Experience-dependent recovery of vision following chronic deprivation amblyopia. Hai-Yan He, Baisali Ray, Katie Dennis and Elizabeth M.
|
|
|
- Kevin Shaw
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Experience-dependent recovery of vision following chronic deprivation amblyopia Hai-Yan He, Baisali Ray, Katie Dennis and Elizabeth M. Quinlan a Deprived eye Non-deprived VCtx * * b Non-deprived VCtx Supplementary Figure 1. Dark exposure in adulthood allowed recovery of function following chronic. a. In the non-deprived VCtx, chronic induced a significant decrease in VEP amplitudes in response to stimulation of the deprived eye (p <.1, t-test vs NR), which recovered when was followed by or (norm VEP amp: control = 2.6 ±.24, = 5 ±.19, - = 1.1 ±.2, - = 1.11 ±.11, - =.97 ±.11, -- = 1.94 ±.2, -- = 2.54 ±.34). Oneway ANOVA (F(5,44) = 8.415, p <.1), * = p <.5 vs.. b. Chronic and subsequent manipulations of visual experience did not regulate the VEP in response to stimulation of the non-deprived eye in the non-deprived VCtx. One-way ANOVA (F(5, 44) = 89, p =.38).
2 a Chronic deprived eye Log of spatial frequency (cycles deg -1) b Monocular spatial acuity (cycles deg -1 ) Rearing condition Supplementary Figure 2. Estimation of spatial acuity with VEPs. a. Log of the spatial frequency of the visual stimulus vs. VEP amplitude in response to stimulation of the chroinically-deprived and non-deprived eye recorded in the hemisphere dominated by that eye. Spatial acuity was estimated by extrapolating the linear regression to zero VEP amplitude. Chronically-deprived eye =.26 cycles deg -1, non-deprived eye = cycles deg -1. b. No change in spatial acuity in the non-deprived eye was observed across experimental conditions (one-way ANOVA (F(5,26) = 1.397, p =.26).
3 -1) Monocular spatial acuity (cycles deg NR 1 Trial 1 Trial 2 day 2 8 Trial 3 day Spatial frequency (cycles deg -1) Days of binocular vision after normal rearing Deprived eye Supplementary Figure 3. Two-choice visual discrimination task revealed no recovery of spatial acuity in the absence of dark exposure. Monocular spatial acuity in non-deprived eye was unchanged following 1 days of normal rearing without exposure to the task (NR =.76 ±.8 cycles deg -1, n = 8). No measurable spatial acuity in the deprived eye was observed after 7 weeks of. Inset: % correct choices vs. spatial frequency of visual stimulus in a single adult subject. The highest spatial frequency at which the subject performed 6% correct choices was the spatial acuity for that trial, and was similar across trials on consecutive days (trials 1 and 2), and a trial that followed 1 days without exposure to the task (trial 3 day 13).
4 Supplementary Methods Long Evans rats were raised with 12 hr light: 12 hr dark per day until adulthood (P7-1) before receiving brief (3 days) via lid suture (4). 3-1 days of dark exposure in a light-tight dark room may precede the brief. Chronic lid suture began at eye opening (~P13) and proceeded to adulthood (P7-P1). Chronic may be followed by binocular vision (opening the deprived eye) or reverse occlusion (opening the deprived eye and closing the non-deprived eye), which may be preceded by 1 days dark exposure. All procedures conformed to the guidelines of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the University of Maryland Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. VEP recordings: Visually evoked potentials (VEPs) were recorded with tungsten microelectrodes (.1 MΩ; MPI, Gaithersburg, ) relative to a ground screw in the frontal bone and a reference electrode in dorsal neck muscle. The dura covering the binocular visual cortex (V1b; ~7. mm posterior to bregma and 5 mm lateral to the midline) was exposed through a 3mm diameter hole in the skull following urethane anesthesia (1.6g/kg i.p.). Electrode placement in V1b was confirmed by capturing a VEP in response to stimulation of the ipsilateral eye. The visual stimuli were full screen vertical square wave gratings of.4 cycles deg 1 reversing at 1 Hz, with 96.28% maximal contrast, presented on a computer monitor 25 cm from eyes, in a darkened room. The amplitude of the primary positive component of the VEP (~15 ms latency) was amplified (1X), filtered (.5-3 Hz band pass followed by 6 Hz low pass) and averaged (1 trials) in synchrony with the stimulus using ENFANT software (Enfant 41, NeuroScientific Corp., Farmingdale, NY). VEP amplitudes were normalized to noise at that recording site, which was the average field potential recorded in response to a blank screen. For spatial acuity estimation, VEPs were recorded from the hemisphere contralateral to the stimulated eye. The VEP amplitude (normalized to the maximal response recorded within that session) was plotted against the log of the spatial frequency of the visual stimulus. The spatial frequency extrapolated to zero amplitude of the linear regression through the last 5-8 data points was reported as estimated spatial acuity (adapted from 11).
