disappears; by fresh additions of cocaine the blocking may be repeated blocking of conduction is obtained almost at once, but it quickly
|
|
|
- Sharlene Clarissa Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE SELECTIVE ACTION OF COCAINE ON NERVE FIBRES. BY W. E. DIXON, M.k, M.D. (Five Figures in Text.) (From the Pharmacological Laboratory, Cambridge.) v. AN RE P first clearly showed that a localised anaesthesia is obtained if cocaine is injected subcutaneously into the tissues or applied directly to any mucous membrane, such as the mouth, pharynx, larynx, or rectum'. Two hypotheses have been advanced to account for this peripheral sensory paralysis. The first points to the fact that cocaine is a general protoplasmic poison and destroys alike all forms of livinig matter. Its exponents explain the anasthesia by pointing out how much more exposed are the sensory fibres, and assert that the motor endings are not afected because the cocaine does not reach then. The second bypothesis assumes that cocaine has a specific effect on the sensory nerve endings, and has been termed by the French school the " curare-sensitif " theory. The present note deals only with the application of cocaine directly to nerve fibres: it will be shown that far frotn its acting on all nerve fibres equally, it usuially, 'in the case of a mixed nerve, paralyses ftinctionally different fibres at different rates; and one set of fibres not uncommonly requires for conmplete paralysis a stronger percentage of the drug than another set. It has been known for a long time that cocaine directly applied to nerve reduces the irritability of the nerve fibres. Langley and Dickinson2 showed that this effect may be very transient: if the cocaine in suitable strength is cautiously applied to the nerve the blocking of conduction is obtained almost at once, but it quickly disappears; by fresh additions of cocaine the blocking may be repeated many times in suiccession. It has been shown also that the diminution of excitability, conductivity, and the action current, all run a parallel I v. Anrep. Pfluiger's Archiv, xxx. p Langley and Dickinson. This Journal, xi. p
2 88 W. E. DIXON. course not only for cocaine but for other drugs, such as chloral, phenol, and chloralosel. The present experiments were performed principally on rabbits, which were always ancesthetised by ether. Dogs and cats were anaesthetised with an A.C.E. mixture, and in the vasomotor experiments curari was also employed. Motor and sensory fibres. Cocaine forms a ready means of paralysing sensory fibres whilst leaving the motor intact. If the drug is strong and allowed to act for a sufficiently long time the motor fibres are also paralysed, but they recover their action first* when the nerve is washed with normal saline. To show this effect all that is necessary is to expose a nerve, say the sciatic of the rabbit, and paint it in a definite spot for a length of 1 or 2 cms. with 10 0/0 solution of cocaine: or to obtain an even quicker result, the brush may be placed in the solid cocaine and the adherent crystals transferred directly to the nerve. On exciting the nerve in continuity, centrally to the cocainised portion, two effects are obtained, (1) reflex movements, rise of blood-pressure and stimulation of respiration by upward conduction, (2) tetanus of the leg muscles by downward conduction through the cocainised nerve. If the nerve be now excited peripherally to the cocaine, tetanuis of the leg muscles alone results, and there are none of the signs of upward conduction. Of course if the concentrated cocaine is employed the motor nerves are also affected after a time, and paralysis of the nerve becomes complete. This type of experiment is not new and has been described by several observers2. I have also employed other drugs, such for examriple as aconitine and always find that the sensory fibres are affected before the motor. Vagus. In the case of the vagus nerve the two sets of fibres, viz., those conducting upwards and downwards respectively, may be quite clearly separated by cocaine. Fig. 1 represents an experiment in which one vagus of a rabbit was painted with a /0 solution of cocaine; the tracing shows the effect of two excitations, first on the cardiac side of the painted spot and the second on the cerebral side. The first effect A is typical both on the respiration and the blood-pressure, but at the second stimulation at B conduction downwards is blocked, though of course it is still perfect towards the brain. Fig. 2 represents another experiment in which the right vagus was treated with a solution of I in 2000 cocaine HCI, the left vagus having I Wedenski. Pfuiger's Archiv, LXXI. p Cp. Binz, Phuarmacology, translated by Latham (New Sydenham Society).
