The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) (Part 2)
|
|
|
- Sophie Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) (Part 2)
2 Announcements Lab Section Meets Tuesday, room 317B Research Proposal If you sent me a precis, I sent you feedback A few themes 3x5 time Approach Section: Methodological details See Guidelines papers Aims and Hypotheses Mediation and Moderation
3 Construct Validity of P300 (P3, P3b) First observed by Sutton, Braren, Zubin, & John (1965) P300 Amplitude; Johnson's model is where P300 Amplitude = f[t x (1/P + M)] P = probability of occurrence, M = Stimulus meaning, & T = amount of information transmitted
4
5
6
7 P3 Latency An index of processing time, independent of response requirements RT measures confounds the two McCarthy & Donchin (1981) experiment: The words "RIGHT" or "LEFT" embedded in a matrix of letters of X's Compatible condition: respond with hand indicated in matrix; Incompatible condition: respond with opposite hand (e.g., LEFT signals right hand response); Results: P300 latency delayed when discriminability more difficult Response compatibility had no effect on P300 latency Note amplitude reduction as function of noise--information transmission)
8
9
10 Not only difficulty in physical discrimination, but difficulty in cognitive categorization
11 Construct Validity? What, then, does the P300 mean in very general terms? A stimulus (or class of stimuli) is "important"; denotes information that is necessary or useful to the task Stimulus is meaningful, important, noticeable Evaluated within context of working memory? (cf. Donchin & Coles, 1988; Verlager 1988; Polich, 2007; Verlager, 2008) The P3a (Squires, Squires, and Hillyard, 1975): P3- like component with a frontal maximum and occurs to improbable stimuli in the "to-be-ignored" class of stimuli; a novelty response.
12 P3a How Many P3s? The Classic P3/P300 Parietal Central Maximum Largest when stimuli rare and task-relevant The P3a (Squires et al., 1975) or Novelty P3 (Courchesne et al., 1975) More anterior scalp distribution Slightly earlier latency Responsive to rare, unexpected, unattended stimuli P3b
13 Simons et. al, 2001 Squires Task was tones (two tones) Courchesne task was digitized speech ( me you and collection of naturally occurring sounds In all cases subjects merely counted Tones
14 P3a Can you see it? Some inconsistencies in finding P3a following the initial Squires, Squires and Hilyard 1975 report Comerchero & Polich (1998) may have resolved the enigma P3a highly dependent on foreground discrimination P3a P3b
15
16 Note: Nontarget peak amplitude was earlier and larger at the frontal electrodes than those from the target stimuli, but especially when foreground discrimination is difficult Comerchero & Polich (1998), Clinical Neurophysiology
17 Polich, Clin Neurophys, 2007
18 Synopsis the manipulation of target-standard stimulus discriminability produced a stimulus environment in which the infrequently occurring nontarget engaged focal attention in a manner similar to that observed previously for novel stimuli. However, all stimuli in the present study were employed because of their typical characteristics, so that the results imply that an anterior P3a component can be produced without using novel stimuli per se. If stimulus context is defined primarily by a difficult targetrstandard discrimination, attentional redirection to the nontarget would occur because of the frontal lobe activation that generates P3a. Comerchero & Polich 1998, p. 47
19 ERPs and Memory Sensitive to both Recognition Likely episodic recollection Sensitive to Encoding
20 Repetition Priming Effects Robust effect that repeated items produce an enhanced late positivity across a broad latency range Magnitude of effect related to strength of memory trace
21 Repetition Priming Are there repetition effects that do not depend on the subjective awareness of the subject? Can use Masked Priming to examine (Schnyer, Allen, Forster, 1997)
22 Schnyer, Allen, Forster, 1997
23 Standard Repetition Effect for Words Seen Unmasked in Previous Blocks Task is to make OLD-NEW decision Schnyer, Allen, Forster, 1997
24 Note consistency with hemispheric encoding/retrieval asymmetry (HERA) model: left encode, right retrieve Standard Repetition Effect for Words Seen Unmasked in Previous Blocks But Task is to make WORD-NONWORD decision Schnyer, Allen, Forster, 1997
25 Masked Repetition Priming Effect for Words Presented only a Trial Previously Schnyer, Allen, Forster, 1997
26 Memory Encoding Words subsequently remembered show enhanced positivity at encoding Strategy interacts, however
27 Note prototypic DM effect on left, but not on right for those that used elaborative strategies. Note enhancement over frontal lead for these latter subjects.
28
29 Indirect Assessments of Recognition Can the ERP detect recognition, independent of subjects overt responses? Two applications Clinical Malingering Forensic Assessment
30 ERP Memory Assessment Procedures Learn a list of words Learn a second list of words Task: Concealed (1 st list) and Nonconcealed (2 nd list) words appear infrequently Item Type Probability Response P3 Amplitude Nonconcealed 1/7 Yes Large Concealed 1/7 No Large if Recognized Small if not Recognized Unlearned 5/7 No Small Similar to procedures by Rosenfeld et al, Farwell & Donchin
31 Motivational Variations Conceal Lie Lie + $$ "YES" for words JUST learned, "NO" for all others Try to hide the fact that you learned the first list of words I taught you "YES" for words learned Lie about words from the first list I taught you "YES" for words learned Lie about words from the first list I taught you $5.00 incentive
32 After Allen & Iacono, 1997
33 The Challenge To provide statistically supported decisions for each and every subject, despite considerable individual variability in ERP morphology
34 P3 Amplitude Sensitivity =.925 Specificity =.920 Raw ERP H 2 Sensitivity =.950 Specificity = ZScore ZScore 1 st Derivative H 2 Sensitivity =.875 Specificity = nd Derivative H 2 Sensitivity =.750 Specificity =.740 Deviation H 2 Sensitivity =.925 Specificity = ZScore ZScore ZScore
35 Bayesian Combination of ERP Indicators: Probability that an ERP was elicited by Learned Items List Learned Unlearned Subject NonConceal Conceal U1 U2 U3 U4 U5 # # # # # # # # # # Note: Only trials in which subjects did not acknowledge concealed items included
36 Classification Accuracy based on ERPs Learned (true pos) Unlearned (true neg) Conceal Lie Lie + $$ Combined Allen, Iacono, & Danielson, Psychophysiology, 1992
37
38
39 The Claim Brain Fingerprinting can determine scientifically whether a suspect has details of a crime stored in his brain Thus these ERP-procedures should be able to identify memories in laboratory studies Two tests of the robustness of this procedure: False recollections Virtual Reality Mock Crime
40 A Laboratory Paradigm for False Recollections: DRM Subjects presented with 15 words highly associated with an omitted critical item
41 A Laboratory Paradigm for False Recollections: DRM Subjects presented with 15 words highly associated with an omitted critical item Bed, rest, awake, tired, dream, wake, snooze, blanket, doze, slumber, snore, nap, peace, yawn, drowsy Sleep
42 Reported Rates of Recogntion 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Forced Choice Likert Confidence Learned Lure Unlearned Allen and Mertens (2008)
43 Learned Unlearned Lure Allen and Mertens (2008)
44 The Box Score Blues Test Verdict Ground Truth Recognized Actually Learned 56% Critical Lure 72% Unlearned 4% Highlights the need to have memorable items in the test Suggests limited utility in substantiating disputed memories; e.g., claims regarding recovered memories Still has low false positive rate when person denies knowledge
45 Virtual Reality Mock Crime Subjects received detailing their Mission Sneak into graduate student office to break in to virtual apartment Apprehended and interrogated using ERP-based procedure Some subjects given details about utilizing countermeasures Innocent subjects tour the same virtual apartment, but with different objects and details.
