Innovative in vitro models of toxicology assessments
|
|
|
- Annabel Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanism based Integrated Systems for the Prediction of Drug-Induced Liver Injury Innovative in vitro models of toxicology assessments Chris Goldring University of Liverpool London EUFEMED 2017
2 Drug-Induced Liver Injury From drugs were withdrawn post-marketing due to ADRs. Hepatotoxicity (81 cases; 18%) Immune-related reactions (79 cases; 17%) Cardiotoxicity (63 cases; 14%) BMC Med Feb 4;14:10
3 Drug-Induced Liver Injury Dose-dependent Species selective Selective individuals Idiosyncratic
4 Chemical Insults and DILI DRUG UPTAKE 1. Mitochondrial impairment DRUG ACCUMULATION METABOLISM CLEARANCE 2. Inhibition of biliary efflux 3. Lysosomal impairment 4. Reactive metabolites/ Covalent Binding Chemical stress Immune activation 5. Inflammation Immune System Innate Adaptive
5 Chemical Insults and DILI DRUG UPTAKE DRUG ACCUMULATION METABOLISM CLEARANCE 1. Mitochondrial impairment 2. Inhibition of biliary efflux 3. Lysosomal impairment 4. Reactive metabolites/ Covalent Binding Chemical stress Immune activation 5. Inflammation Immune System Innate Adaptive Diverse Clinical Presentations of DILI Acute fatty liver with lactic acidosis Acute hepatic necrosis Acute liver failure Acute viral hepatitis-like liver injury Autoimmune-like hepatitis Bland cholestasis Cholestatic hepatitis Cirrhosis Immuno-allergic hepatitis Nodular regeneration Nonalcoholic fatty liver Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome Vanishing bile duct syndrome
6 Genetic Restriction and Drug Hypersensitivity: Discovery of HLA Allele Associations Discovery of associations between HLA alleles and drug hypersensitivity represents an important advance Screening for HLA alleles during clinical practice effectively prevents reactions Abacavir Carbamazepine This is not the case for DILI Pharmacogenetics and Clinical Syndromes Abacavir HLA-B * 5701 OR = 132 hypersensitivity Flucloxacillin HLA-B * 5701 OR = 72 DILI Carbamazepine HLA-B * 1502 (Chinese) OR = 1000 SYS/TEN Carbamazepine HLA-A*3101 (Japanese) OR = 11 Hypersensitivity Carbamazepine HLA-A*3101 (Caucasians) OR = 30 Hypersensitivity So we need biomarkers and models Lumiracoxib HLA-DRB1*1501 OR = 7 DILI HLA-DQA1*0102 Ximelagatran HLA-DRB1*0701 OR = 4.4 Lapatinib HLA-BQA1*0201 OR = 9.0 DILI Mallal, 2008; Kindmark et al., 2008; Daly et al., 2009; Chung et al., 2004; McCormack et al., 2011; Singer et al., 2010; Spraggs et al., 2011
7 MIP-DILI Roadmap - Stratification of In Vitro systems Patient-dependent factors Physiology Pharmacology Toxicology Expression phenotype Tier 1 Transcriptome Proteome Function Cell Signalling Albumin secretion Biomarker secretion Drug Single Accumulation cell 2D systems Transporter Drug Bioactivation PHH inhibition Cholestasis Cell-lines Lysosomal Reporter-signalling impairment GSH depletion ER stress Oxidative stress Tier 2 Multi-dimensional 3D systems Multi-cell culture Spheroids Long term culture Tier 3 Complex systems Viral infection HLA restriction T cells
8 Patient-dependent factors MIP-DILI Roadmap - Stratification of In Vitro systems Tier 1 Physiology Expression phenotype Transcriptome Proteome Function Cell Signalling Albumin secretion Biomarker secretion Single cell 2D systems Pharmacology Drug Accumulation Drug Bioactivation/ Drug Covalent Bioactivation Binding Drug Detoxication Cytotoxicity Transporter inhibition Cholestasis Lysosomal impairment Toxicology Mitotoxicity GSH depletion ER stress Oxidative stress Databases Chemoinformatics Bioanalysis Transcriptomics Proteomics Metabolic profiles Tier 2 Multi-dimensional 3D systems Drug distribution Biomarkers Multi-cell culture Spheroids Long term culture Functional measurements Drug metabolizing enzyme activity Tier 3 Complex systems Viral infection HLA restriction T cells Transporter activity High content analysis Innate Signalling Adaptive response Mathematical modelling
9 Selection of Model Systems Importance of the physiological and pharmacological phenotype for the application of a toxicological test Is a particular test system fit for purpose? What purpose is it fit for?
