Changing tracheostomy tubes
|
|
|
- Eleanore Horton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Changing tracheostomy tubes Changing the tracheostomy tube should be a multidisciplinary decision. The first change should always be performed or supervised by a suitably trained member of the medical staff. Videos of tube changes can be found here. Knowledge and Understanding In order to change a tracheostomy tube safely and appropriately, the practitioner must appreciate the specific clinical indications for the original formation of the individual patient s tracheostomy. In addition they will need to know when and how the tracheostomy was formed. It is considered that a newly formed tracheostomy will close more quickly than an established tracheostomy tract, and indeed within the first 48 hours of a surgical tracheostomy or 7-10 days for a percutaneous tracheostomy, extreme caution must be taken as a tube change may be difficult or even impossible. Patient assessment Indications to change a tracheostomy tube change include: The tube has been in-situ for maximum recommended duration: 30 days for tubes with a removable inner cannula (most manufacturer s recommendations) and 7-10 days for single lumen tubes Facilitating weaning by inserting a smaller, un-cuffed or fenestrated tube The patient needs ventilatory support or resuscitation and requires a change from an un-cuffed to a cuffed tube To improve fit or comfort of tube To replace a faulty tube To resolve a misplaced or displaced tube A tube change may be contra-indicated if the patient: Is in an unstable clinical condition (balancing risks/benefits) Requires high levels of ventilatory support or oxygen The risk of loosing the airway is high The tracheostomy was performed within the last 7 days, especially if percutaneously formed. The patient is undergoing radiotherapy to the neck region (or has completed course in last 2 weeks) In palliative care patients where quality of life will not be improved by tube change Patient refuses Each tracheostomy tube change and each patient should be assessed individually prior to each and every tube change, balancing the risks and benefits. The procedure will require two competent practitioners and more, especially if the patient becomes agitated during the procedure.
2 Particular caution needs to be taken in the following circumstances: First tube change Difficult previous tubes change Patient has a known obstructed or difficult upper airway (this is the back up airway in case of difficulties with the stoma) Early changes (within 2-4 days of surgical tracheostomy and 7-10 days of percutaneous tracheostomy) Patients with a large neck Patients requiring high levels of ventilator support Patients requiring high concentration of inspired oxygen Patients with tumours surrounding the tracheostomy tract Patients with significant granulation tissue around the stoma site Agitated or combative patients NB: If a difficult tube change is anticipated then a clinician experienced in upper airway management (including endotracheal intubation) and a clinician or practitioner proficient and experienced in managing tracheostomy tubes should be present. All relevant equipment and emergency anaesthetic drugs should be available. Plan for loss of airway and failure to cannulate the tracheostomy. Most tube changes are uneventful, but those that don t go smoothly can go badly wrong. Thorough preparation is essential. Following a successful initial change of tube, subsequent tube changes can be performed by a competent and suitably trained person but medical assistance and emergency equipment should be readily available at all times. The availability depends on your risk assessment of the clinical situation. It is essential to record how you changed the tube and any complications that arose. This record should also document recommendations for subsequent tube changes, such as timing and whether any particular equipment or personnel are required. If the tube change was straightforward, this is useful information to pass on also. Record any important details on the bed-head sign. The tubes may be changed like-for-like, changed for a different type of tracheostomy (e.g. fenestrated tube or a different brand), changed for a smaller tube (down-sizing) or removed completely (decannulation). Equipment required for a tracheostomy tube change Two tracheostomy tubes of appropriate make o 1 same size, 1 size smaller Dressing pack Normal saline (0.9%) to clean 10 ml syringe and cuff pressure manometer if the tube has a cuff Suction equipment and suction catheters. Sterile gloves and protective eye wear
3 Water soluble lubricating gel Tracheal dilators (local or individual preference) Pen torch Tracheostomy tube tapes, ties or dedicated holder Stoma dressing Stitch cutter if previous tube has been sutured New closed suction system (this is a good opportunity to change to clean ancillary equipment) Microbacterial swab of the stoma site may me indicated An exchange device such as an Aintree catheter or Bougie may be required Waveform capnography (essential if the patient is ventilator-dependent or a difficult procedure is expected) Resuscitation equipment Fibreoptic scope available Oxygen supply and appropriate masks to deliver oxygen to face or stoma Oxygen saturation monitoring Stethoscope Patient preparation Gaining the patient s trust and co-operation is essential. This is not always possible in the sedated, neurologically impaired or combative patient, but an explanation should always be attempted. The patient is likely to cough, feel a tugging and a pushing sensation in the neck, have blood stained secretions afterwards, but can be reassured that the procedure usually lasts less than 1 minute. Some patients will benefit from a sedative or analgesic premedication. The risks of this should always be balanced against the benefits and sedation should be prescribed and administered by an appropriate person. Sedating patients who are not breathing fully independently or have a high requirement for oxygen should only be done in an appropriate environment. Full resuscitation equipment should be available. Using sedation may mean that future tube changes become more complex to arrange and facilitate. Local anaesthetic gel can also be applied to the stoma for a few minutes prior to the procedure. Lubricating the new tube with local anaesthetic gel will improve any immediate post-procedural discomfort. Pre-oxygenation is essential before a tube change of a patient with oxygen or ventilator dependency, or those in whom the difficulty of the change is unknown.
