Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition. Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AD
|
|
|
- Mavis Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AD
2 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule The schedule of reinforcement should be based on desired behaviors, associations between behaviors and rewards and length of time behaviors should be maintained. Let's try a few scenarios to test your knowledge. In the following scenarios identify which type of reinforcement schedule is being used:
3 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 1: Starbucks wants to ensure a steady flow of customers. The company decides to provide reward cards to its customers - for every five lattes purchased the customer gets one free.
4 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 1: Starbucks wants to ensure a steady flow of customers. The company decides to provide reward cards to its customers - for every five lattes purchased the customer gets one free. The correct response here is fixed ratio schedule.
5 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 2: A teacher gives pop quizzes to ensure students are prepared for every class.
6 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 2: A teacher gives pop quizzes to ensure students are prepared for every class. The correct response is variable interval schedule.
7 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 3: A student receives a grade at the end of every semester, which counts towards credit for graduation.
8 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 3: A student receives a grade at the end of every semester, which counts towards credit for graduation. The correct response here is fixed interval.
9 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 4: A person buys scratch-off lottery tickets in hopes of winning millions. Correct response?
10 How to Condition Behavior Choosing A Schedule Scenario 4: A person buys scratch-off lottery tickets in hopes of winning millions. Correct response? Variable ratio schedule.
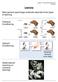
11 So do you learn through observation or through sudden understanding? Let s take a look at two different methods of learning, which can affect your behavior and problem-solving ability. Observational Learning Do answers suddenly come to you in a burst of clarity? Or do you learn by watching others? Most people experience both. One common type of learning involves observing and mimicking others. This social modeling is called observational learning. You may recall that Stanford psychologist Albert Bandura conducted a social experiment that illustrated how aggressive behavior can be learned by watching violence on TV and in real life.
12 Monkey see, monkey do! * Conditioning Observational Learning First, a group of children watched an adult hit, kick and sit on an inflatable boxing toy in the shape of a clown, called a Bobo doll. Next, the kids were allowed to play with toys for a short period, after which the toys were were taken away in order to build a feeling of frustration. Then the children were allowed to play with the Bobo doll. Not surprisingly, the majority of kids imitated the adult's behavior, hitting the Bobo doll, even using the toy hammers and guns provided. While this experiment may seem strange and even a little cruel, there is an important lesson to be learned. We take our cues for appropriate behavior from our parents, brothers, sisters, teachers, friends and other role models.
13 The chimp finally reached the food, not by gradually learning from its previous failed attempts, but by suddenly coming to the realization of a solution. * Conditioning Insight Now think about a time when you were puzzling over a problem and, all at once, a light bulb went on in your head. Suddenly, the solution was clear. Those 'Aha!' moments are called insights. Wolfgang Köhler, one of the founders of Gestalt psychology, contributed to our knowledge of insight learning. Although his research applies to humans, Köhler observed how a chimpanzee solved a problem. Bananas were placed high up in the top of a cage out of reach of the chimp. After its efforts were unsuccessful, the chimp stopped and thought over the situation.
14 Insight Using a stick, he could reach the bananas. So, what do chimps and Bobo dolls have in common? Well, besides the fact that both stories have to do with solving problems by hitting them, they both show ways in which humans can modify behavior. In one case, the method is modeling: after being shown a way to behave, we may employ that method as one that is clearly acceptable. In the other, you need to develop a new way of approaching a problem: there is no modeling to follow, and so a new solution arises and is attempted. In both cases, learning takes place and you have a new way to solve problems.
15 I loved it when I was real little. On a cold day there was nothing like a hot grilled cheese sandwich and a steaming bowl of tomato soup! * Conditioning Insight The two can work together as well. Once you have an insight into a solution, others will see it and model their own behavior on yours. So, how can biological influences affect conditioning? Have you ever had food poisoning? Now, we are going to see how natural responses can accelerate or hinder conditioning. Taste Aversion Is there a food that you won't eat anymore or a drink you can't stomach? For me, it is tomato soup.
16 Taste Aversion For years, it was what was for dinner and lunch when we were home from school, mostly because my mother was a lazy cook! Then one day, it just seemed to taste funny, and I ended up throwing up and being very sick for a couple of days after. Since that time, I have not been able to even stomach the idea of a creamy tomato liquid, and the thought of it makes me ill! Even with pastas, my sauce has to be somewhat chunky to avoid that smooth tomato texture and taste. You don't need to get sick from the same food more than once in order to develop disgust for it. There's an evolutionarily advantage to taste aversion, since it prevents us from eating something twice that might be toxic.
17 The Garcia Effect Taste aversion was first noticed by psychologist John Garcia in the 1950's. He was irradiating rats to see its effect on their behavior, and noticed that rats didn't want to eat the things they'd been fed shortly before being irradiated. Garcia theorized that this was because they were getting nauseous from the radiation. He conducted experiments to directly test this with sweetened vs. unsweetened water: he gave them sweetened water followed by no radiation, mild radiation, or strong radiation. After the experiment, the total sweetened water consumed by nonradiated rats was 80%, mildly radiated rats drank 40% and strongly radiated rats drank only 10% of the sugar water. These patterns were observed after only ONE trial.