3 COCAINE ON NERVE FIBRES. been severed. On stimulating the nerve above the painted spot the heart is not inhibited butt the blood-pressure rises from vaso-constriction. Stimulation below the cocainised portion has the normal effect both on the respiration and heart. Section of the opposite vagus therefore exerts no effect on the result. ~89 Fig. 1. Fig. 2. Fig. 1. Rabbit: ether, respiration, and blood-pressure. 1 cm. of the left vagus nerve has been painted with a /i, solution cocaine HCI. A represents the 'effect of excitation at the cardiac end, and.8 the effect of excitation at the cerebral end. Coil at 17 cms. Time =seconds. Fig. 2. Rabbit: ether, respiration, and blood-pressure. Left vagus cut. 1 cmi. right vagus,painted with a /i, solution cocaine HCIL Shows the effect of stimulation above and below the painted spot. Coil at 15 cms. Time= seconds. In. the dog the same division of the vagal fibres may be brought about, although owing to the comparatively large size of this animal's nerves the separation is not so clearly defined : for this purpose any strength of cocaine up to 0-4 0/,, may be necessary, accordinig to the size of the animal In Fig. 3 the record is shown of an experiment in which the left vagus was painted with a 0-3 0/0 solution of the drug. Excitation at A, below the painted spot affects both the respiration and ci'rculatilon, whilst stimulation at B., above the cocaine regioni, shows only the effect on the respiration. One other use for cocaine may be mentioned : it forms a ready
4 t9o W. E. DIXON. means of producing a temporary block in the vagus, phrenic or other nerve, for all fibres and without an initial excitation such as occurs when the nerves are- severed. For this purpose a i 0/0 solution is appropriate in the rabbit, whilst a 5 0/0 solution applied to the phrenic of a dog produces paralysis lasting about 10 minutes. I venture to suggest that painting the vagi with cocaine may be of value in cases of "suddeni Fig. 3. Dog. A.C.E. 1 cm. of left vagus painted 0 3 0/0 cocaine HC1. A represents period of stimulation below, and B that above the painted spot. Coil at 15 cms. Time= seconds.,death" in the early stage of chloroform narcosis. It is almost certain that these deaths occur from a great excitation (direct or reflex) of the medulla which results in inhibition of the heart. If the va&i are cut Embley and Martin' have shown that the blood-pressure bounds up, and the heart immediately recovers its activity: in a single experiment which I have performed on a morphinised and pithed dog which had received no volatile ansesthetic I obtained the same result by painting with cocaine. Strong chloroform was first given to the dog until there was marked cardiac inhibition, when the vagi were painted with 2 0/. cocaine; almost immediately the blood-pressure rose and the heart recovered. In man, section of the vagi is of course impossible, but I know of no reason why the conduction in these nerves should not be temporarily blocked by cocaine. I Embley and Martin. Brit. Med. Journ. i. p
5 COCATINT ON NER.VE FIBRES. Vasomotor nerves. Experiments with vasomotor nerves were performed on the dog, cat, and rabbit. In dogs and cats the sciatic nerve was chosen and the animals were either anesthetised or killed by pithing, but in either case curari was intravenously administered and artificial respiration kept up. The nerve was exposed and cut high uip so as to allow as long a piece of nerve as possible for manipulation. A glass plethysmograph was then applied to the limb and a volume record obtained either by a bellows or tambour. Blood-pressure was simultaneously recorded. If a 10/0 solution of cocaine is painted over about 1 cm. of the sciatic nerve of the cat the vaso-constrictor uerve fibres are paralysed before the vasodilator. It is not always easy to make this experiment satisfactory, for if the cocaine is too strong or allowed to act too long a time both sets of fibres are paralysed. The details of the experiment are simple; the drug is painted on the central portion of the free nerve- and electrical excitation is then applied both above and below the painted spot Ẇith the dog the large size of the nerve presents difficulties. In the experiment recorded in Fig. 4 the sciatic nerve was painted with a 1 0/0 solution of cocaine 3 minutes previotusly to stimulation, and in 91 Fig. 4a. Dog. A.C.E. Curari. Blood-pressure and limb plethysmograph. 10/0 cocaine HCI applied to about 1 cm. of the sciatic nerve. Effect of excitation below painted spot. Coil at 5 cms. Time=seconds. Fig. 4a the nerve was stimulated below the cocaine, and typical vasoconstriction results. In Fig. 4b the excitation was repeated with the same strength of current above the painted spot, and verv gradual vasodilatation results, which is perhaps most readily recognised by the augmented volume pulse.
6 92 W. E. DIXON. A physical explanation is compatible with these facts. The vasoconstrictor nerves having no sheath would be more rapidly attacked than the vasodilator; the latter according to Bayliss' are identical with the ordinary sensory afferent posterior root-fibres and possess a sheath. Sensory fibres, however, are very susceptible to cocaine, and hence there is an explanation of the difficulty in separating these two sets of fibres. Fig. 4b. Reduced Same. Effect of stimulation above the painted spot. Excitation begins at A and ends at B. Coil at 5 ems. In the rabbit a similar separation of fibres has been obtained by stimgulating the sympathetic nerve whilst measuring the ear-volume. Bronchomotor fibres. Prof. Brodie and myself have already attempted to separate bronchomotor fibres by means of cocaine but only with slight success, perhaps because in our earlier experiments we used anwesthetics which we subsequently showed invalidated the results by partially paralysing the nerve endings. Cocaine, then, whilst paralysing all nerve fibres when it is applied to them in concentrated solutions, yet exerts a selective action in dilute solutions, picking out some fibres and paralvsing them before or to the exclusion of others. Three explanations might be offered to account for these facts. First, the distribution of the fibres in the bundle may be such that those conducting one form of impulse are more exposed to the action of the drug than those conducting another. Such however is not the case, for sensory and motor fibres are freely mixed up together in the mixed nerve; and in the vagus Prof. Langley informs me there is a similar mixing together of the fibres. A second hypothesis accounts for the facts by supposing some fibres to possess a more efficient protection in their sheath than others, and the fact that moderate injury to a nerve is more likely to lead to sensory affections than motor would appear to favour it. Histology however gives I Bayliss. This Journal, xxvi. p
