Anesthesiologist intervention during cataract surgery under topical or peribulbar anesthesia: a propensity model comparison
|
|
|
- Jeffery Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eur J Ophthalmol 2010; 20 ( 4) : Original Article Anesthesiologist intervention during cataract surgery under topical or peribulbar anesthesia: a propensity model comparison Marco Gemma 1, Luigi Gioia 1, Elisa Dedola 1, Benedetta Basta 1, Ingrid Bianchi 2, Francesco Fasce 2, Luigi Beretta 1 1 Anesthesia & Intensive Care Unit, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milano 2 Ophthalmology Unit, Head and Neck Department, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milano - Italy Pu r p o s e. To compare the incidence and type of anesthesiologist intervention during cataract surgery under peribulbar (PA) or topical (TA) anesthesia in a day-surgery monitored anesthesia care setting (monitoring provided by nurses with the anesthesiologist available on an on-call basis). Me t h o d s. From a prospective database of all phacoemulsifications performed in our hospital (January 2008-January 2009), 97 patients submitted to cataract surgery under PA were matched with 97 patients submitted to the same surgery under TA by a propensity model. The resulting groups were homogeneous as to history of antihypertensive therapy administered on the day of surgery and not administered on the day of surgery, cardiologic history, neurologic history, psychiatric history, anxiolytic assumption, and history of diabetes mellitus. We compared the incidence of intervention of the anesthesiologist between groups and the type of adverse event triggering such interventions. Re s u l t s. The anesthesiologist was called in 37 (38.14%) cases in the PA group and in 27 (27.84%) cases in the TA group (37 [38.14%]) (p=0.123). Only the occurrence of agitation differed significantly between groups (9 [9.28%] patients in the TA group vs 24 [24.74%] patients in the PA group; p=0.004). Co n c l u s i o n s. Monitored anesthesia care is feasible for cataract surgery both under PA or TA. PA still remains an appealing alternative to TA during cataract surgery for patients incapable of keeping the operating eye in the primary position or with incoercible blinking, photophobia, or phacodonesis. A greater incidence of agitation is to be expected and adequate premedication with anxiolytics should be considered if PA is chosen. (Eur J Ophthalmol 2010; 20: ) Ke y Wo r d s. Cataract, Monitored anesthesia care, Peribulbar anesthesia, Phacoemulsification, Propensity score, Topical anesthesia Accepted: January 8, 2010 INTRODUCTION Cataract surgery is one of the most frequent surgical procedures on elderly patients in industrialized countries (1, 2). It was traditionally performed under peribulbar anesthesia (PA), but during the last 2 decades improvement in surgical techniques (3-13) boosted the use of topical anesthesia (TA) for cataract surgery. Although some limitations of TA in comparison with PA have been described (14, 15), several works provided evidence that TA is a valid alternative to PA for cataract surgery (16-19). Adequate pain control, short recovery time, and good safety profile make TA an appealing technique for daysurgery phacoemulsification under monitored anesthesia care. In this setting, cost-effectiveness may be improved as perioperative monitoring is provided by nurses and the anesthesiologist is immediately available on an on-call basis (monitored anesthesia care). We studied data from a prospectively collected database of patients submitted to cataract surgery under monitored 2010 Wichtig Editore - ISSN EJO_D_09_611_Gemma.indd :59:11
2 Cataract surgery under topical or peribulbar monitored anesthesia care anesthesia care. We constructed a propensity model to compare the incidence of anesthesiologist call by the attending nurse between a group of patients submitted to PA and a matched group of patients submitted to TA. The type of adverse event triggering the anesthesiologist intervention was also studied. METHODS Clinical data of all consecutive patients submitted to phacoemulsification and intraocular lens (IOL) implantation under TA or PA at the San Raffaele Hospital of Milan from January 2008 to January 2009 were prospectively collected in a database for clinical purposes. The utilization of these data for scientific purposes was approved by our local Ethics Committee. The database included 2005 patients submitted to TA and 97 patients submitted to PA. This reflects our current practice: we consider TA the standard anesthesia for cataract surgery and we administer PA only to patients incapable of keeping the operating eye in the primary position or with incoercible blinking, photophobia, or phacodonesis. We matched our 97 PA patients with an equal number of patients selected among the 2005 TA patients in the database. Case matching was retrospectively obtained with a propensity model. This incorporated 14 variables that were considered possibly relevant with respect to the need of anesthesiologist involvement during monitored anesthesia care (see Statistics section). Outpatient evaluation was performed in all cases within 2 weeks before surgery by 1 of 2 senior internal medicine physicians. Clinical history was acquired and physical examination performed. Preoperative full blood count and coagulation tests were performed in all patients. Electrocardiography was performed if required on a clinical basis. Patients were advised to abstain from food and liquids 6 hours before surgery and to take all their usual preoperative medications on the day of surgery, except for insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs (in these cases immediate preoperative glycemia was determined). Antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy were not interrupted if TA was scheduled, but patients undergoing PA were asked to discontinue antiplatelets 5 days before surgery and anticoagulants 3 days before surgery (in this case low-molecular-weight heparin was initiated). According to the outpatient preoperative evaluation, the ASA physical status score (20) was determined and the presence or absence of the following was assessed: history of antihypertensive therapy administered also on the day of surgery; history of antihypertensive therapy not administered on the day of surgery; cardiologic history (previous diagnosis of cardiac ischemic disease, arrhythmia, valvulopathy, cardiac failure); neurologic history (previous diagnosis of chronic cerebral ischemia, epilepsy, Parkinson disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, dementia, neuromyopathy, migraine); psychiatric history (previous diagnosis of major mood disorder, psychosis, neurosis); anxiolytic assumption; and history of diabetes mellitus (either type I or II). Cataract surgery took place either in the morning (8 am-2 pm) or in the afternoon (2 pm-8 pm) and was performed by 1 of 2 senior ophthalmologists. Patients were admitted on the day of surgery. Before entering the operative room, a nurse established an intravenous line, connected it to a 100-mL saline drip, and applied oxybuprocaine hydrochloride 0.4% and ciprofloxacin 0.3% to both eyes. Tropicamide 0.5% and phenylephrine 10% were applied to the operated eye. Povidone 10% iodine solution was used for primary disinfection of periorbital skin. Thereafter, anesthesia was provided in the operating room. If PA was scheduled, it was administered according to our standard practice (21, 22). Mepivacaine 2% and hyaluronidase 1/10 (total volume 3-5 ml) were administered with a 5-mL syringe. The needle (Atkinson 25G 1.25 ) was inserted inferotemporally and transcutaneously and the drugs were gently injected after aspiration to avoid risk of intravascular injection. Afterwards, ocular compression was applied for 3-5 minutes until a satisfactory anesthesia was achieved. No sedation/analgesia was provided for PA placement. If TA was scheduled, lidocaine hydrochloride 4% was administered and povidone 5% iodine solution was instilled in the operating eye. No intracameral anesthesia was performed as part of the TA protocol. Intraoperative monitoring was provided by senior registered nurses (monitored anesthesia care). Electrocardiography (lead II) and pulse oximetry were continuously measured by a Philips Anaesthesia V24C (Germany) monitoring device. Heart rate and noninvasive arterial blood pressure were recorded every 5 minutes. An on-call anesthesiologist was immediately available and was called by the attending nurse if one or more of the following occurred: nonarterial hypertension: systolic blood 688 EJO_D_09_611_Gemma.indd :59:11
