Harvard Medical School
|
|
|
- Gervase Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Harvard Medical School
2 Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Tests in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
3 Disclosure of Financial Relationships C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Has no relationship with any entity producing, marketing, reselling or distributing health care goods or services consumed by, or used on patients.
4 Case A 56-year-old woman with a history of hypothyroidism and hypertension presents with acute onset of mid-back pain; it began three days ago when she attempted to open a window that was stuck closed. The pain has not been fully relieved with NSAIDs. Other than a pruritic rash on her extensor surface of her right elbow, and occasional diarrhea due to her lactose intolerance, she has no complaints. Examination is remarkable for mid spine tenderness to percussion and the rash on her elbow and back (next slide). BMI is 22.
5 An example of her rash Courtesy Dr. Ciaran Kelly
6 An example of her spinal imaging
7 Case continued Laboratory studies: Hematocrit : 31% Hemoglobin: 10.1 g/dl Platelet count: 260,000 MCV: 78 fl Ferritin: 10 ng/ml ALT: 62 U/L AST: 51 U/L Alkaline phosphatase: 110 U/L TSH, serum calcium, albumin, PT: normal
8 Case Continued Patient is post-menopausal and has no abnormal vaginal bleeding; she denies melena or BRBPR. She undergoes a colonoscopy. The colonoscopy is normal and random biopsies are without abnormalities.
9 Case What diagnosis will most likely account for her symptoms and findings? a. Myelodysplastic syndrome b. Cirrhosis c. Celiac disease d. Lymphoma
10 Case What diagnosis will most likely account for her symptoms and findings? a. Myelodysplastic syndrome b. Cirrhosis c. Celiac disease d. Lymphoma
11 Case Summary: 52-year-old female with new compression fracture, anemia, elevated liver enzymes, and rash on extensor surfaces and on back What is the most likely diagnosis that will tie together all of these findings? What is the best way to confirm this diagnosis?
12 Celiac Disease Autoimmune disorder Tissue transglutaminase (ttg) is the auto-antigen Cross links collagen Antibodies react to ttg inducing a change in charge and structure of gluten Allowing gluten to bind to HLA DQ2 and DQ8 receptors Triggering immune response with cytokine release and lymphocyte infiltration enteropathy Intolerance to gluten: wheat, rye and barley
13 Celiac Disease Classic Symptoms Diarrhea/Malabsorption Iron deficiency anemia Abdominal Pain Weight Loss Fatigue/lethargy Bloating/Gas Dermatitis Herpetiformis Non-Classic Symptoms Aysmptomatic LFT elevations Aphthous ulcers Alopecia Osteopenia/osteoporosis Infertility Dental defects Neuropathy
14 Dermatitis Herpetiformis ttg found in many organs, including skin Antibodies to intestinal ttg can cross-react to skin ttg causing inflammation Pruritic papules, vesicles and macules on extensor surfaces
15 Dermatitis Herpetiformis Courtesy Dr. Ciaran Kelly
16 Audience Question Which region has the lowest prevalence of celiac disease? a. North America b. Europe c. Northern India d. South East Asia e. North Africa
17 Audience Question Which region has the lowest prevalence of celiac disease? a. North America b. Europe c. Northern India d. South East Asia e. North Africa
18 Celiac Disease: Epidemiolgy 1% of the general population (1:100) 10% if first degree relative affected Risk of celiac disease in the following conditions: Chronic diarrhea: 25% Iron deficiency anemia: 10% Any autoimmune disorder: 5% Type I diabetes mellitus: 5% Osteoporosis: 3% More prevalent than Crohn s disease, ulcerative colitis and type 1 diabetes mellitus combined Fasano, Arch Intern Med 2003
19 Recent increase in celiac disease diagnosis (BIDMC, Boston) Courtesy Dr. Ciaran Kelly
20 When to test for Celiac Disease Diarrhea +/- malabsorption IBS like (e.g., mild diarrhea and bloating) Lactose intolerance like but not responding to lactose free diet Nutritional deficiencies Iron deficiency anemia (most common), B12, folate Vitamin D with osteopenia/osteoporosis Other Dermatitis herpetiformis Impaired fertility Ataxia, peripheral neuropathy Severe aphthous stomatitis Abnormal LFTs
21 Audience Question Our patient s anti-ttg returns negative. What is the next step that should be performed? a. Immediately initiate a gluten free diet anyway b. Perform an upper endoscopy with small bowel biopsies c. Perform IgA d. B and C
22 Audience Question Our patient s anti-ttg returns negative. What is the next step that should be performed? a. Immediately initiate a gluten free diet anyway b. Perform an upper endoscopy with small bowel biopsies c. Perform IgA d. B and C
23 Celiac Disease: Diagnosis IgA-tTG is the test of choice Sensitivity/specificity 95% 5-10% of patients with celiac sprue are IgA deficient Patient should not be on gluten diet Must confirm with small bowel biopsy
24 Normal Small Intestine Courtesy of Dr. Ciaran Kelly
25 Subtotal Villous Atrophy in Celiac Sprue Courtesy of Dr. Ciaran Kelly
26 Small intestinal biopsy histology: the diagnostic gold standard Healthy Villi Celiac Disease
27 Diagnosing Celiac Disease CD present CD absent Positive ttg Negative ttg Assume high risk population with 10% risk and a ttg sensitivity and specificity of 95% NPV: TN/FN+TN: 855/860:99%; PPV: TP/FP+TP: 95/140:68%
28 Diagnosis of Celiac Disease Consider a diagnosis of celiac disease <10% Determine pretest probability >10% Serum IgA TTG Negative Diagnosis adequately excluded Positive SI biopsy histology Negative Diagnose Celiac disease Serum IgA TTG & SI biopsy histology Positive Adapted from: Kelly et al; Up-to-date 1998, Am J GE 2001, NEJM 2002
29 Case Summary 56 year old female with prior elevations of ALT/AST thought to be due to celiac disease. Liver studies completely normalized after treatment for celiac disease. Now on strict gluten free diet and normalized TTG After many months on a gluten free diet, the patient is gaining weight. To combat this she has begun an aggressive exercise regimen. She is now found to again have elevation of LFTs (ALT 47; AST 42). Alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin are normal.