46
47
48 Results of Mock Crime Brainwave Procedure Group N Guilty Verdict Innocent Guilty 15 47% 53% Guilty (countermeasure) 45 17% 83% Innocent 15 6% 94% Note: Using Bootstrapping approach, Guilty detection drops to 27%, but innocent subjects classified correctly in 100% of cases. Allows indeterminate outcomes
49 ERPs and Affective Processing IAPS = International Affective Picture System Pleasant, Neutral, Unpleasant Vary in Arousal: Pleasant and Unpleasant tend to be more arousing Predict more significant stimuli produce larger P3
50 Long (6 sec) Presentation Duration Schupp et al (2000), Psycholophysiology
51 1.5 sec Presentation Duration Cuthbert et al (2000), Biological Psychology
52 ERPS and Implicit Affective Processing Ito & Cacioppo (2000) JESP Evaluative Processing (positive vs negative) Nonevaluative (people vs no-people)
53 Ito & Cacioppo (2000) JESP
54 N400 and Language Originally reported by Kutas & Hillyard, Semantic Incongruity is separable from other forms of deviations (e.g. large font) N400 Semantic Deviation P300 Physical Deviation Also seen in semantic differentiation tasks (Polich, 1985); APPLE, BANANA, ORANGE, MANGO, TRUCK Subject-Object mismatch (the Florida group) NOTE: N400 will appear before P3 (which will be ~P550 in word tasks)
55 N400 and Language Sensitive to degree of semantic incongruity
56 Political Evaluations! Morris Squires et al. Political Psychology 2003
57 Congruent or incongruent defined based on idiographic data from pretest Morris Squires et al. Political Psychology 2003
58 Cloze probability: proportion of respondents supplying the word as continuation given preceding context N400 reflects unexpected word given the preceding context This is independent of degree of contextual constraint Larger N400 Low cloze, Contextual constraint high: The bill was due at the end of the hour Low cloze, Contextual constraint low: He was soothed by the gentle wind Smaller N400 The bill was due at the end of the month Kutas & Federmeier, 2011
59 Sentence completion Best (expected) ending small Unexpected but related larger Unexpected and unrelated largest Categorical relations sentence final word is: an expected category exemplar an unexpected, implausible exemplar from the same category as the expected one (related anomalous) from a different category (unrelated anomalous) Note multiple modalities of effect, and graded effect in RVF (LH) Kutas & Federmeier, 2011
60 Word Association, with second word in pair Unrelated to first (eat door) Weakly related to first (eat spoon) Strongly related to first (eat drink) Orthographic neighborhood size (among a list of words, pseudowords, and acronyms) Words that share all but one letter in common with particular word Large hood (e.g., slop) large N400 Small hood (e.g. draw) small N400 Kutas & Federmeier, 2011
61 Math: (e.g., 5 x 8 = ) Correct (40) small Related (32, 24, 16) small if close Unrelated (34, 26, 18) large Movement and Gestures Typical actions (cutting bread with knife) = small Purposeless, inappropriate, or impossible actions = large Cutting jewelry on plate with fork and knife Cutting bread with saw N400 modulated by both: appropriateness of object (e.g., screwdriver instead of key into keyhole) features of motor act per se (e.g., orientation of object to keyhole) Kutas & Federmeier, 2011
62 Repetition effects Repetition creates contextual familiarity, reduced processing demands N400 thus useful in studying memory Appears additive with incongruency effects Kutas & Federmeier, 2011
63 N400 The Unexpected Hero!
64 Contingent Negative Variation O-wave = Orienting; E-Wave = Expectancy, arguably motor-related
65 Response-locked potentials Lateralized Readiness Potential (LRP), a special case of movement-related potentials Error-related Negativity (ERN, aka N E )
66 Eimer 1998, Beh Res Methods Lateralized Readiness Potential LRP can be stimulus-locked or responselocked For stim-locked, latency is time between stimulus onset and LRP onset For rsps-locked latency is time between an LRP deflection and the overt response.
67 Response conflict in the LRP Eimer 1998, Beh Res Methods
68 The ERN Flankers Task: MMNMM Also sometimes termed Ne
69 Gehring et al., 1993
70 Modality Specific? Does not matter what modality stimulus was presented
71 Does not matter what modality response was made Eye Nieuwenhuis et al., 2001: Saccade Task
72 Does not matter what modality response was made Eye Hand Foot
73 Error Detection Vs. Error Compensation If Error Compensation, ERN/Ne should not be present in tasks where compensation impossible Ergo the Go-Nogo! Play along press only for X following X ZKXVXZKXNX
74 Falkenstein Hoormann Christ & Hohnsbein, Biological Psychology, 2000, Summary of Falkenstein et al 1996
75 Error Detection Vs. Outcome Impact Might the cost or importance or salience of an error be relevant to this process? Studies relevant to error salience Speed-accuracy trade off Individual differences
76 Speed Vs. Accuracy
77 Individual Differences Psychopathy (or analog) OCD
78 Deficits in Error Monitoring in Psychopathy Psychopaths appear unable to learn from the consequences of their errors Avoidance learning deficits In the context of rewards and punishments Deficient anticipatory anxiety
79 600 Participants Number of Students Dikman & Allen, 2000, Psychophysiology Thirty participants selected: 15 high SO 15 low SO
80 Procedure Eriksen flanker task: SSHSS Two conditions for each subject Reward (REW), errors No $ Punishment (PUN), errors 95 db tone Consequences of errors could be avoided by self-correcting response within 1700 msec window Response mapping switched at start of each of 10 blocks, total trials 600 Only corrected error trials examined.
