Evaluation of physiological parameters before and after respiratory physiotherapy in newborns with acute viral bronchiolitis
|
|
|
- Hannah Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gonçalves et al. International Archives of Medicine 2014, 7:3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Evaluation of physiological parameters before and after respiratory physiotherapy in newborns with acute viral bronchiolitis Rodrigo A S Gonçalves 1*, Sérgio Feitosa 1, Cláudia de Castro Selestrin 1, Vitor E Valenti 2, Fernando H de Sousa 3, Arnaldo A F Siqueira 1, Márcio Petenusso 1 and Luiz Carlos de Abreu 1 Abstract Background: Acute viral bronchiolitis is a respiratory disease with high morbidity that affects newborn in the first two years of life. Its treatment with physiotherapy has been highlighted as an important tool, however, there is no consensus regarding its effects on patients improvement. We aimed to evaluate the physiological parameters before and after the procedure respiratory therapy in newborn with acute viral bronchiolitis. Method: This was a cross sectional observational study in 30 newborns with acute viral bronchiolitis and indicated for physiotherapy care in a hospitalized Urgency and Emergency Unit. It was collected the clinical data of newborn through evaluation form, and we measured heart rate (HR), oxygen saturation (SpO2) and respiratory rate (RR). We measured the variables before physiotherapy treatment, 3, 6 and 9 minutes after the physiotherapy treatment. Results: There has been no change in HR, however, we observed a decrease in RR at 6 and 9 min compared to 3 min and increase in SpO2 at 3, 6 and 9 min compared to before physiotherapy. Conclusion: Respiratory physiotherapy may be an effective therapy for the treatment of newborn with Acute Viral Bronchitis. Keywords: Bronchiolitis, Circulatory and Respiratory Physiology, Infant, Newborn, Physiotherapy (Techniques) Background The acute viral bronchiolitis (AVB) is a respiratory disease that affects the lower airways through an acute inflammatory process affecting children in the first two years of life and its peak incidence is below 12 months of age. It is of great clinical relevance due to the high morbidity, particularly in the autumn and winter seasons. The mortality of newborns hospitalized with AVB is around 1% [1,2]. Clinically, the AVB is characterized by cough, fever, runny nose, tachypnea, increased respiratory effort and dyspnea. The severity of the symptoms is associated with the inflammatory process caused by viruses, with infiltration of neutrophils, lymphocytes and release of * Correspondence: rodrigoaugustoo@gmail.com 1 Laboratório de Escrita Científica, Departamento de Morfologia e Fisiologia, Faculdade de Medicina do ABC, Av. Príncipe de Gales, 821, Santo André, SP, Brazil Full list of author information is available at the end of the article inflammatory mediators that cause edema, muscle spasm and increased mucus production. Chest radiograph shows hyperinflation, atelectasis and peri-bronchial infiltrate [3]. Currently, respiratory physiotherapy (RP) has emerged as an important tool in the treatment of diseases of the respiratory system, acting to increase mucociliary clearance, airway clearance, facilitation of ventilation and gas exchange. The indication of RP in AVB remains controversial with regard to their effects on patients' clinical improvement and reduced hospitalization time. Some authors do not believe in the efficacy of performing RP in infants with AVB [4]. However, other authors found favorable results in physiologic parameters, mucocilicar increased clearance and improved lung auscultation through the application of respiratory therapy protocols [5-7]. Due to the lack of consensus on the issue, we aimed to evaluate the physiological parameters before and after the RP in newborns with AVB Gonçalves et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Gonçalves et al. International Archives of Medicine 2014, 7:3 Page 2 of 5 Method We conducted a cross sectional observational study in 30 newborns admitted in the Emergency Unit of São Bernardo do Campo, São Paulo, from October to November, This study followed all the criteria for human research and was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of the ABC Foundation, approval number 258/2008. Inclusion criteria Written consent of the responsible for the patient was signed, possessing prescription of physiotherapy care, clinical and radiological diagnosis of bronchiolitis confirmed, aged between 29 days and 6 months of age and be in the acute phase of the disease. Exclusion criteria Patients using any device of positive pressure ventilation via tracheal tube, nasal prong or face mask, under medication of vasoactive drugs, birth defects, heart disease, neurological disorders or genetic syndromes. Variables measured We measured heart rate (HR) and oxygen saturation (SpO2), which were measured and compiled by a multiparameter monitor Dixtal, DX2020 model. During the pre and post care, physiological variables