10 Importance of the physiological and pharmacological phenotype for the application of a toxicological test TIER ONE Tier one cell types Primary Hepatocytes Liver-derived cell lines Fresh Cryo-preserved HepG2 HepaRG UpCytes itraq proteomic comparison
11 Proteomic phenotype HepG2 HepaRG Hepatocytes (PHH) Biological Replicate No. of proteins identified Proteins quantified Total (common to all replicates) 2726 Rowena Sison
12 HLCs Proteomic Phenotype MRP3 Cyp1A2 Cyp2E1 Cyp3A4 Cyp1A2 Cyp2E1 MRP3 Cyp3A4 hent hent Cyp3A5 Cytochrome P450s Phase II drug metabolising enzymes Transporters
13 MIP-DILI Training compounds MIP-DILI Refined Mitotox functional analysis conforms with Literature Compound Mitochondrial Liability Literature MIP-DILI Mitotox Analysis Reference Paracetamol Yes Inhibits ATP synthase, MPTP opener, mitochondrial ROS, Positive Parmar et al, 1995, Kon et al., 2004 Amiodarone Yes OXPHOS uncoupler, inhibits fatty acid oxidation via CPT1 inhibition Positive Fromenty et al., 1990 Kennedy et al., 2006 Nefazodone Yes - complex I > complex IV inhibition of ETC in HepG2 and isolated rat liver Positive Dykens et al., 2008 Tolcapone Yes - OXPHOS uncoupler, interacts with ETC complex proteins, FAO, bile acid synthesis. Forms MPT pores, decreases MMP Positive Korlipara, Cooper and Schapira, 2004 Entacapone Yes mild OXPHOS uncoupler Negative Korlipara et al., 2004 Bosentan No Negative Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2001) 69, Buspirone Yes - complex I inhibition of ETC in HepG2 and isolated rat liver Positive Dykens et al., 2008 Diclofenac Yes MPTP opener, mild OXPHOS uncoupler, inhibits ATP synthase and adenine nucleoside translocase Positive Moreno-Sanchez et al., 1999 Metformin Yes complex I inhibitor Positive Carvalho et al., 2008 Pioglitazone Yes complex I inhibitor Positive Scatena et al., 2004 Garcia-Ruiz, et al Ximelagatran No Negative Kenne et al., 2008 Fialuridine Perhexiline Troglitazone Yes impairs mtdna replication, Yes Inhibits carnitine uptake via CPT1, inhibits fatty acid oxidation Yes reported inhibitor of complex I, II, III, IV, V inhibitor, MPTP opener, OXPHOS uncoupler Negative (chronic toxicity) Negative (mechanistic factors) Positive Lewis et al., 1996 Kennedy et al., 2006 Nadanaciva, 2008 Scatena et al., 2004
14 Fialuridine fatal clinical trial Developed as an antiviral for HIV later considered as a treatment for hepatitis B Preclinical testing in mice, rats, dogs and monkeys Clinical Testing Patients Duration Comments HIV + /CMV + (12) 35 d Duration prolonged to HIV + /HBV + (43) 14 d sustain antiviral (HBV + ) HBV + (24) 28 d No signs of toxicity HBV + (15) 6 mth planned, terminated at wk 13 Sudden Hepatotoxicity & Pancreatitis 5 patients died (ALF) 2 survived after emergency liver transplant 3 recovered 3 showed no adverse effects (lower doses) Clinical Features of Toxicity Delayed (from week 13) Lactic Acidosis Micro and macro vesicular hepatic steatosis Abnormal mitochondria Indicative of mitochondrial dysfunction McKenzie et al, 1995 (333)
15 Fialuridine in vitro requirements Fialuridine KEY FEATURES OF MECHANISM OF TOXICITY Human specific (via hent mitochondrial localisation) Bioactivation to triphosphate (mitochondrial thymidine kinases) Delayed onset (wk 13 of clinical trial) Sudden and rapid acceleration of toxicity (threshold effect) Targets mitochondrial DNA replication Lactic acidosis and steatosis in humans
16 C e ll u la r A T P a n d r e t a i n e d L D H le v e l r e l a t i v e t o t h e v e h ic l e c o n t r o l ( % ) Fialuridine in vitro models: HepG2 vs HepaRG Healthy volunteers (5 mg dose) Cmax 0.6 µm (measured) Patients with DILI ( mg/kg/day) F ila u rid in e -7 d a y s HepG2: Max time course 7 days ~ µm (estimated from volunteers) HepaRG: Max time course 5 weeks d 14 d L D H -G lu c o s e L D H -G a la c to s e 5 0 A T P -G lu c o s e F ia lu r id in e C o n c e n tr a tio n (u M ) Negative mitotoxin A T P -G la lc to s e Positive mitotoxin Cytotoxicity in HepG2 at high concentrations not related to the clinical mitochondrial mechanism of action Extended dosing in HepaRG allows mitochondrial toxicity to develop.
17 Evidence for Mitoxicological Mechanism seen in Man FIAU BIOACTIVATION Mitochondrial uptake MP Phosphorylation TP Incorporation/inhibition of Pol γ DP mtdna replication mito-encoded respiratory complexes OXPHOS and Glycolysis Intracellular presence of FIAU-MP, -DP and TP (LC-MS) Lactate ATP Cell stress Cell death
18 Evidence for Mitoxicological Mechanism seen in Man FIAU Mitochondrial uptake Phosphorylation DECREASED MtDNA LEVELS Incorporation/inhibition of Pol γ mtdna replication mito-encoded respiratory complexes OXPHOS and Glycolysis Lactate ATP Quantified using PCR (mtdna and nudna quantified) Cell stress Cell death
19 OCR (pmol/min/mg protein) Evidence for Mitoxicological Mechanism seen in Man FIAU Mitochondrial uptake Decreased oxidative phosphorylation (using Seahorse Technology to measure oxygen consumption) Phosphorylation Incorporation/inhibition of Pol γ 6 week 2 week 4 mtdna replication 4 mito-encoded respiratory complexes 2 0 OXPHOS and Glycolysis Fialuridine (µm) Lactate ATP ATP-linked respiration Cell stress Indicates the oxygen consumption which is linked to ATP-production by OXPHOS Cell death
20 of vehicle control (%) Evidence for Mitoxicological Mechanism seen in Man FIAU Mitochondrial uptake Phosphorylation Incorporation/inhibition of Pol γ mtdna replication mito-encoded respiratory complexes OXPHOS and Glycolysis Decreased cellular ATP content followed by cell death (11 µm over 4 weeks) Lactate ATP Cell stress 0 Week 1 Week2 Week3 Week4 Cell death Cellular ATP Cell Viability (protein)
21 Importance of the physiological and pharmacological phenotype for the application of a toxicological test Fialuridine FIAU ENT1 FIAU HepG2 TK2 FIAU-MP TMPK HepaRG FIAU-DP FIAU-TP Cytosol Primary Hepatocytes Damaged mtdna Protein Equilibrative nucleoside transporter Thymidine kinase (cytosolic) Thymidine kinase (mitochondrial) HepG2 % HepaRG % Hepatocytes % ENT TK TK Thymidylate kinase TMPK