3 Gemma et al pressure >200 mmhg or diastolic blood pressure >110 mmhg; arterial hypotension: systolic blood pressure <100 mmhg; tachycardia: heart rate >120 beats per minute; bradycardia: heart rate <50 beats per minute; ECG alterations suggestive of arrhythmia, ischemia, or infarction; psychomotor agitation that could hamper surgery; bradypnea: respiratory rate <10 per minute; cough. The need for anesthesiologist involvement as well as the administered treatment was documented. Length of surgery was recorded. At the end of surgery, ciprofloxacin 0.3% and povidone 10% iodine solution were administered to the operated eye. After dressing, monitoring was interrupted and the intravenous line removed. Patients waited for discharge in a recovery room where a nurse was constantly present and were then discharged according to medical advice 2-3 hours after the end of surgery. Statistics The database included 2005 patients submitted to TA and 97 patients submitted to PA. In order to properly match patients submitted to PA with patients submitted to TA, a propensity model was constructed (23-25). Logistic regression analysis was run incorporating 14 variables: gender, age, body mass index, ASA status (1-2 vs 3-4), length of surgery, surgical session (morning vs afternoon), operated eye (first vs second), history of antihypertensive therapy assumed also on the day of surgery, history of antihypertensive therapy not assumed on the day of surgery, cardiologic history, neurologic history, psychiatric history, anxiolytic assumption, and history of diabetes mellitus. Nominal variables were expressed as dummy variables. The resulting coefficients were applied to each variable and to the intercept to calculate the propensity score of each case. For each patient in the PA group the patient with the nearest propensity score was selected among the TA patients. After matching, the resulting TA and PA groups did not differ significantly in any of the 14 variables considered (see Tab. I). Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD and compared with the paired data t test. Nominal variables are expressed as number (%) and compared with the McNemar test. Statistical analyses were performed with dedicated software (Systat 12 version , Systat Software Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). RESULTS Although the anesthesiologist was called by the attending nurse more often for patients in the PA group than in the TABLE I - VARIABLES USED FOR THE CONSTRUCTION OF THE PROPENSITY MODEL topical anesthesia Peribulbar anesthesia p Age, y 66.5± ± Body mass index 25.49± ± Length of surgery, min 18.0± ± Male 49 (50.52) 55 (56.70) ASA (1 2) 86 (88.66) 82 (84.54) Surgical session (morning) 61 (62.89) 58 (59.79) Operating eye (first) 57 (58.76) 57 (58.76) Antihypertensive therapy assumed also on the day of surgery 43 (44.33) 44 (45.36) Antihypertensive therapy not assumed on the day of surgery 12 (12.37) 10 (10.31) Cardiologic history 17 (17.53) 24 (24.74) Neurologic history 5 (5.16) 7 (7.22) Psychiatric history 1 (1.03) 3 (3.09) Anxiolytic assumption 6 (6.19) 5 (5.16) History of diabetes mellitus 15 (15.46) 21 (21.65) After matching, the 2 groups do not differ in any of the variables considered. Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD and compared with the paired data t test. Nominal variables are expressed as n (%) and compared with the McNemar test. 689 EJO_D_09_611_Gemma.indd :59:11
4 Cataract surgery under topical or peribulbar monitored anesthesia care TA group (37 [38.14%] vs 27 [27.84%] cases, respectively), this difference was not significant (p=0.123). Similarly, drug administration by the anesthesiologist was more frequent for patients in the PA group than in the TA group (36 [37.11%] vs 24 [24.74%] cases, respectively), although this difference was not significant (p=0.058). Table II reports on the occurrence of adverse events triggering the anesthesiologist call by the attending nurse. Two events account for the majority of anesthesiologist calls; namely, agitation (10.31% of TA and 24.74% of PA patients) and arterial hypertension (15.46% of TA and 14.43% of PA patients). The incidence of agitation was significantly different between groups (p= 0.004). The incidence of the other categories of adverse event did not differ significantly between groups. Bradypnea never occurred in our patients. Hypotension (2 patients [2.06%]), cough (2 patients [2.06%]), and ECG alterations (1 patient [1.03%] occurred only in the PA group. Table III reports on the occurrence of adverse events requiring drug administration by the anesthesiologist. Only the occurrence of agitation differed significantly between groups (9 [9.28%] patients in the TA group vs 24 [24.74%] patients in the PA group; p=0.004). No life-threatening complications occurred in our patients and intraoperative complications never required the interruption of surgery. DISCUSSION Local (ocular injury, retrobulbar hemorrhage, posterior vitreous hypertension, extraocular muscle damage) and sys- TABLE II - OCCURRENCE OF ADVERSE EVENTS PROMPTING THE ANESTHESIOLOGIST CALL BY THE ATTENDING NURSE Topical anesthesia Peribulbar anesthesia p No. % no. % Agitation * Hypertension Hypotension Bradycardia Tachycardia Bradypnea ECG alteration Cough Anesthesiologist call The single items do not sum up to the total number of anesthesiologist calls as more than one event could have prompted the anesthesiologist s intervention. *p<0.05. TABLE III - OCCURRENCE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION BY THE ANESTHESIOLOGIST ACCORDING TO ADVERSE EVENTS Topicalanesthesia Peribulbaranesthesia p No. % no. % Agitation * Hypertension Hypotension Bradycardia Tachycardia Bradypnea ECG alteration Cough Drug administration by the anesthesiologist The single items do not sum up to the total number of anesthesiologist calls as more than one event could have triggered the anesthesiologist s intervention. *p< EJO_D_09_611_Gemma.indd :59:11
5 Gemma et al temic (anesthetic systemic toxicity, pain, agitation) complications have been described during PA anesthesia for cataract surgery (26, 27). In particular, a variable incidence (3.2%-54%) of intraoperative systemic adverse events during PA has been reported (16, 28-31). The incidence of intraoperative systemic complications during cataract surgery under TA is similarly variable, but tends to be lower (2.9%-25.7%) (16, 32, 33). This contributed to the increasing popularity of TA for cataract surgery, together with the rapid postoperative recovery it warrants (34, 35) and the good level of analgesia it provides (3, 36). Nevertheless, cardiovascular instability and psychomotor agitation have been reported with TA (32, 37, 38) and in a previous randomized study patients significantly preferred PA over TA (14). Other studies that randomly compared PA and TA during cataract surgery reported a similar incidence of complications and suggest that TA may be preferable (17-19). A recent study (16) on 2020 patients found a significantly greater incidence of systemic complications in patients receiving PA. In our hospital, monitored anesthesia care is routinely provided by trained nurses to patients undergoing cataract surgery. The anesthesiologist is immediately available on an on-call basis. Although there is no full agreement about this topic, several authors suggest the safety and efficacy of this strategy (28-29, 32, 39). In our study, we compared the incidence of anesthesiologist intervention between a group of patients submitted to cataract surgery under PA and a paired group of patients submitted to the same type of surgery under TA. Matching of the patients was obtained by a propensity model (23-25). This model allowed homogeneity for a number of items that potentially affect the occurrence of intraoperative systemic complications. For example, the chance of occurrence of systemic complications may be greater as surgery is prolonged, the experience of previous cataract surgery may boost agitation, and elderly patients or patients with comorbidities may have more systemic complications. The latter item is particularly important since elderly patients and patients with comorbidities are the majority of cataract surgery patients (40) and their number is expected to grow (32). It should be noted that patients undergoing PA anesthesia were selected according to our standard practice; namely, they were patients incapable of keeping the operating eye in the primary position or with incoercible blinking, photophobia, or phacodonesis. This patient selection cannot be corrected by the propensity model and could account for any difference we observed between groups. However, our study design allows a retrospective analysis of our series by eliminating several confounding variables. Another limitation of our study, which is intrinsic to the propensity model method, is that the 2 groups may actually differ significantly in items we did not incorporate in the model. The rate of anesthesiologist intervention was not different between groups, although a trend towards a higher rate in the PA group was apparent. This trend was more pronounced as only the anesthesiologist interventions leading to drug administration were considered. It is possible that our study was underpowered to detect this possible difference. With respect to the type of complication that triggered the anesthesiologistís