Working Experience and Smoker Workers Impact on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
|
|
|
- Anissa Lane
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Working Experience and Smoker Workers Impact on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Ahsan Moazzam 1, Manoj Kumar 2 1,2 (Department of ME, Sant longowal Institute of Engineering and Technology, India) Abstract : Carpal Tunnel Syndrome(CTS) is a symptomatic compression neuropathy of the median nerve at the level of the wrist/hand characterized physiologically by evidence of increased pressure within the carpal tunnel and decreased function of the nerve at that level. The objective of this paper is to study the probability of occurrences of Carpal tunnel syndrome of the workers engaged in smoking. The study is conducted on 98 workers comprising of all men and is focused on studying the impact of working experience and smoker workers in industries. Chi-square test is used. Keywords: CTS, Chi-square test, median nerve, smokers, wrist I. Introduction 1.1 ERGONOMICS Ergonomics is the science of designing the job, equipment, and workplace to fit the worker and work environment to suit the capabilities of the workforce whereby it involves matching the task to the worker, rather than attempting to fit the worker to the task/job [1]. Many occupational accidents, injuries, diseases and Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) continue to arise due to a lack of ergonomics, repetitive and forceful work in the workplace, and there is a need to quantitatively assess exposure of individuals to MSDs [2]. This leads to workplace hazards, poor workers health, mechanical equipment injuries, disabilities, and in turn reduces worker productivity and product/work quality, and increases cost. 1.2 CTS AND ITS WORK-RELATEDNESS CTS are divided into acute and chronic depending on its relative duration to develop symptoms from nerve conduction abnormality. The acute case is relatively rare and developed within a short period due to acute compression to the median nerve followed by the abnormal clinical conditions: spontaneous bleeding in hemophiliacs, persistent thrombosis of the median artery, dislocation of the carpal tunnel base, infections, fractures, or during pregnancy [3]. On the other hand, the chronic case induces such pathophysiological changes at the hand and wrist as nerve impairment. If the case is work-related, the compensation system will redeem all costs accompanied to treatment and lost salaries. However, no clear quantitative dose-response relationship between occupational risk factors and CTS prevalence has been yet established. NIOSH provides a set of criteria, including clinical symptoms, objective signs, and evidence of work-relatedness as practical guidelines to define a case of work-related CTS as shown in Table 1. If a person reports one or more of symptoms and he/she shows a positive clinical diagnosis result, he/she is considered as CTS patients [4]. Moreover, if the patient involved a job with one or more of ergonomic hazards, then the case is determined as work-related CTS. Criteria Symptoms Clinical diagnosis Evidence of work relatedness Table 1. NIOSH Case Definition Criteria For Work-related CTS Descriptions A patient reports one or more of the following symptoms in the hand:- pain, numbness, paresthesias (tingling sensation), hypoesthesia (loss of sensation). The patients should show a positive result either in:- physical provocative tests (Tinel's test and Phalen's maneuver), nerve conduction test. The patients should involve a job with one or more of the following ergonomic hazards: repetitive and/or prolonged motions of the hand, forceful exertions by the hand including pinching or gripping, sustained awkward wrist postures, excessive vibration transmitting of the hand, localized mechanical pressure. 1.3 OCCUPATIONAL RISK FACTORS CTS Activities associated with the development of CTS may arise from ordinary movements that include repetitive activities such as griping and reaching. These movements may become hazardous without sufficient rest or recovery time. The major risk factors include; forceful exertion, repetitive motions, awkward postures, localized contact stresses. These risk factors are classified largely into two groups: occupational (physical) 31 Page
2 factors consisting of task and environmental conditions, and other are personal factors including age, gender, anthropometric factors and medical history [5]. Numerous studies identified the repetitive motions as a risk factor associated with development of CTS Many workers perform the same tasks and stereotyped motions over and over, sometimes thousands or tens of thousands time each day [6]. Highly repetitive motions require fast muscle contractions, which become less efficient and demand greater recovery time because muscle capacity to produce force diminishes with increasing contraction speed. 