22 Importance of the physiological and pharmacological phenotype for the application of a toxicological test Fialuridine FIAU ENT1 FIAU HepG2 TK2 FIAU-MP TMPK HepaRG FIAU-DP FIAU-TP Cytosol Primary Hepatocytes Damaged mtdna Protein Equilibrative nucleoside transporter Thymidine kinase (cytosolic) Thymidine kinase (mitochondrial) HepG2 % HepaRG % Hepatocytes % ENT TK TK Thymidylate kinase TMPK
23 Importance of the physiological and pharmacological phenotype for the application of a toxicological test Fialuridine FIAU ENT1 FIAU HepG2 TK2 FIAU-MP TMPK HepaRG FIAU-DP FIAU-TP Cytosol Primary Hepatocytes Damaged mtdna Protein Equilibrative nucleoside transporter Thymidine kinase (cytosolic) Thymidine kinase (mitochondrial) HepG2 % HepaRG % Hepatocytes % ENT TK TK Thymidylate kinase TMPK
24 Importance of the physiological and pharmacological phenotype for the application of a toxicological test Fialuridine HepG2 ENT1 FIAU FIAU TK2 HepaRG FIAU-MP TMPK FIAU-DP Cytosol Primary Hepatocytes FIAU-TP Damaged mtdna HepG2 HepaRG Hepatocytes % % % Protein Equilibrative nucleoside transporter ENT Thymidine kinase (cytosolic) TK Thymidine kinase (mitochondrial) TK TMPK Thymidylate kinase
25 Beyond 2D liver cell culture Phenotype of Spheroids: KI - CDSS Whole proteome: 2D, spheroid, fresh primary hepatocytes and liver from several human donors Data expressed relative to freshly-isolated hepatocytes from corresponding donor Segregation of spheroid culture hepatocytes with fresh liver Bell et al., 2016 Sci Rep
26 Cross-centre assessment of 3D spheroids Compounds negative in a HCA analyses (n=35) were evaluated using the 3D spheroid system and overall 65% of compounds missed in the HCA screening were detected in the 3D spheroids as being hepatotoxic
27 3D spheroids within Industry The application of 3D spheroids would be more focused towards lower compound throughput and/or mechanistic studies # 1000 s Chemical class deselection # 100 s Limited number of chemical classes TIER I High throughput # 10 s Optimized chemical class TIER II Low throughput Cell Health assays 3D PHH spheroids 2D sandwich culture 3D HepaRG spheroids
28 Regeneration and homeostasis of the liver mass: Human In vitro Generation of long-lived human liver-like organoids from biliary ductal epithelial cells Evidence for a role for these cells in human liver regeneration at least in vitro Alternative route for generation of liver models (ie use human liver tissue bipotential stem cells)
29 Patient-dependent factors MIP-DILI Roadmap - Stratification of In Vitro systems Tier 1 Single cell 2D systems Physiology Expression phenotype Transcriptome Proteome Function Cell Signalling Albumin secretion Biomarker secretion Pharmacology Drug Accumulation Drug Bioactivation/ Drug Covalent Bioactivation Binding Drug Detoxication Cytotoxicity Transporter inhibition Cholestasis Lysosomal impairment Toxicology Mitotoxicity GSH depletion ER stress Oxidative stress Tier 2 Multi-dimensional 3D systems Multi-cell culture Spheroids Long term culture Tier 3 Complex systems Patient Factors Viral infection HLA restriction T cells Idiosyncratic
30 Conclusions We can develop a battery test system based on current science which is fit for purpose - refinement and benchmarking. The implementation of novel model systems with respect to industrial application is being conducted - EFPIA workshops. Multidimensional in vitro systems, which have a relevant physiological and pharmacological phenotype and are therefore fit for toxicological application(s) are being progressed - definitive qualitative and quantitative mass spectrometry Current status of novel model systems for idiosyncratic DILI with respect to human relevance - aspirational
31 Acknowledgements Centre for Drug Safety Science Kevin Park Mark Bayliss Ian Copple Lee Faulkner Neil French Roz Jenkins Laleh Kamalian Neil Kitteringham Amy Mercer Dean Naisbitt Rowena Sison-Young Karolinska Institute Magnus Ingelman-Sundberg Catherine Bell Volker Lauschke Sabrina Moro Servier Richard Weaver Riken Bioresource Centre Takao Iwawaki Supported by the European Community under the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) Programme through Grant Agreement number
Chemically Reactive Drug Metabolites in Drug Discovery and Development Detection, Evaluation, and Risk Assessment
 Chemically Reactive Drug Metabolites in Drug Discovery and Development Detection, Evaluation, and Risk Assessment Pacific Northwest Bio Meeting Seattle, WA, August 14, 2012 Thomas A. Baillie, PhD, DSc
Chemically Reactive Drug Metabolites in Drug Discovery and Development Detection, Evaluation, and Risk Assessment Pacific Northwest Bio Meeting Seattle, WA, August 14, 2012 Thomas A. Baillie, PhD, DSc
Mechanisms of Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions
 18/5/213 Mechanisms of Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions Munir Pirmohamed NHS Chair of Pharmacogenetics Department of Molecular and Clinical Pharmacology Institute of Translational Medicine University of
18/5/213 Mechanisms of Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions Munir Pirmohamed NHS Chair of Pharmacogenetics Department of Molecular and Clinical Pharmacology Institute of Translational Medicine University of
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models?
 The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
The liver in poisoning: what can we learn from animal models? Stephan Krähenbühl Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology University Hospital 4031 Basel/Switzerland Kraehenbuehl@uhbs.ch Outcome and causes of
BRIDGE THE GAP A Human Pathways Approach to Disease Research
 BRIDGE THE GAP A Human Pathways Approach to Disease Research BIOMED 21 Brussels December 8 th, 2015 Brigitte Landesmann Systems Toxicology Unit and EURL ECVAM Institute for Health and Consumer Protection
BRIDGE THE GAP A Human Pathways Approach to Disease Research BIOMED 21 Brussels December 8 th, 2015 Brigitte Landesmann Systems Toxicology Unit and EURL ECVAM Institute for Health and Consumer Protection
Is there a common mechanism of DILI, do we need to know?
