Primary or late onset Secondary S/S occur 30 minutes after consumption- abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, diarrhea Diagnosis- history and/or breath hydrogen test Controlling Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance Substitute soy based formula Hard cheese and yogurt allowed to get calcium requirement Limit consumption of milk to one glass daily-small amounts help colonic bacteria adapt to ingested lactose Pre-treated milk (microbial-derived lactase) and enzyme replacements Gastrointestinal Dysfunction Clinical manifestations Dehydration- occurs whenever output exceeds intake. Can result from diseases that cause insensible losses through the skin and respiratory tract through increased renal excretion and through the GI tract 8
9 Water Balance In Infants Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are therefore more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte balance Extracellular fluid Body surface Area (BSA) Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) Kidney function Fluid requirements Daily Maintenance Fluid Requirements 1. Calculate weight of child in kilograms 2. Allow 100 ml/kg for first 10 kg 3. Allow 50 ml/kg for second 10 kg 4. Allow 20 ml/kg for remainder of weight in kilograms 5. Divide total amount by 24 hours to obtain rate in milliliters per hour Example #1: Daily Fluid Calculation Child weighs 32 kg 100 x 10 for 1st 10 kg of body weight = x 10 for 2nd 10 kg of body weight = x 12 for remaining body weight = = 1740 ml/24 hr 9
10 Example 2: Daily Fluid Calculation Child weighs 8.5 kg 100 x 8.5 for 1st 10 kg of body weight = 850 No further calculations 850 ml/24 hr Example 3: Daily Fluid Calculation Child weighs 14 kg 100 x 10 for 1st 10 kg of body weight = x 4 for 2nd 10 kg of body weight = 200 No further calculations = 1200 ml/24 hr Types of Dehydration Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic 10
11 Nursing Management- Dehydration Assessment for signs and extent of dehydration (see table pg. 1495/1251) Conditions that may precipitate dehydration include diarrhea, sweating, fever, diabetes, renal disease, trauma (burns, etc.) Intake and Output Skin assessment Mucous membrane assessment Body weight Fontanel assessment Sensory alterations Disorders of Motility Diarrhea Constipation Hirschsprung disease Vomiting Gastroesophageal reflux Diarrhea Symptom that results from disorders involving digestive, absorptive, and secretory functions. Caused by abnormal intestinal water and electrolyte transport 11
12 Diarrheal Disturbances Gastroenteritis Enteritis Colitis Enterocolitis Types of Diarrhea Acute Acute infectious/infectious gastroenteritis Chronic Intractable diarrhea of infancy Chronic nonspecific diarrhea (CNSD) Etiology of Diarrhea Rotavirus Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter Giardia Cryptosporidium Clostridium difficile Antibiotic therapy 12
13 Diagnostic Evaluation- Diarrhea Complete history Laboratory test Stool samples Therapeutic Management- Diarrhea Monitoring fluid and electrolyte imbalance Rehydration Maintenance fluid therapy Reintroduction of an adequate diet Oral rehydration therapy: pedialyte Preventing diaper dermatitis Clinical Manifestations Decreased urine output Decreased weight Dry mucous membranes Poor skin turgor Sunken fontanels Pale, dry skin Tachycardia Hypotension Prolonged capillary refill > 2 seconds 13
14 Prevention of Diarrhea Most diarrhea is spread by the fecaloral route Teach personal hygiene Clean water supply/protect from contamination Careful food preparation Handwashing! Constipation An alteration in frequency, consistency, or ease of passage of stool May be secondary to other disorders Idiopathic (functional) constipation no known cause Chronic constipation may be due to environmental or psychosocial factors Newborn Period First meconium should be passed within 24 to 36 hours of life; if not, assess for: Hirschsprung disease, hypothyroidism Meconium plug, meconium ileus (CF) 14
15 Infancy Often related to diet Constipation in exclusively breastfed infant almost unknown Infrequent stool may occur because of minimal residue from digested breast milk Formula-fed infants may develop constipation Interventions Constipation in Childhood Often due to environmental changes or control over body functions Encopresis: inappropriate passage of feces, often with soiling May result from stress Management Nursing Considerations History of bowel patterns, medications, diet Educate parents and child Dietary modifications (age appropriate) 15
16 Hirschsprung Disease Also called congenital aganglionic megacolon Mechanical obstruction from inadequate motility of intestine Incidence: 1 in 5000 live births; more common in males and in Down syndrome Absence of ganglion cells in colon Clinical Manifestations of Hirschprung Aganglionic segment usually includes the rectum and proximal colon Accumulation of stool with distention Failure of internal anal sphincter to relax Enterocolitis may occur Diagnostic Evaluation X-ray, barium enema Anorectal manometric exam Confirm diagnosis with rectal biopsy 16