5 Visual discrimination: Spatial acuity was assessed behaviorally with a water-based 2 choice visual discrimination task (developed by Prusky and colleagues, University of Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada), in a plexiglass box (152 x 94 x 76 cm), painted flat black on 3 sides, filled to a height of 36 cm (~14 gallons). Visual stimuli, presented on monitors mounted to the outside of the unpainted end of the box (Lacie 319 LCD, Hillsboro, OR), were generated by Vista 2.2 software (Cerebral Mechanics, Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada). Subjects learned to associate a hidden escape platform (positive stimulus) with a high contrast vertical sinusoidal grating, and the negative stimulus (absence of escape platform) with a grey screen with equal luminance (75 cd/m 2 ), white balance (5K), gamma value (1.8) and contrast (1%; calibrated daily with Lacie Blue eye pro, version 3.4, Hillsboro, OR), which were presented to the left and right screens in pseudo-random order. Short (17.8 cm), medium (35.6 cm) and long dividers (53.4 cm) were gradually introduced between the two monitors to increase the visual discrimination choice point. Once subjects reached the learning criterion (3 correct choices over 3 consecutive trials) at a spatial frequency of.129 cycles deg 1, the spatial frequency of the visual stimulus was increased by increments of.64 cycles deg 1. At spatial frequencies.482 cycles deg -1, testing at the next higher spatial frequency followed a single successful trial. At spatial frequencies >.482 cycles deg 1, a success rate of 6% over 5 trials was required before moving to the next spatial frequency. The highest spatial frequency at which the subject performed 6% correct (out of 5 trials) was the spatial acuity for that trial. Statistical analysis: Student one-tailed t-tests were used to evaluate differences between two independent experimental groups. One-way ANOVAs were used to test for differences among three or more independent experimental groups. F crit was significant when > than F test calculated for the degrees of freedom between groups (factor) and within groups (residual) for each experiment. Fisher s PLSD post hoc comparison was used to identify the source of significant differences, when appropriate.
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
A contrast paradox in stereopsis, motion detection and vernier acuity
 A contrast paradox in stereopsis, motion detection and vernier acuity S. B. Stevenson *, L. K. Cormack Vision Research 40, 2881-2884. (2000) * University of Houston College of Optometry, Houston TX 77204
A contrast paradox in stereopsis, motion detection and vernier acuity S. B. Stevenson *, L. K. Cormack Vision Research 40, 2881-2884. (2000) * University of Houston College of Optometry, Houston TX 77204
Scotopic contrast sensitivity in infants evaluated by evoked potentials
 Scotopic contrast sensitivity in infants evaluated by evoked potentials Adriana Fiorentini, M. Pirchio, and Donatella Spinelli* The contrast sensitivity function of infants 2V% to 6 months old has been
Scotopic contrast sensitivity in infants evaluated by evoked potentials Adriana Fiorentini, M. Pirchio, and Donatella Spinelli* The contrast sensitivity function of infants 2V% to 6 months old has been
CROSSMODAL PLASTICITY IN SPECIFIC AUDITORY CORTICES UNDERLIES VISUAL COMPENSATIONS IN THE DEAF "
 Supplementary Online Materials To complement: CROSSMODAL PLASTICITY IN SPECIFIC AUDITORY CORTICES UNDERLIES VISUAL COMPENSATIONS IN THE DEAF " Stephen G. Lomber, M. Alex Meredith, and Andrej Kral 1 Supplementary
Supplementary Online Materials To complement: CROSSMODAL PLASTICITY IN SPECIFIC AUDITORY CORTICES UNDERLIES VISUAL COMPENSATIONS IN THE DEAF " Stephen G. Lomber, M. Alex Meredith, and Andrej Kral 1 Supplementary
The effect of stimulus duration on the persistence of gratings
 Perception & Psychophysics 1980,27 (6),574-578 The effect of stimulus duration on the persistence of gratings ALISON BOWLING and WILLIAM LOVEGROVE University oftasmania, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia 700/
Perception & Psychophysics 1980,27 (6),574-578 The effect of stimulus duration on the persistence of gratings ALISON BOWLING and WILLIAM LOVEGROVE University oftasmania, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia 700/
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Brief daily binocular vision prevents monocular deprivation effects in visual cortex
 European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 25, pp. 270 280, 2007 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05273.x Brief daily binocular vision prevents monocular deprivation effects in visual cortex D. Samuel Schwarzkopf,
European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 25, pp. 270 280, 2007 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05273.x Brief daily binocular vision prevents monocular deprivation effects in visual cortex D. Samuel Schwarzkopf,
AUTOCORRELATION AND CROSS-CORRELARION ANALYSES OF ALPHA WAVES IN RELATION TO SUBJECTIVE PREFERENCE OF A FLICKERING LIGHT
 AUTOCORRELATION AND CROSS-CORRELARION ANALYSES OF ALPHA WAVES IN RELATION TO SUBJECTIVE PREFERENCE OF A FLICKERING LIGHT Y. Soeta, S. Uetani, and Y. Ando Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kobe
AUTOCORRELATION AND CROSS-CORRELARION ANALYSES OF ALPHA WAVES IN RELATION TO SUBJECTIVE PREFERENCE OF A FLICKERING LIGHT Y. Soeta, S. Uetani, and Y. Ando Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kobe
Representation of negative motivational value in the primate
 Representation of negative motivational value in the primate lateral habenula Masayuki Matsumoto & Okihide Hikosaka Supplementary Figure 1 Anticipatory licking and blinking. (a, b) The average normalized
Representation of negative motivational value in the primate lateral habenula Masayuki Matsumoto & Okihide Hikosaka Supplementary Figure 1 Anticipatory licking and blinking. (a, b) The average normalized
Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
Supplementary Note Psychophysics:
 Supplementary Note More detailed description of MM s subjective experiences can be found on Mike May s Perceptions Home Page, http://www.senderogroup.com/perception.htm Psychophysics: The spatial CSF was
Supplementary Note More detailed description of MM s subjective experiences can be found on Mike May s Perceptions Home Page, http://www.senderogroup.com/perception.htm Psychophysics: The spatial CSF was
Absence of Adaptive Modification in Developing Retinotectal Connections
 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 528-532, March 1971 Absence of Adaptive Modification in Developing Retinotectal Connections in Frogs after Visual Deprivation or Disparate
