ICNIRP 7th International NIR Workshop Edinburgh, United Kingdom, 9-11 May 2012
|
|
|
- Shanon Moody
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RADIOFREQUENCY EFFECTS ON THE HUMAN ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM: ITS RELEVANCE FOR HEALTH AND HOW DO WE EXPLAIN THIS PHENOMENON BLANKA POPHOF FEDERAL OFFICE FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
2 OUTLINE History Cognition Evoked and event related potentials Spontaneous waking EEG Sleep EEG Exposure and dosimetry Possible mechanisms Health relevance Charité Berlin, Competence Center of Sleep Medicine, Prof. H. Danker-Hopfe
3 HISTORY Low Energy Emission Therapy MHz modulated at 42.7 Sleep inducing and promoting effect (Reite et al., Bioelectromagnetics, 1994) Effect of EMF on human brain activity Mega-Wave 150 (150 MHz) D1 Mobile phone 324, GSM Increase of EEG power in Alpha and Beta Band (Reiser, Eur. J. Med. Res., 1995)
4 COGNITION reaction time auditory and visual discrimination short and long term memory Callicot et al Small, single blind, older studies: Effects in both directions, often improvement Large, double blind recent studies, correction for multiple testing: no or very small effects, failed replications. TETRA: 400 MHz, up to 10 W/kg, very few studies. Some minor effects on memory cannot be excluded, replication needed, ongoing study in Germany.
5 COGNITION Barth et al., Occup. Environ. Med. 2008: Results of the meta-analysis suggest that EMFs may have a small impact on human attention and working memory. van Rongen et al., J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. 2009: No consistent significant effects on cognitive performance in adults have been observed. If anything, any effect is small and exposure seems to improve performance. Effects in children did not differ from those in healthy adults. Valentini et al., Occup. Environ. Med. 2010: Mobile phone-like EMF do not seem to induce cognitive and psychomotor effects. Kwon and Hämäläinen, Bioelectromagnetics 2011: Behavioral studies previously reported improved cognitive performance under exposure, but it was likely to have occurred by chance due to multiple comparisons. Recent behavioral studies and replication studies with more conservative statistics found no significant effects compared with original studies. Recent German study (Sauter et al. 2011) no effect of EMF on cognition, but significant influence of time of day.
6 EVOKED AND EVENT RELATED POTENTIALS brain signals recorded by EEG sensory perception auditory, visual intention, awaiting and performing a task many parameters: amplitude, latency, frequency, power acoustically evoked potential movement related cortical potentials motion begin common acoustic signal rare acoustic signal ms Stöhr et al Hegerl 1998
7 EVOKED AND EVENT RELATED POTENTIALS: Australia Changes in spectral power of EEG during an auditory task (Croft et al. 2002) and in amplitude and latency of auditory evoked potentials (Hamblin et al. 2004). Weak methodology dosimetry, single blind, small sample size. Larger, double blind replication study, with a power of 80% to detect a difference of 0.25 SD failed (Hamblin et al. 2006): There was no significant difference between exposure conditions for any auditory or visual event related potential (ERP) component or RT. As previous positive findings were not replicated, it was concluded that there is currently no evidence that acute MP exposure affects these indices of brain activity. Large study including adolescents, adults and elderly has shown effects on auditory evoked potentials (all age groups, 2G only) and event related desynchronization/ synchronization (all age groups, 2G and 3G) during an auditory task which was specially adjusted to individual abilities (Leung et al. 2011): The subtlety of mobile phone effect on cognition in our study suggests that it is important to account for individual differences in future mobile phone research.
8 EVOKED AND EVENT RELATED POTENTIALS: Finland Effects on brain oscillatory activity in the frequency range of 8-12 Hz during auditory and visual memory tasks (Krause et al. 2000) unable to replicate (Krause et al. 2004), but found again later (Krause at. al. 2007). The effects on the EEG were, however, varying, unsystematic and inconsistent with previous reports. We conclude that the effects of EMF on brain oscillatory responses may be subtle, variable and difficult to replicate for unknown reasons. Slight effects on event related desynchronisation/synchronisation during an auditory memory task in children (Krause et al. 2006), but no effect on auditory evoked potentials neither in adults (Kwon et al.2009) nor in children (Kwon et al. 2010). Kwon and Hämäläinen, Bioelectromagnetics 2011: Neurophysiological studies found no significant effects on cochlear and brainstem auditory processing, but only inconsistent results on spontaneous and evoked brain electrical activity. The inconsistent findings suggest possible false positives due to multiple comparisons and thus replication is needed.
9 SPONTANEOUS WAKING EEG Registration of brain electrical activity Frequency bands: δ ( Hz) θ ( Hz) α ( Hz) β ( Hz) eyes closed eyes open Charité Berlin, Competence Center of Sleep Medicine, Prof. H. Danker-Hopfe
10 SPONTANEOUS WAKING EEG significant changes with exposure year N Authors Rösche and Mann Hietanen et al. Increased α-power, decreased δ-power Croft et al. Increased α-power, decreased δ-power Curcio et al Perentos et al. Increased α-power Regel et al. Interhemispheric synchronization in α-band Vecchio et al Kleinogel et al Increased α-power Croft et al. Increased α-power (young adults, 2G) ,42,20 Croft et al. Interhemispheric synchronization in α-band Vecchio et al. Interhemispheric synchronization in α-band Vecchio et al.