30 Audience Question What is the most likely underlying diagnosis and how will you confirm? a. Plan for cholangiogram for primary sclerosing cholangitis b. Check ceruloplasmin for Wilson s disease c. Check AMA for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis d. Check CPK for muscle injury e. Counsel patient on alcohol use
31 Audience Question What is the most likely underlying diagnosis and how will you confirm? a. Plan for cholangiogram for primary sclerosing cholangitis b. Check ceruloplasmin for Wilson s disease c. Check AMA for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis d. Check CPK for muscle injury e. Counsel patient on alcohol use
32 Causes of abnormal ALT/AST with normal liver biopsy Muscle Exercise induced or Metabolic Disorder Both ALT and AST can be elevated Check CPK Celiac Addison s Disease Thyroid Bardella, Hepatology 1999
33 Wilson s Disease Rare genetic disorder of reduced biliary copper excretion and increased deposition Cognitive changes; hemolytic anemia, cardiomyopathy Rare in patients over the age 40 Decreased ceruloplasmin levels (screening test) Reduced in 85% of affected patients Ophthalmologic examination for Kayser-Fleischer rings AST/ALT: mild elevation to fulminant hepatic failures 24 urine for quantitative copper excretion Frequently have low alkaline phosphate Low serum uric acid
34 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Autoimmune condition leading to progressive destruction of bile ducts Resulting in chronic cholestatic liver disease 90% women between years of age Presenting symptoms: pruritis, fatigue, fat malabsorption, hypercholesterolemia Asymptomatic elevation in serum alkaline phosphatase (often 10x normal) Elevated IgM Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA) Titers > 1:40 in greater than 90% of patients with PBC
35 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Almost exclusively in patients with IBD, especially men with ulcerative colitis Present with isolated alkaline phosphatase Pruritis Steatorrhea Vitamin deficiency Diagnosis through cholangiography No confirmatory serologic test No effective treatment
36 PSC and PBC PBC PSC Demographic Asymptomatic women IBD esp. UC/men Laboratory findings alk phos/igm alk phos Serologic Studies AMA none Diagnosis Liver Biopsy Cholangiography Treatment Ursodeoxycholic Acid None
37 Alcohol Abuse AST:ALT greater than 2 > 90% of patients with this ratio have alcoholic liver disease > 96% when ratio > 3:1 Both less than 300 IU/L Ɣ-glutamyltransferase Twice the ULN strongly support the diagnosis Poorly specific so should not be used as a single test Cohen, Dig Dis Sci 1979
38 Hemochromatosis Common genetic disorder characterized by increased intestinal absorption of iron 10% Caucasians heterozygous 0.5% homozygous Excess iron deposition in liver, heart, pancreas and pituitary Cirrhosis, heart disease, arthropathy, hypogonadism, thyroid dysfunction, skin pigmentation & type 1 diabetes mellitus Cost-effective screening starts with serum iron and TIBC Iron saturation > 45% is suggestive of hemochromatosis Ferritin is less specific as it is an acute phase reactant If iron saturation elevated, test for mutations of HFE gene C282Y homozygrous or compound heterozygote C282Y/H63D
39 Case A 67-year-old man just moved to your city and presents as a new patient. He has no complaints. His history is significant for type II diabetes (controlled with diet; last HgbA1c 6.9%). He has never had more than one beer a day. Examination is remarkable for a BMI of 33. Laboratory studies of note include platelet count: 89,000; ALT: 125; AST: 132 Alk phos, bilirubin, viral serologies, iron saturation: normal Albumin 3.1 Liver ultrasound shows diffuse fatty infiltration of the liver
40 Audience Question In addition to weight loss, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in managing this patient s abnormal liver studies? a. Initiate insulin sensitizing medication (e.g., metoformin or pioglitazone) and repeat liver studies in six months b. Refer for a liver biopsy c. Counsel patient on his alcohol consumption d. Send serum ceruloplasmin levels
41 Audience Question In addition to weight loss, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in managing this patient s abnormal liver studies? a. Initiate insulin sensitizing medication (e.g., metoformin or pioglitazone) and repeat liver studies in six months b. Refer for a liver biopsy c. Counsel patient on his alcohol consumption d. Send serum ceruloplasmin levels
42 Case Highlights 67-year-old obese patient with type II diabetes AST:ALT ratio > 1 Limited alcohol intake Ultrasound with steatosis Reasonable evaluation of common causes of liver abnormalities is unrevealing What is the best next step in management?