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 528-532, March 1971 Absence of Adaptive Modification in Developing Retinotectal Connections in Frogs after Visual Deprivation or Disparate
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017
 V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
SPATIAL FREQUENCY (CPD) Contrast evoked potentials in strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia. DENNIS M. LEVI 10; 6 :
 Number 6 Reports 571 Contrast evoked potentials in strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia. DENNIS. VI AND RONALD S. HARWERTH. Steady-state visual evoked potentials were elicited by the appearance I disappearance
Number 6 Reports 571 Contrast evoked potentials in strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia. DENNIS. VI AND RONALD S. HARWERTH. Steady-state visual evoked potentials were elicited by the appearance I disappearance
Differences in temporal frequency tuning between the two binocular mechanisms for seeing motion in depth
 1574 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 25, No. 7/ July 2008 Shioiri et al. Differences in temporal frequency tuning between the two binocular mechanisms for seeing motion in depth Satoshi Shioiri, 1, * Tomohiko
1574 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A/ Vol. 25, No. 7/ July 2008 Shioiri et al. Differences in temporal frequency tuning between the two binocular mechanisms for seeing motion in depth Satoshi Shioiri, 1, * Tomohiko
Effects of different forms of monocular deprivation on primary visual cortex maps
 Visual Neuroscience (2012), 29, 247 253. Copyright Ó Cambridge University Press, 2012 0952-5238/12 $25.00 doi:10.1017/s0952523812000260 Effects of different forms of monocular deprivation on primary visual
Visual Neuroscience (2012), 29, 247 253. Copyright Ó Cambridge University Press, 2012 0952-5238/12 $25.00 doi:10.1017/s0952523812000260 Effects of different forms of monocular deprivation on primary visual
Introduction. Introduction. A Comparison of Contrast Sensitivity and Sweep Visual Evoked Potential (svep) Acuity Estimates in Normal Humans.
 A Comparison of Contrast Sensitivity and Sweep Visual Evoked Potential (svep) Acuity Estimates in Normal Humans. William H. Ridder,III, Apoorva Karsolia, and Deborah Duan. Southern California College of
A Comparison of Contrast Sensitivity and Sweep Visual Evoked Potential (svep) Acuity Estimates in Normal Humans. William H. Ridder,III, Apoorva Karsolia, and Deborah Duan. Southern California College of
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Optical imaging of the intrinsic signal as a measure of cortical plasticity in the mouse
 Visual Neuroscience ~2005!, 22, 685 691. Printed in the USA. Copyright 2005 Cambridge University Press 0952-5238005 $16.00 DOI: 10.10170S0952523805225178 Optical imaging of the intrinsic signal as a measure
Visual Neuroscience ~2005!, 22, 685 691. Printed in the USA. Copyright 2005 Cambridge University Press 0952-5238005 $16.00 DOI: 10.10170S0952523805225178 Optical imaging of the intrinsic signal as a measure
Analysis Of Effect Of Stimulation On Trasient VEP Using Spectral Components
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Medical Simulation Volume 2 Number 1 Analysis Of Effect Of Stimulation On Trasient VEP Using Spectral Components R Sivakumar, G Ravindran Citation R Sivakumar, G Ravindran..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Medical Simulation Volume 2 Number 1 Analysis Of Effect Of Stimulation On Trasient VEP Using Spectral Components R Sivakumar, G Ravindran Citation R Sivakumar, G Ravindran..
Supplemental Figure 1
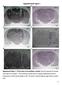 A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
Visual Deprivation Reactivates Rapid Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Adult Visual Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 15, 2006 26(11):2951 2955 2951 Brief Communications Visual Deprivation Reactivates Rapid Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Adult Visual Cortex Hai-Yan He, 2 William Hodos,
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 15, 2006 26(11):2951 2955 2951 Brief Communications Visual Deprivation Reactivates Rapid Ocular Dominance Plasticity in Adult Visual Cortex Hai-Yan He, 2 William Hodos,
Binaural Hearing. Why two ears? Definitions
 Binaural Hearing Why two ears? Locating sounds in space: acuity is poorer than in vision by up to two orders of magnitude, but extends in all directions. Role in alerting and orienting? Separating sound
Binaural Hearing Why two ears? Locating sounds in space: acuity is poorer than in vision by up to two orders of magnitude, but extends in all directions. Role in alerting and orienting? Separating sound
Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey
 3.6.QH Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey Versnel, Huib; Zwiers, Marcel; Van Opstal, John Department of Biophysics University of Nijmegen Geert Grooteplein 655
3.6.QH Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey Versnel, Huib; Zwiers, Marcel; Van Opstal, John Department of Biophysics University of Nijmegen Geert Grooteplein 655
Research Note. Orientation Selectivity in the Cat's Striate Cortex is Invariant with Stimulus Contrast*
 Exp Brain Res (1982) 46:457-461 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Research Note Orientation Selectivity in the Cat's Striate Cortex is Invariant with Stimulus Contrast* G. Sclar and R.D. Freeman School of Optometry,
Exp Brain Res (1982) 46:457-461 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Research Note Orientation Selectivity in the Cat's Striate Cortex is Invariant with Stimulus Contrast* G. Sclar and R.D. Freeman School of Optometry,
Neural correlates of short-term perceptual learning in orientation discrimination indexed by event-related potentials
 Chinese Science Bulletin 2007 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Neural correlates of short-term perceptual learning in orientation discrimination indexed by event-related potentials SONG Yan 1, PENG
Chinese Science Bulletin 2007 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Neural correlates of short-term perceptual learning in orientation discrimination indexed by event-related potentials SONG Yan 1, PENG
Comparison of Pattern VEPs and Preferential-Looking Behavior in 3-Month-Old Infants
 Comparison of Pattern VEPs and Preferential-Looking Behavior in 3-Month-Old Infants Samuel Sokol ond Anne Moskowirz Studies of visual acuity in human infants between 1 and 6 months of age using the visual-evoked
Comparison of Pattern VEPs and Preferential-Looking Behavior in 3-Month-Old Infants Samuel Sokol ond Anne Moskowirz Studies of visual acuity in human infants between 1 and 6 months of age using the visual-evoked
CAN WE PREDICT STEERING CONTROL PERFORMANCE FROM A 2D SHAPE DETECTION TASK?