 Is there a common mechanism of DILI, do we need to know? Neil Kaplowitz, MD USC Research Center for Liver Disease Los Angeles, California IS THERE A COMMON MECHANISM OF DILI? ANSWER YES & NO Mechanisms
Is there a common mechanism of DILI, do we need to know? Neil Kaplowitz, MD USC Research Center for Liver Disease Los Angeles, California IS THERE A COMMON MECHANISM OF DILI? ANSWER YES & NO Mechanisms
Putting Science to Work. Heptox Virtual Liver Platform
 Putting Science to Work A report on TAK-875 analysis using the Heptox Virtual Liver Platform Compound MW TAK 875 524.625 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Simulated exposures based on average drug plasma concentration
Putting Science to Work A report on TAK-875 analysis using the Heptox Virtual Liver Platform Compound MW TAK 875 524.625 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Simulated exposures based on average drug plasma concentration
Serum microrna biomarkers for human DILI
 CLEARANCE DRUG bioactivation covalent binding Detoxication GLUCURONIDE SULPHATE DRUG + METABOLITE chemical stress mitochondrial dysfunction apoptosis necrosis hepatocyte hypertrophy hepatocyte hyperplasia
CLEARANCE DRUG bioactivation covalent binding Detoxication GLUCURONIDE SULPHATE DRUG + METABOLITE chemical stress mitochondrial dysfunction apoptosis necrosis hepatocyte hypertrophy hepatocyte hyperplasia
Hepatotoxicity Test by Stem Cell derived Hepatocyte
 Tuesday, April 24, 2012 Workshop: Genetic Toxicology: Opportunities to Integrate New Approaches Hepatotoxicity Test by Stem Cell derived Hepatocyte Seiichi Ishida National Institute of Health Sciences
Tuesday, April 24, 2012 Workshop: Genetic Toxicology: Opportunities to Integrate New Approaches Hepatotoxicity Test by Stem Cell derived Hepatocyte Seiichi Ishida National Institute of Health Sciences
A shift in paradigm towards human biologybased systems for cholestatic-liver disease
 A shift in paradigm towards human biologybased systems for cholestatic-liver disease Fozia Noor Systems Toxicology In Vitro Metabolomics Biochemical Engineering Institute Saarland University, Germany BioMed21
A shift in paradigm towards human biologybased systems for cholestatic-liver disease Fozia Noor Systems Toxicology In Vitro Metabolomics Biochemical Engineering Institute Saarland University, Germany BioMed21
DMD # Do In Vitro Assays Predict Drug Candidate Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury Risk? J Gerry Kenna
 Do In Vitro Assays Predict Drug Candidate Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury Risk? J Gerry Kenna Safer Medicines Trust, Kingsbridge, UK. Email: gerry@safermedicines.org Tel: +44 1625 432113 Jack Uetrecht
Do In Vitro Assays Predict Drug Candidate Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury Risk? J Gerry Kenna Safer Medicines Trust, Kingsbridge, UK. Email: gerry@safermedicines.org Tel: +44 1625 432113 Jack Uetrecht
SYSTEMS BASED APPROACH FOR PREDICTON OF DRUG- INDUCED LIVER INJURY (DILI)
 SYSTEMS BASED APPROACH FOR PREDICTON OF DRUG- INDUCED LIVER INJURY (DILI) Points to cover Overview of Heptox platform Integration of in vitro and in silico approach Validation set of compounds Simulations
SYSTEMS BASED APPROACH FOR PREDICTON OF DRUG- INDUCED LIVER INJURY (DILI) Points to cover Overview of Heptox platform Integration of in vitro and in silico approach Validation set of compounds Simulations
Mechanistic Toxicology
 SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
Evidence-based selection of training compounds for use in the mechanism-based integrated prediction of drug-induced liver injury in man
 Arch Toxicol DOI 10.1007/s00204-016-1845-1 REVIEW ARTICLE Evidence-based selection of training compounds for use in the mechanism-based integrated prediction of drug-induced liver injury in man Sanja Dragovic1
Arch Toxicol DOI 10.1007/s00204-016-1845-1 REVIEW ARTICLE Evidence-based selection of training compounds for use in the mechanism-based integrated prediction of drug-induced liver injury in man Sanja Dragovic1
Elucidating Differences in the Hepatotoxic Potential of Tolcapone and Entacapone With DILIsym V R. , a Mechanistic Model of Drug-Induced Liver Injury
 Citation: CPT Pharmacometrics Syst. Pharmacol. (2016) 5, 31 39; VC 2016 ASCPT All rights reserved doi:10.1002/psp4.12053 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elucidating Differences in the Hepatotoxic Potential of Tolcapone
Citation: CPT Pharmacometrics Syst. Pharmacol. (2016) 5, 31 39; VC 2016 ASCPT All rights reserved doi:10.1002/psp4.12053 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elucidating Differences in the Hepatotoxic Potential of Tolcapone
BSEP inhibition and Drug Induced Liver Injury
 BSEP inhibition and Drug Induced Liver Injury Gerry Kenna Pharmaceutical Director, Safer Medicines Trust www.safermedicines.org Drug Safety Consultant Overview Drug Induced Liver Injury (DILI) BSEP inhibition
BSEP inhibition and Drug Induced Liver Injury Gerry Kenna Pharmaceutical Director, Safer Medicines Trust www.safermedicines.org Drug Safety Consultant Overview Drug Induced Liver Injury (DILI) BSEP inhibition
Prediction of Drug Induced Liver Disease, Pre and Post Marketing
 Prediction of Drug Induced Liver Disease, Pre and Post Marketing Sovani Vishwas ABSTRACT Drug induced liver disease is one of the most important causes of drug withdrawals post marketing. The liver is
Prediction of Drug Induced Liver Disease, Pre and Post Marketing Sovani Vishwas ABSTRACT Drug induced liver disease is one of the most important causes of drug withdrawals post marketing. The liver is
HEPATIC 3D SPHEROIDS AS A MODEL SYSTEM FOR DRUG-INDUCED LIVER INJURY AND CYTOCHROME P450 INDUCTION
 From the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden HEPATIC 3D SPHEROIDS AS A MODEL SYSTEM FOR DRUG-INDUCED LIVER INJURY AND CYTOCHROME P450 INDUCTION Delilah F.
