Conflicts of interest disclosures
|
|
|
- Joel Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Conflicts of interest disclosures Acute and Chronic Hepatitis Consultant: Gilead Sciences, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Chinweike Ukomadu Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Associate Physician Brigham and Women s Hospital Review Goals Inflammation directed at hepatocytes Understand the meaning of hepatitis Be able to differentiate between acute and chronic hepatitis Understand important features of a select number of causes of hepatitis Hepatitis Pathologic target is hepatocytes ALT and AST >>Alk Phos Can be acute with insult usually less than 6 months in duration Cholangitis Target is mostly biliary ductal cells Alk Phos >> ALT/AST Can also be acute or chronic Sleuthing the cause Acute hepatitis Chronic hepatitis Toxins (e.g. acetaminophen) Toxins Viral: B and C Viral: A-E, CMV, EBV, Metabolic: NAFLD, Glycogenic HSV, VZV hepatopathy Autoimmune hepatitis Genetic Hemochromatosis Vascular compromise α-1 antitrypsin deficiency Fulminant Wilson s Wilson s Disease Immune Autoimmune hepatitis Celiac sprue Vascular Budd-Chiari Rt. Sided Heart failure VOD Viral Hepatitis Hepatotrophic Viruses: Hepatitis A-E Non hepatotrophic Viruses: CMV, EBV, HSV
2 Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) A single-stranded RNA virus. Causes mostly acute and occasionally relapsing episodes of hepatitis. Responsible for between 20 and 40 % of acute hepatitis in the U.S. Fulminant liver failure is very rare but possible, particularly in setting of pre-existing chronic liver disease. At least one study has reported high mortality rates in the setting of chronic HCV infection. Fecal-oral route with incubation period ranging from 2 to 8 weeks with an average of 4 weeks HAV con t Presence of IgM antibodies to HAV signifies acute infection IgG antibodies suggest prior infection or vaccination and thus immunoprotection Post-exposure treatment with IgG effective if given within 2 weeks Post-exposure IgG treatment does not decrease effectiveness of vaccination HBV con t Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Double stranded DNA virus Cause of both acute and chronic hepatitis Common disease, with an estimated world-wide prevalence of 350 million and 250,000 annual deaths. Most prevalent in Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa Modes of transmission are blood borne and sexual Acute infection is characterized the presence of HBsAg and HBV DNA. IgM HBcAb also develops early in the infection and may be the only serologic marker during the window period. Presence of HBsAg for greater than 6 months implies chronicity HBeAg suggests a highly infectious state and correlates with high levels of HBV DNA and hepatocellular damage. The presence of HBsAb signifies immunity, either from vaccination or prior infection HBV con t Serologic Patterns in Acute HBV infection ALT HBV DNA Core IgG SAg SAb Core IgM EAg Time months Age of infection is important determinant of chronic state. Early childhood infection >90%. Adult infections ~5% Chronic HBV infection may be asymptomatic,or cause cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Cirrhosis does not have to be present for HCC to develop. Extrahepatic manifestations related to circulating immune complexes : rashes, arthralgias, glomerulonephritis and polyarteritis nodosa occur in 20% of patients
3 Hepatitis B Key Concepts HBV con t Treatment with interferon alpha, pegylated interferon, lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir or tenofovir can normalize aminotransferases in chronically infected patients, and lead to loss of HBeAg. Loss of HBsAb is seen in only a minority of patients. Liver transplantation is indicated for fulminant liver failure (acute infection) and for decompensated cirrhosis (chronic infections). Double stranded DNA virus HBsAg indicates active infection HBsAb indicates protective immunity Presence of HBsAb and HBcAB indicates protective immunity through prior exposure not through vaccination(hbsab only). HBcAb is not protective! Less than 5% of adult-acquired HBV becomes chronic, whereas 90% of perinatally-acquired HBV becomes chronic 100 fold increase risk of HCC with chronic HBV infection Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Previously known as Non-A, Non-B hepatitis, HCV is an RNA virus Approximately 1.8% of U.S. population is HCV antibody positive, 1.3% are HCV RNA positive. HCV RNA should be evaluated in HCV antibody positive persons before a diagnosis is rendered Antibodies to HCV do not confer protective immunity Responsible for both acute (rare) and chronic (common) hepatitis Less than 20% of infected patients are symptomatic during acute infection HCV con t The modes of transmission are both percutaneous and sexual. IV drug use is the most common mode of acquisition in the USA An estimated 80-85% progress to chronic hepatitis Extrahepatic manifestations: cryoglobulinemia with palpable purpura, arthralgias, leukocytoclastic vasculitis and glomerulonephritis. Porphyria cutanea Tarda (PCT), a blistering rash most prominent in the sun exposed areas of the body HCV con t Variable natural history, but rate of fibrosis affected by alcohol intake HCV genotype 1a and 1b are most common in the U.S., but genotypes 2 and 3 are more easily treated with currently available therapies Progression to cirrhosis in 20%-30% after 20 years HCV is currently the most common indication for liver transplantation in the U.S. HCV con t Therapy for HCV Genotype 1 is combination of pegylated interferon, ribavirin and protease inhibitor for 6 to 12 months Therapy for HCV Genotype 2 and 3 is combination of pegylated interferon and ribavirin Potential side effects of treatment are numerous and include fever, nausea, myalgias, depression, leukopenias, hemolytic anemia and teratogenic effects