4 Due to the risk of vomiting and aspiration associated with tube changes and airway manoeuvres, patients should ideally be nil by mouth for 6 hours for solids, and 2 hours for clear liquids before an elective tube change. If a patient has had many tube changes before without incident, then these guidelines could be reasonably relaxed. Patients fed via a tube feeding system should have this stopped and aspirated, and any gastric drainage tubes in situ should be aspirated also. Positioning the patient with the neck extended brings the trachea anteriorly. This should be done for all patients unless contra-indicated (e.g. cervical spine injury). Tube changes can be performed with the patient supine or reclined in a suitable chair or bed, depending on the clinical condition. The role of any stay sutures should be identified if present as these may elevate and widen the stoma. Any secretions that may have collected above the cuff of the old tube need to be removed prior to cuff deflation. This reduces the risk of contamination of the airway. In the sedated patient, this will involve oral, pharyngeal and subglottic suction with a soft catheter. Awake patients will find this uncomfortable, but it is important to remove secretions from above the cuff if possible. Tubes with specific sub-glottic suction channels allow some of the secretions to be cleared more easily. Any remaining secretions can be removed by timing cuff deflation (prior to tube removal) with expiration. The patient is asked to take a breath in and exhale strongly or cough as the cuff is deflated. If the patient is ventilated, then deflation is timed with the expiratory phase. Changing the tube An elective change of a tracheostomy tube can be performed using essentially 2 techniques: A blind technique where the new tube is inserted directly into the old stoma, or a guided technique using a wire or bougie to remove the old tube over and to railroad the new tube over. There are slight variations in these techniques for different circumstances. Videos of tube changes can be found below and there is a section on the e-learning part of the website
5 Tube changing videos may be found by clicking below: Removing a tracheostomy tube (narrated) Decannulation and application of oxygen to the stoma Tube changes over a bougie Fibreoptic inspection of a tracheostomy tube Blind insertion For well-established stomas that had had uneventful tube changes documented previously, changing the tube by simply removing the existing tube and re-inserting the new tube into the stoma is an accepted technique. The new tube is prepared by leaving the obturator in situ, as shown in the image to the right (purple piece in this image). This provides the tube with a smooth, tapered profile as it enters the neck. The tube is initially introduced with the tracheal portion flat to the stoma as shown in the sequences below. Once the trachea is entered, the tube is rotated through 90 degrees to enter the trachea. This rotation should not occur before the tube is within the trachea as this risks creating a false passage in the anterior tissues of the neck. The image to the left and below demonstrates an tube which has been placed into a false passage. The tube lies in the anterior tissues of the neck. Attaching the tube to any sort of gas supply and attempting ventilation could rapidly result in airway obstruction, pneumothorax, pneumomediatinum or subcutaneous (surgical) emphysema which could rapidly become life threatening. This also means that the stoma is not effective as a means of oxygenation and the trachea itself could be compromised.
6 Guided tube changes For the first tube change, or if there is either an unknown or predicted degree of difficulty in changing the tracheostomy tube, the exchange is usually performed over a guide. This can be a gum elastic bougie, an airway exchange catheter, a guide-wire or suction catheter. The principle is to insert the guide into the trachea via the old tube and leave it in situ when the old tube is removed. This ensures that the path from the skin, through the tissues of the neck to the trachea remains marked and should make insertion of the new tube easier. This technique is especially useful if the patient has a relatively new tracheostomy stoma or the neck is large, making the stoma deep. The superficial and deeper layers in the neck may spring back into their anatomical positions following removal of the existing tracheostomy tube as shown in the images below. Using a guide will help to reduce the impact of this. A selection of guides suitable for this purpose are shown below. It should be remembered that this technique relies on the old tube being correctly placed within the tracheal lumen when the guide is inserted. If there is any doubt about this, a fibreoptic inspection is recommended. Some airway exchange catheters can be first loaded over a suitable fibreoptic endoscope so that the catheter s position within the airway is confirmed visually. New tubes can be rail-roaded directly over a scope, but scopes are more easily damaged than a cheap, disposable bougie. Images (clockwise): Fibreoptic scope, suction catheters, guidewire, gum-elastic bougie
7 Day-to-day management of Tracheostomies & Laryngectomies The image to the left shows a bougie inserted into a tracheostomy tube. Because this is potentially unpleasant for the patient and risks trauma to the trachea, coughing or irritation of the carina (with associated vagal side effects), the bougie should be inserted for as short as possible. This means preparing the patient by first removing the dressings around the tube and the sutures or ties that hold the tube in place. The bougie should be held by a dedicated assistant, so that another pair of hands concentrates on cuff management and tube exchange. It is useful to have a talk through rehearsal between operators before undertaking the procedure. Gum elastic bougies are not primarily designed for tracheostomy tube exchanges. Several specific airway exchange catheters are available. Some of these allow connection to standard anaesthetic circuits to allow oxygenation during the exchange procedure and some have a large enough internal diameter to allow a fibreoptic scope to be inserted as described above. Image above shows a Cook Aintree Catheter connected to a 15mm port.
8 What to do if the new tube won t go in Sometimes, new tubes won t insert easily. It is important not to force a new tube into a stoma. Similarly, blindly attempting to pass a bougie or introducer into a deep or fresh tracheostomy stoma may lead to the creation of a false passage, cause bleeding and delay attempts at more conventional airway management. The key principle is to maintain oxygenation by whatever means necessary. In the elective situation, this may be as simple as reassuring the patient and awaiting a more experienced practitioner. In the oxygen or ventilatordependant patient, this can be more arduous. All necessary equipment, drugs and personnel should be on hand to manage this situation if the patient and clinical area have ben adequately prepared. The commonest solution to this problem is to insert a new tube that is a size smaller than the tube that has been removed. If necessary, the stoma can be formally dilated at a later time. If your experience and local guidelines allow, tracheal dilators (right) may be used to temporarily dilate the stoma whilst a new tube is inserted. If the patient has a patent upper airway, oxygen should be applied to the face whilst more invasive attempts at intubating the stoma are made. The goal is a safely oxygenated patient, and a formal reinsertion of the tube may need to occur in a planned manner in an operating theatre environment. If the clinical condition of the patient means that tube exchange needs to be more urgent, options include: Identification of the tract and trachea using a fibreoptic scope A scope and airway exchange catheter Digital manipulation of a bougie into the trachea* Blind passage of a bougie or guide-wire into the stoma* Formal refashioning of the stoma surgically or percutaneously *These options are more likely to result in incorrect placement of the tube tip and should only be considered in an emergency. A video demonstrating cannulation of a stoma using an Aintree catheter and fibreoptic scope is available here. There is more detail on managing a deteriorating tracheostomy or laryngectomy patient whose airway is compromised in the emergency management section.
