Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Arnold Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D. Research Scientist
2 What we do.. Luxcel Intro may remove Advanced Fluorescence-based technologies Oxygen & ph Sensing Microplate-based Metabolism Assays Cell Metabolism Made Easy
3 More than just an ATP factory Mitochondrial reticulum heavily integrated into cellular processes not just an ATP factory Interplay between metabolism and cell signalling
4 Cell Metabolism Made Easy ph-xtra Glycolysis Assay Cell membrane Glucose ATP ph-xtra Stress Test Glycolysis Pyruvate? Lactate & H + [O 2 ] ATP O 2 H 2 O OxPhos NADH FADH 2 TCA Cycle FAO Glutamate FA MitoXpress -Xtra Oxygen Consumption Assay Mitochondrion Glutamine MitoXpress -Intra MitoXpress Stress Test - Oxygenation Cytosol CO 2 Glutamine Microplate-based cell metabolism assays 2D and 3D compatible Measured on Fluorescence plate reader Multiplexable with conventional assays MitoXpress - FAO Adapted from Nature Reviews Immunology 5,
5 Fluorescent Signal Luxcel Core Technology: O 2 Sensing Family of fluorescent O 2 sensitive probes & dyes O 2 causes a reversible decrease in probe signal Respiration: O 2 = Probe signal [O 2 ] = (Io/I) -1 K D Non-Chemical & Reversible [O 2 ] [O 2 ] [O 2 ] Hypoxic [O 2 ] Normoxic Y. Will, Hynes J. et al. - Nature Protocols, 2007,1:
6 MitoXpress-Xtra Oxygen Consumption Assay
7 Fluorescent Signal Oxygen Consumption: MitoXpress-Xtra Oil (O 2 barrier) Activation Untreated [O 2 ] [O 2 ] Growth media Inhibition Cells Control
8 CLARIOstar Assay Protocol Buttons
9 CLARIOstar Assay Protocol Buttons
10 MitoXpress Xtra: MARS & Data Analysis
11 µs OCR/h MitoXpress Stress Test: Data Output Time (min) FCCP (2.5 µm) Untreated Oligomycin (1 µm) Antimycin (1 µm) Spare capacity ATP coupled Non-ATP coupled Non ETC Basal Maximal Data by Melanie Schwalfenberg
12 Assay Platform Integration Beat Rate hips Cardiomyocytes Cor4U (NCARDIA) Impact of isoproterenol on beat rate and metabolism Data generate by Cristina Bertinetti-Lapatki (Roche) Untreated Isoproterenol (1µM) Antimycin (1µM) % O 2 Untreated Isoproterenol (1µM) Courtesy of NCARDIA Time
13 Glycolytic Flux (ECA): ph-xtra
14 % Effect Slope (µs/hr) % Effect Cor4U Metabolic Characterisation OxPhos, Glycolysis, FAO O 2 Consumption Glycolytic Flux (ECA) ATP ATP depletion is ameliorated through increased glycolytic flux DMSO Antimycin A Rotenone FCCP (1 µm) (1 µm) (2.5 µm) O 2 Consumption Glycolytic Flux (ECA) Baseline LC-FA respiration Non LC-FA respiration Ox Under stressed conditions (FCCP treatment) increased ETC activity is driven mainly by long-chain fatty acid oxidation Facilitates high-throughput metabolic characterisation Non ETC OCR Antimycin (µm) 0 Coupled Uncoupled
15 Summary 1 Measured mitochondrial function (OxPhos) and Glycolytic flux (ECA) Panel of convenient companion kits to probe metabolism further Simple mix and measure assay procedures Plate-reader based metabolism assays convenient and high throughput No requirement for expensive dedicated instrumentation Can be multiplexed with other relevant parameters (MMP, ROS, Cell viability etc) Flexible - Compatible with any plate type (including 3D plates) Also very well suited to suspensions cells (including bacterial, yeast, fungi etc)
16 Oxygenation & Ischemia Reperfusion
17 Monitoring Oxygenation MitoXpress -Intra Intracellular Oxygen Assay Unique cell-penetrating O 2 sensitive nanoparticle probe Long-term stability Simple loading procedure Multiplexable Plate-reader compatible Robust O 2 scale via ratiometic TRF Measurements
18 Ischemia Reperfusion Ischaemia-reperfusion (IR) injury: Occurs when tissue blood supply is restricted and subsequently restored (myocardial infarction, renal failure and stroke) Reperfusion associated with ROS-mediated damage - Triggers inflammatory - cell death. Rational development of targeted therapeutic interventions requires good in vitro model Current In vitro IR models ATP depletion Oil overlays to induce autohypoxia glucose oxidase addition to cause sample deoxygenation N 2 purged hypoxia chambers to induce a slow reduction in dissolved O 2 They do not replicate conditions of IR injury in vitro Need rapid, controlled, transient, ischemic shock and rapid controlled reperfusion Need real-time cellular oxygenation monitoring to allow accurate IR characterisation Need parallel measurements of critical IR injury parameters such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP).