4 HCV Key Concepts 80-85% progress to chronic HCV 1.8% of the population have been exposed to HCV, while 1.3% are infected Antibodies to HCV do not signify immunity Percutaneous and sexual transmission Variable disease progression, but alcohol clearly increases risk of progression 20% progress to cirrhosis over 20 years Leading indication for liver transplantation Hepatitis D (Delta) Virus A defective RNA virus that is dependant upon coinfection with HBV Transmitted percutaneously or sexually May be transmitted with HBV (co-infection) or during active HBV (superinfection) Acute HDV may result in rapid progression in hepatitis leading to fulminant hepatitis HDV con t Hepatitis E Virus Superinfection leads to chronic HDV in 70% of cases Diagnosis is made by anti-hd antibodies. Antibody is not protective No effective specific therapy HDV infection Treatment of the underlying HBV RNA virus Fecal oral transmission Highest prevalence in Asia, Central America, Africa Clinical disease similar to Hepatitis A Incubation period of 2 weeks to 2 months Fulminant hepatitis common during pregnancy with mortality rates reported at 15-25% Metabolic causes of chronic hepatitis Iron Overload (specifically genetic Hemochromatosis) NAFLD specifically NASH Glycogenic Hepatopathy Wilson s Disease a1-antitrypsin Deficiency Hemochromatosis Autosomal recessive disease with increased iron absorption through the GI tract Most common inherited disease among Caucasians, with a gene frequency of 1:12. The prevalence of homozygosity approaches 1:200 Extrahepatic iron accumulation in heart, skin and pancreas may result in cardiomyopathy, bronze discoloration of skin, and diabetes Other extrahepatic manifestations include arthralgias, testicular atrophy and impotence
5 Hemochromatosis cont d More than 50% of patients assymptomatic at presentation. Fasting transferrin saturation (Fe/TIBC) is preferred screening test over ferritin Gene responsible, HFE, isolated in Mutations, C282Y and H63D identified C282Y homozygote present in 85% of affected US residents of Western European extraction Diagnosis either by total iron content of liver tissue on biopsy (next slide) or by HFE genotype Hemochromatosis Courtesy J. Glickman, BWH Pathology Hemochromatosis cont d Why biopsy and who needs it? 1)If C282Y/C282Y Biopsy indicated to rule out cirrhosis. Risk of HCC increases 200 fold in cirrhotic patients If under 40, normal lfts, ferritin<1000, low risk of cirrhosis. No biopsy necessary 2)If no conclusive diagnosis by genetic test Hemochromatosis cont d Treatment Frequent phlebotomy in non-anemic patients until transferrin saturation is <50%, Ferritin less than 50, or Hgb~10g/dl to 11g/dl. Then q3-4 month phlebotomies (Desferoxamine in anemic patients but of little clinical utility) Wilson s Disease A disease impaired biliary copper excretion Autosomal recessive disorder with prevalence of 1:30,000. Gene is a Cu ATPase. Neurological, especially extrapyramidal features, or psychiatric manifestations may dominate presentation Liver disease may present as fulminant Wilson s associated with massive hemolysis, high transaminases(ast>alt), low alkaline phosphatase, jaundice and liver failure. Most often a disease of teenagers, rare >40 yrs. Wilson s Disease cont d Decreased level of serum ceruloplasmin, a circulating protein carrier of copper Increased hepatic copper on biopsy Kayser-Fleischer rings (Fig D, next slide) on slit lamp exam represent copper deposition in the cornea Treatment is copper chelation, usually with Penicillamine or Trientine Decreased GI copper absorption with oral zinc is another therapeutic modality
6 Wilson s Disease Gitlin JD. Gastro; 125:1868(2003) α1-antitrypsin Deficiency An autosomal recessive disease. Most common in people of Northern European descent Emphysema occurs most commonly in the 4 th and 5 th decades, as a result of unopposed activity of leukocyte elastase. Smoking accelerates lung disease Liver disease due accumulation of mutant protein in the endoplasmic reticulum α1-antitrypsin Deficiency cont d α1-antitrypsin deficiency Courtesy J. Glickman, BWH Pathology Diagnosis is through serologic evaluation of antitrypsin levels followed by Pi typing Histological diagnosis shows characteristic PAS positive, diastase resistant globules in hepatocytes (next slide) No effective therapy for liver disease Recombinant α1-at in emphysema Transplantation for advanced cirrhosis Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Part of a spectrum of diseases called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: NAFLD NAFLD includes simple steatosis (fatty liver) and steatosis with inflammation (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis) Fatty accumulation in hepatocytes, often macrovesicular on histology specimens (next slide) No alcohol intake Inflammation +/-fibrosis on biopsy Presenting findings may include hepatomegaly and elevated aminotransferases Simple Steatosis Fibrosis -zone 3 -peri sinusoidal Histology in NAFLD (Courtesy of Dr Hema Khurana, BWH Pathology) NASH -steatosis -lobular inflammation -Ballooning degeneration Cirrhosis -nodule formation -fat may be absent
7 Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis cont d Obesity, hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance or frank diabetes are common Ultrasound, CT or MRI findings are suggestive, although biopsy is necessary to confirm diagnosis and distiguish simple steatosis from steatohepatitis. Natural history is unclear. At least 15-20% of patients have fibrosis on initial biopsy. Cirrhosis is less common but estimates range from 0% to 38% of cases Mortality in NAFLD Angulo P. Hepatology; 51: (2010) Diagnosis Study size Cirrhosis Liver death All deaths F/u( Yrs) Steatosis (35%) 9.6 Steatosis (12.1%) 13.7 Steatosis (1.2%) 1(0.6%) 48(28.2%) 20.7 Steatosis 74 42(56.8%) 2(2.7%) 42 ( 56.8%) 18.5 Total 342 2(0.7%) 3(0.9%) 111(32.5%) 15.6 NASH 26 1(4%) 0 4(155) 8.7 NASH ( 14.1%) 2(2.8%) 19 (26.8%) 13.7 NASH 57 NR 10 (17.5%) 36(63.2%) 18.5 NASH 51 5(9.8%) 3(5.9%) 24 (47.1%) 21 Total ( 10.8%) 15 (7.3%) 83 (40.5%) 15.5 Management Of NAFLD Weight Loss Habit Modifications Pharmcotherapy Bariatric Surgery Insulin sensitizers Thiazolidinediones Metformin Lipid lowering agents Statins Fibrates Anti-oxidants Vitamin E Ursodeoxycholic acid Pentoxyfilline Therapy Guidelines Modality Summary Comment Weight Loss Decreases hepatic steatosis Hypocaloric diet or physical activity. 