9 Summary The table below summarises key actions related to tube changes and their rationales (adapted from NPSA expert working group) Action Rationale Identify need for tracheostomy tube To ensure tube change is necessary change and clarify type of tube to be and the correct tube type is selected inserted for current and on-going patient care needs Patient preparation may include To limit the risk of aspiration during ensuring nil by mouth for 2-6 hours tube change procedure (liquid-solid) and/or aspirate gastric tube Decide on blind or guided technique and assemble appropriate equipment Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain verbal consent if appropriate Ensure appropriate staff and equipment are available Set up bedside suction and oxygen equipment Prepare, check and lubricate new tube. Remove any inner cannulae from both old and new tubes Remove any obstructing clothing or equipment Position patient for procedure by placing a roll under the patient s shoulders, extending the stable neck. Patient may be placed lying down or sitting upright depending on individual patient assessment. Identify the roles of any stay sutures If the tracheostomy tube is sutured insitu, remove all sutures. Skin sutures may be considered for removal if appropriate. Guided techniques more appropriate for first or (potentially) difficult exchanges To ensure the patient understands the procedure & improve co-operation To deal appropriately with additional measures to secure an airway. To ensure oxygen and suction are available (when needed) To ensure new tube has no faults and is prepared for insertion and application. To ensure neck area is accessible for tube change To bring the trachea closer to the skin and to stretch stoma opening in order to aide tube insertion Elevate and open the stoma To allow tube removal and to prevent sutures becoming embedded or an infection risk Pharyngeal and sub-glottic suction Reduces risk of aspirating collections orally or via dedicated port on tube above the cuff Deflate cuff (if present) simultaneously To enable existing tube to be removed suctioning and for secretions to be cleared. Untie tapes and remove dressing To remove old dressings and tapes whilst tube is held firmly in place Insert guide via old tube (if used) Maintains patency of stoma
10 Remove existing tube with a firm out and downwards movement as patient breathes out Observe stoma site and tracheal opening Holding the introducer (obturator) in place, insert new directly tube into stoma OR using the guide, railroad the new tube Remove introducer / guide Check correct positioning: Ask patient to breathe out, air should be felt through end of tracheostomy Auscultate Bilateral chest movement Suction below the end of the tracheostomy to confirm placement within trachea Capnography* Fibreoptic endoscopy* Following successful exchange: To reduce patient coughing To identify signs of infection, granulation tissue and/or bleeding To pass tube along contour of tract To allow patient to breathe and to allow confirmation of correct tube position Evidence of airflow exiting the tube will confirm correct placement within the airway. *Capnography and endoscopy should be immediately available for difficult cases Re-attach any oxygen or ventilation needs To recommence respiratory requirements and secure tube position Inflate cuff and check cuff pressure, (as per guidelines) Apply tapes and dressing (as per guidelines) Re-position patient as to patient requirements and comfort To maintain patient comfort
Tracheostomy and laryngectomy airway emergencies: an overview for medical and nursing staff
 2013 Medical Journal Tracheostomy and laryngectomy airway emergencies: an overview for medical and nursing staff Steven Lobaz 1 and Paul Bush 2 1 ST6 and 2 Consultant Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive
2013 Medical Journal Tracheostomy and laryngectomy airway emergencies: an overview for medical and nursing staff Steven Lobaz 1 and Paul Bush 2 1 ST6 and 2 Consultant Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive
Competency 1: General principles and equipment required to safely manage a patient with a tracheostomy tube.
 Competency 1: General principles and equipment required to safely manage a patient with a tracheostomy tube. Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
Competency 1: General principles and equipment required to safely manage a patient with a tracheostomy tube. Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
Policies and Procedures. I.D. Number: 1154
 Policies and Procedures Title: TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE CHANGE - PEDIATRIC I.D. Number: 1154 Authorization: [X ] SHR Nursing Practice Committee Source: Nursing Date Effective: October 2008 Date Revised: March
Policies and Procedures Title: TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE CHANGE - PEDIATRIC I.D. Number: 1154 Authorization: [X ] SHR Nursing Practice Committee Source: Nursing Date Effective: October 2008 Date Revised: March
All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies
 Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Page 1 of 5 Scope: All bedside percutaneously placed tracheostomies Population: All ICU personnel Outcomes: To standardize and outline the steps necessary to safely perform a percutaneous tracheostomy
Waitin In The Wings. Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider
 Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
Emergency)tracheostomy)management)/)Patent)upper)airway)
 Emergency)tracheostomy)management)/)Patent)upper)airway) Call,for,airway,expert,help,,Look,,listen,&,feel,at,the,mouth,and,tracheostomy) A)Mapleson)C)system)(e.g.) Waters)circuit ))may)help)assessment)if)available)
Emergency)tracheostomy)management)/)Patent)upper)airway) Call,for,airway,expert,help,,Look,,listen,&,feel,at,the,mouth,and,tracheostomy) A)Mapleson)C)system)(e.g.) Waters)circuit ))may)help)assessment)if)available)
Oral care & swallowing
 Oral care & swallowing Oral care is important as it has a role to play in preventing healthcare associated infections. Dental plaque and the oropharynx can become colonized by bacteria and a biofilm can
Oral care & swallowing Oral care is important as it has a role to play in preventing healthcare associated infections. Dental plaque and the oropharynx can become colonized by bacteria and a biofilm can
TRACHEOSTOMY CARE. Tracheostomy- Surgically created hole that extends from the neck skin into the windpipe or trachea.
