27 th Annual SW Conference on Medicine Westin La Paloma Spa Tucson April 27-29
|
|
|
- Tiffany Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 27 th Annual SW Conference on Medicine Westin La Paloma Spa Tucson April Edward G. Stiles, DO, FAAODist. Professor of OPP Kentucky College of Osteopathic Medicine Sturgill Distinguished Professor University of Pikeville Workshop: OMT principles & care
2 Sponsors: Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation Cleveland Clinic
3 Challenges for this workshop: Diversity of participants DOs: improve OPP knowledge & OMT skills MDs: provide / improve OPP knowledge & skills NP: make aware of OPP potential PA: make aware of OPP potential DO students: improve skills Goals: enable all to gain new OPP understanding and OMT skills
4 Greenman: the expert is the one who does the basics the best what makes a DO different is not OMT, but how they think / problem solve. Dispelling some OMT myths Something is not out of place : it can t completely open or close. Your not putting something back in place but restoring physiological motion, doesn t require a lot of force. OMT is not a panacea but can be dramatic when S/D is a major etiological component. One indication for OMT! presence of somatic dysfunction ( S/D ) - not pain, muscle guarding, etc. Osteopathic Joint model: vs out of place model
5 Pardigm shifts: Amount of force utilized with OMT: Mitchell stool demonstration Stiles musculo-skeletal / mesokinetic model: Tensegrity Need to find AGR / sequence: least healthy / functional area Learn principles and get them to work for you : Kimberly Spinal mechanics: facet model Direct techniques Demo the facet model for Dx and Rx ( thoracic, cervical & lumbar ) Using translation to Dx and Rx: the KEY! HV/LA thumb thrust ( Osteopathic Activator ) Thoracic MET: using a patient specific muscle corrective force T 6-11 FRS dysfunctions MET ( 2 steps ) T 12 FRS dysfunctions MET ( 2 steps ) Indirect techniques ( Laughlin - Still ) thoracic, cervical & lumbar Sacral complexity: Left sacral Flexion ( use as example ) Innominate: fine-tuning / activating only prime mover Ribs: basic Dx and Rx
6 Joint Mechanics: an Osteopathic Perspective ( Normal and abnormal - somatic dysfunction ) What is Somatic dysfunction? ( S/D )
7 Normal Joint Mechanics Active ROM Passive ROM A E P P E A Elastic & Physiological barriers: provide support & movement Hypermobility issue: hindered elastic barrier Workman s Compensation: hypomobility significance
8 Normal & Dysfunctional Joint Mechanics Active ROM Passive ROM A E P DBP N A = anatomical barrier: bony shape of the joint ( hip / shoulder ) FX / dislocation E = elastic barrier: ligaments & capsules / dislocations possible P = physiological barrier: myofascial tissues Active ROM: between the physiological barriers / restrictive barrier Passive ROM: between the elastic barriers / restrictive barrier N = neutral: position of ease DBP = dynamic balance point: dysfunctional position of ease R = Restrictive Barrier: not out of place / minimal, moderate, marked, etc. Damaged E. Barrier can account for hypermobility ( Tensegrity / prolo therapy ) R. Barrier will decrease Range of Motion ( O.M.T. ) Nothing is out of place! But functionally disorientated! GOAL OF O.M.T.: not to put something back in place but to re-establish normal range of motion. Remove the functional hindrances. P E A
9 CONSILIENCE: E. O. WILSON PhD: HARVARD BIOLOGIST A CALL FOR A UNITY OF ALL KNOWLEDGE NATURAL SYSTEMS ARE RESILIENT UNTIL WE INTRODUCE MECHANISTIC INTERFACES WITH ALL THE NECESSARY ADJUSTMENTS AND COMPENSATIONS AS A MEANS OF SUSTAINING OURSELVES. THOSE INTERFACES NOT ONLY ISOLATE US FROM NATURE BUT AT THE SAME TIME CREATE SYSTEMS THAT ARE BRITTLE AND DELICATE LOWERED RESISTANCE? INCREASED SUSCEPTIBLITY? BECOME LESS NON-LINEAR! FRAGILE BECOME DIS-EASED HOST A HARVARD DESCRIPTION OF Somatic Dysfucntion H IMPACT? NOTE: EXCHANGE THE WORDS HOST AND S/D-H
10 Paradigm Shift: 2018 looking at familiar data, come to new understanding & new way of explaining old observations Anatomical design OMT mechanisms Learn the principles and get them to work for you. Paul E. Kimberly, DO, FAAO
11 The Musculo-Skeletal System a 21 st. Century Perspective
12 Tensegrity structures are: Light weight Much stronger than experts had predicted Multi / Omni - directional Whole system adapts to stressors Protects the weakest link / the A.G.R. defy gravity Non-metallic materials, organized in a Tensegrity arrangement, can conduct electricity wired : keep eyes level, evenly distribute weight among all 4 quadrants. Conduct vibratory information Would it not make sense to identify, the A.G.R. ( area of greatest restriction - hindrance ) in this flexible & adaptive system?
13 MESOKINETIC SYSTEM Meso ( mesoderm ): gives rise to Connective tissues & fascia Cartilage Bone Striated and smooth muscle Myocardium and pericardium Blood and lymph vessels Kidneys and ureters Adrenal cortex Gonads Tubes, uterus and upper vagina Serous membranes lining the body cavities ( T, A & P ) GI fascial support system Spleen Kinetic: Related to movement of physical objects NOTE: S/D might impact both musculo-skeletal & visceral structures. Netter s Atlas of Human Embryology 16
14 MESOKINETIC SYSTEM Meso ( mesoderm ): gives rise to Connective tissues & fascia Cartilage Bone Striated and smooth muscle Myocardium and pericardium Blood and lymph vessels Kidneys and ureters Adrenal cortex Gonads Tubes, uterus and upper vagina Serous membranes lining the body cavities ( T, A & P ) GI fascial support system Spleen Kinetic: Related to movement of physical objects NOTE: S/D might impact both mysculo-skeletal & visceral structures. Netter s Atlas of Human Embryology 16
15 Passing on the Tradition Alan Becker, DO, FAAO 2010 Journal of AAO fall edition Dr. Still was keen on being very specific. He looked at the patient as a Totality. He looked for the Elusive Key Lesion Hindrance ( somatic dysfunction ) that people have quoted for years. That is what He looked for and when He found it, He fixed it and then left it alone. He said that once done, the body will do its own work because it is designed to do its own work. Our job is to find the Key Restriction Hindrance to homeostatic integrity, and once restored to normalcy, to rest assured that the body will take care of the rest of the work.
16 LBP patient A.G.R. ( Key somatic dysfunction ) L.B.P. Other possible A.G.R.s Cranial: dural tube U.E. L.E. Note: ever see a LBP research strategy which considered S/D in T/RC, UE, LE or cranial? ( Stiles: 100 patients ) T/RC = 60% Lumbar = 24% L.E. = 11% Total: 95% Note: Sacrum and innominates were not the #1 A.G.R.! may have been treated later in the treatment sequence
17 In light of this complexity, how do you clinically view your patients? Stiles Current Perspective complex, dynamic, inter-connected & inter-woven, multiple, simultaneously functioning systems, non-linear, autopoietic functional unit
18 OPP treatment basic principles: 2 technique components Positioning of S/D: re Restrictive Barrier Direct: HV/LA: Kimberly, should be painless and noiseless ( avoid trap of a hypermobile pop ) Muscle Energy Myofascial Indirect: Strain-Counterstrain ( S/CS ) Balanced Ligamentous Tension ( BLT ) Facilitated Positional Release ( FPR ) Still Techniques ( ST ) Functional / Laughlin ( FRT/L ) Corrective Force: Clinician introduced force: a thrust / an impulse Patient introduced force: patient specific muscle effort Intrinsic forces: self-healing forces of body
19 Tell me about Fred L. Mitchell, Sr, DO, FAAO MSU-COM 1972 Picture = 1,000 words Mechanical Engineer Creative Thinker Non-linear Thinker Tensegrity thinker utilized Cybernetics Complex Adaptive Systems Thinker Phenomenologist These attributes enabled Fred to develop: the unique Mitchell Pelvic Axis Model plus a totally new OMT approach utilizing a patient generated corrective force. stressed the importance of starting your treatment at the Key S/D of the total system. 4 Tutorial participants: Greenman, Stiles, Sutton, & Ward are Legends being honored during 2018 Convocation.