 CAN WE PREDICT STEERING CONTROL PERFORMANCE FROM A 2D SHAPE DETECTION TASK? Bobby Nguyen 1, Yan Zhuo 2 & Rui Ni 1 1 Wichita State University, Wichita, Kansas, USA 2 Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy
CAN WE PREDICT STEERING CONTROL PERFORMANCE FROM A 2D SHAPE DETECTION TASK? Bobby Nguyen 1, Yan Zhuo 2 & Rui Ni 1 1 Wichita State University, Wichita, Kansas, USA 2 Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy
Lateral interactions in visual perception of temporal signals: cortical and subcortical components
 PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 2011, 4, 1, 57-65 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2011.1.007 Lateral interactions in visual perception of temporal signals: cortical and subcortical components Claudio
PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 2011, 4, 1, 57-65 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2011.1.007 Lateral interactions in visual perception of temporal signals: cortical and subcortical components Claudio
Behavioral generalization
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Visual Evoked Potentials. Outline. Visual Pathway Anatomy
 Visual Evoked Potentials Elayna Rubens, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Weill Cornell Medical College Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Outline Visual Pathway Anatomy Basic VEP principles -VEP
Visual Evoked Potentials Elayna Rubens, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology Weill Cornell Medical College Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Outline Visual Pathway Anatomy Basic VEP principles -VEP
Supplementary material
 Supplementary material S1. Event-related potentials Event-related potentials (ERPs) were calculated for stimuli for each visual field (mean of low, medium and high spatial frequency stimuli). For each
Supplementary material S1. Event-related potentials Event-related potentials (ERPs) were calculated for stimuli for each visual field (mean of low, medium and high spatial frequency stimuli). For each
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Forsyth et al. 10.1073/pnas.1509262112 SI Methods Inclusion Criteria. Participants were eligible for the study if they were between 18 and 30 y of age; were comfortable reading in
Supporting Information Forsyth et al. 10.1073/pnas.1509262112 SI Methods Inclusion Criteria. Participants were eligible for the study if they were between 18 and 30 y of age; were comfortable reading in
COMMUNICATIONS BIOPHYSICS
 XVIII. * COMMUNICATIONS BIOPHYSICS Prof. W. A. Rosenblith Dr. N. Y-S. Kiang A. H. Crist Prof. M. H. Goldstein, Jr. Dr. J. W. Kuiper**' G. E. Forsen Dr. J. S. Barlowt Dr. T. T. Sandel Margaret Z. Freeman
XVIII. * COMMUNICATIONS BIOPHYSICS Prof. W. A. Rosenblith Dr. N. Y-S. Kiang A. H. Crist Prof. M. H. Goldstein, Jr. Dr. J. W. Kuiper**' G. E. Forsen Dr. J. S. Barlowt Dr. T. T. Sandel Margaret Z. Freeman
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4084
 Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Recording technique Multi-unit activity (MUA) was recorded from electrodes that were chronically implanted (Teflon-coated platinum-iridium wires) in the primary visual cortex representing
Supplemental Material Recording technique Multi-unit activity (MUA) was recorded from electrodes that were chronically implanted (Teflon-coated platinum-iridium wires) in the primary visual cortex representing
Selective attention and cyclopean motion processing
 Vision Research 45 (2005) 2601 2607 Brief communication Selective attention and cyclopean motion processing Robert Patterson *, Lisa R. Fournier, Matt Wiediger, Greg Vavrek, Cheryl Becker-Dippman, Ivan
Vision Research 45 (2005) 2601 2607 Brief communication Selective attention and cyclopean motion processing Robert Patterson *, Lisa R. Fournier, Matt Wiediger, Greg Vavrek, Cheryl Becker-Dippman, Ivan
Neuroscientists frequently need to characterize the sensory abilities of
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual performance in mice: physiology meets behaviour Manuel Teichert, Konrad Lehmann, Jurgen Bolz Teichert M, Lehmann K, Bolz J. Visual performance in mice: physiology meets behaviour.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Visual performance in mice: physiology meets behaviour Manuel Teichert, Konrad Lehmann, Jurgen Bolz Teichert M, Lehmann K, Bolz J. Visual performance in mice: physiology meets behaviour.