 1 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE Definitions: Trachea-Windpipe Tracheostomy- Surgically created hole that extends from the neck skin into the windpipe or trachea. Outer Cannula- The outer part of a trach tube. Usually
1 TRACHEOSTOMY CARE Definitions: Trachea-Windpipe Tracheostomy- Surgically created hole that extends from the neck skin into the windpipe or trachea. Outer Cannula- The outer part of a trach tube. Usually
Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients. Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA
 Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA Learning Objectives Define common terms identified with total (laryngectomy)
Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA Learning Objectives Define common terms identified with total (laryngectomy)
Policy x.xxx. Issued: Artificial Airways and Airway Care. ABC Home Medical Company Policy & Procedure Manual. A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes)
 A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes) A tracheotomy is a surgical procedure whereby an opening is cut into the trachea of the patient for the purpose of inserting a tube (trach tube). The trach tube allows
A. Tracheostomy Tubes ( trach tubes) A tracheotomy is a surgical procedure whereby an opening is cut into the trachea of the patient for the purpose of inserting a tube (trach tube). The trach tube allows
Other methods for maintaining the airway (not definitive airway as still unprotected):
 Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
Page 56 Where anaesthetic skills and drugs are available, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method of securing a definitive airway. This technique comprises: rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia
*gurgle* *snore* *slaver* Tracheostomy Emergencies with Trachy Tracey Helen Lyall ACCP LUHT 03/06/2016
 *gurgle* *snore* *slaver* Tracheostomy Emergencies with Trachy Tracey Helen Lyall ACCP LUHT 03/06/2016 Learning objectives Describe the difference in anatomy between a tracheotomy and a laryngectomy Understand
*gurgle* *snore* *slaver* Tracheostomy Emergencies with Trachy Tracey Helen Lyall ACCP LUHT 03/06/2016 Learning objectives Describe the difference in anatomy between a tracheotomy and a laryngectomy Understand
PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY. Courtesy of Cook Critical Care
 PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY Courtesy of Cook Critical Care EMERGENCY CRICOTHYROTOMY Thyroid Cartilage Access Site Cricoid Cartilage Identify the cricothyroid membrane between the cricoid and thyroid
PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY Courtesy of Cook Critical Care EMERGENCY CRICOTHYROTOMY Thyroid Cartilage Access Site Cricoid Cartilage Identify the cricothyroid membrane between the cricoid and thyroid
Translaryngeal tracheostomy
 Translaryngeal tracheostomy Issued: August 2013 NICE interventional procedure guidance 462 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg462 NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
Translaryngeal tracheostomy Issued: August 2013 NICE interventional procedure guidance 462 guidance.nice.org.uk/ipg462 NICE has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
Adult Patients Going Home with a Tracheostomy
 Physiotherapy Department Adult Patients Going Home with a Tracheostomy Darent Valley Hospital Darenth Wood Road Dartford Kent DA2 8DA www.dvh.nhs.uk In case of emergencies you will need to dial 999 If
Physiotherapy Department Adult Patients Going Home with a Tracheostomy Darent Valley Hospital Darenth Wood Road Dartford Kent DA2 8DA www.dvh.nhs.uk In case of emergencies you will need to dial 999 If
Foundations of Critical Care Nursing Course. Tracheostomy Workbook
 Foundations of Critical Care Nursing Course Tracheostomy Workbook 1 Key Reference: Dawson D (2014) Essential principles:trachepstomy care in the adult patient, Nursing in Critical Care, Vol 19, 2 p.63-72.
Foundations of Critical Care Nursing Course Tracheostomy Workbook 1 Key Reference: Dawson D (2014) Essential principles:trachepstomy care in the adult patient, Nursing in Critical Care, Vol 19, 2 p.63-72.
Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Coeditor/author. Associate Science Editor, American Heart Association
 Tracheotomy Challenges for airway specialists Elizabeth H. Sinz, MD Professor of Anesthesiology & Neurosurgery Associate Dean for Clinical Simulation Disclosures Coeditor/author Associate Science Editor,
Tracheotomy Challenges for airway specialists Elizabeth H. Sinz, MD Professor of Anesthesiology & Neurosurgery Associate Dean for Clinical Simulation Disclosures Coeditor/author Associate Science Editor,
The essential principles of tracheostomy care
 The essential principles of tracheostomy care Deborah Dawson Consultant Nurse Critical Care Excellence in specialist and community healthcare Key publications https://www.stgeorges.nhs.uk/gps-andclinicians/clinical-resources/tracheostomyguidelines/
The essential principles of tracheostomy care Deborah Dawson Consultant Nurse Critical Care Excellence in specialist and community healthcare Key publications https://www.stgeorges.nhs.uk/gps-andclinicians/clinical-resources/tracheostomyguidelines/
CARING FOR THE TRACHEOSTOMISED PATIENT: WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR
 CARING FOR THE TRACHEOSTOMISED PATIENT: WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR DR MOHD NAZRI ALI Anaesthesiologist & Intensivist HRPZ II, Kota Bharu, Kelantan Tracheostomy The Enabling Disability Tracheostomy Are becoming
CARING FOR THE TRACHEOSTOMISED PATIENT: WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR DR MOHD NAZRI ALI Anaesthesiologist & Intensivist HRPZ II, Kota Bharu, Kelantan Tracheostomy The Enabling Disability Tracheostomy Are becoming
Adult Intubation Skill Sheet
 Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
Adult Intubation 2. Opens the airway manually and inserts an oral airway *** 3. Ventilates the patient with BVM attached to oxygen at 15 lpm *** 4. Directs assistant to oxygenate the patient 5. Selects
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
Airway/Breathing. Chapter 5
 Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Rota-Trach Double Lumen Tracheostomy Tube VITALTEC
 Rota-Trach Double Lumen Tracheostomy Tube VITALTEC Contents INTRODUCTION HISTORY REVIEW ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OPERATIVE PROCEDURE THE RANGE OF TRACHEOSTOMY TUBES ROTA-TRACH TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE INTRODUCTION
Rota-Trach Double Lumen Tracheostomy Tube VITALTEC Contents INTRODUCTION HISTORY REVIEW ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OPERATIVE PROCEDURE THE RANGE OF TRACHEOSTOMY TUBES ROTA-TRACH TRACHEOSTOMY TUBE INTRODUCTION
Tracheostomy management Kate Regan MRCP FRCA Katharine Hunt FRCA
 Kate Regan MRCP FRCA Katharine Hunt FRCA The use of tracheostomy has increased over recent years. Traditionally, it was confined to the emergency management of upper airway obstruction; more recently,
Kate Regan MRCP FRCA Katharine Hunt FRCA The use of tracheostomy has increased over recent years. Traditionally, it was confined to the emergency management of upper airway obstruction; more recently,
Airway/Breathing. Chapter 5
 Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur rapidly
Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur rapidly
Information resource for the safer management of patients with tracheostomies and laryngectomies