20 Leon Chaitow, DO Comments about various techniques in light of data presented during the 4 th Fascia Congress: ( Sept ) Muscle Energy Techniques It is not a Post Isometric Relaxation technique ( PIR )! M.E.T. introduce movement which then decreases the pain. Leon felt my hypothesis that introduced movement stimulates the joint mechano-receptors and that inhibits the nociceptors was an appropriate expanded explanation of his statement. ( Wyke 1980 s research yrs. after 1 st M.E.T. Tutorial ) 48
21 MUSCLE ENERGY TECHNIQUES ( MUSCLE ACTIVATION ) SUMMARY 8 ESSENTIALS: also explains why it doesn't work ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS A.G.R. / SEQUENCING... Crucial for FLM,Sr. SEGMENTAL DIAGNOSIS... Specific OMT ACCURATE POSITIONING FEATHER EDGE OF RESTRICTIVE BARRIER... crucial DIRECT BALANCED LIGAMENTOUS TENSION UNYIELDING COUNTER-FORCE... Crucial A.A.O. M.E.T. - 3 VISIONS M.E.T. 3 MASTERS FRED, ED & PHIL SHOW 2005 ( FUNCTIONALLY REVERSES THE ORIGIN AND INSERTION ) APPROPRIATE MUSCLE EFFORT DIRECTION: multiple options ( Findley ) AMOUNT: least amount that produces beneficial change DURATION... Cybernetic loop key COMPLETE Rx SITE BUT DON T GIVE UP WHAT GAINED REPEAT ABOVE STEPS... remaining R. barrier, not new!, # efforts? RE-TEST... Taking money under false pretenses?, confirms Dx / Rx 21
22 Functional: Laughlin-Still basics establish a S/D diagnosis ( works best if start at A.G.R.-H / Key lesion ) start technique at Positional Diagnosis position ( take doodad where it wants to go ) ( position of ease ) ( use translation & have at apex of F/E, SB & R curves ) fine-tune dysfunctional joint so maximally relaxed ( fiddle and diddle to fine-tune positioning at D.B.P. ) ( Dynamic Balance Point ) Biodynamics language: at loose-packed position add vectored compression ( from side towards which dysfunction will initially rotate ) allow to unwind ( initially away from restricted barrier, hits a still point & then spontaneously moves into the previously restricted compartment ) recheck: know made a positive change! 2
23 POSITIONING: FUNCTIONAL TECHNIQUES SINCE AN INDIRECT TECHNIQUE POSITION AT D.B.P. WHICH IS IN THE POSITIONAL DIAGNOSIS QUADRANT ( NOT AT JOINT NEUTRAL BUT AT JOINT S/D-H NEUTRAL ) EX: DIAGNOSIS L 3 FRS L A E P THE D.B.P. WILL BE IN THE P FRS L QUADRANT R.B. E A FLEXION DBP N EXTENSION FUNCTIONAL TECHNIQUES: ALL START AT THE SAME POINT / DIFF. NAMES IF MONITOR THE DYSFUNCTIONAL FACET & TISSUE CHANGES ( FRT/L-Stiles ) [ MECHANORECEPTOR / NOCICEPTOR ROLE WITH PASSIVE UNWINDING ] IF MONITOR LIGAMENTOUS TENSION ( BLT WALES, LIPPINCOTT, BECKER & SUTHERLAND ) IF MONITOR A JONES TENDER POINT ( S/CS JONES ) IF MONITOR SUPERFICIAL OR DEEP MUSCLES ( FPR SHIOWITZ ) IF MONITOR 3 SEGMENTS ( FUNCTIONAL METHODS JOHNSTON ) IF ACTIVELY BRING THROUGH RESTRICTIVE BARRIER ( STILL VAN BUSKIRK ) ( MISINTERPRETED A.T. STILL / SHOULDER VIDEO? ) 23
24 The scientific method of phenomenology ( Goethean Scientific Method ) is used to create a synthesis between modern orthodox embryology and a holistic view of the human being. The human embryo reveals who we are and what we are meant to be. Practitioners have found that comprehending embryological forces supports a holistic and biodynamic approach to healthcare because the same forces that formed the body are continuously at work throughout life, carrying the blueprint of health into manifestation. Jaap van der Waal, MD, PhD The Embryo in Us May A.T. Still: find S/D hindrances, effectively treat the S/D hindrances and enable the blueprint of health to emerge / to manifest. Forces we are tapping into by removing S/D hindrances.
25 Note: I am not saying AGR / sequencing is the only way to approach patients! but our data suggests it is an effective clinical strategy Sequenced OMT Stiles Data: methods Spinoscope / Gracovetsky semg evaluation Ground Reactive Force Fractal Analysis Reactive Fractal Analysis golfers Elite female runners Dynamic Athletic Research Institute ( DARI ) Jason Hunt, DO - orthopod
26 Median of 60 gait cycles ( tons of data ) Statistical & fractal significant changes Immediate changes with sequenced OMT, not with models, chasing pain or exercise. Each patient their own research project Not saying AGR / sequencing right way and other strategies are wrong, just saying we have a lot of data to support the AGR / sequencing strategy utilizing several data collection strategies Ground Reactive Force data: See similar changes 80% of time with new patients
27 Spinal Mechanics an Osteopathic Perspective
28 Spinal Mechanics Bottom line Act like a pile of blocks act like flexible ruler Type I Mechanics: Bodies in control Involves multiple vertebra SB / R occur in opposite directions Rotation is toward produced convexity Compensate for Type II, pelvic or rib cage dysfunctions Type II Mechanics: Facets in control Involves 2 vertebra SB / R occur in the same direction R toward produced concavity Associated with segmental facilitation
29 Key to establishing an accurate diagnosis and quality localization of your treatment forces X TRANSLATION Moving a segment along a line ( introduces forces from both above and below ) Have the segment being diagnosed!!! and treated!!! floating at the apex of the curve... integrates ( using Law III of Fryette s Principles to your advantage ) Minimal dysfunctions can be missed when use just flexion, extension, SB R, SB L or R R, R L ( forces introduced from only above... segment not at apex ) 29 X
30 Spinal Mechanics: Type II palpate over facets Flexion Extension X ERS L ( can t go into Flexion on left ) X FRS L ( Can t go into Extension on right ) Note: both are SB L and R L Need to use both flexion & extension to establish an accurate diagnosis
31 Unyielding Counter Force DIAGNOSIS: ERS L Rx M.E.T. Long mobilizers / restrictors Short mobilizers / restrictors Treatment procedure: Position FRS R against feather edge of R. Barrier ( D-BLT ) Do this using translation in 3 planes Dysfunctional facet pair within normal range of motion fiddle and diddle to fine tune to dysfunctional facet pair ( left ) Patient makes a gentle isometric SB L and / or R L, or both muscle effort against a gentle unyielding counter force! 2 effects occur Inhibits short restrictors ( Golgi receptor / protective role activated ): inhibited, not stretched! Long mobilizers restore some of the lost movement ( micro-isotonic response ) Facet mechano-receptors stimulated and inhibit the pain receptors ( Wyke ) Hold until cybernetic feedback loop displays movement, L. facets pair opens Have patient relax the treated area Reposition against the remaining / not new R. Barrier: take up the slack Repeat 2-3 times not Post Isometric Relaxation technique