19 Ischemia Reperfusion Cor.4U cells MitoXpress -Intra CLARIOstar with ACU
20 MitoXpress-Intra Signal (µs) MitoXpress -Intra Intracellular Oxygen Assay % O 2 Real-time monitoring of cellular oxygenation Data by Conn Carey & Melanie Schwalfenberg
21 MitoXpress -Intra Intracellular Oxygen Assay Real-time monitoring of cellular oxygenation allows us to question key assumptions Assumption 1: To maintain cells at desired [O 2 ], simply set chamber to that value
22 MitoXpress -Intra Intracellular Oxygen Assay Instrument O 2 Antimycin Treated (ETC inhibition) Untreated (Metabolically Active) Real-time monitoring of cellular oxygenation allows us to question key assumptions Assumption 1: To maintain cells at desired [O 2 ], simply set chamber to that value
23 Cellular Oxygenation is Dynamic Basal metabolism has reduced O 2 concentrations to ~14% Treatment with the ETC inhibitor Antimycin ETC & [O 2 ] returns to ambient levels β-adrenoreceptor agonist isoproterenol: beat rate - O 2 consumption - [O 2 ] ~6% Reduction in intracellular O 2 driven by Cor4U respiration % O 2 Compound treatment Antimycin (1µM) Assumption 2: Respiratory deoxygenation is fixed, just requires a simple correction Invalid Untreated Further O 2 depletion caused by Isoproterenol treatment Isoproterenol (1µM) Time (min) Data by Conn Carey Cor4U cardiomyocytes from Ncardia
24 DHE Intensity JC-1 Ratio Multiparametric Analysis (Cor4U) %O Time (min) Data by Conn Carey & Melanie Schwalfenberg ACU Non Respiring Respiring MMP ROS Untreated Untreated Cor4U cells Ncardia ( Antimycin Antimycin
25 Summary 2 Cells in vivo are typically cultured at hyperglycaemic and hyperoxic conditions This can have significant biological consequences Technology exits control cellular oxygen (e.g. BMG CLARIOstar & ACU) Monitoring is the critical aspect MitoXpress -Intra THE ONLY AVAILABLE SOLUTION Not correct that cells experience the O 2 set value (Respiration V Diffusion) Not correct that respiratory contribution to hypoxia is fixed Awareness of these factors can improve physiological relevance of in vitro models Multiparametric analysis - delineate relationship between O 2 & metabolism/ signalling Providing new insights into Tumour metabolism & ischemia reperfusion