43 Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Most common cause of abnormal transaminase levels 30% of Americans have non-alcoholic fatty liver 5% will develop nonalcoholic steatohepatitis 8-26% of pts with NASH will develop cirrhosis Leading cause of cryptogenic cirrhosis No clinical or laboratory feature can predict progression Associated conditions: Obesity (69-100%) Type 2 diabetes (34-75%) Hyperlipidemia (20-80%) Angulo, NEJM 2002
44 Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Diagnosis of NASH is one of exclusion Most patients are asymptomatic AST/ALT ratio less than 1 If ratio reverses, worrisome for development of cirrhosis Normal serum aminotransferases do not exclude presence of advanced liver disease Liver ultrasound is highly sensitive for steatosis but not specific for cause of steatosis or presence fibrosis or more advanced liver disease No distinguishing historical or laboratory features to differentiate from other causes of chronic liver disease
45 Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Differential Diagnosis Alcohol and drug related liver disease: careful history Hepatitis B and C (HBV surface ag and HCV ab) Hereditary hemochromatosis (Fe:TIBC) In right clinical setting consider other causes Liver biopsy is only way to confirm diagnosis of NASH However, high risk to benefit ratio for biopsy as most patients do not progress and frequently does not change management Consider biopsy if suspect NASH and one of the following: Laboratory or PE findings of chronic liver disease Unexplained findings (i.e., elevation of ANA or iron studies) Other RF: Age > 45, Obesity, AST: ALT > 1, Type II DM
46 Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Treatment is directed at risk factor modification Weight loss, lipid control, diabetes control Insulin sensitizing drugs: pioglitazone or metformin Limited data Belfort, NEJM 2006
47 Case A 34-year-old woman with a history of hypothyroidism and hemolytic anemia presents with several months of fatigue. Four months ago she had a serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) of 425 U/L, with normal TSH, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase. Examination is remarkable for the liver edge three cm below the costal margin. Laboratory studies: ALT: 923 AST: 801 Total Bilirubin: 2.2 Alkaline Phosphatase: 98 PT and albumin: normal
48 Case continued Labs continued: Ferritin: 310 ng/ml (normal < 300) Plasma ceruloplasmin: 32 mg/dl Antimitochondrial ab: negative Anti-smooth muscle ab: 1:1280 Hepatitis A, B, C: negative Liver Biopsy: periportal and bridging necrosis
49 Case Which is the most appropriate treatment for this patient? a. Bile salts b. Phlebotomy to reduce iron levels c. Interferon alfa d. Prednisone e. Penicillamine
50 Case Which is the most appropriate treatment for this patient? a. Bile salts b. Phlebotomy to reduce iron levels c. Interferon alfa d. Prednisone e. Penicillamine
51 Case Highlights 34 year old women with history of hypothyroidism with 4+ month history of hepatitis Now with normal AMA, ceruloplasmin Ferritin mildly elevated Negative viral serologies ALT now Anti-smooth muscle (ASMA): 1:1280 Biopsy shows periportal and bridging necrosis What treatment?
52 Liver Transaminase Levels > 500 Common Acute Viral Hepatitis Drug/toxin induced liver injury Especially acetaminophen Amanita phalloides Ischemic hepatitis Severe auto-immune hepatitis Less Common Common Bile Duct Stone Budd-Chiari or Veno-occlusive disease Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy or HELLP Wilson s disease
53 Causes of Fulminant Liver Failure A B C D E F G H Acetaminophen, Hep A, Autoimmune Hep B Hep C Hep D, Drugs Hep E, Esoteric causes (Wilson s, Budd-Chiari) Fatty infiltration (acute fatty liver of pregnancy) (only knows) Herpes simplex virus Dr. Sanjiv Chopra's Liver Book: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery
54 First, make the diagnosis Differential Diagnosis includes: Primary biliary cirrhosis AMA was negative Primary sclerosing cholangitis No history of IBD Viral hepatitis Serologies negative Wilson s disease Ceruloplasmin normal
55 First, make the diagnosis Nearly 10% of chronic hepatitis is caused by autoimmune hepatitis Type I: classic form, accounts for most in US Female predominance Extrahepatic autoimmune manifestations Tests: + ANA > 1:160 or ASMA > 1:40 and hypergammaglobulinemia (associated with auto-antibodies) Type II: less common Presents earlier and progresses more rapidly ANA, ASMA negative but + anti-lkm > 1:20 Heterogeneous and fluctuating nature Often other autoimmune features in over a third
56 Next, assess severity of disease She has very high ALT 10-20X normal, increasing Characteristically transaminase levels are out of proportion to bili or alk phos She has systemic symptoms She has fatigue; can also see anorexia, arthralgia, myalgia, fever, jaundice Biopsy shows an aggressive case in which inflammatory reaction bridges portal tracts (= bridging necrosis) Treat!