3%-5% decrease body weight improves steatosis. ~10% improves inflammation Metformin No effect on liver histology Not recommended as specific treatment for NAFLD Pioglitazone Effective in NASH Long term safety in NASH not known. Data from trials all in nondiabetic patients Vitamin E Effective in NASH Considered first line therapy in nondiabetic, non cirrhotic NASH Ursodeoxycholic acid Not effective Not recommended Omega-3 fatty acids May be effective for treatment of hypertriglyceridemia No clear data as yet for role in NAFLD or NASH Statins Bariatric Surgery Can be used to treat dyslipidemia in NAFLD patients Effective in Obese individuals with NASH No significant evidence to suggest enhanced liver disease in persons with liver disease No clear recommendation to use as specific treatment for NASH Chalasani N et al. Hepatology. Epub ahead of print 4/6/2012 Key Concepts Key concepts Hemochromatosis Transferrin saturation is best screening test High risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis Phlebotomy in nonanemic patients is standard of care NAFLD Risk factors: Obesity, hypertryglyceridemia and diabetes Must eliminate alcohol use as possible cause Normalize lfts by weight loss, decreased triglycerides and euglycemia. Vitamin E is first line agent in new guideline Wilson s Disease Autosomal recessive Copper accumulation in liver and brain Corneal Kayser- Fleischer rings Rarely presents after age 40 May present as fulminant hepatitis or cirrhosis α1- antitrypsin deficiency Autosomal recessive Emphysema and cirrhosis PAS positive globules in liver, diastase resistant
8 Immune Mediated Hepatitis Autoimmune Hepatitis Celiac Sprue Autoimmune Hepatitis Characterized by the presence of auto antibodies and hypergammaglobulinemia Female predominance(3.6:1 Female:Male) Typical onset between 10 and 30, although second peak in middle age Symptoms include fatigue and RUQ pain Hepatomegaly most common finding. Spider nevi in more than 50% of patients. Autoimmune Hepatitis con t Autoimmune hepatitis Auto antibodies include ANA, ASMA and anti- LKM Hyper gamma globulinemia AMA should be negative Viral, EtOH and drug/toxin-induced hepatitis must be excluded Cirrhosis at time of diagnosis common Biopsy necessary for staging Immune suppression for treatment Autoimmune Hepatitis con t Auto antibodies include ANA, ASMA and anti- LKM Hyper gamma globulinemia AMA should be negative Viral, EtOH and drug/toxin-induced hepatitis must be excluded Cirrhosis at time of diagnosis common Biopsy necessary for staging Immune suppression for treatment Treatment of AIH Prednisone alone or in combination with Azathioprine Azathioprine should not be used alone to induce remission Azathioprine can be used for maintenance therapy Patients should be monitored carefully for side effects of immunosuppressive therapy
9 Key Concepts AIH Autoantibodies Increased IgG More common in women Treatment is with immunosuppresives. Induction therapy must include corticosteroids Conflict of interest disclosures Consultant: Gilead Sciences, Vertex Pharmaceuticals References Lok AS, McMahon. Chronic Hepatitis B: update Hepatology 2008 Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, et al. Diagnosis, Management and Treatment of Hepatitis C: An update. Hepatology 2009 Czaja AJ, Freese DK. Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Hepatology 2002 AGA Medical Position Statement: Nonalcohlic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2002 Lindor KD, Gershwin E, Poupon R, et al. Primary Biliary Cirrhosis, Hepatology 2009 Question 1: A 14 year old female is seen for elevated liver enzymes. ALT is 63 and AST is 78. Albumin is 3.3 and the prothrombin time is 20 seconds with and INR of 2.0. A previous A grade student until the last year, she now fails most courses. She is aggressive, angry, irrational and occasionally violent. Which of the following is true? A) She most likely has a defect in the gene for copper transported ATPB7 B) Slit lamp examination may show Kaiser Fleisher rings C) Penicillamine is a good first line therapy D) Ceruloplasmin levels are likely to be low E) All of the above The answer is E. The patient is young, has neurobehavioral issues along with hepatic impairment. The most likely reason is Wilson s disease. Question 2:A 42 year old man is seen for worsening emphysema. He has smoked 2.5 packs of cigarettes per day for 16 years. As part of his pulmonary evaluation he his noted to have an enlarged and nodular liver. A liver biopsy shows PAS positive globules that are diastase resistant. The most likely diagnosis is Ala A eta al. Lancet; 369: 397 ( 2007)
10 Question 2 A) Glycogenic hepatopathy B) Amyloidosis C) Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency D) Gaucher s Disease E) Idiopathic ductopenia Question 2: The correct answer is C. The patient has alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency. Glycogenic hepatopathy is an acquired glycogen deposition disease seen in type 1 diabetics. The glycogen deposits are PAS positive but diastase sensitive (see additional slides for more details). The diagnosis of amylodosis is made on a Congo red stain. Gaucher s disease is a lysosomal storage disorder with deposition of glucocerebrosides in many organs including liver, bone marrow and spleen. Idiopathic ductopenia is a disorder of bile ductular loss Stoller JK and Aboussouan LS. Lancet; 365: 2225 ( 2005) Glycogenic hepatopathy: a type 1 diabetic disorder that may mimic NAFLD Bonus slides: Glycogenic Hepatopathy Patients with poorly controlled type 1 diabetes may present with and are often erroneously given a diagnosis of NAFLD: Elevated aminotransferases Hepatomegaly Right upper quadrant pain Elevated glycosylated hemoglobin hyperglycemia Glycogenic Hepatopathy (Mauriac s syndrome) H&E LP PAS H&E HP PAS+D Hyperglycemia Insulin + (sporadic) glycogen Rogal S et al. NEJM; 364: NASH vs Glycogenic Hepatopathy NASH Glycogenic hepatopathy Type 1 DM Type 2 Diabetes/impaired insulin sensitivity RUQ pain, incr lfts, hepatomegaly Obesity Poor compliance with Incr. Triglycerides insulin therapy HTN Steatosis unusual Radiographs often with Marked hepatic glycogen evidence of fat deposition Biopsy shows fat No significant fibrosis Can progress to advanced Usually responds to stringent liver dz insulin therapy Multimodal therapy