were recorded, according to protocol formulated by the researchers, who were: HR, measured in whole numbers of heartbeats. Bradycardia was considered when the HR dropped below 80 beats per minute for 20 seconds. The SpO2 was measured in whole numbers through the pulse oximeter. Hypoxemia was seen when the fall occurred in 10% or more in saturation for more than 20 seconds. No change was made in the fraction of inspired oxygen for 30 minutes before treatment within 30 minutes, to avoid influence on the variation of saturation. The respiratory rate was measured with the aid of a stopwatch Casio brand, model FS-02, followed by quantification, always by the same investigator and in 60 seconds, through the thoraco-abdominal movements. No control group was used, because each newborn was its own parameter, by comparing the pre and posttherapy. After the initial assessment it was performed the routine physiotherapy care in the Pediatric Nursing team unit, without the intervention of the researchers. Data were collected by the physiotherapist and researcher obtained from a single meeting in the afternoon, between 2p.m.and6p.m.,justbeforebeingcompiled,anduntil9 minutes after the procedure physiotherapy. The completion of the procedures was performed by a physiotherapist care unit, which has not had access to records of data collection. Upon completion of the session, the children underwent a further assessment of physiological parameters for subsequent comparison with previously collected data. The variables were collected at three moments (0 3minutes,3 6 minutes,6 9 minutes). Physiotherapy protocol The neonatal physiotherapy procedures were applied according to the following protocol: measurement of HR, SpO2% and respiratory rate (RR) about 2 minutes before the sessions of physiotherapy and treatment. The protocols included physiotherapy maneuvers reexpansion pulmonary manuals vibration and postural drainage. Statistical analysis At the end of the study, performed the descriptive analysis of qualitative variables, which were presented in terms of their absolute and relative values. Quantitative variables were presented as means and standard deviations. The normality and homogeneity of variances were verified by Kolmogorov-Smirnove and Levene, respectively. To compare the mean values and initial 3, 6, 9 minutes after therapy were statistically different, we used Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) for repeated measures followed by the Friedman post test. In all tests was set at 5% (p <0.05) level for rejection of the null hypothesis, and specific software was used for statistical studies, SPSS 13.0 for Windows. Results The study population consisted of 30 infants aged between 29 days and 6 months old with a mean of 3.4 (± 1.63) months old, of which 66.6% were male. The protocol was applied between the first and seventh day of hospitalization. None of the infants studied were using sedatives or vasoactive drugs, and only three did not use antibiotics. The mean duration of the RP was 18 minutes and 43 seconds (14 20 minutes). We did not observe significant changes in relation to baseline HR compared the four times (pretreatment vs. Treatment vs 3 min. Treatment vs 6 min. 9 min treatment) (Figure 1). Regarding RR, there was a statistically significant difference when comparing each of the periods evaluated between the control condition vs. 3 min (p <0.0001), 3 min vs. 6 min (p = 0.000), 3 min vs. 9 min (p = 0.01), demonstrating a period of stabilization (Figure 2). In relation to the SpO2, it was observed that there was a statistically significant difference between pre and 3 min, pre vs. 6 min and pre vs. 9 min (p <0.0001) (Figure 3). Table 1 shows the variables presented in the Figures 1, 2and3. Discussion In this study, we found that physiotherapy procedures in infants with AVB showed no deleterious effects on
3 Gonçalves et al. International Archives of Medicine 2014, 7:3 Page 3 of 5 Figure 1 Mean values for heart rate (HR) before treatment and physiotherapy 3, 6 and 9 minutes after the physiotherapy session. heart rate and breathing, we observed an increase in the SpO2. The indication of physical therapy for newborns with AVB is in doubt, it is critical that new research is done because there is no consensus in the literature [8]. French researchers recognize its role as a treatment strategy, prescribed by physicians in 80 to 95% of cases, unlike Anglo-Saxon countries that do not recognize it as part of treatment, due to the lack of controlled studies to prove its effectiveness [1,2]. A review of literature (American Academy of Pediatrics) indicated that the RP did not reduce the length of hospitalization and the need for oxygen and did not improve the clinical severity score for children. Pupin et al. [4], in a study of 81 infants with AVB, in order to compare the effects on physiological parameters in two respiratory Figure 2 Mean values for respiratory rate (RR) before treatment and physiotherapy 3, 6 and 9 minutes after the physiotherapy session. *p <0.05: vs. 3 min.
