Metabolic diseases. Metabolism
|
|
|
- Alexis Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Metabolic diseases dr hab. n. med. Sylwia Kołtan Metabolism all biochemical processes and pathways in the body enzymes play a key role in many of these processes; changes in their function, as a result, of genetic mutation can lead to problems in metabolism important role coenzymes and cofactors 1
2 Coenzymes coenzymes are organic molecules that are required by certain enzymes to carry out catalysis they bind to the active site of the enzyme and participate in catalysis but are not considered substrates of the reaction coenzymes often function as intermediate carriers of electrons, specific atoms or functional groups that are transfered in the overall reaction Cofactors inorganic substances that are required for, or increase the rate of, catalysis 2
3 Metabolic diseases - definition any of the diseases or disorders that disrupt normal metabolism etiology: can be inherited, in which case they are also known as inborn errors of metabolism, or they may be acquired during lifetime affect many systems of the body, some of them will only dietary restrictions, other - significantly reduce psychomotor performance, and even lead to death Inborn metabolic diseases individual inborn or congenital errors are very rare but: more than 1400 inherited metabolic diseases have been described many of these disorders are potentially treatable via diet and/or drug therapy it is essentiale a rapid accurate diagnosis and adequate treatment 3
4 Inborn metabolic diseases pathophysiological diagnostics group Disorders that disrupt the synthseis or catabolism of complex molecules with symptomes that are permanent, progressive, independent of intercurrent events and not related to food intake; these include lysosomal disorders, peroxisomal disorders and disorders of intracellular transprt and processing Disorders that lead to an acute or progressive accumulation of toxic compounds as a result of metabolic block; these include disorders of amino acid metabolism (phenylketonuria, homocystynuria, maple syrup urine disease), organic acidurias, congenital urea cycle defects and sugar intolerances (galactosemia) Disorders with symptomes due to a deficiency of energy production or utilisation within the liver, myocardium, muscle or brain; these include congenital lactic acidemias, fatty acid oxydation defects, gluconeogenesis defects and mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders Inborn metabolic diseases (IMD) incidence and prevalance the majority of IMD are inherited by autosomal recessive genetics the individual incidence of metabolic disorders can vary depending on the ethnic origin of the local population especially high risk of incidence in closed population overall incidence of individual IMD can range as follows:: very rare (e.g. maple syrup urine disease 1: , homocystinuria 1: ) extremely rare (1: ) relatively more common but still rare (e.g. phenlketonuria 1 : , galaktozemia 1 : ) however, if there are more than 1000 IMD overall, each occurring at the rate of one in a milion, this means that one in 1000 people will be affected and one in 500 will be a carrier! 4
5 IMD the importance of family history diagnosis of metabolic disease in the family - the risk of repetition, especially in siblings! unexplained deaths of children in the family - an alarm for many congenital diseases, including metabolic! IMD signs and symptomes acute neonatal symptomes non-specific symptoms in apparently healthy baby: respiratory distress without signs of respiratory disease hypotonia poor sucking reflex vomiting diarrhoea dehydration lethargy seizures These can easily be attributed to other causes, such as infection 5
6 IMD signs and symptoms failure to thrive CNS symptoms: developmental delay, movement or psychiatric disorder cerebral palsy sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) SUID - Sudden Unexpected Infant Death IMD signs and symptoms episodic illness - anorexia, vomiting, lethargy, coma cardiomyopathy muscular hypotonic, weakness, cramps gastrointestinal: anorexia vomiting diarrhoea malabsorption 6
7 IMD signs and symptoms liver disease, cholestasis ophtalmic abnormalities Reye s syndrome like illness dysmorphic features metabolic: acidosis hypoglycaemia IMD signs and symptoms a Reye-like syndrome is attributed to inborn errors of metabolism in Reye-like syndrome hypoglycemia, hypoketonemia, elevated ammonia, and organic aciduria are often evident it is well-known that fatty-acid oxidation defects can present as Reye-like syndrome the most commonly diagnosed metabolic disorder in association with Reye syndrome has been medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency the present consensus seems to be that Reye syndrome is very rare, and that any child suspected of manifesting this disorder should undergo investigations for inborn errors of metabolism 7
8 IMD clinical cathegories acute symptoms in neonatal period (as above) babies with metabolic disorders of accumulation show deterioration after a normal initial period of hours to weeks late-onset acute and recurrent symptomes occurs in one third of patients with IMD of toxic accumulation or energy production fhe symptom free period is often over one year and may extend into late childhood, adolescence or even adulthood symptoms may be precipitated by minor viral infection, fever or severe diarrhea witch result in the body reverting to the breakdown of stored protein within the cells and tissue this is known as decompensation children may improve spontaneously without intervention or require intensive care; they may appear normal between attacks IMD clinical cathegories chronic and progressive general symptoms; many apparently delayed onset presentations of metabolic disorders may be preceded by insidious symptoms such as gastrointestinal, neurological and muscular complaints specific and permanent symptoms may reveal or accompany metabolic disorders some symptoms are distinctive but rare (lens discolouration and thromboembolic events in homocystynuria), other are nonspecific and common (hepatomegaly, seizures, mental retardation) 8
9 IMD diagnosis easy, if the disease is detected through screening tests (eg. phenylketonuria) or actively diagnosed disease in families with a positive family history screening tests for suspected metabolic disease, suspected based on the clinical picture (GCMS, tandem mass spectrometry - TANDEM) specialized blood tests, tissue (eg. liver biopsy), fibroblasts in the detection of various metabolic errors genetic studies, confirming the diagnosis of congenital metabolic error at some IMD diagnosis TANDEM is used in some countries for neonatal screening for IMD. 9
10 IMD diagnosis IMD the main aim of managing induce activity, as in the vitamin-responsive disorders 10
11 IMD the main aim of managing counteract the biochemical disturbance and prevent acute intercurrent decompensation prevent chronic and progressive deterioration by diet and/or drug therapy approximately 12% of inborn errors of metabolism can be significantly controlled by therapy in a further 55%, treatment is beneficial but in the remaining 33%, treatment has little efect IMD emergency treatment suspicion of metabolic disease in an infant with acute symptoms - fast diagnosis, symptomatic treatment, and in case of suspicion of the disease, in which it is possible to eliminate the intolerant substance - diet, f.e. in galactosemia 11