18 The Garcia Effect The radiated rats were conditioned to link the taste of sweetened water with nausea and therefore avoided it. Since it accessed an evolutionarily-advantageous bodily defense mechanism, it was learned right away. Similarly, if you burn your finger on the stove, you don't have to do it more than once in order to learn not to. Instincts Being burned is a natural aversive stimulus, so conditioning is immediate. Natural instincts are another biological factor that can interfere with conditioning. Psychologists Keller and Marian Breland trained raccoons to put coins in a piggy bank.
19 Instincts Natural instincts are another biological factor that can interfere with conditioning. Psychologists Keller and Marian Breland trained raccoons to put coins in a piggy bank. They rewarded the raccoons with food for successful deposits. This worked with single coins, but when the researchers gave a raccoon more than one coin, the raccoon would sit and rub the coins together. By associating the coins with food, the raccoons' natural instinct to 'wash' food by rubbing it together was activated. Classical conditioning was inhibited by this natural response.
Unit 5: Learning. Topic: Operant Conditioning
 Unit 5: Learning Topic: Operant Conditioning 1874-1949 key name Edward THORNDIKE Proposed the Law of Effect behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely conducted puzzle box experiments on
Unit 5: Learning Topic: Operant Conditioning 1874-1949 key name Edward THORNDIKE Proposed the Law of Effect behaviors followed by favorable outcomes are more likely conducted puzzle box experiments on
Unit 6 Learning.
 Unit 6 Learning https://www.apstudynotes.org/psychology/outlines/chapter-6-learning/ 1. Overview 1. Learning 1. A long lasting change in behavior resulting from experience 2. Classical Conditioning 1.
Unit 6 Learning https://www.apstudynotes.org/psychology/outlines/chapter-6-learning/ 1. Overview 1. Learning 1. A long lasting change in behavior resulting from experience 2. Classical Conditioning 1.
Outline 3/12/2013. Practice Question. Practice Question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 13: Learning & Memory
 Outline 3/12/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 13: Learning & Memory Learning Observational learning Associative learning Memory? Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays
Outline 3/12/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 13: Learning & Memory Learning Observational learning Associative learning Memory? Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays
Associative Learning
 Learning Learning Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Biological Components of Learning Cognitive Components of Learning Behavioral Therapies Associative
Learning Learning Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Biological Components of Learning Cognitive Components of Learning Behavioral Therapies Associative
Review Sheet Learning (7-9%)
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Learning (7-9%) 1) learning 2) associative learning Classical Conditioning 3) Ivan Pavlov 4) classical conditioning 5) John Watson 6)
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet Learning (7-9%) 1) learning 2) associative learning Classical Conditioning 3) Ivan Pavlov 4) classical conditioning 5) John Watson 6)
Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement. reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited
 OPERANT CONDITIONING Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement CONTINUOUS REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited pro: necessary for initial
OPERANT CONDITIONING Strengthening Operant Behavior: Schedules of Reinforcement CONTINUOUS REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE reinforcement occurs after every desired behavior is exhibited pro: necessary for initial
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn?
 Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Learning Chapter Module 21 Observational Learning Module 21: Observational Learning
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Learning Chapter Module 21 Observational Learning Module 21: Observational Learning
Outline. History of Learning Theory. Pavlov s Experiment: Step 1. Associative learning 9/26/2012. Nature or Nurture
 Outline What is learning? Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning History of Learning Theory Nature or Nurture BEHAVIORISM Tabula Rasa Learning: Systematic,
Outline What is learning? Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning History of Learning Theory Nature or Nurture BEHAVIORISM Tabula Rasa Learning: Systematic,
Learning. Learning. Stimulus Learning. Modification of behavior or understanding Is it nature or nurture?
 Learning Chapter 6 Learning Modification of behavior or understanding Is it nature or nurture? Stimulus Learning Habituation: when you pay less attention to something over time response starts out strong
Learning Chapter 6 Learning Modification of behavior or understanding Is it nature or nurture? Stimulus Learning Habituation: when you pay less attention to something over time response starts out strong
Learning Theories - Behaviourism -
 Learning Theories - Behaviourism - Kimberley A. Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/257e-570 Office Hour: Thursdays 2-3pm Office: S302 Outline What is Learning? Classical Conditioning
Learning Theories - Behaviourism - Kimberley A. Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/257e-570 Office Hour: Thursdays 2-3pm Office: S302 Outline What is Learning? Classical Conditioning
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II
 THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
Marshall High School Psychology Mr. Cline Unit One AA. What is Psychology?
 Marshall High School Psychology Mr. Cline Unit One AA What is Psychology? We are going to begin this semester with a little experiment You have each been provided with the same simple simple math problem
Marshall High School Psychology Mr. Cline Unit One AA What is Psychology? We are going to begin this semester with a little experiment You have each been provided with the same simple simple math problem
Learning Chapter 6 1
 Learning Chapter 6 1 Learning is a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience. 2 Stimulus- Stimulus Learning Learning to associate one stimulus with another. 3 Response- Consequence
Learning Chapter 6 1 Learning is a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience. 2 Stimulus- Stimulus Learning Learning to associate one stimulus with another. 3 Response- Consequence
Chapter 7. Learning From Experience
 Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
Learning From Experience Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Learning From Experience Noticing and Ignoring Learning What Events Signal Learning About the Consequences of Our Behavior
Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches
 Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches What is Learning o What Learning Is and Is Not Learning - a relatively permanent influence on behavior, knowledge, and thinking skills that comes about
Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches What is Learning o What Learning Is and Is Not Learning - a relatively permanent influence on behavior, knowledge, and thinking skills that comes about
CHAPTER 6. Learning. Lecture Overview. Introductory Definitions PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY
 Learning CHAPTER 6 Write down important terms in this video. Explain Skinner s view on Free Will. Lecture Overview Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Cognitive-Social Learning The Biology of Learning
Learning CHAPTER 6 Write down important terms in this video. Explain Skinner s view on Free Will. Lecture Overview Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Cognitive-Social Learning The Biology of Learning
Module 30. Learning by Observation
 Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Name: Period: Chapter 7: Learning. 5. What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning?