11 SPONTANEOUS WAKING EEG Recent German study (Charité Berlin): of GSM and UMTS on waking EEG (power, α-attenuation) after correcting for multiple testing Significant influence of time of day Hz Hz 10.5 Hz Hz blue: time of day red: GSM Charité Berlin, Competence Center of Sleep Medicine Prof. H. Danker-Hopfe
12 SLEEP EEG
13 SLEEP EEG Laboratory studies: Sleep macrostructure significant changes with exposure year N Authors Reduced sleep latency Mann and Röschke Reduced REM-sleep (% SPT) Mann and Röschke Wagner et al Wagner et al. Reduced wake after sleep onset Borbély et al. 2000, Huber et al Huber et al Hinrichs et al. REM-sleep latency Loughran et al. Prolonged sleep latency Hung et al Fritzer et al Regel et al Reduced duration and prolonged latency of SWS Lowden et al.
14 SLEEP EEG German Study: GSM (Danker-Hopfe et al. 2011) NREM1-sleep whole night [min] REM-sleep whole night [min] REM-sleep whole night [% TST] Mean duration of REM-cycles REM-sleep middle sleep cycles [min] REM-sleep 3rd quarter of the night [min] REM-sleep 3rd quarter of the night [%] NREM2-sleep whole night [min] NREM2-sleep whole night [% TST] NREM2-sleep 3rd quarter of the night [min] NREM2-sleep 3rd quarter of the night [% TST] Stage shifts from SWS to NREM1 Movement time 1st sleep cycles [min] Movement time 1st quarter of the night [min] increased increased increased increased increased increased increased increased 14 observed, 12 expected by chance
15 SLEEP EEG German Study: UMTS (Danker-Hopfe et al. 2011) NREM1-sleep whole night [min] NREM1-sleep whole night [% TIB] NREM1-sleep during sleep period time [min] NREM1-sleep [% SPT] NREM1-sleep 2nd third of the night [min] NREM1-sleep 2nd third of the night [% TIB] Mean duration NREM cycles [min TIB] Mean duration REM cycles [min TIB] NREM2-sleep middle cycles [min] increased Less observed that expected by chance of GSM and UMTS on sleep macrostructure
16 SLEEP EEG Laboratory studies: Power spectral analysis significant changes with exposure year N Authors Increased mean power during REM sleep Mann and Röschke Wagner et al Wagner et al. Increased mean power during NREM sleep Increased mean power during NREM sleep Increased mean power during NREM sleep Increased mean power during NREM sleep Increased mean power during NREM sleep , Borbély et al. Huber et al. Huber et al. Regel et al. Loughran et al. spindle frequency range Hinrichs et al. Increased mean power during NREM sleep Increased mean power during NREM sleep Increased mean power during NREM sleep Increased mean power during NREM sleep Hung et al. Loughran et al. Lowden et al. Schmid et al. 1-4 Hz spindle frequency range
17 SLEEP EEG German Study: Spectral power, GSM (Somnolyzer, 400 variables) spindle frequency Charité Berlin, Competence Center of Sleep Medicine, Prof. H. Danker-Hopfe No changes of power in SWS and REM sleep; No changes under UMTS
18 SLEEP EEG German Study: spindle detection Automatic detection Somnolyzer 24x7: 810 variables GSM UMTS 23 significant results 11 significant results 41 statistically significant results are expected by chance No systematic changes in frequency, density, amplitude and duration of spindles Young healthy men no information about female, elderly Individual variability?
