Handouts for Patients and Families (available on the accompanying CD) are included in the index and are indicated by CD rather than page numbers.
|
|
|
- Miranda Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 index Handouts for Patients and Families (available on the accompanying CD) are included in the index and are indicated by CD rather than page numbers. AAC. See Augmentative communication system (AAC) AAC-RERC. See Rehabilitation Engineering Research Center on AAC (AAC-RERC) Academy of Neurologic Communication Disorders and Sciences (ANCDS), CD Acetylcholine, 79 Acid indigestion, CD Acquired Parkinson s disease, 69 ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), 152 ADA (Americans With Disabilities Act), 154 Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), 152 Advanced health care directive, 177 Affective disorders. See also Depression with ALS, 8, 12, 30, 222 with multiple sclerosis, 150 AFO. See Ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) Akinesia, Alerting systems, 37 Alimentation, 221 Alphabet boards and alphabet supplementation, 37, 102, , 163, 221 ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) ALS Association of America (ALSA), 7, CD ALS Functional Rating Scale Revised, 4 ALS Health State Scale, 4 5 ALS Severity Scale, 24 29, 42, 43 44, Alternate motion rates, American Academy of Neurology, 6, 14, 17 American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA), CD American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), CD Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA), 154 Amplifier, 221 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) age at onset of, x alternate motion rates with, 178 aphasia with, 20 aspiration management and, aspiration pneumonia with, 184 assessment of respiratory problems with, assessment of swallowing function in, assessment of, with ALS Severity Scale, 24 29, 42, 43 44, association on, CD benefits of early diagnosis, 6 cause of, 3 4 clinical stages of ambulatory function in, 9 cognitive changes with, x, compared with other motor neuron diseases, 1 2 definition, 1,
2 228 diagnosis, 5 6 eating habits and, emotional and psychosocial aspects of, 8, 12, 30 employment for individuals with, 40 exercise for, 7 8 frontal lobe syndrome and, 11 frontotemporal dementia (FTD)/ALS and, gender ratio in, 2 goals of rehabilitation for, 7 grief and depression with, 8 handout, CD hospice admission criteria for, 10 incidence of, 2 management of respiratory problems with, medications for, x, 6 7 muscle cramping and spasms in, 8 neurological changes with, x, 2 3 palliative care for, 9 10 patient autonomy and, 8 9 rate of speech changes in, 20, rate of swallowing disorders in, references on, rehabilitation medicine for, 7 10 respiratory problems with, saliva management and, signs and symptoms of, ix, x, 1, 2, 3, CD speech disorders with, x, 18 41, CD speech intelligibility related to other variables in, 20, speech treatment for, 29 41, CD surgery for swallowing disorders with, 52, survival data on, 2 swallowing disorders management for, swallowing disorders with, x, 42 54, CD typical course of, x, 4 5 weakness and, 3, 7, 8 ANCDS. See Academy of Neurologic Communication Disorders and Sciences (ANCDS) Ankle-foot orthosis (AFO), 221 Anticholinergic drugs, 79 APDA. See American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA) Aphasia, 20 Arizona Battery for Communication Disorders, 149 Artane, 79 Articulation definition, 221 with Parkinson s disease, 87, 88 ASHA. See American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) Aspiration, 221, CD Aspiration management, Aspiration pneumonia, 184 Aspirator, 221 Assessment. See also Diagnosis; Interviews; Speech and swallowing examination of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 24 29, 42, 43 44, of conversation and interaction, , of dehydration, 51 Levels of Speech Usage Categorical Rating Scale, , of lower and upper extremity function in ALS, 27 29, of multiple sclerosis severity, of Parkinsonian dysarthria, 95, 99
3 of respiratory problems with ALS, 14 15, of speech disorders (dysarthria) in ALS, 25 26, 55 of speech disorders (dysarthria) in Multiple sclerosis, of speech function during clinical examination, 183, 187, of swallowing function during clinical examination, 183, , 191 of swallowing function in ALS, 26 27, 42, 43 44, 56, 184 of swallowing function in Huntington s disease, of swallowing function in multiple sclerosis, 166 of swallowing function in Parkinson s disease, Assistive technology. See also Augmentative communication system (AAC) with Huntington s disease, 138 with multiple sclerosis, 154 Assistive ventilatory, Associations and organizations, CD Ataxia, 153, 157, , 221, CD Athetosis, 71 Atrophy, 221, CD Audio recording of conversation, 199, , Auditory comprehension, 124 Augmentative communication system (AAC) alerting systems and, 37 alphabet boards and alphabet supplementation, 37, 102, , 163, 221 ALS Severity Scale and, 26 for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), classification of functional capabilities for, for conversations, , , 206, 208 definition, 221, CD employment of individuals with ALS using, 40 funding of, handout, CD for Huntington s disease, 130 for multiple sclerosis, 163, CD multipurpose systems for, for Parkinson s disease, 102, CD patterns of system use, 39 portable writing systems and, 37 research center on, CD speech-language pathologists (SLPs) and, telephone communication and, 37 timing of AAC intervention, 36 Autonomy of patients, 8 9 Avonex, Basal ganglia, 70 71, 103, 122, 123, 221, CD Behavioral rate-control techniques, Betaseron, 152 Bilevel Positive Air Pressure (BiPAP), 16 BiPAP (Bilevel Positive Air Pressure), 16 Bolus, 221 Bradykinesia, 71 73, 221, CD Breathiness, 221 Bromocriptine, 78 Buccal/frontal/orbital muscles, Buccinators, , 187 Cachexia, 221 Calendars and memory aids, 132, 154 Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), 79
4 230 Center for Neurologic Study Lability Scale, 12 Centers for Disease Control, 182 Central nervous system (CNS), 147, 150, 221 Charcot s disease. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Choking first aid for, 46, CD multiple sclerosis and, 166 Chorea, 71, 122, 124, 221 Clinical examination. See Speech and swallowing examination CNS. See Central nervous system (CNS) Cognitive problems with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), x, frontal lobe syndrome and, 11 frontotemporal dementia (FTD)/ALS, with Huntington s disease, x, , with multiple sclerosis, x, , 154 with Parkinson s disease, x, 81 82, CD Cogwheel rigidity, 221 Communication. See Conversation and interaction Communication Independence for the Neurologically Impaired, 38 Computerized Speech Lab, COMT. See Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) Comtan, 79 Contractures, 222 Conversation and interaction assessment of, , augmentative communication system (AAC) for, , , 206, 208 case examples, conversation starters for people with Huntington s disease, direct observation/analysis of, , , gaining attention for, 205 Huntington s disease and, 124 impact of dysarthria on, importance and organization of, interview for assessment of, , 207, Levels of Speech Usage Categorical Rating Scale, , management of, opportunities for, 198 perception of current problems with, 198 preferences and styles in, 198 problems with, , CD profiles of conversation partnership, recording of, 199, , references on, role of speech language pathologists in, showing understanding for, 205, 206 strategies for, 199 tips for, CD topic initiation and topic change for, 206 turn design for, 206 Copaxone, 152 Cough, 14, 17, 182 Counseling. See Psychological services and counseling Cuirass, 222 DAF. See Delayed auditory feedback (DAF) DBS. See Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
5 Decomposition, CD Deep brain stimulation (DBS), 79 80, 91 Degenerative diseases. See specific diseases Dehydration, 51. See also Liquid intake Delayed auditory feedback (DAF), 101, 222 Dementia definition, 222 frontotemporal dementia (FTD)/ALS, with Parkinson s disease, 81, 82 Deprenyl, Depression. See also Affective disorders with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 8 with Huntington s disease, 123 major depressive disorder (MDD), 150 with multiple sclerosis, 150 with Parkinson s disease, 80 81, 82 Diadochokinetic rates, 160, , 222 Diagnosis. See also Assessment; Speech and swallowing examination of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 5 6 of Huntington s disease, of multiple sclerosis, 150 of Parkinson s disease, 73 Dietary changes for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), CD Huntington s disease and, 138 Parkinson s disease and, 109 for swallowing difficulties, 27, 47 48, CD Direct observation/analysis of conversation, , , Direct selection, 222 Disease-modifying therapy, 152 Dopamine, 222, CD Dopamine breakdown inhibition, Dopamine imitators, 78 Dopamine replacement, 78 Double swallow, 46 Drug management. See Medications Durable power of attorney for health care, 222 Dysarthria. See Speech disorders (dysarthria) Dyskinesia, 222 Dysmetria, 153 Dysphagia. See Swallowing disorders (dysphagia) Dysphagia Severity Rating Scale, 107, 108 Dystonia, CD Dystonic syndrome, Eating. See Dietary changes; Feeding; Swallowing disorders (dysphagia); Tube feeding EDSS (Expanded Disability Status Scale), 151 El Escorial criteria, 5 Eldepryl, Emergency procedures for choking, 46, CD Emotional lability, 12, 222. See also Affective disorders; Depression Employment compensatory techniques for individuals with multiple sclerosis in, 155 of individuals with ALS using AAC, 40 of individuals with multiple sclerosis, Entacapone, 79 Epiglottic sew-down procedures, 17, 54