Independence of Visual Awareness from the Scope of Attention: an Electrophysiological Study
 Cerebral Cortex March 2006;16:415-424 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhi121 Advance Access publication June 15, 2005 Independence of Visual Awareness from the Scope of Attention: an Electrophysiological Study Mika
Cerebral Cortex March 2006;16:415-424 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhi121 Advance Access publication June 15, 2005 Independence of Visual Awareness from the Scope of Attention: an Electrophysiological Study Mika
Disparity- and velocity- based signals for 3D motion perception in human MT+ Bas Rokers, Lawrence K. Cormack, and Alexander C. Huk
 Disparity- and velocity- based signals for 3D motion perception in human MT+ Bas Rokers, Lawrence K. Cormack, and Alexander C. Huk Supplementary Materials fmri response (!% BOLD) ).5 CD versus STS 1 wedge
Disparity- and velocity- based signals for 3D motion perception in human MT+ Bas Rokers, Lawrence K. Cormack, and Alexander C. Huk Supplementary Materials fmri response (!% BOLD) ).5 CD versus STS 1 wedge
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings
 Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplemental Information: Task-specific transfer of perceptual learning across sensory modalities
 Supplemental Information: Task-specific transfer of perceptual learning across sensory modalities David P. McGovern, Andrew T. Astle, Sarah L. Clavin and Fiona N. Newell Figure S1: Group-averaged learning
Supplemental Information: Task-specific transfer of perceptual learning across sensory modalities David P. McGovern, Andrew T. Astle, Sarah L. Clavin and Fiona N. Newell Figure S1: Group-averaged learning
Nov versus Fam. Fam 1 versus. Fam 2. Supplementary figure 1
 a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
Human experiment - Training Procedure - Matching of stimuli between rats and humans - Data analysis
 1 More complex brains are not always better: Rats outperform humans in implicit categorybased generalization by implementing a similarity-based strategy Ben Vermaercke 1*, Elsy Cop 1, Sam Willems 1, Rudi
1 More complex brains are not always better: Rats outperform humans in implicit categorybased generalization by implementing a similarity-based strategy Ben Vermaercke 1*, Elsy Cop 1, Sam Willems 1, Rudi
Electrophysiological Indices of Target and Distractor Processing in Visual Search
 Electrophysiological Indices of Target and Distractor Processing in Visual Search Clayton Hickey 1,2, Vincent Di Lollo 2, and John J. McDonald 2 Abstract & Attentional selection of a target presented among
Electrophysiological Indices of Target and Distractor Processing in Visual Search Clayton Hickey 1,2, Vincent Di Lollo 2, and John J. McDonald 2 Abstract & Attentional selection of a target presented among
ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS
 37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
Early Treatment of Congenital Unilateral Cataract Minimizes Unequal Competition
 Early Treatment of Congenital Unilateral Cataract Minimizes Unequal Competition 12 Eileen E. Birch, 12 David Stager? Joel Leffler? and David Weakley 23 PURPOSE. Dense congenital unilateral cataracts may
Early Treatment of Congenital Unilateral Cataract Minimizes Unequal Competition 12 Eileen E. Birch, 12 David Stager? Joel Leffler? and David Weakley 23 PURPOSE. Dense congenital unilateral cataracts may
Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves
 SICE Annual Conference 27 Sept. 17-2, 27, Kagawa University, Japan Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves Seiji Nishifuji 1, Kentaro Fujisaki 1 and Shogo Tanaka 1 1
SICE Annual Conference 27 Sept. 17-2, 27, Kagawa University, Japan Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves Seiji Nishifuji 1, Kentaro Fujisaki 1 and Shogo Tanaka 1 1
Characterization of mouse cortical spatial vision
 Vision Research 44 (2004) 3411 3418 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Characterization of mouse cortical spatial vision G.T. Prusky a, *, R.M. Douglas b a Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, Canadian
Vision Research 44 (2004) 3411 3418 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Characterization of mouse cortical spatial vision G.T. Prusky a, *, R.M. Douglas b a Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, Canadian
ISCEV standard for clinical visual evoked potentials: (2016 update)
 Doc Ophthalmol (2016) 133:1 9 DOI 10.1007/s10633-016-9553-y ISCEV STANDARDS ISCEV standard for clinical visual evoked potentials: (2016 update) J. Vernon Odom. Michael Bach. Mitchell Brigell. Graham E.
Doc Ophthalmol (2016) 133:1 9 DOI 10.1007/s10633-016-9553-y ISCEV STANDARDS ISCEV standard for clinical visual evoked potentials: (2016 update) J. Vernon Odom. Michael Bach. Mitchell Brigell. Graham E.