19 Exposure and dosimetry exposure intensity exposure duration pulsed continuous wave near field far field sleep: prior to sleep during sleep waking: tests during or before and after exposure mobile phone, simulated mobile phone, homogeneous exposure of a hemispehre left right side
20 Exposure and Dosimetry Nokia 6110 Patch antenna Planar antenna GSM UMTS Boutry et al. 2007, Murbach et al. 2012, Bahr et al. 2007
21 Possible mechanisms Thalamus: - central role in spindle generation - sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness Hypothalamus: thermoregulation, circadian rhythm, sleep Influence of EMF: direct, or via cortical stimulation Thermal or non-thermal? Sensitivity of neurons: ~ 0.1 C; neuronal Networks: 0.03 C Peak exposure of thalamus: Nokia 6110: Turku: W/kg; Swinburne: W/kg Patch antenna: 0.16 W/kg (Boutry et al. 2007) Planar antenna (TETRA, 6 W/kg) 0.08 W/g (Schmid et al. 2012) Temperature increase at 2 W/kg (simulated mobile phone): cortex < 0.1 C, thalamus < 0.01 C (Schmid et al. 2007)
22 Possible mechanisms Circadian rhythm Thermoregulation Sleep regulation Warming: sleep induction Activation of warm-sensitive neurons of Hypothalamus triggers NREM-sleep onset. These neurons are activated by direct warming as well as by peripheral thermo sensory input. Core body temperature N = 8 Kräuchi et al. 2007
23 Health relevance on cognition on evoked and event related potential on waking EEG on sleep macrostructure and sleep quality Possible effect on sleep EEG Probably sleep inducing and promoting effects, no sleep disturbance Apparently dose dependent Role of pulse modulation not clarified Possibly thermal Physiologically interesting, differences between laboratories should be clarified Age, gender and individual variability insufficiently investigated Probably no adverse health relevant effects
Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields: Effects on the Sleeping Brain
 Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields: Effects on the Sleeping Brain Sarah Loughran Australian Centre for Electromagnetic Bioeffects Research Wollongong University 8th ICNIRP International NIR Workshop
Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields: Effects on the Sleeping Brain Sarah Loughran Australian Centre for Electromagnetic Bioeffects Research Wollongong University 8th ICNIRP International NIR Workshop
Questions. Analysis of the sleep EEG. Brain activity is influenced by RF EMF: The role of pulsemodulation
 Brain activity is influenced by RF EMF: The role of pulsemodulation parameters Peter Achermann University of Zurich Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology Zurich Center for Integrative Human Physiology
Brain activity is influenced by RF EMF: The role of pulsemodulation parameters Peter Achermann University of Zurich Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology Zurich Center for Integrative Human Physiology
Effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by mobile phones (GSM 900 and WCDMA UMTS) on the macrostructure of sleep
 J. Sleep Res. (2011) 20, 73 81 Mobile phones and sleep doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2010.00850.x Effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by mobile phones (GSM 900 and WCDMA UMTS) on the macrostructure of
J. Sleep Res. (2011) 20, 73 81 Mobile phones and sleep doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2010.00850.x Effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by mobile phones (GSM 900 and WCDMA UMTS) on the macrostructure of
Section 11. Effects of Exposure to Radiofrequency Waves from Mobile Phones on Neurophysiology and Cognitive Performance
 Section 11 Effects of Exposure to Radiofrequency Waves from Mobile Phones on Neurophysiology and Cognitive Performance Table of Contents Summary... 286 11.1 Introduction... 286 11.2 Methods... 287 11.2.1
Section 11 Effects of Exposure to Radiofrequency Waves from Mobile Phones on Neurophysiology and Cognitive Performance Table of Contents Summary... 286 11.1 Introduction... 286 11.2 Methods... 287 11.2.1
Pulse modulated radiofrequency exposure influences cognitive performance
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Social Sciences - Papers Faculty of Social Sciences 2016 Pulse modulated radiofrequency exposure influences cognitive performance Adam Verrender University
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Social Sciences - Papers Faculty of Social Sciences 2016 Pulse modulated radiofrequency exposure influences cognitive performance Adam Verrender University
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY
 states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
New international developments in RF bioeffect mechanism research
 New international developments in RF bioeffect mechanism research bernard.veyret@ims-bordeaux.fr Effects and mechanisms Physics Biophysics Biochem Biology Health Bioeffects database ICNIRP blue books National
New international developments in RF bioeffect mechanism research bernard.veyret@ims-bordeaux.fr Effects and mechanisms Physics Biophysics Biochem Biology Health Bioeffects database ICNIRP blue books National
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Exposure to pulsed high-frequency electromagnetic eld during waking affects human sleep EEG
 SLEEP Exposure to pulsed high-frequency electromagnetic eld during waking affects human sleep EEG Reto Huber, Thomas Graf, Kimberly A. Cote, Lutz Wittmann, Eva Gallmann, Daniel Matter, JuÈrgen Schuderer,
SLEEP Exposure to pulsed high-frequency electromagnetic eld during waking affects human sleep EEG Reto Huber, Thomas Graf, Kimberly A. Cote, Lutz Wittmann, Eva Gallmann, Daniel Matter, JuÈrgen Schuderer,
Cross-sectional study on subjective symptoms due to electromagnetic fields from mobile-phone base stations among adults
 Cross-sectional study on subjective symptoms due to electromagnetic fields from mobile-phone base stations among adults BfS Workshop 12.12.06: Acute Health Effects 1 University of Bielefeld: Gabriele Berg,
Cross-sectional study on subjective symptoms due to electromagnetic fields from mobile-phone base stations among adults BfS Workshop 12.12.06: Acute Health Effects 1 University of Bielefeld: Gabriele Berg,
Analysis of the Effect of Cell Phone Radiation on the Human Brain Using Electroencephalogram
 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal Published By: Oriental Scientific Publishing Co., India. www.computerscijournal.org ISSN:
ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal Published By: Oriental Scientific Publishing Co., India. www.computerscijournal.org ISSN:
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
What do you notice? Woodman, Atten. Percept. Psychophys., 2010
 What do you notice? Woodman, Atten. Percept. Psychophys., 2010 You are trying to determine if a small amplitude signal is a consistent marker of a neural process. How might you design an experiment to
What do you notice? Woodman, Atten. Percept. Psychophys., 2010 You are trying to determine if a small amplitude signal is a consistent marker of a neural process. How might you design an experiment to
Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves
 SICE Annual Conference 27 Sept. 17-2, 27, Kagawa University, Japan Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves Seiji Nishifuji 1, Kentaro Fujisaki 1 and Shogo Tanaka 1 1
SICE Annual Conference 27 Sept. 17-2, 27, Kagawa University, Japan Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves Seiji Nishifuji 1, Kentaro Fujisaki 1 and Shogo Tanaka 1 1
The Sonification of Human EEG and other Biomedical Data. Part 3
 The Sonification of Human EEG and other Biomedical Data Part 3 The Human EEG A data source for the sonification of cerebral dynamics The Human EEG - Outline Electric brain signals Continuous recording
The Sonification of Human EEG and other Biomedical Data Part 3 The Human EEG A data source for the sonification of cerebral dynamics The Human EEG - Outline Electric brain signals Continuous recording
Students will be able to determine what stage of sleep someone is in by analyzing their EEG.
 Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to engage students with the concept of the neural circuit. The lesson and unit as a whole use sleep, a behavior everyone is familiar
Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to engage students with the concept of the neural circuit. The lesson and unit as a whole use sleep, a behavior everyone is familiar
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122
 EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
This brief animation illustrates the EEG patterns of the different stages of sleep, including NREM and REM sleep.
 Brain wave frequency and amplitude This brief animation illustrates the EEG patterns of the different stages of sleep, including NREM and REM sleep. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u WYwMnMMEoU&feature=related
Brain wave frequency and amplitude This brief animation illustrates the EEG patterns of the different stages of sleep, including NREM and REM sleep. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u WYwMnMMEoU&feature=related
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
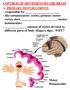 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
WHO Research Agenda for RF fields
 WHO Research Agenda for RF fields Dr E. van Deventer 1 Outline Introduction The WHO RF Research Agenda Motivation Background Content Discussion 2 3 Established in 1996 Coordinated by WHO HQ (SDE/PHE/RAD)
WHO Research Agenda for RF fields Dr E. van Deventer 1 Outline Introduction The WHO RF Research Agenda Motivation Background Content Discussion 2 3 Established in 1996 Coordinated by WHO HQ (SDE/PHE/RAD)
A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to
 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms. Reading: BCP Chapter 19
 Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep)
 EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
Circadian rhythm and Sleep. Radwan Banimustafa MD
 Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Sleep)
 EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Sleep) Slow-Wave Sleep: What Is it? All of us can relate to feeling sleepy, foggy-headed and hungry after a night of poor sleep. The answer to why we feel this way can be found
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Sleep) Slow-Wave Sleep: What Is it? All of us can relate to feeling sleepy, foggy-headed and hungry after a night of poor sleep. The answer to why we feel this way can be found
Outline 3/5/2013. Practice Question. Practice question. PSYC 120 General Psychology. Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness
 Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Outline 3/5/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 11: States of consciousness The Nature of Consciousness Sleep and Dreams Psychoactive Drugs Hypnosis Meditation Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu
Lecture 8. Arousal & Sleep. Cogs17 * UCSD
 Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Heidi Danker-Hopfe and Hans Dorn
 Studies of the effects of exposure to electromagnetic fields emitted from mobile phones on volunteers Investigation of sleep quality in subjects living near a mobile base station Experimental study on
Studies of the effects of exposure to electromagnetic fields emitted from mobile phones on volunteers Investigation of sleep quality in subjects living near a mobile base station Experimental study on
****REVISED 4/27/2015****
 Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Exam 2 Study Guide Disclaimer: This is intended as a study aid. It is not a complete description of everything discussed in class, nor an exhaustive list of information that might be tested on an exam.
Chapter 5. Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition
 Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms
 203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
EEG Electrode Placement
 EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
CELL PHONE RADIATION AND HEALTH: STRESS RESPONSE, PROTEOMICS, BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER AND OTHER SELECTED ISSUES
 CELL PHONE RADIATION AND HEALTH: STRESS RESPONSE, PROTEOMICS, BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER AND OTHER SELECTED ISSUES Dariusz Leszczynski University of Helsinki, Finland Frontiers, Lausanne, Switzerland 1 SCOPE
CELL PHONE RADIATION AND HEALTH: STRESS RESPONSE, PROTEOMICS, BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER AND OTHER SELECTED ISSUES Dariusz Leszczynski University of Helsinki, Finland Frontiers, Lausanne, Switzerland 1 SCOPE
New human experimental studies on HF
 New human experimental studies on HF Gunnhild Oftedal Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) New studies: Papers published in 2011 2015 13.05.2016 Author Searches and reviews mostly done
New human experimental studies on HF Gunnhild Oftedal Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) New studies: Papers published in 2011 2015 13.05.2016 Author Searches and reviews mostly done
Sleep - 10/5/17 Kelsey
 Sleep - 10/5/17 Kelsey Thursday, October 5, 2017 10:59 AM How to Study and Measure Sleep Sleep: Absence of overt behavior, absence of consciousness. -> measures are indirect Methods to measure sleep characteristics:
Sleep - 10/5/17 Kelsey Thursday, October 5, 2017 10:59 AM How to Study and Measure Sleep Sleep: Absence of overt behavior, absence of consciousness. -> measures are indirect Methods to measure sleep characteristics:
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS
 STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS LEVELS OF CONSCIOUSNESS Taiwanese Letter Example We know that various levels exists beyond the conscious level. Mere-exposure effect Priming Blind sight WHAT IS CONSCIOUSNESS? William
Exclusion criteria and outlier detection
 1 Exclusion criteria and outlier detection 1 2 Supplementary Fig. 1 31 subjects complied with the inclusion criteria as tested during the familiarization session. The upper part of the figure (ovals) indicates
1 Exclusion criteria and outlier detection 1 2 Supplementary Fig. 1 31 subjects complied with the inclusion criteria as tested during the familiarization session. The upper part of the figure (ovals) indicates
NOTE. This online version of the thesis may have different page formatting and pagination from the paper copy held in the Swinburne Library.