57 Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis Type I is very responsive to glucocorticoid therapy Long-term remission is seen on low-dose prednisone Start at mg/d and taper Maintain on 5 mg/d 20 mg/d until in remission 6-24 months, then taper Restart if recurs Can use steroid sparing agents (azathioprine, etc) in select patients
58 Audience Question In a patient with asymptomatic elevation in ALT/AST, and auto-immune hepatitis is suspected, which is the best screening test? a. Hypergammaglobulin (> 1.5 x the ULN) b. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers c. Anti-smooth muscle antibody titers (ASMA) d. Ferritin level e. ESR
59 Audience Question In a patient with asymptomatic elevation in ALT/AST, and auto-immune hepatitis is suspected, which is the best screening test? a. Hypergammaglobulin (> 1.5 x the ULN) b. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers c. Anti-smooth muscle antibody titers (ASMA) d. Ferritin level e. ESR
60 Diagnosing Auto-immune Hepatitis Serum protein electrophoresis is a useful screening test > 80% of patients with autoimmune hepatitis have hypergammaglobulinemia Polyclonal immunoglobulins > 2 x ULN is most suggestive ANA: 28% sensitive ASMA: 40% sensitive Czaja, Semin Liver Dis, 1984
61 A patient presents to your clinic A 34 year old female presents to your clinic to establish care with her new PCP. She has no complaints or significant past medical history, but is seeking prenatal counseling. She was born and raised in China, but has been in the United States for the last 10 years and works in the healthcare industry. You check a hepatitis B panel with the following results: HBsAg: positive HBcAb: positive HBsAb: negative
62 Questions How did she acquire HBV? Is she at risk for transmission to others? Does how and when she acquired HBV alter outcomes? How does HBV compare and contrast to HCV? What is the difference between HBV carrier and HBV (chronic) infection and why does it matter? What other studies should be performed?
63 Hepatitis B Worldwide HBV accounts for over a million deaths annually 2 billion with past/present infection 350 million actively infected worldwide (5% of world population) Leading cause of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (15-40%) Hepatocellular carcinoma has increased worldwide, killing 300,000 to 500,000 each year Prevalence varies by region Greatest in Southeast Asia, China, Africa and Alaska More than half the population infected at some point 8% chronic carriers Maynard, Vaccine,
64 Prevalence of Chronic Hepatitis B CDC Travelers Health: Yellow Book, 2008
65 High Risk Groups for HBV Injection drug use Healthcare and public safety workers Hemodialysis patients History of STD Men who have sex with men Sex contacts of infected persons or multiple sex partners Infants born to infected mothers Children of immigrants from endemic country Household contact of chronically infected persons CDC. Hepatitis B Fact Sheet, 2004
66 2002 Transmission Factors of HBV in U.S. CDC Hepatitis Surveillance Report, 2004
67 HBV vs. HCV Much more contagious and easily spread than HCV 1,000,000 HBV virons for every HCV viron Present in all bodily secretions except for feces HBV is very hardy Higher prevalence of HCV in U.S. - 2% vs. 0.5% Higher prevalence reflects natural history of disease
68 HCV Course Rarely fulminant and fatal Acute infection causes symptoms in <20% After acute infection, 20% clear virus from blood and have full recovery Remaining 80% have viremia that persists for life Seroconversion (positive antibody test) may take 3 months
69 Natural History of Hepatitis C Exposure HCV Annual rate 80% Chronic HCV Infection 20 years Cirrhosis 20% Decompensation 6% HCC 4% Death 4%
70 % Developing Chronic Infection Age and Mode of Acquisition of HBV Development of chronic infection varies by mode and age of transmission Perinatal infection (most common mode of transmission worldwide) 90% develop chronic infection Acquired between ages 1 and 5 years % risk Adult acquisition: <5% risk of chronic infection Neonate Infant Adult Stevens, NEJM, 1975 Beasley, J Infect Dis 1983
71 Outcomes of Acute Hepatitis B Recovery Subclinical Acute Hepatitis Fulminant Hepatitis Chronic Infection Ostapowicz, Ann Intern Med, 2002
72 Outcomes of Chronic Hepatitis B Chronic HBV Inactive Carrier (nonreplicative) Chronic Hepatitis (replicative) Cirrhosis Hepatocellular Carcinoma
73 Diagnosis of Hepatitis B Serologic Marker HBsAg anti-hbs HBeAg anti-hbe anti-hbc IgM anti-hbc IgG & HBsAg anti-hbc IgG & anti-hbs HBV-DNA Clinical Significance Acute/Chronic Infection Immunity High infectivity Low infectivity Acute Infection Chronic Infection Resolved Infection Viral replication/correlates with infectivity
74 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc + - IgM a. Acute HBV Infection b. Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B c. Remote Past Infection d. A or B
75 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc + - IgM a. Acute HBV Infection b. Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B c. Remote Past Infection d. A or B
76 Causes of Acute Hepatitis in HBsAg positive Patients Acute HBV infection anti-hbc IgM Seroconversion HBeAg anti-hbe HBV reactivation Superinfection HAV HDV HCV Non-viral liver injury Drugs Toxins
77 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc - + IgG a. Active infection b. Remote past infection c. Window period following acute infection d. Patient immune due to vaccination
78 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc - + IgG a. Active infection b. Remote past infection c. Window period following acute infection d. Patient immune due to vaccination
79 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc Vaccination with no prior exposure to HBV
80 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs + + a. Recovery phase of acute infection b. Remote infection that has cleared c. Chronic HBV infection with HBsAb directed against different subtypes d. A or C
81 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs + + a. Recovery phase of acute infection b. Remote infection that has cleared c. Chronic HBV infection with HBsAb directed against different subtypes d. A or C
82 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc Which of the following would explain the above scenario? A. Low level HBV carrier B. Remote past infection (recovered HBV) C. False positive test result D. Window phase of acute hepatitis B E. Any of the above
83 Serology Cases HBsAg Anti-HBs Anti-HBc Which of the following would explain the above scenario? A. Low level HBV carrier B. Remote past infection (recovered HBV) C. False positive test result D. Window phase of acute hepatitis B E. Any of the above
84 A 46-year-old woman with a 4-year history of chronic HBV and substance abuse is admitted with 3 days of jaundice, fatigue, and nonbloody vomiting. She does not take medications (including no acetaminophen). She reports drinking four shots of whiskey a day, with ongoing intravenous use of heroin. Her vital signs are stable. She is icteric. Abdominal examination reveals a smooth liver edge one cm below the costal margin but no splenomegaly or ascites. No manifestations of cirrhosis.