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant. Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
Viral Hepatitis. Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital
 Viral Hepatitis Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Viral Hepatitis HAV HBV HCV HDV HEV Other viral: CMV, EBV, HSV Unknown Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Transmitted via the faecal-oral route
Viral Hepatitis Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Viral Hepatitis HAV HBV HCV HDV HEV Other viral: CMV, EBV, HSV Unknown Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Transmitted via the faecal-oral route
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
IN THE NAME OF GOD. D r. MANIJE DEZFULI AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST
 IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
Metabolic Liver Diseases
 Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Liver Disease. By: Michael Martins
 Liver Disease By: Michael Martins Recently I have been getting a flurry of patients that have some serious liver complications. This week s literature review will be the dental management of the patients
Liver Disease By: Michael Martins Recently I have been getting a flurry of patients that have some serious liver complications. This week s literature review will be the dental management of the patients
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Hepatitis. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 5/2/2019. Mob:
 Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Viral hepatitis Blood Born hepatitis. Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH
 Viral hepatitis Blood Born hepatitis Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH Outline Introduction to hepatitis Characteristics of viral hepatitis Mode of transmission Markers of hepatitis
Viral hepatitis Blood Born hepatitis Dr. MONA BADR Assistant Professor College of Medicine & KKUH Outline Introduction to hepatitis Characteristics of viral hepatitis Mode of transmission Markers of hepatitis
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease None Disclosures Arslan Kahloon M.D Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Tennessee College of Medicine Chattanooga Objectives Understand the
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease None Disclosures Arslan Kahloon M.D Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Tennessee College of Medicine Chattanooga Objectives Understand the
Viral hepatitis. Supervised by: Dr.Gaith. presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a
 Viral hepatitis Supervised by: Dr.Gaith presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a Etiology Common: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Less common: Cytomegalovirus EBV Rare: Herpes
Viral hepatitis Supervised by: Dr.Gaith presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a Etiology Common: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Less common: Cytomegalovirus EBV Rare: Herpes
Chronic Hepatitis C. Risk Factors
 Chronic Hepatitis C The hepatitis C virus is one of the most important causes of chronic liver disease in the United States. Almost 4 million Americans or 1.8 percent of the U.S. population have an antibody
Chronic Hepatitis C The hepatitis C virus is one of the most important causes of chronic liver disease in the United States. Almost 4 million Americans or 1.8 percent of the U.S. population have an antibody
9/28/2016. Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach. Objectives. Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
 Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes
 Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes Donald Gardenier, DNP, FNP-BC Assistant Professor and Clinical Program Director Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, NY Conflict of Interest
Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes Donald Gardenier, DNP, FNP-BC Assistant Professor and Clinical Program Director Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, NY Conflict of Interest
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic
 Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Disclosure. Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes
 Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland
 Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Viral Hepatitis in Children DR. HOSSAIN IBRAHIM AGEEL PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST PEDIATRIC DEPARTMENT KFCH JAZAN
 Viral Hepatitis in Children DR. HOSSAIN IBRAHIM AGEEL PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST PEDIATRIC DEPARTMENT KFCH JAZAN General Concepts Hepatitis = 'inflammation of the liver'. Virus causes: Hepatotropic and
Viral Hepatitis in Children DR. HOSSAIN IBRAHIM AGEEL PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGIST PEDIATRIC DEPARTMENT KFCH JAZAN General Concepts Hepatitis = 'inflammation of the liver'. Virus causes: Hepatotropic and
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee
 Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee Hereditary Haemochromatosis A disorder of iron metabolism Inherited disorder Iron Essential micro-nutrient Toxicity when
Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee Hereditary Haemochromatosis A disorder of iron metabolism Inherited disorder Iron Essential micro-nutrient Toxicity when
VIRAL AND AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS WHAT IS HEPATITIS?
 VIRAL AND AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Arthur M. Magun, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Inflammation of the liver Almost always, inflammation implies elevation in liver enzymes AST and ALT