6 232 Evaluation. See Assessment; Diagnosis; Speech and swallowing examination Exacerbations, CD Examination. See Speech and swallowing examination Exercise, 7 8. See also Rehabilitation Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS), 151, 165 Extrapyramidal system, 222 Extremity function. See Lower extremity function; Upper extremity function Eye-gaze systems, 41 Fasciculations, 222 Fatigue, 149, , 167 Feeding. See also Dietary changes; Swallowing disorders; Swallowing disorders management; Tube feeding alternative feeding for people with Huntington s disease, 138 calorie-dense foods, 47 control of eating rate and bite size, 138 definition, 222 early eating problems and ALS, 45, multiple sclerosis and, 165 normal eating habits and ALS, 45 Parkinson s disease and, 109 slowed eating, CD Festination, 222 Fibrillations, 222 First aid for choking, 46, CD Flaccid dysarthria, 223 Flaccidity, 223, CD Food. See Dietary changes; Feeding; Swallowing disorders Forced vital capacity (FVC), 14 15, 44, 182 Frontal lobe syndrome, 11 Frontotemporal dementia (FTD)/ALS, FTD. See Frontotemporal dementia (FTD)/ALS Functional status, FVC. See Forced vital capacity (FVC) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), 122 Gag reflex, 223 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), 122 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), CD Gastrostomy, 223 GERD. See Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Glatiramer, 152 Grief. See Depression Harshness, 223 HDSA. See Huntington s Disease Society of America (HDSA) Heartburn, CD Heat sensitivity, 150 Heimlich maneuver, CD Hemiballismus, 71 Hoarseness, 223 Hoehn and Yahr Functional Rating Scale for Parkinson s disease, Hospice admission for ALS, 10 Huntington s disease age at onset of, x alphabet boards for people with, alternative feeding for people with, 138 assistive devices for people with, 138 association on, CD
7 augmentative communication system (AAC) for, 130 calendars and memory aids for people with, 132 characteristics of generally, ix clinical variants of, 122 cognitive problems with, x, , conversation starters for people with, definition, 121, 223 diagnosis, dietary changes for, 138 emotional disturbances with, 123 handout, CD hereditary nature of, 121, 125, 126 incidence of, 121 making choices for people with, 132 management of mild dysarthria and cognitive changes with, management of moderate dysarthria and cognitive changes with, management of severe dysarthria with, 129, measurement of functional progression of, 125 medical management of, 126 medications for, x motor disturbances with, natural speech with supportive partners, 131 neurological changes with, x, postural and positional changes for people with, references on, remotivation therapy for people with, 134 respiratory chorea with, 124 signs and symptoms of, x, 121, , CD speech characteristics associated with, speech disorders with, x, 124, 126, , CD speech treatment for, , CD supervision to control eating rate and bite size for people with, 138 swallowing characteristics associated with, 135, 136 swallowing disorders management for, swallowing disorders with, x, , CD yes/no system for people with, , 139 Huntington s Disease Society of America (HDSA), CD Hyperkinetic dysarthria, 86, 127, 223 Hypernasality, 223 Hypokinetic dysarthria, 86, 223 Hypotonia, ICF. See International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Idiopathic Parkinson s disease, 69 Immunomodulatory agents, 152 Incidence, definition of, 223 Intention tremor, 147, 153, 155 Interaction. See Conversation and interaction Interferon beta-1a, 152 Interferon beta-1b, 152 International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF), 130 Interviews. See also Assessment for assessment of conversation, , 207, for assessment of Parkinsonian dysarthria, 95 for speech assessment in multiple sclerosis, Swallowing Disorders Interview Worksheet, 191 for swallowing evaluation in Huntington s disease, 136 for swallowing evaluation in Parkinson s disease, 106
8 234 Jobs. See Employment Juvenile Huntington s disease, 122 KayPENTAX, 162 Kennedy disease, 1, 2 Language deficits. See also Speech disorders (dysarthria) with Huntington s disease, management of, with Huntington s disease, with multiple sclerosis, 149 with Parkinson s disease, 82 Laryngeal penetration, 223 Laryngectomy, 17, 54 Laryngotracheal separation, 17 Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT), 80, Lenticuar nucleus, 70 Lentiform nucleus, 70 Levels of Speech Usage Categorical Rating Scale, , Levodopa, 78, 79, 83, 103, 223 Lips, examination of, , 186 Liquid intake assessment and treatment of dehydration, 51 maintenance of, 46, 47 swallowing disorders and, 46, 47 48, CD taste, temperature, texture sensations of liquids, washing foods down with liquids, 47 Living will, 177, 223 Lou Gehrig s disease. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Lower extremity function assessment of, with ALS Severity Scale, 27 29, 57 definition, 223 Lower motor neurons, 223, CD LSVT. See Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), 5, , 150 Major depressive disorder (MDD). See Depression MAO. See Monoamine oxidase (MAO) Mastication muscles, , 187 Mayo Clinic, 69, 78 MDA. See Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) MDD (major depressive disorder). See Depression Mechanical insufflation/exsufflation (MIE), 17 Medical history, , 176, 185 Medical management. See also Medications; Speech and swallowing examination; Surgery of Huntington s disease, 126 of Parkinson s disease, 77 80, 81 Medicare, Medications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), x, 6 7 disease-modifying therapy with, 152 for Huntington s disease, x for multiple sclerosis, x, 152 for Parkinson s disease, x, 77 79, 83, for saliva management, for speech disorders (dysarthria), for swallowing disorders (dysphagia), 107, 109 Memory aids and calendars, 132, 154 Memory problems. See Cognitive problems
9 MIE. See Mechanical insufflation/exsufflation (MIE) Mirapex, 78 Mitoxantrone, 152 MNDs. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); Motor neuron diseases (MNDs) Monoamine oxidase (MAO), 78 Monoamine oxidase-b, 78 Motor disturbances with Huntington s disease, with multiple sclerosis, 147, Motor neuron diseases (MNDs), 1 2. See also Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Motor neurons, CD MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), 5, , 150 MSA. See Multiple system atrophy (MSA) Multiple sclerosis affective disorders with, 150 age at onset of, x, 146, 151 alphabet board supplementation for, 163 associations on, CD ataxia and, 153, 157, , CD characteristics of generally, ix choking with, 166 cognitive changes with, x, , 154 definition, 145, 224 diagnosis, 150 early stages of, employment and, epidemiology of, 146 fatigue with, 149, , 167 functional status of, handout, CD heat sensitivity with, 150 late stages of, 167 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and, , 150 medications for, x, 152 mild dysarthria with, moderate dysarthria with, 161, motor symptoms of, 147, neurological changes with, x, 145 paced speech for, primary progressive MS, 151 prognosis of, progression of changing function in, x, progressive-relapsing MS, 151 references on, rehabilitation for, relapsing-remitting MS, 149, 151 respiratory pattern stabilization program for, 162 respiratory patterning for, 163 risk factors for, 146 secondary progressive MS, 151 sensory symptoms of, 148, 155 severe dysarthria with, 161, signs and symptoms of, x, , 153, CD sites of central nervous system (CNS) lesions and impairment in, 147, 150 spasticity with, 147, 153, , 162 speech assessment issues for, speech characteristics associated with, 156 speech disorders with, x, , CD 235