85 Patient value Reference ALT AST Alk phos Total bili Albumin INR 1.3 Hep A IgM: Neg; IgG: Pos HBV: sag: Pos; core IgG Ab: Pos; core IgM Ab: Neg; e Ag: Neg HBV DNA Viral Load: 1200 HCV: Ab: Neg; RNA: Neg
86 Which one of the following diagnoses is most likely? a) Alcoholic hepatitis b) Hepatitis E virus infection c) Hepatitis B virus reactivation d) Hepatitis D virus infection e) Ischemic hepatitis
87 Which one of the following diagnoses is most likely? a) Alcoholic hepatitis b) Hepatitis E virus infection c) Hepatitis B virus reactivation d) Hepatitis D virus infection e) Ischemic hepatitis
88 Causes of Acute Hepatitis in HBsAg positive Patients Acute HBV infection anti-hbc IgM Seroconversion HBeAg anti-hbe HBV reactivation Superinfection HAV HDV HCV Non-viral liver injury Drugs Toxins
89 Hepatitis A Spread via fecal-oral route Person to person Homosexual contact Institutional transmission Daycare centers Contaminated food or water (inadequate sanitation, undercooked shellfish or infected food handlers)
90 Hepatitis A Usually acute, self-limited illness More symptomatic in adults Marked elevation aminotransferases and bilirubin <1% fulminant hepatic failure More common in patients with underlying liver disease Serum IgM anti-hav in acute setting
91 Hepatitis D Parenteral transmission Anti-HDV may appear late Especially true in immunodeficient patients Defective virus Requires HBV to complete virion assembly and secretion Therefore, HBV must be present Progresses to chronic HDV infection Suppression of HBV replication Accelerated course to cirrhosis
92 Hepatitis E Spread by fecal-oral route Most common by fecally contaminated water Self-limited illness More severe course than HAV Fulminant hepatitis 0.5-3% 15-25% mortality in pregnancy
93 Laboratory Tests to Assess Asymptomatic Patient with Elevated Aminotransferase Levels Initial Tests HCV ab HBV sag, sab coreab Iron and TIBC Serum ceruloplasmin Serum protein electrophoresis Additional Tests TTG CPK TSH Alpha1-antitrypsin phenotyping
94 Questions from the Audience?
95
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland
 Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Hepatitis. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 5/2/2019. Mob:
 Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
Viral hepatitis. Supervised by: Dr.Gaith. presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a
 Viral hepatitis Supervised by: Dr.Gaith presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a Etiology Common: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Less common: Cytomegalovirus EBV Rare: Herpes
Viral hepatitis Supervised by: Dr.Gaith presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a Etiology Common: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Less common: Cytomegalovirus EBV Rare: Herpes
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
IN THE NAME OF GOD. D r. MANIJE DEZFULI AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST
 IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant. Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Viral Hepatitis. Background
 Viral Hepatitis Background Hepatitis or inflammation of the liver can be caused by infectious and noninfectious problems. Infectious etiologies include viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Noninfectious
Viral Hepatitis Background Hepatitis or inflammation of the liver can be caused by infectious and noninfectious problems. Infectious etiologies include viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Noninfectious
9/28/2016. Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach. Objectives. Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
 Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Viral Hepatitis. Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital
 Viral Hepatitis Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Viral Hepatitis HAV HBV HCV HDV HEV Other viral: CMV, EBV, HSV Unknown Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Transmitted via the faecal-oral route
Viral Hepatitis Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Viral Hepatitis HAV HBV HCV HDV HEV Other viral: CMV, EBV, HSV Unknown Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Transmitted via the faecal-oral route
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing. Origins of Liver Science
 Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Liver Disease. By: Michael Martins
 Liver Disease By: Michael Martins Recently I have been getting a flurry of patients that have some serious liver complications. This week s literature review will be the dental management of the patients
Liver Disease By: Michael Martins Recently I have been getting a flurry of patients that have some serious liver complications. This week s literature review will be the dental management of the patients
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management
 Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview
 Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust
 ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
Viral Hepatitis. Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Viral Hepatitis Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Viral hepatitis Viral hepatitis must be considered in any patient presenting with hepatitis on LFTs (high
Viral Hepatitis Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Viral hepatitis Viral hepatitis must be considered in any patient presenting with hepatitis on LFTs (high
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C
 S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
Viral hepatitis Blood Born hepatitis. Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH
 Viral hepatitis Blood Born hepatitis Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH Outline Introduction to hepatitis Characteristics of viral hepatitis Mode of transmission Markers of hepatitis
Viral hepatitis Blood Born hepatitis Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH Outline Introduction to hepatitis Characteristics of viral hepatitis Mode of transmission Markers of hepatitis