1.4 RECOGNITION OF CTS Victims of CTS often consult a doctor. The evaluation of occupational CTS includes identifying workplace risks. Evaluation begins with a discussion of the victims' employment and requires a detailed description of all the processes involved in a typical day s work. It also requires consideration of the frequency, intensity, duration and regularity of each task performed at work. Diagnosis of CTS is confirmed by performing certain tests to detect damage to the median nerve [7]. i. Tinel's test- The physician taps the median nerve at the wrist. A tingling response in one or more fingers indicates damage to the median nerve. ii. Phalen's test - The patient puts the backs of the hands together and bends the wrists for one minute. Tingling of the fingers indicates damage to the median nerve. iii. Electromyography- Electrodes are placed on the forearm and electrical current is passed through the patient. Measurements on how fast and how well the median nerve transmits messages to muscle indicate, if there is damage to this nerve. II. Experimentation In this paper consists of 98 manual manufacturing workers. Health surveillance was designed according to the information required like age, height, weight, duration of job, levels of potential symptoms to study the prevalence of potential CTS symptoms amongst manufacturing workers [8]. Also the standardized health surveillance guidelines were used to authenticate the design considered in present study by experts from industry and medical profession. Job categorization is done according to level of repetition (per sec), force involved (kg), BMI (kg/m2) of the workers. The participants ranged in age from 24 to 60 years with a mean of 47.9 (SD 9.15) years (Table 2). The mean body mass index (BMI; kg/m2) of the participants of this study was 24.6 kg/m2 (SD3.72), and it ranged from 17.2 kg/m2 to 37.9 kg/m2. The workers had been performing work for a mean of 24.6 years (SD 8.2). Factor of concern Number of workers Age (years) Table 2. Baseline characteristics of workers Weight Height BMI(kg/m2) Employment time at present (kg) (feet) site (years) Statistics ± ± ± ± ± IMPACT OF WORKING EXPERIENCE ON CTS USING CHI-SQUARE TEST The primary occupational risk factors of CTS include repetition, forceful hand exertions, and deviated wrist postures, lack of rest and recovery, and vibration [9]. Workers in railway workshop use to do repetitive and forceful work i.e. fitting of locomotive parts, welding, Painting and hammering jobs and does the same work for a number of years so an attempt has been made to establish the relationship of working experiences and potential CTS symptoms with the help of statistical tools i.e. Chi-Square Test [10]. To study the impact of potential CTS symptoms on work experience, raw data from health surveillance in manufacturing industry workers has been classified according to duration of job/tenure in year as shown in Table 3 [11]. As trend in literature shows that due to repetitive and forceful work occupation injuries and illness occurs in males of years of with 1-6 month of working experience. A hypothesis is assumed that the number of work experience does not affect the occurrence of potential CTS symptoms. The data is divided into two groups i.e. (i) workers having less than 25years work experience (level 1) and (ii) workers having more than 25 year work experience (level 2). Basis of this classification is that the average life long experience of workers may be an average of years. 32 Page
3 Now, to check that what is the effect of work experience of potential CTS symptoms raw data which is taken from the Surveillance form on the basis of exposure level is shown in a 2 2 contingency Table 3. Table 3. Exposure level based (2 2) contingency table of workers for chi square test Symptom Level 1 Level 2 CTS sufferers Non CTS sufferers Calculation of Observed, expected and χ2 calculations have been shown in table 4, 5 and 6 Table 4. Survey based observed frequency data for Smokers and Non- Smokers. Level 1 Level 2 Total Row Row Total Table 5. Expected frequencies for Smokers and Non- Smokers Row 1 E1=38x29/98= E2=38x69/98= Row 2 E3=70x29/98= E4=70x69/98= Total Table 6. Calculated χ2 values of Smokers and Non- Smokers Fo Ft (fo- ft)2 (fo- ft)2/ft Calculated χ2 = Σ (fo- ft) 2/ft = 1.54 The number of degrees of freedom is required in order to apply the Chi Square Test. In a (2 x 2) contingency table 3.6, the degrees of freedom v = (2-1) (2-1) = 1. In general, for r rows and c columns, the number of degrees of freedom is (r-1) (c-1). The standard value for degree of freedom 1 at 5% level is Since the calculated value is 1.54 of χ2 is less than the standard value (3.84), the hypothesis is accepted. Hence, the number of work experience does not affect the occurrence of potential CTS symptoms. It means that working experience does not affect the occurrence of potential CTS symptoms. The reason that would explain this relationship between the working experience and CTS symptoms is not well understood. 2.2 IMPACT OF SMOKER WORKERS ON CTS USING CHI-SQUARE TEST Smoking which may contribute to CTS by affecting the blood flow to the median nerve. CTS is an illness, not an injury, and health factors such as obesity, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, diabetes, and thyroid disease are much more likely to contribute substantially to the onset of CTS than workplace activities. It indicates smoking may affect the occurrence of potential CTS symptoms [12]. To study the impact of potential CTS symptoms on smoker s workers in industry, Raw data from health surveillance in manufacturing industry workers is classified according to category of as shown in Table 8.Smokers and non-smokers and potential CTS sufferers [13]. A hypothesis is assumed that the smoking habit does not affect the occurrence of potential CTS symptoms. The data has been divided into two groups i.e. smokers (level 1) and another non-smoker (level 2) 33 Page