32 Unyielding Counter Force DIAGNOSIS: FRS L Rx - M.E.T. X Long mobilizers / restrictors Short mobilizers / restrictors ( timing gear problem ) Treatment procedure: Position ERS R against feather edge of R. Barrier ( D-BLT ) Do this using translation in 3 planes Dysfunctional facet pair within normal range of motion fiddle and diddle to fine tune to dysfunctional facet pair ( right ) Patient makes a gentle isometric SB L and / or R L, or both muscle effort against a gentle unyielding counter force! 2 effects occur Using the left long mobilizers activates the law of reciprocal innervation, inhibits contralateral short restrictors... Doesn t stretch short restrictors, inhibits them. Then long mobilizers restore some of the lost movement ( micro-isotonic response ) As closes, stimulates mechano-receptors which then inhibit pain receptors. ( Wyke ) Hold until cybernetic feedback loop displays movement... SB R &R R closes R. facet pair Have patient relax the treated area Reposition against the remaining / not new R. Barrier: take up the slack Repeat 2-3 times not Post Isometric Relaxation technique
33 CNS RESPONSE: A VIRUS IN THE SOFT-WARE PROGRAM OF THE C.N.S. ( AN ANALOGY ) DYSFUNCTIONS PLUS ADAPTIVE PATTERNS ARE PRESENT IN THE MESOKINETIC SYSTEM BUT MAINTAINED IN THE C.N.S.? NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL ROLE Our Eugene & Golf data support this concept 33 X X
34 virus in software analogy OKC 1994 Bob Foreman, PhD Ch: Physiology OUMed S/D-H pattern maintained in cerebellum? Cerebellum enables total body adaptations to occur to: Keep eyes level Evenly distribute weight in all 4 quadrants Why finding KEY is important! Treating Pr. or Sec. S/D? AFTER 2008: Engineering Biomechanics of Human Motion Robert L. Williams, PhD Ohio University willar4@ohio.edu
35 T 7 ERS L : Functional Position: instruct patient to Sit up and push stomach forward You then translate T 7/8 area to right These 2 movements close the left facet pair ( taking doodad where wants to go ) ( fiddle & diddle to fine tune & add rotation ) Add vectored compression toward dysfunctional facet pair Allow to unwind in both directions maintain compression during whole treatment ends up at FRS R, may be neutral. Recheck: realize self healing potential Palpate where? 6
36 T 7 FRS L Functional Positioning: instruct patient to Slump forward / apex of F/E curve You then add translation T 7/8 to right so at apex of both flexion & SB L curves. These 2 movements open the right facet pair ( taking doodad where it wants to go ) ( fiddle & diddle to fine tune & add R ) Add vectored compression toward dysfunctional facet pair Allow to unwind in both directions Maintain compression throughout treatment usually ends up at ERS R, or may be neutral. Palpate where? 7
37 ESSENTIALS: ANT. LUMBAR IS LOOKING LEFT ( SIDE LOAD I.T. ) RIGHT FACET PR. IS DYSFUNCTIONAL ( SIDE FLOAT ) FASCIAL LOAD TOWARD R. FACET PAIR POSITION: L 3 FRS L USING TRANSLATION FLOAT R. FACET PAIR LOAD OR BEAR WEIGHT ON L. I/T AS SLOWLY ADD COMPRESSION TOWARD RIGHT FACET PAIR, THE BODY WILL AUTOMATICALLY ROTATE LEFT HIT A STILL POINT THEN SPONTANEOUSLY ROTATES TO RIGHT TOWARD RESOLVED RESTRICTED BARRIER LUMBAR DYSFUNCTION: L 3 FRS L Functional 37
38 Cervical Region During extension: using fingertip translation, facets should close. If facets don t close, test both sides for resistance using diagonal translation. During flexion: using lateral translation, facets should open, test both sides for resistance Treatment: either direct ( MET or HV/LA) indirect: at position of ease
39 FUNCTIONAL TECHNIQUES cervical area SCREENING EXAMINATION PATIENT IS SEATED OPERATOR STANDS NEXT TO THE PATIENT WITH ONE HAND ON THE PATIENT S HEAD THE OTHER HAND PALPATES ALONG THE ARTICULAR COLUMN UTILIZING THE DISTAL PAD THE THUMB ( OVER THE FACETS ) THUMB SLIDES CEPHLAD OVER ARTICULAR COLUMN AS THE NECK IS ROTATED... USE COMPRESSION LOOK FOR SPEED-BUMPS PASSIVELY Dx... FINDING D.B.P. / POSITION OF EASE 39
40 FUNCTIONAL TECHNIQUES lower cervical area DIAGNOSIS: FRS R PATIENT IS SITTING PASSIVELY POSITION THE DYSFUNCTIONAL DBP OF FRS R THEN FIDDLE & DIDDLE TO FINE-TUNE ADD GENTLE CAUDAD COMPRESSION TOWARD SEGMENT ( DYSFUNCTIONAL FACET PAIR ) ALLOW IT TO UNWIND TO THE RIGHT, HITS A STILL POINT AND THEN SPONTANEOUSLY ROTATES & SIDEBENDS LEFT AND EXTENDS NOTE: VAN BUSKIRK DOES ACTIVELY & STOOD IN FRONT OF PATIENT RETEST... TO SEE IF CORRECTED! FEW MEDICAL RESPONSES OCCUR THIS QUICKLY 40
41 Rib Cage Mechanics an Osteopathic Perspective
42 Rib Cage Mechanics Pump-Handle Bucket-Handle Exhaled Inhaled Clinical Application: pseudo-angina Waterville Data Impact ( Medicare codes)
43 MUSCLES: CLINICAL USE ( EXPIRED DYSFUNCTIONS ) X X X TREATMENT PRINCIPLES: EXHALED vs EXPIRED STABILIZES SCAPULA ALTERNATIVE METHOD 43
44 MUSCLES: CLINICAL USE ( INSPIRED DYSFUNCTIONS ) LOWER RIBS: BUCKET-HANDLE WANT TO USE SIDE-BENDING THEN STRETCH OUT FASCIA UPPER RIBS: PUMP-HANDLE WANT TO USE FLEXION POSTERIOR M.E.T. EFFORT AT END ( GLIDES POSTERIOR END CEPHLAD ) 44
45 Stiles Pelvic model: an evolving model
46 PELVIC REGION AN EVOLVING PERSPECTIVE 1960 s VIEW 1970 MITCHELL s 2013
47 TENSEGRITY & FRACTAL GEOMETRY: SI/J UNIQUE SIDE TO SIDE FRACTAL / ROUGH & NON-LINEAR PROVIDES A PROTECTIVE DESIGN! WHY DENSE POST. S/I LIGAMENTS? ( HOLDING TWO SURFACES APART? ) ENABLE COMPLEX SACRAL MOVEMENT? FLOATING COMPRESSION PLUS 6 FUNCTIONAL AXES... QUANTUM # ( INTERSECTING ITA AND OA s ) NOTE: STA IS ANTERIOR TO ITA... ROLE? IF TENSEGRITY IS FUNCTIONING DO WE NEED FORM / FORCE CLOSURE? IS THAT A BACKUP SYSTEM? HAS SIGNIFICANCE OF ROUGHNESS BEEN MISINTERPRETED? ( OCCURS DURING 2d & 3d DECADES ) MITCHELL- TENSEGRITY DESIGN ENABLE COMPLEX MOVEMENT PATTERNS AND PREVENT WEAR & TEAR? 47
48 FLOATING COMPRESSION DESCRIBES A CLOSED STRUCTURAL SYSTEM COMPOSED OF A SET OF THREE OR MORE ELONGATED COMPRESSION STRUTS WITHIN A NETWORK OF TENSION TISSUES, THE COMBINED PARTS ARE MUTUALLY SUPPORTIVE IN SUCH A WAY THAT THE STRUTS DO NOT TOUCH EACH OTHER, BUT PRESS OUTWARD AGAINST NODAL POINTS IN THE TENSION NETWORK TO FORM A FIRM, TRIANGULATED, PRESTRESSED TENSION AND COMPRESSION UNIT BEFORE AFTER
49 PALPATING THE SACRAL BASE ( 1970 TUTORIAL ) Locate the P.S.I.S. Glide thumbs medial & anterior to sacrum ( sulcus ) Then glide thumbs superior to sacral base I.L.A.: palpate sacral hiatus Palpate inferior lateral to I.L.A. 49
50 Biomechanical Complexity: anatomical ( Mitchell, Sr. always stressed this principle for every anatomical area ) adduction-abduction int. / ext. rotation Key to fine-tuning Key: modify technique to patient uniqueness!!! ( mastery rather than competency )