12 IMD suppoprtive care in acute decompensation ventilatory and circulatory support correction of electrolyte imbalance rehydration and maintenance hydration to counter poor feeding, increased renal fluid loss and to ensure efficient diuresis of toxic metabolites correction of acidosis, although mild acidosis can be protective against hyperammonemia in urea cycle defects adequate nutricion exogenus toxin removal peritoneal dialysis, haemofiltration or hemodialysis can be effective in removing toxic metabolites, such as ammonemia in urea cycle defects vitamins mega-doses of specific vitamins can act as cofactors to induce metabolism in various metabolic disorders Question to the students Which of the following situations may suggest a inborn metabolic disease in a child? 1. newborn to 3 weeks of age, in the opinion of the parents - previously healthy; admitted to the ward because of a lack of appetite from the day before, vomiting, muscle flaccidity, pathological sleepiness - the child did not respond even to very strong pain stimuli; in additional studies - hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis 2. newborn to 3 weeks of age, previously healthy; from two days more anxious, rhinitis, sporadic cough. On admission to the ward poor apetite, quickly gets tired during breastfeeding; tachypnea, tachycardia; in additional studies, decreased oxygen saturation (89%), compensated respiratory acidosis 12
13 Selected IMD Congenital hypothyroidism definition: thyroid deficiency present at birth the most common congenital human endocrinopathy from 1: 2000 to 1: 4000 births the most common preventable causes of mental retardation clinical manifestations are often subtle or not present at birth due to: trans-placental passage of some maternal thyroid hormone and/or many infants have some thyroid production of their own 13
14 Permanent CH in iodine sufficient countries 85% of CH is due to thyroid dysgenesis (thyroid ectopy, athyreosis and thyroid hypoplasia) 10-15% of cases can be attributed to the inborn errors of thyroid hormone synthesis dyshormonogenesis permanent CH requires life-long treatment Transient CH a temporary deficiency of thyroid hormones at birth, but then recovering to normal thyroid hormone production recovery to euthyroidism typically occurs in the first few months or years of life most commonly occurs in preterm infants born in areas of endemic iodine deficiency 14
15 15
16 Clinical manifestations of CH depend on the degree of thyroid hormones deficiency and its duration in the neonatal period can be very discreet the only way of the early diagnosis can be newborn thyroid screening test CH 16
17 CH common symptoms at birth: decreased activity feeding difficulty constipation prolonged jaundice common signs in newborns and infants: myxedematous facies large fontanelles macroglossia a distandet abdomen with umbilical hernia hypotonia 17
18 Signs and symptoms of CH in untreated older children and adults mild to severe impairment of both physical and mental growth and development poor length growth is apparent as early as the first year of life; adult stature without treatment ranges from 1 to 1.6 metres, depending on severity, sex and other genetic factors bone maturation and puberty are severely delayed; ovulation is impeded and infertility is common neurological impairment may be mild, with reduced muscle tone and coordination, or so severe that the person cannot stand or walk cognitive impairment may also range from mild to so severe that the person is nonverbal and dependent on others for basic care thought and reflexes are slower other signs may include thickened skin, enlarged tongue, or a protruding abdomen Signs and symptoms of CH in untreated older children and adults 18
19 Signs and symptoms of CH in untreated older children and adults October 08, 2009By Sandra E. Kurtin, RN, MS CH lack of diagnosis and treatment from neonatal period - irreversible developmental disorders, especially the central nervous system Early treatment excellent recovery!!! 19
20 CH newborn thyroid screening tests very important to early diagnosis but of the worlwide birth population of 127 million, it is estimated that 25% undergo screening for congenital hypothyroidism various algorithms using measurement of T4, TSH, or both CH diagnostic algorithm 20
21 CH diagnostic algorithm CH other evaluation X-ray of the long bones retarded bone age ECG - ST-segment changes EEG - low voltage, excess slow activities, delay of bioelectric maturation CBC - normocytic anemia 21
22 Treatment and prognosis Levothyroxine the treatment of choice the recommended starting dose is mcg/kg/day the immediate goal of treatment are to rapidly raise the serum T4 above 10 ug/dl and normalize serum TSH levels frequent laboratory monitoring in infancy is essential to ensure optimal neurocognitive outcome; serum TSH and T4 should be measured every 1-2 month in the first 6 months of life and every 3-4 months thereafter in general, the prognosis of infants detected by screening and started on treatment easly is excellent, with IQs similar to sibling or classmate controls a lower neurognitive outcome may occur in those infants started at a later age (>30 days of age), on lower l-thyroxine doses than currently recommended, and in those infants with more sever hypothyroidism Introduction to galactosemi 22
23 Introduction to galactosemia galactose is a monosaccharide sugar galactose + glucose = lactose (disacharide) in nature, lactose is found primarily in milk and milk products galactose metabolism, which converts galactose into glucose, is carried out by the three principal enzymes in a mechanism known as the Leloir pathway; the enzymes are listed in the order of the metabolic pathway: galactokinase (GALK), galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT), and UDP-galactose-4 -epimerase (GALE) galactose forms part of glycolipids and glycoproteins, which is found in many tissues galactose is a component of the antigens present on blood cells that determine blood type within the ABO blood group system; in O and A antigens, there are two monomers of galactose on the antigens, whereas in the B antigens there are three monomers of glucose Introduction to galactosemia 23
24 Galactosemia there are three forms of the disease: galactose-1 phosphate uridyl transferase deficiency (classic galactosemia, the most common and most severe form) deficiency of galactose kinase deficiency of galactose-6-phosphate epimerase Galactosemia an inherited disorder autosomal recessive disease occurs in approximately 1 of every births among Caucasians; the rate is different for other groups: from 1 : to in Europe to 1 : in Japan 24
25 Biochemical abnormalities a high level of: galactose-1-phosphate galctose galactilol additionally: hypoglicemia hyperbilirubinemia Clinical description a child with galactosemia is born apparently healthy, although there have been cases intrauterine fetal damage symptoms appear several hours or days after the first milk feeding 25