intervention, we found that agitation was significantly more frequent in the PA group, and this was more evident as only the agitation episodes requiring drug administration were considered. This feature is important since agitation was the most frequent adverse event in our patients and since it has a straightforward interpretation. In fact, it is conceivable that the invasive PA maneuver may generate anxiety and possibly pain without providing better analgesia than TA during surgery. This result is in contrast with a previous work (15) that reports on a significantly greater need for additional sedation in patients under TA than in patients under PA, but patients in that study received routine fentanyl administration before surgery and it is possible that this may have reduced patient collaboration during surgery. On the other hand, it is conceivable that our practice of administering no routine premedication before cataract surgery may have increased the occurrence of intraoperative agitation. Routine preoperative and intraoperative sedation is provided in many centers, but may actually increase the occurrence of systemic complications (30) and has been found not to improve operative conditions and outcome (15). We reported both the global incidence of anesthesiologist interventions and the incidence of drug administration by the anesthesiologist. This issue may help in understanding the real severity of systemic adverse events during monitored anesthesia care. Unfortunately, it is underreported by previous works. Since drug administration occurred in the majority of the reported interventions, it is conceivable that the anesthesiologist calls by the attending nurses were correctly motivated. 691 EJO_D_09_611_Gemma.indd :59:12
6 Cataract surgery under topical or peribulbar monitored anesthesia care Our data suggest that monitored anesthesia care is feasible for cataract surgery under PA or TA. PA remains an appealing alternative to TA during cataract surgery for patients incapable of keeping the operating eye in the primary position or with incoercible blinking, photophobia, or phacodonesis. A greater incidence of agitation is to be expected and adequate premedication with anxiolytics should be considered as PA is chosen. Address for correspondence: Marco Gemma, MD Anesthesia and Intensive Care Unit San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milano, Italy Via Olgettina 60 Milano, Italy gemma.marco@hsr.it The authors report no proprietary interest or financial support. REFERENCES 1. Klein BE, Klein R, Moss SE. Incident cataract surgery: The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology 1997; 104: Panchapakesan J, Mitchell P, Tumuluri K, Rochtchina E, Foran S, Cumming RG. Five year incidence of cataract surgery: The Blue Mountains Eye Study. Br J Ophthalmol 2003; 87: Virtanen P, Huha T. Pain in scleral pocket incision cataract surgery using topical and peribulbar anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998; 24: Tseng S-H, Chen FK. A randomized clinical trial of combined topical-intracameral anesthesia in cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 1998; 105: Jacobi PC, Dietlein TS, Jacobi FK. A comparative study of topical vs retrobulbar anesthesia in complicated cataract surgery. Arch Ophthalmol 2000; 118: Leaming DV. Practice styles and preferences of ASCRS membersó2003 survey. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004; 30: Fichman RA. Use of topical anesthesia alone in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1996; 22: Roman S, Auclin F, Ullern M. Topical versus peribulbar anesthesia in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1996; 22: Maclean H, Burton T, Murray A. Patient comfort during cataract surgery with modified topical and peribulbar anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg 1997; 23: Patel BC, Clinch TE, Burns TA, Shomaker ST, Jessen R, Crandall AS. Prospective evaluation of topical versus retrobulbar anesthesia: a converting surgeonís experience. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998; 24: Bellucci R. Anesthesia for cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 1999; 10: Naor J, Slomovic AR. Anesthesia modalities for cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2000; 11: Nielsen PJ, Allerød CW. Evaluation of local anesthesia techniques for small incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998; 24: Boezaart A, Berry R. Topical anesthesia versus retrobulbar block for cataract surgery: the patientsí perspective. J Clin Anesth 2000; 12: Kallio H, Uusitalo RJ, Maunuksela E-L. Topical anesthesia with or without Propofol sedation versus retrobulbar/peribulbar anesthesia for cataract extraction. J Cataract Refract Surg 2001; 27: Stupp T, Hassouna I, Soppart K, Thanos S, Foerster W. Systemic adverse events: a comparison between topical and peribulbar anaesthesia in cataract surgery. Ophthalmologica 2007; 221: Sauder G, Jonas JB. Topical versus peribulbar anaesthesia for cataract surgery. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2003; 81: Zehetmayer M, Radax U, Skorpik C, et al. Topical versus peribulbar anesthesia in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1996; 22: Johnston RL, Whitefield LA, Giralt J, et al. Topical versus peribulbar anesthesia, without sedation, for clear corneal cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998; 24: Owens WD, Felts JA, Spitznagel EL Jr. ASA physical status classifications: a study of consistency of ratings. Anesthesiology 1978; 49: Gioia L, Prandi E, Codenotti M, et al. Peribulbar anesthesia with either 0.75% ropivacaine or a 2% lidocaine and bupivacaine mixture for vitreoretinal surgery: a double-blinded study. Anesth Analg 1999; 89: Gioia L, Fanelli G, Casati A, et al. A prospective, randomized, double-blinded comparison of 0,5%, 0,75% and 1% Ropivacaine for peribulbar block. J Clin Anesth 2004; 16: Rosenbaum PR, Rubin DB. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika 1983; 70: EJO_D_09_611_Gemma.indd :59:12
7 Gemma et al 24. Rubin DB. Estimating causal effects from large data sets using propensity scores. Ann Intern Med 1997; 127: Blackstone EH. Comparing apples and oranges. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002; 123: Eke T, Thompson JR. Safety of local anaesthesia for cataract surgery: why we should look again. Eye 2003; 17: Han SK, Kim JH, Hwang JM. Persistent diplopia after retrobulbar anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004; 30: Rosenfeld SI, Litinsky SM, Snyder DA, Plosker H, Altrove AW, Schiffman J. Effectiveness of monitored anesthesia care in cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 1997; 106: Romero Aroca P, Perena Soriano F, Salvat Serra M, Perena Soriano MJ, Cuenca Pena J. Is basic the anesthesiologist presence in cataract surgery? Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol 2002; 77: Katz J, Feldman M, Bass E, et al. Adverse intraoperative medical events and their association with anesthesia management strategies in cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 2001; 108: Pecka SL, Dexter F. Anesthesia providersí interventions during cataract extraction under monitored anesthesia care. AANA J 1997; 65: Jonas JB, Pakdaman B, Sauder G, Bender HJ. Is intraoperative monitoring necessary in cataract surgery under topical anesthesia? J Cataract Refract Surg 2004; 30: Zakrzewski PA, Friel T, Fox G, Braga-Mele R. Monitored anesthesia care provided by registered respiratory care practitioners during cataract surgery: a report of 1957 cases. Ophthalmology 2005; 112: Kershner RM. Topical anesthesia for small incision self-sealing cataract surgery. A prospective evaluation of the first 100 patients. J Cataract Refract Surg 1993; 19: Novak KD, Koch DD. Topical anesthesia for phacoemulsification: initial 20-case series with one month follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg 1995; 21: Katz J, Feldman M, Bass E, et al. Injectable versus topical anesthesia for cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 2000; 107: Fung D, Cohen MM, Stewart S, Davies A. What determines patient satisfaction with cataract care under topical local anesthesia and monitored sedation in a community hospital setting? Anesth Analg 2005; 100: Yap YC, Woo WW, Kathirgamanathan T, Kosmin A, Faye B, Kodati S. Variation of blood pressure during topical phacoemulsification. Eye 2009; 23: Tantri A, Clark C, Huber P, et al. Anesthesia monitoring by registered Nurses during cataract surgery: assessment of need for intraoperative anesthesia consultation. J Cataract Refract Surg 2006; 32: Fisher SJ, Cunningham RD. The medical profile of cataract patients. Clin Geriatr Med 1985; 1: EJO_D_09_611_Gemma.indd :59:12
8 Copyright of European Journal of Ophthalmology is the property of Wichtig Editore and its content may not be copied or ed to multiple sites or posted to a listserv without the copyright holder's express written permission. However, users may print, download, or articles for individual use.