17 Therapeutic Management Surgery Two stages Temporary ostomy Second stage pull-through procedure Nursing Considerations Preoperative care Postoperative care Discharge care Vomiting Forceful ejection of gastric contents through the mouth 17
18 Causes of Vomiting Infectious diseases Food intolerances Allergies Mechanical obstruction Metabolic disorders Psychogenic problems Management of Vomiting Antiemetic medications Assessment of type of vomiting Administer glucose-electrolyte solutions Include carbohydrates in diet to spare body protein Position child on abdomen to prevent aspiration Promote oral hygiene Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) Defined as transfer of gastric contents into the esophagus Occurs in everyone Frequency and persistency may make it abnormal May occur without GERD GERD may occur without regurgitation 18
19 Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) Diagnostics Therapeutic management Nursing considerations Intestinal Parasitic Diseases Giardiasis Enterobiasis (pinworms) Giardiasis Etiology- protozoan Giardia lambllia Transmission- person to person, bodies of water, food, and pets Manifestations Infants- diarrhea, vomiting, anorexia, failure to thrive Children over 5 years of age- abdominal cramps, loose stools, constipation, watery/pale/greasy stools 19
20 Giardiasis (cont) Diagnosis- stool specimen, string test, EIA Management- Medications: Flagyl, Atabrine, Quinacrine, Furoxone Prevention- education Enterobiasis (Pinworms) Etiology- nematode enterobius vermicularis Transmission- crowded conditions, eggs are ingested or inhaled, eggs hatch in intestine. With scratching, eggs are transferred to hands and fingernails Clinical manifestations- intense perinanal itching Enterobiasis (cont.) Diagnosis- tape test Management Medications: Vermox, Pripsen, Povan (stains bright red). ALL family members are treated Education: prevent reinfection 20
21 Inflammatory Disorders Acute Appendicitis Meckel Diverticulum Inflammatory Bowel Disease Peptic Ulcer Disease Acute Appendicitis Inflammation of the vermiform appendix and is the most common condition requiring abdominal surgery during childhood Etiology Pathophysiology Acute Appendicitis (cont.) Clinical manifestations Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Ruptured appendix Prognosis Nursing considerations 21
22 Meckel Diverticulum It is the most common congenital malformation of the GI tract Occurs in 1% to 3% of the population Pathophysiology Meckel Diverticulum (cont.) Clinical manifestations Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Nursing considerations Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Includes ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn disease (CD) Etiology and pathophysiology Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Medical treatment Nursing considerations 22
23 Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) Etiology and pathophysiology Clinical manifestations Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Medical Surgical Nursing considerations Hepatic Disorders Acute hepatitis Cirrhosis Biliary atresia Acute Hepatitis Causes Virus Chemical reaction Drug reaction Other disease processes 23
24 Types of Hepatitis Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Hepatitis G Hepatitis Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Prognosis Nursing considerations Infection control Cirrhosis Occurs at the end stage of many chronic liver diseases including biliary atresia and chronic hepatitis Clinical manifestations Therapeutic management Nursing considerations 24
25 Biliary Atresia Also called extrahepatic biliary atresia Etiology and pathophysiology Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Prognosis Nursing considerations Structural Defects Cleft lip and/or cleft palate Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) Hernias Cleft Lip and/or Cleft Palate Facial malformations that occur during embryonic development May appear separately or together Etiology and pathophysiology Diagnostic evaluation 25
26 Surgical Correction of Cleft Lip Closure of lip defect precedes correction of the palate Z-plasty to minimize retraction of scar Protect suture line with Logan bow or other methods Surgical Correction of Cleft Palate Typically 12 to 18 months of age Effect on speech development Prognosis Nursing considerations Cleft Lip and Palate Feeding Issues Techniques and interventions Special feeding equipment Breastfeeding issues 26
27 Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF) Failure of esophagus to develop as a continuous passage May occur separately or in combination Etiology and pathophysiology Diagnostic evaluation Clinical manifestations Management of TEF Surgical interventions Prognosis Associated tracheomalacia Nursing considerations Hernias Definition: a protrusion of portion of an organ through an abnormal opening Danger of incarceration/strangulation 27
28 Pediatric Hernias Diaphragmatic Hiatal Umbilical/abdominal wall defects Omphalocele Gastroschisis Obstructive Disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) Intussesception Malrotation and Volvulus Anorectal malformations Pyloric Stenosis Constriction of pyloric sphincter with obstruction of gastric outlet Pathophysiology Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Prognosis Nursing considerations 28