26 Any Questions?
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux
 Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
MitoXpress FAO Assay. For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation
 MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment
 Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer
 icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function
 Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Application Note. Introduction
 Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
ab Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay
 Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction
 Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
ab Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay
 Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
Cell Metabolism Assays. for. Immunology. Research
 the immunity-metabolism link Cell Metabolism Assays for Immunology Research GOLD STANDARD ASSAYS FOR MEASURING METABOLIC RePROGRAMMING Metabolic Signatures Cell activation, amplification, and effector
the immunity-metabolism link Cell Metabolism Assays for Immunology Research GOLD STANDARD ASSAYS FOR MEASURING METABOLIC RePROGRAMMING Metabolic Signatures Cell activation, amplification, and effector
ab Intracellular O 2 Probe
 ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department
 Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Electron Transport and Oxidative. Phosphorylation
 Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron-transport chain electron- Definition: The set of proteins and small molecules involved in the orderly sequence of transfer to oxygen within the
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron-transport chain electron- Definition: The set of proteins and small molecules involved in the orderly sequence of transfer to oxygen within the
Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation The cheetah, whose capacity for aerobic metabolism makes it one of the fastest animals Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 1 14.4 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation The cheetah, whose capacity for aerobic metabolism makes it one of the fastest animals Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 1 14.4 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Cellular Respiration Part V: Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Cellular Respiration Part V: Oxidative Phosphorylation Figure 9.16 Electron shuttles span membrane 2 NADH or 2 FADH 2 MITOCHONDRION 2 NADH 2 NADH 6 NADH 2 FADH 2 Glucose Glycolysis 2 Pyruvate Pyruvate
Cellular Respiration Part V: Oxidative Phosphorylation Figure 9.16 Electron shuttles span membrane 2 NADH or 2 FADH 2 MITOCHONDRION 2 NADH 2 NADH 6 NADH 2 FADH 2 Glucose Glycolysis 2 Pyruvate Pyruvate
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate
 Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
RESPIRATION Worksheet
 A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter 6 Introduction: How Is a Marathoner Different from a Sprinter? Individuals inherit various percentages of the two main types of muscle fibers, slow and fast The
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter 6 Introduction: How Is a Marathoner Different from a Sprinter? Individuals inherit various percentages of the two main types of muscle fibers, slow and fast The
4. Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules? a. 2. d. 5
 1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways In General
 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
Life Sciences METABOLISM. Transform Your Metabolic Research
 METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Citric Acid Cycle and Electron Transport
 Carbohydrate Metabolism: Citric Acid Cycle and Electron Transport The respiratory pathways in the plant mitochondria include the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain and ADP phosphorylation.
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Citric Acid Cycle and Electron Transport The respiratory pathways in the plant mitochondria include the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain and ADP phosphorylation.
Cell Metabolism Assays. for OMICS. Research
 Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
Electron Transport and oxidative phosphorylation (ATP Synthesis) Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college
 Electron Transport and oxidative phosphorylation (ATP Synthesis) Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved
Electron Transport and oxidative phosphorylation (ATP Synthesis) Dr. Howaida Nounou Biochemistry department Sciences college The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Electron Transport Chain (overview) The NADH and FADH 2, formed during glycolysis, β- oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O 2 to H 2 O. Electron transfer occurs through
Electron Transport Chain (overview) The NADH and FADH 2, formed during glycolysis, β- oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O 2 to H 2 O. Electron transfer occurs through
Chapter 9 Notes. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Chapter 9 Notes Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Objectives Distinguish between fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the cell
Chapter 9 Notes Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Objectives Distinguish between fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the cell
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
Bell Work. b. is wrong because combining two glucose molecules requires energy, it does not release energy
 Bell Work How is energy made available to the cell to move large starch molecules across the cell membrane through the process of endocytosis? a. removing a phosphate from ATP b. combining two glucose
Bell Work How is energy made available to the cell to move large starch molecules across the cell membrane through the process of endocytosis? a. removing a phosphate from ATP b. combining two glucose
Multiparametric assessment of the effects of chemotherapeutic drugs on the (electro)physiology of Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes
 Multiparametric assessment of the effects of chemotherapeutic drugs on the (electro)physiology of Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes Event Presenter Date Ncardia Workshop Tessa de Korte, MSc December 1, 2017 Page
Multiparametric assessment of the effects of chemotherapeutic drugs on the (electro)physiology of Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes Event Presenter Date Ncardia Workshop Tessa de Korte, MSc December 1, 2017 Page
SOD1 inhibition reduces non-small cell lung cancer by inducing cell death
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION SOD1 inhibition reduces non-small cell lung cancer by inducing cell death Andrea Glasauer, Laura A. Sena, Lauren P. Diebold, Andrew P. Mazar & Navdeep S. Chandel Inventory of Supplemental
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION SOD1 inhibition reduces non-small cell lung cancer by inducing cell death Andrea Glasauer, Laura A. Sena, Lauren P. Diebold, Andrew P. Mazar & Navdeep S. Chandel Inventory of Supplemental
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2
 Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2 Biol 638, Exam-2 (Code-1) 1. Assume that 16 glucose molecules enter into a liver cell and are attached to a liner glycogen one by one. Later, this glycogen is broken-down
Biology 638 Biochemistry II Exam-2 Biol 638, Exam-2 (Code-1) 1. Assume that 16 glucose molecules enter into a liver cell and are attached to a liner glycogen one by one. Later, this glycogen is broken-down
Supplementary Figure 1
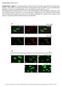 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY
 CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
Cell Respiration Ch 7. Both autotrophs and heterotrophs use cellular respiration to make CO2 and water from
 Cell Respiration Ch 7 Objectives: Identify the 2 major steps of cellular respiration Describe the major events in glycolysis Compare lactic acid fermentation with alcoholic fermentation Calculate the efficiency
Cell Respiration Ch 7 Objectives: Identify the 2 major steps of cellular respiration Describe the major events in glycolysis Compare lactic acid fermentation with alcoholic fermentation Calculate the efficiency
2. What is molecular oxygen directly converted into? a. Carbon Dioxide b. Water c. Glucose d. None of the Above
 Biochem 1 Mock Exam 3 Chapter 11: 1. What is glucose completely oxidized into? a. Carbon Dioxide and Water b. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen c. Oxygen and Water d. Water and Glycogen 2. What is molecular oxygen
Biochem 1 Mock Exam 3 Chapter 11: 1. What is glucose completely oxidized into? a. Carbon Dioxide and Water b. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen c. Oxygen and Water d. Water and Glycogen 2. What is molecular oxygen
Reading Assignments. A. Energy and Energy Conversions. Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. gasoline) or elevated mass.
 Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Cellular Respiration Assignment
 I. MULTIPLE CHOICES. Select the best answer. Write the letter of your choice on the space provided. 1. Electron transport chain allows the electron to. a) transfer from grana to stroma. b) transfer from
I. MULTIPLE CHOICES. Select the best answer. Write the letter of your choice on the space provided. 1. Electron transport chain allows the electron to. a) transfer from grana to stroma. b) transfer from
Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology
 White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES. Bratislav M. Janjic
 ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES by Bratislav M. Janjic Diplom in Biology, Univerziteta u Beogradu, Yugoslavia, 1996 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the
ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES by Bratislav M. Janjic Diplom in Biology, Univerziteta u Beogradu, Yugoslavia, 1996 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the
Cellular Respiration Checkup Quiz. 1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans?
 1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans? I. Pyruvate II. III. ATP Lactate A. I only B. I and II only C. I, II and III D. II and III
1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans? I. Pyruvate II. III. ATP Lactate A. I only B. I and II only C. I, II and III D. II and III
Active Learning Exercise 5. Cellular Respiration
 Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 5. Cellular Respiration Reference: Chapter 9 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) 1. Give the overall balanced chemical equation for aerobic cellular
Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 5. Cellular Respiration Reference: Chapter 9 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) 1. Give the overall balanced chemical equation for aerobic cellular
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I
 Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I Agenda I. Overview (Big Pictures) of Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration II. Making Glucose - Photosynthesis III. Making ATP - Cellular
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I Agenda I. Overview (Big Pictures) of Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration II. Making Glucose - Photosynthesis III. Making ATP - Cellular
Muscle Metabolism. Dr. Nabil Bashir
 Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Name Class Date. 1. Cellular respiration is the process by which the of "food"
 Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
KEY CONCEPT The overall process of cellular respiration converts sugar into ATP using oxygen.
 KEY CONCEPT The overall process of cellular respiration converts sugar into ATP using oxygen. ! Cellular respiration makes ATP by breaking down sugars. Cellular respiration is aerobic, or requires oxygen.
KEY CONCEPT The overall process of cellular respiration converts sugar into ATP using oxygen. ! Cellular respiration makes ATP by breaking down sugars. Cellular respiration is aerobic, or requires oxygen.