An Evaluation of Topical and Local Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification
 An Evaluation of Topical and Local Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification Z. Rizvi,T. Rehman,S. Malik,A. Qureshi,L. Paul,K. Qureshi,S. Memon,S Rafi,A. Ali ( Final Year Medical Students and Department of Ophthalmology*,
An Evaluation of Topical and Local Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification Z. Rizvi,T. Rehman,S. Malik,A. Qureshi,L. Paul,K. Qureshi,S. Memon,S Rafi,A. Ali ( Final Year Medical Students and Department of Ophthalmology*,
Comparison of ropivacaine 0.75% and bupivacaine 0.5% in peribulbar block for cataract surgery.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 23 Number 2 Comparison of ropivacaine 0.75% and bupivacaine 0.5% in peribulbar block for cataract surgery. L Trivedi, H Trivedi, D Tripathi, P Jha,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 23 Number 2 Comparison of ropivacaine 0.75% and bupivacaine 0.5% in peribulbar block for cataract surgery. L Trivedi, H Trivedi, D Tripathi, P Jha,
Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery
 (Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2008, 59, 27-32) Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery O. YALCIN COK (*), A. ERTAN (**) and M. BAHADIR (**) Abstract : We compared the effect
(Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2008, 59, 27-32) Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery O. YALCIN COK (*), A. ERTAN (**) and M. BAHADIR (**) Abstract : We compared the effect
Penetrating keratoplsty (PKP) is traditionally performed under
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Combined Topical and Intracameral Anesthesia in Penetrating Keratoplasty Fani Segev, MD,* Aristotle N. Voineskos,* Gladwin Hui,* Michael S. H. Law, MD,* Robert Paul, MD,* Frances Chung,
CLINICAL SCIENCES Combined Topical and Intracameral Anesthesia in Penetrating Keratoplasty Fani Segev, MD,* Aristotle N. Voineskos,* Gladwin Hui,* Michael S. H. Law, MD,* Robert Paul, MD,* Frances Chung,
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/95 Comparative Evaluation of Ropivacaine and Lignocaine with Ropivacaine, Lignocaine, and Clonidine Combination during
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/95 Comparative Evaluation of Ropivacaine and Lignocaine with Ropivacaine, Lignocaine, and Clonidine Combination during
Comparison of topical versus peribulbar anaesthesia for manual small incision cataract surgery with intraocular lens implantation
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Joseph B et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Nov;4(11):4862-4866 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20163781
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Joseph B et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Nov;4(11):4862-4866 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20163781
Phacoemulsification with topical anesthesia: Resident experience
 J CATARACT REFRACT SURG - VOL 32, AUGUST 2006 Phacoemulsification with topical anesthesia: Resident experience Mustafa Ünal, MD, _Iclal Yücel, MD, Ahmet Sarıcı, MD, Özgür Artunay, MD, Kazım Devranoğlu,
J CATARACT REFRACT SURG - VOL 32, AUGUST 2006 Phacoemulsification with topical anesthesia: Resident experience Mustafa Ünal, MD, _Iclal Yücel, MD, Ahmet Sarıcı, MD, Özgür Artunay, MD, Kazım Devranoğlu,
CLINICAL SCIENCES. A Comparative Study of Topical vs Retrobulbar Anesthesia in Complicated Cataract Surgery
 CLINICAL SCIENCES A Comparative Study of Topical vs Retrobulbar Anesthesia in Complicated Cataract Surgery Philipp C. Jacobi, MD; Thomas S. Dietlein, MD; Felix K. Jacobi, MD Objectives: To evaluate and
CLINICAL SCIENCES A Comparative Study of Topical vs Retrobulbar Anesthesia in Complicated Cataract Surgery Philipp C. Jacobi, MD; Thomas S. Dietlein, MD; Felix K. Jacobi, MD Objectives: To evaluate and
Day 1 10:50. Panel Discussions/Group Photo Coffee/Tea Break 11:15-11:30 (Networking) Different types of. Anesthesia. Day 2
 Day 1 Evening Sessions Morning Sessions Reception/Registration 08:3009:30 General Session Time 09:3009:55 Inaugural Address 10:0010:25 Keynote/Plenary Talk 1 Least of 3 Keynote/Plenary 10:25Talks 10:50
Day 1 Evening Sessions Morning Sessions Reception/Registration 08:3009:30 General Session Time 09:3009:55 Inaugural Address 10:0010:25 Keynote/Plenary Talk 1 Least of 3 Keynote/Plenary 10:25Talks 10:50
Patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction during cataract surgery using topical anesthesia with or without dexmedetomidine sedation
 361-367 Erdurmus:Shoja 7-04-2008 16:33 Pagina 361 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 3, 2008 / pp. 361-367 Patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction during cataract surgery using topical anesthesia
361-367 Erdurmus:Shoja 7-04-2008 16:33 Pagina 361 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 3, 2008 / pp. 361-367 Patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction during cataract surgery using topical anesthesia
Efficacy Of Ropivacaine - Fentanyl In Comparison To Bupivacaine - Fentanyl In Epidural Anaesthesia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 33 Number 1 Efficacy Of Ropivacaine - Fentanyl In Comparison To Bupivacaine - Fentanyl In Epidural Anaesthesia S Gautam, S Singh, R Verma, S Kumar,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 33 Number 1 Efficacy Of Ropivacaine - Fentanyl In Comparison To Bupivacaine - Fentanyl In Epidural Anaesthesia S Gautam, S Singh, R Verma, S Kumar,
REVIEW ARTICLE. Ophthalmologic Procedures and Local/Regional Anesthetic Techniques
 REVIEW ARTICLE David C. Warltier, M.D., Ph.D., Editor Anesthesiology 2007; 107:502 8 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sedation and Anesthesia
REVIEW ARTICLE David C. Warltier, M.D., Ph.D., Editor Anesthesiology 2007; 107:502 8 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sedation and Anesthesia
ISSN: (Paper) eissn: (Online) JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ACADEMIC RESEARCH (JAAR) April 2017
 Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
A Comparative Study of Topical Versus Peribulbar Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification and Implantation of Foldable Intraocular Lens in Cataract Surgery
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Ophthalmology and Visual Science Volume 2 Number 1 A Comparative Study of Topical Versus Peribulbar Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification and Implantation of K Said, M Hassan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Ophthalmology and Visual Science Volume 2 Number 1 A Comparative Study of Topical Versus Peribulbar Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification and Implantation of K Said, M Hassan,
Yuna Rapoport 1,2,3*, Laura L. Wayman 1,2 and Amy S. Chomsky 1,2
 Rapoport BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:85 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0479-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The effect of post-traumatic-stress-disorder on intra-operative analgesia in a veteran population during
Rapoport BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:85 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0479-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The effect of post-traumatic-stress-disorder on intra-operative analgesia in a veteran population during
The effect of anterior chamber lidocaine injection on pain reduction after cataract surgery under general anesthesia
 The effect of anterior chamber lidocaine injection on pain reduction after cataract surgery under general anesthesia Ahmareza Mouhtadi, MD Gholamreaza Khateminia, MD Reza Akhondzadeh, MD Farahzad Jannatmakan,
The effect of anterior chamber lidocaine injection on pain reduction after cataract surgery under general anesthesia Ahmareza Mouhtadi, MD Gholamreaza Khateminia, MD Reza Akhondzadeh, MD Farahzad Jannatmakan,