VIRAL AND AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS Arthur M. Magun, M.D. Clinical Professor of Medicine WHAT IS HEPATITIS? Inflammation of the liver Almost always, inflammation implies elevation in liver enzymes AST and ALT
HBV in HIV Forgotten but not Gone
 Activity Code FA376 HBV in HIV Forgotten but not Gone Richard K. Sterling, MD, MSc VCU Hepatology Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Learning Objectives
Activity Code FA376 HBV in HIV Forgotten but not Gone Richard K. Sterling, MD, MSc VCU Hepatology Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Learning Objectives
Steatosis/Steatohepatitis
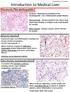 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
Harvard Medical School
 Harvard Medical School Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Tests in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Harvard Medical School Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Tests in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
4/27/2018. Disclosures LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none none Risk Factors for Alcoholic Liver Disease Amount of alcohol consumed Duration of alcohol consumption Gender
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none none Risk Factors for Alcoholic Liver Disease Amount of alcohol consumed Duration of alcohol consumption Gender
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
Disclosure. Objectives. Smash the Nash: A practical approach to fatty liver disease
 Smash the Nash: A practical approach to fatty liver disease Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic
Smash the Nash: A practical approach to fatty liver disease Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
The Long Term Care Risk
 Hepatitis C The Long Term Care Risk Objectives Basics of the disease Disease progression Comorbid factors Treatment Long term care risk Basics of Hepatitis C Caused by an RNA virus Clinical Course Acute
Hepatitis C The Long Term Care Risk Objectives Basics of the disease Disease progression Comorbid factors Treatment Long term care risk Basics of Hepatitis C Caused by an RNA virus Clinical Course Acute
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management
 Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Dr David Rowbotham NHS. The Leeds Teaching Hospitals. NHS Trust
 Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Nurses Update June 2010 Chronic Hepatitis HBV / HCV David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Nurses Update June 2010 Chronic Hepatitis HBV / HCV David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
Viral Hepatitis. Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Viral Hepatitis Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Viral hepatitis Viral hepatitis must be considered in any patient presenting with hepatitis on LFTs (high
Viral Hepatitis Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Viral hepatitis Viral hepatitis must be considered in any patient presenting with hepatitis on LFTs (high
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases
 Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University
 Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
WHEN HCV TREATMENT IS DEFERRED WV HEPC ECHO PROJECT
 WHEN HCV TREATMENT IS DEFERRED WV HEPC ECHO PROJECT October 13, 2016 Reminder - treatment is recommended for all patients with chronic HCV infection Except short life expectancies that cannot be remediated
WHEN HCV TREATMENT IS DEFERRED WV HEPC ECHO PROJECT October 13, 2016 Reminder - treatment is recommended for all patients with chronic HCV infection Except short life expectancies that cannot be remediated
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Primary NAFLD. April 13, 2012
 NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Primary NAFLD Simple Steatosis Fatty hepatocytes Intracellular fat
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Primary NAFLD Simple Steatosis Fatty hepatocytes Intracellular fat
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
Fatty Liver Disease A growing epidemic
 Fatty Liver Disease A growing epidemic Updates in GIM for Primary Care Don C. Rockey March 9 th, 2018 Disclosures 2018 Research Funding (all to MUSC) NIH/NIDDK Actelion Pharmaceuticals Gilead Sciences
Fatty Liver Disease A growing epidemic Updates in GIM for Primary Care Don C. Rockey March 9 th, 2018 Disclosures 2018 Research Funding (all to MUSC) NIH/NIDDK Actelion Pharmaceuticals Gilead Sciences
Hepatitis B (Part 1 - intro)
 Hepatitis B (Part 1 - intro) The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) l Virology Discovered in 1966 double-stranded DNA virus l family of hepadnaviruses l HBV unique to Humans (Primates too in laboratory studies) no
Hepatitis B (Part 1 - intro) The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) l Virology Discovered in 1966 double-stranded DNA virus l family of hepadnaviruses l HBV unique to Humans (Primates too in laboratory studies) no
HEPATITIS VIRUSES. Other causes (not exclusively hepatitis v.)also called sporadic hepatitis: HEPATITIS A(infectious hepatitis)
 Dept.of Microbiology/Virology Assist.prof. Shatha F. Abdullah HEPATITIS VIRUSES Medically important hepatitis v. (liver)are: 1.HAV 2.HBV 3.HCV 4.HDV 5.HEV 6.HGV Other causes (not exclusively hepatitis
Dept.of Microbiology/Virology Assist.prof. Shatha F. Abdullah HEPATITIS VIRUSES Medically important hepatitis v. (liver)are: 1.HAV 2.HBV 3.HCV 4.HDV 5.HEV 6.HGV Other causes (not exclusively hepatitis
Viral Hepatitis. Background
 Viral Hepatitis Background Hepatitis or inflammation of the liver can be caused by infectious and noninfectious problems. Infectious etiologies include viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Noninfectious
Viral Hepatitis Background Hepatitis or inflammation of the liver can be caused by infectious and noninfectious problems. Infectious etiologies include viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. Noninfectious
Wilson Disease - Our Experience
 Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