4 Table 7. A (2 2) contingency table set-up used for Chi Square test Description Level 1 Level Total Symptom Present (Test positive) a b a + b Symptom not Present (Test negative) c d c + d Totals a + c b + d a + b + c +d= n Table 8. Exposure level based (2 2) contingency table of Smokers for chi square test Symptom Smokers Non-smokers CTS sufferers Non CTS sufferers Observed, expected and χ2 calculations have been shown in table 9, 10 and 11. Table 9. Survey based observed frequency data for Smokers and Non- Smokers. Row Row Total Table 10. Expected frequencies for Smokers and Non- Smokers Row 1 E 1 =54x42/98=23.14 E 2 =54x56/98= Row 2 E 3 =44x42/98=18.86 E 4 =44x56/99= Total Table 11. Calculated χ2 values of Smokers and Non- Smokers workers Fo ft (fo- ft)2 (fo- ft) 2 /ft Calculated χ2 for wrist pain = Σ (fo- ft) 2 /ft = 5.77 The number of degrees of freedom is required in order to apply the Chi Square Test. In a (2 x 2) contingency Table 3.6, the degrees of freedom v = (2-1) (2-1) = 1. In general, for r rows and c columns, the number of degrees of freedom is (r-1) (c-1). The standard value for degree of freedom 1 at 5% level is Since the calculated value is 5.77 of χ2 is greater than the standard value (3.84), the hypothesis is rejected hence the probability of having CTS is more amongst Smokers. It means that smoking may be one of the risk factors, which helps in contribution of the occurrence of potential CTS symptoms. III CONCLUSION. In this paper work effect of Repetitive hand movements and forceful work has been studied on human body in terms of potential CTS symptoms. Chi-square test is used to achieve the objectives. Following conclusions have been made from this dissertation: i. Chi square test results revealed that working experience does not affect the occurrence of potential CTS symptoms ii. Chi square test results revealed that smokers are more prone to potential CTS symptoms than that of nonsmokers 34 Page
5 REFERENCES [1] Ajimotokan H. A, The Effects Of Coupling Repetitive Motion Tasks With A Manually-Stressed Work Environment, Researcher,1(2),2009,37-40 [2] Babski-Reeves K.L., Crumpton-Young L.L. Comparison of measures for quantifying repetition in predicting carpal tunnel syndrome International Journal of Industrial ergonomics. 30 (2002), 1-6. [3] Barcenilla Annica, March M. Lyn, Chen Sheng Jian and Sambrook N. Philip Carpal tunnel syndrome and its relationship to occupation: a meta-analysis, Rheumatology (2012);51:250_261Cherniack Martin, Anthony J, Brammer, Ronnie Lundstrom, Tim F. Morse, Greg Neely, Tohr Nilsson, Donald Peterson, Esko Toppila, Nicholas Warren, Ulysses Diva,Marc Croteau, Jevrey Dussetschleger Syndromes from segmental vibration and nerve entrapment: observations on case defenitions for carpal tunnel syndrome Int Arch Occup Environ Health (2008) 81: [4] Daniel H Solomon,, Katz N Jeffrey, and Avorn Jerry, Nonoccupational Risk Factors for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 1988 [5] Finneran Aoife, Leonard O Sullivan Force, posture and repetition induced discomfort as a mediatorin self-paced cycle time International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 40 (2010) [6] Fredriksson K, Bildt C, Hagg G, Kilbom A. The impact on musculoskeletal disorders of changing physical and psychosocial work environment conditions in the automobile industry International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 28(2001) [7] Gerdle B, Karlsson S, Day S, Djupsjöbacka M (1999) Acquisition, Processing and Analysis of the Surface Electromyogram. Modern Techniques in Neuroscience. Chapter 26: Eds: Windhorst U and Johansson H. Springer Verlag, Berlin. [8] Helenice Jane Cote Gil Coury, Isabel Aparecida Porcatti, Michelle E.R. Alem, Jorge Oishi Influence of gender on work-related musculoskeletal disorders in repetitive tasks International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 29,2002, [9] Hui Dong, Peter Loomer, Alan Barr, Charles LaRoche, Ed Young, David Rempel, The effect of tool handle shape on hand muscle load and pinch force in a simulated dental scaling task Applied Ergonomics 38,2007, [10] K. Fredriksson, C. Bildt, G. Hagg, A. Kilbom The impact on musculoskeletal disorders of changing physical and psychosocial work environment conditions in the automobile industry International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 28,2001,31 45 [11] Ling Lei, Patrick G. Dempsey, Jian-guo Xu, Lin-na Ge, You-xin Liang Risk factors for the prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders among chinese foundry workers International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 35,2005, [12] Wenzhou Yu, Ignatius T.S. Yu, Zhimin Li, Xiaorong Wang, Trevor Sun, Hui Lin, Sabrina Wan, Hong Qiu, Shaohua Xie Work-related injuries and musculoskeletal disorders among factory workers in a major city of China Accident Analysis and Prevention 48, 2012, [13] Yves Roquelaure, Jean Mariel, Corinne Dano, Serge Fanello and Dominique Penneaufontbonne Prevalence incidence and risk factors of carpal tunnel syndrome in a large footwear factory International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, Vol. 14, No. 4, 2001, Page
Three SIMPLE Questions to Assess Work Relatedness of Non-Traumatic Conditions! Brian D. Harrison MD Affinity Occupational Health June 11, 2013
 Three SIMPLE Questions to Assess Work Relatedness of Non-Traumatic Conditions! Brian D. Harrison MD Affinity Occupational Health June 11, 2013 But before we get to them... What defines work causation in
Three SIMPLE Questions to Assess Work Relatedness of Non-Traumatic Conditions! Brian D. Harrison MD Affinity Occupational Health June 11, 2013 But before we get to them... What defines work causation in
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries. Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist
 Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Repetitive Upper Limb Tasks. Introductions. ' Crown Copyright Health & Safety Laboratory. 1. Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist.
 Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(2): 61-65(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : ISSN No. (Online) :
 e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(2): 61-65(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 REBA Technique on Small Scale Casting Industry Er. Girish Joshi* and Harvinder
e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(2): 61-65(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 REBA Technique on Small Scale Casting Industry Er. Girish Joshi* and Harvinder
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Description, Diagnosis, and Treatment
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Description, Diagnosis, and Treatment Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Repetitive stress injury Due to inflammation of the tissues around the median nerve Results in reduced nerve transmission;
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Description, Diagnosis, and Treatment Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Repetitive stress injury Due to inflammation of the tissues around the median nerve Results in reduced nerve transmission;
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
Susan Burt, ScD Stephen Bao, PhD Barbara Silverstein, PhD Fred Gerr, MD Linda Merlino, MS David Rempel, MD. #aihce
 Personal, psychosocial, and biomechanical risk factors associated with work disability from carpal tunnel syndrome: Findings from the NIOSH Consortium Studies. Carisa Harris Adamson, PhD Ellen A Eisen,
Personal, psychosocial, and biomechanical risk factors associated with work disability from carpal tunnel syndrome: Findings from the NIOSH Consortium Studies. Carisa Harris Adamson, PhD Ellen A Eisen,
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS
 Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
The Ergonomic Alternative
 The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
2/28/2017. EMC Insurance Companies Risk Improvement Department. Ergonomics for School Districts. Objectives. What is Ergonomics?
 Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Ergonomic Risk Factors associated with Muscuslokeletal Disorders in Computer Workstation
 Ergonomic Risk Factors associated with Muscuslokeletal Disorders in Computer Workstation Mohd Nasrull Abdol Rahman* Ibrahim Masood Nur Farahanim Awalludin Mohd Fahrul Hassan Department of Material and
Ergonomic Risk Factors associated with Muscuslokeletal Disorders in Computer Workstation Mohd Nasrull Abdol Rahman* Ibrahim Masood Nur Farahanim Awalludin Mohd Fahrul Hassan Department of Material and
Introduction to Ergonomics Ergonomics (er'gõ nom'iks):
 March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
Dr David Ruttenberg MBChB.,MSc(Med).,FAFOEM
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Dr David Ruttenberg MBChB.,MSc(Med).,FAFOEM General Practitioners Outpatient Clinics Occupational Health Clinics 5-10% Prevalence in Community Is it common? Common Usually Females,
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Dr David Ruttenberg MBChB.,MSc(Med).,FAFOEM General Practitioners Outpatient Clinics Occupational Health Clinics 5-10% Prevalence in Community Is it common? Common Usually Females,
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS)
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness
 Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Preventing Workplace Injuries with Ergonomics
 Preventing Workplace Injuries with Ergonomics Richard W. Bunch, PhD, PT, CBES ISR Institute / Dr. Bunch Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) Low Back Injuries- #1 Disabling Orthopedic Injury Among
Preventing Workplace Injuries with Ergonomics Richard W. Bunch, PhD, PT, CBES ISR Institute / Dr. Bunch Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) Low Back Injuries- #1 Disabling Orthopedic Injury Among
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
POLICY NUMBER: POL 91
 Summary of Proposed Amendments Amendments to the policy, Repetitive Strain Injuries (POL 91), are proposed to set out the criteria for acceptance of repetitive strain injuries and provide clarification
Summary of Proposed Amendments Amendments to the policy, Repetitive Strain Injuries (POL 91), are proposed to set out the criteria for acceptance of repetitive strain injuries and provide clarification
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
Ergonomics Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa (515) Copyright
 2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
Ergonomics in Sonography
 Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Institute for Work & Health. Overview. Trigger Finger Steroid Injections. David Rempel WOHC
 Institute for Work & Health Research Update: Upper Extremity Disorders and the Workplace David Rempel, MD, MPH, FACOEM Division of Occupational and Environmental Medicine University of California, San
Institute for Work & Health Research Update: Upper Extremity Disorders and the Workplace David Rempel, MD, MPH, FACOEM Division of Occupational and Environmental Medicine University of California, San
Meta-analysis of Published Studies of Workrelated Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Meta-analysis of Published Studies of Workrelated Carpal Tunnel Syndrome MOUSTAFA A. F. ABBAS, MD, ABDELMONEM A. AFIFI, PHD, Z. W. ZHANG, PHD, JESS F. KRAUS, PHD The published information about work-related
Meta-analysis of Published Studies of Workrelated Carpal Tunnel Syndrome MOUSTAFA A. F. ABBAS, MD, ABDELMONEM A. AFIFI, PHD, Z. W. ZHANG, PHD, JESS F. KRAUS, PHD The published information about work-related
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY
 CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
Ergonomics and the Farm. Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist
 Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
Muscular Skeletal Disorders
 Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
REVIEW CONTROL ASSESS IDENTIFY CONSULT CONSULT CONSULT CONSULT
 REVIEW CONTROL ASSESS IDENTIFY CONSULT CONSULT CONSULT CONSULT MANUAL HAZARDOUS TASKS RISK MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE (Adopted from the SafeWork Australia Code of Practice) Follow this step by step process to