Normal Ipsilateral/Contralateral Asymmetries in Infant Multiple Auditory Steady-State Responses to Air- and Bone-Conduction Stimuli
 Normal Ipsilateral/Contralateral Asymmetries in Infant Multiple Auditory Steady-State Responses to Air- and Bone-Conduction Stimuli Susan A. Small and David R. Stapells Objectives: Two-channel recordings
Normal Ipsilateral/Contralateral Asymmetries in Infant Multiple Auditory Steady-State Responses to Air- and Bone-Conduction Stimuli Susan A. Small and David R. Stapells Objectives: Two-channel recordings
The impact of numeration on visual attention during a psychophysical task; An ERP study
 The impact of numeration on visual attention during a psychophysical task; An ERP study Armita Faghani Jadidi, Raheleh Davoodi, Mohammad Hassan Moradi Department of Biomedical Engineering Amirkabir University
The impact of numeration on visual attention during a psychophysical task; An ERP study Armita Faghani Jadidi, Raheleh Davoodi, Mohammad Hassan Moradi Department of Biomedical Engineering Amirkabir University
Active suppression after involuntary capture of attention
 Psychon Bull Rev (2013) 20:296 301 DOI 10.3758/s13423-012-0353-4 BRIEF REPORT Active suppression after involuntary capture of attention Risa Sawaki & Steven J. Luck Published online: 20 December 2012 #
Psychon Bull Rev (2013) 20:296 301 DOI 10.3758/s13423-012-0353-4 BRIEF REPORT Active suppression after involuntary capture of attention Risa Sawaki & Steven J. Luck Published online: 20 December 2012 #
Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
Effects of Tetrachloroethylene on Visual and Cognitive Function in Rats
 Effects of Tetrachloroethylene on Visual and Cognitive Function in Rats Philip J. Bushnell William K. Boyes Vernon A. Benignus Elaina M. Kenyon Wendy M. Oshiro For the National Research Council Committee
Effects of Tetrachloroethylene on Visual and Cognitive Function in Rats Philip J. Bushnell William K. Boyes Vernon A. Benignus Elaina M. Kenyon Wendy M. Oshiro For the National Research Council Committee
The Parameters of Pattern Visual Evoked Potential in the Severe Visual Loss Patients in Korean
 pissn: 0894 eissn: 09938 Korean J Ophthalmol 05;9(3):8589 http://dx.doi.org/0.334/kjo.05.9.3.85 Original Article The Parameters of Pattern Visual Evoked Potential in the Severe Visual Loss Patients in
pissn: 0894 eissn: 09938 Korean J Ophthalmol 05;9(3):8589 http://dx.doi.org/0.334/kjo.05.9.3.85 Original Article The Parameters of Pattern Visual Evoked Potential in the Severe Visual Loss Patients in
Supplemental Information. Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking. Activity in Early Visual Cortex. Supplemental Information Inventory:
 Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Table 1 Patient characteristics Preoperative. language testing
 Categorical Speech Representation in the Human Superior Temporal Gyrus Edward F. Chang, Jochem W. Rieger, Keith D. Johnson, Mitchel S. Berger, Nicholas M. Barbaro, Robert T. Knight SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Categorical Speech Representation in the Human Superior Temporal Gyrus Edward F. Chang, Jochem W. Rieger, Keith D. Johnson, Mitchel S. Berger, Nicholas M. Barbaro, Robert T. Knight SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
REACTION TIME AS A MEASURE OF INTERSENSORY FACILITATION l
 Journal oj Experimental Psychology 12, Vol. 63, No. 3, 289-293 REACTION TIME AS A MEASURE OF INTERSENSORY FACILITATION l MAURICE HERSHENSON 2 Brooklyn College In measuring reaction time (RT) to simultaneously
Journal oj Experimental Psychology 12, Vol. 63, No. 3, 289-293 REACTION TIME AS A MEASURE OF INTERSENSORY FACILITATION l MAURICE HERSHENSON 2 Brooklyn College In measuring reaction time (RT) to simultaneously
ABR assesses the integrity of the peripheral auditory system and auditory brainstem pathway.
 By Prof Ossama Sobhy What is an ABR? The Auditory Brainstem Response is the representation of electrical activity generated by the eighth cranial nerve and brainstem in response to auditory stimulation.
By Prof Ossama Sobhy What is an ABR? The Auditory Brainstem Response is the representation of electrical activity generated by the eighth cranial nerve and brainstem in response to auditory stimulation.
Thalamic activity that drives visual cortical plasticity. Supplementary Materials
 Thalamic activity that drives visual cortical plasticity Monica L. Linden, Arnold J. Heynen, Robert H. Haslinger and Mark F. Bear of 4 Figure S Normalized VEP amplitude 3 2 0 MC * Day 0 Day 5 3 2 0 MI
Thalamic activity that drives visual cortical plasticity Monica L. Linden, Arnold J. Heynen, Robert H. Haslinger and Mark F. Bear of 4 Figure S Normalized VEP amplitude 3 2 0 MC * Day 0 Day 5 3 2 0 MI
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Speech Communication Session 4aSCb: Voice and F0 Across Tasks (Poster
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Speech Communication Session 4aSCb: Voice and F0 Across Tasks (Poster
Temporal Feature of S-cone Pathway Described by Impulse Response Function
 VISION Vol. 20, No. 2, 67 71, 2008 Temporal Feature of S-cone Pathway Described by Impulse Response Function Keizo SHINOMORI Department of Information Systems Engineering, Kochi University of Technology
VISION Vol. 20, No. 2, 67 71, 2008 Temporal Feature of S-cone Pathway Described by Impulse Response Function Keizo SHINOMORI Department of Information Systems Engineering, Kochi University of Technology
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation. Jacobs et al.
 Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation Jacobs et al. Supplementary Information Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects
Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation Jacobs et al. Supplementary Information Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG
 Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 3 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 3 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 3 Psychological and Physiological Acoustics Session 3aPP: Auditory Physiology and
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 9, 3 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 3 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 3 Psychological and Physiological Acoustics Session 3aPP: Auditory Physiology and
Most aspects of spatial vision are quite immature in the
 Development of VEP Vernier Acuity and Grating Acuity in Human Infants Ann M. Skoczenski and Anthony M. Norcia PURPOSE. To compare the developmental sequences of two basic measures of pattern vision, Vernier
Development of VEP Vernier Acuity and Grating Acuity in Human Infants Ann M. Skoczenski and Anthony M. Norcia PURPOSE. To compare the developmental sequences of two basic measures of pattern vision, Vernier
The role of selective attention in visual awareness of stimulus features: Electrophysiological studies
 Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience 2008, 8 (2), 195-210 doi: 10.3758/CABN.8.2.195 The role of selective attention in visual awareness of stimulus features: Electrophysiological studies MIKA
Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience 2008, 8 (2), 195-210 doi: 10.3758/CABN.8.2.195 The role of selective attention in visual awareness of stimulus features: Electrophysiological studies MIKA
Development of the Human Visual System: Monocular and Binocular Pattern VEP Latency
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol., o., July Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Development of the Human Visual System: Monocular and Binocular Pattern VEP Latency
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol., o., July Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Development of the Human Visual System: Monocular and Binocular Pattern VEP Latency
Neural Networks: Tracing Cellular Pathways. Lauren Berryman Sunfest 2000
 Neural Networks: Tracing Cellular Pathways Lauren Berryman Sunfest 000 Neural Networks: Tracing Cellular Pathways Research Objective Background Methodology and Experimental Approach Results and Conclusions
Neural Networks: Tracing Cellular Pathways Lauren Berryman Sunfest 000 Neural Networks: Tracing Cellular Pathways Research Objective Background Methodology and Experimental Approach Results and Conclusions
Suprathreshold spatial frequency detection and binocular interaction in strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia
 Suprathreshold spatial frequency detection and binocular interaction in strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia Dennis M. Levi, Ronald S. Harwerth, and Ruth E. Manny We have investigated suprathreshold
Suprathreshold spatial frequency detection and binocular interaction in strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia Dennis M. Levi, Ronald S. Harwerth, and Ruth E. Manny We have investigated suprathreshold
Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling
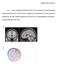 Supplementary materials 1 Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling analyses placed the source of the No Go N2 component in the dorsal ACC, near the ACC source
Supplementary materials 1 Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling analyses placed the source of the No Go N2 component in the dorsal ACC, near the ACC source
Visual cortical plasticity
 Visual cortical plasticity Deprivation-induced changes in representation Ocular dominance plasticity Retinal scotoma and cortical re-organization Perceptual learning-related plasticity Timing-dependent
Visual cortical plasticity Deprivation-induced changes in representation Ocular dominance plasticity Retinal scotoma and cortical re-organization Perceptual learning-related plasticity Timing-dependent
Image-Based Grouping during Binocular Rivalry Is Dictated by Eye-Of-Origin
 Image-Based Grouping during Binocular Rivalry Is Dictated by Eye-Of-Origin Sjoerd M. Stuit 1 *, Chris L. E. Paffen 1, Maarten J. van der Smagt 1, Frans A. J. Verstraten 1,2 1 Universiteit Utrecht, Neuroscience
Image-Based Grouping during Binocular Rivalry Is Dictated by Eye-Of-Origin Sjoerd M. Stuit 1 *, Chris L. E. Paffen 1, Maarten J. van der Smagt 1, Frans A. J. Verstraten 1,2 1 Universiteit Utrecht, Neuroscience
The role of cognitive effort in subjective reward devaluation and risky decision-making
 The role of cognitive effort in subjective reward devaluation and risky decision-making Matthew A J Apps 1,2, Laura Grima 2, Sanjay Manohar 2, Masud Husain 1,2 1 Nuffield Department of Clinical Neuroscience,
The role of cognitive effort in subjective reward devaluation and risky decision-making Matthew A J Apps 1,2, Laura Grima 2, Sanjay Manohar 2, Masud Husain 1,2 1 Nuffield Department of Clinical Neuroscience,
Aging and the Detection of Collision Events in Fog
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2009 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 23rd, 12:00 AM Aging and the Detection of Collision Events in Fog Zheng Bian University of California,
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2009 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 23rd, 12:00 AM Aging and the Detection of Collision Events in Fog Zheng Bian University of California,
Visual Evoked Potentials and Event Related Potentials in Congenitally Deaf Subjects
 Physiol. Res. 54: 577-583, 25 Visual Evoked Potentials and Event Related Potentials in Congenitally Deaf Subjects J. CHLUBNOVÁ, J. KREMLÁČEK, Z. KUBOVÁ, M. KUBA Department of Pathophysiology, Faculty of