29 Intussusception Telescoping or invagination of one portion of intestine into another Occasionally due to intestinal lesions Often cause is unknown Intussusception (cont d) Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Prognosis Nursing consideration Malrotation and Volvulus Malrotation is due to abnormal rotation around the superior mesenteric artery during embryonic development Volvulus occurs when intestine is twisted around itself and compromises blood supply to intestines May cause intestinal perforation, peritonitis, necrosis, and death 29
30 Anorectal Malformations Imperforate anus Persistent cloaca Cloacal exstrophy Genitalia may be indefinite Diagnostic evaluation Management Malabsorption Syndromes Celiac disease Short bowel syndrome Characterized by chronic diarrhea and malabsorption of nutrients May result in failure to thrive Celiac Disease Also called gluten-induced enteropathy and celiac sprue Four characteristics Steatorrhea General malnutrition Abdominal distention Secondary vitamin deficiencies 30
31 Celiac Disease Pathophysiology Diagnostic evaluation Therapeutic management Nursing considerations Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS) A malabsorptive disorder Results from decreased mucosal surface area, usually as result of small bowel resection Etiology and pathophysiology Therapeutic management Nursing considerations Ingestion of Injurious Agents Principles of emergency treatment Medical evaluation is necessary with all episodes of poisoning Telephone the Poison Control Center before initiating any intervention Assessment: treat the child first not the poison. Vital signs, signs of shock, respiratory and/or circulatory compromise 31
32 Principles of Emergency Treatment (cont.) Gastric decontamination Administration of antidotes Prevention of poisonings Heavy Metal Poisonings Mercury toxicity Clinical manifestations Treatment: chelation therapy Lead Poisoning Causes: non-intact lead based paint in older homes and contaminated soil. Water and food can be contaminated with lead Pathophysiology Clinical manifestations Diagnostic evaluation 32
33 Lead Poisoning Screening Universal screening at ages 1 and 2 Any child not previously tested, should be tested between 3-6 years Targeted screening is acceptable when an area has been determined by existing data to have less risk Lead Poisoning- Therapeutic Management Education Treatment depends on lead blood levels Chelation therapy When a child has a blood level of 45 ug/l calcium disodium edetate (EDTA) and succimer are given Level > 70 ug/l BAL is administered Rebound effect Lead Poisoning- Nursing Considerations Prevent the child s initial or further exposure to lead Identify sources of lead in the environment Accurate I & O because EDTA and lead are toxic to kidneys Seizure precautions are instituted at the bedside of children with high blood lead levels Psychological support 33
Chapter Outline. Structural defects. Obstructive disorders. Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 98. Cleft lip and cleft palate
 Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 20 Caring for Clients with Bowel Disorders Diarrhea Pathophysiology Result from impaired water absorption
Chapter 34. Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
Chapter 34 Nursing Care of Patients with Lower Gastrointestinal Disorders Lower Gastrointestinal System Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum Anus Constipation Fecal Mass Held In Rectum Feces Become
PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA 1 DEFINITION Prolongation of acute diarrhoea / dysentery for more than 14 days Generally associated with weight loss. 2 PROTRACTED DIARRHOEA Prolongation of acute diarrhoea or dysentery
PERSISTENT DIARRHOEA 1 DEFINITION Prolongation of acute diarrhoea / dysentery for more than 14 days Generally associated with weight loss. 2 PROTRACTED DIARRHOEA Prolongation of acute diarrhoea or dysentery
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Gastroenterology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Gastroenterology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the general pediatrician in the assessment and management of patients with
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Gastroenterology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the general pediatrician in the assessment and management of patients with
Gastro Intestinal pg 1 of 6
 Gastro Intestinal pg 1 of 6 Diabetic Ketoacidosis -Treatment differences True Na: adjust upward 1.6 mleq/l for every 100 mg/dl increase in blood glucose Potential serious CNS effects; 2-5% mortality rate
Gastro Intestinal pg 1 of 6 Diabetic Ketoacidosis -Treatment differences True Na: adjust upward 1.6 mleq/l for every 100 mg/dl increase in blood glucose Potential serious CNS effects; 2-5% mortality rate
Differentiate IgE-mediated food allergy from non-ige mediated food allergy. List the foods and formulas most commonly associated with food allergy.