10 236 speech treatment for, , CD swallowing difficulty management for, swallowing disorders with, x, , CD visual-motor problems with, vocabulary selection for, 164 Multiple system atrophy (MSA), 69, 73 74, 82, 86 Muscle cramping and spasms, 8 Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA), CD Naming, 124 Nasal emission, 224 Nasogastric tube, 224 Natalizumab, 152 National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), 7, CD National Multiple Sclerosis Society, 152, CD National Parkinson Foundation (NPF), CD NINDS. See National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) NIV. See Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV), Normal eating habits, 45 Normal speech production, 31 32, CD Normal swallowing, CD Nothing by mouth. See NPO (nothing by mouth) Novantrone, 152 NPO (nothing by mouth) ALS Severity Scale and, 27 definition, 224 dysphagia and, 49 Observation/analysis of conversation, , , Occupational therapy, 81 Oculogyric crisis, 224 Olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA), 74 On-off effect, 224 OPCA. See Olivopontocerebellar atrophy (OPCA) Organizations and associations, CD Paced speech, Pacing board, 102 Palatal lift prosthesis, 35, 224 Palate, , 187 Palilalia, 102, 224 Palliative care, 9 10 Pallidotomy, 79, 91 Paralysis agitans, 224 Parkinson Alliance, CD Parkinson plus syndromes, 69, 73 75, 86 Parkinson s disease age at onset of, x associations on, CD behavioral intervention (speech treatment) for, characteristics of generally, ix cognitive problems with, x, 81 82, CD compared with Parkinson plus syndromes, 69, 73 75, 86 compared with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), 69, 74 75, 86, , 224 definition, 69, 224 depression with, 80 81, 82
11 diagnosis, 73 feeding and dietary modifications for, 109 handout, CD Hoehn and Yahr Functional Rating Scale for, idiopathic Parkinson s disease, 69 incidence of, 69 language deficits with, 82 medical management of, medications for, x, 77 79, 83 natural course of, x neurological changes with, x, problems associated with, progression of dysarthria with, rate of progression of, references on, rehabilitation for, 80, 81 respiratory problems with, 82 83, 86 87, 97 secondary or acquired Parkinson s disease, 69 sensitivity of clinical signs of, 73 signs and symptoms of, x, 71 73, CD specificity of clinical signs of, 73, speech characteristics associated with, speech disorders with, x, , CD speech scale for, 90 speech treatment for, , CD surgery for, 79 80, 91 swallowing disorders management for, swallowing disorders with, x, , CD Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), 76, 77 Parkinson s Disease Foundation (PDF), 78, CD Parlodel, 78 Patient autonomy. See Autonomy of patients Patient s history, , 185 PBP. See Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP) PDF. See Parkinson s Disease Foundation (PDF) Peak expiratory cough flow (PECF), 14, 17 PECF. See Peak expiratory cough flow (PECF) PEG. See Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG), 14, 44, 48, 109, 224 Peripheral nervous system, 224 Pharmacological intervention. See Medications Pharyngeal constrictors, , 187 Phonation with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 181 definition, 224 with Parkinson s disease, 87, sustained phonation measure, 160 Phonatory instability, 224 Physical examination. See Speech and swallowing examination Physical therapy, 81 PLS. See Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) PMA. See Primary progressive muscular (spinal) atrophy (PMA) Portable writing systems, 37 Postural instability, Pramipexole, 78 Prevalence, definition of, 224 Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS), 2 237
12 238 Primary progressive muscular (spinal) atrophy (PMA), 2 Procedural memory, 224 Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP), 2 Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), 69, 74 75, 86, , 224 PSP. See Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) Psychological services and counseling, 81. See also Affective disorders Pulmonary function tests, 15, 182, 224 Randomly selected sentences, 160 Rate-control techniques for Parkinsonian dysarthria, Rating scales Dysphagia Severity Rating Scale, 107, 108 Levels of Speech Usage Categorical Rating Scale, , for Parkinson s disease, 75 77, 99 for speech characteristics in Parkinson s disease, 99 Swallowing Performance Scale, 166 Reading of a standard passage, 160 Reading of randomly selected sentences, 160 Rebif, 152 Recording of conversation, 199, , Rehabilitation for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 7 10 exercise and, 7 8 goals of, 7 for multiple sclerosis, palliative care and, 9 10 for Parkinson s disease, 80, 81 patient autonomy and, 8 9 Rehabilitation Engineering Research Center on AAC (AAC-RERC), CD Remissions, CD Remotivation therapy, 134 Requip, 78 Respiration, 224. See also Respiratory problems Respiratory pattern stabilization program, 162 Respiratory patterning, 163 Respiratory problems with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 12 17, assessment of, 14 15, assistive ventilatory, examination of respiratory muscles, , 187 management of, with multiple sclerosis, with Parkinson s disease, 82 83, 86 87, 97 respiratory chorea with Huntington s disease, 124 speech production and, 86 87, 97 swallowing disorders and, Respiratory pump muscles, Respiratory valve muscles, 182 Respirometer, 182, 224 Resting tremor, CD, 71 72, 224 Rigid syndrome, 71 Rigidity definition, 225 with Huntington s disease, 122 with Parkinson s disease, 71 73, CD Riluzole, 6 Ropinirole, 78
13 Saliva management, 49 52, CD Scanning speech, 156 Secondary or acquired Parkinson s disease, 69 Selegiline, Sensitivity of clinical signs of Parkinson s disease, 73 Sensory symptoms of multiple sclerosis, 148, 155 Shy-Drager syndrome, 74, 86 SLPs. See Speech language pathologists (SLPs) SND. See Striatonigral degeneration (SND) Social interaction. See Conversation and interaction Spastic dysarthria, 86, 225 Spasticity with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), CD definition, 225, CD with multiple sclerosis, 147, 153, , 162 Specificity of clinical signs of Parkinson s disease, 73 Speech and swallowing examination of buccal/frontal/orbital muscles, sternocleidomastoid/trapezius muscles, and vocal folds, current health care management, , 186 diadochokinetic rates, 160, , 222 form for, for Huntington s disease, 136 Levels of Speech Usage Categorical Rating Scale, , medical history, 176, 185 for multiple sclerosis, 160 of palate, muscles of mastication, pharyngeal constrictors, and buccinators, , 187 for Parkinson s disease, 95, 107 patient s history, , 185 physical examination, , reading of a standard passage, 160 reading of randomly selected sentences, 160 references on, of respiratory muscles, , 187 speech function assessment, 183, 187, sustained phonation, 160 Swallowing Disorders Interview Worksheet, 191 swallowing function assessment, , , 191 of tongue and lips, , 186 Speech disorders (dysarthria). See also Conversation and interaction; Language deficits; Speech and swallowing examination; Speech production; Speech treatment with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), x, 18 41, CD articulation and, 87, 88 assessment of, in clinical examination, 183, 187, assessment of Parkinsonian dysarthria, 95, 99 assessment of, with ALS Severity Scale, 25 26, 55 assessment of, with multiple sclerosis, ataxia and, 153, 157, , CD compensation strategies for, CD definition of dysarthria, 222, CD handout, CD with Huntington s disease, x, 124, 126, , CD impact of, on conversations, medications for, mild dysarthria and cognitive change with Huntington s disease, mild dysarthria with multiple sclerosis, mild Parkinsonian dysarthria, moderate dysarthria and cognitive change with Huntington s disease,
14 240 moderate dysarthria with multiple sclerosis, 161, moderate Parkinsonian dysarthria, 96, with multiple sclerosis, x, , CD with Parkinson plus syndromes, 86 with Parkinson s disease, x, , CD phonation and, 87, rate of progression of, in Parkinson s disease, rate of speech changes in ALS, 20, respiration and, scanning speech, 156 severe dysarthria with Huntington s disease, 129, severe dysarthria with multiple sclerosis, 161, severe Parkinsonian dysarthria, 96, spasticity and, , 162 speech intelligibility related to other variables in ALS, 20, speech rate and, 87, 88 stages of, velopharyngeal function and, 87, 88 Speech-generating devices, 102 Speech intelligibility, 225 Speech language pathologists (SLPs), Speech production. See also Speech disorders (dysarthria) articulation and, 87, 88 components of, in Parkinson s disease, handout, CD normal speech processes with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), normal speech production, CD phonation and, 87, respiration and, 86 87, 97 speech rate, 87, 88 structures for, CD velopharyngeal function and, 87, 88 Speech rate with Parkinson s disease, 87, 88 Speech treatment. See also Augmentative communication system (AAC) alphabet boards and alphabet board supplementation, 37, 102, , 163, 221 for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 29 41, CD behavioral intervention for, behavioral modifications and, 31, behavioral rate-control techniques, calendars and memory aids, 132, 154 communication for patients on ventilators, 41 conversation starters, delayed auditory feedback (DAF), 101 for detectable speech disturbance, 31, eye-gaze systems, 41 for Huntington s disease, , CD Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT), 80, loss of useful speech and, 41 making choices, 132 for mild dysarthria and cognitive change with Huntington s disease, for mild dysarthria with multiple sclerosis, for mild Parkinsonian dysarthria, for moderate dysarthria and cognitive change with Huntington s disease, for moderate dysarthria with multiple sclerosis, 161, for moderate Parkinsonian dysarthria, 96, for multiple sclerosis, , CD natural speech with supportive partners, 131