51 L. SACRAL FLEXION: Rx MET PATIENT IS PRONE Greenman: technique description ( ABD 15 0 & I/R ) ABD /ADDUCT THE L.. LEG TO LOOSE-PACK THE LEFT S/I JOINT ( ALSO INT./EXT. ROTATE LEG ) LOCATE THE MTA OPERATOR DETERMINES THE MOST EFFICIENT VECTOR DIRECTION WITH THEIR R. HAND ON LEFT ILA USE RESPIRATORY ASSIST: RE-TEST INSPIRATION MISTAKES: NOT REALIZING ABOVE TASKS / ASSUME ALL SI/Js ARE THE SAME... SKILLS DEVELOP RAPIDLY WITH THIS APPROACH! TEXT: GREENMAN 2d & 4 th EDITIONS ABD / ADDUCT TO APPROX INT. ROTATE THIGH TO OPEN S/IJ BUT.... VECTOR 51 MONITOR
52 LEFT SACRAL FLEXION ( functional ) FASCIAL LOAD ( SLOWLY ADD COMPRESSION TOWARD DYSFUNCTIONAL JOINT ) + A/D R L P/N FLOAT LEFT S/IJ ( AS SIDEBEND TO RIGHT ) MTA ( LOCATE WITH A/P TRANSLATION ) LOAD OR BEAR WEIGHT ON R. I/T ( BY SIDEBENDING TRUNK TO RIGHT ) THE I/T SACRUM LOOKING AT FOOD FOR THOUGHT: LOADED RIGHT I/T, LOOSE PACKED LEFT S/IJ & FIND MTA THIS LOCATES THE DBP FOR THE DYSFUNCTIONAL S/IJ ADDED COMPRESSION TO ACTIVATE TENSEGRITY IT WILL UNWIND AWAY FROM RESTRICTIVE BARRIER AFTER THE STILL POINT, THE BODY AUTOMATICALLY GOES TOWARD THE PREVIOUS RESTRICTED BARRIER FINDS THE NEW DBP & AXIS AUTOMATICALLY!!! ILLUSTRATE THE RAPID AND DYNAMIC PLASTICITY OF THE CNS? BUOYANCY AND RESILIENCY POTENTIAL! I/P 52
53 RIGHT ANTERIOR INNOMINATE: Rx MET PATIENT IS SUPINE OPERATOR FLEXES R. HIP UNTIL THE ITA IS LOCATED THE R. S/I JOINT IS THEN LOOSE- PACKED UTILIZING ABD/ ADDUCTION AND I/R & E/R TO FLOAT AGAINST RESTRICTIVE BARRIER... Only prime movers activate PATIENT ATTEMPTS TO EXTEND THE HIP vs YOUR COUNTER-FORCE MISTAKES: NOT REALIZE ABOVE TASKS.. SYNERGISTS AND ANTAGONISTS ACTIVATED WITH MET EFFORT. NOT CLEAN M.E.T. RESPONSE ALTERNATIVES: LATERAL AND PRONE 53
54 ESSENTIALS: ANT. PELVIS IS LOOKING LEFT ( SIDE LOAD ) RIGHT I/SJ IS DYSFUNCTIONAL ( SIDE FLOAT ) R N LEVEL S + FASCIAL LOAD LOAD OR BEAR WEIGHT ON L. I/T LEVEL FLOAT RIGHT S/IJ ( WHERE PALPATE ) LOCATE ITA RIGHT ANTERIOR INNOMINATE: Functional 54
55 SACRAL FINDINGS: ANTERIOR SACRAL BASE L. SACRAL FLEXION R. SACRAL EXTENSION L/L SACRAL TORSION L/R SACRAL TORSION LEFT LEFT RIGHT RIGHT SULCUS LEFT DEEP RIGHT NORMAL LEFT NORMAL RIGHT SHALLOW RIGHT DEEP LEFT NORMAL RIGHT NORMAL LEFT SHALLOW SITTING F.B.T. LEFT RIGHT RIGHT LEFT L 5 ROTATION R L R L R R R R LORDOSIS POST / INF. I.L.A. SL. INCREASED SL. DECREASED SL. INCREASED DECREASED FLAT LEFT LEFT LEFT LEFT AXIS INVOLVED M.T.A. M.T.A. L.O.A. R.O.A. SPHINX TEST NEGATIVE POSITIVE NEGATIVE POSITIVE L. LEG LENGTH ( MECHANICS ) L. LONG L. LONG R. SHORT L. SHORT R. LONG L. SHORT
56 Clinical Application: Host + Disease = Illness ( clinical presentation ) host + DISEASE = Illness HOST + disease = Illness HOST + DISEASE = Illness Additional mechanisms: for explaining OMT outcomes Cybernetics ( dynamic feedback loops ) Gen. Adaptive systems ( 1 system ) Complex systems ( multiple systems ) Fractal Geometry ( distribution issues ) Fractal / Chaos Physiology ( homeo-dynamics ) Autopoiesis ( dynamic S/F changes ) Multi-agent Modeling Network of Networks Emergent Properties S/D can impact: 1, all, any combo of arms 7 Competencies: ( P/P mirror strategy ) Osteopathic integration Medical Knowledge Patient Care Interpersonal Communications Professionalism Practice-Based Care System-Based Care
57 Complexity & Family Practice: Systems & Complex Thinking Annals of Family Medicine Vol 12 no 1 Jan / Feb 2014 THE NEW CONCEPTS AND LANGUAGE AVAILABLE TO OSTEOPATHY CYBERNETICS: BILL JOHNSTON AND CHARLES BOWLES FUNCTIONAL METHODS AUTOPOESIS: COMPLEX & DYNAMIC STRUCTURE - FUNCTIONAL RELATIONSHIPS ( TERM NOW IN LITERATURE ) 21 CENTURY MECHANISMS AVAILABLE TO EXPLAIN O.P.P. OUTCOMES BODY IS A COMPLEX FUNCTIONAL UNIT OF INTERCONNECTED SYSTEMS
58 A.C.G.M.E. Educational Model Experiential Educational Model ( utilizing a patho-physiological mirror strategy ) Action / Experience / cc. / symptom / sign Reflection / gather data / develop hypothesis Abstraction treat / test hypothesis / develop theory ( establish a final diagnosis ) Application / old, new or other BOTTOM LINE Educational Phenomenology
59 What is that all about? I have a better understanding now! Osteopathic Management
OMED 2017 Philadelphia 10/7-10/17. Functional: Laughlin-Still techniques
 OMED 2017 Philadelphia 10/7-10/17 American Academy of Osteopathy Functional: Laughlin-Still techniques Tuesday 9:45-11:45 am Harriet Shaw, DO Edward Stiles, DO, FAAO When is gait diagnosis and treatment
OMED 2017 Philadelphia 10/7-10/17 American Academy of Osteopathy Functional: Laughlin-Still techniques Tuesday 9:45-11:45 am Harriet Shaw, DO Edward Stiles, DO, FAAO When is gait diagnosis and treatment
AAO Convocation 2018 Anatole Hotel Dallas, TX 3/21-25/ 2018
 AAO Convocation 2018 Anatole Hotel Dallas, TX 3/21-25/ 2018 Stiles Approach to Dx & Rx My Osteopathic Clinical Approach was profoundly impacted by both Fred L. Mitchell, Sr., DO, FAAO George Andrew Laughlin,
AAO Convocation 2018 Anatole Hotel Dallas, TX 3/21-25/ 2018 Stiles Approach to Dx & Rx My Osteopathic Clinical Approach was profoundly impacted by both Fred L. Mitchell, Sr., DO, FAAO George Andrew Laughlin,
Authorized Osteopathic Thesaurus December, 2003 Terms
 s 100-199 USE (s) Elevated Rib Inhalation Rib Dysfunction Item number: 100 Broader (s) Related (s) End Feel Tissue Texture Abnormality Movement Barrier Item number: 101 Perceived quality of motion as an
s 100-199 USE (s) Elevated Rib Inhalation Rib Dysfunction Item number: 100 Broader (s) Related (s) End Feel Tissue Texture Abnormality Movement Barrier Item number: 101 Perceived quality of motion as an
OMT Without An OMT Table. Ann L. Habenicht DO, FAAO, FACOFP, CS AAO Convocation- Student Program March12, 2015
 OMT Without An OMT Table Ann L. Habenicht DO, FAAO, FACOFP, CS AAO Convocation- Student Program March12, 2015 BASIC STUFF WE HAVE TO WADE THROUGH TO MAKE SURE WE RE ALL ON THE SAME PAGE A.T. Still To find
OMT Without An OMT Table Ann L. Habenicht DO, FAAO, FACOFP, CS AAO Convocation- Student Program March12, 2015 BASIC STUFF WE HAVE TO WADE THROUGH TO MAKE SURE WE RE ALL ON THE SAME PAGE A.T. Still To find
OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop. Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP
 OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP Cervical Somatic Dysfunction (C5 SR RR) - Seated 1. Patient position: seated. 2. Physician position: standing facing
OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP Cervical Somatic Dysfunction (C5 SR RR) - Seated 1. Patient position: seated. 2. Physician position: standing facing
Manual Manipulative Medicine: A Structural Examination for Lower Back Pain. Friday, October 2, :30 AM - 12:00 PM W116.