Cell Respiration - 1
 Cell Respiration - 1 All cells must do work to stay alive and maintain their cellular environment. The energy needed for cell work comes from the bonds of ATP. Cells obtain their ATP by oxidizing organic
Cell Respiration - 1 All cells must do work to stay alive and maintain their cellular environment. The energy needed for cell work comes from the bonds of ATP. Cells obtain their ATP by oxidizing organic
XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System
 Application Note Normalization XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System Authors Yoonseok Kam Kellie Chadwick Ned Jastromb Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies,
Application Note Normalization XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System Authors Yoonseok Kam Kellie Chadwick Ned Jastromb Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies,
Chapter 6 : How Cells Harvest Energy (B) Dr. Chris Doumen 10/28/14 CITRIC ACID CYCLE. Acetyl CoA CoA CoA CO 2 NAD + FADH 2 NADH FAD + 3 H + ADP + ATP
 Chapter 6 : How Cells Harvest Energy (B) Dr. Chris Doumen Acetyl CoA CoA CoA Oxaloacetate Citrate CITRIC ACID CYCLE CO FADH 3 NAD + FAD 3 NADH ADP + P + 3 1 Pyruvate oxida.on and Citric Acid Cycle Thus
Chapter 6 : How Cells Harvest Energy (B) Dr. Chris Doumen Acetyl CoA CoA CoA Oxaloacetate Citrate CITRIC ACID CYCLE CO FADH 3 NAD + FAD 3 NADH ADP + P + 3 1 Pyruvate oxida.on and Citric Acid Cycle Thus
10/10/2018. Pro-Normoxia During Cardiopulmonary Bypass. The Paradigm of Oxygen. Cellular Respiration Under Normal Oxygen Conditions
 The Paradigm of Oxygen Oxygen is Critical to life Current race to find an Oxygen/Water planet Pro-Normoxia During Cardiopulmonary Bypass Joseph Deptula, MS-P, LP, CCP Unfortunately, too much oxygen can
The Paradigm of Oxygen Oxygen is Critical to life Current race to find an Oxygen/Water planet Pro-Normoxia During Cardiopulmonary Bypass Joseph Deptula, MS-P, LP, CCP Unfortunately, too much oxygen can
Lesson Overview. Cellular Respiration: An Overview. 9.2 process of cell respiration
 9.2 process of cell respiration Glycolysis During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon molecule pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid is a reactant in the Krebs cycle. ATP and NADH
9.2 process of cell respiration Glycolysis During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon molecule pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid is a reactant in the Krebs cycle. ATP and NADH
Ch 9: Cellular Respiration
 Ch 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration An overview Exergonic reactions and catabolic pathway Energy stored in bonds of food molecules is transferred to ATP Cellular respiration provides the energy
Ch 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration An overview Exergonic reactions and catabolic pathway Energy stored in bonds of food molecules is transferred to ATP Cellular respiration provides the energy
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular
 III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia
 J Neurosurg 77: 169-184, 1992 Review Article Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia Part I: Pathophysiology Bo K. SIESJO, M.D. Laborutory for Experimental Bruin Reseurch, Experrmc~ntul
J Neurosurg 77: 169-184, 1992 Review Article Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia Part I: Pathophysiology Bo K. SIESJO, M.D. Laborutory for Experimental Bruin Reseurch, Experrmc~ntul
Electron transport chain,oxidative phosphorylation & mitochondrial transport systems. M.Kohutiar, B.Sopko
 Electron transport chain,oxidative phosphorylation & mitochondrial transport systems. M.Kohutiar, B.Sopko Content 1. Structure of mitochondria Mitochondrial transport systems 2. Electron transport 3. Parts
Electron transport chain,oxidative phosphorylation & mitochondrial transport systems. M.Kohutiar, B.Sopko Content 1. Structure of mitochondria Mitochondrial transport systems 2. Electron transport 3. Parts
Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer. Bioenergetics and Metabolism
 7/3/8 Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer Jianhua Zhang Department of Pathology University of Alabama at Birmingham 8 Bioenergetics and Metabolism Neurodegeneration: Parkinson s, Huntington
7/3/8 Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer Jianhua Zhang Department of Pathology University of Alabama at Birmingham 8 Bioenergetics and Metabolism Neurodegeneration: Parkinson s, Huntington
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3891
 Supplementary Figure 1. Subjective responses. Thermal sensation, thermal comfort and self-reported shivering, determined at several time points (from t = min until t = 36 min) after entering the cold room,
Supplementary Figure 1. Subjective responses. Thermal sensation, thermal comfort and self-reported shivering, determined at several time points (from t = min until t = 36 min) after entering the cold room,
Cellular Respiration. How our body makes ATP, ENERGY!!