REVIEW CONTROL ASSESS IDENTIFY CONSULT CONSULT CONSULT CONSULT MANUAL HAZARDOUS TASKS RISK MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE (Adopted from the SafeWork Australia Code of Practice) Follow this step by step process to
DECISION OF THE WORKERS COMPENSATION APPEAL TRIBUNAL
 Decision Number: A1801732 (September 11, 2018) DECISION OF THE WORKERS COMPENSATION APPEAL TRIBUNAL Decision Number: A1801732 Decision Date: September 11, 2018 Introduction [1] The worker has appealed
Decision Number: A1801732 (September 11, 2018) DECISION OF THE WORKERS COMPENSATION APPEAL TRIBUNAL Decision Number: A1801732 Decision Date: September 11, 2018 Introduction [1] The worker has appealed
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job
 Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence
 Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
Goals. Vibration I njury in the Workplace. Definitions HAVS. HAVS (cont.) HAVS (Cont.)
 Goals Vibration I njury in the Workplace Stewart Russell D.O.,M.P.H. October, 2014 OMED Seattle Be able to define the types of vibration injury Recognize the probable causes of vibration injury Interventions
Goals Vibration I njury in the Workplace Stewart Russell D.O.,M.P.H. October, 2014 OMED Seattle Be able to define the types of vibration injury Recognize the probable causes of vibration injury Interventions
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs
 KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
HAVS Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome
 HAVS Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome A review of the scientific evidence FACULTY OF OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE MISSION Everyone should have access to advice from a competent occupational physician as part of comprehensive
HAVS Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome A review of the scientific evidence FACULTY OF OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE MISSION Everyone should have access to advice from a competent occupational physician as part of comprehensive
Ergonomics in General Industry
 Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Ergonomics for Dental Professionals
 Original Research Article Meenakshi Rana 1,*, Binita Srivastava 2, Nidhi Gupta 3, Natasha Gambhir 4, Rashi Singh 5, Neeti Mittal 6 Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry Santosh Dental College,
Original Research Article Meenakshi Rana 1,*, Binita Srivastava 2, Nidhi Gupta 3, Natasha Gambhir 4, Rashi Singh 5, Neeti Mittal 6 Department of Pedodontics & Preventive Dentistry Santosh Dental College,
Anatomic Distribution of Sensory Symptoms in the Hand and Their Relation to Neck Pain, Psychosocial Variables, and Occupational Activities
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 157, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwf225 Anatomic Distribution
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 157, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwf225 Anatomic Distribution
CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK.
 CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK. Nurhayati Mohd Nur 1, Siti Zawiah Md Dawal 2 1 University of Kuala Lumpur-MIAT, Jenderam Hulu, 43800 Dengkil,
CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK. Nurhayati Mohd Nur 1, Siti Zawiah Md Dawal 2 1 University of Kuala Lumpur-MIAT, Jenderam Hulu, 43800 Dengkil,
Ergonomics Application to Work Design on Seafood Processing Line
 Ergonomics Application to Work Design on Seafood Processing Line Chung Van Nguyen Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering International University-Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City,
Ergonomics Application to Work Design on Seafood Processing Line Chung Van Nguyen Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering International University-Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City,
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist
 Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW
 ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST. Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: BODY PART RISK FACTORS NECK/SHOULDER ELBOW HAND/WRIST Carpel tunnel
 ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: Job Description Job Risk priority as per Risk Assessment ( X applicable column) H H-M M M-L L ERGONOMIC FACTORS Repetition BODY PART RISK FACTORS
ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: Job Description Job Risk priority as per Risk Assessment ( X applicable column) H H-M M M-L L ERGONOMIC FACTORS Repetition BODY PART RISK FACTORS
This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks
 This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks You are at risk of hand arm vibration syndrome, HAVs, if you regularly use
This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks You are at risk of hand arm vibration syndrome, HAVs, if you regularly use
Digital Human Modeling of Non-Occupational Risk Factors for
 Digital Human Modeling of Non-Occupational Risk Factors for Manufacturing Breakout Work Session Task Design 2014 Iowa Governor s Safety & Health Conference Cedar Rapids, IA ; November 7, 2013 1 st International
Digital Human Modeling of Non-Occupational Risk Factors for Manufacturing Breakout Work Session Task Design 2014 Iowa Governor s Safety & Health Conference Cedar Rapids, IA ; November 7, 2013 1 st International
Identifying and Solving Ergonomics Problems in Coal Preparation and Mineral Processing Plants Jonisha P. Pollard
 Identifying and Solving Ergonomics Problems in Coal Preparation and Mineral Processing Plants Jonisha P. Pollard National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Office of Mine Safety and Health Research
Identifying and Solving Ergonomics Problems in Coal Preparation and Mineral Processing Plants Jonisha P. Pollard National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Office of Mine Safety and Health Research
Stooped. Squatting Postures. Workplace. and. in the. July 29 30, 2004 Oakland, California, USA CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
 CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS Stooped and Squatting Postures in the Workplace July 29 30, 2004 Oakland, California, USA Center for Occupational and Environmental Health n University of California: Berkeley n
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS Stooped and Squatting Postures in the Workplace July 29 30, 2004 Oakland, California, USA Center for Occupational and Environmental Health n University of California: Berkeley n
Electrician s Job Demands Literature Review Manual & Power Tools
 Electrician s Job Demands Literature Review Manual & Power Tools An electrician s job is physical in nature, and the physical demands of the job are affected by the use of handheld manual and power tools
Electrician s Job Demands Literature Review Manual & Power Tools An electrician s job is physical in nature, and the physical demands of the job are affected by the use of handheld manual and power tools
Manual Handling/Manual Tasks Checklist
 Manual Handling/Manual Instruction: Complete for all manual tasks in consultation with workers undertaking the task. Date checklist completed Date for review Name of person completing checklist Position
Manual Handling/Manual Instruction: Complete for all manual tasks in consultation with workers undertaking the task. Date checklist completed Date for review Name of person completing checklist Position
C H A P T E R. Assessment of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders & Postural Stress. Posture & Stress
 C H A P T E R 3 Assessment of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders & Postural Stress Posture & Stress 56 3.1. Abstract Background: The goldsmiths used to work in particular working postures for prolonged
C H A P T E R 3 Assessment of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders & Postural Stress Posture & Stress 56 3.1. Abstract Background: The goldsmiths used to work in particular working postures for prolonged
Relationship Between Work Activities and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Relationship Between Work Activities and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Super EMG Plus 2012 William S. Pease, MD Ernest W. Johnson Professor of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1 Carpal Anatomy Carpal tunnel
Relationship Between Work Activities and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Super EMG Plus 2012 William S. Pease, MD Ernest W. Johnson Professor of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1 Carpal Anatomy Carpal tunnel
Ergonomics and Back Safety PPT-SM-BACKSFTY V.A.0.0
 Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Dimensional Requirements. Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways.
 Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Interventions for the primary prevention of work-related carpal tunnel syndrome Lincoln A E, Vernick J S, Ogaitis S, Smith G S, Mitchell C S, Agnew J
 Interventions for the primary prevention of work-related carpal tunnel syndrome Lincoln A E, Vernick J S, Ogaitis S, Smith G S, Mitchell C S, Agnew J Authors' objectives To evaluate interventions for the
Interventions for the primary prevention of work-related carpal tunnel syndrome Lincoln A E, Vernick J S, Ogaitis S, Smith G S, Mitchell C S, Agnew J Authors' objectives To evaluate interventions for the
Determination of Ergonomic Hazards at a Semiconductor Manufacturing Company: An Initial Study
 Journal of Asian Vocational Education and Training Vol. 8, pp. 25-35, 2015 ISSN 2005-0550 Determination of Ergonomic Hazards at a Semiconductor Manufacturing Company: An Initial Study Zuraini Gani*, Shukriah
Journal of Asian Vocational Education and Training Vol. 8, pp. 25-35, 2015 ISSN 2005-0550 Determination of Ergonomic Hazards at a Semiconductor Manufacturing Company: An Initial Study Zuraini Gani*, Shukriah
Aims of presentation. Strategies to reduce musculoskeletal disorders in underground coal mining. Low back Musculoskeletal disorders
 Queensland Mining Industry Health and Safety Conference Townsville, August 2003 Aims of presentation Strategies to reduce musculoskeletal disorders in underground coal mining Professor Tony Parker Queensland
Queensland Mining Industry Health and Safety Conference Townsville, August 2003 Aims of presentation Strategies to reduce musculoskeletal disorders in underground coal mining Professor Tony Parker Queensland
Strains and Sprains. Signs and Symptoms of MSI
 Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Heecheon You Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802
 PROCEEDINGS of ihe HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 42nd ANNUAL MEETING-1998 841 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN CLINICAL SCALES ON SEVERITY OF SYMPTOMS AND ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEASURES ON ABNORMALITY OF NERVE
PROCEEDINGS of ihe HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 42nd ANNUAL MEETING-1998 841 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN CLINICAL SCALES ON SEVERITY OF SYMPTOMS AND ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEASURES ON ABNORMALITY OF NERVE
International Journal of Advancements in Technology ISSN
 Ergonomic evaluation of effects of handle shape and task orientation on human performance in screw driving task. Asmar Husain 1, Abid Ali Khan and Faisal Hasan Ergonomics Research Division, Department
Ergonomic evaluation of effects of handle shape and task orientation on human performance in screw driving task. Asmar Husain 1, Abid Ali Khan and Faisal Hasan Ergonomics Research Division, Department
Identification, Causes And Prevention Of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) In The Construction Industry In Nigeria
 Identification, Causes And Prevention Of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) In The Construction Industry In Nigeria By C. A. JOHN (Ph.D) Department Of The Technology Education, Federal University of Technology,
Identification, Causes And Prevention Of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) In The Construction Industry In Nigeria By C. A. JOHN (Ph.D) Department Of The Technology Education, Federal University of Technology,