Hepatitis B (Part 1 - intro)
 Hepatitis B (Part 1 - intro) The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) l Virology Discovered in 1966 double-stranded DNA virus l family of hepadnaviruses l HBV unique to Humans (Primates too in laboratory studies) no
Hepatitis B (Part 1 - intro) The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) l Virology Discovered in 1966 double-stranded DNA virus l family of hepadnaviruses l HBV unique to Humans (Primates too in laboratory studies) no
4/27/2018. Disclosures LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
Disclosure. Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes
 Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Tips for Managing Celiac Disease. Robert Berger MD FRCPC Gastroenterology New Brunswick Internal Medicine Update April 22, 2016
 Tips for Managing Celiac Disease Robert Berger MD FRCPC Gastroenterology New Brunswick Internal Medicine Update April 22, 2016 Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Objectives Briefly review the
Tips for Managing Celiac Disease Robert Berger MD FRCPC Gastroenterology New Brunswick Internal Medicine Update April 22, 2016 Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Objectives Briefly review the
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers
 Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
Acute Hepatitis: An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes. Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC
 : An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC Faculty: Dr. Mary Anne Cooper Relationships with commercial interests: Consulting Fees: Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Canada Objectives
: An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC Faculty: Dr. Mary Anne Cooper Relationships with commercial interests: Consulting Fees: Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Canada Objectives
ACCME/Disclosures. The Overlap Syndromes: Do They Exist? Key Points and Questions 4/6/2016. Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University
 Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Coeliac Disease: Diagnosis and clinical features
 Coeliac Disease: Diagnosis and clinical features Australasian Gastrointestinal Pathology Society AGM 28 Oct 2016 Dr. Hooi Ee Gastroenterologist, Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital Coeliac disease Greek: koiliakos
Coeliac Disease: Diagnosis and clinical features Australasian Gastrointestinal Pathology Society AGM 28 Oct 2016 Dr. Hooi Ee Gastroenterologist, Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital Coeliac disease Greek: koiliakos
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update. Primary Causes of Chronic Liver Disease in the U.S. Hepatitis Definition. Hepatitis Viruses.
 Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Hepatitis B Virus. Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019
 Hepatitis B Virus Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019 Epidemiology 3218 cases of acute HBV reported in 2016 847,000 non-institutionalized persons living with chronic HBV in 2011-2012 Viral
Hepatitis B Virus Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019 Epidemiology 3218 cases of acute HBV reported in 2016 847,000 non-institutionalized persons living with chronic HBV in 2011-2012 Viral
Lifetime risk of infection >60% Early childhood infections common
 Hepatitis Community Medicine HBV Public health sig HBV is 100 times more infectious than HIV. >350 million chronically infected worldwide. >1 million people die annually of HBV- related chronic liver disease.
Hepatitis Community Medicine HBV Public health sig HBV is 100 times more infectious than HIV. >350 million chronically infected worldwide. >1 million people die annually of HBV- related chronic liver disease.
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests
 Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 5 PURPOSE To provide guidelines on the treatment and care of patients with Hepatitis. POLICY Hepatitis is an injury to hepatic cells and an inflammatory process in the liver. The major causes
PAGE 1 of 5 PURPOSE To provide guidelines on the treatment and care of patients with Hepatitis. POLICY Hepatitis is an injury to hepatic cells and an inflammatory process in the liver. The major causes
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Hepatitis A Virus: Old Things Made New
 Hepatitis A Virus: Old Things Made New Cody A. Chastain, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Viral Hepatitis Program Division of Infectious Diseases Vanderbilt University Medical Center Cody.A.Chastain@VUMC.org
Hepatitis A Virus: Old Things Made New Cody A. Chastain, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Viral Hepatitis Program Division of Infectious Diseases Vanderbilt University Medical Center Cody.A.Chastain@VUMC.org
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
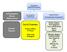 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes
 Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes Donald Gardenier, DNP, FNP-BC Assistant Professor and Clinical Program Director Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, NY Conflict of Interest
Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes Donald Gardenier, DNP, FNP-BC Assistant Professor and Clinical Program Director Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, NY Conflict of Interest
CELIAC DISEASE. A Family Physician Perspective. Dr. Kanwal Brar BSc MD CCFP June 6, 2015
 CELIAC DISEASE A Family Physician Perspective Dr. Kanwal Brar BSc MD CCFP June 6, 2015 Conflict of interest: No conflicts of interest or medical disclosures pertaining to this talk Objectives: Through
CELIAC DISEASE A Family Physician Perspective Dr. Kanwal Brar BSc MD CCFP June 6, 2015 Conflict of interest: No conflicts of interest or medical disclosures pertaining to this talk Objectives: Through
Celiac Disease. M. Nedim Ince, MD University of Iowa Hospital