7 COCAINE ON NER VE FIBRES. no support to this view. Thirdly, cocaine may have a greater specificity for some fibres than for others, that is, the chemistry of the two sets of fibres may be slightly different. A fact which appears to favour the latter hypothesis is the extraordinary way in which drugs of all kinds attack not only sensory nerve fibres but sensory nerve cells before the motor, and this fact obtains, no matter whether the effect is one of stimulation or depression. Thus caffeine may be regarded as an example of a typical stimulant to the cerebrum, and the most characteristic effect of the drug is increased perception, a more perfect consciousness (i.e. the sum total of sensory impulses both as regards intensity and number at any one moment), and hence the wakefulness. Morphine on the other hand depresses sensory cells; perception and object consciousness are diminished, and hence the train of mental symptoms characteristic of the drug. Or to take the cord, we have again the strongest evidence to show that stimulants such as strycbnine exert their effect entirely on the sensory cells' and that depressants such as CHCI32 certainly attack the sensory cells before the motor. If cocaine is injected into the spinal canal of a man between the second and third lumbar vertebrse complete sensory paralysis of the lower extremities quickly follows; and if the dose is moderate (15 mgrs.) a partial motor paralysis is also later developed, consciousness of course being retained. Recovery begins with motion, and sensation is the last to revive. As regards nerve fibres I have already pointed out that the sensory are invariably affected both more easily and with smaller doses than the motor, not only with cocaine as has been shown by several observers, but by other drugs, such as aconitine, carbolic acid, chloroform, ether, etc. When we come however to the nerve endings this rule certainly does not hold: many drugs have a specific action on the motor nerve endings without in any way influencing sensory. This however is of little significance to our argument, since the term " nerve ending in no way means that the structure is nervous. Further, we have no evidence that cocaine paralyses the sensory nerve endings: all we can say is that a subcutaneous injection paralyses some part of the peripheral sensory apparatus, and quite possibly the fine nerve fibrils before the endings. At all events it is quite impossible, as far as we can judge by administering cocaine internally, to affect sensory endings, although it must be remembered that we have no very good way of testing the activity of 3 Houghton and Muirhead. Med. News, z. p Bernstein. Moleschott's Untersuch. x. p
8 .94 W.. E. DIXON. sensory endings when the sensory cells become paralysed, as in the case after big doses of cocaine. Mosso, after strongly cocainising a dog's foot, excited it electrically and obtained visual refle'xes, from which he attempted to show that the nerve endings were not essentially affected1. His experiments were not valid on account of the diffusible stimulus he employed. Sympathetic motor nerve endings cannot be paralysed with cocaine. If artificial perfusions are performed through the limb vessels of cats it is found that before adrenalin ceases to produce constriction of the vessels 50/G of cocaine must be added to the blood; when this amount is reached the muscle is killed, since such drugs as BaCl, induce no contraction. That is to say, the cocaine does not specially act on these endings, nor do I know of any evidence tending to show that it has a paralysing action on any form of nerve ending in the body in such dosage as would entitle it to the name specific. CONCLUSIONS. Cocaine locally applied to nerve fibres picks out and paralyses some fibres before others; sensory before motor, vagal fibres conducting upwards, before those conducting downwards, vaso-constrictor fibres before vaso-dilator, broncho-constrictor before broncho-dilator. It is suggested that the local application of cocaine to the vagi may be a means of combating death during early chloroform narcosis. Drugs which attack the central nervous system, brain, or spinal cord or nerve fibres almost invariably attack the sensory cells and fibres before the motor. There is no reason to suppose that cocaine has a specific action on sensory nerve endings. [The expense of this research has been defrayed by a grant from the Royal Society.] I Mosso. Arch. Ital. de Biol. xiv. iii
however, to have been directly studied in any of the numerous observations
 ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
increasing pressure registered in kilograms was applied until the subject began to feel a sensation of pain. With an intelligent person the responses
 VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
King's College, London.)
 THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
it by the sympathetic nerve.
 OBSERVATIONS ON AUGMENTED SALIVARY SECRETION. BY G. V. ANREP. * (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) IN 1889 Langley described a peculiar effect of stimulation of the cerebral
OBSERVATIONS ON AUGMENTED SALIVARY SECRETION. BY G. V. ANREP. * (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) IN 1889 Langley described a peculiar effect of stimulation of the cerebral
Cannon(3) and Elliott(4). The action of these fibres has thrown a new
 ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
6I :6I2.I83 BY ALISON S. DALE. concluded that the apparent vaso-constriction obtained by F r6 hli c h and
 6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
experimer,ts, and more particularly from the fact that adrenalin apnoea
 THE ACTION OF ADRENALIN ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. BYA. ST G. HUGGETT (Beit Memorial Research Fellow) AND J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) IN a previous
THE ACTION OF ADRENALIN ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. BYA. ST G. HUGGETT (Beit Memorial Research Fellow) AND J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) IN a previous
University of Leeds.)
 6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
Orbeli are of sympathetic origin. Moreover he found relatively little
 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE SKIN OF THE TOAD. BY K. UYENO. THE general scheme of sympathetic innervation in the frog has been determined by Langley and Orbeli(i) on the basis of the visceromotor
THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE SKIN OF THE TOAD. BY K. UYENO. THE general scheme of sympathetic innervation in the frog has been determined by Langley and Orbeli(i) on the basis of the visceromotor
striking difference between these two animals in respect of the sympathetic
 THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
[Gaskell, 1880] produced vaso-dilatation of muscle, and in a concentration
![[Gaskell, 1880] produced vaso-dilatation of muscle, and in a concentration [Gaskell, 1880] produced vaso-dilatation of muscle, and in a concentration](/thumbs/91/104969218.jpg) 6I2.741.6i DOES MUSCULAR CONTRACTION AFFECT THE LOCAL BLOOD SUPPLY IN THE ABSENCE OF LACTIC ACID FORMATION? BY TSANG-G. NI. (From the Laboratory of Zoophysiology, University of Copenhagen.) IT is generally
6I2.741.6i DOES MUSCULAR CONTRACTION AFFECT THE LOCAL BLOOD SUPPLY IN THE ABSENCE OF LACTIC ACID FORMATION? BY TSANG-G. NI. (From the Laboratory of Zoophysiology, University of Copenhagen.) IT is generally
Cambridge. University of Cambridge.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, abnormally low blood-pressure to a normal height, that is to say the
 THE EFFECT OF ADRENALIN UPON RESPIRATION. BY FF. ROBERTS, M.D., M.R.C.P., Fellow of Clare College, Cambridge. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Cambridge.) IT has long been known that adrenalin,
THE EFFECT OF ADRENALIN UPON RESPIRATION. BY FF. ROBERTS, M.D., M.R.C.P., Fellow of Clare College, Cambridge. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Cambridge.) IT has long been known that adrenalin,
In studying reciprocal innervation I considered only the reflexes. THE position of the labyrinth in space, and the position of the neck
 ON THE RECIPROCAL INNERVATION IN TONIC REFLEXES FROM THE LABYRINTHS AND THE NECK. BY J. S. BERITOFF (Petrograd). THE position of the labyrinth in space, and the position of the neck with regard to the
ON THE RECIPROCAL INNERVATION IN TONIC REFLEXES FROM THE LABYRINTHS AND THE NECK. BY J. S. BERITOFF (Petrograd). THE position of the labyrinth in space, and the position of the neck with regard to the
University College, London.)