 Name: Period: Chapter 7: Learning Introduction, How We Learn, & Classical Conditioning (pp. 291-304) 1. Learning: 2. What does it mean that we learn by association? 3. Habituation: 4. Associative Learning:
Name: Period: Chapter 7: Learning Introduction, How We Learn, & Classical Conditioning (pp. 291-304) 1. Learning: 2. What does it mean that we learn by association? 3. Habituation: 4. Associative Learning:
Chapter Six. Learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning
 Chapter Six Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Part One: Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning is conditioning by association, such as a pet getting excited
Chapter Six Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Part One: Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning is conditioning by association, such as a pet getting excited
What is Learning? Learning: any relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice
 CHAPTER 5 learning What is Learning? Learning: any relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice When people learn anything, some part of their brain is physically changed
CHAPTER 5 learning What is Learning? Learning: any relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice When people learn anything, some part of their brain is physically changed
CHAPTER 6. Test Yourself, p. 228
 CHAPTER 6 Test Yourself, p. 228 1. What is classical conditioning? How was it discovered? A. Pavlov s Experiments 1. Classical conditioning is sometimes called Pavlovian conditioning because it was discovered
CHAPTER 6 Test Yourself, p. 228 1. What is classical conditioning? How was it discovered? A. Pavlov s Experiments 1. Classical conditioning is sometimes called Pavlovian conditioning because it was discovered
Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events.
 Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events. behaviorism - the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science
Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events. behaviorism - the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science
Psychology 020 Chapter 7: Learning Tues. Nov. 6th, 2007
 Psychology 020 Chapter 7: Learning Tues. Nov. 6th, 2007 What is involved in learning? Evolution -The changes in behaviour that accumulate across generations are stored in the genes Combined with natural
Psychology 020 Chapter 7: Learning Tues. Nov. 6th, 2007 What is involved in learning? Evolution -The changes in behaviour that accumulate across generations are stored in the genes Combined with natural
Unit 6 REVIEW Page 1. Name: Date:
 Unit 6 REVIEW Page 1 Name: Date: 1. Little Albert was conditioned by John B. Watson to fear furry white rats. After conditioning, Albert also showed fear to rabbits, dogs, and fur coats. This best illustrates
Unit 6 REVIEW Page 1 Name: Date: 1. Little Albert was conditioned by John B. Watson to fear furry white rats. After conditioning, Albert also showed fear to rabbits, dogs, and fur coats. This best illustrates
Ohio SNAP-Ed Adult & Teen Programs Foods to Decrease
 Page 1 Ohio SNAP-Ed Adult & Teen Programs Foods to Decrease Task Topic: Task Title: Teaching Message(s): Resources: MyPlate Foods to Decrease Use MyPlate to make food choices for a healthy lifestyle. Use
Page 1 Ohio SNAP-Ed Adult & Teen Programs Foods to Decrease Task Topic: Task Title: Teaching Message(s): Resources: MyPlate Foods to Decrease Use MyPlate to make food choices for a healthy lifestyle. Use
Module 29 Biology, Cognition, and Learning
 Module 29 Biology, Cognition, and Learning Part IV Objectives: Explain how biological constraints affect classical and operant conditioning. Explain how cognitive processes affect classical and operant
Module 29 Biology, Cognition, and Learning Part IV Objectives: Explain how biological constraints affect classical and operant conditioning. Explain how cognitive processes affect classical and operant
Chapter 7 - Learning
 Chapter 7 - Learning How Do We Learn Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Defining Learning Learning a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience.
Chapter 7 - Learning How Do We Learn Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Defining Learning Learning a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience.
Healthy Eating for Kids
 Healthy eating and being active are very important for your child to grow up in a proper way. The food plate is a guide to help you and your child know what and how much should be eaten every day. The
Healthy eating and being active are very important for your child to grow up in a proper way. The food plate is a guide to help you and your child know what and how much should be eaten every day. The
Group Session 11. Altering eating patterns: dining out Planning ahead Problem Solving
 Group Session 11 at a Glance Key Behavioral Strategies Participant Behavioral Strategies Process Objectives & Session Content Handouts Altering eating patterns: dining out Planning ahead Problem Solving
Group Session 11 at a Glance Key Behavioral Strategies Participant Behavioral Strategies Process Objectives & Session Content Handouts Altering eating patterns: dining out Planning ahead Problem Solving
Learning. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice.
 Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice. What is Learning? Learning is the process that allows us to adapt (be flexible) to the changing conditions
Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice. What is Learning? Learning is the process that allows us to adapt (be flexible) to the changing conditions
Episode #036. Speak English Now Podcast. English Food Vocabulary Lesson Eat Healthy at. a Restaurant
 Speak English Now Podcast The Podcast That Will Help You Speak English Fluently. With No Grammar and No Textbooks! Episode #036 With your host GEORGIANA Founder of SpeakEnglishPod.com and Profesoraingles.com
Speak English Now Podcast The Podcast That Will Help You Speak English Fluently. With No Grammar and No Textbooks! Episode #036 With your host GEORGIANA Founder of SpeakEnglishPod.com and Profesoraingles.com
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version
 Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
Goals for STAR Kids. Work together, pick a goal, offer encouragement. You can do it!
 10-2-1-0 Goals for STAR Kids Sleep at least 10 hours a night. A bedtime schedule and routine can help kids get the sleep they need! No more than 2 hours per day of screen time. That includes TV, DVDs,
10-2-1-0 Goals for STAR Kids Sleep at least 10 hours a night. A bedtime schedule and routine can help kids get the sleep they need! No more than 2 hours per day of screen time. That includes TV, DVDs,
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Learning Chapter 8 2 Learning How Do We Learn? Classical Conditioning Pavlov s Experiments
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Learning Chapter 8 2 Learning How Do We Learn? Classical Conditioning Pavlov s Experiments
#032: HOW TO SAY YOU'RE SICK IN ENGLISH
 #032: HOW TO SAY YOU'RE SICK IN ENGLISH Hi, everyone! I'm Georgiana, founder of SpeakEnglishPodcast.com. My mission is to help YOU to speak English fluently and confidently. In today's episode: I'll talk
#032: HOW TO SAY YOU'RE SICK IN ENGLISH Hi, everyone! I'm Georgiana, founder of SpeakEnglishPodcast.com. My mission is to help YOU to speak English fluently and confidently. In today's episode: I'll talk
Schedules of Reinforcement 11/11/11
 Schedules of Reinforcement 11/11/11 Reinforcement Schedules Intermittent Reinforcement: A type of reinforcement schedule by which some, but not all, correct responses are reinforced. Intermittent reinforcement
Schedules of Reinforcement 11/11/11 Reinforcement Schedules Intermittent Reinforcement: A type of reinforcement schedule by which some, but not all, correct responses are reinforced. Intermittent reinforcement
What a Family Needs to Know. About Eating Well. And Being Clever with Food
 What a Family Needs to Know About Eating Well And Being Clever with Food This book was written by Sarah Scotland, Freelance Nutritionist and Founder of Wise about Food. Copyright 2015 by Sarah Scotland
What a Family Needs to Know About Eating Well And Being Clever with Food This book was written by Sarah Scotland, Freelance Nutritionist and Founder of Wise about Food. Copyright 2015 by Sarah Scotland
Reliability and Validity
 Reliability and Validity Why Are They Important? Check out our opening graphics. In a nutshell, do you want that car? It's not reliable. Would you recommend that car magazine (Auto Tester Weakly) to a
Reliability and Validity Why Are They Important? Check out our opening graphics. In a nutshell, do you want that car? It's not reliable. Would you recommend that car magazine (Auto Tester Weakly) to a
PSY402 Theories of Learning. Chapter 9 Biological Influences on Learning
 PSY402 Theories of Learning Chapter 9 Biological Influences on Learning Limits to Learning How general are the laws of learning? Skinner s rules work in both lab and real-world settings, across species.
PSY402 Theories of Learning Chapter 9 Biological Influences on Learning Limits to Learning How general are the laws of learning? Skinner s rules work in both lab and real-world settings, across species.
Operant Conditioning
 Operant Conditioning Classical vs. Operant Conditioning With classical conditioning you can teach a dog to salivate, but you cannot teach it to sit up or roll over. Why? Salivation is an involuntary reflex,
Operant Conditioning Classical vs. Operant Conditioning With classical conditioning you can teach a dog to salivate, but you cannot teach it to sit up or roll over. Why? Salivation is an involuntary reflex,
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 6 Learning 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 6.1 How Do the Parts of Our Brains Function? 6.1 What Are
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 6 Learning 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 6.1 How Do the Parts of Our Brains Function? 6.1 What Are
Classical Conditioning. Operant Conditioning. Operant Conditioning. Observational Learning. Classical versus operant conditioning
 LP 6D Learned Helplessness and schedules of reinforcement 1 Classical Conditioning What is learning? What is conditioning? Pavlov and the Dogs o UCS o UCR o NS o CS o CR Other examples of classical conditioning
LP 6D Learned Helplessness and schedules of reinforcement 1 Classical Conditioning What is learning? What is conditioning? Pavlov and the Dogs o UCS o UCR o NS o CS o CR Other examples of classical conditioning
I. Classical Conditioning
 Learning Chapter 8 Learning A relatively permanent change in an organism that occur because of prior experience Psychologists must study overt behavior or physical changes to study learning Learning I.
Learning Chapter 8 Learning A relatively permanent change in an organism that occur because of prior experience Psychologists must study overt behavior or physical changes to study learning Learning I.