26 Signs and symptoms in neonates Finding Percent Additional details Hepatocellular damage 89% Food intolerance 76% Failure to thrive 29% Lethargy 16% Seizures 1% Sepsis 10% Jaundice (74%) Hepatomegaly (43%) Abnormal liver function tests (10%) Coagulation disorders (9%) Ascites (4%) Vomiting (47%) Diarrhea (12%) Poor feeding (23%) E.Coli (26 cases) Klebsiella (3) Enterobacter (2) Staphylococcus (1) Beta-Streptococcus (1) Streptococcus faecalis (1) From a survey reporting in 270 symptomatic neonates (Waggoner et al. 1990) Signs and symptoms if a lactose-restricted diet is provided during the first 10 days of life, the neonatal signs usually quickly resolve and the complications of liver failure, sepsis and neonatal death are prevented despite adequate treatment from an early age, children with classic galactosemia remain at increased risk for: developmental delays speech problems (childhood apraxia of speech and dysarthria) abnormalities of motor function (tremors, cerebellar ataxia, dystonia) cataract diminished bone density almost all females premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) 26
27 Signs and symptoms Organs damage high levels of galactose 1-phosphate cause of brain damage excessive hydration and environmental hypertonia due to high concentration of galactilol - cataracts Galactosemia GALT mutations three variants of disease: classic galactosemia: severe GALT enzyme deficiency with absent or barely detectable activty in erythrocytes and liver clinical variant galactosemia: 1-10% residual GALT enzyme activity in erythrocytes and liver biochemical variant galactosemia: 15-33% residual GALT enzyme activity in erythrocytes; is associated with specific mutations in GALT (Duarte variant D2) 27
28 Galactosemia: diagnosis classic galactosemia and clinical variant galactosemia may be suspected and confirmed in three clinical scenarios: a newborn who is positive on newborn screening (NBS) a newborn with a previously affected sib and/or high-risk ethnicity an infant, child, or adult with signs and/or symptoms suggestive of classic galactosemia or clinical variant galactosemia 28
29 Galactosemia: newborn screening newborn screening utilizes a small amount of blood obtained from a heel prick to quantify: total content of erythrocyte galactose-1-phosphate and blood galactose concentration AND/OR erythrocyte GALT enzyme activity Clinical Chemistry 56: (2010) WRI, within reference interval Galactosemia: other laboratory tests concentration of glucose liver function tests (ALT, AST, GGTP, bilirubin) coagulogram albumin level electrolytes serum levels CBC urine analysis 29
30 Differential diagnosis infectious diseases but very important: establishing the diagnosis of sepsis does not exclude the possibility of galactosemia, as sepsis, particularly E. coli sepsis occurs commonly in infants with classic galactosemia hereditary spherocytosis biliary atresia other metabolic diseases Differential diagnosis 30
31 Treatment prevention of primary manifestations: standard of care in any newborn who is screen-positive for galactosemia or suspected of galactosemia is immediate dietary intervention while diagnostic testing is underway if erythrocyte galactose-1-phosphate concentration is >10 mg/dl and erythrocyte GALT enzyme activity is 10% of control activity (i.e., the child has classic galactosemia or clinical variant galactosemia), restriction of galactose intake is continued and all milk products are replaced with lactose-free formulas (e.g., Isomil or Prosobee ) containing non-galactose carbohydrates management of the diet becomes less important after infancy and early childhood Treatment treatment of manifestations: in rare instances cataract surgery may be needed in the first year of life childhood apraxia of speech and dysarthria require expert speech therapy developmental assessment at age one year by a psychologist is recommended in order to formulate a treatment plan with the speech therapist and treating physician for school age children, an individual education plan and/or professional help with learning skills and special classrooms as needed hormone replacement therapy as needed for delayed pubertal development and/or primary or secondary amenorrhea. 31
32 Treatment and surveillance prevention of secondary complications: recommended calcium and vitamin intake to help prevent decreased bone mineralization routine monitoring for: the accumulation of toxic analytes (e.g., erythrocyte galactose-1-phosphate and urinary galactitol) cataracts speech and development premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) osteoporosis Avoindance agents/circumstances to avoid: breast milk, proprietary infant formulas containing lactose, cow s milk, dairy products, and casein or whey-containing foods; medications with lactose and galactose 32
33 Hereditary fructose intolerance - introduction Hereditary fructose intolerance - introduction fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple ketonic monosaccharide found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose 33
34 Hereditary fructose intolerance - introduction other fructose metabolism in liver, muscle and adipose tissue muscle and adipose tissue: fructose phosphorylation by hexokinase fructose-6-phosphate entrance to glycolysis liver: fructokinase converts fructose to fructose-1-phosphate cleavage by fructose-1-phosphate aldolase to glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate entrance to glycolysis Abnormalities in fructose metabolism inborn errors in fructose metabolism: essential fructosuria: the absence of fructokinase asymptomatic condition hereditary fructose intolerance: the absence of fructose-1- phosphate aldolase (aldolase B) very serious consequences 34
35 Hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI) autosomal recessive disorder the incidence of HFI in Europe is about 1: the accumulated fructose-1-phosphate inhibits glycogen breakdown and glucose synthesis severe hypoglicaemia following ingestion of fructose accumulation of fructose-1-phosphate hepatic and/or kidney failure and death Hereditary fructose intolerance signs and symptoms the condition is manifested usually during infancy at weaning, when the child is introduced to fruits and vegetables, or when feeding is transferred from breast milk to artificial nutrients usually very serious, occur after the intake of fructose: hypoglycemia severe metabolic acidosis seizures jaundice hepatomegaly coagulation disorders emaciation coma renal Fanconi syndrome vomiting affected children soon develop an aversion to all foods and protect themselves by self-imposed fructose and sucrose restriction 35
36 Hereditary fructose intolerance diagnosis current diagnostic methods include the measurement of clinical symptoms upon intravenous fructose challenge or the direct assay of aldolase activity in liver biopsy samples both of these diagnostic methods are relatively invasive and the clinical analyses of fructose loading tests or aldolase assays are not routinely available in addition, diagnosis by a fructose tolerance test leads to the same acute symptoms that can be life threatening Hereditary fructose intolerance tretment the treatment for HFI is the exclusion of fructose, sucrose, and sorbitol (less than 40 mg/kg per day) from the diet and results in complete alleviation of most symptoms and a normal life span older HFI subjects who adhere to a self-imposed fructose-restricted diet may continue to live undiagnosed and lead relatively normal lives complete exclusion of fructose is often difficult, however, and many HFI patients develop a syndrome of chronic fructose intoxication characterized by retarded growth, chronic liver disease, and hepatomegaly; furthermore, if not treated properly, these patients suffer episodes of hypoglycemia, general ill health, and strained relationships with family members due to their peculiar eating habits constant daily risk remains for HFI individuals due to the increasingly widespread use of these sugars as nutrients and sweeteners 36