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE BLOOD SUPPLY ON PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY B. P. BABKIN. (From the Physiological Institute, University College, London.) THE importance of the normal blood supply of a gland for its
THE INFLUENCE OF THE BLOOD SUPPLY ON PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY B. P. BABKIN. (From the Physiological Institute, University College, London.) THE importance of the normal blood supply of a gland for its
Overton,1 who has worked exhaustively at the subject, looked upon. considered by some to be due to the state of the fluid originally in the
 THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
Fellow of King's College, Cambridge.
 ON AN APPARENT MUSCULAR INHIBITION PRO- DUCED BY EXCITATION OF THE NINTH SPINAL NERVE OF THE FROG, WITH A NOTE ON THE WEDENSKY INHIBITION. BY V. J. WOOLLEY, Fellow of King's College, Cambridge. (From the
ON AN APPARENT MUSCULAR INHIBITION PRO- DUCED BY EXCITATION OF THE NINTH SPINAL NERVE OF THE FROG, WITH A NOTE ON THE WEDENSKY INHIBITION. BY V. J. WOOLLEY, Fellow of King's College, Cambridge. (From the
Since, for many months after section of the right vagus in the neck,
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
Circulation," Anrep and Starling(l) were unable to obtain evidence of
 CARDIOVASCULAR REFLEXES. BY I. DE BURGH DALY AND E. B. VERNEY (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Physiology Institute, Cardi.) DURING an investigation of the "Central and Reflex Regulation of the
CARDIOVASCULAR REFLEXES. BY I. DE BURGH DALY AND E. B. VERNEY (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Physiology Institute, Cardi.) DURING an investigation of the "Central and Reflex Regulation of the
subsequently, morning, noon, and night, tested the conductibility of the College, and WILLIAM MURRELL, M.R.C.P., Assistant
 CONCERNING THE ACTION OF ACONITIA ON THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULAR SYSTEM OF FROGS. By SYDNEY RINGER, M.D., Professor of Medicine at University College, and WILLIAM MURRELL, M.R.C.P., Assistant Physician to
CONCERNING THE ACTION OF ACONITIA ON THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULAR SYSTEM OF FROGS. By SYDNEY RINGER, M.D., Professor of Medicine at University College, and WILLIAM MURRELL, M.R.C.P., Assistant Physician to
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
Pfluiger's Archiv, LXIV
 THE PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF EXTRACTS OF THE PITUITARY BODY. BY E. A. SCHAFER, F.R.S., AND SWALE VINCENT, M.B. (Six Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) Results
THE PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF EXTRACTS OF THE PITUITARY BODY. BY E. A. SCHAFER, F.R.S., AND SWALE VINCENT, M.B. (Six Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) Results
milliamperes, and the frequency of interruption to be varied from 2 to action(1). reflex effects on the heart. It is advisable to do this previous to
 STUDIES OF REFLEX ACTIVITY IN THE INVOLUNTARY NERVOUS SYSTEM. I. Depressor Reflexes. BY SAMSON WRIGHT, (Physiological Laboratory, Middlesex Hospital.) THE vaso-motor effects of stimulating the central
STUDIES OF REFLEX ACTIVITY IN THE INVOLUNTARY NERVOUS SYSTEM. I. Depressor Reflexes. BY SAMSON WRIGHT, (Physiological Laboratory, Middlesex Hospital.) THE vaso-motor effects of stimulating the central
stimulated, although the atropine prevents any apparent action upon the
 THE DIFFERENTIAL PARALYSIS OF CARDIAC NERVE ENDINGS AND MUSCLE. BY W. R. WITANOWSKI (Fellow of the Rockefeller Foundation). (From the Pharmacological Department, University College, London.) 0. L 0 EWI
THE DIFFERENTIAL PARALYSIS OF CARDIAC NERVE ENDINGS AND MUSCLE. BY W. R. WITANOWSKI (Fellow of the Rockefeller Foundation). (From the Pharmacological Department, University College, London.) 0. L 0 EWI
products2. Clearly, if similar results to those obtained by Ginezinsky
 THE EFFECT ON MUSCLE CONTRACTION O1NJ.j SYMPATHETIC STIMULATION AND OF VARIOUS MODIFICATIONS OF CONDITIONS. BY DR HELENE WASTL (VIENNA). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE question, whether
THE EFFECT ON MUSCLE CONTRACTION O1NJ.j SYMPATHETIC STIMULATION AND OF VARIOUS MODIFICATIONS OF CONDITIONS. BY DR HELENE WASTL (VIENNA). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE question, whether
(From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
University College, Cork.)