4 Gonçalves et al. International Archives of Medicine 2014, 7:3 Page 4 of 5 Figure 3 Mean values for oxygen saturation (SpO2) before treatment and physiotherapy 3, 6 and 9 minutes after the physiotherapy session. *p <0.05: vs pre. therapy protocols, increased expiratory flow (IEF) and vibrocompression associated with postural drainage, decreased RR observed in infants undergoing physiotherapy techniques in relation the control group and the evolution of the HR showed an increase after 10 minutes after the procedure, the group submitted to the IEF protocol followed a decline at the end of the assessment, common to all groups. An important issue is the fact that the resources used for application of physiotherapy in the pediatric age group were initially adapted from methods used in adult patients, such as tapping, postural drainage and vibration therapy, resources no longer used today because over the years emerged specific techniques appropriate for each age group, consistent with the anatomical and physiological differences of infants [9]. Among them is the increased expiratory flow (IEF) and expiration prolonged slow (ELPr) for use in infants, which were used in this research. Another study [8] used protocol respiratory therapy in 19 infants with moderate AVB associating ELPr to cough Table 1 Mean values for heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR) and oxygen saturation (SpO 2 ) before treatment and physiotherapy 3, 6 and 9 minutes after the physiotherapy session Variable Before 3 min 6 min 9 min HR (bpm) ± ± ± ± 14 RR (cpm) 62.1 ± ± 11* 63.1 ± 11** 60.7 ± 12** SpO 2 (%) 94.9 ± ± 1.3* 96.6 ± 0.7* 97.3 ± 0.5* Bpm: Beats per minute; cpm: Cycles per minute). *p <0.05: vs pre; **p <0.05: vs. 3 min. stimulation. The authors observed improvement in symptoms of bronchial obstruction, as well as a decrease in HR and increase in SpO2. The authors stated that there is no risk in implementing this technique and discuss the deleterious results of the application of respiratory therapy in infants with AVB in the literature may be related to protocols that used techniques like tapping and postural drainage. It has been observed that the performance of respiratory physiotherapy in patients hospitalized for AVB promoted reduction of respiratory distress, eliminating much of secretion aspirated and qualitative improvement auscultation groups who underwent vibration therapy and tapping [10]. The authors believe that reducing respiratory distress is due to increased secretion clearance, which leads to decreased airway resistance and thereby improves the ventilation-perfusion [11,12], since the present study demonstrated improvement of the physiological parameters in the study population following the procedure of physical therapy as noted in the study, against the results obtained with our work. Using similar method to this study, an investigation evaluated the variability of physiological parameters in 27 preterm infants undergoing physiotherapy and showed a decrease in HR and RR and increased SpO2, suggesting that the reduction in HR and RR leads to decreased energy expenditure because less adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is required to perform the cardiac muscle contractions and bronchial smooth. It is also worth to note that this reduction was accompanied by SpO2 inversely proportional effect [5]. It is also important to mention that physiotherapy protocols in children are different from those applied in
5 Gonçalves et al. International Archives of Medicine 2014, 7:3 Page 5 of 5 adults because it is related to chest expansion [13,14] These results, although applied in different population, corroborate the findings of this research, contributing to the clinical stability of infants. Our study has some important points to be discussed. The absence of a control group is a limitation of our study, however, this is due to ethical reasons. Another limitation is the short time period assessed that does not allow us to observe how long the beneficial effects are induced. Nonetheless, the advantage of it is the reproducibility of the method, which does not require any change in routine or use of equipment for specific application, it uses the pulse oximeter. We opted for the observation of a single professional in the application of respiratory therapy protocol, in order to avoid technical variations that occur in the application of the maneuvers, because since it is a manual therapy, the human factor is predominant hindering the validation and reliability of the reproducibility of the technique. Studies comparing results of applying the same technique by different professionals are needed to elucidate this issue. Conclusions In this study the application of the protocol of chest physiotherapy in infants with AVB caused no acute effects on beneficial physiological variables of the study population. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions All authors participated in the acquisition of data and revision of the manuscript. All authors determined the design, interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and gave final approval for the version submitted for publication. 3. American Academy of Pediatrics. Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Management of bronchiolitis: Diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 2006, 118: Pupin MK, Riccetto AG, Ribeiro JD, Baracat EC: Comparison of the effects that two different respiratory physical therapy techniques have on cardiorespiratory parameters in infants with acute viral bronchiolitis. J Bras Pneumol 2009, 35: Selestrin CC, Oliveira AG, Ferreira C, Siqueira AAF, Abreu LC, Murad N: Evaluation of physiological parameters in newborn preterm infants on mechanical ventilation after neonatal physiotherapy procedures. J Hum Growth Develop 2007, 17: de Abreu LC, Valenti VE, de Oliveira AG, Leone C, Siqueira AA, Herreiro D, Wajnsztejn R, Manhabusque KV, Júnior HM, de Mello Monteiro CB, Fernandes LL, Saldiva PH: Chest associated to motor physiotherapy improves cardiovascular variables in newborns with respiratory distress syndrome. Int Arch Med 2011, 26: Abreu LC, Valenti VE, OLIVEIRA AG, Leone C, Siqueira AAF, Gallo PR, Fonseca FLA, Nascimento VG, Saldiva PHN: Effects of physiotherapy on hemodynamic variables in newborns with acute respiratory distress syndrome. HealthMED Journal 2011, 5: Postiaux G, Dubois R, Marchand E, Demay M, Jacquy J, Margiaracina M: Effets de la kinésithérapie respiratoire associant expiration lente prolongée et toux provoquée dans la bronchiolite du nourrisson. Kinesither Rev 2006, 55: Bruurs ML, van der Giessen LJ, Moed H: The effectiveness of physiotherapy in patients with asthma: a systematic review of the literature. Respir Med Epub ahead of print. 10. Lanza FC: Respiratory therapy in infants with bronchiolitis: Perform or not? O Mundo da Saúde São Paulo 2008, 2: Deschildre A, Thumerelle C, Bruno B, Dubos F, Santos C, Dumonceaux A: Acute bronchiolitis in infants. Arch Pediatr 2000, 1: Hough JL, Flenady V, Johnston L, Woodgate PG: Chest physiotherapy for reducing respiratory morbidity in infants requiring ventilatory support. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008, 3:CD Mainenti MR, de Sousa RC, Dias CM, Costa SO, Ferreira AS, de Souza CP, Araújo AP: Body composition and chest expansion of type II and III spinal muscular atrophy patients. J Hum Growth Develop 2013, 23: Lustosa WA, Melo ML, Isidório UA, de Sousa MA, de Abreu LC, Valenti VE, Cardoso MA, de Assis EV: Risk factors for recurrent wheezing in infants. J Hum Growth Develop 2013, 23: doi: / Cite this article as: Gonçalves et al.: Evaluation of physiological parameters before and after respiratory physiotherapy in newborns with acute viral bronchiolitis. International Archives of Medicine :3. Acknowledgements This manuscript received financial support from UNESP. The funding body provided financial support to make all procedures and in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Author details 1 Laboratório de Escrita Científica, Departamento de Morfologia e Fisiologia, Faculdade de Medicina do ABC, Av. Príncipe de Gales, 821, Santo André, SP, Brazil. 2 Programa de Pós-Graduação em Fisioterapia, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, UNESP, Rua Roberto Simonsen, 305, Presidente Prudente, SP, Brazil. 3 Faculdade de Ciências, UNESP, Av. Eng. Luiz Edmundo Carrijo Coube, 14-01, Bauru, SP, Brazil. Received: 4 February 2013 Accepted: 13 December 2013 Published: 8 January 2014 References 1. de Bilderling G, Bodart E: Bronchiolitis management by the Belgian paediatrician: discrepancies between evidence-based medicine and practice. Acta Clin Belg 2003, 58(2): Halna M, Leblond P, Aissi E, Dumonceaux A, Delepoulle F, El Kohe R: Impact of the consensus conference on outpatient treatment of infant bronchiolitis. Three-year study in the Nord district of France. Presse Med 2005, 34: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Gabriela R Gomes PT MSc, Fernanda PG Calvete PT, Gabriela F Rosito PT, and Márcio VF Donadio PT PhD
 Rhinopharyngeal Retrograde Clearance Induces Less Respiratory Effort and Fewer Adverse Effects in Comparison With Nasopharyngeal Aspiration in Infants With Acute Viral Bronchiolitis Gabriela R Gomes PT
Rhinopharyngeal Retrograde Clearance Induces Less Respiratory Effort and Fewer Adverse Effects in Comparison With Nasopharyngeal Aspiration in Infants With Acute Viral Bronchiolitis Gabriela R Gomes PT
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY IN NICU PURPOSE POLICY STATEMENTS SITE APPLICABILITY PRACTICE LEVEL/COMPETENCIES. The role of chest physiotherapy in the NICU
 PURPOSE The role of chest physiotherapy in the NICU POLICY STATEMENTS In principle chest physiotherapy should be limited to those infants considered most likely to benefit with significant respiratory
PURPOSE The role of chest physiotherapy in the NICU POLICY STATEMENTS In principle chest physiotherapy should be limited to those infants considered most likely to benefit with significant respiratory
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the
 Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy
 An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
RESPIRATORY REHABILITATION
 RESPIRATORY REHABILITATION By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak University of kerbala College of nursing CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY Chest physiotherapy (CPT) includes: 1.Postural drainage. 2.Chest percussion and vibration.
RESPIRATORY REHABILITATION By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak University of kerbala College of nursing CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY Chest physiotherapy (CPT) includes: 1.Postural drainage. 2.Chest percussion and vibration.
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Appendix E Choose the sign or symptom that best indicates severe respiratory distress.
 Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
Active Cycle of Breathing Technique
 Active Cycle of Breathing Technique Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Version: 3 Ratified by: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when
Active Cycle of Breathing Technique Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Version: 3 Ratified by: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when
Master of Physical Therapy Program: Year 2 CARDIORESPIRATORY COURSE OUTLINES SUMMARY
 Master of Physical Therapy Program: Year 2 CARDIORESPIRATORY COURSE OUTLINES SUMMARY Course: PT 6124 Physical Therapy and Hospital based Care Through lecture, tutorial and laboratory sessions, students
Master of Physical Therapy Program: Year 2 CARDIORESPIRATORY COURSE OUTLINES SUMMARY Course: PT 6124 Physical Therapy and Hospital based Care Through lecture, tutorial and laboratory sessions, students
Protocol for performing chest clearance techniques by nursing staff
 Protocol for performing chest clearance techniques by nursing staff Rationale The main indications for performing chest clearance techniques (CCT) are to assist in the removal of thick, tenacious secretions
Protocol for performing chest clearance techniques by nursing staff Rationale The main indications for performing chest clearance techniques (CCT) are to assist in the removal of thick, tenacious secretions
AFCH NEUROMUSCULAR DISORDERS (NMD) PROTOCOL
 AFCH NEUROMUSCULAR DISORDERS (NMD) PROTOCOL A. Definition of Therapy: 1. Cough machine: 4 sets of 5 breaths with a goal of I:E pressures approximately the same of 30-40. Inhale time = 1 second, exhale
AFCH NEUROMUSCULAR DISORDERS (NMD) PROTOCOL A. Definition of Therapy: 1. Cough machine: 4 sets of 5 breaths with a goal of I:E pressures approximately the same of 30-40. Inhale time = 1 second, exhale
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
DAYTON CHILDREN S HOSPITAL CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DISCLAIMER: This Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) generally describes a recommended course of treatment for patients with the identified health
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Levine Children s Hospital. at Carolinas Medical Center. Respiratory Care Department
 Page 1 of 7 at Carolinas Medical Center 02.04 Pediatric Patient-Centered Respiratory Care Protocol Application of Chest Physical Therapy Created: 1/98 Reviewed: 4/03, 1/05, 6/08 Revised: Purpose: To describe
Page 1 of 7 at Carolinas Medical Center 02.04 Pediatric Patient-Centered Respiratory Care Protocol Application of Chest Physical Therapy Created: 1/98 Reviewed: 4/03, 1/05, 6/08 Revised: Purpose: To describe
A Trust Guideline for the Management of. Bronchiolitis in Infants and Children under the age of 24 months
 A Clinical Guideline recommended Children s Assessment Unit (CAU), Buxton Ward, For use in: Children s Day Ward, Jenny Lind Out-patients Department, Accident and Emergency Department By: Medical and Nursing
A Clinical Guideline recommended Children s Assessment Unit (CAU), Buxton Ward, For use in: Children s Day Ward, Jenny Lind Out-patients Department, Accident and Emergency Department By: Medical and Nursing
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Guidelines and Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide
 Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Discuss the benefits for developing an outpatient bronchiolitis clinic.
 Diana L Mark, RRT Pediatric Clinical Specialist Respiratory Care Wesley Medical Center Discuss the benefits for developing an outpatient bronchiolitis clinic. 1 Definition Inflammation of the bronchioles
Diana L Mark, RRT Pediatric Clinical Specialist Respiratory Care Wesley Medical Center Discuss the benefits for developing an outpatient bronchiolitis clinic. 1 Definition Inflammation of the bronchioles
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children. Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital
 FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
Appendix D An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires:
 Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be
 1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in hospital
1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in hospital
Oxygenation. Chapter 45. Re'eda Almashagba 1
 Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Objectives. Apnea Definition and Pitfalls. Pathophysiology of Apnea. Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes 5/18/2015
 Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Problem Based Learning Session. Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days.
 Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
Increased difference between slow and forced vital capacity is associated with reduced exercise tolerance in COPD patients
 Yuan et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2014, 14:16 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Increased difference between slow and forced vital capacity is associated with reduced exercise tolerance in COPD patients Wei
Yuan et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2014, 14:16 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Increased difference between slow and forced vital capacity is associated with reduced exercise tolerance in COPD patients Wei
Airway Clearance Devices
 Print Page 1 of 11 Wisconsin.gov home state agencies subject directory department of health services Search Welcome» August 2, 2018 5:18 PM Program Name: BadgerCare Plus and Medicaid Handbook Area: Durable
Print Page 1 of 11 Wisconsin.gov home state agencies subject directory department of health services Search Welcome» August 2, 2018 5:18 PM Program Name: BadgerCare Plus and Medicaid Handbook Area: Durable
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call
 AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database
 Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Respiratory Management in Pediatrics
 Respiratory Management in Pediatrics Children s Hospital Omaha Critical Care Transport Sue Holmer RN, C-NPT Objectives Examine the differences between the pediatric and adults airways. Recognize respiratory
Respiratory Management in Pediatrics Children s Hospital Omaha Critical Care Transport Sue Holmer RN, C-NPT Objectives Examine the differences between the pediatric and adults airways. Recognize respiratory
BRONCHIOLITIS. See also the PSNZ guideline - Wheeze & Chest Infections in infants under 1 year (www.paediatrics.org.nz)
 Definition What is Bronchiolitis? Assessment Management Flow Chart Admission Guidelines Investigations Management Use of Bronchodilators Other treatments Discharge Planning Bronchiolitis & Asthma References
Definition What is Bronchiolitis? Assessment Management Flow Chart Admission Guidelines Investigations Management Use of Bronchodilators Other treatments Discharge Planning Bronchiolitis & Asthma References
POLICY. Number: Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Authorization
 POLICY Number: 7311-60-024 Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Authorization [ ] President and CEO [ x ] Vice President, Finance and Corporate Services Source:
POLICY Number: 7311-60-024 Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Authorization [ ] President and CEO [ x ] Vice President, Finance and Corporate Services Source:
Respiratory Physio Protocol for Paediatric Patients on BIPAP via a tracheotomy (uncuffed tube)
 This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Respiratory Physio Protocol for Paediatric Patients on BIPAP via a tracheotomy (uncuffed tube) Reference Number: NHSCT/12/547
This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Respiratory Physio Protocol for Paediatric Patients on BIPAP via a tracheotomy (uncuffed tube) Reference Number: NHSCT/12/547
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Autogenic Drainage versus Acapella for Airway Clearance in Patients with Bronchiectasis: Randomized
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Autogenic Drainage versus Acapella for Airway Clearance in Patients with Bronchiectasis: Randomized
Abstract: Introduction: Sumbla A 1, Rafaqat A 2, Shaukat A 3, Kanwal R 4, Janjua UI 5
 Effectiveness of Manual Hyperinflation Therapy plus Postural Drainage and Suctioning To Prevent Ventilator Associated Complications Sumbla A 1, Rafaqat A 2, Shaukat A 3, Kanwal R 4, Janjua UI 5 Abstract:
Effectiveness of Manual Hyperinflation Therapy plus Postural Drainage and Suctioning To Prevent Ventilator Associated Complications Sumbla A 1, Rafaqat A 2, Shaukat A 3, Kanwal R 4, Janjua UI 5 Abstract:
3. Identify the importance in the prehospital setting for the administration of nebulized bronchodilator.
 TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
Potential public health impact of RSV vaccines. R. Karron December 2016
 Potential public health impact of RSV vaccines R. Karron December 2016 1. RSV is The leading cause of hospitalization in infants and in many high-income countries; >2 million medical visits annually in
Potential public health impact of RSV vaccines R. Karron December 2016 1. RSV is The leading cause of hospitalization in infants and in many high-income countries; >2 million medical visits annually in
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Epiglottitis. Bronchitis. Bronchiolitis. Pneumonia. Croup syndrome. Miss. kamlah 2
 Miss. kamlah 1 Epiglottitis. Bronchitis. Bronchiolitis. Pneumonia. Croup syndrome. Miss. kamlah 2 Acute Epiglottitis Is an infection of the epiglottis, the long narrow structure that closes off the glottis
Miss. kamlah 1 Epiglottitis. Bronchitis. Bronchiolitis. Pneumonia. Croup syndrome. Miss. kamlah 2 Acute Epiglottitis Is an infection of the epiglottis, the long narrow structure that closes off the glottis
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) NICU POCKET GUIDE
 Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of
 Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
Sample Case Study. The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on
 Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Community Acquired Pneumonia
 April 2014 References: 1. Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, Alverson B, Carter ER, Harrison C, Kaplan SL Mace SE, McCracken Jr. GH, Moor MR, St. Peter SD, Stockwell JA, and Swanson JT. The Management of
April 2014 References: 1. Bradley JS, Byington CL, Shah SS, Alverson B, Carter ER, Harrison C, Kaplan SL Mace SE, McCracken Jr. GH, Moor MR, St. Peter SD, Stockwell JA, and Swanson JT. The Management of
Research in Medical Physics: Physiological Signals and Dynamics
 Research in Medical Physics: Physiological Signals and Dynamics Incidents of apnea or of sepsis create critical situations in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Of the 4.2 million babies born annually
Research in Medical Physics: Physiological Signals and Dynamics Incidents of apnea or of sepsis create critical situations in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Of the 4.2 million babies born annually
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS (RSV) ALL THAT WHEEZES IS NOT ASTHMA
 PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS (RSV) ALL THAT WHEEZES IS NOT ASTHMA Season changes here in Ohio can send the census numbers in our local P.I.C.U. s, N.I.C.U. s and Emergency Rooms through the roof.
PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS (RSV) ALL THAT WHEEZES IS NOT ASTHMA Season changes here in Ohio can send the census numbers in our local P.I.C.U. s, N.I.C.U. s and Emergency Rooms through the roof.
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis
 Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis Gal S, Riskin A, Chistyakov I, Shifman N, Srugo I, and Kugelman A Pediatric Department and Pediatric Pulmonary Unit Bnai Zion
Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis Gal S, Riskin A, Chistyakov I, Shifman N, Srugo I, and Kugelman A Pediatric Department and Pediatric Pulmonary Unit Bnai Zion
Respiratory Emergencies. Chapter 11
 Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Chapter 13. Respiratory Emergencies
 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
Home Pulse Oximetry for Infants and Children
 Last Review Date: April 21, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.12aC2v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: April 21, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.12aC2v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach
 Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach Suchada Sritippayawan, MD. Div. Pulmonology & Crit Care Dept. Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Kanokporn Udomittipong, MD.
Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach Suchada Sritippayawan, MD. Div. Pulmonology & Crit Care Dept. Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Kanokporn Udomittipong, MD.