Physiol. Res. 54: 577-583, 25 Visual Evoked Potentials and Event Related Potentials in Congenitally Deaf Subjects J. CHLUBNOVÁ, J. KREMLÁČEK, Z. KUBOVÁ, M. KUBA Department of Pathophysiology, Faculty of
Exclusion criteria and outlier detection
 1 Exclusion criteria and outlier detection 1 2 Supplementary Fig. 1 31 subjects complied with the inclusion criteria as tested during the familiarization session. The upper part of the figure (ovals) indicates
1 Exclusion criteria and outlier detection 1 2 Supplementary Fig. 1 31 subjects complied with the inclusion criteria as tested during the familiarization session. The upper part of the figure (ovals) indicates
Spatial scale of visual analysis for vernier acuity does not vary over time
 Vision Research 40 (2000) 163 171 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Spatial scale of visual analysis for vernier acuity does not vary over time Sarah J. Waugh a, *, Dennis M. Levi b a Neurosciences Research
Vision Research 40 (2000) 163 171 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Spatial scale of visual analysis for vernier acuity does not vary over time Sarah J. Waugh a, *, Dennis M. Levi b a Neurosciences Research
Processing in the probed-sinewave paradigm is likely retinal
 Visual Neuroscience (2001), 18, 1003 1010. Printed in the USA. Copyright 2001 Cambridge University Press 0952-5238001 $12.50 DOI: 10.1017.S0952523801186177 Processing in the probed-sinewave paradigm is
Visual Neuroscience (2001), 18, 1003 1010. Printed in the USA. Copyright 2001 Cambridge University Press 0952-5238001 $12.50 DOI: 10.1017.S0952523801186177 Processing in the probed-sinewave paradigm is
From last week: The body is a complex electrical machine. Basic Electrophysiology, the Electroretinogram ( ERG ) and the Electrooculogram ( EOG )
 From last week: Differential Amplification This diagram shows a low frequency signal from the patient that differs between the two inputs and is therefore amplified, with an interfering high frequency
From last week: Differential Amplification This diagram shows a low frequency signal from the patient that differs between the two inputs and is therefore amplified, with an interfering high frequency
Rewiring of hindlimb corticospinal neurons after spinal cord injury
 Rewiring of hindlimb corticospinal neurons after spinal cord injury Arko Ghosh, Florent Haiss, Esther Sydekum, Regula Schneider, Miriam Gullo, Matthias T. Wyss, Thomas Mueggler, Christof Baltes, Markus
Rewiring of hindlimb corticospinal neurons after spinal cord injury Arko Ghosh, Florent Haiss, Esther Sydekum, Regula Schneider, Miriam Gullo, Matthias T. Wyss, Thomas Mueggler, Christof Baltes, Markus
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Introduction to Electrophysiology
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Basic Electrophysiology, the Electroretinogram (ERG) and the Electrooculogram (EOG) - Signal origins, recording methods and clinical applications
 Basic Electrophysiology, the Electroretinogram (ERG) and the Electrooculogram (EOG) - Signal origins, recording methods and clinical applications The body is a complex machine consisting of the central
Basic Electrophysiology, the Electroretinogram (ERG) and the Electrooculogram (EOG) - Signal origins, recording methods and clinical applications The body is a complex machine consisting of the central
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Monocular and Binocular Mechanisms of Contrast Gain Control. Izumi Ohzawa and Ralph D. Freeman
 Monocular and Binocular Mechanisms of Contrast Gain Control Izumi Ohzawa and alph D. Freeman University of California, School of Optometry Berkeley, California 9472 E-mail: izumi@pinoko.berkeley.edu ABSTACT
Monocular and Binocular Mechanisms of Contrast Gain Control Izumi Ohzawa and alph D. Freeman University of California, School of Optometry Berkeley, California 9472 E-mail: izumi@pinoko.berkeley.edu ABSTACT
Neuromuscular Consequences of Reflexive Covert Orienting
 Neuromuscular Consequences of Reflexive Covert Orienting Brian D. Corneil, Douglas P. Munoz, Brendan B. Chapman, Tania Admans, Sharon L. Cushing Fixation Cue (3 ms) CTOA 5, 2 or 6 ms Fixation Target Supplementary
Neuromuscular Consequences of Reflexive Covert Orienting Brian D. Corneil, Douglas P. Munoz, Brendan B. Chapman, Tania Admans, Sharon L. Cushing Fixation Cue (3 ms) CTOA 5, 2 or 6 ms Fixation Target Supplementary
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Beyond Blind Averaging: Analyzing Event-Related Brain Dynamics. Scott Makeig. sccn.ucsd.edu
 Beyond Blind Averaging: Analyzing Event-Related Brain Dynamics Scott Makeig Institute for Neural Computation University of California San Diego La Jolla CA sccn.ucsd.edu Talk given at the EEG/MEG course
Beyond Blind Averaging: Analyzing Event-Related Brain Dynamics Scott Makeig Institute for Neural Computation University of California San Diego La Jolla CA sccn.ucsd.edu Talk given at the EEG/MEG course
DATA MANAGEMENT & TYPES OF ANALYSES OFTEN USED. Dennis L. Molfese University of Nebraska - Lincoln
 DATA MANAGEMENT & TYPES OF ANALYSES OFTEN USED Dennis L. Molfese University of Nebraska - Lincoln 1 DATA MANAGEMENT Backups Storage Identification Analyses 2 Data Analysis Pre-processing Statistical Analysis
DATA MANAGEMENT & TYPES OF ANALYSES OFTEN USED Dennis L. Molfese University of Nebraska - Lincoln 1 DATA MANAGEMENT Backups Storage Identification Analyses 2 Data Analysis Pre-processing Statistical Analysis
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
1- Cochlear Impedance Telemetry
 INTRA-OPERATIVE COCHLEAR IMPLANT MEASURMENTS SAMIR ASAL M.D 1- Cochlear Impedance Telemetry 1 Cochlear implants used presently permit bi--directional communication between the inner and outer parts of
INTRA-OPERATIVE COCHLEAR IMPLANT MEASURMENTS SAMIR ASAL M.D 1- Cochlear Impedance Telemetry 1 Cochlear implants used presently permit bi--directional communication between the inner and outer parts of