From the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden HEPATIC 3D SPHEROIDS AS A MODEL SYSTEM FOR DRUG-INDUCED LIVER INJURY AND CYTOCHROME P450 INDUCTION Delilah F.
HIV long term complications
 HIV- 2015 long term complications 4th Asian Conference on Hepatitis & AIDS 22-23 May 2015, Xi'an, China Kees Brinkman Amsterdam The Netherlands NL 2012: known 17.000 (0,1%) treatment 85% (all) China 2011:
HIV- 2015 long term complications 4th Asian Conference on Hepatitis & AIDS 22-23 May 2015, Xi'an, China Kees Brinkman Amsterdam The Netherlands NL 2012: known 17.000 (0,1%) treatment 85% (all) China 2011:
HBV Forum 2 April 18 th 2017 Hilton Amsterdam.
 HBV Forum 2 April 18 th 2017 Hilton Amsterdam www.forumresearch.org Detection, Assessment and Management of DILI During Drug Development for HBV: The IQ DILI Initiative. Arie Regev, MD Global Patient Safety
HBV Forum 2 April 18 th 2017 Hilton Amsterdam www.forumresearch.org Detection, Assessment and Management of DILI During Drug Development for HBV: The IQ DILI Initiative. Arie Regev, MD Global Patient Safety
DILI: Clinical Pharmacology Considerations for Risk Assessment
 DILI: Clinical Pharmacology Considerations for Risk Assessment Raj Madabushi, PhD Office of Clinical Pharmacology Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June 06, 2017 Disclaimer: The views expressed
DILI: Clinical Pharmacology Considerations for Risk Assessment Raj Madabushi, PhD Office of Clinical Pharmacology Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June 06, 2017 Disclaimer: The views expressed
Summary of the Risk Management Plan
 Summary of the Risk Management Plan Summary of Risk Management Plan for Esmya (Ulipristal Acetate) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Esmya. The RMP details important risks of Esmya,
Summary of the Risk Management Plan Summary of Risk Management Plan for Esmya (Ulipristal Acetate) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Esmya. The RMP details important risks of Esmya,
Fundamentals of Membrane Transporters and their Role in In Vivo PK/PD of Drugs
 Fundamentals of Membrane Transporters and their Role in In Vivo PK/PD of Drugs Jash Unadkat, Ph.D. Department of Pharmaceutics University of Washington Seattle, WA 98195 http://depts.washington.edu/pceut/faculty_research/faculty_members/unadkat_jashvant.html
Fundamentals of Membrane Transporters and their Role in In Vivo PK/PD of Drugs Jash Unadkat, Ph.D. Department of Pharmaceutics University of Washington Seattle, WA 98195 http://depts.washington.edu/pceut/faculty_research/faculty_members/unadkat_jashvant.html
Agents that inhibit the BSEP and mitochondrial function what do we know? Prepared by Michael D. Aleo, Ph.D. Groton, Investigative Toxicology
 Agents that inhibit the BSEP and mitochondrial function what do we know? Prepared by Michael D. Aleo, Ph.D. Groton, Investigative Toxicology Declarations Nonclinical studies All procedures performed on
Agents that inhibit the BSEP and mitochondrial function what do we know? Prepared by Michael D. Aleo, Ph.D. Groton, Investigative Toxicology Declarations Nonclinical studies All procedures performed on
Inhibition of Human Hepatic Bile Acid Transporters as Contributing Factors to Drug-Induced Liver Injury
 Inhibition of Human Hepatic Bile Acid Transporters as Contributing Factors to Drug-Induced Liver Injury Kenneth R. Brouwer, Ph.D., RPh Chief Scientific Officer DDI Meeting June 2017 Seattle, Washington
Inhibition of Human Hepatic Bile Acid Transporters as Contributing Factors to Drug-Induced Liver Injury Kenneth R. Brouwer, Ph.D., RPh Chief Scientific Officer DDI Meeting June 2017 Seattle, Washington
Pharmacological Strategies for facilitating the excretion of Homogentisic acid in Alkaptonuria. DominicWilliams
 Pharmacological Strategies for facilitating the excretion of Homogentisic acid in Alkaptonuria DominicWilliams Background MRC Centre for Drug Safety Science Helpmeasure HGA in patients & rodents Led to
Pharmacological Strategies for facilitating the excretion of Homogentisic acid in Alkaptonuria DominicWilliams Background MRC Centre for Drug Safety Science Helpmeasure HGA in patients & rodents Led to
Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms?
 Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms? Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Disclosures No financial or other conflicts
Do Histological Features Inform DILI mechanisms? Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Conference XVII June, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Disclosures No financial or other conflicts
Metabolic diseases of the liver
 Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Metabolic diseases of the liver Central role in metabolism Causes and mechanisms of dysfunction Clinical patterns of metabolic disease Clinical approach to problem-solving Specific disorders Liver s central
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux
 Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
BCM 317 LECTURE OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 317 LECTURE BY OJEMEKELE O. JAUNDICE Jaundice is yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclera and mucous membrane, resulting from an increased bilirubin concentration in the body fluid. It is usually
BCM 317 LECTURE BY OJEMEKELE O. JAUNDICE Jaundice is yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclera and mucous membrane, resulting from an increased bilirubin concentration in the body fluid. It is usually
Application Note. Introduction
 Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
PREDICTING PHARMACOKINETICS FOLLOWING TOPICAL APPLICATION USING NON-ANIMAL METHODS IAN SORRELL, MI-YOUNG LEE, RICHARD CUBBERLEY
 PREDICTING PHARMACOKINETICS FOLLOWING TOPICAL APPLICATION USING NON-ANIMAL METHODS IAN SORRELL, MI-YOUNG LEE, RICHARD CUBBERLEY UNILEVER APPLICATIONS KINETICS Need for estimates of local and systemic concentrations
PREDICTING PHARMACOKINETICS FOLLOWING TOPICAL APPLICATION USING NON-ANIMAL METHODS IAN SORRELL, MI-YOUNG LEE, RICHARD CUBBERLEY UNILEVER APPLICATIONS KINETICS Need for estimates of local and systemic concentrations
Hepatic Transporter Proteins involved in Bile Formation
 Bile salt synthesis Hepatic Transporter Proteins involved in Bile Formation Basolateral membrane transporter proteins fx: NTCP uptake of bile salts OATP bulky organic anions Canalicular membrane transporter
Bile salt synthesis Hepatic Transporter Proteins involved in Bile Formation Basolateral membrane transporter proteins fx: NTCP uptake of bile salts OATP bulky organic anions Canalicular membrane transporter
Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
 Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
THBA Platform - Bile acid imbalance
 - Bile acid imbalance Bile acids play an important role in maintaining human health by means of signaling molecules in the regulation of bile formation, liver function and metabolism. The detergent effect
- Bile acid imbalance Bile acids play an important role in maintaining human health by means of signaling molecules in the regulation of bile formation, liver function and metabolism. The detergent effect
Falk Symposium 156: Genetics in Liver Disease. Pharmacogenetics. Gerd Kullak-Ublick
 Falk Symposium 156: Genetics in Liver Disease Pharmacogenetics Gerd Kullak-Ublick Division of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Department of Internal Medicine University Hospital Zurich Freiburg, 8.
Falk Symposium 156: Genetics in Liver Disease Pharmacogenetics Gerd Kullak-Ublick Division of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Department of Internal Medicine University Hospital Zurich Freiburg, 8.
Drug-induced toxicity on mitochondria and lipid metabolism: Mechanistic diversity and deleterious consequences for the liver
 Drug-induced toxicity on mitochondria and lipid metabolism: Mechanistic diversity and deleterious consequences for the liver Karima Begriche 1, Julie Massart 2, Marie-Anne Robin 2, Annie Borgne-Sanchez
Drug-induced toxicity on mitochondria and lipid metabolism: Mechanistic diversity and deleterious consequences for the liver Karima Begriche 1, Julie Massart 2, Marie-Anne Robin 2, Annie Borgne-Sanchez
Cryo Characterization Report (CCR)
 Human Cryopreserved Hepatocytes Lot number: HUM4061B Date: October 19, 2014 Cryo Characterization Report (CCR) Lot Overview Qualification Catalog Number Quantity Cryopreserved human hepatocytes, Qualyst
Human Cryopreserved Hepatocytes Lot number: HUM4061B Date: October 19, 2014 Cryo Characterization Report (CCR) Lot Overview Qualification Catalog Number Quantity Cryopreserved human hepatocytes, Qualyst
Systems biology approach to ximelagatran injury
 Note - presentation notes may be read by double clicking on the icon to the left FDA/CDER, PhRMA, AASLD: Recent Research Advances in Drug-Induced Liver Injury 2009-04-08 Systems biology approach to ximelagatran
Note - presentation notes may be read by double clicking on the icon to the left FDA/CDER, PhRMA, AASLD: Recent Research Advances in Drug-Induced Liver Injury 2009-04-08 Systems biology approach to ximelagatran
Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer
 icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
The Importance of ADME/PK to Inform Human Safety Assessments Based on Animal Studies: Example with Furan. Gregory L. Kedderis, PhD Chapel Hill, NC
 The Importance of ADME/PK to Inform Human Safety Assessments Based on Animal Studies: Example with Furan Gregory L. Kedderis, PhD Chapel Hill, NC Conflict of Interest None This research was conducted at
The Importance of ADME/PK to Inform Human Safety Assessments Based on Animal Studies: Example with Furan Gregory L. Kedderis, PhD Chapel Hill, NC Conflict of Interest None This research was conducted at
INTRODUCTION. Liver is the main organ responsible for the major metabolic and secretory functions in the
 INTRODUCTION Liver is the main organ responsible for the major metabolic and secretory functions in the body and hence appears to be a sensitive target site for substances modulating biotransformation
INTRODUCTION Liver is the main organ responsible for the major metabolic and secretory functions in the body and hence appears to be a sensitive target site for substances modulating biotransformation
Comparison Between the US FDA, Japan PMDA and EMA In Vitro DDI Guidance: Are we Close to Harmonization?