 612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
Behaviour of the enervated intestine. Local refieces. In order to cut off the intestines from the influence of the central
 THE MOVEMENTS AND INNERVATION OF THE SMALL INTESTINE. BY W. M. BAYLISS AND E. H. STARLING. (Eleven Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) IN a previous paper
THE MOVEMENTS AND INNERVATION OF THE SMALL INTESTINE. BY W. M. BAYLISS AND E. H. STARLING. (Eleven Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) IN a previous paper
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
Babkin, Savitsch) that pancreatic secretion is due, in part, to reflex
 THE MECHANISM OF PANCREATIC DIGESTION-THE FUNCTION OF SECRETIN. BY J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) A SECRETION of pancreatic juice may be evoked by appropriate
THE MECHANISM OF PANCREATIC DIGESTION-THE FUNCTION OF SECRETIN. BY J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) A SECRETION of pancreatic juice may be evoked by appropriate
McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of
![McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of](/thumbs/83/87976616.jpg) 6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
increasing the pressure within the vessels of the human forearm, and if so, Bayliss in 1902 and Folkow in 1949 found that increasing or decreasing the
 501 J. Physiol. (I954) I25, 50I-507 THE BLOOD FLOW IN THE HUMAN FOREARM FOLLOWING VENOUS CONGESTION By G. C. PATTERSON AND J. T. SHEPHERD From the Department of Physiology, The Queen's University of Belfast
501 J. Physiol. (I954) I25, 50I-507 THE BLOOD FLOW IN THE HUMAN FOREARM FOLLOWING VENOUS CONGESTION By G. C. PATTERSON AND J. T. SHEPHERD From the Department of Physiology, The Queen's University of Belfast
blood-vessels of the isolated perfused lungs of the rat. Both Hirakawa
 547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
possibility of a secretion of adrenaline from the suprarenal glands resulting
 355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
ansesthesia; an oncometer was used for measurement of the splenic Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
skeletal muscle, it was concluded that the vasodilatation is brought about by
 289 J. Physiol. (I954) I23, 289-3 THE EFFECTS OF NICOTINE ON THE BLOOD VESSELS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN THE CAT. AN INVESTIGATION OF VASOMOTOR AXON REFLEXES BY S. M. HILTON From the Physiological Laboratory,
289 J. Physiol. (I954) I23, 289-3 THE EFFECTS OF NICOTINE ON THE BLOOD VESSELS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN THE CAT. AN INVESTIGATION OF VASOMOTOR AXON REFLEXES BY S. M. HILTON From the Physiological Laboratory,
physiological action. The effects it produces on the normal
 THE ACTION OF TETRAHYDROPAPAVEROLINE HYDROCHLORIDE. BY P. P. LAIDLAW, M.A., B.C. (From the Wellcome Physiological Research Laboratories.) TETRAHYDROPAPAVEROLINE hydrochloride is a new alkaloid which was
THE ACTION OF TETRAHYDROPAPAVEROLINE HYDROCHLORIDE. BY P. P. LAIDLAW, M.A., B.C. (From the Wellcome Physiological Research Laboratories.) TETRAHYDROPAPAVEROLINE hydrochloride is a new alkaloid which was
ganglia, or if the temperature had already decreased to the level
 STUDIES ON THE COURSE OF VASOMOTOR FIBERS AS MEASURED BY THERMIC CHANGES IN THE FEET AFTER ARTERIAL LIGATION AND SECTION OF THE SPINAL CORD AT VARIOUS LEVELS By ASHLEY W. OUGHTERSON, SAMUEL C. HARVEY,
STUDIES ON THE COURSE OF VASOMOTOR FIBERS AS MEASURED BY THERMIC CHANGES IN THE FEET AFTER ARTERIAL LIGATION AND SECTION OF THE SPINAL CORD AT VARIOUS LEVELS By ASHLEY W. OUGHTERSON, SAMUEL C. HARVEY,
(Received March 21, 1934.)
 382 612. I78.4 THE PRODUCTION OF CARDIAC IRREGULARITIES BY EXCITATION OF THE HYPOTHALMIC CENTRES. BY B. B. DIKSHIT. (From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh.) (Received March 21, 1934.)
382 612. I78.4 THE PRODUCTION OF CARDIAC IRREGULARITIES BY EXCITATION OF THE HYPOTHALMIC CENTRES. BY B. B. DIKSHIT. (From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh.) (Received March 21, 1934.)
Glasgow University.) blood-pressure following the administration of carbon dioxide we
 THE ACTION OF BARIUM CHLORIDE ON THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. A CONTRIBUTION TO THE STUDY OF THE ANTAGONISTIC ACTION OF NICOTINE AND CURARE. BY E. P. CATHCART AND G. H. CLARK. (From the Physiological and Pharmacological
THE ACTION OF BARIUM CHLORIDE ON THE VASCULAR SYSTEM. A CONTRIBUTION TO THE STUDY OF THE ANTAGONISTIC ACTION OF NICOTINE AND CURARE. BY E. P. CATHCART AND G. H. CLARK. (From the Physiological and Pharmacological
sigmoid curve was obtained by plotting the fall of blood-pressure rapid fall of blood-pressure after a quick i.v. injection was followed
 612.014.465: 612.17: 612.13 THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM EVIPAN ON THE HEART AND CIRCULATION. By S. C. DAS. From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh. (Received for publication 8th May 1941.)
612.014.465: 612.17: 612.13 THE INFLUENCE OF SODIUM EVIPAN ON THE HEART AND CIRCULATION. By S. C. DAS. From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh. (Received for publication 8th May 1941.)
Rehberg who also repeated with an improved technique many of the earlier experiments.
 STUDIES ON THE PHYSIOLOGY OF CAPILLARIES. III. The innervation of the blood vessels in the hind legs of the frog. BY A. KROGH, G. A. HARROP AND P. BRANDT REHBERG. (From the Laboratory of Zoophysiology,
STUDIES ON THE PHYSIOLOGY OF CAPILLARIES. III. The innervation of the blood vessels in the hind legs of the frog. BY A. KROGH, G. A. HARROP AND P. BRANDT REHBERG. (From the Laboratory of Zoophysiology,
6I2.368:6I developmental and physiological connection between the large bowel and. (From the Institute of Physiology, the University, Glasgow.