81 Dikman & Allen, 2000, Psychophysiology
82 Hi SO 0 mv Pun Rew -9 mv Low SO AL Results replicate AL with RT-matched trials
83 ERN in OCD And amplitude of ERN correlates with Symptom severity (correlation magnitude ~.50); Gehring et al. (2000)
84 Potential (µv) Potential (µv) Potential (µv) OC Typical OC Specific Worry Anxiety Control OC Typical OC Specific Worry Anxiety Control Zambrano-Vazquez & Allen, 2014
85 Error Detection Vs. Conflict Trials on which errors occur will entail greater response conflict than those without errors So, is it error detection, or response conflict? Stay tuned
86 Errors and Feedback Endogenous Error Detection Exogenous Error Feedback Common Mechanism?
87 The Feedback Medial Frontal Negativity Time Estimation Task Cue, then press button 1 second later Feedback in visual, auditory, or somatosensory modality Width of correct time window varied dynamically to titrate to 50% accuracy Miltner, Braun, & Coles, (1997) Journal of Cognititive Neuroscience
88 The Feedback Medial Frontal Negativity Time Estimation Task Cue, then press button 1 second later Feedback in visual, auditory, or somatosensory modality Width of correct time window varied dynamically to titrate to 50% accuracy Miltner, Braun, & Coles, (1997) Journal of Cognititive Neuroscience
89 The Gambling Task Gehring and Willoughby, 2002 Science
90 Gehring and Willoughby, 2002 Science
91 Error, or motivation? Gehring and Willoughby, 2002 Science
92 Effect may depend on relevant dimension of feedback Nieuwenhuis, Yeung, Holroyd, Schurger, & Cohen (2004), Cerebral Cortex
93 FRN and Problem Gambling Why do Gamblers Gamble?
94 Black Jack Study 20 Problem Gamblers, 20 Controls Black Jack BUST! 21! Hewig et al. (2010). Biological Psychiatry
95 Black Jack Study Prob hit at 16 Hewig et al. (2010). Biological Psychiatry
96 FRN may be absence of Reward Positivity Foti et al. (2011). HBM
The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) A continuation
 The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) A continuation Ongoing EEG Stimuli Visual Event-related Potential (ERP) N400 N1 P1 P2 P3 Construct Validity of P300 (P3, P3b) First observed by Sutton, Braren,
The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) A continuation Ongoing EEG Stimuli Visual Event-related Potential (ERP) N400 N1 P1 P2 P3 Construct Validity of P300 (P3, P3b) First observed by Sutton, Braren,
Announcements. The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) 4/8/2013. Applications of Early Components. Prediction of recovery from coma
 Announcements The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) The Home Stretch Papers due April 29 Take home final available April 29, due May 7 3x5s times three! (that s 9x15 ) Applications of Early Components
Announcements The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) The Home Stretch Papers due April 29 Take home final available April 29, due May 7 3x5s times three! (that s 9x15 ) Applications of Early Components
Announcements. Advanced Signal Processing I. N400 and Language. ERPs N400, ERN, FRN. Political Evaluations! 4/22/2013
 Announcements Advanced Signal Processing I Digital Filters Time Frequency Approaches Ocular Artifacts Research Proposals due next Monday (April 29) no later than 3 pm via email to instructor Word format
Announcements Advanced Signal Processing I Digital Filters Time Frequency Approaches Ocular Artifacts Research Proposals due next Monday (April 29) no later than 3 pm via email to instructor Word format
Announcements. 3x5s for two weeks Back to lecture
 Announcements 3x5s for two weeks Back to lecture The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) Overview Event-related potentials are patterned voltage changes embedded in the ongoing EEG that reflect a process
Announcements 3x5s for two weeks Back to lecture The Event-Related Potential (aka the ERP) Overview Event-related potentials are patterned voltage changes embedded in the ongoing EEG that reflect a process
A bit more on Frequency-domain EEG. and then. The Event-related Brain Potential (Part 1)
 A bit more on Frequency-domain EEG and then The Event-related Brain Potential (Part 1) Announcements Papers: 1 or 2 paragraph prospectus due a few minutes ago! Feedback coming soon if you ve not received
A bit more on Frequency-domain EEG and then The Event-related Brain Potential (Part 1) Announcements Papers: 1 or 2 paragraph prospectus due a few minutes ago! Feedback coming soon if you ve not received
Oscillatory EEG (continued) Event-related Potentials
 Oscillatory EEG (continued) then Event-related Potentials Synchronization and Desynchronization Supposition that alpha blocking meant that the EEG had become desynchronized Yet the activity is still highly
Oscillatory EEG (continued) then Event-related Potentials Synchronization and Desynchronization Supposition that alpha blocking meant that the EEG had become desynchronized Yet the activity is still highly
Longterm Memory. Declarative Memory Consolidation and Sleep. Current Memory Models. Traditional Memory Models. Why Sleep?
 1 Longterm Memory Declarative Memory Consolidation and Sleep Kimberly Fenn Cognitive Psychology Psych 200 January 13, 2011 Declarative Memory Memory for facts, information, and events Procedural Memory
1 Longterm Memory Declarative Memory Consolidation and Sleep Kimberly Fenn Cognitive Psychology Psych 200 January 13, 2011 Declarative Memory Memory for facts, information, and events Procedural Memory
Memory II. Reconstructive Memory Forgetting
 Memory II Reconstructive Memory Forgetting Observe this crime scene What does a penny look like? Memory Biases Memory is better for meaningful significant features than for details of language or perception
Memory II Reconstructive Memory Forgetting Observe this crime scene What does a penny look like? Memory Biases Memory is better for meaningful significant features than for details of language or perception
Memory part I. Memory Distortions Eyewitness Testimony Lineup Studies
 Memory part I Memory Distortions Eyewitness Testimony Lineup Studies Memory for detail vs. gist Overview Memory distortions due to Schematic knowledge/general knowledge Semantic associations Misinformation
Memory part I Memory Distortions Eyewitness Testimony Lineup Studies Memory for detail vs. gist Overview Memory distortions due to Schematic knowledge/general knowledge Semantic associations Misinformation
PERCEPTUAL TUNING AND FEEDBACK-RELATED BRAIN ACTIVITY IN GAMBLING TASKS
 PERCEPTUAL TUNING AND FEEDBACK-RELATED BRAIN ACTIVITY IN GAMBLING TASKS by Yanni Liu A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Psychology)
PERCEPTUAL TUNING AND FEEDBACK-RELATED BRAIN ACTIVITY IN GAMBLING TASKS by Yanni Liu A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Psychology)
Attentional Blink Paradigm
 Attentional Blink Paradigm ATTENTIONAL BLINK 83 ms stimulus onset asychrony between all stimuli B T D A 3 N P Z F R K M R N Lag 3 Target 1 Target 2 After detection of a target in a rapid stream of visual
Attentional Blink Paradigm ATTENTIONAL BLINK 83 ms stimulus onset asychrony between all stimuli B T D A 3 N P Z F R K M R N Lag 3 Target 1 Target 2 After detection of a target in a rapid stream of visual
Reward prediction error signals associated with a modified time estimation task
 Psychophysiology, 44 (2007), 913 917. Blackwell Publishing Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2007 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2007.00561.x BRIEF REPORT Reward prediction
Psychophysiology, 44 (2007), 913 917. Blackwell Publishing Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2007 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2007.00561.x BRIEF REPORT Reward prediction
Experimental Design!