Quick Read Series. Information for people with seizure disorders
 Quick Read Series Information for people with seizure disorders 2003 Epilepsy Foundation of America, Inc. This pamphlet is designed to provide general information about epilepsy to the public. It does
Quick Read Series Information for people with seizure disorders 2003 Epilepsy Foundation of America, Inc. This pamphlet is designed to provide general information about epilepsy to the public. It does
Top Tips for Top Kids Leaflet 2016 v1_4.indd 1 02/03/ :17
 2905096 Top Tips for Top Kids Leaflet 2016 v1_4.indd 1 02/03/2016 16:17 Fun, free and easy ways to get your kids happy and healthy We all want our children to grow up to be happy, healthy adults. But it
2905096 Top Tips for Top Kids Leaflet 2016 v1_4.indd 1 02/03/2016 16:17 Fun, free and easy ways to get your kids happy and healthy We all want our children to grow up to be happy, healthy adults. But it
Learning. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers. Learning. Chapter 8. How Do We Learn? Classical Conditioning
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Learning Chapter 8 2 Learning How Do We Learn? Classical Conditioning Pavlov s Experiments
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Learning Chapter 8 2 Learning How Do We Learn? Classical Conditioning Pavlov s Experiments
Psychology, Ch. 6. Learning Part 1
 Psychology, Ch. 6 Learning Part 1 Two Main Types of Learning Associative learning- learning that certain events occur together Cognitive learning- acquisition of mental information, by observing or listening
Psychology, Ch. 6 Learning Part 1 Two Main Types of Learning Associative learning- learning that certain events occur together Cognitive learning- acquisition of mental information, by observing or listening
3/7/2010. Theoretical Perspectives
 Theoretical Perspectives REBT (1955) Albert Ellis Action & Result Oriented Teaches how to identify self-defeating thoughts Replaces thoughts w/ life enhancing ones 1 A B C s of personality formation: A
Theoretical Perspectives REBT (1955) Albert Ellis Action & Result Oriented Teaches how to identify self-defeating thoughts Replaces thoughts w/ life enhancing ones 1 A B C s of personality formation: A
Managing Anger. More Practice With Bugs and I STOP'D 3 Cs F. Preparation. Vocabulary adrenaline
 Managing Anger More Practice With Bugs and I STOP'D 3 Cs F I care about myself. F I care about my community. Help students to understand and invite them to state clearly: I have the right to care about
Managing Anger More Practice With Bugs and I STOP'D 3 Cs F I care about myself. F I care about my community. Help students to understand and invite them to state clearly: I have the right to care about
Learning: a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience.
 Learning: a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience. Instinct: unlearned behaviors due to evolution. Ex. bears hibernating. Habituation: an organism s decreasing response
Learning: a relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience. Instinct: unlearned behaviors due to evolution. Ex. bears hibernating. Habituation: an organism s decreasing response
Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience
 Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning, even
Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning, even
Self-Improvement Paper Becky Sanchez PSYC 10, M, W 8:10-9:35 a.m. The Strategy(ies) for Academic Success I plan to Work Towards and Why I first saw
 1 Self-Improvement Paper Becky Sanchez PSYC 10, M, W 8:10-9:35 a.m. The Strategy(ies) for Academic Success I plan to Work Towards and Why I first saw the strategies for academic success handout in a workshop
1 Self-Improvement Paper Becky Sanchez PSYC 10, M, W 8:10-9:35 a.m. The Strategy(ies) for Academic Success I plan to Work Towards and Why I first saw the strategies for academic success handout in a workshop
Information Sheet. Diabetes. Accessible information about diabetes for adults with Learning Disabilities
 Information Sheet Diabetes Accessible information about diabetes for adults with Learning Disabilities It is important to: Eat a healthy diet Keep active Take your medication Breakfast Cereals with bran,
Information Sheet Diabetes Accessible information about diabetes for adults with Learning Disabilities It is important to: Eat a healthy diet Keep active Take your medication Breakfast Cereals with bran,
Test Name: Psych1Test2SP b. complexity Feedback: The complexity of light is related to our perception of saturation.
 Test Name: Psych1Test2SP2012 1. b. complexity The complexity of light is related to our perception of saturation. 2. a. a secondary punisher. This is an example of a learned or secondary punisher, a low
Test Name: Psych1Test2SP2012 1. b. complexity The complexity of light is related to our perception of saturation. 2. a. a secondary punisher. This is an example of a learned or secondary punisher, a low
Jason Garner, M.A. ABA Clinical Director
 Jason Garner, M.A. ABA Clinical Director Discuss Autism Definition Prevalence rates Discuss Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Discuss challenging behavior Functions of Behavior Discuss behavior management
Jason Garner, M.A. ABA Clinical Director Discuss Autism Definition Prevalence rates Discuss Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Discuss challenging behavior Functions of Behavior Discuss behavior management
UNIT THREE LESSON 9 OUTLINE
 UNIT THREE LESSON 9 OUTLINE Welcome participants to the final lesson in Unit Three. Find out how they are doing in terms of counting carbohydrates as learned in Lesson 8. Read and briefly describe objectives
UNIT THREE LESSON 9 OUTLINE Welcome participants to the final lesson in Unit Three. Find out how they are doing in terms of counting carbohydrates as learned in Lesson 8. Read and briefly describe objectives
Learning. Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning.
 Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
How will you know if you ate contaminated food? Diarrhea Stomach cramps Fever Nausea/Vomiting
 A H E A L T H Y H O U S E You Can Prevent Food Poisoning! The food you eat can make you sick. Many people go to the hospital each year because they get food poisoning. Learn what you can do to prevent
A H E A L T H Y H O U S E You Can Prevent Food Poisoning! The food you eat can make you sick. Many people go to the hospital each year because they get food poisoning. Learn what you can do to prevent
Description: an energetic four-year-old.