 Cellular Respiration How our body makes ATP, ENERGY!! Useable Energy Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) Adenosine Ribose Sugar 3 Phosphates November 27, 2017 November 27, 2017 Where do our cells get energy?
Cellular Respiration How our body makes ATP, ENERGY!! Useable Energy Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) Adenosine Ribose Sugar 3 Phosphates November 27, 2017 November 27, 2017 Where do our cells get energy?
Pyruvate + NADH + H + ==== Lactate + NAD +
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR ANAEROBIC METABOLISM - An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR ANAEROBIC METABOLISM - An Overview
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP]
![3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP]](/thumbs/72/66350985.jpg) 3.7 Cell respiration ( Chapter 9 in Campbell's book) 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] Organic compounds store
3.7 Cell respiration ( Chapter 9 in Campbell's book) 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] Organic compounds store
Glycolysis. Cellular Respiration
 Glucose is the preferred carbohydrate of cells. In solution, it can change from a linear chain to a ring. Energy is stored in the bonds of the carbohydrates. Breaking these bonds releases that energy.
Glucose is the preferred carbohydrate of cells. In solution, it can change from a linear chain to a ring. Energy is stored in the bonds of the carbohydrates. Breaking these bonds releases that energy.
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation How do plants and animals obtain the glucose they need? Plants: Animals: Cellular Respiration the process that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation How do plants and animals obtain the glucose they need? Plants: Animals: Cellular Respiration the process that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen
CELLULAR RESPIRATION: AEROBIC HARVESTING OF CELLULAR ENERGY Pearson Education, Inc.
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION: AEROBIC HARVESTING OF CELLULAR ENERGY 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Introduction In chemo heterotrophs, eukaryotes perform cellular respiration That harvests energy from food which
CELLULAR RESPIRATION: AEROBIC HARVESTING OF CELLULAR ENERGY 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Introduction In chemo heterotrophs, eukaryotes perform cellular respiration That harvests energy from food which
Aerobic vs Anaerobic Respiration. 1. Glycolysis 2. Oxidation of Pyruvate and Krebs Cycle
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION Student Packet SUMMARY ALL LIVING SYSTEMS REQUIRE CONSTANT INPUT OF FREE ENERGY Cellular respiration is a catabolic pathway in which glucose and other organic fuels (such as starch,
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Student Packet SUMMARY ALL LIVING SYSTEMS REQUIRE CONSTANT INPUT OF FREE ENERGY Cellular respiration is a catabolic pathway in which glucose and other organic fuels (such as starch,
FREE ENERGY Reactions involving free energy: 1. Exergonic 2. Endergonic
 BIOENERGETICS FREE ENERGY It is the portion of the total energy change in a system that is available for doing work at constant temperature and pressure; it is represented as ΔG. Reactions involving free
BIOENERGETICS FREE ENERGY It is the portion of the total energy change in a system that is available for doing work at constant temperature and pressure; it is represented as ΔG. Reactions involving free
CELLULAR RESPIRATION. Chapter 7
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chapter 7 7.1 GLYCOLYSIS AND FERMENTATION If I have a $10.00 bill and a $10.00 check, which is better? ATP is like cash in the cell Glucose, NADH, FADH2 are like checks in a cell.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chapter 7 7.1 GLYCOLYSIS AND FERMENTATION If I have a $10.00 bill and a $10.00 check, which is better? ATP is like cash in the cell Glucose, NADH, FADH2 are like checks in a cell.