 Gastroenterology Description: The resident will be exposed to various clinical symptoms and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract which are commonly seen by the gastroenterologist. The resident will be
Gastroenterology Description: The resident will be exposed to various clinical symptoms and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract which are commonly seen by the gastroenterologist. The resident will be
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
3/22/2011. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Appendicitis. Lemone and Burke Chapter 26
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Lemone and Burke Chapter 26 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Objectives: Discuss etiology, patho and clinical manifestations of Appendicitis Peritonitis Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s
PEDIATRICS. Module Topic/Content Student Learning Outcomes Resources Clinical Assessment Activities Course/Clinical Outcomes
 PEDIATRICS N332 Outline 1 Welcome back: Instructor Role and Student Role Discuss course requirements. Explain personal learning style and study patterns. Explain critical thinking and clinical judgment
PEDIATRICS N332 Outline 1 Welcome back: Instructor Role and Student Role Discuss course requirements. Explain personal learning style and study patterns. Explain critical thinking and clinical judgment
Pediatric Surgery MUHC MCH Siste. Objectives of Training
 Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ RWJMS
 Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ RWJMS Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of
Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of Pediatrics UMDNJ RWJMS Daniel Hirsch, MD Director of Neonatology Somerset Medical Center Assistant Professor of
Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems
 Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Evaluation of Failure to Thrive in a Young Child: Case Example of Jeff. Andrew Hsi, MD, MPH Family Medicine Pediatric Grand Rounds, 8 August 2012
 Evaluation of Failure to Thrive in a Young Child: Case Example of Jeff Andrew Hsi, MD, MPH Family Medicine Pediatric Grand Rounds, 8 August 2012 Objectives for Presentation At the end of this talk; the
Evaluation of Failure to Thrive in a Young Child: Case Example of Jeff Andrew Hsi, MD, MPH Family Medicine Pediatric Grand Rounds, 8 August 2012 Objectives for Presentation At the end of this talk; the
Topics for discussion. Pediatric General Surgery. Physiology. Surgical Newborns. Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction
 Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases
 Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
Nutrition Management in GI Diseases Aryono Hendarto MD Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases Division Department of Child Health Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital University of Indonesia 1 Patient s Care 1. Drugs 2.