15 normal speech processes and, paced speech, pacing board, 102 for Parkinson s disease, 81, , CD principles for intervention, respiratory pattern stabilization program, 162 respiratory patterning, 163 for severe dysarthria with Huntington s disease, 129, for severe dysarthria with multiple sclerosis, 161, for severe Parkinsonian dysarthria, 96, speech-generating devices, 102 staging of intervention, theater voice, 100 visual-motor problems with multiple sclerosis, vocabulary selection and, 164 voice amplifiers, 101 yes/no systems, 41, , 139 Spinemet, 225 Spinobulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy disease), 1, 2 Spirantization, 225 Sternocleidomastoid/trapezius muscles, Steroids, 152 Strained-strangled voice, 225 Striatonigral degeneration (SND), 74 Subchoreatic state of Huntington s disease, 122 Substantia nigra, CD Surgery. See also Tube feeding for aspiration management, for Parkinson s disease, 79 80, 91 for saliva management, 52 for speech disorders with Parkinson s disease, 91 for swallowing disorders with ALS, 52, Sustained phonation, 160 Swallow apnea, 43 Swallowing. See also Speech and swallowing examination; Swallowing disorders; Swallowing disorders management correct and incorrect positions for, 46, CD double swallow, 46 neck flexion position for, 46 normal swallowing, CD stages of, 225, CD Swallowing disorders (dysphagia). See also Speech and swallowing examination; Swallowing disorders management with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), x, 42 54, CD assessment of, in clinical examination, 183, , assessment of, with ALS Severity Scale, 26 27, 42, 43 44, 56 assessment of, with Huntington s disease, assessment of, with Parkinson s disease, definition, 222 early eating problems and, 45, esophageal stage difficulties, 136, 137, CD handouts, CD with Huntington s disease, x, , CD interview worksheet for assessment of, 191 with multiple sclerosis, x, , CD oral preparatory and oral stage difficulties, 136, 137, CD with Parkinson s disease, x, 81, , CD 241
16 242 pharyngeal stage difficulties, 136, 137, CD with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), rate of progression of, in ALS, respiratory problems and, Severity Rating Scale for, 107, 108 slowed eating due to, CD stages of, swallow apnea, 43 symptoms of, with Parkinson s disease, warning signs of, 184, CD Swallowing disorders management for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), aspiration management, assistive devices for, 138 compensation strategies, 109, CD dietary changes for, 27, 47 48, 109, 138, CD double swallow, 46 for Huntington s disease, liquid intake, 46, medications, for multiple sclerosis, normal eating habits, 45 NPO (nothing by mouth), 27, 49 for Parkinson s disease, postural and positional changes for, saliva management, 49 52, CD staging of intervention, supervision to control eating rate and bite size for, 138 tube feeding, Tasmar, 79 Telephone communication, 37 Thalamotomy, 79, 91 Theater voice, 100 TIV. See Tracheostomy invasive ventilation (TIV) Tolcapone, 79 Tongue, , 186 Tracheal diversion, 54 Tracheoesophageal anastomosis, 17 Tracheostomy, 225 Tracheostomy invasive ventilation (TIV), 16 Treatment. See Medications; Speech treatment; Surgery Tremor definition, 225 intention tremor in multiple sclerosis, 147, 153, 155 Parkinson s disease and, resting tremor, CD Trihexyphenidyl, 79 Tube feeding ALS Severity Scale and, 27 definition of nasogastric tube, 27, 224 intervention strategies, 48 management of, 49 PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) for, 14, 44, 48, 109, 224 symptoms indicating need for, 48 timing of, Tysabri, 152
17 Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), 76, 77 University of Nebraska AAC Center, 38 UPDRS. See Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) Upper extremity function assessment of, with ALS Severity Scale, 27 29, 58 definition, 225 Upper motor neurons, 225, CD 243 Velopharyngeal function, with Parkinson s disease, 87, 88 Velopharyngeal mechanism, definition, 225 Ventilators, 41, 225 Ventilatory assistance, Video recording of conversation, 199, , Vital capacity, 182, 225 Vocabulary selection, 164 Vocal fold closure, 54 Vocal folds, Voice amplifiers, 101 Weakness in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), 3, 7, 8 definition of, 225 in multiple sclerosis, 147, 153, 155 Web sites, CD Westphal s variant of Huntington s disease, 122 WHO. See World Health Organization (WHO) Workplace. See Employment World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Neuromuscular Disease, 5 World Health Organization (WHO), 130 Yes/no systems, 41, , 139
Clinical Swallowing Exam
 Clinical Evaluation Template 1 Clinical Exam Name: ID/Medical record number: Date of exam: Referred by: Reason for referral: Medical diagnosis: Date of onset of diagnosis: Other relevant medical history/diagnoses/surgery
Clinical Evaluation Template 1 Clinical Exam Name: ID/Medical record number: Date of exam: Referred by: Reason for referral: Medical diagnosis: Date of onset of diagnosis: Other relevant medical history/diagnoses/surgery
Communication and Swallowing with PSP/CBD. Megan DePuy, MBA, MS, CCC-SLP Private Speech Pathologist
 Communication and Swallowing with PSP/CBD Megan DePuy, MBA, MS, CCC-SLP Private Speech Pathologist A Speech Therapist? Why? Swallowing (Dysphagia) Speech (Dysarthria, Dysphonia) Language (Aphasia) An Experienced
Communication and Swallowing with PSP/CBD Megan DePuy, MBA, MS, CCC-SLP Private Speech Pathologist A Speech Therapist? Why? Swallowing (Dysphagia) Speech (Dysarthria, Dysphonia) Language (Aphasia) An Experienced
Parkinson s Disease. Sirilak yimcharoen
 Parkinson s Disease Sirilak yimcharoen EPIDEMIOLOGY ~1% of people over 55 years Age range 35 85 years peak age of onset is in the early 60s ~5% of cases characterized by an earlier age of onset (typically
Parkinson s Disease Sirilak yimcharoen EPIDEMIOLOGY ~1% of people over 55 years Age range 35 85 years peak age of onset is in the early 60s ~5% of cases characterized by an earlier age of onset (typically
Dysarthria and Dysphagia: a Neurology Perspective William Meador, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology, UAB
 Dysarthria and Dysphagia: a Neurology Perspective William Meador, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology, UAB 2.11.16 Disclosures I have no relevant conflicts or potential conflicts to disclose regarding
Dysarthria and Dysphagia: a Neurology Perspective William Meador, MD Assistant Professor of Neurology, UAB 2.11.16 Disclosures I have no relevant conflicts or potential conflicts to disclose regarding
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Parkinson s Disease Current Treatment Options
 Parkinson s Disease Current Treatment Options Daniel Kassicieh, D.O., FAAN Sarasota Neurology, P.A. PD: A Chronic Neurodegenerative Ds. 1 Million in USA Epidemiology 50,000 New Cases per Year Majority
Parkinson s Disease Current Treatment Options Daniel Kassicieh, D.O., FAAN Sarasota Neurology, P.A. PD: A Chronic Neurodegenerative Ds. 1 Million in USA Epidemiology 50,000 New Cases per Year Majority
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders
 Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Dr Donald Grosset Consultant Neurologist - Honorary Professor Institute of Neurological Sciences - Glasgow University Hypokinetic Parkinson's Disease
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokinetic Movement Disorders Dr Donald Grosset Consultant Neurologist - Honorary Professor Institute of Neurological Sciences - Glasgow University Hypokinetic Parkinson's Disease
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE
 MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
Progressive Degenerative Communication Disorders of Older Adults: Incidence, Pathology and Treatment
 Progressive Degenerative Communication Disorders of Older Adults: Incidence, Pathology and Treatment Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis And Huntington Disease Robert M. Miller, Ph.D. Levels of Degenerative
Progressive Degenerative Communication Disorders of Older Adults: Incidence, Pathology and Treatment Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis And Huntington Disease Robert M. Miller, Ph.D. Levels of Degenerative
Overview. Overview. Parkinson s disease. Secondary Parkinsonism. Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits
 Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview
 Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective. Dr John Coyle
 Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
SWALLOWING DIFFICULTIES IN HD
 Nutrition, eating and swallowing needs, challenges and solutions Workshop SWALLOWING DIFFICULTIES IN HD Angela Nuzzi Speech and Language Pathologist (SLP) EHDN Language Coordinator - Italy The role of
Nutrition, eating and swallowing needs, challenges and solutions Workshop SWALLOWING DIFFICULTIES IN HD Angela Nuzzi Speech and Language Pathologist (SLP) EHDN Language Coordinator - Italy The role of
Speech Therapy Care in ALS. Brittney Skidmore, MS, CCC-SLP
 Speech Therapy Care in ALS Brittney Skidmore, MS, CCC-SLP I have the following relevant financial relationship(s) in the products or services described, reviewed, evaluated or compared in this presentation.
Speech Therapy Care in ALS Brittney Skidmore, MS, CCC-SLP I have the following relevant financial relationship(s) in the products or services described, reviewed, evaluated or compared in this presentation.
Table of Contents. Preface... xi. Part I: Introduction to Movement Disorders
 Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Speech and Language Therapy. Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist
 Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity. Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS
 Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
The symptoms of the Parkinson s disease may vary from person to person. The symptoms might include the following:
 1 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson's disease is a long term disease related to the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system, resulting in the loss of dopamine, which helps in producing
1 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson's disease is a long term disease related to the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system, resulting in the loss of dopamine, which helps in producing
20/11/2013. Dr. Sinead Maguire Neurology Registrar 22 nd November 2013
 Dr. Sinead Maguire Neurology Registrar 22 nd November 2013 The active total care of patients whose disease is not responsive to curative treatment. Control of pain, of other symptoms, and psychological,
Dr. Sinead Maguire Neurology Registrar 22 nd November 2013 The active total care of patients whose disease is not responsive to curative treatment. Control of pain, of other symptoms, and psychological,
Professor Tim Anderson
 Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
Professor Tim Anderson Neurologist University of Otago Christchurch 11:00-11:55 WS #91: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition and Differential Diagnosis 12:05-13:00 WS #102: Shakes Jerks and Spasms - Recognition
2: Symptoms and management
 2: Symptoms and management This section will help you to find out about the likely symptoms of motor neurone disease (MND) and how these can be managed. The following information is an extracted section
2: Symptoms and management This section will help you to find out about the likely symptoms of motor neurone disease (MND) and how these can be managed. The following information is an extracted section
How Speech and Swallowing are Affected with ALS
 Patient Education How Speech and Swallowing are Affected with ALS This handout describes how ALS affects speech and swallowing. For speech issues it covers tips for listeners and speakers and what can
Patient Education How Speech and Swallowing are Affected with ALS This handout describes how ALS affects speech and swallowing. For speech issues it covers tips for listeners and speakers and what can
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
Optimizing Clinical Communication in Parkinson s Disease:
 Optimizing Clinical Communication in Parkinson s Disease:,Strategies for improving communication between you and your neurologist PFNCA Symposium March 25, 2017 Pritha Ghosh, MD Assistant Professor of
Optimizing Clinical Communication in Parkinson s Disease:,Strategies for improving communication between you and your neurologist PFNCA Symposium March 25, 2017 Pritha Ghosh, MD Assistant Professor of
MAXIMIZING FUNCTION IN PARKINSON S DISEASE
 1 MAXIMIZING FUNCTION IN PARKINSON S DISEASE September 13, 2016 End Falls This Falls Conference Jan Goldstein Elman One Step Ahead Mobility Toronto, Ontario Outline An overview of Parkinson s disease (PD):
1 MAXIMIZING FUNCTION IN PARKINSON S DISEASE September 13, 2016 End Falls This Falls Conference Jan Goldstein Elman One Step Ahead Mobility Toronto, Ontario Outline An overview of Parkinson s disease (PD):
Pharmacologic Treatment of Parkinson s Disease. Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology
 + Pharmacologic Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology + Overview n Brief review of Parkinson s disease (PD) n Clinical manifestations n Pathophysiology
+ Pharmacologic Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology + Overview n Brief review of Parkinson s disease (PD) n Clinical manifestations n Pathophysiology
Speech and Swallowing in KD: Soup to Nuts. Neil C. Porter, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Maryland
 Speech and Swallowing in KD: Soup to Nuts Neil C. Porter, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Maryland Disclosures I will not be speaking on off-label use of medications I have no relevant
Speech and Swallowing in KD: Soup to Nuts Neil C. Porter, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Maryland Disclosures I will not be speaking on off-label use of medications I have no relevant
Parkinson s Disease. Prevalence. Mark S. Baron, M.D. Cardinal Features. Clinical Characteristics. Not Just a Movement Disorder
 Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Parkinson Disease. Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC. Presented by: Ontario s Geriatric Steering Committee
 Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
Pharmacologic Treatment of Parkinson s Disease. Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology
 + Pharmacologic Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology + Disclosures n NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT + Learning
+ Pharmacologic Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology + Disclosures n NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT + Learning
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Margo J Nell Dept Pharmacology
 Margo J Nell Dept Pharmacology 1 The extra pyramidal system Separation of cortico-spinal system (pyramidal system, (PS)) from the basal ganglia (extra pyramidal motor system (EPS)) because they produce
Margo J Nell Dept Pharmacology 1 The extra pyramidal system Separation of cortico-spinal system (pyramidal system, (PS)) from the basal ganglia (extra pyramidal motor system (EPS)) because they produce
10/26/2017. Dysphagia in Neurodegenerative Disease: Focus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis & Parkinson s Disease. Disclosures. What we ll discuss
 Dysphagia in Neurodegenerative Disease: Focus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis & Parkinson s Disease Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division
Dysphagia in Neurodegenerative Disease: Focus on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis & Parkinson s Disease Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division
COMMUNICATION. Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT. Impact of Tracheostomy. Normal Speech. Facilitating Communication
 Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT 1. 2. 3. Management of communication needs. Management of swallowing issues. Working with the multidisciplinary team to facilitate weaning. Impact
Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT 1. 2. 3. Management of communication needs. Management of swallowing issues. Working with the multidisciplinary team to facilitate weaning. Impact
parts of the gastrointenstinal tract. At the end of April 2008, it was temporarily withdrawn from the US Market because of problems related to
 parts of the gastrointenstinal tract. At the end of April 2008, it was temporarily withdrawn from the US Market because of problems related to crystallization of the drug, which caused unreliable drug
parts of the gastrointenstinal tract. At the end of April 2008, it was temporarily withdrawn from the US Market because of problems related to crystallization of the drug, which caused unreliable drug
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
EATING SAFELY AND TALKING ABOUT IT KIERA N BERGGREN, MA/CCC-SLP, MS 2018 FSHD CONNECT CONFERENCE
 EATING SAFELY AND TALKING ABOUT IT KIERA N BERGGREN, MA/CCC-SLP, MS 2018 FSHD CONNECT CONFERENCE DISCLOSURES I have no personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
EATING SAFELY AND TALKING ABOUT IT KIERA N BERGGREN, MA/CCC-SLP, MS 2018 FSHD CONNECT CONFERENCE DISCLOSURES I have no personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
The PSP Association. Presentation on the symptoms, care and support of patients with PSP.