Hand-Arm Vibration. Table 1 Stages of Vibration White Finger (Taylor-Pelmear System)
 Physical Agent Data Sheet (PADS) Description Hand-Arm Vibration Hand-arm vibration is caused by the use of vibrating hand-held tools, such as pneumatic jack hammers, drills, gas powered chain saws, and
Physical Agent Data Sheet (PADS) Description Hand-Arm Vibration Hand-arm vibration is caused by the use of vibrating hand-held tools, such as pneumatic jack hammers, drills, gas powered chain saws, and
An Old Controversy: Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Work Related? Dolores A. Loveless, MD Medical Director CarePoint Occupational Medicine Jacksonville, FL
 An Old Controversy: Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Work Related? Dolores A. Loveless, MD Medical Director CarePoint Occupational Medicine Jacksonville, FL Occupational Medicine Is the medical specialty that
An Old Controversy: Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Work Related? Dolores A. Loveless, MD Medical Director CarePoint Occupational Medicine Jacksonville, FL Occupational Medicine Is the medical specialty that
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2469 2474 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) WORK POSTURE ASSESSMENT OF TAILORS BY RULA AND REBA ANALYSIS Upasana and Deepa
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2469 2474 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) WORK POSTURE ASSESSMENT OF TAILORS BY RULA AND REBA ANALYSIS Upasana and Deepa
Hand discomfort in production assembly workers
 Agronomy Research 11 (2), 407 412, 2013 Hand discomfort in production assembly workers K. Jansen¹,*, M. Luik², M. Reinvee², V. Viljasoo², J. Ereline¹, H. Gapeyeva¹ and M. Pääsuke¹ ¹Institute of Exercise
Agronomy Research 11 (2), 407 412, 2013 Hand discomfort in production assembly workers K. Jansen¹,*, M. Luik², M. Reinvee², V. Viljasoo², J. Ereline¹, H. Gapeyeva¹ and M. Pääsuke¹ ¹Institute of Exercise
Ergonomics questions will account for 13% or 26 questions of the ASP exam.
 1 Ergonomics questions will account for 13% or 26 questions of the ASP exam. This lesson will help in preparing you for those questions, to include several review and sample questions for practice. 2 Carpal
1 Ergonomics questions will account for 13% or 26 questions of the ASP exam. This lesson will help in preparing you for those questions, to include several review and sample questions for practice. 2 Carpal
ERGONOMICS in Office.
 ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville
 Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
Table of Contents. 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders?
 Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations
 Preventing workrelated upper limb disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations Aims of the programme - To increase awareness of work-related upper limb disorders (WRULDs) associated
Preventing workrelated upper limb disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations Aims of the programme - To increase awareness of work-related upper limb disorders (WRULDs) associated
This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management
 Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management Procedure for Managing Injury
Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management Procedure for Managing Injury
ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL)
 ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) 1(6) ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) General description and development of the method The ACGIH HAL TLV uses HAL (Hand activity level) and peak hand forces
ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) 1(6) ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) General description and development of the method The ACGIH HAL TLV uses HAL (Hand activity level) and peak hand forces
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics
 Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
Manual Materials Handling
 Introduction to the Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling OR-OSHA 206 9512 SC 206 Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling 7/96 1 OR-OSHA Services Oregon OSHA offers a wide variety of safety and health
Introduction to the Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling OR-OSHA 206 9512 SC 206 Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling 7/96 1 OR-OSHA Services Oregon OSHA offers a wide variety of safety and health
Surveillance under SENSOR
 V. The Selection and Definition of Targeted Work-Related Conditions for Surveillance under SENSOR THOMAS D. MArrE, MD, MPH Medical Epidemiologist Office of the Director National Institute for Occupational
V. The Selection and Definition of Targeted Work-Related Conditions for Surveillance under SENSOR THOMAS D. MArrE, MD, MPH Medical Epidemiologist Office of the Director National Institute for Occupational
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. 5th Edition
 Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Carpal tunnel syndrome
 Condition Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this condition. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely
Condition Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this condition. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely
International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology E-ISSN
 Research Article WORK-RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS OF WORKERS IN BRICK MAKING FACTORIES OF UTTAR PRADESH-AN ERGONOMIC APPROACH Kumkum Pandey 1, Aditi Vats 2 Address for Correspondence 1 Research Scholar,
Research Article WORK-RELATED MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS OF WORKERS IN BRICK MAKING FACTORIES OF UTTAR PRADESH-AN ERGONOMIC APPROACH Kumkum Pandey 1, Aditi Vats 2 Address for Correspondence 1 Research Scholar,
Evidence on Work-related Causation of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome / David Rempel, MD, MPH, FACOEM!!