37 Phenylalanine an essential amino acid (the human body cannot make it so it is essential to the diet) phenylalanine that is ingested is largely transformed (hydroxylated) to form the amino acid tyrosine, which is used in protein synthesis Metabolic pathways the conversion of Phe to Tyr occurs by a hydroxylating system consisting of: phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) the unconjugated pterin cofactor, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) enzymes which serve to regenerate BH4, namely dihydropteridine reductase and 4α-carbinolamine dehydratase 37
38 Hyperphenyloalaninemia may be classified into: classical phenylketonuria (PKU) mild PKU non-pku HPA, depending on the level of serum phenylalanine at the time of diagnosis; this level provides an estimate of the residual enzyme activity that partly depends on the mutation in the PAH gene and makes it possible to define the biochemical phenotype atypical PKU (variant PKU), results from the deficient biosynthesis or regeneration of the PAH cofactor, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) Phenylketonuria 38
39 Phenylketonuria autosomal recessive disorder prevalence: varies by country ranging from between one in 10,000 and one in 20,000 births in U.S.A. and Europe 39
40 PKU natural history infants appear until normal thay are a few months old the natural history of the phenylketonuria consists in a progressive irreversible neurological impairment during infancy and childhood the most common outcome is severe mental retardation a mousy odor, eczema and reduced hair skin and iris pigmentation reduced growth, microcephaly and neurological signs as tremor, epilepsy all untreated patients have behavioral problems as hyperactivity, stereotypy and anxiety the severity of the clinical phenotype directly correlates with blood phenylalanine levels that reflect the degree of enzymatic deficiency PKU - diagnosis in advanced clinical presentation is easy, confirmed by the high levels of phenylalanine in serum - but there is no possibility of effective treatment in most european countries newborn screening is routinely carried out within 72 hours of birth, by taking a small pin prick of blood from the baby s heel for laboratory analysis 40
41 PKU - treatment the foundation of PKU treatment is a low Phe diet which, by reducing or normalising Phe concentrations, prevents the development of the neurological and psychological changes since neurological changes have been demonstrated within one month of birth, it is recommended that dietary restriction should be started early and be continued through childhood when neural development is maximal clinical neurological abnormalities, affected neuropsychological performance and brain imaging in adults with PKU has led to a consensus opinion that the PKU diet should be followed for life an even more stringent regime of Phe restriction is required for women with PKU contemplating starting a family, particularly during pregnancy, as elevated blood Phe concentrations are teratogenic towards the developing foetus PKU - treatment but early treated PKU patients have normal intellectual quotients (I.Q.), but can have an I.Q. gap when compared to their non-pku siblings patients with PKU frequently have lower scores for certain neuropsychological functions, with executive function being the most affected area the Phe-restricted diet with semi-synthetic supplementation is not without risk PKU patients under dietary treatment can have low concentrations of trace elements and cholesterol, and some disturbance to folate metabolism as well as distortion of their fatty acid profile 41
42 Phe in food New Strategies for the Treatment of Phenylketonuria (PKU) 42
43 43
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) IAP UG Teaching slides
 INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM (IEM) 1 OBJECTIVES What are IEMs? Categories When to suspect? History and clinical pointers Metabolic presentation Differential diagnosis Emergency and long term management
Disorders of Carbohydrates. Disorders of Galactose Metabolism Glycogen Storage Diseases Diabetes Mellitus
 Disorders of Carbohydrates Metabolism Disorders of Galactose Metabolism Glycogen Storage Diseases Diabetes Mellitus Disorders of Galactose Metabolism GALACTOSE Galactose is a sugar that is found mainly
Disorders of Carbohydrates Metabolism Disorders of Galactose Metabolism Glycogen Storage Diseases Diabetes Mellitus Disorders of Galactose Metabolism GALACTOSE Galactose is a sugar that is found mainly
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 16 Done Huda shaheen by Corrected by حسام أبو عوض Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 In the previous lecture, we talked about glycogen metabolism and regulation. In this sheet we will talk about the metabolism
number 16 Done Huda shaheen by Corrected by حسام أبو عوض Doctor Nayef Karadsheh 1 In the previous lecture, we talked about glycogen metabolism and regulation. In this sheet we will talk about the metabolism
7 Medical Genetics. Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobinopathies. Protein and Gene Structure. and Biochemical Genetics
 SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES
 HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES Particular risk factors are: Advanced maternal age (e.g. Down's syndrome) Family history of inherited diseases (e.g. fragile X syndrome, Huntington's chorea) Previous child
HEREDITARY METABOLIC DISEASES Particular risk factors are: Advanced maternal age (e.g. Down's syndrome) Family history of inherited diseases (e.g. fragile X syndrome, Huntington's chorea) Previous child
So Much More Than The PKU Test
 Newborn Metabolic Screening So Much More Than The PKU Test Sarah Viall, MSN, PPCNP BC Newborn Screening Program Coordinator Division of Genetics & Metabolism Conflicts of Interest I have no conflicts of
Newborn Metabolic Screening So Much More Than The PKU Test Sarah Viall, MSN, PPCNP BC Newborn Screening Program Coordinator Division of Genetics & Metabolism Conflicts of Interest I have no conflicts of
Inborn Error Of Metabolism :
 Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Most common metabolic disorders in childhood. Neonatal screening and diagnostic approach to the. Inborn errors of metabolism (IEM)
 Department of Pediatrics and Developmental Disorders Medical University of Bialystok Most common metabolic disorders in childhood. Neonatal screening and diagnostic approach to the inborn errors of metabolism
Department of Pediatrics and Developmental Disorders Medical University of Bialystok Most common metabolic disorders in childhood. Neonatal screening and diagnostic approach to the inborn errors of metabolism
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose. Jana Novotna
 Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
Nutritional Management of Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Kay Davis, RD, CSP Esther Berenhaut, RD, CSP, CSR Aug 28, 2017
 Nutritional Management of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Kay Davis, RD, CSP Esther Berenhaut, RD, CSP, CSR Aug 28, 2017 OBJECTIVES Brief overview of newborn screening of metabolic disorders, inheritance patterns.