 422 6I2.368:6I2.898 THE NERVOUS CONTROL OF THE CAUDAL REGION OF THE LARGE BOWEL IN THE CAT. BY R. C. GARRY. (From the Institute of Physiology, the University, Glasgow.) To find the influence of a nervous
422 6I2.368:6I2.898 THE NERVOUS CONTROL OF THE CAUDAL REGION OF THE LARGE BOWEL IN THE CAT. BY R. C. GARRY. (From the Institute of Physiology, the University, Glasgow.) To find the influence of a nervous
that tyramine has no dilator action on the denervated pupil of
 459 J. Physiol. (1938) 91, 459-473 547.562-233-262:6 I 2.896 THE ACTION OF TYRAMINE AND ADRENALINE ON THE DENERVATED NICTITATING MEMBRANE BY EDITH BtTLBRING AND J. H. BURN From the Pharmacological Laboratory,
459 J. Physiol. (1938) 91, 459-473 547.562-233-262:6 I 2.896 THE ACTION OF TYRAMINE AND ADRENALINE ON THE DENERVATED NICTITATING MEMBRANE BY EDITH BtTLBRING AND J. H. BURN From the Pharmacological Laboratory,
THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION
 Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
Langendorff(2) and Maas(3) that arrest of the heart diminished the
 THE CORONARY CIRCULATION IN THE ISOLATED HEART. BY M. HAMMOUDA AND R. KINOSITA. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) THE correct interpretation of experiments
THE CORONARY CIRCULATION IN THE ISOLATED HEART. BY M. HAMMOUDA AND R. KINOSITA. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) THE correct interpretation of experiments
J. Physiol. (I957) I35, (Received 20 July 1956) The interpretation ofthe experimental results ofthe preceding paper (Matthews
 263 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 263-269 THE RELATIVE SENSITIVITY OF MUSCLE NERVE FIBRES TO PROCAINE BY PETER B. C. MATTHEWS AND GEOFFREY RUSHWORTH From the Laboratory of Physiology, University of Oxford (Received
263 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 263-269 THE RELATIVE SENSITIVITY OF MUSCLE NERVE FIBRES TO PROCAINE BY PETER B. C. MATTHEWS AND GEOFFREY RUSHWORTH From the Laboratory of Physiology, University of Oxford (Received
susceptibility of either the axons in the dorsal and ventral roots, or the intramedullary
 213 J. Physiol. (31958) I40, 2I3-2I9 THE SITE OF ACTION OF PROCAINE ON THE ISOLATED SPINAL CORD OF THE FROG BY M. HARMEL AND J. L. MALCOLM From the Department of Physiology, State University of New York,
213 J. Physiol. (31958) I40, 2I3-2I9 THE SITE OF ACTION OF PROCAINE ON THE ISOLATED SPINAL CORD OF THE FROG BY M. HARMEL AND J. L. MALCOLM From the Department of Physiology, State University of New York,
distinguished author's Physiological Researches. He has, in particular, convincing than the proof afforded by Dr. J. Reid's experiments, that
 710 ON THE IRRITABILITY OF THE MUSCULAR FIBRE. By MARSHALL HALL, M.D., F.R.S. A WELL-KNOWN physiological reviewer has often, in his various publications, kindly called my attention to the experiments and
710 ON THE IRRITABILITY OF THE MUSCULAR FIBRE. By MARSHALL HALL, M.D., F.R.S. A WELL-KNOWN physiological reviewer has often, in his various publications, kindly called my attention to the experiments and
612.I73:6I2.I3. mammary and mediastinal vessels tied off. The thoracic wall on the left
 612.I73:6I2.I3 CARDIAC OUTPUT AND BLOOD DISTRIBUTION. By H. BAR CROFT (Harmsworth Scholar, St Mary's Hospital, London). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE methods for the measurement of
612.I73:6I2.I3 CARDIAC OUTPUT AND BLOOD DISTRIBUTION. By H. BAR CROFT (Harmsworth Scholar, St Mary's Hospital, London). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE methods for the measurement of
following its stimulation. joined each superior thyroid artery and was found just cephalad to
 612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
Department of Physiology, Okayama University Medical School
 The Japanese Journal of Physiology 15, pp.243-252, 1965 Department of Physiology, Okayama University Medical School BAYLISS and STARLING 1) and others 6, 7, 9, 12, 14, 15) have reported that the stimulation
The Japanese Journal of Physiology 15, pp.243-252, 1965 Department of Physiology, Okayama University Medical School BAYLISS and STARLING 1) and others 6, 7, 9, 12, 14, 15) have reported that the stimulation
PROCEEDI NGS. OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL May 2,3, 1925.