 The PSP Association Presentation on the symptoms, care and support of patients with PSP. 1 Presented by: Kathy Miller-Hunt Development Officer Southwest Other names Steele Richardson Olszewski Syndrome
The PSP Association Presentation on the symptoms, care and support of patients with PSP. 1 Presented by: Kathy Miller-Hunt Development Officer Southwest Other names Steele Richardson Olszewski Syndrome
Parts of the motor circuits
 MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA
 TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA ANNE URIKO SPORTS MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION CLINIG OF TARTU UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL 17.09.2010 DYSPHAGIA DIFFICULTY MOVING FOOD FROM MOUTH TO STOMACH
TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA ANNE URIKO SPORTS MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION CLINIG OF TARTU UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL 17.09.2010 DYSPHAGIA DIFFICULTY MOVING FOOD FROM MOUTH TO STOMACH
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
COMMUNICATION AND SWALLOWING DISORDERS IN PARKINSON S DISEASE Challenges, Treatments, and Resources
 COMMUNICATION AND SWALLOWING DISORDERS IN PARKINSON S DISEASE Challenges, Treatments, and Resources Rosemary B. Loftin, M.S. CCC/SLP Supervisor of Speech Pathology Services Mayo Clinic Hospital Arizona
COMMUNICATION AND SWALLOWING DISORDERS IN PARKINSON S DISEASE Challenges, Treatments, and Resources Rosemary B. Loftin, M.S. CCC/SLP Supervisor of Speech Pathology Services Mayo Clinic Hospital Arizona
Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y
 Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y Educational Objectives Improved history taking in patients with movement disorders. Develop a systematic approach to observing and describing
Disorders of Movement M A R T I N H A R L E Y N E U R O L O G Y Educational Objectives Improved history taking in patients with movement disorders. Develop a systematic approach to observing and describing
LSVT LOUD Professional Webinar Series
 LSVT LOUD Professional Webinar Series Title: Atypical and Advanced Parkinsonian Disorders: An Overview and Discussion of Application to LSVT LOUD Presenters: Elizabeth Peterson, MA, CCC-SLP Cynthia Fox,
LSVT LOUD Professional Webinar Series Title: Atypical and Advanced Parkinsonian Disorders: An Overview and Discussion of Application to LSVT LOUD Presenters: Elizabeth Peterson, MA, CCC-SLP Cynthia Fox,
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Parkinsonism is a progressive neurological disorder of muscle movement, usually
Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Parkinsonism is a progressive neurological disorder of muscle movement, usually
PARKINSON S PRIMER. Dr. Kathryn Giles MD, MSc, FRCPC Cambridge, Ontario, Canada
 PARKINSON S PRIMER Dr. Kathryn Giles MD, MSc, FRCPC Cambridge, Ontario, Canada COPYRIGHT 2017 BY SEA COURSES INC. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
PARKINSON S PRIMER Dr. Kathryn Giles MD, MSc, FRCPC Cambridge, Ontario, Canada COPYRIGHT 2017 BY SEA COURSES INC. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Multiple System Atrophy
 Multiple System Atrophy This document has been prepared to help you become more informed about Multiple System Atrophy. It is designed to answer questions about the condition and includes suggestions on
Multiple System Atrophy This document has been prepared to help you become more informed about Multiple System Atrophy. It is designed to answer questions about the condition and includes suggestions on
Movement Disorders. Eric Kraus, MD! Neurology!
 Movement Disorders Eric Kraus, MD! Neurology! Classify Bradykinesia! Tic! Myoclonus! Tremor! Dystonia! Athetosis! Chorea! Ballismus! Case 1 This 64 year-old female has had progression of a tremor over
Movement Disorders Eric Kraus, MD! Neurology! Classify Bradykinesia! Tic! Myoclonus! Tremor! Dystonia! Athetosis! Chorea! Ballismus! Case 1 This 64 year-old female has had progression of a tremor over
Best Medical Treatments for Parkinson s disease
 Best Medical Treatments for Parkinson s disease Bernadette Schöneburg, M.D. June 20 th, 2015 What is Parkinson s Disease (PD)? Progressive neurologic disorder that results from the loss of specific cells
Best Medical Treatments for Parkinson s disease Bernadette Schöneburg, M.D. June 20 th, 2015 What is Parkinson s Disease (PD)? Progressive neurologic disorder that results from the loss of specific cells
Martin A. Samuels, M.D. MOVEMENT DISORDERS
 Martin A. Samuels, M.D. MOVEMENT DISORDERS I. Nomenclature of Movement Disorders A. Too Little Movement 1. Paralysis (paresis) 2. Rigidity a. spasticity (pyramidal) b. "lead pipe" (extra pyramidal) c.
Martin A. Samuels, M.D. MOVEMENT DISORDERS I. Nomenclature of Movement Disorders A. Too Little Movement 1. Paralysis (paresis) 2. Rigidity a. spasticity (pyramidal) b. "lead pipe" (extra pyramidal) c.
A Case Study: Multiple Sclerosis. Kayla Jensen February 2013
 A Case Study: Multiple Sclerosis Kayla Jensen February 2013 Patient Profile SL is a 59 year old Caucasian Woman Lives in Utah Retired School teacher Separated from husband No Hx of tobacco/alcohol use
A Case Study: Multiple Sclerosis Kayla Jensen February 2013 Patient Profile SL is a 59 year old Caucasian Woman Lives in Utah Retired School teacher Separated from husband No Hx of tobacco/alcohol use
Extrapyramidal Motor System. Basal Ganglia or Striatum. Basal Ganglia or Striatum 3/3/2010
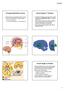 Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
PARKINSON S DISEASE. Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons 5/11/16 CARDINAL FEATURES OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Parkinson s disease
 5/11/16 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease Prevalence increases with age (starts 40s60s) Seen in all ethnic groups, M:F about 1.5:1 Second most common neurodegenerative disease Genetics role greater
5/11/16 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease Prevalence increases with age (starts 40s60s) Seen in all ethnic groups, M:F about 1.5:1 Second most common neurodegenerative disease Genetics role greater
Communicating About OFF Episodes With Your Doctor
 Communicating About OFF Episodes With Your Doctor Early in Parkinson s disease (PD), treatment with levodopa and other anti-pd drugs provides continuous benefit. As the disease progresses, however, symptom
Communicating About OFF Episodes With Your Doctor Early in Parkinson s disease (PD), treatment with levodopa and other anti-pd drugs provides continuous benefit. As the disease progresses, however, symptom
Disclosures. This speaker has indicated there are no relevant financial relationships to be disclosed.