9-1 Chemical Pathways
 2 of 39 Food serves as a source of raw materials for the cells in the body and as a source of energy. Animal Cells Animal Mitochondrion Plant Plant Cells 3 of 39 1 Both plant and animal cells carry out
2 of 39 Food serves as a source of raw materials for the cells in the body and as a source of energy. Animal Cells Animal Mitochondrion Plant Plant Cells 3 of 39 1 Both plant and animal cells carry out
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the general flow of energy and food in living cells 2. Describe the organization of the mitochondria 3. Explain the main purpose and events of aerobic
CELLULAR RESPIRATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the general flow of energy and food in living cells 2. Describe the organization of the mitochondria 3. Explain the main purpose and events of aerobic
Cellular Respiration. Unit 5: Plants, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Unit 5: Plants, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration Overview! Organisms obtain energy (ATP) by breaking down (catabolic pathway, exergonic reaction) organic molecules (glucose)
Cellular Respiration Unit 5: Plants, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration Overview! Organisms obtain energy (ATP) by breaking down (catabolic pathway, exergonic reaction) organic molecules (glucose)
Table of Contents. Section 1 Glycolysis and Fermentation. Section 2 Aerobic Respiration
 Table of Contents Section 1 Glycolysis and Fermentation Section 2 Aerobic Respiration Objectives Identify the two major steps of cellular respiration. Describe the major events in glycolysis. Compare lactic
Table of Contents Section 1 Glycolysis and Fermentation Section 2 Aerobic Respiration Objectives Identify the two major steps of cellular respiration. Describe the major events in glycolysis. Compare lactic
Chemical Energy. Valencia College
 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
NOTES: Ch 9, part & Fermentation & Regulation of Cellular Respiration
 NOTES: Ch 9, part 4-9.5 & 9.6 - Fermentation & Regulation of Cellular Respiration 9.5 - Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen Cellular respiration requires O 2 to produce
NOTES: Ch 9, part 4-9.5 & 9.6 - Fermentation & Regulation of Cellular Respiration 9.5 - Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen Cellular respiration requires O 2 to produce
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20-1
 Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20-1 Learning Objectives 1. What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Met.? 2. What Are the Reduction Potentials for the Electron Transport Chain?
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20-1 Learning Objectives 1. What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Met.? 2. What Are the Reduction Potentials for the Electron Transport Chain?
Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 9-1 Chemical Pathways Food serves as a source of raw materials for the cells in the body and as a source of energy. Animal Cells Animal Mitochondrion Plant Plant Cells 3 of 39 Both
Biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 9-1 Chemical Pathways Food serves as a source of raw materials for the cells in the body and as a source of energy. Animal Cells Animal Mitochondrion Plant Plant Cells 3 of 39 Both
MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW
 1 MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW A. MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW Mitochondrial Structure The arrangement of membranes: distinct inner and outer membranes, The location of ATPase, DNA and ribosomes The
1 MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW A. MITOCHONDRIA LECTURES OVERVIEW Mitochondrial Structure The arrangement of membranes: distinct inner and outer membranes, The location of ATPase, DNA and ribosomes The
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.)
 This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC 2010. (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.) Topic 10: CELLULAR RESPIRATION (lectures 14-16) OBJECTIVES: 1. Know the basic reactions that
This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC 2010. (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.) Topic 10: CELLULAR RESPIRATION (lectures 14-16) OBJECTIVES: 1. Know the basic reactions that
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular I can describe cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways releasing energy from a foodstuff e.g. glucose. This yields energy in the form of ATP adenosine P i P
Cellular I can describe cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways releasing energy from a foodstuff e.g. glucose. This yields energy in the form of ATP adenosine P i P
(A) Urea cycle (B) TCA cycle (C) Glycolysis (D) Pyruvate oxidation (E) Respiratory chain
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate
 Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
Collin County Community College BIOL Muscle Physiology. Muscle Length-Tension Relationship
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Muscle Physiology 1 Muscle Length-Tension Relationship The Length-Tension Relationship Another way that muscle cells can alter their force capability, is determined
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Muscle Physiology 1 Muscle Length-Tension Relationship The Length-Tension Relationship Another way that muscle cells can alter their force capability, is determined
Bioenergetics: Energy for Exercise. Chapter 3 pp 28-47
 Bioenergetics: Energy for Exercise Chapter 3 pp 28-47 ATP ATP Adenosine Ribose 3 Phosphates ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out Energy In
Bioenergetics: Energy for Exercise Chapter 3 pp 28-47 ATP ATP Adenosine Ribose 3 Phosphates ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out Energy In
Ch. 9 Cell Respiration. Title: Oct 15 3:24 PM (1 of 53)
 Ch. 9 Cell Respiration Title: Oct 15 3:24 PM (1 of 53) Essential question: How do cells use stored chemical energy in organic molecules and to generate ATP? Title: Oct 15 3:28 PM (2 of 53) Title: Oct 19
Ch. 9 Cell Respiration Title: Oct 15 3:24 PM (1 of 53) Essential question: How do cells use stored chemical energy in organic molecules and to generate ATP? Title: Oct 15 3:28 PM (2 of 53) Title: Oct 19
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
ROS Activity Assay Kit
 ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
A cell has enough ATP to last for about three seconds.