Single Injection versus Double Injection Peribulbar Anaesthesia in Eye Camp Surgery: a Comparative evaluation of Akinesia and Anaesthesia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 18 Number 2 Single Injection versus Double Injection Peribulbar Anaesthesia in Eye Camp Surgery: a Comparative P Singh, A Jadon, B Singh Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 18 Number 2 Single Injection versus Double Injection Peribulbar Anaesthesia in Eye Camp Surgery: a Comparative P Singh, A Jadon, B Singh Citation
Outcomes of manual small incision cataract surgery under topical anesthesia with lignocaine 2% jelly
 Original articles Outcomes of manual small incision cataract surgery under topical anesthesia with lignocaine 2% jelly Mithal C, Agarwal P, Mithal N Upgraded Department of Ophthalmology LLRM Medical College
Original articles Outcomes of manual small incision cataract surgery under topical anesthesia with lignocaine 2% jelly Mithal C, Agarwal P, Mithal N Upgraded Department of Ophthalmology LLRM Medical College
Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical Trial
 J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries and Perineal Surgeries
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/229 Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/229 Comparative Study of Equal Doses of Intrathecal Isobaric Bupivacaine and Isobaric Ropivacaine for Lower Limb Surgeries
Eye (2008) 22, & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved X/08 $30.00
 (2008) 22, 425 429 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye Comparative clinical trial of topical anaesthetic agents for cataract surgery with phacoemulsification:
(2008) 22, 425 429 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye Comparative clinical trial of topical anaesthetic agents for cataract surgery with phacoemulsification:
COMPLICATION RATE IN PRELIMINARY EXPERIENCE IN PHACOEMULSIFICATION CATARACT SURGERY
 ORIGINAL article COMPLICATION RATE IN PRELIMINARY EXPERIENCE IN PHACOEMULSIFICATION CATARACT SURGERY Mushtaq Ahmad 1, Sanaullah Khan 2, Muhammad Naeem 3, Sofia Iqbal 4, Nasir Saeed 5 ABSTRACT Objective:
ORIGINAL article COMPLICATION RATE IN PRELIMINARY EXPERIENCE IN PHACOEMULSIFICATION CATARACT SURGERY Mushtaq Ahmad 1, Sanaullah Khan 2, Muhammad Naeem 3, Sofia Iqbal 4, Nasir Saeed 5 ABSTRACT Objective:
Uneventful recovery following accidental epidural injection of dobutamine
 1 Case report Uneventful recovery following accidental epidural injection of dobutamine Bastiaan M. Gerritse, M.D., Ph.D., Daan de Vos, R.N.A, Anton W. Visser, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Anesthesiology,
1 Case report Uneventful recovery following accidental epidural injection of dobutamine Bastiaan M. Gerritse, M.D., Ph.D., Daan de Vos, R.N.A, Anton W. Visser, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Anesthesiology,
Richard M H Lee 1, John R Thompson 2, Tom Eke 3. 1 Department of Ocular Biology and Therapeutics, Institute of Ophthalmology, London
 Severe adverse events associated with local anaesthesia in cataract surgery: one year national survey of practice and complications in the United Kingdom. Richard M H Lee 1, John R Thompson 2, Tom Eke
Severe adverse events associated with local anaesthesia in cataract surgery: one year national survey of practice and complications in the United Kingdom. Richard M H Lee 1, John R Thompson 2, Tom Eke
Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation. Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016
 Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016 Introduction Repetitive collapse of the upper airway > sleep fragmentation, > hypoxemia, hypercapnia, > marked variations in intrathoracic
Sleep Apnea and ifficulty in Extubation Jean Louis BOURGAIN May 15, 2016 Introduction Repetitive collapse of the upper airway > sleep fragmentation, > hypoxemia, hypercapnia, > marked variations in intrathoracic
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction a neverending story
 Postoperative cognitive dysfunction a neverending story Adela Hilda Onuţu, MD, PhD Cluj-Napoca, Romania adela_hilda@yahoo.com No conflict of interest Contents Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD)
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction a neverending story Adela Hilda Onuţu, MD, PhD Cluj-Napoca, Romania adela_hilda@yahoo.com No conflict of interest Contents Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD)
Diabetes mellitus: A risk factor affecting visual outcome in branch retinal vein occlusion
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 648-652 Diabetes mellitus: A risk factor affecting visual outcome in branch retinal vein occlusion J. SWART 1,2, J.W. REICHERT-THOEN 1, M.S.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 648-652 Diabetes mellitus: A risk factor affecting visual outcome in branch retinal vein occlusion J. SWART 1,2, J.W. REICHERT-THOEN 1, M.S.
Role and safety of epidural analgesia
 Anaesthesia for Liver Resection Surgery The Association of Anaesthetists Seminars 21 Portland Place, London Thursday 15 th December 2005 Role and safety of epidural analgesia Lennart Christiansson MD,
Anaesthesia for Liver Resection Surgery The Association of Anaesthetists Seminars 21 Portland Place, London Thursday 15 th December 2005 Role and safety of epidural analgesia Lennart Christiansson MD,
The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adverse drug events, polypharmacy and perioperative considerations in elderly patients, 377 389 Age, and risk of postoperative urinary retention,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adverse drug events, polypharmacy and perioperative considerations in elderly patients, 377 389 Age, and risk of postoperative urinary retention,
Risks and Benefits of Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Medication Use before Cataract Surgery
 Risks and Benefits of Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Medication Use before Cataract Surgery Joanne Katz, ScD, 1,2 Marc A. Feldman, MD, MPH, 3 Eric B. Bass, MD, MPH, 4 Lisa H. Lubomski, PhD, 2 James M.
Risks and Benefits of Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Medication Use before Cataract Surgery Joanne Katz, ScD, 1,2 Marc A. Feldman, MD, MPH, 3 Eric B. Bass, MD, MPH, 4 Lisa H. Lubomski, PhD, 2 James M.
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures
 Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE FOLLOWING ENUCLEATION: A RESULT OF SURGERY OR ANESTHESIA?
 INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE FOLLOWING ENUCLEATION: A RESULT OF SURGERY OR ANESTHESIA? - A Case Report - DIDEM DAL *, AYDIN ERDEN *, FATMA SARICAOĞLU * AND ULKU AYPAR * Summary Choroidal melanoma is the most
INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE FOLLOWING ENUCLEATION: A RESULT OF SURGERY OR ANESTHESIA? - A Case Report - DIDEM DAL *, AYDIN ERDEN *, FATMA SARICAOĞLU * AND ULKU AYPAR * Summary Choroidal melanoma is the most
A Nationwide Survey on the Knowledge and Attitudes of Malaysian Optometry Students on Patients Visual Experiences During Cataract Surgery
 72 Original Article A Nationwide Survey on the Knowledge and Attitudes of Malaysian Optometry Students on Patients Visual Experiences During Cataract Surgery Colin SH Tan, 1 MBBS, M Med (Ophth), MRCS (Edin),
72 Original Article A Nationwide Survey on the Knowledge and Attitudes of Malaysian Optometry Students on Patients Visual Experiences During Cataract Surgery Colin SH Tan, 1 MBBS, M Med (Ophth), MRCS (Edin),
WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML)
 , 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
, 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government
 Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Trends in Anesthesia Use in Cataract Extraction with Lens Insertion: AAAHC Institute for Quality Improvement Study Results