 Disclosures This speaker has indicated there are no relevant financial relationships to be disclosed. Parkinson s Disease, Huntington s Disease and ALS: A brief overview of three diagnoses Leo G. Rafail,
Disclosures This speaker has indicated there are no relevant financial relationships to be disclosed. Parkinson s Disease, Huntington s Disease and ALS: A brief overview of three diagnoses Leo G. Rafail,
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders
 Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Reluctance or refusal to feed or eat. Understanding Feeding Aversion in a City Full of Foodies. Presentation Outline. Learning Objectives
 Understanding Feeding Aversion in a City Full of Foodies Amy Houtrow, MD, MPH Pediatric Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation UCSF Department of Pediatrics June 2, 2007 Learning Objectives Learners will be
Understanding Feeding Aversion in a City Full of Foodies Amy Houtrow, MD, MPH Pediatric Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation UCSF Department of Pediatrics June 2, 2007 Learning Objectives Learners will be
Pediatric Patients. Neuromuscular Disease. Teera Kijmassuwan, MD Phetcharat Netmuy, B.N.S., MA Oranee Sanmaneechai, MD : Preceptor
 Patient Management Pediatric Patients with Neuromuscular Disease Teera Kijmassuwan, MD Phetcharat Netmuy, B.N.S., MA Oranee Sanmaneechai, MD : Preceptor Case Thai boy 1 year old Present with Respiratory
Patient Management Pediatric Patients with Neuromuscular Disease Teera Kijmassuwan, MD Phetcharat Netmuy, B.N.S., MA Oranee Sanmaneechai, MD : Preceptor Case Thai boy 1 year old Present with Respiratory
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), sometimes called Lou Gehrig's disease, is a rapidly progressive, invariably fatal neurological
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), sometimes called Lou Gehrig's disease, is a rapidly progressive, invariably fatal neurological
Chapter 20. Media Directory. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Alzheimer s Disease. Huntington s Chorea. Multiple Sclerosis
 Chapter 20 Drugs for Degenerative Diseases of the Nervous System Slide 18 Media Directory Levadopa Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Alzheimer s Disease Amyotrophic Lateral
Chapter 20 Drugs for Degenerative Diseases of the Nervous System Slide 18 Media Directory Levadopa Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Alzheimer s Disease Amyotrophic Lateral
The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us. Introduction
 The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division of Communication Sciences & Disorders
The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division of Communication Sciences & Disorders
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Part I Curriculum & Weights
 American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
I do not have any disclosures
 Alzheimer s Disease: Update on Research, Treatment & Care Clinicopathological Classifications of FTD and Related Disorders Keith A. Josephs, MST, MD, MS Associate Professor & Consultant of Neurology Mayo
Alzheimer s Disease: Update on Research, Treatment & Care Clinicopathological Classifications of FTD and Related Disorders Keith A. Josephs, MST, MD, MS Associate Professor & Consultant of Neurology Mayo
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Motor neurone disease: the use of non-invasive ventilation in the management of motor neurone disease 1.1 Short title Motor
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Motor neurone disease: the use of non-invasive ventilation in the management of motor neurone disease 1.1 Short title Motor
Parkinson s Disease Update. Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Movement disorder neurologist Providence St. Vincent s
 Parkinson s Disease Update Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Movement disorder neurologist Providence St. Vincent s What is a movement disorder? Neurological disorders that affect ability to move by causing
Parkinson s Disease Update Presented by Joanna O Leary, MD Movement disorder neurologist Providence St. Vincent s What is a movement disorder? Neurological disorders that affect ability to move by causing
CASE STUDIES CONTENTS PART REINKE' S EDEMA, 3 VOCAL CORD DYSFUNCTION, 7. fiabit COUGH, 15 MUSCLE TENSION DYSPHONIA, 18 PUBERPHONIA, 33
 CONTENTS PART I CASE STUDIES REINKE' S EDEMA, 3 CASE STUDY 1-1: Postoperative Reinke's Edema, 4 VOCAL CORD DYSFUNCTION, 7 CASE STUDY 2-1: Vocal Cord Dysfunction, 8 CASE STUDY 2-2: Vocal Cord Dysfunction,
CONTENTS PART I CASE STUDIES REINKE' S EDEMA, 3 CASE STUDY 1-1: Postoperative Reinke's Edema, 4 VOCAL CORD DYSFUNCTION, 7 CASE STUDY 2-1: Vocal Cord Dysfunction, 8 CASE STUDY 2-2: Vocal Cord Dysfunction,
The Role of the Speech Language Pathologist & Spinal Cord Injury
 The Role of the Speech Language Pathologist & Spinal Cord Injury Facts According to the National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center (NSCISC) there are approxiamtely 12,000 new spinal cord injuries (SCI)
The Role of the Speech Language Pathologist & Spinal Cord Injury Facts According to the National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center (NSCISC) there are approxiamtely 12,000 new spinal cord injuries (SCI)
POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN
 POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN WHAT IS POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS)? Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is a condition that affects polio survivors years after recovery
POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN WHAT IS POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS)? Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is a condition that affects polio survivors years after recovery
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161,
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1990, 161, Suppl., 21-27 Involuntary Movements OLAF B. PAULSON Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, 9 Blegdamsvej, DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark PAULSON, O.B. Involuntary Movements.
Objectives. Emerging Treatments in Parkinson s s Disease. Pathology. As Parkinson s progresses it eventually affects large portions of the brain.
 Objectives Emerging Treatments in Parkinson s s Disease 1) Describe recent developments in the therapies for Parkinson s Disease Jeff Kraakevik MD Assistant Professor OHSU/Portland VAMC Parkinson s Center
Objectives Emerging Treatments in Parkinson s s Disease 1) Describe recent developments in the therapies for Parkinson s Disease Jeff Kraakevik MD Assistant Professor OHSU/Portland VAMC Parkinson s Center
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Amyotrophic
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Amyotrophic
Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation David A. Muir Course Outline Physiology of Swallow
 Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation Mary Spremulli, MA, CCC-SLP Passy-Muir Clinical Consultant spre713@hotmail.com (949) 833-8255 David A. Muir 23 year-old ventilator
Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation Mary Spremulli, MA, CCC-SLP Passy-Muir Clinical Consultant spre713@hotmail.com (949) 833-8255 David A. Muir 23 year-old ventilator
MOVEMENT DISORDERS UPDATE H. MURRAY TODD, M.D., F.A.A.N.
 MOVEMENT DISORDERS UPDATE H. MURRAY TODD, M.D., F.A.A.N. Movement Disorders Hypokinesia : decreased voluntary and automatic movements Hyperkinesia : excessive movements HYPOKINESIAS Parkinson s disease
MOVEMENT DISORDERS UPDATE H. MURRAY TODD, M.D., F.A.A.N. Movement Disorders Hypokinesia : decreased voluntary and automatic movements Hyperkinesia : excessive movements HYPOKINESIAS Parkinson s disease
ROLE OF THE DIETITIAN. Aims of Dietetic Treatment NUTRITIONAL ISSUES WHY? MALNUTRITION NUTRITONAL MANAGEMENT OF MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE.