 PROCEEDI NGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL May 2,3, 1925. SOCIETY, Insulin and sodium aceto-acetate. By J. H. BURN. The appearance of acetone bodies in the blood is usually supposed to be due to their abnormal
PROCEEDI NGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL May 2,3, 1925. SOCIETY, Insulin and sodium aceto-acetate. By J. H. BURN. The appearance of acetone bodies in the blood is usually supposed to be due to their abnormal
INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT
 Brit. J. Phawmacol. (1951), 6, 289. INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT BY From the Pharmacological Laboratory, University of St. Andrews, Medical School, Dundee (Received February 2, 1951)
Brit. J. Phawmacol. (1951), 6, 289. INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT BY From the Pharmacological Laboratory, University of St. Andrews, Medical School, Dundee (Received February 2, 1951)
GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which
 ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
Nervous System. Jan 23 3:17 PM. Parts of the Body System
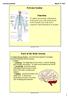 Nervous System Function To gather and interpret information from inside your body and from the world outside your body and to respond to that information as needed. Parts of the Body System I) Central
Nervous System Function To gather and interpret information from inside your body and from the world outside your body and to respond to that information as needed. Parts of the Body System I) Central
6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) heart-lung preparation. The object of this communication is to show that
 6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33 III. THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. The dependence of changes in the coronary blood flow on cardiac and local vascular factors. BY H. HA.USLER (Rockefeller Travelling Fellow). (From the Physiological
6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33 III. THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. The dependence of changes in the coronary blood flow on cardiac and local vascular factors. BY H. HA.USLER (Rockefeller Travelling Fellow). (From the Physiological
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
disagreement, that of the existence of sensory endings responding to
 332 6I2.287 AFFERENT IMPULSES IN THE VAGUS AND THEIR EFFECT ON RESPIRATION. BY E. D. ADRIAN. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IN an early paper on sensory nerve impulses [Adrian, 1926] the
332 6I2.287 AFFERENT IMPULSES IN THE VAGUS AND THEIR EFFECT ON RESPIRATION. BY E. D. ADRIAN. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IN an early paper on sensory nerve impulses [Adrian, 1926] the
show-n to give off a branch, and sometimes two or three branches, to
 THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
ON THE EXCITATION OF CRUSTACEAN MUSCLE
 159 ON THE EXCITATION OF CRUSTACEAN MUSCLE IV. INHIBITION BY C. F. A. PANTIN, M.A., Sc.D. (From the Zoological Laboratory, Cambridge, and the Stazione Zoologica, Naples) (Received Augtut 10, 1935) (With
159 ON THE EXCITATION OF CRUSTACEAN MUSCLE IV. INHIBITION BY C. F. A. PANTIN, M.A., Sc.D. (From the Zoological Laboratory, Cambridge, and the Stazione Zoologica, Naples) (Received Augtut 10, 1935) (With
PROCEEDINGS OF THE No. IV. CAMBRIDGE. May 18.
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL 1895. No. IV. CAMBRIDGE. May 18. SOCIETY, Experiments on the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands. BY WALTER EDMUNDS. IT has long been known that in dogs and cats excision of
PROCEEDINGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL 1895. No. IV. CAMBRIDGE. May 18. SOCIETY, Experiments on the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands. BY WALTER EDMUNDS. IT has long been known that in dogs and cats excision of
(Received 13 July 1938)
 136 J. Physiol. (I938) 94, I36-I47 6I2.833.94:6I5*783*22 ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE SPINAL CORD BY ALFRED SCHWEITZER AND SAMSON WRIGHT From the Department of Physiology, Middlesex Hospital Medical School
136 J. Physiol. (I938) 94, I36-I47 6I2.833.94:6I5*783*22 ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE SPINAL CORD BY ALFRED SCHWEITZER AND SAMSON WRIGHT From the Department of Physiology, Middlesex Hospital Medical School
During a class experiment conducted by one of the authors in England in 1949
 59 J Physiol. (I953) I22, 59-65 ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SWEAT GLANDS DURING EXPOSURE TO COLD BY E. M. GLASER AND T. S. LEE From the Department of Physiology, University of Malaya, Singapore (Received 9 February
59 J Physiol. (I953) I22, 59-65 ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SWEAT GLANDS DURING EXPOSURE TO COLD BY E. M. GLASER AND T. S. LEE From the Department of Physiology, University of Malaya, Singapore (Received 9 February
PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY,
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY, March 16, 1929. A central chemical control of the heart rate. By R. J. S. MCDOWALL. (King's College, London.) Provided adequate measures are taken to avoid the
PROCEEDINGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY, March 16, 1929. A central chemical control of the heart rate. By R. J. S. MCDOWALL. (King's College, London.) Provided adequate measures are taken to avoid the
administration of adrenaline or in cases of increased perfusion pressure. approximately the same within fairly wide variations of the systemic
 6I2. I72. I THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE BLOOD IN THE CORONARY BLOOD VESSELS. BY G. V. ANREP, A. BLALOCK AND M. HAMMOUDA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) As a result of experiments on perfused
6I2. I72. I THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE BLOOD IN THE CORONARY BLOOD VESSELS. BY G. V. ANREP, A. BLALOCK AND M. HAMMOUDA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) As a result of experiments on perfused
(Received 13 February 1958)
 226 J. Physiol. (I958) I43, 226-235 TH MCHANISM OF TH CHANGS IN FORARM VASCULAR RSISTANC DURING HYPOXIA By J.. BLACK AND I. C. RODDI From the Department of Physiology, The Queen's University of Belfast
226 J. Physiol. (I958) I43, 226-235 TH MCHANISM OF TH CHANGS IN FORARM VASCULAR RSISTANC DURING HYPOXIA By J.. BLACK AND I. C. RODDI From the Department of Physiology, The Queen's University of Belfast
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 The Nervous System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Highly complex system of two
The Nervous System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Highly complex system of two
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Smith, Miller and Grab er(4) state that the maintenance of an efficient
 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
(Received February 6, 1934.)
 218 6I2.327:6I2.826 THE EFFECTS OF HYPOTHALAMIC STIMULATION ON GASTRIC MOTILITY. BY J. BEATTIE AND D. SHE E HAN (Rockefeller Research Fellow). (From the Department of Anatomy, McGill University, Montreal.)
218 6I2.327:6I2.826 THE EFFECTS OF HYPOTHALAMIC STIMULATION ON GASTRIC MOTILITY. BY J. BEATTIE AND D. SHE E HAN (Rockefeller Research Fellow). (From the Department of Anatomy, McGill University, Montreal.)