 Trends in Anesthesia Use in Cataract Extraction with Lens Insertion: 2010 2015 AAAHC Institute for Quality Improvement Study Results BK Lerner, NJ Kuznets & K Kilgore Abstract Aim: To examine the trend
Trends in Anesthesia Use in Cataract Extraction with Lens Insertion: 2010 2015 AAAHC Institute for Quality Improvement Study Results BK Lerner, NJ Kuznets & K Kilgore Abstract Aim: To examine the trend
Prevention and Treatment Patrick Levelle, MD
 Prevention and Treatment Patrick Levelle, MD LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY 1. PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCKS 2. ROLE OF THE PERIANESTHESIA RN 3. LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY Use of Lipid Emulsion Regional and Peripheral
Prevention and Treatment Patrick Levelle, MD LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY 1. PERIPHERAL NERVE BLOCKS 2. ROLE OF THE PERIANESTHESIA RN 3. LOCAL ANESTHETIC TOXICITY Use of Lipid Emulsion Regional and Peripheral
Relevant and Reliable Systematic Review Mapped to this Section. Relevance of Review to other sections of AAO PPP- 2011
 Table 1. American Academy for Ophthalmology s (AAO) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Nonsurgical Hodge, 2005 Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2005 Jul;(117):1-6. Effects of omega- 3 fatty acids on eye
Table 1. American Academy for Ophthalmology s (AAO) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Nonsurgical Hodge, 2005 Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2005 Jul;(117):1-6. Effects of omega- 3 fatty acids on eye
An Epidural Initial Dose is Unnecessary in Combined Spinal Epidural Anesthesia for Caesarean Section
 Original An Epidural Initial Dose is Unnecessary in Combined Spinal Epidural Anesthesia for Caesarean Section Takashi Hongo, Akira Kitamura, Motoi Yokozuka, Chol Kim and Atsuhiro Sakamoto Department of
Original An Epidural Initial Dose is Unnecessary in Combined Spinal Epidural Anesthesia for Caesarean Section Takashi Hongo, Akira Kitamura, Motoi Yokozuka, Chol Kim and Atsuhiro Sakamoto Department of
Type of intervention Anaesthesia. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Astigmatic Outcomes of Temporal versus Nasal Clear Corneal Phacoemulsification
 Astigmatic Outcomes of Temporal versus Nasal Clear Corneal Phacoemulsification Mohammad Pakravan, MD; Homayoun Nikkhah, MD; Shahin Yazdani, MD Camelia Shahabi, MD; Massih Sedigh-Rahimabadi, MD Labbafinejad
Astigmatic Outcomes of Temporal versus Nasal Clear Corneal Phacoemulsification Mohammad Pakravan, MD; Homayoun Nikkhah, MD; Shahin Yazdani, MD Camelia Shahabi, MD; Massih Sedigh-Rahimabadi, MD Labbafinejad
SURGERY OR ANESTHESIA
 Patient Safety Event Report Hospital SURGERY OR ANESTHESIA Use this form to report an event involving a surgical or other invasive procedure (e.g., colonoscopy), or the administration of anesthesia. Do
Patient Safety Event Report Hospital SURGERY OR ANESTHESIA Use this form to report an event involving a surgical or other invasive procedure (e.g., colonoscopy), or the administration of anesthesia. Do
ASCRS 2016 Instructional Course Mastering Femtosecond Laser Assisted Phacoemulsification. An Evidence-Based Review
 ASCRS 2016 Instructional Course 07-410 Mastering Femtosecond Laser Assisted Phacoemulsification An Evidence-Based Review TIMOTHY V ROBERTS MBBS (NSW), MMed (Syd), FRANZCO, FRACS, GAICD Vision Eye Institute,
ASCRS 2016 Instructional Course 07-410 Mastering Femtosecond Laser Assisted Phacoemulsification An Evidence-Based Review TIMOTHY V ROBERTS MBBS (NSW), MMed (Syd), FRANZCO, FRACS, GAICD Vision Eye Institute,
Visual perception during phacoemulsification cataract surgery under subtenons anaesthesia
 (23) 17, 51 55 & 23 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 95-222X/3 $25. www.nature.com/eye Visual perception during phacoemulsification cataract surgery under subtenons anaesthesia SS Wickremasinghe,
(23) 17, 51 55 & 23 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 95-222X/3 $25. www.nature.com/eye Visual perception during phacoemulsification cataract surgery under subtenons anaesthesia SS Wickremasinghe,
Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent Option For Day Care Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
Comparison of Surgically Induced Astigmatisms after Clear Corneal Incisions of Different Sizes
 Comparison of Surgically Induced Astigmatisms after Clear Corneal Incisions of Different Sizes Sung Chur Moon, MD, PhD, Tarek Mohamed, MD, I. Howard Fine, MD Oregon Eye Institute, Eugene, Oregon, USA Purpose:
Comparison of Surgically Induced Astigmatisms after Clear Corneal Incisions of Different Sizes Sung Chur Moon, MD, PhD, Tarek Mohamed, MD, I. Howard Fine, MD Oregon Eye Institute, Eugene, Oregon, USA Purpose:
Internet Journal of Medical Update
 Internet Journal of Medical Update 2011 July;6(2):20-24. Internet Journal of Medical Update Journal home page: http://www.akspublication.com/ijmu Original Work Circulatory responses to propofol-ketamine
Internet Journal of Medical Update 2011 July;6(2):20-24. Internet Journal of Medical Update Journal home page: http://www.akspublication.com/ijmu Original Work Circulatory responses to propofol-ketamine
Sub-Tenon Versus Peribulbar Anaesthesia for Cataract Surgery
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No.3, September 2003 Sub-Tenon Versus Peribulbar Anaesthesia for Cataract Surgery Nada Al-Yousuf, FRCSEd * Purpose: The aim of this study is to compare the efficacy of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No.3, September 2003 Sub-Tenon Versus Peribulbar Anaesthesia for Cataract Surgery Nada Al-Yousuf, FRCSEd * Purpose: The aim of this study is to compare the efficacy of
Cardiothoracic Fellow Expectations Division of Cardiac Anesthesia, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 The fellowship in Cardiothoracic Anesthesia at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is intended to provide the foundation for a career as either an academic cardiothoracic anesthesiologist or clinical
The fellowship in Cardiothoracic Anesthesia at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is intended to provide the foundation for a career as either an academic cardiothoracic anesthesiologist or clinical
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
This scenario depicts the oculocardiac reflex (OCR) which includes the trigeminal (afferent) and vagus (efferent) nerves (C).
 The questions below represent original material contained within the AnesthesiaPrep question database. Please note that our live questions are offered on a web-based platform that is fully accessible on
The questions below represent original material contained within the AnesthesiaPrep question database. Please note that our live questions are offered on a web-based platform that is fully accessible on
ANESTHESIA EXAM (four week rotation)
 SPARROW HEALTH SYSTEM ANESTHESIA SERVICES ANESTHESIA EXAM (four week rotation) Circle the best answer 1. During spontaneous breathing, volatile anesthetics A. Increase tidal volume and decrease respiratory
SPARROW HEALTH SYSTEM ANESTHESIA SERVICES ANESTHESIA EXAM (four week rotation) Circle the best answer 1. During spontaneous breathing, volatile anesthetics A. Increase tidal volume and decrease respiratory
Paediatric neuraxial anaesthesia asleep or awake, what is the best for safety?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 1 Paediatric neuraxial anaesthesia asleep or awake, what is the best for safety? A Shabana, A Shorrab Citation A Shabana, A Shorrab. Paediatric
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 21 Number 1 Paediatric neuraxial anaesthesia asleep or awake, what is the best for safety? A Shabana, A Shorrab Citation A Shabana, A Shorrab. Paediatric
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine, fentanyl, tympanoplasty, monitored anaesthesia care. INTRODUCTION:
 13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
Setting The setting was tertiary care. The economic study appears to have been performed in Heidelberg, Germany.