Respiratory Disease. Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician
 Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Respiratory Management- Your Questions Answered! Michelle Chatwin, PhD Consultant Physiotherapist
 Respiratory Management- Your Questions Answered! Michelle Chatwin, PhD Consultant Physiotherapist Why Are People Affected Differently Neuromuscular Disease; A Spectrum Its severity varies widely within
Respiratory Management- Your Questions Answered! Michelle Chatwin, PhD Consultant Physiotherapist Why Are People Affected Differently Neuromuscular Disease; A Spectrum Its severity varies widely within
Lecture Notes. Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Evaluation of electromyographic activity and heart rate responses to isometric exercise. The role played by muscular mass and type
 Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
The objectives of this presentation are to
 1 The objectives of this presentation are to 1. Review the mechanics of airway clearance 2. Understand the difference between secretion mobilization and secretion clearance 3. Identify conditions that
1 The objectives of this presentation are to 1. Review the mechanics of airway clearance 2. Understand the difference between secretion mobilization and secretion clearance 3. Identify conditions that
OXYGEN USE IN PHYSICAL THERAPY PRACTICE. Rebecca H. Crouch, PT,DPT,MS,CCS,FAACVPR
 OXYGEN USE IN PHYSICAL THERAPY PRACTICE Rebecca H. Crouch, PT,DPT,MS,CCS,FAACVPR Supplemental Oxygen Advantages British Medical Research Council Clinical Trial Improved survival using oxygen 15 hrs/day
OXYGEN USE IN PHYSICAL THERAPY PRACTICE Rebecca H. Crouch, PT,DPT,MS,CCS,FAACVPR Supplemental Oxygen Advantages British Medical Research Council Clinical Trial Improved survival using oxygen 15 hrs/day
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: NURSING PROCEDURE Management, Monitoring & Documentation of a Clinically Significant Cardiopulmonary Event (CSCPE) (NUR47) DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 9/09 9/17 1 of 6 PS1094
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: NURSING PROCEDURE Management, Monitoring & Documentation of a Clinically Significant Cardiopulmonary Event (CSCPE) (NUR47) DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 9/09 9/17 1 of 6 PS1094
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease () 8.18.18 Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Description Airflow limitation not fully reversible progressive Abnormal inflammatory response of lungs
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease () 8.18.18 Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Description Airflow limitation not fully reversible progressive Abnormal inflammatory response of lungs
Motor Neurone Disease NICE to manage Management of ineffective cough. Alex Long Specialist NIV/Respiratory physiotherapist June 2016
 Motor Neurone Disease NICE to manage Management of ineffective cough Alex Long Specialist NIV/Respiratory physiotherapist June 2016 Content NICE guideline recommendations Respiratory involvement in MND
Motor Neurone Disease NICE to manage Management of ineffective cough Alex Long Specialist NIV/Respiratory physiotherapist June 2016 Content NICE guideline recommendations Respiratory involvement in MND
Measure #6: ALS Noninvasive Ventilation Treatment for Respiratory Insufficiency Discussed Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
 Measure #6: ALS Noninvasive Ventilation Treatment for Respiratory Insufficiency Discussed Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Measure Description Percentage of patients diagnosed with ALS and respiratory insufficiency
Measure #6: ALS Noninvasive Ventilation Treatment for Respiratory Insufficiency Discussed Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Measure Description Percentage of patients diagnosed with ALS and respiratory insufficiency
Effect of the rest interval duration between contractions on muscle fatigue
 Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Escola de Artes, Ciências e Humanidades - EACH Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - EACH 2012 Effect of the rest interval
Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Escola de Artes, Ciências e Humanidades - EACH Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - EACH 2012 Effect of the rest interval
BPD. Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care. Disease. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Baby Jane
 1 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Disease 2 Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia 3 is a 33-day-old prematurely born girl who weighs 1420 g. At birth, her estimated gestational age was 28 weeks. Her initial
1 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Disease 2 Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia 3 is a 33-day-old prematurely born girl who weighs 1420 g. At birth, her estimated gestational age was 28 weeks. Her initial
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment
 A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
Carole Wegner RN, MSN And Lori Leiser CRT
 Airway Clearance Carole Wegner RN, MSN And Lori Leiser CRT Topics Suctioning and suctioning equipment Medications to facilitate t airway clearance Bronchial hygiene modalities Preparing for suctioning
Airway Clearance Carole Wegner RN, MSN And Lori Leiser CRT Topics Suctioning and suctioning equipment Medications to facilitate t airway clearance Bronchial hygiene modalities Preparing for suctioning
Pulmonary Care for Patients with Mitochondrial Disorders
 Pulmonary Care for Patients with Mitochondrial Disorders Rajeev Bhatia, MD, MBBS, DCH, FAAP Pediatric Pulmonologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, NEOMED Medical Director, Clinical Exercise Physiology
Pulmonary Care for Patients with Mitochondrial Disorders Rajeev Bhatia, MD, MBBS, DCH, FAAP Pediatric Pulmonologist Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, NEOMED Medical Director, Clinical Exercise Physiology
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
CYSTIC FIBROSIS INPATIENT PROTOCOL PURPOSE POLICY STATEMENTS SITE APPLICABILITY PRACTICE LEVEL/COMPETENCIES DEFINITIONS EQUIPMENT
 PURPOSE Physiotherapy role for inpatients with cystic fibrosis. POLICY STATEMENTS On admission to hospital all patients will be assessed by the physiotherapist within 24 hours. Physiotherapists have standing