KENT STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH CARE OF CHILDREN Nursing Pediatrics Case Studies: Child Dehydration
 Courtney Wiener 9/9/10 KENT STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH CARE OF CHILDREN Nursing 30020 - Pediatrics Case Studies: Child Dehydration Introduction: Dehydration can be life threatening to a child since a majority
Courtney Wiener 9/9/10 KENT STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH CARE OF CHILDREN Nursing 30020 - Pediatrics Case Studies: Child Dehydration Introduction: Dehydration can be life threatening to a child since a majority
Definition. Failure to Thrive. No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles
 Failure to Thrive Karen Swarts, MD 6/4/2004 Definition No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles 1 Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics,
Failure to Thrive Karen Swarts, MD 6/4/2004 Definition No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles 1 Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics,
Esophageal Disorders. Gastrointestinal Diseases. Peptic Ulcer Disease. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Diseases of the Small Intestine 7/24/2010
 Esophageal Disorders Gastrointestinal Diseases Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 Dysphagia Difficulty Swallowing and passing food from mouth via the esophagus Diagnostic aids: Endoscopy, Barium x ray, Cineradiology,
Esophageal Disorders Gastrointestinal Diseases Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 Dysphagia Difficulty Swallowing and passing food from mouth via the esophagus Diagnostic aids: Endoscopy, Barium x ray, Cineradiology,
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
Digestion. Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional
 Digestive System 1 Digestion Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional Food behaviors can become just as addictive as any other pleasurable
Digestive System 1 Digestion Intake and assimilation of nutrients Elimination of waste Eating Required physically Pleasurable Social Emotional Food behaviors can become just as addictive as any other pleasurable
Trachoesophageal fistula Esophageal atresia
 Miss.kamlah 1 Trachoesophageal fistula Esophageal atresia Esophageal atresia: Is a malformation that results from failure of the esophagus to develop as a contentious tube during the forth to fifth weeks
Miss.kamlah 1 Trachoesophageal fistula Esophageal atresia Esophageal atresia: Is a malformation that results from failure of the esophagus to develop as a contentious tube during the forth to fifth weeks
Chapter 4 Fluid Management
 Chapter 4 Fluid Management First Nations and Inuit Health Branch (FNIHB) Pediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines for Nurses in Primary Care. The content of this chapter has been reviewed October 2009. Table
Chapter 4 Fluid Management First Nations and Inuit Health Branch (FNIHB) Pediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines for Nurses in Primary Care. The content of this chapter has been reviewed October 2009. Table
Viral gastroenteritis Gastrointestinal infections caused by viruses are the most common and the most contagious.3
 CMA Today Quick Clinic May/Jun 2017 (Issue 3/Volume 50) GI woes Gastroenteritis affects patients at home and abroad By Nancy Solomon We expect patients to come into the office a few times a year with that
CMA Today Quick Clinic May/Jun 2017 (Issue 3/Volume 50) GI woes Gastroenteritis affects patients at home and abroad By Nancy Solomon We expect patients to come into the office a few times a year with that
Interpret clinical and laboratory tests to identify conditions that require surgical intervention, including:
 Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University
 Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University objectives Overview Definition of dehydration Causes of dehydration Types of dehydration Diagnosis, signs and symptoms Management of dehydration Complications
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University objectives Overview Definition of dehydration Causes of dehydration Types of dehydration Diagnosis, signs and symptoms Management of dehydration Complications
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Malabsorption Syndromes in Children
 Malabsorption Syndromes in Children Oxana Turcu, PhD, assistant professor Department of Pediatrics Malabsorption syndromes include a number of different clinical manifestations, that result in chronic
Malabsorption Syndromes in Children Oxana Turcu, PhD, assistant professor Department of Pediatrics Malabsorption syndromes include a number of different clinical manifestations, that result in chronic
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
MODULE VI. Diarrhea and Dehydration
 MODULE VI Diarrhea and Dehydration ACUTE DIARRHEA Increased number of bowel movements! Loose and watery stools Fluid and electrolyte loss ACUTE DIARRHEA TYPES Watery Bloody diarrhea (dysentery) DIARRHEA
MODULE VI Diarrhea and Dehydration ACUTE DIARRHEA Increased number of bowel movements! Loose and watery stools Fluid and electrolyte loss ACUTE DIARRHEA TYPES Watery Bloody diarrhea (dysentery) DIARRHEA
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration. May 16/17
 Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Pediatric Dehydration and Oral Rehydration May 16/17 Volume Depletion (hypovolemia): refers to any condition in which the effective circulating volume is reduced. It can be produced by salt and water loss
Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology
 Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health
Digestion: Small and Large Intestines Pathology Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified health
Pediatric Gastroenterology Referral Guidelines
 Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
Suggested Pre-Referral Workup This is a general suggestion of possible testing to confirm a suspected diagnosis. Although referrals will be accepted without the suggested work up being complete, to ensure
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery
 Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
In addition, GI bacteria break down lactose and release hydrogen Which causes excess gas production, bloating, and abdominal pain.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 PEDIATRIC G & I Nursing 210 Lactose Intolerance The inability to tolerate lactose, the sugar found in dairy products. A inability to tolerate lactose develops as a result of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 PEDIATRIC G & I Nursing 210 Lactose Intolerance The inability to tolerate lactose, the sugar found in dairy products. A inability to tolerate lactose develops as a result of
Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C
 Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C Texas Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric General Surgery Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Objectives 1. Define Pediatric Surgical
Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C Texas Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric General Surgery Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Objectives 1. Define Pediatric Surgical
Biology 1400 Fundamentals of Nutrition
 Biology 1400 Fundamentals of Nutrition Course Outcomes 1. Identify the six classes of nutrients and their relationship to health. 2. Indicate function and requirements of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Biology 1400 Fundamentals of Nutrition Course Outcomes 1. Identify the six classes of nutrients and their relationship to health. 2. Indicate function and requirements of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Identify electrolytes that should be monitored whenever prolonged or severe diarrhea is present
 Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
Chapter 35 Drugs Used to Treat Constipation and Diarrhea Learning Objectives State the underlying causes of constipation Explain the meaning of normal bowel habits Cite nine causes of diarrhea Describe
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System
 USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
USMLE Step 1 Problem Drill 17: Gastrointestinal System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A surgeon is planning to remove a patient s gallbladder endoscopically. During the procedure, the endoscope will traverse
64a Pathology: Digestive System!