 NUTRITONAL MANAGEMENT OF MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE. ROLE OF THE DIETITIAN SALLY DARBY NEUROLOGY DIETITIAN Not just tube feeding Referral soon after diagnosis Advise on healthy eating for MND Monitor nutritional
NUTRITONAL MANAGEMENT OF MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE. ROLE OF THE DIETITIAN SALLY DARBY NEUROLOGY DIETITIAN Not just tube feeding Referral soon after diagnosis Advise on healthy eating for MND Monitor nutritional
Swallowing Screen Why? How? and So What? พญ.พวงแก ว ธ ต สก ลช ย ภาคว ชาเวชศาสตร ฟ นฟ คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล
 Swallowing Screen Why? How? and So What? พญ.พวงแก ว ธ ต สก ลช ย ภาคว ชาเวชศาสตร ฟ นฟ คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Dysphagia in Stroke The incidence of dysphagia after stroke ranging from 23-50% 1 Location
Swallowing Screen Why? How? and So What? พญ.พวงแก ว ธ ต สก ลช ย ภาคว ชาเวชศาสตร ฟ นฟ คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Dysphagia in Stroke The incidence of dysphagia after stroke ranging from 23-50% 1 Location
Medication for the Terminal Patient Who Can t Swallow. Annette T. Carron, DO Director Geriatrics & Palliative Care Botsford Hospital
 Medication for the Terminal Patient Who Can t Swallow Annette T. Carron, DO Director Geriatrics & Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose Route and medication
Medication for the Terminal Patient Who Can t Swallow Annette T. Carron, DO Director Geriatrics & Palliative Care Botsford Hospital Disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose Route and medication
Applied physiology. 7- Apr- 15 Swallowing Course/ Anatomy and Physiology
 Applied physiology Temporal measures: Oral Transit Time (OTT) Pharyngeal Delay Time (PDT) Pharyngeal Transit Time (PTT) Oropharyngeal Swallowing Efficiency Score (OPSE score) 7- Apr- 15 Swallowing Course/
Applied physiology Temporal measures: Oral Transit Time (OTT) Pharyngeal Delay Time (PDT) Pharyngeal Transit Time (PTT) Oropharyngeal Swallowing Efficiency Score (OPSE score) 7- Apr- 15 Swallowing Course/
Drugs Affecting the Central Nervous System
 Asst Prof Inam S Arif isamalhaj@yahoo.com Drugs Affecting the Central Nervous System Ass Efferent neurons in ANS Neurodegenerative Diseases Parkinson s Disease Multiple Sclerosis Alzheimer s Disease
Asst Prof Inam S Arif isamalhaj@yahoo.com Drugs Affecting the Central Nervous System Ass Efferent neurons in ANS Neurodegenerative Diseases Parkinson s Disease Multiple Sclerosis Alzheimer s Disease
Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE
 Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Course Participant will: 1. Be familiar with the pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease (PD) 2. Understand clinical
Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Course Participant will: 1. Be familiar with the pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease (PD) 2. Understand clinical
Neurological Conditions: Disease Trajectory and Hospice Eligibility
 Neurological Conditions: Disease Trajectory and Hospice Eligibility Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources/HEN Course Materials & Disclosure Course materials including
Neurological Conditions: Disease Trajectory and Hospice Eligibility Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources/HEN Course Materials & Disclosure Course materials including
The Shaking Palsy of 1817
 The Shaking Palsy of 1817 A Treatment Update on Parkinson s Disease Dr Eitzaz Sadiq Neurologist CH Baragwanath Acadamic Hospital Parkinson s Disease O Premature death of dopaminergic neurons O Symptoms
The Shaking Palsy of 1817 A Treatment Update on Parkinson s Disease Dr Eitzaz Sadiq Neurologist CH Baragwanath Acadamic Hospital Parkinson s Disease O Premature death of dopaminergic neurons O Symptoms
Objectives. Distinguishing Parkinson s disease from other parkinsonian and tremor syndromes. Characteristics. Basal Ganglia Structures
 12:45 1:30 pm PD or not PD? Distinguishing Parkinson s Disease From Other Parkinsonian and Tremor Syndromes SPEAKER Jennifer G. Goldman, MD, MS Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships
12:45 1:30 pm PD or not PD? Distinguishing Parkinson s Disease From Other Parkinsonian and Tremor Syndromes SPEAKER Jennifer G. Goldman, MD, MS Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships
Medicaid Provider Manual
 2.4 SPEECH, LANGUAGE AND HEARING THERAPY (INCLUDES ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY DEVICE SERVICES) 2.4.A. SPEECH, LANGUAGE AND HEARING THERAPY Definition Prescription Provider Qualifications Evaluations for Speech
2.4 SPEECH, LANGUAGE AND HEARING THERAPY (INCLUDES ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY DEVICE SERVICES) 2.4.A. SPEECH, LANGUAGE AND HEARING THERAPY Definition Prescription Provider Qualifications Evaluations for Speech
Course Handouts & Disclosure
 ALS: DISEASE TRAJECTORY AND HOSPICE ELIGIBILITY Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources Inc Hospice Education Network Inc Course Handouts & Disclosure To download presentation
ALS: DISEASE TRAJECTORY AND HOSPICE ELIGIBILITY Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources Inc Hospice Education Network Inc Course Handouts & Disclosure To download presentation
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
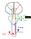 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Radicava (edaravone)
 *- Florida Healthy Kids Radicava (edaravone) Override(s) Prior Authorization Approval Duration 1 year Medications Radicava (edaravone) APPROVAL CRITERIA Requests for Radicava (edaravone) may be approved
*- Florida Healthy Kids Radicava (edaravone) Override(s) Prior Authorization Approval Duration 1 year Medications Radicava (edaravone) APPROVAL CRITERIA Requests for Radicava (edaravone) may be approved
DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS
 DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS Drugs for Neurodegenerative Diseases 2 Dr Karamallah S. Mahmood PhD Clinical Pharmacology 1 DRUGS USED IN PARKINSON S DISEASE/ B. Selegiline and rasagiline Selegiline, also called
DRUGS THAT ACT IN THE CNS Drugs for Neurodegenerative Diseases 2 Dr Karamallah S. Mahmood PhD Clinical Pharmacology 1 DRUGS USED IN PARKINSON S DISEASE/ B. Selegiline and rasagiline Selegiline, also called
Symptom management in ALS. David Walk, M.D. Medical Director ALS Certified Center of Excellence University of Minnesota Health
 Symptom management in ALS David Walk, M.D. Medical Director ALS Certified Center of Excellence University of Minnesota Health Outline of today s points Overview Disease state Clinic team Assessment Functional
Symptom management in ALS David Walk, M.D. Medical Director ALS Certified Center of Excellence University of Minnesota Health Outline of today s points Overview Disease state Clinic team Assessment Functional
475 GERIATRIC PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY (p.1)
 475 GERIATRIC PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY (p.1) I. General Information? Use lower doses? Start low and go slow? Expect prolonged elimination ½ lives? Expect sedative-hypnotics to be dementing, to impair cognitive
475 GERIATRIC PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY (p.1) I. General Information? Use lower doses? Start low and go slow? Expect prolonged elimination ½ lives? Expect sedative-hypnotics to be dementing, to impair cognitive
Dysphagia and Swallowing. Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern
 Dysphagia and Swallowing Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern Scope of the Problem and Incidence 15 million people in the US have some form of Dysphagia. Every year, 1 million people are diagnosed with
Dysphagia and Swallowing Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern Scope of the Problem and Incidence 15 million people in the US have some form of Dysphagia. Every year, 1 million people are diagnosed with
Multiple Sclerosis , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. nr Last reviewed: 04/17/2017 1
 Multiple Sclerosis Introduction Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a disease of the brain and spinal cord. Most patients with multiple sclerosis are able to lead a very functional life. However, MS causes a
Multiple Sclerosis Introduction Multiple sclerosis, or MS, is a disease of the brain and spinal cord. Most patients with multiple sclerosis are able to lead a very functional life. However, MS causes a
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
2/18/ yo man with history of mild developmental delay and chorea of unclear etiology, with new complaints of speech difficulty
 18 yo man with history of mild developmental delay and chorea of unclear etiology, with new complaints of speech difficulty Audrey Foster-Barber UCSF Child Neurology February 18, 2011 Several years of
18 yo man with history of mild developmental delay and chorea of unclear etiology, with new complaints of speech difficulty Audrey Foster-Barber UCSF Child Neurology February 18, 2011 Several years of
History Parkinson`s disease. Parkinson's disease was first formally described in 1817 by a London physician named James Parkinson
 Parkinsonismm History Parkinson`s disease Parkinson's disease was first formally described in 1817 by a London physician named James Parkinson Definition : Parkinsonism: Parkinsonism is a progressive neurological
Parkinsonismm History Parkinson`s disease Parkinson's disease was first formally described in 1817 by a London physician named James Parkinson Definition : Parkinsonism: Parkinsonism is a progressive neurological