Nutritional Management of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Kay Davis, RD, CSP Esther Berenhaut, RD, CSP, CSR Aug 28, 2017 OBJECTIVES Brief overview of newborn screening of metabolic disorders, inheritance patterns.
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM)
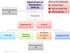 Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
Clinical Presentation Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) Click on the following: - Clinical Pearl - link to movie clip - link to picture Investigations Blood Work Urine No Acidosis NH 4 + Metabolic Acidosis
The spectrum and outcome of the. neonates with inborn errors of. metabolism at a tertiary care hospital
 The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry
 Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Paediatric Clinical Chemistry Dr N Oosthuizen Dept Chemical Pathology UP 2011 Paediatric biochemistry The child is not a miniature adult Physiological development Immature organ systems Growing individual
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when
 CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders
 Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
Newborn Screening: Blood Spot Disorders Arizona s Newborn Screening Program Program Overview Panel of Disorders Disorder Descriptions Program Components Hospitals ADHS Lab ADHS Follow-up ADHS Billing Medical
Summary. Syndromic versus Etiologic. Definitions. Why does it matter? ASD=autism
 Summary It is becoming clear that multiple genes with complex interactions underlie autism spectrum (ASD). A small subset of people with ASD, however, actually suffer from rare single-gene Important to
Summary It is becoming clear that multiple genes with complex interactions underlie autism spectrum (ASD). A small subset of people with ASD, however, actually suffer from rare single-gene Important to
Glycogen Storage Disease
 Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
Glycogen Storage Disease 1 Introduction The food we eat is usually used for growth, tissue repair and energy. The body stores what it does not use. Excess sugar, or glucose, is stored as glycogen in the
Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.014 02/18/2000 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 08/23/2013 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Medical Foods for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.014 02/18/2000 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 08/23/2013 Section: Medicine Place(s)
GALACTOSEMIA. Incidence
 GALACTOSEMIA Lactose, or milk sugar, is broken down into its constituent simple sugars, glucose and galactose, before absorption in the intestine. Galactosemia, which is an increased concentration of galactose
GALACTOSEMIA Lactose, or milk sugar, is broken down into its constituent simple sugars, glucose and galactose, before absorption in the intestine. Galactosemia, which is an increased concentration of galactose
GENOTYPE-PHENOTYPE CORRELATIONS IN GALACTOSEMIA COMPLICATIONS COMPLICATIONS COMPLICATIONS LONG-TERM CHRONIC COMPLICATIONS WITH NO CLEAR CAUSE
 Galactosemia Deficiency: galactose-1-phosphate-uridyltransferase(galt) GENOTYPE-PHENOTYPE CORRELATIONS IN GALACTOSEMIA GALT D-galactose-1-phosphate UDPgalactose + + UDPglucose D-glucose-1-phosphate DIVISION
Galactosemia Deficiency: galactose-1-phosphate-uridyltransferase(galt) GENOTYPE-PHENOTYPE CORRELATIONS IN GALACTOSEMIA GALT D-galactose-1-phosphate UDPgalactose + + UDPglucose D-glucose-1-phosphate DIVISION
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis)
 Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Newborn Screen & Development Facts about the genetic diseases new since March 2006 (Excluding Cystic Fibrosis) 1) Argininosuccinic acidemia (ASA) a) Incidence: ~1 in 70,000 b) Deficiency in an enzyme of
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department. Will Davies June 2014
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Will Davies June 2014 Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Emergency Department Overview Although individually rare, altogether they are 1:1000-2500
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2
 Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Module : Clinical correlates of disorders of metabolism Block 3, Week 2 Department of Paediatrics and Child Health University of Pretoria Tutor : Prof DF Wittenberg : dwittenb@medic.up.ac.za Aim of this
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS
 Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated July 2006 This syllabus is intended as a guide. Whilst the training should be comprehensive,
Training Syllabus CLINICAL SYLLABUS SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated July 2006 This syllabus is intended as a guide. Whilst the training should be comprehensive,
Genética e Hígado: Cómo contribuye la genética en el algoritmo diagnóstico de la enfermedad hepática pediátrica? Nicholas Ah Mew, MD
 Genética e Hígado: Cómo contribuye la genética en el algoritmo diagnóstico de la enfermedad hepática pediátrica? Nicholas Ah Mew, MD April 24, 2017 SAP 2017 Buenos Aires Genetic disorders are rare why
Genética e Hígado: Cómo contribuye la genética en el algoritmo diagnóstico de la enfermedad hepática pediátrica? Nicholas Ah Mew, MD April 24, 2017 SAP 2017 Buenos Aires Genetic disorders are rare why
Most common is the congenital adrenogenital syndrome (AGS) or congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
 Newborn Screening Examination parameters: TSH-neonatal (hypothyreosis), 17-OH progesterone (AGS), galactose (galactosemia), galactose-uridyl transferase (galacto semia), biotinidase (biotinidase ), phenylalanine
Newborn Screening Examination parameters: TSH-neonatal (hypothyreosis), 17-OH progesterone (AGS), galactose (galactosemia), galactose-uridyl transferase (galacto semia), biotinidase (biotinidase ), phenylalanine
Pathophysiology of the Phenylketonuria