 64a Pathology: Digestive System! 64a Pathology: Digestive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
64a Pathology: Digestive System! 64a Pathology: Digestive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
Paediatric Directorate
 Paediatric Directorate Dehydration Guidelines Primary cause of dehydration diarrhoea +/- vomiting. Approximately 10%Children < 5yrs present with gastroenteritis each year Diagnosis History - sudden change
Paediatric Directorate Dehydration Guidelines Primary cause of dehydration diarrhoea +/- vomiting. Approximately 10%Children < 5yrs present with gastroenteritis each year Diagnosis History - sudden change
Hirschprung s. Meconium plug R/S >1 R/S <1
 NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia
 Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition August 12, 2012 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Gastroenterology and Feeding Issues in Fanconi Anemia Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition August 12, 2012 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Human Anatomy rectum
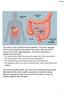 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. Maxibar % w/w powder for oral suspension. Barium sulfate
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Maxibar 98.45 % w/w powder for oral suspension Barium sulfate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. Keep this leaflet. You may
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Maxibar 98.45 % w/w powder for oral suspension Barium sulfate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine. Keep this leaflet. You may
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success
 Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Victor Tambunan Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia
 Victor Tambunan Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia 1 References Krause s Food & Nutrition Therapy 12th ed., 2008 ---- L.K. Mahan & S. Escott-Stump Modern Nutrition in Health
Victor Tambunan Department of Nutrition Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia 1 References Krause s Food & Nutrition Therapy 12th ed., 2008 ---- L.K. Mahan & S. Escott-Stump Modern Nutrition in Health
General description: Detailed description:
 18. Course Description: General description: This course focuses on Gastro Intestinal system to understand structures, biochemical aspects, physiological functions, pathological disorders, microbial, parasitic
18. Course Description: General description: This course focuses on Gastro Intestinal system to understand structures, biochemical aspects, physiological functions, pathological disorders, microbial, parasitic
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions
 2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
Algorithms & Information Sheets
 Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Geographical and Cultural Food-related Symptoms, Food Avoidance and Elimination
 Geographical and Cultural Food-related Symptoms, Food Avoidance and Elimination Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG, AGAF Digestive Health Center of Excellence University of Virginia Adverse Reactions
Geographical and Cultural Food-related Symptoms, Food Avoidance and Elimination Sheila E. Crowe, MD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG, AGAF Digestive Health Center of Excellence University of Virginia Adverse Reactions
Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion
 Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Teresa Liang Suspected Foreign Body Ingestion 1. General Presentation Background: Of more than 100,000 cases of foreign body ingestion reported each year in the United States, 80% occur in children, with
Roundtable Presentation Hirschsprung s Disease
 Roundtable Presentation Hirschsprung s Disease Disclosure Information There were no financial interests or relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose for any of the Hirschsprung s Disease roundtable
Roundtable Presentation Hirschsprung s Disease Disclosure Information There were no financial interests or relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose for any of the Hirschsprung s Disease roundtable
VOMITING. Tan Lay Zye
 VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
VOMITING Tan Lay Zye Vomiting is a common symptom. It is a complex reflex behavioural response involving forceful expulsion of the stomach contents through oral cavity. Contents Emetic reflex Causes of
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints. Jennifer Curtis, MD
 A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
A Trip Through the GI Tract: Common GI Diseases and Complaints Jennifer Curtis, MD Colon Cancer How does it develop? Most cancers arise from polyps Over time these can turn into cancer Combination of genetic
Objectives: Resources:
 Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
Objectives: Realize the impact of Age : - Where/who are the history sources Recognize and interpret the : - Important symptoms - Important signs Resources: Davidson s. Slides Surgical recall. Raslan s
PLEASE COMPLETE ALL SECTIONS OF THIS FORM
 PLEASE COMPLETE ALL SECTIONS OF THIS FORM Patient Name: Date of Birth: Referring Doctor? (Name, telephone number and address) Chief Complaint: Why have you come here? How did it start? What are the symptoms?