 Title: Page: 1 1. Every child or student with autism spectrum disorder or ASD has his or her own strengths, classroom needs, and challenges. Let s briefly meet four students with ASD. 2. This is Drew,
Title: Page: 1 1. Every child or student with autism spectrum disorder or ASD has his or her own strengths, classroom needs, and challenges. Let s briefly meet four students with ASD. 2. This is Drew,
Good Grinding for Wise Dining. Choosing Foods Lesson 12: Meal Planning. Let s make a meal plan, yes, we can
 Good Grinding for Wise Dining Let s make a meal plan, yes, we can Ask the following questions: Ask someone in the audience to assist you. Give the tally sheet to this person and have them count the number
Good Grinding for Wise Dining Let s make a meal plan, yes, we can Ask the following questions: Ask someone in the audience to assist you. Give the tally sheet to this person and have them count the number
05/26/2011 Page 1 of 26
 Number of IYS 2010 Respondents N Total Grade 52 53 60 165 Age Avg N Avg N Avg How old are you? 14.1 52 16.0 53 17.9 60 Gender % N % N % N Female 5 29 4 23 4 27 Male 4 21 5 29 5 33 Race/Ethnicity N % N
Number of IYS 2010 Respondents N Total Grade 52 53 60 165 Age Avg N Avg N Avg How old are you? 14.1 52 16.0 53 17.9 60 Gender % N % N % N Female 5 29 4 23 4 27 Male 4 21 5 29 5 33 Race/Ethnicity N % N
The big problem. Trying to change without actually changing
 Welcome to Fit4Life and our Weight Loss Solution Program! Losing weight isn t easy; there is ONLY one path to successful permanent weight loss. Permanent life-long weight loss comes from two things: 1.
Welcome to Fit4Life and our Weight Loss Solution Program! Losing weight isn t easy; there is ONLY one path to successful permanent weight loss. Permanent life-long weight loss comes from two things: 1.
continue t tube feeding. You learn how to get used Health plans the Helping your child eat is havingg
 Helping your child eat while on a tube feed This handout will help: You learn how to help your child continue to eat and drink orally o (by mouth) throughout t tube feeding. Your child to get off of his
Helping your child eat while on a tube feed This handout will help: You learn how to help your child continue to eat and drink orally o (by mouth) throughout t tube feeding. Your child to get off of his
Smoking and Quitting Assessment
 Smoking and Quitting Assessment A. Which of the following describes you? q I m not interested in trying to quit smoking. q I know I need to quit smoking, but I m not quite ready yet. q I m ready to quit
Smoking and Quitting Assessment A. Which of the following describes you? q I m not interested in trying to quit smoking. q I know I need to quit smoking, but I m not quite ready yet. q I m ready to quit
I LOVE HIM, HE LOVES ME NOT. I LOVE HIM, HE LOVES ME NOT: How I Left a Codependent Relationship
 : How I Left a Codependent Relationship Copyright 2014 SeasOfMintaka.com All Rights Reserved Cover Design by SeasOfMintaka.com Legal Disclaimer: The material contained in this book is provided for general
: How I Left a Codependent Relationship Copyright 2014 SeasOfMintaka.com All Rights Reserved Cover Design by SeasOfMintaka.com Legal Disclaimer: The material contained in this book is provided for general
Low Carb Meals: How To Make Vitamin Rich Smoothies And Superfood Recipes By Sandra Connolly READ ONLINE
 Low Carb Meals: How To Make Vitamin Rich Smoothies And Superfood Recipes By Sandra Connolly READ ONLINE Making a green smoothie is one of the fastest ways to get an array of On top of all this, this green
Low Carb Meals: How To Make Vitamin Rich Smoothies And Superfood Recipes By Sandra Connolly READ ONLINE Making a green smoothie is one of the fastest ways to get an array of On top of all this, this green
What and when to feed your child (6 to 24 months)
 Page 1 of 8 0:00:20.2 All parents want their children to grow up to be fit and healthy adults. In the first two years of a child s life their brains and bodies grow and develop more than at any other time.
Page 1 of 8 0:00:20.2 All parents want their children to grow up to be fit and healthy adults. In the first two years of a child s life their brains and bodies grow and develop more than at any other time.
Observational Learning. The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224).