 Celiac Disease M. Nedim Ince, MD University of Iowa Hospital Contents Cases Definition Etiopathogenesis Pathology Diagnosis Management of the disease Management of complications Case I Five year old boy
Celiac Disease M. Nedim Ince, MD University of Iowa Hospital Contents Cases Definition Etiopathogenesis Pathology Diagnosis Management of the disease Management of complications Case I Five year old boy
Testing for Viral Hepatitis A Practice Parameter
 AJCP / TESTING FOR VIRAL HEPATITIS Testing for Viral Hepatitis A Practice Parameter Ronald A. Sacher, MD, FRCPC, 1 Stephen M. Peters, PhD, FAAM, 2 and John A. Bryan, MD 3 Key Words: Viral hepatitis; Laboratory
AJCP / TESTING FOR VIRAL HEPATITIS Testing for Viral Hepatitis A Practice Parameter Ronald A. Sacher, MD, FRCPC, 1 Stephen M. Peters, PhD, FAAM, 2 and John A. Bryan, MD 3 Key Words: Viral hepatitis; Laboratory
Viral Hepatitis in Children DR. HOSSAIN IBRAHIM AGEEL PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST PEDIATRIC DEPARTMENT KFCH JAZAN
 Viral Hepatitis in Children DR. HOSSAIN IBRAHIM AGEEL PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST PEDIATRIC DEPARTMENT KFCH JAZAN General Concepts Hepatitis = 'inflammation of the liver'. Virus causes: Hepatotropic and
Viral Hepatitis in Children DR. HOSSAIN IBRAHIM AGEEL PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST PEDIATRIC DEPARTMENT KFCH JAZAN General Concepts Hepatitis = 'inflammation of the liver'. Virus causes: Hepatotropic and
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
GI DISEASE WORKSHOP CASE STUDIES
 GI DISEASE WORKSHOP CASE STUDIES American Academy of Insurance Medicine Triennial Course in Insurance Medicine 2012 Clifton Titcomb Jr., MD (Hannover Re) James Topic, MD (Protective Life) 1 CASE #1 Application
GI DISEASE WORKSHOP CASE STUDIES American Academy of Insurance Medicine Triennial Course in Insurance Medicine 2012 Clifton Titcomb Jr., MD (Hannover Re) James Topic, MD (Protective Life) 1 CASE #1 Application
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Outline. Updates in the Clinical Management of Hepatitis B and C. Who should be screened for HBV? Chronic Hepatitis B 10/7/2018
 Outline Updates in the Clinical Management of Hepatitis B and C Jennifer C. Lai, MD, MBA Transplant Hepatologist Associate Professor of Medicine In Residence University of California, San Francisco Initial
Outline Updates in the Clinical Management of Hepatitis B and C Jennifer C. Lai, MD, MBA Transplant Hepatologist Associate Professor of Medicine In Residence University of California, San Francisco Initial
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice
 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases
 Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Hepatitis B screening and surveillance in primary care
 Hepatitis B screening and surveillance in primary care Catherine Stedman Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Otago, Christchurch Gastroenterology Department, Christchurch Hospital Disclosures
Hepatitis B screening and surveillance in primary care Catherine Stedman Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Otago, Christchurch Gastroenterology Department, Christchurch Hospital Disclosures
Viral Hepatitis in Reproductive Health
 Viral Hepatitis in Reproductive Health Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2010 Dr José M Bengoa Dr Pierre Jean Malè Consultants Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Viral Hepatitis in Reproductive Health Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2010 Dr José M Bengoa Dr Pierre Jean Malè Consultants Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease. Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya
 Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM
 EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
Summary for the Diagnosis of Gluten-Sensitive Entropathy Celiac Disease
 Summary for the Diagnosis of Gluten-Sensitive Entropathy Celiac Disease Celiac disease is an immune medical condition that is caused by ingestion of gluten in genetically susceptible individuals. The damage
Summary for the Diagnosis of Gluten-Sensitive Entropathy Celiac Disease Celiac disease is an immune medical condition that is caused by ingestion of gluten in genetically susceptible individuals. The damage
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans
 Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
What Is Cirrhosis? CIRRHOSIS. Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is. by chronic conditions and diseases. permanently scarred or injured
 What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
Serologic Markers CONVENTIONAL ANTIBODIES ANTIBODIES UNCONVENTIONAL. AIH Type I
 Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
HEPATITIS VIRUSES. Other causes (not exclusively hepatitis v.)also called sporadic hepatitis: HEPATITIS A(infectious hepatitis)
 Dept.of Microbiology/Virology Assist.prof. Shatha F. Abdullah HEPATITIS VIRUSES Medically important hepatitis v. (liver)are: 1.HAV 2.HBV 3.HCV 4.HDV 5.HEV 6.HGV Other causes (not exclusively hepatitis
Dept.of Microbiology/Virology Assist.prof. Shatha F. Abdullah HEPATITIS VIRUSES Medically important hepatitis v. (liver)are: 1.HAV 2.HBV 3.HCV 4.HDV 5.HEV 6.HGV Other causes (not exclusively hepatitis
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic
 Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Conflicts of interest disclosures
 Conflicts of interest disclosures Acute and Chronic Hepatitis Consultant: Gilead Sciences, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Chinweike Ukomadu Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Associate Physician
Conflicts of interest disclosures Acute and Chronic Hepatitis Consultant: Gilead Sciences, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Chinweike Ukomadu Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Associate Physician
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
 Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for liver cancer.
Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for liver cancer.