PLEASE COMPLETE ALL SECTIONS OF THIS FORM Patient Name: Date of Birth: Referring Doctor? (Name, telephone number and address) Chief Complaint: Why have you come here? How did it start? What are the symptoms?
Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 5/ August 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies AUREL
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 5/ August 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Congenital Digestive Malformation and Associated Anomalies AUREL
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes
 Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Copyright The Food Intolerance Testing Group. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
 Copyright 2018 The Food Intolerance Testing Group All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording,
Copyright 2018 The Food Intolerance Testing Group All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including photocopying, recording,
ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS IN CHILDREN
 ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS IN CHILDREN Prof. Alok Kumar Professor of Pediatrics & Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medical Sciences The University of the West Indies (Cave Hill) 11/6/2017 1 DEFINITION Gastroenteritis
ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS IN CHILDREN Prof. Alok Kumar Professor of Pediatrics & Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medical Sciences The University of the West Indies (Cave Hill) 11/6/2017 1 DEFINITION Gastroenteritis
Spleen indications of splenectomy complications OPSI
 Intestinal obstruction Differences between adynamic ileus and mechanical obstruction Aetiology Pathophysiology (Cluster contractions- bowel proximal to the obstruction dilate- wall of obstructed gut is
Intestinal obstruction Differences between adynamic ileus and mechanical obstruction Aetiology Pathophysiology (Cluster contractions- bowel proximal to the obstruction dilate- wall of obstructed gut is
Nivolumab. Other Names: Opdivo. About this Drug. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Warnings and Precautions
 Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA
 Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 29, 2014 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal, Hepatic, and Nutritional Challenges in FA Sarah Jane Schwarzenberg, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition June 29, 2014 GI problems in FA 5% have gastrointestinal tract
Paediatric Food Allergy. Introduction to the Causes and Management
 Paediatric Food Allergy Introduction to the Causes and Management Allergic Reactions in Children Prevalence of atopic disorders in urbanized societies has increased significantly over the past several
Paediatric Food Allergy Introduction to the Causes and Management Allergic Reactions in Children Prevalence of atopic disorders in urbanized societies has increased significantly over the past several
Digestive System. Digestion Myths
 Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Appropriate prescribing of specialist infant formula feeds
 Appropriate Prescribing of Specialist Infant Formula Feeds Purpose of the guidance These guidelines aim to assist GPs and Health Visitors with information on the appropriate use of infant formula that
Appropriate Prescribing of Specialist Infant Formula Feeds Purpose of the guidance These guidelines aim to assist GPs and Health Visitors with information on the appropriate use of infant formula that
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION. RNs WITH ADDITIONAL AUTHORIZED PRACTICE CLINICAL DECISION TOOL AUGUST 2017
 DEFINITION Gastroenteritis is an inflammatory process (usually infectious) involving the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and resulting in diarrhea and vomiting. Though often considered a benign process, acute
DEFINITION Gastroenteritis is an inflammatory process (usually infectious) involving the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and resulting in diarrhea and vomiting. Though often considered a benign process, acute
RECTAL PROLAPSE objectives
 RECTAL PROLAPSE objectives 1.Classify rectal prolapse 2. Enumerate the causes of rectal prolapse 3. Differentiate between complete rectal prolapse and intussusception 4. List the modalities of treatment
RECTAL PROLAPSE objectives 1.Classify rectal prolapse 2. Enumerate the causes of rectal prolapse 3. Differentiate between complete rectal prolapse and intussusception 4. List the modalities of treatment
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Diarrhea National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Neonatology ICD-10 documentation
 Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Lower GI Tract A&P Small Intestine Anatomy Duodenum, jejunum, ileum Maximum surface area for digestion and absorption Specialized enterocytes from stem cells of crypts