 LP 6E observational learning 1 Observational Learning The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224). Observational learning LP 6E observational
LP 6E observational learning 1 Observational Learning The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224). Observational learning LP 6E observational
The Cognitive Perspective
 The Cognitive Perspective Many psychologists do not totally agree with an operant or behavioral interpretation of learning. They argue that classical and operant conditioning processes overly simplify
The Cognitive Perspective Many psychologists do not totally agree with an operant or behavioral interpretation of learning. They argue that classical and operant conditioning processes overly simplify
Learning. AP PSYCHOLOGY Unit 4
 Learning AP PSYCHOLOGY Unit 4 Learning Learning is a lasting change in behavior or mental process as the result of an experience. There are two important parts: a lasting change a simple reflexive reaction
Learning AP PSYCHOLOGY Unit 4 Learning Learning is a lasting change in behavior or mental process as the result of an experience. There are two important parts: a lasting change a simple reflexive reaction
Meal Planning Chapter 17. Glencoe Applying Life Skills Chapter 17 Meal Planning
 Meal Planning Chapter 17 Menu Planning Considerations When planning menus consider: Meal patterns time and convenience of prep Appeal - #1 concern for most people Nutrition all people have different nutritional
Meal Planning Chapter 17 Menu Planning Considerations When planning menus consider: Meal patterns time and convenience of prep Appeal - #1 concern for most people Nutrition all people have different nutritional
Quit for You. Quit for your Baby. Quit Smoking Self Help Guide for Pregnant Women
 Quit for You Quit for your Baby Quit Smoking Self Help Guide for Pregnant Women I am strong. I can do anything I put my mind to. I will raise my baby to be as strong as I am. And I will start today, by
Quit for You Quit for your Baby Quit Smoking Self Help Guide for Pregnant Women I am strong. I can do anything I put my mind to. I will raise my baby to be as strong as I am. And I will start today, by
NUTRITION 101. Kelly Hughes, MS, RD, LD Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Allen (972)
 NUTRITION 101 Kelly Hughes, MS, RD, LD Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Allen (972) 747-6149 KellyHughes@texashealth.org Alastair & Wendy Hunte Health & Wellness Coaches Nutrition Avenue (214) 509-8141
NUTRITION 101 Kelly Hughes, MS, RD, LD Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Allen (972) 747-6149 KellyHughes@texashealth.org Alastair & Wendy Hunte Health & Wellness Coaches Nutrition Avenue (214) 509-8141
APPENDIX C: MATERIALS FOR STEP 5 DATA ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 Appendix C: Materials for Step 5 Data Analysis Exercises C-73 APPENDIX C: MATERIALS FOR STEP 5 DATA ANALYSIS EXERCISES C-74 Appendix C: Materials for Step 5 Data Analysis Exercises APPENDIX C: MATERIALS
Appendix C: Materials for Step 5 Data Analysis Exercises C-73 APPENDIX C: MATERIALS FOR STEP 5 DATA ANALYSIS EXERCISES C-74 Appendix C: Materials for Step 5 Data Analysis Exercises APPENDIX C: MATERIALS
Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviors Questionnaire (KAB)
 Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviors Questionnaire (KAB) Version G Spring 000 Student ID: Grade: 05 Student Name: (last) (first, middle init.) Class ID: Teacher: Paste label to left or print information
Knowledge, Attitudes and Behaviors Questionnaire (KAB) Version G Spring 000 Student ID: Grade: 05 Student Name: (last) (first, middle init.) Class ID: Teacher: Paste label to left or print information
Understanding Emotional TRIGGER. What are triggers?
 What are triggers? We all have emotional triggers. Perhaps someone makes an off-hand comment about how you look, your new project at work, how you seem a little tired lately, or a comment about someone
What are triggers? We all have emotional triggers. Perhaps someone makes an off-hand comment about how you look, your new project at work, how you seem a little tired lately, or a comment about someone
Behaviorism & Education
 Behaviorism & Education Early Psychology (the use of nonobjective methods such as Introspection) Learning = behavior change movement toward objective methods Behaviorism Pavlov, Skinner (Focus on SàR)
Behaviorism & Education Early Psychology (the use of nonobjective methods such as Introspection) Learning = behavior change movement toward objective methods Behaviorism Pavlov, Skinner (Focus on SàR)
Bingo - Teacher Answer Key
 Bingo - Teacher Answer Key Please choose questions at random. Read the question or statement a loud and have the students guess the answer. The answers are what is found on the drug prevention Bingo card.
Bingo - Teacher Answer Key Please choose questions at random. Read the question or statement a loud and have the students guess the answer. The answers are what is found on the drug prevention Bingo card.