 Experimental Design! Variables!! Independent Variables: variables hypothesized by the experimenter to cause changes in the measured variables.!! Conditions: Different values of the independent variables!!
Experimental Design! Variables!! Independent Variables: variables hypothesized by the experimenter to cause changes in the measured variables.!! Conditions: Different values of the independent variables!!
Spring, 2004, Mondays, P.M. Room 317B Psychology Syllabus
 PSYC401A/501A: Principles of Psychophysiology Spring, 2004, Mondays, 1100-150 P.M. Room 317B Psychology Syllabus General Issues Definition Scope Problems of inference Problems and Prospects for the field
PSYC401A/501A: Principles of Psychophysiology Spring, 2004, Mondays, 1100-150 P.M. Room 317B Psychology Syllabus General Issues Definition Scope Problems of inference Problems and Prospects for the field
Event-Related Potentials Recorded during Human-Computer Interaction
 Proceedings of the First International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME2005) May 15-18, 2005, Takamatsu, Japan (Organized Session No. 20). Paper No. 150, pp. 715-719. Event-Related Potentials
Proceedings of the First International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME2005) May 15-18, 2005, Takamatsu, Japan (Organized Session No. 20). Paper No. 150, pp. 715-719. Event-Related Potentials
1 Performance monitoring and anxiety Running head: Performance monitoring and anxiety
 1 Running head: Anxiety disrupts the evaluative component of performance monitoring: An ERP study Kristien Aarts and Gilles Pourtois Department of Experimental Clinical and Health Psychology, Ghent University,
1 Running head: Anxiety disrupts the evaluative component of performance monitoring: An ERP study Kristien Aarts and Gilles Pourtois Department of Experimental Clinical and Health Psychology, Ghent University,
Announcements (2/16/04)
 Announcements (2/16/04) Electricity Test Today Video Library -- http://svl.arizona.edu. Information on Papers (last week) Online syllabus and links: http://www.u.arizona.edu/~jallen/courses.htm Review
Announcements (2/16/04) Electricity Test Today Video Library -- http://svl.arizona.edu. Information on Papers (last week) Online syllabus and links: http://www.u.arizona.edu/~jallen/courses.htm Review
Supplementary Materials: Materials and Methods Figures S1-S2 Tables S1-S17 References
 Supplementary Materials: Materials and Methods Figures S1-S2 Tables S1-S17 References Materials and Methods Simon Task Participants were randomly assigned to one of four versions of the task. Upon return
Supplementary Materials: Materials and Methods Figures S1-S2 Tables S1-S17 References Materials and Methods Simon Task Participants were randomly assigned to one of four versions of the task. Upon return
Event-related potentials as an index of similarity between words and pictures
 Psychophysiology, 42 (25), 361 368. Blackwell Publishing Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 25 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 1.1111/j.1469-8986.25.295.x BRIEF REPORT Event-related potentials
Psychophysiology, 42 (25), 361 368. Blackwell Publishing Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 25 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 1.1111/j.1469-8986.25.295.x BRIEF REPORT Event-related potentials
Psychology Midterm Exam October 20, 2010 Answer Sheet Version A. 1. a b c d e 13. a b c d e. 2. a b c d e 14. a b c d e
 1 7 Psychology 3450 - Midterm Exam October 20, 2010 Answer Sheet Version A Name: MUN ID: Indicate your answer by crossing out the appropriate letter. Answer 20 questions only. 1. a b c d e 13. a b c d
1 7 Psychology 3450 - Midterm Exam October 20, 2010 Answer Sheet Version A Name: MUN ID: Indicate your answer by crossing out the appropriate letter. Answer 20 questions only. 1. a b c d e 13. a b c d
Design and ERP data: Basic concepts. Caitlin M. Hudac Graduate student, Developmental Brain Laboratory
 Design and ERP data: Basic concepts Caitlin M. Hudac Graduate student, Developmental Brain Laboratory 1 Describe ERPs in terms of.. Peaks (positive or negative) Latency (post stimulus onset) Duration (e.g.,
Design and ERP data: Basic concepts Caitlin M. Hudac Graduate student, Developmental Brain Laboratory 1 Describe ERPs in terms of.. Peaks (positive or negative) Latency (post stimulus onset) Duration (e.g.,
A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition
 RESEARCH ARTICLE A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition Sameer Sethi 1 *, Dr. Simon Rigoulot 2, Dr. Marc D. Pell 3 1 Faculty of Science, McGill University,
RESEARCH ARTICLE A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition Sameer Sethi 1 *, Dr. Simon Rigoulot 2, Dr. Marc D. Pell 3 1 Faculty of Science, McGill University,
of concealed information with event-related brain potentials 1 Faculty of Psychology and Neuroscience, Maastricht University, the Netherlands
 A comment on Farwell (2012): Brain fingerprinting: A comprehensive tutorial review of detection of concealed information with event-related brain potentials Ewout H. Meijer 1,2, Gershon Ben-Shakhar 2,
A comment on Farwell (2012): Brain fingerprinting: A comprehensive tutorial review of detection of concealed information with event-related brain potentials Ewout H. Meijer 1,2, Gershon Ben-Shakhar 2,
The application of subliminal priming in lie detection: Scenario for identification of members of a terrorist ring
 Psychophysiology, 46 (29), 889 93. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 29 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 1.1111/j.1469-8986.29.81.x The application of subliminal priming
Psychophysiology, 46 (29), 889 93. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 29 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 1.1111/j.1469-8986.29.81.x The application of subliminal priming
The Brain and the Mind Fall 1999 (Lecture V) Ceci n est pas une Slide. The discovery of the P300. The Oddball Paradigm. To resolve multiple components
 Ceci n est pas une Slide The Brain and the Mind Fall 1999 (Lecture V) Imaging the Brain (and the Mind?) The discovery of the P3 Sutton et al 1965 Subjects presented with random or known sequences of tones.
Ceci n est pas une Slide The Brain and the Mind Fall 1999 (Lecture V) Imaging the Brain (and the Mind?) The discovery of the P3 Sutton et al 1965 Subjects presented with random or known sequences of tones.