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Lower GI Tract A&P Small Intestine Anatomy Duodenum, jejunum, ileum Maximum surface area for digestion and absorption Specialized enterocytes from stem cells of crypts
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory
 Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank
 UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
Bacillary Dysentery (Shigellosis)
 Bacillary Dysentery (Shigellosis) An acute bacterial disease involving the large and distal small intestine, caused by the bacteria of the genus shigella. Infectious agent Shigella is comprised of four
Bacillary Dysentery (Shigellosis) An acute bacterial disease involving the large and distal small intestine, caused by the bacteria of the genus shigella. Infectious agent Shigella is comprised of four
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 30 The Digestive System Lesson 2: Pathology of the Digestive System Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Chapter 20. Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids
 Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
34th St. and Civic Center Blvd, Philadelphia, PA 19104, phone
 34th St. and Civic Center Blvd, Philadelphia, PA 19104, phone 215-590-3630 www.chop.edu/gastroenterology Please complete this form prior to your child s visit. Please fax to (215) 590-7224 or e-mail it
34th St. and Civic Center Blvd, Philadelphia, PA 19104, phone 215-590-3630 www.chop.edu/gastroenterology Please complete this form prior to your child s visit. Please fax to (215) 590-7224 or e-mail it
Giardiasis. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Chapter 17. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
Chapter 17 Vocabulary digestion bile nephrons absorption indigestion ureters elimination heartburn bladder mastication hiatal hernia urethra peristalsis appendicitis cystitis gastric juices peptic ulcer
Medical Policy Enteral Nutrition Formulas and Supplements
 Document Number: 017 Medical Policy Enteral Nutrition Formulas and Supplements Commercial and Qualified Health Plans MassHealth Authorization required X X No notification or authorization Not covered Overview
Document Number: 017 Medical Policy Enteral Nutrition Formulas and Supplements Commercial and Qualified Health Plans MassHealth Authorization required X X No notification or authorization Not covered Overview
Gastroenterology. Chapter 28
 Gastroenterology Chapter 28 Gastroenterology Intestinal Infection Acute gastroenteritis is the most common cause of infant mortality worldwide Viral gastroenteritis is usually associated with small bowel
Gastroenterology Chapter 28 Gastroenterology Intestinal Infection Acute gastroenteritis is the most common cause of infant mortality worldwide Viral gastroenteritis is usually associated with small bowel
ESSENTIAL QUESTION. What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING. Quak Seng Hock
 SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Anal Atresia FACTS: There is no known cause for anal atresia. Children with anal atresia can lead very happy lives post surgery!
 Anal Atresia FACTS: Anal atresia affects 1 in 5,000 births and is slightly more common in boys. There is no known cause for this condition. With anal atresia, any of the following can occur: The anal passage
Anal Atresia FACTS: Anal atresia affects 1 in 5,000 births and is slightly more common in boys. There is no known cause for this condition. With anal atresia, any of the following can occur: The anal passage
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST
 COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
COMMON PROBLEMS IN PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY AKSHAY BATRA CONSULTANT PAEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST Paediatric Gastroenterology : Referral Base Common problems Feeding difficulties in infancy Recurrent
DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities Wyeth (received advisory board & speaker honoraria) Potential for conflicts of interest wit
 GASTROENTERITIS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities Wyeth (received advisory board & speaker honoraria) Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation fidaxomicin (which
GASTROENTERITIS DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities Wyeth (received advisory board & speaker honoraria) Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation fidaxomicin (which
Clinical Assessment Tool
 Clinical Assessment Tool Child with Suspected Gastroenteritis 0-5 Years Diarrhoea is defined as the passage of three or more loose/watery stools per day, the most common cause of diarrhoea in children
Clinical Assessment Tool Child with Suspected Gastroenteritis 0-5 Years Diarrhoea is defined as the passage of three or more loose/watery stools per day, the most common cause of diarrhoea in children