SAMPLE 3 - ASSESSMENT CRITERIA AND LEARNING OUTCOMES
 SAMPLE 3 - ASSESSMENT CRITERIA AND LEARNING OUTCOMES PSYCHOLOGY Behaviourism and social learning theory are two perspectives of psychology; discuss how they explain learning: PK1/3/AA/11G (2014-15 VERSION)
SAMPLE 3 - ASSESSMENT CRITERIA AND LEARNING OUTCOMES PSYCHOLOGY Behaviourism and social learning theory are two perspectives of psychology; discuss how they explain learning: PK1/3/AA/11G (2014-15 VERSION)
Module One: Booklet #7
 Module One: Booklet #7 Is a relatively permanent change in behaviour that results from experience There are various ways is which people learn (we will look at some learning styles in Module 2) We will
Module One: Booklet #7 Is a relatively permanent change in behaviour that results from experience There are various ways is which people learn (we will look at some learning styles in Module 2) We will
Cognitive Functions of the Mind
 Chapter 6 Learning Cognitive Functions of the Mind Mediate adaptive behaviours Interactions between person and world Form internal representations of the world Perception, memory Reflect on this knowledge
Chapter 6 Learning Cognitive Functions of the Mind Mediate adaptive behaviours Interactions between person and world Form internal representations of the world Perception, memory Reflect on this knowledge
Portion Size Leader Directions Author: Gail Peitzmeier, Ed.D, RD Extension Director, Youth/Health Educator Crawford County Area 2
 Portion Size Leader Directions Author: Gail Peitzmeier, Ed.D, RD gpeitzme@purdue.edu Extension Director, Youth/Health Educator Crawford County Area 2 Description How does your portion size measure up to
Portion Size Leader Directions Author: Gail Peitzmeier, Ed.D, RD gpeitzme@purdue.edu Extension Director, Youth/Health Educator Crawford County Area 2 Description How does your portion size measure up to
QUICK START CARDS. Copyright 2012, 2013 Gottalook Productions LLC
 QUICK START CARDS Copyright 2012, 2013 Gottalook Productions LLC LESSON 1: We Have Bodies KEY MESSAGE: It s important to take care of our bodies. We need them for everything we do in life. Can each student
QUICK START CARDS Copyright 2012, 2013 Gottalook Productions LLC LESSON 1: We Have Bodies KEY MESSAGE: It s important to take care of our bodies. We need them for everything we do in life. Can each student
Food & Nutrition Environment Assessment
 SESSION 2 FOOD & NUTRITION Food & Nutrition Environment Assessment This fun activity will give you and your preteen a chance to take a closer look at your home food and nutrition surroundings by looking
SESSION 2 FOOD & NUTRITION Food & Nutrition Environment Assessment This fun activity will give you and your preteen a chance to take a closer look at your home food and nutrition surroundings by looking
2 ( ) 5
 2 ( ) 5 http://likasuni.tistory.com Back to the English The Meaning of Labor Recently, I spent some time with a former student of mine, Stephen.He worked for a large bank and had been devoting himself
2 ( ) 5 http://likasuni.tistory.com Back to the English The Meaning of Labor Recently, I spent some time with a former student of mine, Stephen.He worked for a large bank and had been devoting himself
The Mirror on the Self: The Myers- Briggs Personality Traits
 Lastname 1 Maria Professor L. Irvin English 1301-163 25 November 2014 The Mirror on the Self: The Myers- Briggs Personality Traits Isabel Brigg Myers said, It is up to each person to recognize his or her
Lastname 1 Maria Professor L. Irvin English 1301-163 25 November 2014 The Mirror on the Self: The Myers- Briggs Personality Traits Isabel Brigg Myers said, It is up to each person to recognize his or her
Apply Your knowledge of the Psychology of Learning
 LP 9A applying operant cond 1 Apply Your knowledge of the Psychology of Learning You should start relating the psychology of learning to your list of occupations and/or social issues. Where do you see
LP 9A applying operant cond 1 Apply Your knowledge of the Psychology of Learning You should start relating the psychology of learning to your list of occupations and/or social issues. Where do you see
Chapter 18 ECE 105 Feeding Toddlers and Young Children
 Chapter 18: Feeding Toddlers and Young Child ECE105 Profile of Toddlers and Preschoolers Toddlers (1-2 ½ year olds) are a challenge. They want to assert their independence but need and want limits. Toddlers
Chapter 18: Feeding Toddlers and Young Child ECE105 Profile of Toddlers and Preschoolers Toddlers (1-2 ½ year olds) are a challenge. They want to assert their independence but need and want limits. Toddlers
Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community
 2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
Teacher Lesson Plan Let s Get Allergy Aware! Primary (Grades 1-3)
 Teacher Lesson Plan Let s Get Allergy Aware! Primary (Grades 1-3) Respecting Differences Common Allergens Inclusion Hand Washing Healthy Food Choices Signs & Symptoms Epinephrine Topic 1: Respecting Differences
Teacher Lesson Plan Let s Get Allergy Aware! Primary (Grades 1-3) Respecting Differences Common Allergens Inclusion Hand Washing Healthy Food Choices Signs & Symptoms Epinephrine Topic 1: Respecting Differences
SEE AGGRESSION... DO AGGRESSION!
 1 SEE AGGRESSION... DO AGGRESSION! Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63, 575-582.
1 SEE AGGRESSION... DO AGGRESSION! Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63, 575-582.
Level 5-6 What Katy Did
 Level 5-6 What Katy Did Workbook Teacher s Guide and Answer Key A. Summary 1. Book Summary Teacher s Guide Once there was a girl named Katy. She tried to be good, but she always ended up doing the wrong
Level 5-6 What Katy Did Workbook Teacher s Guide and Answer Key A. Summary 1. Book Summary Teacher s Guide Once there was a girl named Katy. She tried to be good, but she always ended up doing the wrong
Innate? Learned? Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Aggression and Violence. What is violence?
 Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan
 Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan GOAL Students will recognize that eating a variety of colors (a rainbow) of fruits and vegetables provides the different nutrients their bodies need. OBJECTIVES
Fruits and Vegetables 2 nd grade lesson plan GOAL Students will recognize that eating a variety of colors (a rainbow) of fruits and vegetables provides the different nutrients their bodies need. OBJECTIVES
Fitting in Your Fitness
 Fitting in Your Fitness Workplace Health Promotion Program UBC BodyWorks Fitness Centre www.kin.educ.ubc.ca/bodyworks Presented by Christina WM Sequeira MKIN Candidate, ACSM CES, CSEP CEP, Exercise is
Fitting in Your Fitness Workplace Health Promotion Program UBC BodyWorks Fitness Centre www.kin.educ.ubc.ca/bodyworks Presented by Christina WM Sequeira MKIN Candidate, ACSM CES, CSEP CEP, Exercise is