Chapter 6. Attention. Attention
 Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function:
 Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
Cardiac and electro-cortical responses to performance feedback reflect different aspects of feedback processing
 Cardiac and electro-cortical responses to performance feedback reflect different aspects of feedback processing Frederik M. van der Veen 1,2, Sander Nieuwenhuis 3, Eveline A.M Crone 2 & Maurits W. van
Cardiac and electro-cortical responses to performance feedback reflect different aspects of feedback processing Frederik M. van der Veen 1,2, Sander Nieuwenhuis 3, Eveline A.M Crone 2 & Maurits W. van
Two neurocognitive mechanisms of semantic integration during the comprehension of visual real-world events
 Two neurocognitive mechanisms of semantic integration during the comprehension of visual real-world events Tatiana Sitnikova a, Phillip J. Holcomb b, and Gina R. Kuperberg ba Abstract How do comprehenders
Two neurocognitive mechanisms of semantic integration during the comprehension of visual real-world events Tatiana Sitnikova a, Phillip J. Holcomb b, and Gina R. Kuperberg ba Abstract How do comprehenders
Early posterior ERP components do not reflect the control of attentional shifts toward expected peripheral events
 Psychophysiology, 40 (2003), 827 831. Blackwell Publishing Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2003 Society for Psychophysiological Research BRIEF REPT Early posterior ERP components do not reflect the
Psychophysiology, 40 (2003), 827 831. Blackwell Publishing Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2003 Society for Psychophysiological Research BRIEF REPT Early posterior ERP components do not reflect the
Perceptual properties of feedback stimuli influence the feedback-related negativity in the flanker gambling task
 Psychophysiology, 51 (014), 78 788. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright 014 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/psyp.116 Perceptual properties of feedback stimuli influence
Psychophysiology, 51 (014), 78 788. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright 014 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/psyp.116 Perceptual properties of feedback stimuli influence
Memory (1) Visual Sensory Store. Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory
 Memory (1) Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory Visual Sensory Store It appears that our visual system is able to hold a great deal of information but that if we do not attend to this information
Memory (1) Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory Visual Sensory Store It appears that our visual system is able to hold a great deal of information but that if we do not attend to this information
4 P300 in detecting concealed information
 4 P300 in detecting concealed information J. Peter Rosenfeld Overview: This chapter reviews the use of the P300 ERP in the detection of concealed information since the first published papers in the late
4 P300 in detecting concealed information J. Peter Rosenfeld Overview: This chapter reviews the use of the P300 ERP in the detection of concealed information since the first published papers in the late
Cognitive Neuroscience and Addiction
 Cognitive Neuroscience and Addiction Giuseppe Sartori Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience University of Padua Consciousness and free will Libet et al (1983) Conscious experiences related to actions are
Cognitive Neuroscience and Addiction Giuseppe Sartori Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience University of Padua Consciousness and free will Libet et al (1983) Conscious experiences related to actions are
Brain Fingerprinting Technology
 Brain Fingerprinting Technology Anubha Saxena Ankit Kumar Mishra Department of Computer Science Poornima College of Engineering Jaipur, India Abstract Brain fingerprinting is based on finding that the
Brain Fingerprinting Technology Anubha Saxena Ankit Kumar Mishra Department of Computer Science Poornima College of Engineering Jaipur, India Abstract Brain fingerprinting is based on finding that the
Brainpotentialsassociatedwithoutcome expectation and outcome evaluation
 COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE AND NEUROPSYCHOLOGY Brainpotentialsassociatedwithoutcome expectation and outcome evaluation Rongjun Yu a and Xiaolin Zhou a,b,c a Department of Psychology, Peking University, b State
COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE AND NEUROPSYCHOLOGY Brainpotentialsassociatedwithoutcome expectation and outcome evaluation Rongjun Yu a and Xiaolin Zhou a,b,c a Department of Psychology, Peking University, b State
Cognition. Post-error slowing: An orienting account. Wim Notebaert a, *, Femke Houtman a, Filip Van Opstal a, Wim Gevers b, Wim Fias a, Tom Verguts a
 Cognition 111 (2009) 275 279 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Cognition journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cognit Brief article Post-error slowing: An orienting account Wim Notebaert a,
Cognition 111 (2009) 275 279 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Cognition journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cognit Brief article Post-error slowing: An orienting account Wim Notebaert a,
The auditory P3 from passive and active three-stimulus oddball paradigm
 Research paper Acta Neurobiol Exp 2008, 68: 362 372 The auditory P3 from passive and active three-stimulus oddball paradigm Eligiusz Wronka 1,2 *, Jan Kaiser 1, and Anton M.L. Coenen 2 1 Institute of Psychology,
Research paper Acta Neurobiol Exp 2008, 68: 362 372 The auditory P3 from passive and active three-stimulus oddball paradigm Eligiusz Wronka 1,2 *, Jan Kaiser 1, and Anton M.L. Coenen 2 1 Institute of Psychology,
The Effects of Temporal Preparation on Reaction Time
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School January 2013 The Effects of Temporal Preparation on Reaction Time Glen Robert Forester University of South
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School January 2013 The Effects of Temporal Preparation on Reaction Time Glen Robert Forester University of South
Sensitivity of Electrophysiological Activity from Medial Frontal Cortex to Utilitarian and Performance Feedback
 Sensitivity of Electrophysiological Activity from Medial Frontal Cortex to Utilitarian and Performance Feedback Sander Nieuwenhuis 1, Nick Yeung 1, Clay B. Holroyd 1, Aaron Schurger 1 and Jonathan D. Cohen
Sensitivity of Electrophysiological Activity from Medial Frontal Cortex to Utilitarian and Performance Feedback Sander Nieuwenhuis 1, Nick Yeung 1, Clay B. Holroyd 1, Aaron Schurger 1 and Jonathan D. Cohen
Language Speech. Speech is the preferred modality for language.