 Manual Manipulative Medicine: A Structural Examination for Lower Back Pain Friday, October 2, 2015 10:30 AM - 12:00 PM W116. Level: Beginner No Financial Disclosures Amir Mahajer, DO Ronald Tolchin, DO
Manual Manipulative Medicine: A Structural Examination for Lower Back Pain Friday, October 2, 2015 10:30 AM - 12:00 PM W116. Level: Beginner No Financial Disclosures Amir Mahajer, DO Ronald Tolchin, DO
DIAGNOSIS ANTERIOR PELVIC ROTATION DIAGNOSIS DIAGNOSIS. Direct techniques to treat sacrum and pelvis somatic dysfunction (HVLA, MET)
 American Academy of Osteopathy Convocation PHYSICIAN STUDENT Thursday, March 18, 2010 Friday, March 19, 2010 2:30 4:00 PM 8:00 9:30 AM 4:30 6:00 PM 10:00 11:30 AM Direct techniques to treat sacrum and
American Academy of Osteopathy Convocation PHYSICIAN STUDENT Thursday, March 18, 2010 Friday, March 19, 2010 2:30 4:00 PM 8:00 9:30 AM 4:30 6:00 PM 10:00 11:30 AM Direct techniques to treat sacrum and
OMT Without The Table Saroj Misra, DO, FACOFP and Marissa Rogers, DO
 OMT Without The Table Saroj Misra, DO, FACOFP and Marissa Rogers, DO Why bother? May not always have the table present Patient may not be able to lay prone or supine Some techniques may be easier to accomplish
OMT Without The Table Saroj Misra, DO, FACOFP and Marissa Rogers, DO Why bother? May not always have the table present Patient may not be able to lay prone or supine Some techniques may be easier to accomplish
Richard L Van Buskirk, DO, PhD, FAAO
 Richard L Van Buskirk, DO, PhD, FAAO I approach the osteopathic concept as if the body is a biomechanical, electrochemical machine: If a part is not working quite right then the body will find a compensating
Richard L Van Buskirk, DO, PhD, FAAO I approach the osteopathic concept as if the body is a biomechanical, electrochemical machine: If a part is not working quite right then the body will find a compensating
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner
 Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Information within the handout. Brief Introduction Anatomy & Biomechanics Assessment & Diagnosis Treatment through Muscle Energy
 Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
Manual Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction of the Pelvis Through Muscle Energy Greenman s Priciples of Manual Medicine (5 th Ed.)- Lisa DeStefano,DO Speaker disclosure I declare I
THE OSTEOPATHIC WORKSHOP: NECK PAIN
 THE OSTEOPATHIC WORKSHOP: NECK PAIN Trevine R. Albert, D.O. M.S. Family Medicine Neuromusculoskeletal Medicine PGY-3 2018 FSACOFP Convention DISCLOSURES There are no actual or potential personal, financial
THE OSTEOPATHIC WORKSHOP: NECK PAIN Trevine R. Albert, D.O. M.S. Family Medicine Neuromusculoskeletal Medicine PGY-3 2018 FSACOFP Convention DISCLOSURES There are no actual or potential personal, financial
A.T. STILL, MD, DO BODY IS A UNIT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION ARE RECIPROCALLY INTER-RELATED
 A.T. STILL, MD, DO COMPLEX THINKER - REVISITED ( 21 st CENTURY PERSPECTIVE ) OSTEOPATHIC TENETS OF STILL: 1952 KCOS K.C.O.S. BODY IS A UNIT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION ARE RECIPROCALLY INTER-RELATED BODY POSSESSES
A.T. STILL, MD, DO COMPLEX THINKER - REVISITED ( 21 st CENTURY PERSPECTIVE ) OSTEOPATHIC TENETS OF STILL: 1952 KCOS K.C.O.S. BODY IS A UNIT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION ARE RECIPROCALLY INTER-RELATED BODY POSSESSES
Seated & Standing OMT
 Copyright 2018, Kansas City University of Medicine & Biosciences (KCUMB). This presentation is intended for KCUMB educational use only. No part of this presentation may be distributed or reproduced without
Copyright 2018, Kansas City University of Medicine & Biosciences (KCUMB). This presentation is intended for KCUMB educational use only. No part of this presentation may be distributed or reproduced without
OMT for the Pregnant Patient
 OMT for the Pregnant Patient Presented by: Kristie Petree, DO Assistant Professor of Neuromusculoskeletal Medicine and Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Georgia Campus Philadelphia College of Osteopathic
OMT for the Pregnant Patient Presented by: Kristie Petree, DO Assistant Professor of Neuromusculoskeletal Medicine and Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Georgia Campus Philadelphia College of Osteopathic
Rotational Forces. : Their impact; our treatments
 Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
The Schiowitz Approach
 The Schiowitz Approach American Academy of Osteopathy Annual Convocation March 23 rd, 2018 2:00-3:30 PM & 4:00 5:30 PM Dennis J. Dowling, D.O., M.A., F.A.A.O. F.P.R. Developed by Stanley Schiowitz, D.O.,
The Schiowitz Approach American Academy of Osteopathy Annual Convocation March 23 rd, 2018 2:00-3:30 PM & 4:00 5:30 PM Dennis J. Dowling, D.O., M.A., F.A.A.O. F.P.R. Developed by Stanley Schiowitz, D.O.,
Lumbar. Physician. Technique: Continue this. back pain is. bent. under the contralatera. Copyright
 Lumbar myofascial releasee Lumbar spine Brief description: Low back pain is a common problem and lumbar myofascial releasee can be useful as part of a comprehensiv ve treatment of low back pain. By usingg
Lumbar myofascial releasee Lumbar spine Brief description: Low back pain is a common problem and lumbar myofascial releasee can be useful as part of a comprehensiv ve treatment of low back pain. By usingg
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
OMT for Chronic Low Back Pain: OSTEOPATHIC Trial Protocol. Learning Objectives. Chronic Low Back Pain 8/5/2016
 OMT for Chronic Low Back Pain: OSTEOPATHIC Trial Protocol David C. Mason, DO, MBA, FACOFP Chair Family Medicine and Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Texas College of Osteopathic Medicine Learning Objectives
OMT for Chronic Low Back Pain: OSTEOPATHIC Trial Protocol David C. Mason, DO, MBA, FACOFP Chair Family Medicine and Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine Texas College of Osteopathic Medicine Learning Objectives
MUSCLE ENERGY FOR CERVICAL SPINE. Dr. Gabrielle Koczab, DO Medical director Bedford Primary Care Core Teaching Faculty UH Regional Hospitals