PURPOSE Physiotherapy role for inpatients with cystic fibrosis. POLICY STATEMENTS On admission to hospital all patients will be assessed by the physiotherapist within 24 hours. Physiotherapists have standing
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Pediatric Bronchiolitis. Janie Robles, PharmD, AE-C Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice Pediatrics School of Pharmacy TTUHSC Lubbock, Texas
 This PowerPoint file is a supplement to the video presentation. Some of the educational content of this program is not available solely through the PowerPoint file. Participants should use all materials
This PowerPoint file is a supplement to the video presentation. Some of the educational content of this program is not available solely through the PowerPoint file. Participants should use all materials
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
Thorax Online First, published on February 14, 2008 as /thx Title page
 Thorax Online First, published on February 14, 2008 as 10.1136/thx.2007.088195 Title page Title of the article: Chest physical therapy for children hospitalized with acute pneumonia: a randomized controlled
Thorax Online First, published on February 14, 2008 as 10.1136/thx.2007.088195 Title page Title of the article: Chest physical therapy for children hospitalized with acute pneumonia: a randomized controlled
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System
 County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
Trial protocol - NIVAS Study
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Trial protocol - NIVAS Study METHODS Study oversight The Non-Invasive Ventilation after Abdominal Surgery
Therapeutic efficacy of Antimonium arsenicosum in the acute presentation of obstructive pulmonary disease (OPD) in children
 arsenicosum in the acute presentation of obstructive pulmonary disease (OPD) in children Dr Ivan Nestorov Sofia, Bulgaria Acute obstructive pulmonary disease (OPD) Why OPD? OPD is seen in several common
arsenicosum in the acute presentation of obstructive pulmonary disease (OPD) in children Dr Ivan Nestorov Sofia, Bulgaria Acute obstructive pulmonary disease (OPD) Why OPD? OPD is seen in several common
Diagnostic aid to rule out pneumonia in adults with cough and feeling of fever. A validation study in the primary care setting
 Held et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:355 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic aid to rule out pneumonia in adults with cough and feeling of fever. A validation study in the primary care setting
Held et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:355 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic aid to rule out pneumonia in adults with cough and feeling of fever. A validation study in the primary care setting
Benefit of Selective Inspiratory Muscles Training on Respiratory Failure Patients
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(5): 49-54 Benefit of Selective Inspiratory Muscles Training on Respiratory Failure
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2017, 6(5): 49-54 Benefit of Selective Inspiratory Muscles Training on Respiratory Failure
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER
 MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
Annamalai Nagar, Tamil Nadu India. Corresponding Author: Riya Teresa Joseph
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 4 Ver. IV (Jul Aug 2017), PP 01-07 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Nebulization with Hypertonic
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 12, Issue 4 Ver. IV (Jul Aug 2017), PP 01-07 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Nebulization with Hypertonic
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Fariba Rezaeetalab Associate Professor,Pulmonologist
 Fariba Rezaeetalab Associate Professor,Pulmonologist rezaitalabf@mums.ac.ir Patient related risk factors Procedure related risk factors Preoperative risk assessment Risk reduction strategies Age Obesity
Fariba Rezaeetalab Associate Professor,Pulmonologist rezaitalabf@mums.ac.ir Patient related risk factors Procedure related risk factors Preoperative risk assessment Risk reduction strategies Age Obesity
October Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE
 October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
acapella vibratory PEP Therapy System Maximizing Therapy Effectiveness, Empowering Patient Compliance
 acapella vibratory PEP Therapy System Maximizing Therapy Effectiveness, Empowering Patient Compliance Investigating Questions Each acapella vibratory PEP therapy system uniquely provides PEP therapy by
acapella vibratory PEP Therapy System Maximizing Therapy Effectiveness, Empowering Patient Compliance Investigating Questions Each acapella vibratory PEP therapy system uniquely provides PEP therapy by
Pedi-Cap CO 2 detector
 Pedi-Cap CO 2 detector Presentation redeveloped for this program by Rosemarie Boland from an original presentation by Johnston, Adams & Stewart, (2006) Background Clinical methods of endotracheal tube
Pedi-Cap CO 2 detector Presentation redeveloped for this program by Rosemarie Boland from an original presentation by Johnston, Adams & Stewart, (2006) Background Clinical methods of endotracheal tube
COMMISSION ON ACCREDITATION FOR RESPIRATORY CARE TMC DETAILED CONTENT OUTLINE COMPARISON
 A. Evaluate Data in the Patient Record I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Patient history e.g., admission data orders medications progress notes DNR status / advance directives social history
A. Evaluate Data in the Patient Record I. PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Patient history e.g., admission data orders medications progress notes DNR status / advance directives social history
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
Alveolar recruitment maneuver in refractory hypoxemia and lobar atelectasis after cardiac surgery: A case report
 Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Departamento de Cirurgia - FM/MCG Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - FM/MCG 2012 Alveolar recruitment maneuver in
Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Departamento de Cirurgia - FM/MCG Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - FM/MCG 2012 Alveolar recruitment maneuver in
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
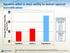 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION
 Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