 Comparison Between the US FDA, Japan PMDA and EMA In Vitro DDI Guidance: Are we Close to Harmonization? Brian Ogilvie, Ph.D. VP Scientific Consulting XenoTech, LLC bogilvie@xenotechllc.com 14 Jun, 2018
Comparison Between the US FDA, Japan PMDA and EMA In Vitro DDI Guidance: Are we Close to Harmonization? Brian Ogilvie, Ph.D. VP Scientific Consulting XenoTech, LLC bogilvie@xenotechllc.com 14 Jun, 2018
Toxicology Research REVIEW. Introduction. Rosa Chan and Leslie Z. Benet * View Article Online View Journal
 REVIEW View Article Online View Journal Cite this: DOI: 10.1039/c8tx00016f Received 11th January 2018, Accepted 17th April 2018 DOI: 10.1039/c8tx00016f rsc.li/toxicology-research Evaluation of the relevance
REVIEW View Article Online View Journal Cite this: DOI: 10.1039/c8tx00016f Received 11th January 2018, Accepted 17th April 2018 DOI: 10.1039/c8tx00016f rsc.li/toxicology-research Evaluation of the relevance
Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology
 White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
HEPAMAP: A ROADMAP FOR HEPATOLOGY RESEARCH IN EUROPE: AN OVERVIEW FOR POLICY MAKERS
 HEPAMAP: A ROADMAP FOR HEPATOLOGY RESEARCH IN EUROPE: AN OVERVIEW FOR POLICY MAKERS HEPAMAP: A Roadmap For Hepatology Research In Europe: An Overview For Policy Makers Liver diseases are extremely costly
HEPAMAP: A ROADMAP FOR HEPATOLOGY RESEARCH IN EUROPE: AN OVERVIEW FOR POLICY MAKERS HEPAMAP: A Roadmap For Hepatology Research In Europe: An Overview For Policy Makers Liver diseases are extremely costly
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
Hepatic Efflux Transporters: Relevance to Drug-Drug Interactions and Drug Toxicity
 Hepatic Efflux Transporters: Relevance to Drug-Drug Interactions and Drug Toxicity Kim L. R. Brouwer, PharmD, PhD W.R. Kenan, Jr., Distinguished Professor Associate Dean for Research and Graduate Education
Hepatic Efflux Transporters: Relevance to Drug-Drug Interactions and Drug Toxicity Kim L. R. Brouwer, PharmD, PhD W.R. Kenan, Jr., Distinguished Professor Associate Dean for Research and Graduate Education
Life Sciences METABOLISM. Transform Your Metabolic Research
 METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Diagnostic evaluation of suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury
 Diagnostic evaluation of suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury Ynto de Boer, MD Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure No disclosures Drug-induced liver injury? Outline What is DILI? What,
Diagnostic evaluation of suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury Ynto de Boer, MD Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure No disclosures Drug-induced liver injury? Outline What is DILI? What,
Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):
 Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 A schematic representation of the most relevant
Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 A schematic representation of the most relevant
Drug-induced liver injury
 Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
Integrating Multiple Data using Syngene s Virtual Liver
 Integrating Multiple Data using Syngene s Virtual Liver Objective Use microarray results as input to the virtual liver model for prediction of toxicity Combine multiple experimental information for toxicity
Integrating Multiple Data using Syngene s Virtual Liver Objective Use microarray results as input to the virtual liver model for prediction of toxicity Combine multiple experimental information for toxicity
The role of Hepatitis C Virus in hepatocarcinogenesis
 The role of Hepatitis C Virus in hepatocarcinogenesis Laura Beretta Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center l8 Incidence and mortality of the five most common cancers worldwide, 2000 Incidence Lung Breast
The role of Hepatitis C Virus in hepatocarcinogenesis Laura Beretta Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center l8 Incidence and mortality of the five most common cancers worldwide, 2000 Incidence Lung Breast
Cellular Respiration. Cellular Respiration. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O > 6CO 2 + 6H energy. Heat + ATP. You need to know this!
 Cellular Respiration LISA Biology Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 - - - - - > 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy You need to know this! Heat + ATP 1 Did that equation look familiar? * The equation for cellular
Cellular Respiration LISA Biology Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 - - - - - > 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy You need to know this! Heat + ATP 1 Did that equation look familiar? * The equation for cellular
Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International
 Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International Ethanol and Glutathione Reduced glutathione plays a critical role in cellular detoxification processes including the metabolism of peroxides,
Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International Ethanol and Glutathione Reduced glutathione plays a critical role in cellular detoxification processes including the metabolism of peroxides,
RESPIRATION Worksheet
 A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure
 Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Disclosures Drug-induced Acute Liver Failure I have nothing to disclose. Raga Ramachandran, MD, PhD UCSF Pathology May 25, 2012 Acute liver failure (Fulminant hepatitis) Definition - onset of hepatic encephalopathy
Chemical Energy. Valencia College
 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
Phenotypic analysis of primary colorectal cancer to inform the management of metastatic disease
 Phenotypic analysis of primary colorectal cancer to inform the management of metastatic disease Paul Sutton CR(UK) Clinical Research Training Fellow Chester Colorectal Research Disclosures Holder of CR(UK)
Phenotypic analysis of primary colorectal cancer to inform the management of metastatic disease Paul Sutton CR(UK) Clinical Research Training Fellow Chester Colorectal Research Disclosures Holder of CR(UK)
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis
 Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Visit for Videos, Questions and Revision Notes. Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction
 Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Q1.(a) Describe how acetylcoenzyme A is formed in the link reaction. (b) In the Krebs cycle, acetylcoenzyme A combines with four-carbon oxaloacetate to form six-carbon citrate. This reaction is catalysed
Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Cellular Therapy
 Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Cellular Therapy Jason Lapetoda 1, Lee K Landeen, PhD 1, George K Michalopoulos, MD 2, Patricia W Bedard, PhD 1 1 Vital Therapies, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA 2 University of Pittsburgh
Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Cellular Therapy Jason Lapetoda 1, Lee K Landeen, PhD 1, George K Michalopoulos, MD 2, Patricia W Bedard, PhD 1 1 Vital Therapies, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA 2 University of Pittsburgh
Antiviral Chemotherapy
 12 Antiviral Chemotherapy Why antiviral drugs? Vaccines have provided considerable success in preventing viral diseases; However, they have modest or often no therapeutic effect for individuals who are
12 Antiviral Chemotherapy Why antiviral drugs? Vaccines have provided considerable success in preventing viral diseases; However, they have modest or often no therapeutic effect for individuals who are
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular
 III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Mechanisms of Cell Injury
 Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified
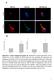 Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment
 Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20-1
 Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20-1 Learning Objectives 1. What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Met.? 2. What Are the Reduction Potentials for the Electron Transport Chain?
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20-1 Learning Objectives 1. What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Met.? 2. What Are the Reduction Potentials for the Electron Transport Chain?