 Information resource for the safer management of patients with tracheostomies and laryngectomies Draft guidance for review November 2010 2 Introduction This guide is a resource to help promote and facilitate
Information resource for the safer management of patients with tracheostomies and laryngectomies Draft guidance for review November 2010 2 Introduction This guide is a resource to help promote and facilitate
Interfacility Protocol Protocol Title:
 Interfacility Protocol Protocol Title: Mechanical Ventilator Monitoring & Management Original Adoption Date: 05/2009 Past Protocol Updates 05/2009, 12/2013 Date of Most Recent Update: March 23, 2015 Medical
Interfacility Protocol Protocol Title: Mechanical Ventilator Monitoring & Management Original Adoption Date: 05/2009 Past Protocol Updates 05/2009, 12/2013 Date of Most Recent Update: March 23, 2015 Medical
COMMUNICATION. Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT. Impact of Tracheostomy. Normal Speech. Facilitating Communication
 Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT 1. 2. 3. Management of communication needs. Management of swallowing issues. Working with the multidisciplinary team to facilitate weaning. Impact
Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT 1. 2. 3. Management of communication needs. Management of swallowing issues. Working with the multidisciplinary team to facilitate weaning. Impact
Tracheostomy. Information for patients and relatives
 Tracheostomy Information for patients and relatives page 2 What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy is a small hole (stoma) made at the front of the neck, which goes into the trachea (windpipe). A tube called
Tracheostomy Information for patients and relatives page 2 What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy is a small hole (stoma) made at the front of the neck, which goes into the trachea (windpipe). A tube called
TRACHEOSTOMY EMERGENCIES
 TRACHEOSTOMY EMERGENCIES MODULE: AIRWAY TARGET: ALL ANAESTHETISTS, INTENSIVISTS, ED & ACUTE PHYSICIANS, FOUNDATION DOCTORS BACKGROUND: Around 16% of ICU patients may have a tracheostomy. Life- threatening
TRACHEOSTOMY EMERGENCIES MODULE: AIRWAY TARGET: ALL ANAESTHETISTS, INTENSIVISTS, ED & ACUTE PHYSICIANS, FOUNDATION DOCTORS BACKGROUND: Around 16% of ICU patients may have a tracheostomy. Life- threatening
DIFFICULT AIRWAY MANAGMENT. Dr.N.SANTHOSH KUMAR MD ANESTHESIA (2 nd Yr)
 DIFFICULT AIRWAY MANAGMENT Dr.N.SANTHOSH KUMAR MD ANESTHESIA (2 nd Yr) AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND MAINTAINING OXYGENATION ARE THE FUNDAMENTAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF ANY BASIC DOCTOR. TO MANAGE A DIFFICULT AIRWAY,
DIFFICULT AIRWAY MANAGMENT Dr.N.SANTHOSH KUMAR MD ANESTHESIA (2 nd Yr) AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND MAINTAINING OXYGENATION ARE THE FUNDAMENTAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF ANY BASIC DOCTOR. TO MANAGE A DIFFICULT AIRWAY,
Kapitex Healthcare. making things clearer for tracheostomy patients
 Kapitex Healthcare making things clearer for tracheostomy patients preface In publishing this booklet, Kapitex Healthcare Ltd hopes to provide information and understanding for both the patient and carer
Kapitex Healthcare making things clearer for tracheostomy patients preface In publishing this booklet, Kapitex Healthcare Ltd hopes to provide information and understanding for both the patient and carer
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
Tracheostomy Sim Course
 Patients Name: Robert Smith Patients Age / DOB: 45 year old gentleman on medical ward Major Medical Problem Displaced tracheostomy tube Learning Goal Medical Early recognition of displaced tracheostomy
Patients Name: Robert Smith Patients Age / DOB: 45 year old gentleman on medical ward Major Medical Problem Displaced tracheostomy tube Learning Goal Medical Early recognition of displaced tracheostomy
This interdisciplinary clinical support document provides guidelines for the safe establishment of an artificial airway.
 PURPOSE This interdisciplinary clinical support document provides guidelines for the safe establishment of an artificial airway. POLICY STATEMENTS Endotracheal intubation will be performed by the Most
PURPOSE This interdisciplinary clinical support document provides guidelines for the safe establishment of an artificial airway. POLICY STATEMENTS Endotracheal intubation will be performed by the Most
(ix) Difficult & Failed Intubation Queen Charlotte s Hospital
 (ix) Difficult & Failed Intubation Queen Charlotte s Hospital Pre-operative Assessment Clinical assessment of airway and risk of difficult intubation: (can be performed in a matter of seconds): 1. Mouth
(ix) Difficult & Failed Intubation Queen Charlotte s Hospital Pre-operative Assessment Clinical assessment of airway and risk of difficult intubation: (can be performed in a matter of seconds): 1. Mouth
Review July Page 1 of 36. Title of Guideline. Contact Names and Job Title (authors) Directorate & Speciality
 Title of Guideline Contact Names and Job Title (authors) Directorate & Speciality Date of submission 06/07/2017 Date on which guideline must be reviewed Explicit definition of patient group to which it
Title of Guideline Contact Names and Job Title (authors) Directorate & Speciality Date of submission 06/07/2017 Date on which guideline must be reviewed Explicit definition of patient group to which it
Tracheostomy discharge information. Information for community nurses, patients and carers
 Tracheostomy discharge information Information for community nurses, patients and carers What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy is a surgical incision (cut) through the neck tissues into the trachea leaving
Tracheostomy discharge information Information for community nurses, patients and carers What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy is a surgical incision (cut) through the neck tissues into the trachea leaving
Summary Report for Individual Task Perform a Surgical Cricothyroidotomy Status: Approved
 Report Date: 12 Jul 2011 Summary Report for Individual Task 081-833-3005 Perform a Surgical Cricothyroidotomy Status: Approved DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
Report Date: 12 Jul 2011 Summary Report for Individual Task 081-833-3005 Perform a Surgical Cricothyroidotomy Status: Approved DISTRIBUTION RESTRICTION: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
Risky Extubation. Andy Higgs. Warrington Hospitals Cheshire UK
 Andy Higgs Warrington Hospitals Cheshire UK Declaration COOKMEDICAL Extubation plan DAS guideline Airway Exchange Catheters # 11 CAEC post maxillo-facial surgery Used as intubation stylets Airway Exchange
Andy Higgs Warrington Hospitals Cheshire UK Declaration COOKMEDICAL Extubation plan DAS guideline Airway Exchange Catheters # 11 CAEC post maxillo-facial surgery Used as intubation stylets Airway Exchange
Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction
 Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative.
Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative.
This information was created and reviewed through a partnership with the UAMS Patient and Family Advisory Councils.
 Tracheostomy Care You have a: Cuffed Tracheostomy Cuffless Tracheostomy What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy (sometimes called a trach rhymes with cake ) is a small opening, or stoma, in your throat.
Tracheostomy Care You have a: Cuffed Tracheostomy Cuffless Tracheostomy What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy (sometimes called a trach rhymes with cake ) is a small opening, or stoma, in your throat.