 Comparative analysis of costs of total intravenous anaesthesia with propofol and remifentanil vs. balanced anaesthesia with isoflurane and fentanyl Epple J, Kubitz J, Schmidt H, Motsch J, Bottiger B W,
Comparative analysis of costs of total intravenous anaesthesia with propofol and remifentanil vs. balanced anaesthesia with isoflurane and fentanyl Epple J, Kubitz J, Schmidt H, Motsch J, Bottiger B W,
Beta Blockers for ENT Surgery
 Beta Blockers for ENT Surgery Dr. Giuliano Michelagnoli U.O. Anestesia e Rianimazione Nuovo Ospedale di Prato Perioperative Beta-Blockade 1. Reduction of perioperative cardiovascular risk 2. Multimodal
Beta Blockers for ENT Surgery Dr. Giuliano Michelagnoli U.O. Anestesia e Rianimazione Nuovo Ospedale di Prato Perioperative Beta-Blockade 1. Reduction of perioperative cardiovascular risk 2. Multimodal
Perioperative Myocardial Infarction in Noncardiac Surgery: Focusing on Intraoperative and Postoperative Risk Factors
 Perioperative Myocardial Infarction in Noncardiac Surgery: Focusing on Intraoperative and Postoperative Risk Factors Cardiac Unit, Department of Medicine, Prapokklao Hospital, Chantaburi Abstract Perioperative
Perioperative Myocardial Infarction in Noncardiac Surgery: Focusing on Intraoperative and Postoperative Risk Factors Cardiac Unit, Department of Medicine, Prapokklao Hospital, Chantaburi Abstract Perioperative
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings
 Original Articles 232 Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings Elley H.H. Chiu 1,2, Teng-Yeow Tan 1,3, Ku-Chou Chang 1,3, and Chia-Wei Liou 1,3 Abstract- Background: Standard 12-lead
Original Articles 232 Risk Factors for Ischemic Stroke: Electrocardiographic Findings Elley H.H. Chiu 1,2, Teng-Yeow Tan 1,3, Ku-Chou Chang 1,3, and Chia-Wei Liou 1,3 Abstract- Background: Standard 12-lead
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title:Efficacy of 1% carboxymethylcellulose sodium for treating dry eye after phacoemulsification: results from a multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled study Authors:
Author's response to reviews Title:Efficacy of 1% carboxymethylcellulose sodium for treating dry eye after phacoemulsification: results from a multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled study Authors:
Visual outcome with superior, superotemporal and temporal incisions used in phacoemulsification surgery - a comparative study
 Research Article Visual outcome with superior, superotemporal and temporal incisions used in phacoemulsification surgery - a comparative study Snehal P Gade 1*, Bhaskar S Khaire 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Research Article Visual outcome with superior, superotemporal and temporal incisions used in phacoemulsification surgery - a comparative study Snehal P Gade 1*, Bhaskar S Khaire 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Activated partial thromboplastin time abnormality, perioperative approach to, 104 105 Acute kidney injury, perioperative, 89 99 early
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Activated partial thromboplastin time abnormality, perioperative approach to, 104 105 Acute kidney injury, perioperative, 89 99 early
Catheter-directed Thrombolysis
 Scan for mobile link. Catheter-directed Thrombolysis Catheter-directed thrombolysis treats vascular blockages and improves blood flow by dissolving abnormal blood clots. A blood clot, or thrombus, can
Scan for mobile link. Catheter-directed Thrombolysis Catheter-directed thrombolysis treats vascular blockages and improves blood flow by dissolving abnormal blood clots. A blood clot, or thrombus, can
Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point Using the Cricoid Cartilage as Landmark Through X-ray Review
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
A decision analysis of anesthesia management for cataract surgery Reeves S W, Friedman D S, Fleisher A, Lubomski L H, Schein O D, Bass E B
 A decision analysis of anesthesia management for cataract surgery Reeves S W, Friedman D S, Fleisher A, Lubomski L H, Schein O D, Bass E B Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
A decision analysis of anesthesia management for cataract surgery Reeves S W, Friedman D S, Fleisher A, Lubomski L H, Schein O D, Bass E B Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
Complication and Visual Outcome after Peadiatric Cataract Surgery with or Without Intra Ocular Lens Implantation
 Original Article Complication and Visual Outcome after Peadiatric with or Without Intra Ocular Lens Implantation Mazhar-ul-Hasan, Umair A. Qidwai, Aziz-ur-Rehman, Nasir Bhatti, Rashid H. Alvi Pak J Ophthalmol
Original Article Complication and Visual Outcome after Peadiatric with or Without Intra Ocular Lens Implantation Mazhar-ul-Hasan, Umair A. Qidwai, Aziz-ur-Rehman, Nasir Bhatti, Rashid H. Alvi Pak J Ophthalmol
Original contribution. Department of Anesthesiology, Sapporo Medical University, School of Medicine, Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan
 Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 25 29 Original contribution A comparison of spinal anesthesia with small-dose lidocaine and general anesthesia with fentanyl and propofol for ambulatory prostate
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 25 29 Original contribution A comparison of spinal anesthesia with small-dose lidocaine and general anesthesia with fentanyl and propofol for ambulatory prostate
ASA Closed Claims Project: Regional Anesthesia Claims 1990 or later Lorri A. Lee MD Department of Anesthesiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA
 ASA Closed Claims Project: Regional Anesthesia Claims 1990 or later Lorri A. Lee MD Department of Anesthesiology, Seattle, WA OVERVIEW 1. Closed Claims Project 2. Peripheral Nerve Blocks 3. Neuraxial Claims
ASA Closed Claims Project: Regional Anesthesia Claims 1990 or later Lorri A. Lee MD Department of Anesthesiology, Seattle, WA OVERVIEW 1. Closed Claims Project 2. Peripheral Nerve Blocks 3. Neuraxial Claims
prilocaine hydrochloride 2% hyperbaric solution for injection (Prilotekal ) SMC No. (665/10) Goldshield Group
 prilocaine hydrochloride 2% hyperbaric solution for injection (Prilotekal ) SMC No. (665/10) Goldshield Group 17 December 2010 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
prilocaine hydrochloride 2% hyperbaric solution for injection (Prilotekal ) SMC No. (665/10) Goldshield Group 17 December 2010 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
84 Year Old with Rosacea
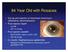 84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
Unexpected Cardiac Arrest In The Anesthetized Child
 Unexpected Cardiac Arrest In The Anesthetized Child Historical Background Jeffrey Morray, MD Outcomes for anesthetized children have improved over the past 50 years, as reflected in anesthesia-related
Unexpected Cardiac Arrest In The Anesthetized Child Historical Background Jeffrey Morray, MD Outcomes for anesthetized children have improved over the past 50 years, as reflected in anesthesia-related
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/600 Randomized Clinical Comparison of Epidural Bupivacaine with Fentanyl and Epidural Levobupivacaine with Fentanyl
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/600 Randomized Clinical Comparison of Epidural Bupivacaine with Fentanyl and Epidural Levobupivacaine with Fentanyl
MD (Anaesthesiology) Title (Plan of Thesis) (Session )
 S.No. 1. To study the occurrence of postoperative hyponatremia in paediatric patients under 2 years of age 2. Influence of timing of intravenous fluid therapy on maternal hemodynamics in patients undergoing
S.No. 1. To study the occurrence of postoperative hyponatremia in paediatric patients under 2 years of age 2. Influence of timing of intravenous fluid therapy on maternal hemodynamics in patients undergoing
Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view
 Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view 1st Geneva International SCIENTIFIC DAY February 3 rd 2010 E. Schiffer Dept APSI, HUG 1 Fast-Track in colorectal
Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view 1st Geneva International SCIENTIFIC DAY February 3 rd 2010 E. Schiffer Dept APSI, HUG 1 Fast-Track in colorectal
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia
 The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation
 Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Medical Science. Research Paper. 2nd yr post graduate, Dept. Of Ophthalmology, SVS Medical College
 Dr. A.Narasimha Rao Dr. N.Deepika Dr. D.Chandrakanth Reddy Dr. M. Vijaya Ramaraju ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Research Paper Medical Science Comparative Evaluation of the Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Topical 1 %
Dr. A.Narasimha Rao Dr. N.Deepika Dr. D.Chandrakanth Reddy Dr. M. Vijaya Ramaraju ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Research Paper Medical Science Comparative Evaluation of the Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Topical 1 %
Diabetic Retinopathy and its Impact on Ocular Heamodynamics during Local Anesthesia Comparing Peribulbar and Subtenon in Phacoemulsification
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, December: 169-173, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Diabetic Retinopathy and its Impact on Ocular Heamodynamics during Local Anesthesia Comparing Peribulbar
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, December: 169-173, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Diabetic Retinopathy and its Impact on Ocular Heamodynamics during Local Anesthesia Comparing Peribulbar