 MUSCLE ENERGY FOR CERVICAL SPINE Dr. Gabrielle Koczab, DO Medical director Bedford Primary Care Core Teaching Faculty UH Regional Hospitals LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List conditions in which muscle energy
MUSCLE ENERGY FOR CERVICAL SPINE Dr. Gabrielle Koczab, DO Medical director Bedford Primary Care Core Teaching Faculty UH Regional Hospitals LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List conditions in which muscle energy
OMT for the child with ENT problems
 SEATED INNOMINATE AND PELVIC BOWL BALANCED LIGAMENTOUS TENSION 1. The physician is seated behind the child with both hands, each contacting an innominate and the sacrum. The fingers contact the ASIS bilaterally
SEATED INNOMINATE AND PELVIC BOWL BALANCED LIGAMENTOUS TENSION 1. The physician is seated behind the child with both hands, each contacting an innominate and the sacrum. The fingers contact the ASIS bilaterally
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
West Virginia Osteopathic Medical Association Annual CME Conference. Josephine Shen, DO, MAOM November 3, 2018
 West Virginia Osteopathic Medical Association Annual CME Conference Josephine Shen, DO, MAOM November 3, 2018 Anterior Cervical Fascia Lift Rib Ligamentous Articular Strain Twelfth Rib/Arcuate Ligament/Diaphragm
West Virginia Osteopathic Medical Association Annual CME Conference Josephine Shen, DO, MAOM November 3, 2018 Anterior Cervical Fascia Lift Rib Ligamentous Articular Strain Twelfth Rib/Arcuate Ligament/Diaphragm
Chiropractic Glossary
 Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
OMT Boot Camp. OMT Applications for Systemic Somatic Dysfunctions of the Spine. Natalie Nevins, DO, MSHPE
 ACOFP 54 th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars OMT Boot Camp OMT Applications for Systemic Somatic Dysfunctions of the Spine Natalie Nevins, DO, MSHPE Lumbar, Innominate, Sacrum Diagnosis and Treatment
ACOFP 54 th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars OMT Boot Camp OMT Applications for Systemic Somatic Dysfunctions of the Spine Natalie Nevins, DO, MSHPE Lumbar, Innominate, Sacrum Diagnosis and Treatment
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
The Swimmer s Shoulder: An Osteopathic Approach
 The Swimmer s Shoulder: An Osteopathic Approach Mary Solomon, D.O. Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Cleveland, OH 440-914-7865 1 I have no relevant relationships/affiliations with any proprietary
The Swimmer s Shoulder: An Osteopathic Approach Mary Solomon, D.O. Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Cleveland, OH 440-914-7865 1 I have no relevant relationships/affiliations with any proprietary
Robert P Schneider DO FAAFP MYOFASCIAL RELEASE
 Robert P Schneider DO FAAFP MYOFASCIAL RELEASE Objectives Review basic anatomy. Describe diagnosis of somatic dysfunction using a fascial model. Summarize the basic concepts of myofascial release (MFR)
Robert P Schneider DO FAAFP MYOFASCIAL RELEASE Objectives Review basic anatomy. Describe diagnosis of somatic dysfunction using a fascial model. Summarize the basic concepts of myofascial release (MFR)
Jennifer Lorine, DO. Practical Application of OMT in the Office: The Counterstrain Edition. Disclosures. Objectives
 Practical Application of OMT in the Office: The Counterstrain Edition August 4, 2018 POFPS Disclosures Dr. Lorine has provided no disclosures. Objectives For the audience to have a better understanding
Practical Application of OMT in the Office: The Counterstrain Edition August 4, 2018 POFPS Disclosures Dr. Lorine has provided no disclosures. Objectives For the audience to have a better understanding
VIRGINIA ORTHOPEDIC MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY INSTITUTE TECHNIQUE MANUAL
 VIRGINIA ORTHOPEDIC MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY INSTITUTE TECHNIQUE MANUAL Lumbar and Thoracic Spine Lumbar AROM Assessment -Patient Positioning: Standing, appropriately undressed so that the lumbar and thoracic
VIRGINIA ORTHOPEDIC MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY INSTITUTE TECHNIQUE MANUAL Lumbar and Thoracic Spine Lumbar AROM Assessment -Patient Positioning: Standing, appropriately undressed so that the lumbar and thoracic
What is the most frequently sprained ligament with inversion ankle sprains? 1/30/2014
 What is the most frequently sprained ligament with inversion ankle sprains? A. Anterior Talofibular B. Anterior Tibiofibular C. Calcaniofibular D. Posterior Talofibular E. Deltoid Lateral ligaments of
What is the most frequently sprained ligament with inversion ankle sprains? A. Anterior Talofibular B. Anterior Tibiofibular C. Calcaniofibular D. Posterior Talofibular E. Deltoid Lateral ligaments of
Solving Today s Pain and Injury Puzzle with Erik Dalton An Online Workshop for ABMP Members Session 1 Handout
 Solving Today s Pain and Injury Puzzle with Erik Dalton An Online Workshop for ABMP Members Session 1 Handout Please Note: Erik Dalton teaches his Myoskeletal Alignment Techniques with the expectation
Solving Today s Pain and Injury Puzzle with Erik Dalton An Online Workshop for ABMP Members Session 1 Handout Please Note: Erik Dalton teaches his Myoskeletal Alignment Techniques with the expectation
OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017
 OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017 POTENTIAL SEQUENCE Address lymphatics including all transition zones/diaphragms Address somatic dysfunction in spine Focus on upper cervical spine
OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017 POTENTIAL SEQUENCE Address lymphatics including all transition zones/diaphragms Address somatic dysfunction in spine Focus on upper cervical spine
Solving Today s Pain and Injury Puzzle with Erik Dalton An Online Workshop for ABMP Members Session 4 Handout
 Solving Today s Pain and Injury Puzzle with Erik Dalton An Online Workshop for ABMP Members Session 4 Handout Please Note: Erik Dalton teaches his Myoskeletal Alignment Techniques with the expectation
Solving Today s Pain and Injury Puzzle with Erik Dalton An Online Workshop for ABMP Members Session 4 Handout Please Note: Erik Dalton teaches his Myoskeletal Alignment Techniques with the expectation
Total Body Balancing An integrative approach to optimum treatment and balance Kerry D Ambrogio D.O.M., A.P., P.T., D.O.-M.T.P.