Wilson Disease Our Experience Hussein Shamaly M.D.. Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit Pediatric Department Clalit Health Services French Hospital, Nazareth Key Concepts Wilson disease is more often considered
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update. Primary Causes of Chronic Liver Disease in the U.S. Hepatitis Definition. Hepatitis Viruses.
 Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Il trapianto di cellule staminali emopoietiche nel paziente portatore di virus epatitici
 Il trapianto di cellule staminali emopoietiche nel paziente portatore di virus epatitici Anna Locasciulli Ematologia e Trapianto di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Ospedale S.Camillo, Roma Il trapianto
Il trapianto di cellule staminali emopoietiche nel paziente portatore di virus epatitici Anna Locasciulli Ematologia e Trapianto di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Ospedale S.Camillo, Roma Il trapianto
Outline. Updates in the Clinical Management of Hepatitis B and C. Who should be screened for HBV? Chronic Hepatitis B 10/7/2018
 Outline Updates in the Clinical Management of Hepatitis B and C Jennifer C. Lai, MD, MBA Transplant Hepatologist Associate Professor of Medicine In Residence University of California, San Francisco Initial
Outline Updates in the Clinical Management of Hepatitis B and C Jennifer C. Lai, MD, MBA Transplant Hepatologist Associate Professor of Medicine In Residence University of California, San Francisco Initial
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust
 ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABCs of Viral Hepatitis What Primary Care Physicians Need to Know
 ABCs of Viral Hepatitis What Primary Care Physicians Need to Know Dr Kenny C.P. Sze Associate Consultant Division of Gastroenterology Department of General Medicine Outline and Keypoints Hepatitis A Recap;
ABCs of Viral Hepatitis What Primary Care Physicians Need to Know Dr Kenny C.P. Sze Associate Consultant Division of Gastroenterology Department of General Medicine Outline and Keypoints Hepatitis A Recap;
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C
 Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Hepatitis B Update. Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL. Gastroenterology
 Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
The Skinny On Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 The Skinny On Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease UCSF Advances in Internal Medicine Monika Sarkar, MD, MAS UCSF Division of GI/Hepatology June 24th, 2015 Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Outline Pathogenesis
The Skinny On Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease UCSF Advances in Internal Medicine Monika Sarkar, MD, MAS UCSF Division of GI/Hepatology June 24th, 2015 Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Outline Pathogenesis
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE:
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE: ROLE OF THE PRIMARY PROVIDER Archita P. Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Arizona 25 th Annual Southwestern Conference on Medicine Outline Pathophysiology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE: ROLE OF THE PRIMARY PROVIDER Archita P. Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Arizona 25 th Annual Southwestern Conference on Medicine Outline Pathophysiology
Acute Hepatitis: An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes. Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC
 : An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC Faculty: Dr. Mary Anne Cooper Relationships with commercial interests: Consulting Fees: Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Canada Objectives
: An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC Faculty: Dr. Mary Anne Cooper Relationships with commercial interests: Consulting Fees: Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Canada Objectives
World Health Organization. Western Pacific Region
 Basic modules for hepatitis 1 Basic Module 1 Liver anatomy and physiology 2 Position of liver Midline Located in right upper abdomen Protected by the right rib cage Right upper Measures: 12 15 cm in vertical
Basic modules for hepatitis 1 Basic Module 1 Liver anatomy and physiology 2 Position of liver Midline Located in right upper abdomen Protected by the right rib cage Right upper Measures: 12 15 cm in vertical
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C
 S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
 Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Mohssen Nassiri Toosi, MD Imam Khomeinin Hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Virus : HBs Ag Positive Host Liver Health Chronic Hepatitis
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Mohssen Nassiri Toosi, MD Imam Khomeinin Hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Virus : HBs Ag Positive Host Liver Health Chronic Hepatitis
Chronic Hepatitis. Andrew Bathgate Chris Bellamy Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh
 Chronic Hepatitis Andrew Bathgate Chris Bellamy Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Autoimmune Hepatitis Annual incidence 1.9/100 000 in N Europe Prevalence 16.9/100 000 ~5% all liver transplants Female preponderance
Chronic Hepatitis Andrew Bathgate Chris Bellamy Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Autoimmune Hepatitis Annual incidence 1.9/100 000 in N Europe Prevalence 16.9/100 000 ~5% all liver transplants Female preponderance
Hepatitis B screening and surveillance in primary care
 Hepatitis B screening and surveillance in primary care Catherine Stedman Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Otago, Christchurch Gastroenterology Department, Christchurch Hospital Disclosures
Hepatitis B screening and surveillance in primary care Catherine Stedman Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Otago, Christchurch Gastroenterology Department, Christchurch Hospital Disclosures
What are LFTs? What are LFTs? 3/20/2017. Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistry Tests. Transaminases. Alkaline phosphatase.
 Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistry Tests James Panetta, DO What are LFTs? Transaminases Alkaline phosphatase Bilirubin Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase What are LFTs? 5 nucleosidase Lactate Dehydrogenase
Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistry Tests James Panetta, DO What are LFTs? Transaminases Alkaline phosphatase Bilirubin Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase What are LFTs? 5 nucleosidase Lactate Dehydrogenase
Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis C LAUREN MYERS MMSC, PA-C OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY
 Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis C LAUREN MYERS MMSC, PA-C OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis
Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis C LAUREN MYERS MMSC, PA-C OREGON HEALTH & SCIENCE UNIVERSITY Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Assessing the patient with a new diagnosis of Hepatitis
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
Hepatitis B Virus. Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019
 Hepatitis B Virus Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019 Epidemiology 3218 cases of acute HBV reported in 2016 847,000 non-institutionalized persons living with chronic HBV in 2011-2012 Viral
Hepatitis B Virus Taylor Page PharmD Candidate 2019 February 1, 2019 Epidemiology 3218 cases of acute HBV reported in 2016 847,000 non-institutionalized persons living with chronic HBV in 2011-2012 Viral
Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases
 Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FAASLD Director, Liver Care Network and Organ Care Research Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA Postgraduate Course: Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases Challenges in Management of
Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FAASLD Director, Liver Care Network and Organ Care Research Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA Postgraduate Course: Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases Challenges in Management of
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans
 Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice
 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: a rare cause of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
 Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: a rare cause of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Naoki Tanaka 1, Akira Horiuchi 2, Takahide Yokoyama 3, Shigeyuki Kawa 1, and Kendo Kiyosawa 1 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: a rare cause of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Naoki Tanaka 1, Akira Horiuchi 2, Takahide Yokoyama 3, Shigeyuki Kawa 1, and Kendo Kiyosawa 1 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
DISEASE LEVEL MEDICAL EVIDENCE PROTOCOL
 DISEASE LEVEL MEDICAL EVIDENCE PROTOCOL 1. This Protocol sets out the medical evidence that must be delivered to the Administrator for proof of Disease Level. It is subject to such further and other Protocols
DISEASE LEVEL MEDICAL EVIDENCE PROTOCOL 1. This Protocol sets out the medical evidence that must be delivered to the Administrator for proof of Disease Level. It is subject to such further and other Protocols
Hepatitis. Causes: - infectious Hepatitis: viral, Bacterial, Parasitic, and Helminthic - Autoimmune Hepatitis - Drug- and Toxin (Alcohol) - Metabolic
 Liver diseases II Hepatitis Causes: - infectious Hepatitis: viral, Bacterial, Parasitic, and Helminthic - Autoimmune Hepatitis - Drug- and Toxin (Alcohol) - Metabolic infectious Hepatitis Several clinical
Liver diseases II Hepatitis Causes: - infectious Hepatitis: viral, Bacterial, Parasitic, and Helminthic - Autoimmune Hepatitis - Drug- and Toxin (Alcohol) - Metabolic infectious Hepatitis Several clinical
Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy. Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH
 Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement None Who are we talking about today? Treatment naïve Chronic infection This patient seems complicated
Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement None Who are we talking about today? Treatment naïve Chronic infection This patient seems complicated
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs
 Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers
 Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
 NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD, MSc Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Terminology Pathogenesis
NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE Kiran Bambha, MD, MSc Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver April 13, 2012 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Terminology Pathogenesis
Hepatitis C in Disclosures
 Hepatitis C in 2018 Sandeep Mukherjee, MD CHI Health and Creighton University Medical Center Division of Gastroenterology Grant support: Abbvie Disclosures Speaker: Abbvie, Gilead, Merck Section editor
Hepatitis C in 2018 Sandeep Mukherjee, MD CHI Health and Creighton University Medical Center Division of Gastroenterology Grant support: Abbvie Disclosures Speaker: Abbvie, Gilead, Merck Section editor
-sheet 3. -Waseem Alhaj. Maha Shomaf
 -sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
-sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
Primary Care Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Hepatitis C Brian Viviano, D.O.