 Evidence on Work-related Causation of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome / David Rempel, MD, MPH, FACOEM 1 Evidence on Work-related Causation of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome David Rempel, MD, MPH, FACOEM Professor, Occupational
Evidence on Work-related Causation of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome / David Rempel, MD, MPH, FACOEM 1 Evidence on Work-related Causation of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome David Rempel, MD, MPH, FACOEM Professor, Occupational
Development and application of a hand force measurement system
 Development and application of a hand force measurement system B.D. Lowe a, Y. Kong b, and J. Han c a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, USA b Systems Management Engineering,
Development and application of a hand force measurement system B.D. Lowe a, Y. Kong b, and J. Han c a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, USA b Systems Management Engineering,
1. Common Health Problem/Condition: MSK Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 Midwifery Management Process for Common Health Problems 1. Common Health Problem/Condition: MSK Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is an upper extremity disability. It
Midwifery Management Process for Common Health Problems 1. Common Health Problem/Condition: MSK Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is an upper extremity disability. It
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
Conquering Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Conquering Carpal Tunnel Syndrome PainReliefSciences.com 1 Copyright 2016 NutriFrontier Limited All rights reserved Published by Kevin Richardson. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Conquering Carpal Tunnel Syndrome PainReliefSciences.com 1 Copyright 2016 NutriFrontier Limited All rights reserved Published by Kevin Richardson. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Introduction. Safety Tip For more data on ergonomic injuries, go to the BLS website at
 Introduction Ergonomics in Construction Welcome Given current OSHA and industry information regarding construction worksite incidents and disabling injuries, the student should be able to recognize the
Introduction Ergonomics in Construction Welcome Given current OSHA and industry information regarding construction worksite incidents and disabling injuries, the student should be able to recognize the
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Physiology of Injuries
 Presented By: Du-All Safety, 2019 Physiology of Injuries Strains: the muscles and tendons that support the spine are twisted, pulled or torn. Ex. Overstretching when carrying extra weight. Over flexion:
Presented By: Du-All Safety, 2019 Physiology of Injuries Strains: the muscles and tendons that support the spine are twisted, pulled or torn. Ex. Overstretching when carrying extra weight. Over flexion:
Office Ergonomics OSHA Resources. Risk Factors for Developing MSDs taken from OSHA voluntary guidelines. Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
Stockholm workshop scales
 Occup Environ Med 2000;57:35 42 35 Consultant in Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome, 19 Stanely Avenue, Paisley, Scotland, UK K L McGeoch Departments of Public Health and Statistics, University of Glasgow, UK
Occup Environ Med 2000;57:35 42 35 Consultant in Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome, 19 Stanely Avenue, Paisley, Scotland, UK K L McGeoch Departments of Public Health and Statistics, University of Glasgow, UK
OCCUPATIONAL HAND INJURIES: Impacts on Impairments and Disability
 OCCUPATIONAL HAND INJURIES: Impacts on Impairments and Disability Anthony Mollano MD Specializing in Hand, Wrist, and Elbow Surgery Concord Orthopaedics, Concord, NH BACKGROUND -Eight years in practice
OCCUPATIONAL HAND INJURIES: Impacts on Impairments and Disability Anthony Mollano MD Specializing in Hand, Wrist, and Elbow Surgery Concord Orthopaedics, Concord, NH BACKGROUND -Eight years in practice
Work, vibration, & the neurosensory system. Close effects Remote effects Stress and pressure
 Work, vibration, & the neurosensory system Close effects Remote effects Stress and pressure Temporary neurosensory effects Reduced sensibility due to: - Temporary threshold shift Reduced motor control
Work, vibration, & the neurosensory system Close effects Remote effects Stress and pressure Temporary neurosensory effects Reduced sensibility due to: - Temporary threshold shift Reduced motor control
Carpal tunnel syndrome
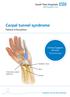 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East Uses Lazy Susan Design to Prevent Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East Uses Lazy Susan Design to Prevent Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East in Cherry Point, NC is one of six fleet readiness centers operated
Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East Uses Lazy Susan Design to Prevent Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East in Cherry Point, NC is one of six fleet readiness centers operated
Vibration injuries. Increase your productivity whilst taking care of your operators.
 Vibration injuries Increase your productivity whilst taking care of your operators. Reduce vibration exposure and improve productivity Hand-arm vibration related injuries are one of the most common injuries
Vibration injuries Increase your productivity whilst taking care of your operators. Reduce vibration exposure and improve productivity Hand-arm vibration related injuries are one of the most common injuries