Attenuation of the Hemodynamic Responses to Endotracheal Intubation with Gabapentin Versus Fentanyl: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 2 Ser. 1 (February. 2019), PP 83-88 www.iosrjournals.org Attenuation of the Hemodynamic Responses
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 2 Ser. 1 (February. 2019), PP 83-88 www.iosrjournals.org Attenuation of the Hemodynamic Responses
Induction position for spinal anaesthesia: Sitting versus lateral position
 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Induction position for spinal anaesthesia: Sitting versus lateral position Khurrum Shahzad, Gauhar Afshan Abstract Objective: To compare the effect of induction position on block characteristics
11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Induction position for spinal anaesthesia: Sitting versus lateral position Khurrum Shahzad, Gauhar Afshan Abstract Objective: To compare the effect of induction position on block characteristics
The Effect of Cranial Electrotherapy on Preoperative Anxiety and Hemodynamic Responses
 The Effect of Cranial Electrotherapy on Preoperative Anxiety and Hemodynamic Responses Page 1 Cranial Electrotherapy (CES) is a non pharmaceutical treatment for anxiety, depression, insomnia, stress, headache
The Effect of Cranial Electrotherapy on Preoperative Anxiety and Hemodynamic Responses Page 1 Cranial Electrotherapy (CES) is a non pharmaceutical treatment for anxiety, depression, insomnia, stress, headache
Vanderbilt Eye Institute
 Vanderbilt Eye Institute Joshua Ki Hu Vanderbilt Eye Institute Ophthalmology, PGY-4 DATE 05.30.08 Introduction Cataract surgery is one of the most commonly performed surgeries in the world, with over 1
Vanderbilt Eye Institute Joshua Ki Hu Vanderbilt Eye Institute Ophthalmology, PGY-4 DATE 05.30.08 Introduction Cataract surgery is one of the most commonly performed surgeries in the world, with over 1
Changes in intraocular pressure during low dose intravenous sedation with propofol before cataract
 British Journal of Ophthalmology 1995; 79: 1093-1097 Department of Ophthalmology, Indiana University School ofmedicine, and Roudebush Veteran's Hospital of Indianapolis, Indiana, USA S Neel R Deitch Jr
British Journal of Ophthalmology 1995; 79: 1093-1097 Department of Ophthalmology, Indiana University School ofmedicine, and Roudebush Veteran's Hospital of Indianapolis, Indiana, USA S Neel R Deitch Jr
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
 Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
Comparison Of Intrathecal Hyperbaric Ropivacaine And Bupivacaine For Caesarean Delivery
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 30 Number 4 Comparison Of Intrathecal Hyperbaric Ropivacaine And Bupivacaine For Caesarean Delivery U Srivastava, K Joshi, A Gupta, Y Dwivedi, H
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 30 Number 4 Comparison Of Intrathecal Hyperbaric Ropivacaine And Bupivacaine For Caesarean Delivery U Srivastava, K Joshi, A Gupta, Y Dwivedi, H
9/25/2017 CASE. 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years. Rx: +3.0 RE LE
 CASE 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115 LE IOP : 17 RE 19 LE CD: 0.5 RE 0.6 LE 1 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115
CASE 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115 LE IOP : 17 RE 19 LE CD: 0.5 RE 0.6 LE 1 67 years old On 2 topical meds since 3 years Rx: +3.0 /-0.5@65 RE +2.5/-0.5@115
Anesthesia for Cardiac Patients for Non Cardiac Surgery. Kimberly Westra DNP, MSN, CRNA
 Anesthesia for Cardiac Patients for Non Cardiac Surgery Kimberly Westra DNP, MSN, CRNA Anesthesia for Cardiac Patients for Non Cardiac Surgery Heart Disease is a significant problem in the United States:
Anesthesia for Cardiac Patients for Non Cardiac Surgery Kimberly Westra DNP, MSN, CRNA Anesthesia for Cardiac Patients for Non Cardiac Surgery Heart Disease is a significant problem in the United States:
Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 17(2) : (2009)
 Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 17(2) : 55-60 (2009) COMPARISON OF PROPHYLACTIC INTRAMUSCULAR EPHEDRINE WITH PRELOADING VERSUS PRELOADING ALONE IN PREVENTION OF HYPOTENSION DURING ELECTIVE CAESAREAN
Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 17(2) : 55-60 (2009) COMPARISON OF PROPHYLACTIC INTRAMUSCULAR EPHEDRINE WITH PRELOADING VERSUS PRELOADING ALONE IN PREVENTION OF HYPOTENSION DURING ELECTIVE CAESAREAN
INTRAVENOUS LIDOCAINE INFUSIONS AND INTRALIPID RESCUE
 INTRAVENOUS LIDOCAINE INFUSIONS AND INTRALIPID RESCUE Acute Pain Service-LHSC VH and UH sites HISTORY Lidocaine and procaine used by IV infusion in the 1950s and 1960s for general analgesia Often continued
INTRAVENOUS LIDOCAINE INFUSIONS AND INTRALIPID RESCUE Acute Pain Service-LHSC VH and UH sites HISTORY Lidocaine and procaine used by IV infusion in the 1950s and 1960s for general analgesia Often continued
Which Patients are Too High Risk for Ambulatory Surgery?
 Which Patients are Too High Risk for Ambulatory Surgery? BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D. Director, Anesthesia Perioperative Medicine Clinic Professor of Anesthesia and Critical Care Professor of Medicine University
Which Patients are Too High Risk for Ambulatory Surgery? BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D. Director, Anesthesia Perioperative Medicine Clinic Professor of Anesthesia and Critical Care Professor of Medicine University
2018 ABG QCDR Measure Specifications. (changes to old measures from 2017 in red font)
 2018 ABG QCDR Measure Specifications (changes to old measures from 2017 in red font) Calculations Reporting Rate = Performance Met + Performance Not Met + Denominator Exceptions + Denominator Exclusions
2018 ABG QCDR Measure Specifications (changes to old measures from 2017 in red font) Calculations Reporting Rate = Performance Met + Performance Not Met + Denominator Exceptions + Denominator Exclusions
Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block
 Original Research Article Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block S. Arul Rajan 1, N. Sathyan 2*, T. Murugan 3 1 Assistant
Original Research Article Comparison of clonidine adjuvants to ropivacaine in subclavian perivascular approach of supra clavicular brachial plexus block S. Arul Rajan 1, N. Sathyan 2*, T. Murugan 3 1 Assistant
Prevalence of diplopia related to cataract surgery among cases of diplopia
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 6, 2007 / pp. 914-918 Prevalence of diplopia related to cataract surgery among cases of diplopia D. KARAGIANNIS, K. CHATZISTEFANOU, A. DAMANAKIS 1 st Department
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 6, 2007 / pp. 914-918 Prevalence of diplopia related to cataract surgery among cases of diplopia D. KARAGIANNIS, K. CHATZISTEFANOU, A. DAMANAKIS 1 st Department
Safety and efficacy of two ocular anesthetic methods for phacoemulsification: Topical anesthesia and viscoanesthesia (VisThesia TM )
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 2, 2007 / pp. 171-177 Safety and efficacy of two ocular anesthetic methods for phacoemulsification: Topical anesthesia and viscoanesthesia (VisThesia TM
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 2, 2007 / pp. 171-177 Safety and efficacy of two ocular anesthetic methods for phacoemulsification: Topical anesthesia and viscoanesthesia (VisThesia TM
The Roles and Responsibilities of Nurse Before and After Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery
 + The Roles and Responsibilities of Nurse Before and After Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery Elif GEZGINCI Gulhane Military Medical Academy School of Nursing Ankara 1 + 2 PREOPERATİVE + Preoperative (Patient
+ The Roles and Responsibilities of Nurse Before and After Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery Elif GEZGINCI Gulhane Military Medical Academy School of Nursing Ankara 1 + 2 PREOPERATİVE + Preoperative (Patient
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetaminophen, for geriatric surgical patients, 569 570 Acute kidney injury, critical care issues in geriatric patients with, 555 556
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetaminophen, for geriatric surgical patients, 569 570 Acute kidney injury, critical care issues in geriatric patients with, 555 556
Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve block vs procedural sedation for the treatment of upper extremity emergencies
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2008) 26, 706 710 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve vs procedural for the treatment of upper extremity
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2008) 26, 706 710 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve vs procedural for the treatment of upper extremity
Phone [850] Fax [850] Web Send s to: Search Millseye to download App Page 1 of 5
![Phone [850] Fax [850] Web Send s to: Search Millseye to download App Page 1 of 5 Phone [850] Fax [850] Web Send s to: Search Millseye to download App Page 1 of 5](/thumbs/81/84009052.jpg) YAG PC (Posterior Capsulotomy) Consent Form 1) I,, hereby authorize: David M. Mills, MD, FACS and/or whomever he may designate as his assistant(s), to perform upon myself the following operation(s): YAG
YAG PC (Posterior Capsulotomy) Consent Form 1) I,, hereby authorize: David M. Mills, MD, FACS and/or whomever he may designate as his assistant(s), to perform upon myself the following operation(s): YAG