 Primary Care Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Hepatitis C Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Epidemiology of chronic hepatitis C CDC guidelines on screening or hepatitis C Diagnosing hepatitis
Primary Care Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Hepatitis C Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Epidemiology of chronic hepatitis C CDC guidelines on screening or hepatitis C Diagnosing hepatitis
The ABCs of Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis. Ila Singh, M.D., Ph.D. P & S Viral Hepatitis. Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E and G viruses
 The ABCs of Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis Ila Singh, M.D., Ph.D. P & S 14-453 is132@columbia.edu Viral Hepatitis Hepatotropic viruses Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E and G viruses Generalized infection plus infection
The ABCs of Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis Ila Singh, M.D., Ph.D. P & S 14-453 is132@columbia.edu Viral Hepatitis Hepatotropic viruses Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E and G viruses Generalized infection plus infection
VIRAL AND AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS WHAT IS HEPATITIS? CAUSES OF ACUTE HEPATITIS SYMPTOMS OF ACUTE VIRAL HEPATITIS
 VIRAL AND AUTOIMMUNE Arthur M. Magun, M.D. linical Professor of Medicine Human Hepatitis Viruses Human Hepatitis Viruses Virus Genome Genome Envelope Family / genus size (kb) HAV RNA 7.5 - Picornaviridae
VIRAL AND AUTOIMMUNE Arthur M. Magun, M.D. linical Professor of Medicine Human Hepatitis Viruses Human Hepatitis Viruses Virus Genome Genome Envelope Family / genus size (kb) HAV RNA 7.5 - Picornaviridae
Management of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: The Alaska Experience
 Management of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: The Alaska Experience Brian J McMahon, MACP, FAASLD Liver Disease and Hepatitis Program Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Disclosures I have no conflicts
Management of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: The Alaska Experience Brian J McMahon, MACP, FAASLD Liver Disease and Hepatitis Program Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Disclosures I have no conflicts
NAFLD/NASH. Definitions. Pathology NASH. Vicki Shah PA-C, MMS Rush University Hepatology
 NAFLD/NASH Vicki Shah PA-C, MMS Rush University Hepatology Definitions NAFLD Evidence of hepatic steatosis by histology (5%) or imaging No causes for secondary fat accumulation EtOH, Drugs, hereditary
NAFLD/NASH Vicki Shah PA-C, MMS Rush University Hepatology Definitions NAFLD Evidence of hepatic steatosis by histology (5%) or imaging No causes for secondary fat accumulation EtOH, Drugs, hereditary
HBV : Structure. HBx protein Transcription activator
 Hepatitis B Virus 1 Hepatitis B Virus 2 Properties of HBV a member of the hepadnavirus group Enveloped, partially double-stranded DNA viruses, smallest DNA virus Replication involves a reverse transcriptase
Hepatitis B Virus 1 Hepatitis B Virus 2 Properties of HBV a member of the hepadnavirus group Enveloped, partially double-stranded DNA viruses, smallest DNA virus Replication involves a reverse transcriptase
Who to Treat? Consider biopsy Treat. > 2 ULN Treat Treat Treat Treat CIRRHOTIC PATIENTS Compensated Treat HBV DNA detectable treat
 Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
Hepatitis B. ECHO November 29, Joseph Ahn, MD, MS Associate Professor of Medicine Director of Hepatology Oregon Health & Science University
 Hepatitis B ECHO November 29, 2017 Joseph Ahn, MD, MS Associate Professor of Medicine Director of Hepatology Oregon Health & Science University Disclosures Advisory board Gilead Comments The speaker Joseph
Hepatitis B ECHO November 29, 2017 Joseph Ahn, MD, MS Associate Professor of Medicine Director of Hepatology Oregon Health & Science University Disclosures Advisory board Gilead Comments The speaker Joseph
March 29, :15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D
 March 29, 2017 12:15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D Provided by #IM2017 This lunch symposium is not part of the official Internal Medicine Meeting 2017 Education Program. #IM2017
March 29, 2017 12:15 PM 1:15 PM San Diego, CA Convention Center Ballroom 20D Provided by #IM2017 This lunch symposium is not part of the official Internal Medicine Meeting 2017 Education Program. #IM2017
Transmission of HCV in the United States (CDC estimate)
 Transmission of HCV in the United States (CDC estimate) Past and Future US Incidence and Prevalence of HCV Infection Decline among IDUs Overall incidence Overall prevalence Infected 20+ years Armstrong
Transmission of HCV in the United States (CDC estimate) Past and Future US Incidence and Prevalence of HCV Infection Decline among IDUs Overall incidence Overall prevalence Infected 20+ years Armstrong
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Pretreatment Evaluation
 Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