 Language Speech Speech is the preferred modality for language. Outer ear Collects sound waves. The configuration of the outer ear serves to amplify sound, particularly at 2000-5000 Hz, a frequency range
Language Speech Speech is the preferred modality for language. Outer ear Collects sound waves. The configuration of the outer ear serves to amplify sound, particularly at 2000-5000 Hz, a frequency range
MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES
 MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES Carryl L. Baldwin and Joseph T. Coyne Department of Psychology Old Dominion University
MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES Carryl L. Baldwin and Joseph T. Coyne Department of Psychology Old Dominion University
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015
 Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
The Complex Trial Protocol (CTP): A new, countermeasure-resistant, accurate P300-based
 In Press, Psychophysiology, 2008. The Complex Trial Protocol (CTP): A new, countermeasure-resistant, accurate P300-based method for detection of concealed information J. Peter Rosenfeld, Elena Labkovsky,
In Press, Psychophysiology, 2008. The Complex Trial Protocol (CTP): A new, countermeasure-resistant, accurate P300-based method for detection of concealed information J. Peter Rosenfeld, Elena Labkovsky,
The effect of response execution on P3 latency, reaction time, and movement time
 Psychophysiology, 36 ~1999!, 351 363. Cambridge University Press. Printed in the USA. Copyright 1999 Society for Psychophysiological Research The effect of response execution on P3 latency, reaction time,
Psychophysiology, 36 ~1999!, 351 363. Cambridge University Press. Printed in the USA. Copyright 1999 Society for Psychophysiological Research The effect of response execution on P3 latency, reaction time,
The Impact of Cognitive Deficits on Conflict Monitoring Predictable Dissociations Between the Error-Related Negativity and N2
 PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Article The Impact of Cognitive Deficits on Conflict Monitoring Predictable Dissociations Between the Error-Related Negativity and N2 Nick Yeung 1 and Jonathan D. Cohen 2,3
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Article The Impact of Cognitive Deficits on Conflict Monitoring Predictable Dissociations Between the Error-Related Negativity and N2 Nick Yeung 1 and Jonathan D. Cohen 2,3
ANALYZING EVENT-RELATED POTENTIALS
 Adavanced Lifespan Neurocognitive Development: EEG signal processing for lifespan research Dr. Manosusos Klados Liesa Ilg ANALYZING EVENT-RELATED POTENTIALS Chair for Lifespan Developmental Neuroscience
Adavanced Lifespan Neurocognitive Development: EEG signal processing for lifespan research Dr. Manosusos Klados Liesa Ilg ANALYZING EVENT-RELATED POTENTIALS Chair for Lifespan Developmental Neuroscience
Effect of intensity increment on P300 amplitude
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 Effect of intensity increment on P300 amplitude Tim Skinner University of South Florida Follow this and
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 Effect of intensity increment on P300 amplitude Tim Skinner University of South Florida Follow this and
Neurophysiological correlates of memory illusion in both encoding and retrieval phases
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Neurophysiological correlates of memory illusion in both encoding and retrieval phases Haiyan Geng a,, Yaqiong Qi a,
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Neurophysiological correlates of memory illusion in both encoding and retrieval phases Haiyan Geng a,, Yaqiong Qi a,
Acute aerobic exercise effects on event-related brain potentials
 8 Acute aerobic exercise effects on event-related brain potentials Charles H. Hillman, Matthew Pontifex and Jason R. Themanson The study of acute exercise effects on neurocognitive function has grown in
8 Acute aerobic exercise effects on event-related brain potentials Charles H. Hillman, Matthew Pontifex and Jason R. Themanson The study of acute exercise effects on neurocognitive function has grown in
Activation of brain mechanisms of attention switching as a function of auditory frequency change
 COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE Activation of brain mechanisms of attention switching as a function of auditory frequency change Elena Yago, MarõÂa Jose Corral and Carles Escera CA Neurodynamics Laboratory, Department
COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE Activation of brain mechanisms of attention switching as a function of auditory frequency change Elena Yago, MarõÂa Jose Corral and Carles Escera CA Neurodynamics Laboratory, Department
No Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of Polygraphy. No Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of Polygraphy. Roadmap. The Polygraph Test
 Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of y John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of y John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona The Test does not detect lies The
Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of y John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of y John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona The Test does not detect lies The
Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B
 Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B Cortical Analysis of Visual Context Moshe Bar, Elissa Aminoff. 2003. Neuron, Volume 38, Issue 2, Pages 347 358. Visual objects in context Moshe Bar.
Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B Cortical Analysis of Visual Context Moshe Bar, Elissa Aminoff. 2003. Neuron, Volume 38, Issue 2, Pages 347 358. Visual objects in context Moshe Bar.
What do you notice? Woodman, Atten. Percept. Psychophys., 2010
 What do you notice? Woodman, Atten. Percept. Psychophys., 2010 You are trying to determine if a small amplitude signal is a consistent marker of a neural process. How might you design an experiment to
What do you notice? Woodman, Atten. Percept. Psychophys., 2010 You are trying to determine if a small amplitude signal is a consistent marker of a neural process. How might you design an experiment to
State sadness reduces neural sensitivity to nonrewards versus rewards Dan Foti and Greg Hajcak
 Neurophysiology, basic and clinical 143 State sadness reduces neural sensitivity to nonrewards versus rewards Dan Foti and Greg Hajcak Both behavioral and neural evidence suggests that depression is associated
Neurophysiology, basic and clinical 143 State sadness reduces neural sensitivity to nonrewards versus rewards Dan Foti and Greg Hajcak Both behavioral and neural evidence suggests that depression is associated
Biological Psychology
 Biological Psychology 87 (2011) 25 34 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biological Psychology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/biopsycho Dissociated roles of the anterior cingulate cortex
Biological Psychology 87 (2011) 25 34 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biological Psychology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/biopsycho Dissociated roles of the anterior cingulate cortex
The P300 and reward valence, magnitude, and expectancy in outcome evaluation
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report The P300 and reward valence, magnitude, and expectancy in outcome evaluation Yan Wu a,b, Xiaolin Zhou c,d,e, a Research
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report The P300 and reward valence, magnitude, and expectancy in outcome evaluation Yan Wu a,b, Xiaolin Zhou c,d,e, a Research
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Master Thesis: Can the negative deflections found with EEG on frontocentral electrodes be explained by one underlying process?
 Master Thesis: Can the negative deflections found with EEG on frontocentral electrodes be explained by one underlying process? Name: Gerben Klein Studentnr: 3029182 Master: Neuroscience and Cognition,
Master Thesis: Can the negative deflections found with EEG on frontocentral electrodes be explained by one underlying process? Name: Gerben Klein Studentnr: 3029182 Master: Neuroscience and Cognition,
No Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of Polygraphy. John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona
 No Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of Polygraphy John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona No Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of Polygraphy John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona jallen.faculty.arizona.edu/polygraph
No Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of Polygraphy John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona No Lie! Caveats and Cautions in the use of Polygraphy John JB Allen, Ph.D. University of Arizona jallen.faculty.arizona.edu/polygraph
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Time Course of Processes and Representations Supporting Visual Object Identification and Memory
 Time Course of Processes and Representations Supporting Visual Object Identification and Memory Haline E. Schendan 1 and Marta Kutas 2 Abstract & Event-related potentials (ERPs) were used to delineate
Time Course of Processes and Representations Supporting Visual Object Identification and Memory Haline E. Schendan 1 and Marta Kutas 2 Abstract & Event-related potentials (ERPs) were used to delineate
Neuropsychologia 49 (2011) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Neuropsychologia
 Neuropsychologia 49 (2011) 405 415 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Dissociable correlates of response conflict and
Neuropsychologia 49 (2011) 405 415 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Dissociable correlates of response conflict and
PAUL S. MATTSON AND LISA R. FOURNIER
 Memory & Cognition 2008, 36 (7), 1236-1247 doi: 10.3758/MC/36.7.1236 An action sequence held in memory can interfere with response selection of a target stimulus, but does not interfere with response activation
Memory & Cognition 2008, 36 (7), 1236-1247 doi: 10.3758/MC/36.7.1236 An action sequence held in memory can interfere with response selection of a target stimulus, but does not interfere with response activation
Dissociable neural correlates for familiarity and recollection during the encoding and retrieval of pictures
 Cognitive Brain Research 18 (2004) 255 272 Research report Dissociable neural correlates for familiarity and recollection during the encoding and retrieval of pictures Audrey Duarte a, *, Charan Ranganath
Cognitive Brain Research 18 (2004) 255 272 Research report Dissociable neural correlates for familiarity and recollection during the encoding and retrieval of pictures Audrey Duarte a, *, Charan Ranganath
Study of the Brain. Notes
 Study of the Brain Notes 1. Three Components of the Brain Cerebrum. Most high-level brain functions take place in the cerebrum. It is divided into the left and right hemispheres. Many motor and sensory
Study of the Brain Notes 1. Three Components of the Brain Cerebrum. Most high-level brain functions take place in the cerebrum. It is divided into the left and right hemispheres. Many motor and sensory
Learning-related changes in reward expectancy are reflected in the feedback-related negativity
 European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 27, pp. 1823 1835, 2008 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06138.x Learning-related changes in reward expectancy are reflected in the feedback-related negativity Christian
European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 27, pp. 1823 1835, 2008 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06138.x Learning-related changes in reward expectancy are reflected in the feedback-related negativity Christian
Extraversion-Related Differences in Stimulus Analysis: Effectiveness of the Lateralized. Readiness Potential. Dianna Monteith. Saint Thomas University
 Extraversion and the LRP 1 Running head: EXTRAVERSION AND THE LRP Extraversion-Related Differences in Stimulus Analysis: Effectiveness of the Lateralized Readiness Potential Dianna Monteith Saint Thomas
Extraversion and the LRP 1 Running head: EXTRAVERSION AND THE LRP Extraversion-Related Differences in Stimulus Analysis: Effectiveness of the Lateralized Readiness Potential Dianna Monteith Saint Thomas
25 Things To Know. Pre- frontal
 25 Things To Know Pre- frontal Frontal lobes Cognition Touch Sound Phineas Gage First indication can survive major brain trauma Lost 1+ frontal lobe Gage Working on a railroad Gage (then 25) Foreman on
25 Things To Know Pre- frontal Frontal lobes Cognition Touch Sound Phineas Gage First indication can survive major brain trauma Lost 1+ frontal lobe Gage Working on a railroad Gage (then 25) Foreman on
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology
 Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
Neuropsychologia 50 (2012) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Neuropsychologia
 Neuropsychologia 50 (2012) 1286 1296 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia j ourna l ho me pag e: ww w.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Anxiety disrupts the evaluative
Neuropsychologia 50 (2012) 1286 1296 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia j ourna l ho me pag e: ww w.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Anxiety disrupts the evaluative
A mock terrorism application of the P300-based concealed information test
 Psychophysiology, 48 (2011), 149 154. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2010 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01050.x A mock terrorism application
Psychophysiology, 48 (2011), 149 154. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2010 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.01050.x A mock terrorism application
(Visual) Attention. October 3, PSY Visual Attention 1
 (Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
(Visual) Attention Perception and awareness of a visual object seems to involve attending to the object. Do we have to attend to an object to perceive it? Some tasks seem to proceed with little or no attention
A systems neuroscience approach to memory
 A systems neuroscience approach to memory Critical brain structures for declarative memory Relational memory vs. item memory Recollection vs. familiarity Recall vs. recognition What about PDs? R-K paradigm
A systems neuroscience approach to memory Critical brain structures for declarative memory Relational memory vs. item memory Recollection vs. familiarity Recall vs. recognition What about PDs? R-K paradigm
Running head: AFFECTIVE EVALUATION OF ACTIONS
 Running head: AFFECTIVE EVALUATION OF ACTIONS Erroneous and correct actions have a different affective valence: Evidence from ERPs Kristien Aarts, Jan De Houwer, and Gilles Pourtois Department of Experimental-Clinical
Running head: AFFECTIVE EVALUATION OF ACTIONS Erroneous and correct actions have a different affective valence: Evidence from ERPs Kristien Aarts, Jan De Houwer, and Gilles Pourtois Department of Experimental-Clinical
Two neurocognitive mechanisms of semantic integration during the comprehension of visual realworld
 Two neurocognitive mechanisms of semantic integration during the comprehension of visual realworld events Tatiana Sitnikova a, Phillip J. Holcomb b, Kristi A. Kiyonaga c, and Gina R. Kuperberg ba a MGH
Two neurocognitive mechanisms of semantic integration during the comprehension of visual realworld events Tatiana Sitnikova a, Phillip J. Holcomb b, Kristi A. Kiyonaga c, and Gina R. Kuperberg ba a MGH
Experimental Design. Outline. Outline. A very simple experiment. Activation for movement versus rest
 Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
Running Head: CONFLICT ADAPTATION FOLLOWING ERRONEOUS RESPONSE
 Running Head: CONFLICT ADAPTATION FOLLOWING ERRONEOUS RESPONSE PREPARATION When Cognitive Control Is Calibrated: Event-Related Potential Correlates of Adapting to Information-Processing Conflict despite
Running Head: CONFLICT ADAPTATION FOLLOWING ERRONEOUS RESPONSE PREPARATION When Cognitive Control Is Calibrated: Event-Related Potential Correlates of Adapting to Information-Processing Conflict despite
DATA MANAGEMENT & TYPES OF ANALYSES OFTEN USED. Dennis L. Molfese University of Nebraska - Lincoln
 DATA MANAGEMENT & TYPES OF ANALYSES OFTEN USED Dennis L. Molfese University of Nebraska - Lincoln 1 DATA MANAGEMENT Backups Storage Identification Analyses 2 Data Analysis Pre-processing Statistical Analysis
DATA MANAGEMENT & TYPES OF ANALYSES OFTEN USED Dennis L. Molfese University of Nebraska - Lincoln 1 DATA MANAGEMENT Backups Storage Identification Analyses 2 Data Analysis Pre-processing Statistical Analysis
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 11: Attention & Decision making Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 11: Attention & Decision making Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis
Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
Error-preceding brain activity: Robustness, temporal dynamics, and boundary conditions $
 Biological Psychology 70 (2005) 67 78 www.elsevier.com/locate/biopsycho Error-preceding brain activity: Robustness, temporal dynamics, and boundary conditions $ Greg Hajcak a, *, Sander Nieuwenhuis b,
Biological Psychology 70 (2005) 67 78 www.elsevier.com/locate/biopsycho Error-preceding brain activity: Robustness, temporal dynamics, and boundary conditions $ Greg Hajcak a, *, Sander Nieuwenhuis b,
Importance of Deficits
 Importance of Deficits In complex systems the parts are often so integrated that they cannot be detected in normal operation Need to break the system to discover the components not just physical components
Importance of Deficits In complex systems the parts are often so integrated that they cannot be detected in normal operation Need to break the system to discover the components not just physical components
Final Summary Project Title: Cognitive Workload During Prosthetic Use: A quantitative EEG outcome measure
 American Orthotic and Prosthetic Association (AOPA) Center for Orthotics and Prosthetics Leraning and Outcomes/Evidence-Based Practice (COPL) Final Summary 2-28-14 Project Title: Cognitive Workload During
American Orthotic and Prosthetic Association (AOPA) Center for Orthotics and Prosthetics Leraning and Outcomes/Evidence-Based Practice (COPL) Final Summary 2-28-14 Project Title: Cognitive Workload During
Event-Related Potentials Steven J. Luck Center for Mind & Brain and Department of Psychology University of California, Davis
 In Press in Long, D.L. (Ed.), APA Handbook of Research Methods in Psychology Event-Related Potentials Steven J. Luck Center for Mind & Brain and Department of Psychology University of California, Davis
In Press in Long, D.L. (Ed.), APA Handbook of Research Methods in Psychology Event-Related Potentials Steven J. Luck Center for Mind & Brain and Department of Psychology University of California, Davis
Accounts for the N170 face-effect: a reply to Rossion, Curran, & Gauthier
 S. Bentin, D. Carmel / Cognition 85 (2002) 197 202 197 COGNITION Cognition 85 (2002) 197 202 www.elsevier.com/locate/cognit Discussion Accounts for the N170 face-effect: a reply to Rossion, Curran, & Gauthier
S. Bentin, D. Carmel / Cognition 85 (2002) 197 202 197 COGNITION Cognition 85 (2002) 197 202 www.elsevier.com/locate/cognit Discussion Accounts for the N170 face-effect: a reply to Rossion, Curran, & Gauthier
D. Debatisse, E. Fornari, E. Pralong, P. Maeder, H Foroglou, M.H Tetreault, J.G Villemure. NCH-UNN and Neuroradiology Dpt. CHUV Lausanne Switzerland
 Vegetative comatose and auditory oddball paradigm with Cognitive evoked potentials (CEPs) and fmri: Implications for the consciousness model of Damasio and Guerit D. Debatisse, E. Fornari, E. Pralong,
Vegetative comatose and auditory oddball paradigm with Cognitive evoked potentials (CEPs) and fmri: Implications for the consciousness model of Damasio and Guerit D. Debatisse, E. Fornari, E. Pralong,
Aerobic Fitness and Cognitive Development: Event-Related Brain Potential and Task Performance Indices of Executive Control in Preadolescent Children
 Illinois Wesleyan University From the SelectedWorks of Jason R. Themanson, Ph.D 2009 Aerobic Fitness and Cognitive Development: Event-Related Brain Potential and Task Performance Indices of Executive Control
Illinois Wesleyan University From the SelectedWorks of Jason R. Themanson, Ph.D 2009 Aerobic Fitness and Cognitive Development: Event-Related Brain Potential and Task Performance Indices of Executive Control
Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling
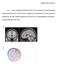 Supplementary materials 1 Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling analyses placed the source of the No Go N2 component in the dorsal ACC, near the ACC source
Supplementary materials 1 Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling analyses placed the source of the No Go N2 component in the dorsal ACC, near the ACC source
Title of Thesis. Studies on Mechanisms of Visual and Auditory Attention in Temporal or Spatial Cueing Paradigm
 Title of Thesis Studies on Mechanisms of Visual and Auditory Attention in Temporal or Spatial Cueing Paradigm 2015 September Xiaoyu Tang The Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology (Doctor s
Title of Thesis Studies on Mechanisms of Visual and Auditory Attention in Temporal or Spatial Cueing Paradigm 2015 September Xiaoyu Tang The Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology (Doctor s
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention
 Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
Learning to Become an Expert: Reinforcement Learning and the Acquisition of Perceptual Expertise
 Learning to Become an Expert: Reinforcement Learning and the Acquisition of Perceptual Expertise Olav E. Krigolson 1,2, Lara J. Pierce 1, Clay B. Holroyd 1, and James W. Tanaka 1 Abstract & To elucidate
Learning to Become an Expert: Reinforcement Learning and the Acquisition of Perceptual Expertise Olav E. Krigolson 1,2, Lara J. Pierce 1, Clay B. Holroyd 1, and James W. Tanaka 1 Abstract & To elucidate
Memory: Storage and Retrieval. Lecture 19
 Memory: Storage and Retrieval Lecture 19 1 The Storage Phase of Memory Processing Assume that a Memory Trace has been Adequately Encoded What Happens over the Retention Interval? Forgetting 2 Retention
Memory: Storage and Retrieval Lecture 19 1 The Storage Phase of Memory Processing Assume that a Memory Trace has been Adequately Encoded What Happens over the Retention Interval? Forgetting 2 Retention
CONGRUENCE EFFECTS IN LETTERS VERSUS SHAPES: THE RULE OF LITERACY. Abstract
 CONGRUENCE EFFECTS IN LETTERS VERSUS SHAPES: THE RULE OF LITERACY Thomas Lachmann *, Gunjan Khera * and Cees van Leeuwen # * Psychology II, University of Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany # Laboratory
CONGRUENCE EFFECTS IN LETTERS VERSUS SHAPES: THE RULE OF LITERACY Thomas Lachmann *, Gunjan Khera * and Cees van Leeuwen # * Psychology II, University of Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany # Laboratory
BRIEF REPORTS Modes of cognitive control in recognition and source memory: Depth of retrieval
 Journal Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 2005,?? 12 (?), (5),???-??? 852-857 BRIEF REPORTS Modes of cognitive control in recognition and source memory: Depth of retrieval LARRY L. JACOBY, YUJIRO SHIMIZU,
Journal Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 2005,?? 12 (?), (5),???-??? 852-857 BRIEF REPORTS Modes of cognitive control in recognition and source memory: Depth of retrieval LARRY L. JACOBY, YUJIRO SHIMIZU,
3/31/2017. Seven Sins of Memory. Seven Sins of Memory. Seven Sins of Memory
 Seven Sins of Memory Memory Retrieval 2 Seven Sins of Memory Dan Schacter (Harvard) Compared seven common memory errors to deadly sins If you avoid these, you are rewarded with good memory! But, sinning
Seven Sins of Memory Memory Retrieval 2 Seven Sins of Memory Dan Schacter (Harvard) Compared seven common memory errors to deadly sins If you avoid these, you are rewarded with good memory! But, sinning
ERP Correlates of Feedback and Reward Processing in the Presence and Absence of Response Choice
 Cerebral Cortex May 2005;15:535-544 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh153 Advance Access publication August 18, 2004 ERP Correlates of Feedback and Reward Processing in the Presence and Absence of Response Choice
Cerebral Cortex May 2005;15:535-544 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh153 Advance Access publication August 18, 2004 ERP Correlates of Feedback and Reward Processing in the Presence and Absence of Response Choice
Ingroup categorization and response conflict: Interactive effects of target race, flanker compatibility, and infrequency on N2 amplitude
 Psychophysiology, 47 (2010), 596 601. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2010 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.00963.x BRIEF REPORT Ingroup categorization
Psychophysiology, 47 (2010), 596 601. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Printed in the USA. Copyright r 2010 Society for Psychophysiological Research DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2010.00963.x BRIEF REPORT Ingroup categorization