 Problem 4. Pathophysiology of the Phenylketonuria Readings for this problem are found on pages: 79-82, 84, 85-6, 945-6 and 1019 of your Pathophysiology (5 th edition) textbook. (This problem was based
Problem 4. Pathophysiology of the Phenylketonuria Readings for this problem are found on pages: 79-82, 84, 85-6, 945-6 and 1019 of your Pathophysiology (5 th edition) textbook. (This problem was based
Metabolic diseases of the liver
 Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 16 Outline Why is glucose such a prominent fuel in all life forms? 1. Glucose
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 16 Outline Why is glucose such a prominent fuel in all life forms? 1. Glucose
Newborn Screening Improving Children s Health
 Newborn Screening Improving Children s Health By Frans Sardi Satyawirawan* Ina Susianti Timan ** * Dep. Of Clinical Pathology, Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital (1974-2006) **Dep. of Clinical Pathology, Cipto
Newborn Screening Improving Children s Health By Frans Sardi Satyawirawan* Ina Susianti Timan ** * Dep. Of Clinical Pathology, Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital (1974-2006) **Dep. of Clinical Pathology, Cipto
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018
 ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Phenylketonuria A. Macdonald (UK) Approach to Dietary Management of PKU Conflicts of interest Anita MacDonald has received research funding and honoraria
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Phenylketonuria A. Macdonald (UK) Approach to Dietary Management of PKU Conflicts of interest Anita MacDonald has received research funding and honoraria
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children
 National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
National Metabolic Biochemistry Network Guidelines for the investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and children Aim To provide guidance on the biochemical investigation of hypoglycaemia in infants and
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition
 Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
Suspected Metabolic Disease in the Newborn Period Acute Management "What do I do?" Barbara Marriage, PhD RD Abbott Nutrition Introduction Review clinical findings that may be suspicious of a metabolic
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up
 HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal Newborn Metabolic Screening Results Causes, Management and Follow up Dr. Josephine Chong Clinical Professional Consultant Centre of Inborn Errors
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review -
 Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
Guideline for the diagnosis and management of isovaleryl-coa-dehydrogenase deficiency (isovaleric acidemia) - a systematic review - Guideline development group International interdisciplinary guideline
SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE
 SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated December 2014: Vassili Valayannopoulos and Andrew Morris Paediatrics is an independent medical specialty based on the knowledge and
SYLLABUS FOR TRAINING IN CLINICAL PAEDIATRIC METABOLIC MEDICINE Updated December 2014: Vassili Valayannopoulos and Andrew Morris Paediatrics is an independent medical specialty based on the knowledge and
3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES
 3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
3 HYDROXY 3 METHYLGLUTARYL CoA (3 HMG CoA) LYASE DEFICIENCY RECOMMENDATIONS ON EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF METABOLIC DISEASES Patient s name: Date of birth: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet
 Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet Website:www.tipn.org.tw Telephone:(02)85962050 Ext. 401-403 Service line:(02)85962065 Fax:(02)85962067
Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet Website:www.tipn.org.tw Telephone:(02)85962050 Ext. 401-403 Service line:(02)85962065 Fax:(02)85962067
Routine Newborn Screening, Testing the Newborn Inherited Metabolic Disorders Update August 2015
 Routine Newborn Screening, Testing the Newborn Inherited Metabolic Disorders Update August 2015 Metabolic birth defects can cause physical problems, mental retardation and, in some cases, death. It is
Routine Newborn Screening, Testing the Newborn Inherited Metabolic Disorders Update August 2015 Metabolic birth defects can cause physical problems, mental retardation and, in some cases, death. It is
The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments
 CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
Methylmalonic aciduria
 Methylmalonic aciduria Introductory information Written by: F. Hörster, S. Kölker & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Methylmalonic aciduria MMA 2 Methylmalonic aciduria
Methylmalonic aciduria Introductory information Written by: F. Hörster, S. Kölker & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Methylmalonic aciduria MMA 2 Methylmalonic aciduria
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child
 Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency
 Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase
Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Very-long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase
Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY
 THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY WHAT IS THE THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY (hthtr2)? The thiamine transporter type 2 deficiency (hthtr2) is a inborn error of thiamine metabolism caused by
THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY WHAT IS THE THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY (hthtr2)? The thiamine transporter type 2 deficiency (hthtr2) is a inborn error of thiamine metabolism caused by
Introduction to Organic Acidemias. Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.
 Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Introduction to Organic Acidemias Hilary Vernon, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Genetic Medicine Johns Hopkins University 7.25.2014 A Brief Historical Overview Garrod, Archibald E. 1902. The Incidence of
Clinical evaluation Jaundice skin and mucous membranes
 JAUNDICE Framework The definition of Neonatal Jaundice Billirubin Metabolism Special characteristic in neonates Dangerous of the Hyperbillirubinemia The diseases in relation with Neonatal Jaundice Objectives:
JAUNDICE Framework The definition of Neonatal Jaundice Billirubin Metabolism Special characteristic in neonates Dangerous of the Hyperbillirubinemia The diseases in relation with Neonatal Jaundice Objectives:
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks
 A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
A Lawyer s Perspective on Genetic Screening Performed by Cryobanks As a lawyer practicing in the area of sperm bank litigation, I have, unfortunately, represented too many couples that conceived a child
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 33 Done by Omar Sami Corrected by Waseem abu obeida Doctor Diala Too late for second guessing, too late to go back to sleep 1 P age Just try defying gravity This sheet will be divided to two parts,
number 33 Done by Omar Sami Corrected by Waseem abu obeida Doctor Diala Too late for second guessing, too late to go back to sleep 1 P age Just try defying gravity This sheet will be divided to two parts,
Amino Acid Disorders. What is ASAL deficiency? Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Clinical aspects of pterin disorders
 Clinical aspects of pterin disorders Thomas Opladen, MD University Children s Hospital Department of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Heidelberg Germany Introductory words Brain function depends on the capacity
Clinical aspects of pterin disorders Thomas Opladen, MD University Children s Hospital Department of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Heidelberg Germany Introductory words Brain function depends on the capacity
Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide
 Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide Introduction Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is an inborn error of the leucine pathway caused by defects of the isovaleryl-oadehydrogenase (IV). The clinical presentation
Isovaleric Acidemia: Quick reference guide Introduction Isovaleric acidemia (IVA) is an inborn error of the leucine pathway caused by defects of the isovaleryl-oadehydrogenase (IV). The clinical presentation
Glycogen Storage Diseases (A group of genetic diseases)
 Glycogen Storage Diseases (A group of genetic diseases) Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSD) Inherited genetic defects related to glycogen metabolism. Glycogenosis. Characterized by deposition of glycogen in
Glycogen Storage Diseases (A group of genetic diseases) Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSD) Inherited genetic defects related to glycogen metabolism. Glycogenosis. Characterized by deposition of glycogen in
Diseases Associated with Glycogen Synthesis
 Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module: 29 Principal Investigator, Dr. S.K.Khare, Professor IIT Delhi. Paper Coordinator Content Writer Dr. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dr. Vijaya Khader UGC-CAS Dr.
Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module: 29 Principal Investigator, Dr. S.K.Khare, Professor IIT Delhi. Paper Coordinator Content Writer Dr. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dr. Vijaya Khader UGC-CAS Dr.
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate. Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics
 Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
A Guide for Prenatal Educators
 A Guide for Prenatal Educators Why Teach Newborn Screening This booklet is designed to make it easy for you, a prenatal educator, to effectively inform expectant parents about newborn screening. All of
A Guide for Prenatal Educators Why Teach Newborn Screening This booklet is designed to make it easy for you, a prenatal educator, to effectively inform expectant parents about newborn screening. All of
Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism Patricia Jones, PhD DABCC FACB UT Southwestern Medical Center Children s Medical Center Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives Justify
Newborn Screening & Methods for Diagnosing Inborn Errors of Metabolism Patricia Jones, PhD DABCC FACB UT Southwestern Medical Center Children s Medical Center Dallas, Texas Learning Objectives Justify
Chapter 9. Biotransformation
 Chapter 9 Biotransformation Biotransformation The term biotransformation is the sum of all chemical processes of the body that modify endogenous or exogenous chemicals. Focus areas of toxicokinetics: Biotransformation
Chapter 9 Biotransformation Biotransformation The term biotransformation is the sum of all chemical processes of the body that modify endogenous or exogenous chemicals. Focus areas of toxicokinetics: Biotransformation
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
Chapter 1: What is PKU?
 Chapter 1: What is PKU? A Parent's Perspective "If our child with PKU had been our first instead of our third, or if we had wanted more children after we had her, we would have done so, even knowing the
Chapter 1: What is PKU? A Parent's Perspective "If our child with PKU had been our first instead of our third, or if we had wanted more children after we had her, we would have done so, even knowing the
Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency
 Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase MCAD
Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Introductory information Written by: V. Prietsch & P. Burgard Reviewed & Revised for North America by: S. van Calcar Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase MCAD
Childhood epilepsy: the biochemical epilepsies. Dr Colin D Ferrie Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Leeds General Infirmary
 Childhood epilepsy: the biochemical epilepsies Dr Colin D Ferrie Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Leeds General Infirmary Definitions Epileptic Seizure Manifestation(s) of epileptic (excessive and/or
Childhood epilepsy: the biochemical epilepsies Dr Colin D Ferrie Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Leeds General Infirmary Definitions Epileptic Seizure Manifestation(s) of epileptic (excessive and/or
1 Cognitive, Psychological and Behavioral Assessment Based Evidence
 1 Cognitive, Psychological and Behavioral Assessment Based Evidence Preface Current medical evidence has led experts on PKU to suspect that current therapy for PKU may leave individuals with an increased
1 Cognitive, Psychological and Behavioral Assessment Based Evidence Preface Current medical evidence has led experts on PKU to suspect that current therapy for PKU may leave individuals with an increased
HYPOTHYROIDISM IN CHILDREN. IAP UG Teaching slides
 HYPOTHYROIDISM IN CHILDREN 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction Congenital hypothyroidism Etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, approach, treatment and prognosis Acquired hypothyroidism Etiology, clinical features,
HYPOTHYROIDISM IN CHILDREN 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction Congenital hypothyroidism Etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, approach, treatment and prognosis Acquired hypothyroidism Etiology, clinical features,
PKU PKU. Phenylketonuria TEMPLE. Information for families following Information for families after a positive newborn screening
 PKU Phenylketonuria PKU Information for families following newborn a positive screening newborn screening Information for families after a positive newborn screening Information for families after a positive
PKU Phenylketonuria PKU Information for families following newborn a positive screening newborn screening Information for families after a positive newborn screening Information for families after a positive
Symptoms Common symptoms that result from untreated biotinidase deficiency are listed in below:
 N ewborn screening tests are available to identify those babies who have specific conditions that put them at risk of health problems. Depending on where you live certain tests may be carried out routinely