 NOTE This online version of the thesis may have different page formatting and pagination from the paper copy held in the Swinburne Library. Abstract Abstract The use of mobile phones is continually increasing
NOTE This online version of the thesis may have different page formatting and pagination from the paper copy held in the Swinburne Library. Abstract Abstract The use of mobile phones is continually increasing
Circadian Rhythm and Sleep in Healthy
 Optimizing Circadian Rhythm and Characterizing Brain Function in Prolonged Disorders of Consciousness Dr Kudret C. Yelden, MRCP Consultant in Neuro-rehabilitation LLM-Medical Law and Ethics September 2016
Optimizing Circadian Rhythm and Characterizing Brain Function in Prolonged Disorders of Consciousness Dr Kudret C. Yelden, MRCP Consultant in Neuro-rehabilitation LLM-Medical Law and Ethics September 2016
Acute effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field emitted by mobile phone. on brain function
 Running head: Phone and Brain Acute effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field emitted by mobile phone on brain function Jun Zhang 1, Alexander Sumich 2, and Grace Y Wang 3* 1 School of Electrical
Running head: Phone and Brain Acute effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field emitted by mobile phone on brain function Jun Zhang 1, Alexander Sumich 2, and Grace Y Wang 3* 1 School of Electrical
Understanding Sleep Regulatory Processes to Improve Waking Performance
 Understanding Sleep Regulatory Processes to Improve Waking Performance 1 st :envihab Symposium Cologne, Germany May 23, 2011 Daniel Aeschbach Division of Sleep Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard
Understanding Sleep Regulatory Processes to Improve Waking Performance 1 st :envihab Symposium Cologne, Germany May 23, 2011 Daniel Aeschbach Division of Sleep Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming. Elaine M. Hull
 Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Neurophysiology & EEG
 Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE. Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D.
 SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
What is Consciousness?
 What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
AOS1 How do levels of consciousness affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview
 UNIT 4- How is Wellbeing Developed and Maintained? AOS1 How do levels of affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview Following is the key knowledge and concepts for unit 4 AOS 1. The black represents
UNIT 4- How is Wellbeing Developed and Maintained? AOS1 How do levels of affect mental processes and behaviour? An Overview Following is the key knowledge and concepts for unit 4 AOS 1. The black represents
Recent Advances in Bioelectromagnetics Research on Mobile Telephony and Health An Introduction
 192 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Recent Advances in Bioelectromagnetics Research on Mobile Telephony and Health An Introduction S. Lang Nokia Corporation,
192 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 Recent Advances in Bioelectromagnetics Research on Mobile Telephony and Health An Introduction S. Lang Nokia Corporation,
The Possible Harmful Biological Effects of Low Level Electromagnetic Fields of Frequencies up to 300 GHz. IEE Position Statement - May 2002
 Summary The Possible Harmful Biological Effects of Low Level Electromagnetic Fields of Frequencies up to 300 GHz IEE Position Statement - May 2002 The Institution of Electrical Engineers Policy Advisory
Summary The Possible Harmful Biological Effects of Low Level Electromagnetic Fields of Frequencies up to 300 GHz IEE Position Statement - May 2002 The Institution of Electrical Engineers Policy Advisory
Name: Per:_ Advanced Placement Psychology Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide
 Name: Per:_ Advanced Placement Psychology Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1: Foundations & History 1. Describe the following perspectives of psychology. Behavioral Perspective Evolutionary Perspective
Name: Per:_ Advanced Placement Psychology Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1: Foundations & History 1. Describe the following perspectives of psychology. Behavioral Perspective Evolutionary Perspective
Effects of electromagnetic waves emitted from mobile phone on auditory evoked potential in school children.