Basic Airway Management
 Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
1 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management 2 Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to
 1 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management 2 Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only. In
1 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management 2 Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only. In
Collaborative Regional Benchmarking Group (North of England, North Yorkshire & Humber and West Yorkshire)
 Collaborative Regional Benchmarking Group (North of England, North Yorkshire & Humber and West Yorkshire) Best Practice Guidance Endo Tracheal Tube Care These recommendations are based on the current evidence
Collaborative Regional Benchmarking Group (North of England, North Yorkshire & Humber and West Yorkshire) Best Practice Guidance Endo Tracheal Tube Care These recommendations are based on the current evidence
Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only.
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 40 Advanced Airway Management Advanced Airway Management The advanced airway management techniques discussed in this chapter are to introduce the EMT-B student to these procedures only.
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS
 KAPITEX HEALTHCARE - SPECIALIST KNOWLEDGE, SUPPORT AND CARE AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS Specialist tracheostomy management solutions you can trust Kapitex - Adding Quality of Life to Airway Management
KAPITEX HEALTHCARE - SPECIALIST KNOWLEDGE, SUPPORT AND CARE AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS Specialist tracheostomy management solutions you can trust Kapitex - Adding Quality of Life to Airway Management
CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR
 CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR 801-467-0800 Phone 800-800-HFJV (4358) Hotline TABLE OF CONTENTS Respiratory Care Considerations..3 Physician Considerations
CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR 801-467-0800 Phone 800-800-HFJV (4358) Hotline TABLE OF CONTENTS Respiratory Care Considerations..3 Physician Considerations
Tracheostomy. Intensive Care Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 Tracheostomy Intensive Care Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for patients having a tracheostomy and their relatives. It gives information on the procedure, and its benefits
Tracheostomy Intensive Care Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for patients having a tracheostomy and their relatives. It gives information on the procedure, and its benefits
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia
 1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
Tracheostomy. Hope Building Neurosurgery
 Tracheostomy Hope Building Neurosurgery 0161 206 5055 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Unique Identifier: CS36(17). Review date: November 2019 What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy
Tracheostomy Hope Building Neurosurgery 0161 206 5055 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Unique Identifier: CS36(17). Review date: November 2019 What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy
TRUSTED SOLUTIONS FOR SIMPLIFIED PATIENT CARE. Shiley Tracheostomy Product Guide GettyImages
 TRUSTED SOLUTIONS FOR SIMPLIFIED PATIENT CARE. Shiley Tracheostomy Product Guide GettyImages 503532118 TABLE OF CONTENTS Shiley Flexible Adult Tracheostomy Tubes 3 Shiley Extended-Length Tracheostomy Tubes
TRUSTED SOLUTIONS FOR SIMPLIFIED PATIENT CARE. Shiley Tracheostomy Product Guide GettyImages 503532118 TABLE OF CONTENTS Shiley Flexible Adult Tracheostomy Tubes 3 Shiley Extended-Length Tracheostomy Tubes
Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile)
 Patient information - Radiology Unit Tel 0118 322 7991 Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile) Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedures known as
Patient information - Radiology Unit Tel 0118 322 7991 Inserting a percutaneous biliary drain and biliary stent (a tube to drain bile) Introduction This leaflet tells you about the procedures known as
Respiratory Physio Protocol for Paediatric Patients on BIPAP via a tracheotomy (uncuffed tube)
 This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Respiratory Physio Protocol for Paediatric Patients on BIPAP via a tracheotomy (uncuffed tube) Reference Number: NHSCT/12/547
This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Respiratory Physio Protocol for Paediatric Patients on BIPAP via a tracheotomy (uncuffed tube) Reference Number: NHSCT/12/547
Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO:
 Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710805 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit is
Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710805 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 24FR Pull PEG kit is
Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO 2 table Warm
 NRP Skills Stations Performance Skills Station OR Integrated Skills Station STATION: Assisting with and insertion of endotracheal tube (ETT) Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO
NRP Skills Stations Performance Skills Station OR Integrated Skills Station STATION: Assisting with and insertion of endotracheal tube (ETT) Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO
This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home.
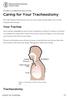 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
Educational Session: Evaluation and Management of the Difficult Airway
 Educational Session: Evaluation and Management of the Difficult Airway Diane M. Birnbaumer, MD, FACEP 3/24/2010 7:30 AM - 8:30 AM The Difficult Airway What s Up YOUR Sleeve? Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D.,
Educational Session: Evaluation and Management of the Difficult Airway Diane M. Birnbaumer, MD, FACEP 3/24/2010 7:30 AM - 8:30 AM The Difficult Airway What s Up YOUR Sleeve? Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D.,
H: Respiratory Care. Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 79
 H: Respiratory Care Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 79 Competency: H-1 Airway Management H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge
H: Respiratory Care Saskatchewan Association of Licensed Practical Nurses, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 79 Competency: H-1 Airway Management H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge
Major complications of airway management in the United Kingdom
 The Royal College of Anaesthetists The Difficult Airway Society 4th National Audit Project of The Royal College of Anaesthetists and The Difficult Airway Society Major complications of airway management
The Royal College of Anaesthetists The Difficult Airway Society 4th National Audit Project of The Royal College of Anaesthetists and The Difficult Airway Society Major complications of airway management
Full Range of Tracheostomy Solutions
 Full Range of Tracheostomy Solutions Every Breath Counts Choices by Setting Throughout the hospital or home Smiths Medical tracheostomy tubes are designed for performance ER The Portex Cricothyroidotomy
Full Range of Tracheostomy Solutions Every Breath Counts Choices by Setting Throughout the hospital or home Smiths Medical tracheostomy tubes are designed for performance ER The Portex Cricothyroidotomy
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 8.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12 15, 21, 24, 31-34, 39, 40, 54 8.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the upper and lower