 Total Body Balancing An integrative approach to optimum treatment and balance Kerry D Ambrogio D.O.M., A.P., P.T., D.O.-M.T.P. Each day as a practitioner I am faced with the challenge of trying to understand,
Total Body Balancing An integrative approach to optimum treatment and balance Kerry D Ambrogio D.O.M., A.P., P.T., D.O.-M.T.P. Each day as a practitioner I am faced with the challenge of trying to understand,
3. Demonstrate and have a lab for treating ilial somatic dysfunction
 2 nd Annual Osteopathic CME Flagstaff, AZ 8/27/16 My goals for this session are to: 1. Introduce the concept of Biotensegrity as a model that explains how structure and function are intimately related
2 nd Annual Osteopathic CME Flagstaff, AZ 8/27/16 My goals for this session are to: 1. Introduce the concept of Biotensegrity as a model that explains how structure and function are intimately related
WEEKEND 1 CERVICAL SPINE
 Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - Technique Manual WEEKEND 1 CERVICAL SPINE Cervical Active Range of Motion Testing Rotation CT Flexion Mid Cervical Flexion Extension Side-Bending
Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - Technique Manual WEEKEND 1 CERVICAL SPINE Cervical Active Range of Motion Testing Rotation CT Flexion Mid Cervical Flexion Extension Side-Bending
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques. Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright
 Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column 24 articulating vertebrae 31 pairs of spinal nerves Abdominal muscles some
The Trunk and Spinal Column Kinesiology Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column 24 articulating vertebrae 31 pairs of spinal nerves Abdominal muscles some
Main Menu. Trunk and Spinal Column click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
The Use of Seated Facet Release in Children
 The Use of Seated Facet Release in Children Karen M. Steele, DO, FAAO Professor Emerita, West Virginia School of Osteopathic Medicine Former AAO President Outline of lab Pedigree Basic Principles Diagnosis
The Use of Seated Facet Release in Children Karen M. Steele, DO, FAAO Professor Emerita, West Virginia School of Osteopathic Medicine Former AAO President Outline of lab Pedigree Basic Principles Diagnosis
A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course
 2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
AQUATIC ARSENAL. Shoulders & More By Melanie Sparks
 AQUATIC ARSENAL Shoulders & More By Melanie Sparks According to Livestron.com website, The shoulder is the most mobile and flexible joint in the human body. The truth is, we all use our shoulders a lot
AQUATIC ARSENAL Shoulders & More By Melanie Sparks According to Livestron.com website, The shoulder is the most mobile and flexible joint in the human body. The truth is, we all use our shoulders a lot
Integrating Osteopathic Care In A Rural Family Medicine Residency. Jennifer Kingery, D.O October 3, 2013
 Integrating Osteopathic Care In A Rural Family Medicine Residency Jennifer Kingery, D.O October 3, 2013 Disclaimer I have no financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Tensegrity
Integrating Osteopathic Care In A Rural Family Medicine Residency Jennifer Kingery, D.O October 3, 2013 Disclaimer I have no financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Tensegrity
The Seated Nodding Test for O-A Atlas TPs
 Anterior is at the top of the illustrations. Putting the occiput on the atlas would be like closing facing pages of a book. Atlas superior facets converge anteriorly; their surfaces slope superiorly going
Anterior is at the top of the illustrations. Putting the occiput on the atlas would be like closing facing pages of a book. Atlas superior facets converge anteriorly; their surfaces slope superiorly going
SCS FAMILY MEDICINE Introduction in Osteopathic Principles & Initial Osteopathic Evaluation for Low Back Pain
 SCS FAMILY MEDICINE Introduction in Osteopathic Principles & Initial Osteopathic Evaluation for Low Back Pain CATHERINE DONAHUE D.O. ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF OMM MSUCOM WHAT WE WILL COVER Osteopathic
SCS FAMILY MEDICINE Introduction in Osteopathic Principles & Initial Osteopathic Evaluation for Low Back Pain CATHERINE DONAHUE D.O. ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF OMM MSUCOM WHAT WE WILL COVER Osteopathic
Manual Muscle Testing. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
The Bambach Saddle Seat in rehabilitation
 7 The Bambach Saddle Seat in rehabilitation The Musculo-skeletal System Good design recognises that our body has a centre of gravity (as does each limb) and maintaining posture close to the neutral centre
7 The Bambach Saddle Seat in rehabilitation The Musculo-skeletal System Good design recognises that our body has a centre of gravity (as does each limb) and maintaining posture close to the neutral centre
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival. 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back
 Low Back Pain 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of
Low Back Pain 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK
 ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
OSTEOPATHIC PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE: OMT IN 2018
 OSTEOPATHIC PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE: OMT IN 2018 Walter B. Flesner III, D.O. Medical Director, ICPR, Cape Coral Florida. Past President, Florida Osteopathic Medical Association 1996-1997. Jon P. Burdzy,
OSTEOPATHIC PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE: OMT IN 2018 Walter B. Flesner III, D.O. Medical Director, ICPR, Cape Coral Florida. Past President, Florida Osteopathic Medical Association 1996-1997. Jon P. Burdzy,
3 Movements of the Trunk. Flexion Rotation Extension
 3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL
 ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS
 CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
Manipulation according to Maigne
 1 Manipulation according to Maigne Roger Baecher, MD Roger BAECHER, MD March 2001 1st International Congress of Osteopathic Medicine Freiburg / Breisgau Germany, 15-18 September 1st International Congress
1 Manipulation according to Maigne Roger Baecher, MD Roger BAECHER, MD March 2001 1st International Congress of Osteopathic Medicine Freiburg / Breisgau Germany, 15-18 September 1st International Congress
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection
 The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
Sacral Dysfunction: Bilateral Flexed Sacrum & Bilateral Extended Sacrum
 Sacral Dysfunction: Bilateral Flexed Sacrum & Bilateral Extended Sacrum Cherise Russo D.O. Northwestern Orthopaedic Institute, LLC Clinical Instructor, Northwestern University School of Medicine April
Sacral Dysfunction: Bilateral Flexed Sacrum & Bilateral Extended Sacrum Cherise Russo D.O. Northwestern Orthopaedic Institute, LLC Clinical Instructor, Northwestern University School of Medicine April
Subluxation and Muscle Patterns for the Lower Thoracics Marc Heller, DC
 Subluxation and Muscle Patterns for the Lower Thoracics Marc Heller, DC An extremely common subluxation pattern is a lack of extension, with restricted lateral bending and rotation to one side in the lower
Subluxation and Muscle Patterns for the Lower Thoracics Marc Heller, DC An extremely common subluxation pattern is a lack of extension, with restricted lateral bending and rotation to one side in the lower
Osteoporosis Protocol
 PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Osteoporosis Protocol Rehabilitation using the Resistance Chair General Information Osteoporosis is a condition where bones gradually decrease in mass or density
PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Osteoporosis Protocol Rehabilitation using the Resistance Chair General Information Osteoporosis is a condition where bones gradually decrease in mass or density
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players.
 Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Cronicon ORTHOPAEDICS
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article A Comparative Study of the Effectiveness of Two Manual Therapy Techniques on Pain and Lumbar Range of Motion Bhojan Kannabiran*, J Divya J Pawani and
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article A Comparative Study of the Effectiveness of Two Manual Therapy Techniques on Pain and Lumbar Range of Motion Bhojan Kannabiran*, J Divya J Pawani and
The Vertebral Column
 The Vertebral Column The vertebral column (also called the backbone, spine, or spinal column) consists of a series of 33 irregularly shaped bones, called vertebrae. These 33 bones are divided into five
The Vertebral Column The vertebral column (also called the backbone, spine, or spinal column) consists of a series of 33 irregularly shaped bones, called vertebrae. These 33 bones are divided into five
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
Side Split Squat. The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time
 GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
P ERFORMANCE CONDITIONING. Postural Priorities - Rib Cage Influences on the Volleyball Player s Shoulder VOLLEYBALL
 P ERFORMANCE VOLLEYBALL CONDITIONING A NEWSLETTER DEDICATED TO IMPROVING VOLLEYBALL PLAYERS www.performancecondition.com/volleyball Postural Priorities - Rib Cage Influences on the Volleyball Player s
P ERFORMANCE VOLLEYBALL CONDITIONING A NEWSLETTER DEDICATED TO IMPROVING VOLLEYBALL PLAYERS www.performancecondition.com/volleyball Postural Priorities - Rib Cage Influences on the Volleyball Player s
Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017
 Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017 Lisa Westlake www.physicalbest.com Pilates, fitball and physiotherapy blend perfectly to fine tune movement and postural awareness and provide a focus on technique,
Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017 Lisa Westlake www.physicalbest.com Pilates, fitball and physiotherapy blend perfectly to fine tune movement and postural awareness and provide a focus on technique,
Assessing and Treating the Restricted Hip. Objectives. and how does this become that? When did this become bad? Neurodevelopment.