 Curr Pediatr Res 2012; 16 (1): 37-41 Effects of electromagnetic waves emitted from mobile phone on auditory evoked potential in school children. Malla Uzwali 1, Limbu Nirmala 1, Das A 1, Paudel BH 1, Mathur
Curr Pediatr Res 2012; 16 (1): 37-41 Effects of electromagnetic waves emitted from mobile phone on auditory evoked potential in school children. Malla Uzwali 1, Limbu Nirmala 1, Das A 1, Paudel BH 1, Mathur
Modelling the relation of body temperature and sleep: importance of the circadian rhythm in skin temperature
 Modelling the relation of body temperature and sleep: importance of the circadian rhythm in skin temperature EUS J.W. VAN SOMEREN NETHERLANDS INSTITUTE FOR BRAIN RESEARCH, AMSTERDAM A close relation between
Modelling the relation of body temperature and sleep: importance of the circadian rhythm in skin temperature EUS J.W. VAN SOMEREN NETHERLANDS INSTITUTE FOR BRAIN RESEARCH, AMSTERDAM A close relation between
CSE 599E Introduction to Brain-Computer Interfacing
 CSE 599E Introduction to Brain-Computer Interfacing Instructor: Rajesh Rao TA: Sam Sudar The Matrix (1999) Firefox(1982) Brainstorm (1983) Spiderman 2 (2004) Hollywood fantasy apart, why would we want
CSE 599E Introduction to Brain-Computer Interfacing Instructor: Rajesh Rao TA: Sam Sudar The Matrix (1999) Firefox(1982) Brainstorm (1983) Spiderman 2 (2004) Hollywood fantasy apart, why would we want
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events
 The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events Summary of Updates in Version 2.1 July 1, 2014 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring that The AASM Manual
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events Summary of Updates in Version 2.1 July 1, 2014 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring that The AASM Manual
EEG- A Brief Introduction
 Fatemeh Hadaeghi EEG- A Brief Introduction Lecture Notes for BSP, Chapter 4 Master Program Data Engineering 1 4 Introduction Human brain, as the most complex living structure in the universe, has been
Fatemeh Hadaeghi EEG- A Brief Introduction Lecture Notes for BSP, Chapter 4 Master Program Data Engineering 1 4 Introduction Human brain, as the most complex living structure in the universe, has been
Classification of Pre-Stimulus EEG of K-complexes using Competitive Learning Networks
 Classification of Pre-Stimulus EEG of K-complexes using Competitive Learning Networks Martin Golz 1, David Sommer 1, Thomas Lembcke 2, Brigitte Kurella 2 1 Fachhochschule Schmalkalden, Germany 2 Wilhelm-Griesinger-Krankenhaus,
Classification of Pre-Stimulus EEG of K-complexes using Competitive Learning Networks Martin Golz 1, David Sommer 1, Thomas Lembcke 2, Brigitte Kurella 2 1 Fachhochschule Schmalkalden, Germany 2 Wilhelm-Griesinger-Krankenhaus,
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus)
 EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus) Introduction 17 subjects were tested to measure effects of a Brain.fm focus session on cognition. With 4 additional subjects, we recorded EEG data during baseline and while
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus) Introduction 17 subjects were tested to measure effects of a Brain.fm focus session on cognition. With 4 additional subjects, we recorded EEG data during baseline and while
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT.
 CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
Overview. Surviving shift work. What is the circadian rhythm? Components of a Generic Biological Timing System 31/10/2017
 Overview Surviving shift work Dr Claire M. Ellender Respiratory and Sleep Physician Princess Alexandra Hospital Conflicts nil relevant Circadian rhythm Impacts of shift work on health Case example Circadian
Overview Surviving shift work Dr Claire M. Ellender Respiratory and Sleep Physician Princess Alexandra Hospital Conflicts nil relevant Circadian rhythm Impacts of shift work on health Case example Circadian
Sleep. No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness,
 Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep. No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness,
 Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Sleep Neil B. Kavey, MD Columbia Presbyterian Medical Center No longer think of sleep as an isolated block of time at the end of the day. Sleep is not just the absence of wakefulness, It is an active physiologic
Recognition of Sleep Dependent Memory Consolidation with Multi-modal Sensor Data
 Recognition of Sleep Dependent Memory Consolidation with Multi-modal Sensor Data The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Recognition of Sleep Dependent Memory Consolidation with Multi-modal Sensor Data The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms
 Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Electroencephalographic Study of Essential Oils for Stress Relief
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-10-11 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 437, pp 1085-1088 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.437.1085 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Electroencephalographic
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-10-11 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 437, pp 1085-1088 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.437.1085 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Electroencephalographic
The effect of caffeine on cerebral asymmetry in rats
 , pp.476-482 The effect of caffeine on cerebral asymmetry in rats Voiculescu M, Segarceanu A, Negutu M, Ghita I, Fulga I, Coman OA Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy, Faculty of Medicine, Carol
, pp.476-482 The effect of caffeine on cerebral asymmetry in rats Voiculescu M, Segarceanu A, Negutu M, Ghita I, Fulga I, Coman OA Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy, Faculty of Medicine, Carol
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL. Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program)
 SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
pdf NIH Overview Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from:
 1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
1 of 8 6/20/2012 10:25 AM Sleep and Dreams Sleep and the Brain pdf NIH Overview 3.2-3.3 Some Basic Background: Back to Course Schedule (The material below on the neuron is adapted from: http://vv.carleton.ca/~neil/neural/neuron-a.html)
Mobile phones and Cognition in Children
 Mobile phones and Cognition in Children Report on studies by Alan W. Preece and Christian Haarala Gerd Friedrich e.v. Istanbul, 10th of June 2004 Starting points Assumption: Effects have been identified
Mobile phones and Cognition in Children Report on studies by Alan W. Preece and Christian Haarala Gerd Friedrich e.v. Istanbul, 10th of June 2004 Starting points Assumption: Effects have been identified
Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old
 Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old V. Mohan Kumar Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram 1 What is sleep? As per behavioral criteria: Reduced motor
Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old V. Mohan Kumar Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram 1 What is sleep? As per behavioral criteria: Reduced motor
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Similarities between deep slow wave sleep and absence epilepsy
 Similarities between deep slow wave sleep and absence epilepsy A.M.L. COENEN NICI, DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF NIJMEGEN P.O. BOX 9104 6500 HE NIJMEGEN THE NETHERLANDS Prologue Deep slow wave
Similarities between deep slow wave sleep and absence epilepsy A.M.L. COENEN NICI, DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF NIJMEGEN P.O. BOX 9104 6500 HE NIJMEGEN THE NETHERLANDS Prologue Deep slow wave
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
BIOPAC Systems, Inc BIOPAC Inspiring people and enabling discovery about life
 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 2016 BIOPAC Inspiring people and enabling discovery about life 1 BIOPAC s Guide to EEG for Research: Mobita Wireless EEG Housekeeping Attendees are on Mute Headset is Recommended!
BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 2016 BIOPAC Inspiring people and enabling discovery about life 1 BIOPAC s Guide to EEG for Research: Mobita Wireless EEG Housekeeping Attendees are on Mute Headset is Recommended!
Week 4 Psychology. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding that they and others think, feel, perceive, and have private experiences.
 Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
Week 4 Psychology Before we explore the concept in detail, let us understand Theory of Mind as well as what Consciousness and Stream of Consciousness are. Theory of mind is an individual s understanding
Sleep & Wakefulness Disorders in Parkinson s Disease: The Challenge of Getting a Good Night s Sleep
 Sleep & Wakefulness Disorders in Parkinson s Disease: The Challenge of Getting a Good Night s Sleep Helene A. Emsellem, MD March 25, 2017 The Center for Sleep & Wake Disorders PFNCA Symposium Sleep is
Sleep & Wakefulness Disorders in Parkinson s Disease: The Challenge of Getting a Good Night s Sleep Helene A. Emsellem, MD March 25, 2017 The Center for Sleep & Wake Disorders PFNCA Symposium Sleep is
RF and Health: A WHO Perspective
 RF and Health: A WHO Perspective Dr E. van Deventer Team Leader, Radiation Programme Department of Public Health, Social and Environmental Determinants of Health OUTLINE Introduction Assessing the health
RF and Health: A WHO Perspective Dr E. van Deventer Team Leader, Radiation Programme Department of Public Health, Social and Environmental Determinants of Health OUTLINE Introduction Assessing the health
EE 4BD4 Lecture 11. The Brain and EEG
 EE 4BD4 Lecture 11 The Brain and EEG 1 Brain Wave Recordings Recorded extra-cellularly from scalp (EEG) Recorded from extra-cellularly from surface of cortex (ECOG) Recorded extra-cellularly from deep
EE 4BD4 Lecture 11 The Brain and EEG 1 Brain Wave Recordings Recorded extra-cellularly from scalp (EEG) Recorded from extra-cellularly from surface of cortex (ECOG) Recorded extra-cellularly from deep
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by GSM phones on working memory: A metaanalysis.
 Effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by GSM phones on working memory: A metaanalysis. Zubko O 1, Gould RL 1, Gay HC 1, Cox HJ 1, Coulson MC 3 and Howard RJ 1,2 1 Department of Old Age Psychiatry,
Effects of electromagnetic fields emitted by GSM phones on working memory: A metaanalysis. Zubko O 1, Gould RL 1, Gay HC 1, Cox HJ 1, Coulson MC 3 and Howard RJ 1,2 1 Department of Old Age Psychiatry,
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 9: Sleep and Biological Rhythms This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public
AccuScreen ABR Screener
 AccuScreen ABR Screener Test Methods Doc no. 7-50-1015-EN/02 0459 Copyright notice No part of this Manual or program may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any
AccuScreen ABR Screener Test Methods Doc no. 7-50-1015-EN/02 0459 Copyright notice No part of this Manual or program may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any
Normal EEG of wakeful resting adults of years of age. Alpha rhythm. Alpha rhythm. Alpha rhythm. Normal EEG of the wakeful adult at rest
 Normal EEG of wakeful resting adults of 20-60 years of age Suthida Yenjun, M.D. Normal EEG of the wakeful adult at rest Alpha rhythm Beta rhythm Mu rhythm Vertex sharp transients Intermittent posterior
Normal EEG of wakeful resting adults of 20-60 years of age Suthida Yenjun, M.D. Normal EEG of the wakeful adult at rest Alpha rhythm Beta rhythm Mu rhythm Vertex sharp transients Intermittent posterior
German Mobile Telecommunication Research Program German Federal Office on Radiation Protection (BfS)
 German Mobile Telecommunication Research Program German Federal Office on Radiation Protection (BfS) International Workshop on Long Term Effects München-Ismaning, Germany Oct. 11-12, 2007 EFFECTS OF CHRONIC
German Mobile Telecommunication Research Program German Federal Office on Radiation Protection (BfS) International Workshop on Long Term Effects München-Ismaning, Germany Oct. 11-12, 2007 EFFECTS OF CHRONIC
Physiology of Sleep. Dr Nervana
 Physiology of Sleep Dr Nervana Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between sleep and coma. 2. Define NREM (non-rapid eye movement, SWS) and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 3. Describe how NREM and REM
Physiology of Sleep Dr Nervana Objectives: 1. Explain the difference between sleep and coma. 2. Define NREM (non-rapid eye movement, SWS) and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. 3. Describe how NREM and REM
EEG Changes (Research Abstracts)