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 8.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12 15, 21, 24, 31-34, 39, 40, 54 8.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the upper and lower
Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO:
 Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710802 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 20FR Guidewire
Initial placement 20FR Guidewire PEG kit REORDER NO: 00710802 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 1 of 5 These products have been manufactured not to include latex. Intended Use: The Initial placement 20FR Guidewire
Facility Name: Name: Date: Tracheostomy Care Evaluation Checklist
 Name: Date: Tracheostomy Care Evaluation Checklist Objective: Learner will be able to demonstrate tracheostomy care with a disposable inner cannula. Review facility protocol for caring for Airway Management:
Name: Date: Tracheostomy Care Evaluation Checklist Objective: Learner will be able to demonstrate tracheostomy care with a disposable inner cannula. Review facility protocol for caring for Airway Management:
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female)
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care
 Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care Date Revised: January 2015 Course Description Student Learning Objectives:
Bergen Community College Division of Health Professions Department of Respiratory Care Fundamentals of Respiratory Critical Care Date Revised: January 2015 Course Description Student Learning Objectives:
Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions
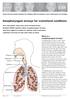 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Nasopharyngeal airways for craniofacial conditions This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH)
Ponsky * PEG Safety System - "Pull" Bard * PEG Safety System - "Guidewire" Information for Use
 Ponsky * PEG Safety System - "Pull" Bard * PEG Safety System - "Guidewire" Information for Use Rx only Single patient use DEHP-Free This product and package do not contain natural rubber latex STERILE
Ponsky * PEG Safety System - "Pull" Bard * PEG Safety System - "Guidewire" Information for Use Rx only Single patient use DEHP-Free This product and package do not contain natural rubber latex STERILE
Day-to-day management of Tracheostomies & Laryngectomies
 Humidification It is mandatory that a method of artificial humidification is utilised when a tracheostomy tube is in situ, for people requiring oxygen therapy dry oxygen should never be given to someone
Humidification It is mandatory that a method of artificial humidification is utilised when a tracheostomy tube is in situ, for people requiring oxygen therapy dry oxygen should never be given to someone
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 14 Practical Anesthesia Key Points 2 14.1 General Anesthesia Have a clear plan before starting anesthesia Never use an unfamiliar anesthetic technique in an emergency
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 14 Practical Anesthesia Key Points 2 14.1 General Anesthesia Have a clear plan before starting anesthesia Never use an unfamiliar anesthetic technique in an emergency
Tracheostomy Guidelines for NHS Wales
 Tracheostomy Guidelines for NHS Wales Prepared by the All Wales Tracheostomy Advisory Group, chaired by Duncan Ingrams, Assistant Medical Director ABUHB. 1 Introduction April 2018 Formulating one set of
Tracheostomy Guidelines for NHS Wales Prepared by the All Wales Tracheostomy Advisory Group, chaired by Duncan Ingrams, Assistant Medical Director ABUHB. 1 Introduction April 2018 Formulating one set of
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
Airway Management Essentials Self-Study Guide
 Airway Management Essentials Self-Study Guide Fourth Quarter 2010 Self-Study Guide Learning Objectives Cognitive Domain 1. Describe the various conditions that cause concern during treatment in the field
Airway Management Essentials Self-Study Guide Fourth Quarter 2010 Self-Study Guide Learning Objectives Cognitive Domain 1. Describe the various conditions that cause concern during treatment in the field
Use of the Aintree Intubation Catheter with the Laryngeal Mask Airway and a Fiberoptic Bronchoscope in a Patient with an Unexpected Difficult Airway
 Case Report Use of the Aintree Intubation Catheter with the Laryngeal Mask Airway and a Fiberoptic Bronchoscope in a Patient with an Unexpected Difficult Airway Andrew Zura MD, D. John Doyle MD PhD FRCPC,
Case Report Use of the Aintree Intubation Catheter with the Laryngeal Mask Airway and a Fiberoptic Bronchoscope in a Patient with an Unexpected Difficult Airway Andrew Zura MD, D. John Doyle MD PhD FRCPC,
Comparison of the Berman Intubating Airway and the Williams Airway Intubator for fibreoptic orotracheal intubation in anaesthetised patients.
 Title Comparison of the Berman Intubating Airway and the Williams Airway Intubator for fibreoptic orotracheal intubation in anaesthetised patients Author(s) Greenland, KB; Ha, ID; Irwin, MG Citation Anaesthesia,
Title Comparison of the Berman Intubating Airway and the Williams Airway Intubator for fibreoptic orotracheal intubation in anaesthetised patients Author(s) Greenland, KB; Ha, ID; Irwin, MG Citation Anaesthesia,
student handbook BARS handbook September 2012.indd Front Cover 27/11/12 12:08 PM
 student handbook BARS handbook September 2012.indd Front Cover 27/11/12 12:08 PM All materials regarding the Basic Airway Resuscitation Strategy Course were written and developed by Dr. Richard Morris
student handbook BARS handbook September 2012.indd Front Cover 27/11/12 12:08 PM All materials regarding the Basic Airway Resuscitation Strategy Course were written and developed by Dr. Richard Morris
Policies & Procedures. RNSP - RN Procedure. I.D. Number: 1097
 Policies & Procedures Title: ESOPHAGEAL TAMPONADE TUBE (MINNESOTA Tube) ASSISTING WITH INSERTION, CARE OF A PATIENT, ASSISTING WITH REMOVAL RNSP - RN Procedure I.D. Number: 1097 Authorization [x] Nursing
Policies & Procedures Title: ESOPHAGEAL TAMPONADE TUBE (MINNESOTA Tube) ASSISTING WITH INSERTION, CARE OF A PATIENT, ASSISTING WITH REMOVAL RNSP - RN Procedure I.D. Number: 1097 Authorization [x] Nursing
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Cricothyroidotomy LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define cricothyroidotomy. 3-2. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Cricothyroidotomy LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-7. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define cricothyroidotomy. 3-2. Identify
Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation David A. Muir Course Outline Physiology of Swallow
 Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation Mary Spremulli, MA, CCC-SLP Passy-Muir Clinical Consultant spre713@hotmail.com (949) 833-8255 David A. Muir 23 year-old ventilator
Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation Mary Spremulli, MA, CCC-SLP Passy-Muir Clinical Consultant spre713@hotmail.com (949) 833-8255 David A. Muir 23 year-old ventilator
Western General Hospital Tubefeeding Group Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Protocol, October 2008
 Lothian University Hospitals Division Western General Hospital Protocol for the Care of Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Tube 14 FG Medicina G Tube CARE OF PATIENT FOLLOWING TUBE INSERTION OBSERVATIONS
Lothian University Hospitals Division Western General Hospital Protocol for the Care of Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Tube 14 FG Medicina G Tube CARE OF PATIENT FOLLOWING TUBE INSERTION OBSERVATIONS
Chapter 11. Children with Special Healthcare Needs. Objectives. Definition 9/11/2012. Define children with special healthcare needs.