N ewborn screening tests are available to identify those babies who have specific conditions that put them at risk of health problems. Depending on where you live certain tests may be carried out routinely
Neonatal Hypoglycemia
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Neonatal Hypoglycemia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Neonatal Hypoglycemia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Information for health professionals
 Introduction of a new screening test for newborn babies in Wales Newborn bloodspot screening for Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) Newborn bloodspot screening for MCADD is being introduced
Introduction of a new screening test for newborn babies in Wales Newborn bloodspot screening for Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) Newborn bloodspot screening for MCADD is being introduced
Amal Alamri. Phenylketonuria
 Amal Alamri Phenylketonuria Norwegian doctor Asbjørn Følling (left) discovered phenylpyrouvica (later termed phenylketonuria) in 1934 upon discovering that ten mentally retarded patients had phenylpyruvic
Amal Alamri Phenylketonuria Norwegian doctor Asbjørn Følling (left) discovered phenylpyrouvica (later termed phenylketonuria) in 1934 upon discovering that ten mentally retarded patients had phenylpyruvic
Inborn errors of metabolism
 ESPEN Congress Nice 2010 From child to adult nutrition Inborn errors of metabolism Pascal Crenn Inborn errors of metabolism: from child to adult Pascal Crenn Hôpital Raymond Poincaré 92380 Garches. France
ESPEN Congress Nice 2010 From child to adult nutrition Inborn errors of metabolism Pascal Crenn Inborn errors of metabolism: from child to adult Pascal Crenn Hôpital Raymond Poincaré 92380 Garches. France
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 PBL SEMINAR ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview Sites
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 PBL SEMINAR ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview Sites
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social
Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 12 12.1 Identify and differentiate between macronutrients (lipids, amino acids and saccharides) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Master Tutor Section
Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 12 12.1 Identify and differentiate between macronutrients (lipids, amino acids and saccharides) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Master Tutor Section
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz )
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
e-learning Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects Camilla Reed and Dr Simon Olpin Sheffield Children s Hospital
 e-learning Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects Camilla Reed and Dr Simon Olpin Sheffield Children s Hospital Fatty Acids Fatty acids are a major source of energy and body fat is an energy dense material. They
e-learning Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects Camilla Reed and Dr Simon Olpin Sheffield Children s Hospital Fatty Acids Fatty acids are a major source of energy and body fat is an energy dense material. They
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes
 Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
TITLE: NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA. Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD
 NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
NO. OF PAGES: Page 1 of 17 SUPERCEDES: N/A NURSING GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIA NAME/ Eilish O Connell, Clinical Education Facilitator, NCIMD SIGNATURE: DATE: NAME/
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Human inherited diseases
 Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
Attachment 1. Newborn Screening Program Description
 Attachment 1 Newborn Screening Program Description The core mission of Texas Newborn Screening Program is to save children s lives through the early detection of life-threatening disorders. 34 Newborn
Attachment 1 Newborn Screening Program Description The core mission of Texas Newborn Screening Program is to save children s lives through the early detection of life-threatening disorders. 34 Newborn
Low Blood Sugar in Dogs & Cats Figuring Out Hypoglycemia
 Low Blood Sugar in Dogs & Cats Figuring Out Hypoglycemia Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, is a relatively common biochemical abnormality documented in sick dogs and cats presented to the emergency
Low Blood Sugar in Dogs & Cats Figuring Out Hypoglycemia Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia, is a relatively common biochemical abnormality documented in sick dogs and cats presented to the emergency
Dr. R. Pradheep. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern. Railway. Hospital.
 Hyperbilirubinemia in an Infant Pradheep Railway Dr. R. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern Hospital. A 2 ½ month old male baby born out of 3 rd degree consanguinity presented to us with c/o yellow discolouration
Hyperbilirubinemia in an Infant Pradheep Railway Dr. R. DNB Resident Pediatrics. Southern Hospital. A 2 ½ month old male baby born out of 3 rd degree consanguinity presented to us with c/o yellow discolouration
Disorder name: Argininemia / Arginase deficiency Acronym: ARG 1 deficiency
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview
 ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple
ACUTE & CHRONIC ETHANOL EFFECTS An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
M3 Pediatric Clerkship
 M3 Pediatric Clerkship The overall goals for the third year Pediatric Clerkship are to educate future physicians to provide competent, effective and compassionate care of patients by developing clinical
M3 Pediatric Clerkship The overall goals for the third year Pediatric Clerkship are to educate future physicians to provide competent, effective and compassionate care of patients by developing clinical
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Carbohydrate Lipid and Protein! Metabolism! In the catabolism of carbohydrates, glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, which is then metabolized into acetyl CoA. Prepared
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Carbohydrate Lipid and Protein! Metabolism! In the catabolism of carbohydrates, glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, which is then metabolized into acetyl CoA. Prepared
Urea Cycle Defects. Dr Mick Henderson. Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust. MetBioNet IEM Introductory Training
 Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
There are four different forms of Tarui disease, which are classed by their signs and symptoms and age of presentation.
 Tarui Disease Tarui disease (also known as phosphofructokinase deficiency, or glycogen storage disease type VII) was first described in 1965 by the Japanese physician Seiichiro Tarui and his co-workers.
Tarui Disease Tarui disease (also known as phosphofructokinase deficiency, or glycogen storage disease type VII) was first described in 1965 by the Japanese physician Seiichiro Tarui and his co-workers.
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
220 SUBJECT INDEX. D Diarrhea and sodium balance, 74 weanling, 161,179,208,212; see also Infection
 Subject Index Acid balance, see ph Allergy, food, see also Immunity and beikost, 143-144 and breast milk, 91,143 and formula, 89-90 Antidiuretic hormone, 66 67 Antigens, see also Immunity determinants,
Subject Index Acid balance, see ph Allergy, food, see also Immunity and beikost, 143-144 and breast milk, 91,143 and formula, 89-90 Antidiuretic hormone, 66 67 Antigens, see also Immunity determinants,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Neonatal Screening I - INTRODUCTION 1- Neonatal screening for a metabolic disease must address a frequent pathology for which there is an
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Neonatal Screening I - INTRODUCTION 1- Neonatal screening for a metabolic disease must address a frequent pathology for which there is an
Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Metabolic Pathways
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44441 1 Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Metabolic Pathways OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m44441 1 Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Metabolic Pathways OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Nutrients. Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