 Assessing and Treating the Restricted Hip New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute Fall Symposium Bedford, NH September 14, 2013 Scott Lawrance, DHS, LAT, ATC, MSPT, CSCS University of Indianapolis Objectives
Assessing and Treating the Restricted Hip New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute Fall Symposium Bedford, NH September 14, 2013 Scott Lawrance, DHS, LAT, ATC, MSPT, CSCS University of Indianapolis Objectives
Functional Movement Test. Deep Squat
 Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
WHY BASIC HIP FLEXOR STRETCHES DON'T ALWAYS WORK
 WHY BASIC HIP FLEXOR STRETCHES DON'T ALWAYS WORK Do you do a daily stretching routine only to find that your muscles tighten back up throughout the day? Do you continue to stretch your hamstrings but still
WHY BASIC HIP FLEXOR STRETCHES DON'T ALWAYS WORK Do you do a daily stretching routine only to find that your muscles tighten back up throughout the day? Do you continue to stretch your hamstrings but still
Massage and Movement. Patrick A. Ward, MS CSCS LMT OptimumSportsPerformance.com
 Massage and Movement Patrick A. Ward, MS CSCS LMT OptimumSportsPerformance.com Massage and Movement Massage comes in all kinds of varieties. From spa massage, to clinical/treatment based massage, to the
Massage and Movement Patrick A. Ward, MS CSCS LMT OptimumSportsPerformance.com Massage and Movement Massage comes in all kinds of varieties. From spa massage, to clinical/treatment based massage, to the
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual
 Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Physical Examination of the Shoulder
 General setup Patient will be examined in both the seated and supine position so exam table needed 360 degree access to patient Expose neck and both shoulders (for comparison); female in gown or sports
General setup Patient will be examined in both the seated and supine position so exam table needed 360 degree access to patient Expose neck and both shoulders (for comparison); female in gown or sports
PT Final Exam Live July 2018 CCR # 10 With JB. Copyright 2015 PT Final Exam
 PT Final Exam Live July 2018 CCR # 10 With JB CCR 10 Wahoo!!! Contact info: jonathan@ptfinalexam.com Email to set up a phone call, FaceTime, Skype, or Google Hangout Availability What is your outlet? !QQQ!
PT Final Exam Live July 2018 CCR # 10 With JB CCR 10 Wahoo!!! Contact info: jonathan@ptfinalexam.com Email to set up a phone call, FaceTime, Skype, or Google Hangout Availability What is your outlet? !QQQ!
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
Possible diagnoses. and extension OA ES L RR. deep. equal. with flexion OA ES R RL. the leftt. equal. deep. equal. equal. for flexion.
 Cervical Diagnosis Occipitoatlantal (OA) joint Possible diagnoses Diagnosis OA FS L RR OA FS R RL OA ES L RR OA ES R RL Sulci findings Left sulcus is shallow and right sulcus is deep Right sulcus is shallow
Cervical Diagnosis Occipitoatlantal (OA) joint Possible diagnoses Diagnosis OA FS L RR OA FS R RL OA ES L RR OA ES R RL Sulci findings Left sulcus is shallow and right sulcus is deep Right sulcus is shallow
External Obliques Abdominal muscles that attaches at the lower ribs, pelvis, and abdominal fascia.
 The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist. Concept ENGSTRÖM
 FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
Mobility sequencing!
 Mobility sequencing When practicing joint mobility drills we have the opportunity to improve our movement. The muscles associated with the joint being mobilised as well as the joint itself will improve
Mobility sequencing When practicing joint mobility drills we have the opportunity to improve our movement. The muscles associated with the joint being mobilised as well as the joint itself will improve
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018
 Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Muscle Energy Technique
 PRACTICE SESSION: Muscle Energy Technique BE AN ARTIST and work out the best way for you to use the Muscle Energy Technique (MET). This technique works best when muscles are shortened. If you try MET on
PRACTICE SESSION: Muscle Energy Technique BE AN ARTIST and work out the best way for you to use the Muscle Energy Technique (MET). This technique works best when muscles are shortened. If you try MET on
position to influence or control the content of this No faculty or planning committee member in a presentation has any relevant financial
 Introduction to Osteopathic Principles and Practice Presented by Brandon Isaacs, DO, FAAFP Associate Dean of Postdoctoral Education Associate Professor of Family Medicine Pacific Northwest University of
Introduction to Osteopathic Principles and Practice Presented by Brandon Isaacs, DO, FAAFP Associate Dean of Postdoctoral Education Associate Professor of Family Medicine Pacific Northwest University of
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Effective Treatments for Sciatica
 Effective Treatments for Sciatica Exact data on the incidence and prevalence of sciatica are lacking. In general an estimated 5%-10% of patients with low back pain have sciatica, whereas the reported lifetime
Effective Treatments for Sciatica Exact data on the incidence and prevalence of sciatica are lacking. In general an estimated 5%-10% of patients with low back pain have sciatica, whereas the reported lifetime
Contact to the ground
 Contact to the ground Lie down on the floor, as flat as possible. Let your arms and legs rest on the ground. Close your eyes if it feels comfortable. Focus on how your body takes contact to the ground.
Contact to the ground Lie down on the floor, as flat as possible. Let your arms and legs rest on the ground. Close your eyes if it feels comfortable. Focus on how your body takes contact to the ground.
PT Final Exam July 2018 Core Content Review 2 Presented by Mark. Copyright 2017 PT Final Exam
 PT Final Exam July 2018 Core Content Review 2 Presented by Mark Copyright 2017 PT Final Exam Started as a PTA in 2006 About me Graduated as a PT from The University of Liverpool, England June 2012 Moved
PT Final Exam July 2018 Core Content Review 2 Presented by Mark Copyright 2017 PT Final Exam Started as a PTA in 2006 About me Graduated as a PT from The University of Liverpool, England June 2012 Moved
Hip Arthroscopy. Labral Repair/Debridement with Femoroplasty
 Precautions for weeks 1 4 post-op: Hip Arthroscopy Labral Repair/Debridement with Femoroplasty Patient Education o For 1 week, Assist the involved LE during all transfers o For 2 weeks, Do not sit with
Precautions for weeks 1 4 post-op: Hip Arthroscopy Labral Repair/Debridement with Femoroplasty Patient Education o For 1 week, Assist the involved LE during all transfers o For 2 weeks, Do not sit with
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership
 Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
WTC II Term 3 Notes & Assessments
 Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE
 GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
THE SELECTIVE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT
 - 33 - THE SELECTIVE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT SFMA SCORING FP DP Active Cervical Flexion Active Cervical Extension Cervical Rotation Upper Extremity Pattern 1(MRE) Upper Extremity Pattern 2 (LRF)
- 33 - THE SELECTIVE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT SFMA SCORING FP DP Active Cervical Flexion Active Cervical Extension Cervical Rotation Upper Extremity Pattern 1(MRE) Upper Extremity Pattern 2 (LRF)
Algorithm #1 Lumbo-Pelvic Region Examination
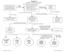 Red Screen for Potentially Serious Conditions (i.e., Red Flags) including Neurologic when indicated Positive Findings Algorithm #1 Lumbo-Pelvic Region Clinical Prediction Rule Screening: Duration of symptoms
Red Screen for Potentially Serious Conditions (i.e., Red Flags) including Neurologic when indicated Positive Findings Algorithm #1 Lumbo-Pelvic Region Clinical Prediction Rule Screening: Duration of symptoms
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
Benefits of Weight bearing increased awareness of the involved side decreased fear improved symmetry regulation of muscle tone
 From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