 EEG Changes (Research Abstracts) Kennerly, Richard. QEEG analysis of cranial electrotherapy: a pilot study. Journal of Neurotherapy (8)2, 2004. Presented at the International Society for Neuronal Regulation
EEG Changes (Research Abstracts) Kennerly, Richard. QEEG analysis of cranial electrotherapy: a pilot study. Journal of Neurotherapy (8)2, 2004. Presented at the International Society for Neuronal Regulation
Section 1. Executive Summary
 Section 1 Executive Summary The toolkit was written by public health scientists and is intended as a background document, current to 2012, to assist medical health officers and environmental health officers
Section 1 Executive Summary The toolkit was written by public health scientists and is intended as a background document, current to 2012, to assist medical health officers and environmental health officers
I documenti di: quotidianosanità.it. Quotidiano online di informazione sanitaria
 I documenti di: quotidianosanità.it Quotidiano online di informazione sanitaria Dossier Documentazione legislativa Studi e ricerche Interventi e relazioni Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified
I documenti di: quotidianosanità.it Quotidiano online di informazione sanitaria Dossier Documentazione legislativa Studi e ricerche Interventi e relazioni Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified
Ebea, Erice (Sicily), 29/03/2008 Fixed site transmitter studies
 Ebea, Erice (Sicily), 29/03/2008 Fixed site transmitter studies M. Röösli, PhD University of Bern Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine Content > Introduction > Methodological challenges of studying
Ebea, Erice (Sicily), 29/03/2008 Fixed site transmitter studies M. Röösli, PhD University of Bern Institute of Social and Preventive Medicine Content > Introduction > Methodological challenges of studying
AGING AND SLEEP STAGE EFFECTS ON ENTROPY OF ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM SIGNALS
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge University of Kentucky Master's Theses Graduate School 2008 AGING AND SLEEP STAGE EFFECTS ON ENTROPY OF ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM SIGNALS Swetha Vennelaganti University of
University of Kentucky UKnowledge University of Kentucky Master's Theses Graduate School 2008 AGING AND SLEEP STAGE EFFECTS ON ENTROPY OF ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM SIGNALS Swetha Vennelaganti University of
OPINION of the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety
 The Director General Maisons-Alfort, 1 October 2013 OPINION of the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety concerning the update of the Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields
The Director General Maisons-Alfort, 1 October 2013 OPINION of the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety concerning the update of the Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields
Electrohypersensitivity a moving target from VDT to WiFi
 Electrohypersensitivity a moving target from VDT to WiFi Kjell Hansson Mild 1 and Monica Sandström 2 1. Dept. of Radiation Sciences, 2. Dept. of Occup. and Environ. Medicine, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden
Electrohypersensitivity a moving target from VDT to WiFi Kjell Hansson Mild 1 and Monica Sandström 2 1. Dept. of Radiation Sciences, 2. Dept. of Occup. and Environ. Medicine, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden
in Motion analysis TRAMA Project September th 2007
 First Course Basics in Motion analysis TRAMA Project September 10-12 th 2007 Prof. Guy CHERON Laboratory of Neurophysiology and Movement Biomechanics Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium Objectives Neurophysiology
First Course Basics in Motion analysis TRAMA Project September 10-12 th 2007 Prof. Guy CHERON Laboratory of Neurophysiology and Movement Biomechanics Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium Objectives Neurophysiology
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Durrenberger, G., Hillert, L., Kandel, S., Oftedal, G., Rubin, G. J., van Rongen, E., &
King s Research Portal Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Durrenberger, G., Hillert, L., Kandel, S., Oftedal, G., Rubin, G. J., van Rongen, E., &
D. Debatisse, E. Fornari, E. Pralong, P. Maeder, H Foroglou, M.H Tetreault, J.G Villemure. NCH-UNN and Neuroradiology Dpt. CHUV Lausanne Switzerland
 Vegetative comatose and auditory oddball paradigm with Cognitive evoked potentials (CEPs) and fmri: Implications for the consciousness model of Damasio and Guerit D. Debatisse, E. Fornari, E. Pralong,
Vegetative comatose and auditory oddball paradigm with Cognitive evoked potentials (CEPs) and fmri: Implications for the consciousness model of Damasio and Guerit D. Debatisse, E. Fornari, E. Pralong,