NASH Bench to Bedside
 NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
Metabolic complications of HIV and HAART: The hyperlactataemia syndromes
 Metabolic complications of HIV and HAART: The hyperlactataemia syndromes Colin Menezes Division of Infectious Diseases Department of Internal Medicine Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University
Metabolic complications of HIV and HAART: The hyperlactataemia syndromes Colin Menezes Division of Infectious Diseases Department of Internal Medicine Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University
Pharmacologic Considerations when using DAAs in Cirrhosis
 Pharmacologic Considerations when using DAAs in Cirrhosis Jennifer J. Kiser, PharmD Assistant Professor University of Colorado Denver 1 st International Workshop on the Optimal Use of DAAs in Liver Transplant
Pharmacologic Considerations when using DAAs in Cirrhosis Jennifer J. Kiser, PharmD Assistant Professor University of Colorado Denver 1 st International Workshop on the Optimal Use of DAAs in Liver Transplant
Electron Transport and Oxidative. Phosphorylation
 Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron-transport chain electron- Definition: The set of proteins and small molecules involved in the orderly sequence of transfer to oxygen within the
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron-transport chain electron- Definition: The set of proteins and small molecules involved in the orderly sequence of transfer to oxygen within the
How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response that Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction
 How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response that Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction Jack Uetrecht, M.D., Ph.D. jack.uetrecht@utoronto.ca It is very difficult to study the mechanisms
How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response that Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction Jack Uetrecht, M.D., Ph.D. jack.uetrecht@utoronto.ca It is very difficult to study the mechanisms
How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response that Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction
 How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response that Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction Jack Uetrecht, M.D., Ph.D. jack.uetrecht@utoronto.ca It is very difficult to study the mechanisms
How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response that Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction Jack Uetrecht, M.D., Ph.D. jack.uetrecht@utoronto.ca It is very difficult to study the mechanisms
Elise Cook. BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology. BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology
 Acute and chronic toxicity of methamphetamine exposure in cultured neuronal cells Elise Cook BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology This thesis is
Acute and chronic toxicity of methamphetamine exposure in cultured neuronal cells Elise Cook BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology This thesis is
DILI PATHOLOGY. PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting
 DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
Muscle Metabolism. Dr. Nabil Bashir
 Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Over the past decade, the introduction of
 MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS C IN HIV-INFECTED PATIENTS: CLINICAL EXPERIENCE WITH PEGYLATED INTERFERON α PLUS RIBAVIRIN Raymond T. Chung, MD* ABSTRACT Coinfection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) is common
MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS C IN HIV-INFECTED PATIENTS: CLINICAL EXPERIENCE WITH PEGYLATED INTERFERON α PLUS RIBAVIRIN Raymond T. Chung, MD* ABSTRACT Coinfection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) is common
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It?
 MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
In Vitro ADMET Laboratories Inc. A Hepatocyte Enterocyte Research Organization. Columbia, MD and Malden, MA
 In Vitro ADMET Laboratories Inc. A Hepatocyte Enterocyte Research Organization Columbia, MD and Malden, MA In Vitro ADMET Laboratories (IVAL) Locations: Columbia, MD and Malden, MA Date of Incorporation:
In Vitro ADMET Laboratories Inc. A Hepatocyte Enterocyte Research Organization Columbia, MD and Malden, MA In Vitro ADMET Laboratories (IVAL) Locations: Columbia, MD and Malden, MA Date of Incorporation:
Chapter 3. Toxicity and the Factors That Modify Toxic Responses
 Chapter 3 Toxicity and the Factors That Modify Toxic Responses Cellular Basis of Toxicity All chemicals have the potential to produce toxicity. Toxicity may be generally defined as any adverse effect of
Chapter 3 Toxicity and the Factors That Modify Toxic Responses Cellular Basis of Toxicity All chemicals have the potential to produce toxicity. Toxicity may be generally defined as any adverse effect of
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function
 Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Drug-Induced Liver Injury
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Drug-Induced Liver Injury Neil Kaplowitz Gastroenterology/Liver Division, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles Drug-induced hepatotoxicity is a frequent
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Drug-Induced Liver Injury Neil Kaplowitz Gastroenterology/Liver Division, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles Drug-induced hepatotoxicity is a frequent
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA
 LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
Mechanisms of Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions and Their Implications for Risk Prediction
 Mechanisms of Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions and Their Implications for Risk Prediction Jack Uetrecht, M.D., Ph.D. Canada Research Chair in Adverse Drug Reactions University of Toronto jack.uetrecht@utoronto.ca
Mechanisms of Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions and Their Implications for Risk Prediction Jack Uetrecht, M.D., Ph.D. Canada Research Chair in Adverse Drug Reactions University of Toronto jack.uetrecht@utoronto.ca
MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW
 1 MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW A. MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW Mitochondrial Structure The arrangement of membranes: distinct inner and outer membranes, The location of ATPase, DNA and ribosomes The
1 MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW A. MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW Mitochondrial Structure The arrangement of membranes: distinct inner and outer membranes, The location of ATPase, DNA and ribosomes The
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW macrophages
 Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
An In Vitro Alternative For Predicting Systemic Toxicity. By: James McKim, Ph.D., DABT Chief Science Officer
 An In Vitro Alternative For Predicting Systemic Toxicity By: James McKim, Ph.D., DABT Chief Science Officer What is Systemic Toxicity and What do We Want From Alternative Methods? Toxicity that occurs
An In Vitro Alternative For Predicting Systemic Toxicity By: James McKim, Ph.D., DABT Chief Science Officer What is Systemic Toxicity and What do We Want From Alternative Methods? Toxicity that occurs
Chapter 14. Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior
 Chapter 14 Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior Why do you Eat and Breath? To generate ATP Foods, Oxygen, and Mitochodria Cells Obtain Energy by the Oxidation of Organic Molecules Food making ATP making
Chapter 14 Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior Why do you Eat and Breath? To generate ATP Foods, Oxygen, and Mitochodria Cells Obtain Energy by the Oxidation of Organic Molecules Food making ATP making
Strategy on Drug Transporter Investigation Why, How, Which & When. Jasminder Sahi
 Strategy on Drug Transporter Investigation Why, How, Which & When Jasminder Sahi Intestine Drug Absorption PEPT1 OATPs MCTs AE2 Epithelial Cell MCTs MRP3 Liver Excretion via Liver Kidney MRPs OATPs N PT1
Strategy on Drug Transporter Investigation Why, How, Which & When Jasminder Sahi Intestine Drug Absorption PEPT1 OATPs MCTs AE2 Epithelial Cell MCTs MRP3 Liver Excretion via Liver Kidney MRPs OATPs N PT1
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department
 Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