 Chapter 11 Children with Special Healthcare Needs Objectives Define children with special healthcare needs. Define technology-assisted children. Discuss specific assessment and management considerations
Chapter 11 Children with Special Healthcare Needs Objectives Define children with special healthcare needs. Define technology-assisted children. Discuss specific assessment and management considerations
Welcome to the Specialized Medical Services respiratory training webinar series!
 Welcome to the Specialized Medical Services respiratory training webinar series! SMS is your LTC facility single source for oxygen, medical equipment, respiratory care services and supplies nationwide.
Welcome to the Specialized Medical Services respiratory training webinar series! SMS is your LTC facility single source for oxygen, medical equipment, respiratory care services and supplies nationwide.
How do you use a bougie as an airway adjunct for endotracheal intubation?
 Ruth Bird, MBBCh -Specialist Registrar: Anaesthesia & Paediatric Trauma Fellow Daniel Nevin, MBBCh -Consultant in Anaesthesia & Pre-Hospital Care The Royal London Hospital London s Air Ambulance (HEMS)
Ruth Bird, MBBCh -Specialist Registrar: Anaesthesia & Paediatric Trauma Fellow Daniel Nevin, MBBCh -Consultant in Anaesthesia & Pre-Hospital Care The Royal London Hospital London s Air Ambulance (HEMS)
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Overview. Chapter 37. Advanced Airway Techniques. Sellick Maneuver 9/11/2012
 Chapter 37 Advanced Airway Techniques Slide 1 Sellick Maneuver Purpose Anatomic Location Technique Special Considerations Overview Advanced Airway Management of Adults Esophageal Tracheal Combitubes Tracheal
Chapter 37 Advanced Airway Techniques Slide 1 Sellick Maneuver Purpose Anatomic Location Technique Special Considerations Overview Advanced Airway Management of Adults Esophageal Tracheal Combitubes Tracheal
Airway/Breathing. Chapter 5
 Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid, assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid, assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Advanced Airway Management. University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track
 Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
Introducing the Fastrach-LMA. Prepared by Jim Medeiros, NREMT-P Regional Field Coordinator Lord Fairfax EMS Council
 Introducing the Fastrach-LMA Prepared by Jim Medeiros, NREMT-P Regional Field Coordinator Lord Fairfax EMS Council Objectives Review Anatomy of the Upper Airway Review LFEMSC LMA Protocol Discuss Indications
Introducing the Fastrach-LMA Prepared by Jim Medeiros, NREMT-P Regional Field Coordinator Lord Fairfax EMS Council Objectives Review Anatomy of the Upper Airway Review LFEMSC LMA Protocol Discuss Indications
Emergency First Response (EFR) Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017
 Emergency First Response () Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017 Airway management & ventilation Airway management & ventilation Trauma jaw thrust 1 Hand positions 2 Perform jaw thrust / mouth open 3
Emergency First Response () Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017 Airway management & ventilation Airway management & ventilation Trauma jaw thrust 1 Hand positions 2 Perform jaw thrust / mouth open 3
LEVITAN S FIBREOPTIC STYLET: BEYOND BARRIERS. - Our Perspective.
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 LEVITAN S FIBREOPTIC STYLET: BEYOND BARRIERS - Our Perspective. Justin Ebenezer Sargunaraj * Dr.Balasubramaniam Thiagarajan * *Stanley Medical College ABSTRACT: This
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 LEVITAN S FIBREOPTIC STYLET: BEYOND BARRIERS - Our Perspective. Justin Ebenezer Sargunaraj * Dr.Balasubramaniam Thiagarajan * *Stanley Medical College ABSTRACT: This
Changing Your Trach Tube
 Patient & Family Guide 2017 Changing Your Trach Tube www.nshealth.ca Changing Your Trach Tube Your entire trach tube should be changed about once a month, or sooner if you notice an odour (smell) or get
Patient & Family Guide 2017 Changing Your Trach Tube www.nshealth.ca Changing Your Trach Tube Your entire trach tube should be changed about once a month, or sooner if you notice an odour (smell) or get
NHS GREATER GLASGOW & CLYDE CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) INSERTION & MAINTENANCE OF INDWELLING
 Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
DEPARTMENT NAME GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT
 GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
RSPT Tracheal Aspiration. Tracheal Aspiration. RSPT 1410 Tracheal Aspiration
 1 RSPT 1410 2 is the use of to facilitate the removal of secretions from the respiratory tract. Under normal circumstances, patients with normal coughing do not have difficulty in removing secretions.
1 RSPT 1410 2 is the use of to facilitate the removal of secretions from the respiratory tract. Under normal circumstances, patients with normal coughing do not have difficulty in removing secretions.
If you suspect airway problems, get a second opinion before you anaesthetise, not after!
 Assessing the airway It is more important to be aware of the various methods of dealing with difficult laryngoscopy than to expect to be able to accurately identify the rare difficult patients without
Assessing the airway It is more important to be aware of the various methods of dealing with difficult laryngoscopy than to expect to be able to accurately identify the rare difficult patients without
F: Respiratory Care. College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 59
 F: Respiratory Care College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 59 Competency: F-1 Airway Management F-1-1 F-1-2 F-1-3 F-1-4 F-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability
F: Respiratory Care College of Licensed Practical Nurses of Alberta, Competency Profile for LPNs, 3rd Ed. 59 Competency: F-1 Airway Management F-1-1 F-1-2 F-1-3 F-1-4 F-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge and ability
I. Subject: Therapeutic Bronchoscopy and Bronchoscope Assisted Intubation
 I. Subject: Therapeutic Bronchoscopy and Bronchoscope Assisted Intubation II. Policy: Therapeutic flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedures and bronchoscope assisted intubations will be performed by
I. Subject: Therapeutic Bronchoscopy and Bronchoscope Assisted Intubation II. Policy: Therapeutic flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy procedures and bronchoscope assisted intubations will be performed by
Bronchoscopy SICU Protocol
 Bronchoscopy SICU Protocol Updated January 2013 Outline Clinical indications Considerations Preparation Bronchoscopy technique Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) Post-procedure Purpose Bronchoscopy is a procedure
Bronchoscopy SICU Protocol Updated January 2013 Outline Clinical indications Considerations Preparation Bronchoscopy technique Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) Post-procedure Purpose Bronchoscopy is a procedure