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6
 Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6 The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages
Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6 The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages
Releasing Chemical Energy
 Releasing Chemical Energy Ø Energy From Carbohydrates Ø Aerobic Respiration/ Stages Ø Fermentation Ø Food as a Source of Energy How Do Cells Access the Chemical Energy in Carbohydrayes? Aerobic Respiration
Releasing Chemical Energy Ø Energy From Carbohydrates Ø Aerobic Respiration/ Stages Ø Fermentation Ø Food as a Source of Energy How Do Cells Access the Chemical Energy in Carbohydrayes? Aerobic Respiration
CELL INJURY. Severity of Cell Injury
 GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
Cellular Respiration. Honors Biology I
 Cellular Respiration Honors Biology I Anaerobic vs. Aerobic 1) Respiration vs. Cellular respiration 2) When you run, you re using respiration to make energy in the form of ATP to allow your muscles to
Cellular Respiration Honors Biology I Anaerobic vs. Aerobic 1) Respiration vs. Cellular respiration 2) When you run, you re using respiration to make energy in the form of ATP to allow your muscles to
Higher Biology. Unit 2: Metabolism and Survival Topic 2: Respiration. Page 1 of 25
 Higher Biology Unit 2: Metabolism and Survival Topic 2: Respiration Page 1 of 25 Sub Topic: Respiration I can state that: All living cells carry out respiration. ATP is the energy currency of the cell
Higher Biology Unit 2: Metabolism and Survival Topic 2: Respiration Page 1 of 25 Sub Topic: Respiration I can state that: All living cells carry out respiration. ATP is the energy currency of the cell
How to Integrate Cellular Metabolism Assays Into Your Research: Considerations and Challenges
 How to Integrate Cellular Metabolism Assays Into Your Research: Considerations and Challenges Donna Leippe Sr Research Scientist Outline for Today s Webinar Introduction to Cell Metabolism Metabolite Detection
How to Integrate Cellular Metabolism Assays Into Your Research: Considerations and Challenges Donna Leippe Sr Research Scientist Outline for Today s Webinar Introduction to Cell Metabolism Metabolite Detection
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Chemical Equation 6 O 2 + C 6 H 12 O 6 6 H 2 O + 6 CO 2 + Page 107 Adenosine Triphosphate Adenosine Diphosphate Background Aerobic= requires oxygen Anaerobic= does not require oxygen
Cellular Respiration Chemical Equation 6 O 2 + C 6 H 12 O 6 6 H 2 O + 6 CO 2 + Page 107 Adenosine Triphosphate Adenosine Diphosphate Background Aerobic= requires oxygen Anaerobic= does not require oxygen
Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream signals in in vitro Symbol Gene ID RefSeqID Clone ID
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream
7 Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
 7 Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of Glucose Metabolism? How Is Energy Harvested
7 Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of Glucose Metabolism? How Is Energy Harvested
Measuring Cardiac Activity:
 icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Measuring Cardiac Activity: Intracellular Calcium Flux Detection on the FLIPR Tetra System Introduction icell Cardiomyocytes are human cardiomyocytes that recapitulate
icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Measuring Cardiac Activity: Intracellular Calcium Flux Detection on the FLIPR Tetra System Introduction icell Cardiomyocytes are human cardiomyocytes that recapitulate