-HCV genome is about 9400 nucleotides long, it is ssrna and positive sense -the 10 viral proteins are first made as a large polyprotein -individual
 2013: HCV Genome -HCV genome is about 9400 nucleotides long, it is ssrna and positive sense -the 10 viral proteins are first made as a large polyprotein -individual proteins are released from polyprotein
2013: HCV Genome -HCV genome is about 9400 nucleotides long, it is ssrna and positive sense -the 10 viral proteins are first made as a large polyprotein -individual proteins are released from polyprotein
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
HBV : Structure. HBx protein Transcription activator
 Hepatitis B Virus 1 Hepatitis B Virus 2 Properties of HBV a member of the hepadnavirus group Enveloped, partially double-stranded DNA viruses, smallest DNA virus Replication involves a reverse transcriptase
Hepatitis B Virus 1 Hepatitis B Virus 2 Properties of HBV a member of the hepadnavirus group Enveloped, partially double-stranded DNA viruses, smallest DNA virus Replication involves a reverse transcriptase
Clinical Case Maria Butí, MD, PhD
 Clinical Case Maria Butí, MD, PhD Liver Unit, Internal Medicine Department Vall d Hebron Hospital 1 Clinical Case 70 year-old male Smoker, no alcohol intake No risk factors Diabetes Mellitus treated with
Clinical Case Maria Butí, MD, PhD Liver Unit, Internal Medicine Department Vall d Hebron Hospital 1 Clinical Case 70 year-old male Smoker, no alcohol intake No risk factors Diabetes Mellitus treated with
Confirmed (Laboratory Tests) Serum positive for IgM anti-hbc or, hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg).
 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations. Viral Hepatitis Language. Types of Viral Hepatitis 7/1/2013
 Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
 Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
Media centre. WHO Hepatitis B. Key facts. 1 of :12 AM.
 1 of 5 2013-08-02 7:12 AM Media centre Hepatitis B Share Print Fact sheet N 204 Updated July 2013 Key facts Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic
1 of 5 2013-08-02 7:12 AM Media centre Hepatitis B Share Print Fact sheet N 204 Updated July 2013 Key facts Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic
LIVER DISEASES. Anatomy
 LIVER DISEASES Anatomy PHYSIOLOGY Bilirubin metabolism: 250-300 mg/d SER Bile UDPG-A B. diglucuronide Unc. B B. monoglucuronide Albumin Glucuronyltransferase 100-200 mg/d Bacteria 4mg In urine urobilinogen
LIVER DISEASES Anatomy PHYSIOLOGY Bilirubin metabolism: 250-300 mg/d SER Bile UDPG-A B. diglucuronide Unc. B B. monoglucuronide Albumin Glucuronyltransferase 100-200 mg/d Bacteria 4mg In urine urobilinogen
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
World Health Organization. Western Pacific Region
 Basic modules for hepatitis 1 Basic Module 1 Liver anatomy and physiology 2 Position of liver Midline Located in right upper abdomen Protected by the right rib cage Right upper Measures: 12 15 cm in vertical
Basic modules for hepatitis 1 Basic Module 1 Liver anatomy and physiology 2 Position of liver Midline Located in right upper abdomen Protected by the right rib cage Right upper Measures: 12 15 cm in vertical
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none none Risk Factors for Alcoholic Liver Disease Amount of alcohol consumed Duration of alcohol consumption Gender
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none none Risk Factors for Alcoholic Liver Disease Amount of alcohol consumed Duration of alcohol consumption Gender
March 29, :15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D
 March 29, 2017 12:15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D Provided by #IM2017 This lunch symposium is not part of the official Internal Medicine Meeting 2017 Education Program. #IM2017
March 29, 2017 12:15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D Provided by #IM2017 This lunch symposium is not part of the official Internal Medicine Meeting 2017 Education Program. #IM2017
Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis C LAUREN MYERS MMSC, PA-C OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY
 Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis C LAUREN MYERS MMSC, PA-C OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis
Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis C LAUREN MYERS MMSC, PA-C OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management Kapil Chopra M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Transplant Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona PSC Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management Kapil Chopra M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Transplant Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona PSC Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases
 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
The Alphabet Soup of Viral Hepatitis Testing
 The Alphabet Soup of Viral Hepatitis Testing August 18, 2011 Patricia Slev, PhD, DABCC Medical Director, Serologic Hepatitis and Retrovirus Laboratory, ARUP Laboratories Assistant Professor of Pathology,
The Alphabet Soup of Viral Hepatitis Testing August 18, 2011 Patricia Slev, PhD, DABCC Medical Director, Serologic Hepatitis and Retrovirus Laboratory, ARUP Laboratories Assistant Professor of Pathology,
Hepadnaviridae family (DNA) Numerous antigenic components Humans are only known host May retain infectivity for more than 7 days at room temperature
 Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
Understanding Liver Disease
 Visit us on the Web at: clevelandclinic.org/liver To make an appointment call: 888.410.1775, option 1 International patients call: 001.216.444.8184 WOULD YOU LIKE A SECOND OPINION? If you would like a
Visit us on the Web at: clevelandclinic.org/liver To make an appointment call: 888.410.1775, option 1 International patients call: 001.216.444.8184 WOULD YOU LIKE A SECOND OPINION? If you would like a
Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective
 Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective Infectious A E Enterically transmitted Viral hepatitis NANB Serum B D F, G,? other C Parenterally transmitted Before the discovery of hepatitis A virus (HAV) and
Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective Infectious A E Enterically transmitted Viral hepatitis NANB Serum B D F, G,? other C Parenterally transmitted Before the discovery of hepatitis A virus (HAV) and
Hepatitis STARS Program. Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003
 Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs
 Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
Lab Underwriting Puzzler. Presented by: Bill Rooney, M.D.
 Lab Underwriting Puzzler Presented by: Bill Rooney, M.D. Obtaining Best Results from this presentation For best results please do the following: Select Slide Show from the menu option on top Select From
Lab Underwriting Puzzler Presented by: Bill Rooney, M.D. Obtaining Best Results from this presentation For best results please do the following: Select Slide Show from the menu option on top Select From