London. exclusively of afferent fibres, has been challenged in recent years. observations, however, are not very convincing, and Sherrington$ was
 ON EFFERENT FIBRES IN THE POSTERIOR ROOTS OF THE FROG. BY R. J. HORTON-SMITH, B.A., Scholar of St John's College, Cambridge, and of St Thomas's Hospital, London. PART I. THE accuracy of the belief that
ON EFFERENT FIBRES IN THE POSTERIOR ROOTS OF THE FROG. BY R. J. HORTON-SMITH, B.A., Scholar of St John's College, Cambridge, and of St Thomas's Hospital, London. PART I. THE accuracy of the belief that
ISOLATED AND INNERVATED ATRIA AND VESSELS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 117. THE ACTION OF SYMPATHETIC BLOCKING AGENTS ON ISOLATED AND INNERVATED ATRIA AND VESSELS BY S. HUKOVIC* From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (RECEIVED
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 117. THE ACTION OF SYMPATHETIC BLOCKING AGENTS ON ISOLATED AND INNERVATED ATRIA AND VESSELS BY S. HUKOVIC* From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (RECEIVED
College of Medicine, Newcastle-on-Tyne.)
 INTERRELATION OF PARATHYROIDS, SUPRA- RENALS AND PANCREAS. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Durham University College of Medicine, Newcastle-on-Tyne.) THAT the parathyroid glands have
INTERRELATION OF PARATHYROIDS, SUPRA- RENALS AND PANCREAS. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Durham University College of Medicine, Newcastle-on-Tyne.) THAT the parathyroid glands have
Prom the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
 365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
Edmunds and Roth, using both nicotine and physostigmine(3) (cp.
 THE PHYSIOLOGICAL ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND ITS ACTION ON DENERVATED SKELETAL MUSCLE. BY J. N. LANGLEY AND TOYOJIRO KATO. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IN the previous observations
THE PHYSIOLOGICAL ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND ITS ACTION ON DENERVATED SKELETAL MUSCLE. BY J. N. LANGLEY AND TOYOJIRO KATO. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IN the previous observations
THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON VASOMOTOR REFLEXES.
 577.174.6:612.181 THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON VASOMOTOR REFLEXES. By LIANG-WEI CHU and FONG-YEN Hsu. From the Institute of Psychology, Academia Sinica, Nanking. (Received for publication 23rd October 1937.)
577.174.6:612.181 THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON VASOMOTOR REFLEXES. By LIANG-WEI CHU and FONG-YEN Hsu. From the Institute of Psychology, Academia Sinica, Nanking. (Received for publication 23rd October 1937.)
CHANGES IN THE HEART RATE AFTER PROCAINE
 CHANGES IN THE HEART RATE AFTER PROCAINE MICHIO TANIKAWA Department of Pharmacoiogy, Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka Received for publication November 10, 1953 In studying "the inhibitory
CHANGES IN THE HEART RATE AFTER PROCAINE MICHIO TANIKAWA Department of Pharmacoiogy, Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka Received for publication November 10, 1953 In studying "the inhibitory
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
post-ganglionic nerves. The importance of this consideration from regenerated distal trunk. He was able in such cases by stimulating
 THE ARRANGEMENT OF NERVE FIBRES IN A RE- GENERATED NERVE TRUNK. BY W. A. OSBORNE AND BASIL KILVINGTON. (From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, University of Melbourne.) IN the course of our research on axon
THE ARRANGEMENT OF NERVE FIBRES IN A RE- GENERATED NERVE TRUNK. BY W. A. OSBORNE AND BASIL KILVINGTON. (From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, University of Melbourne.) IN the course of our research on axon
University College, London.)
 6I2.I2I:547.472*3 LACTIC ACID FORMATION AND REMOVAL WITH CHANGE OF BLOOD REACTION. BY M. GRACE EGGLETON1 AND C. LOVATT EVANS. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.)
6I2.I2I:547.472*3 LACTIC ACID FORMATION AND REMOVAL WITH CHANGE OF BLOOD REACTION. BY M. GRACE EGGLETON1 AND C. LOVATT EVANS. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.)
but that the section when the lumbar sympathetic had been
 THE OXYGEN USE OF MUSCLE AND THE EFFECT OF SYMPATHETIC NERVES ON IT. -By HIROMU NAKAMURA, M.D. (JAPAN). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) MANSFELD and LuKIcs have recently given an account
THE OXYGEN USE OF MUSCLE AND THE EFFECT OF SYMPATHETIC NERVES ON IT. -By HIROMU NAKAMURA, M.D. (JAPAN). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) MANSFELD and LuKIcs have recently given an account
SOME surgeons have been of the opinion for a number of
 DOES ETHER AFFECT THE EXTENSIBILITY OR ELASTIC RECOIL OF MUSCLE? By J. D. P. GRAHAM and the late R. ST. A. HEATHCOTE Department of Pharmacology, Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff SOME surgeons
DOES ETHER AFFECT THE EXTENSIBILITY OR ELASTIC RECOIL OF MUSCLE? By J. D. P. GRAHAM and the late R. ST. A. HEATHCOTE Department of Pharmacology, Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff SOME surgeons
M1. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A 1. in dim light / low light levels 1. because circular muscles (in iris) relax 1
 M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Sodium chloride,3 sodium bromide,4 sodium iodide,3 and sodium rhodanate5. Clowes reports that ephedrine has a well-founded clinical use in combating
 VOL. 17, 1931 CHEMISTRY: BANCROFT AND RUTZLER, JR. RE VERSIBLE COA GULA TION IN LI VING TISS UE. By WILDER D. BANCROFT AND JOHN E. RUTZLER, JR.** BAKER CHEMICAL LABORATORY, CORNELL UNIVERSITY Communicated
VOL. 17, 1931 CHEMISTRY: BANCROFT AND RUTZLER, JR. RE VERSIBLE COA GULA TION IN LI VING TISS UE. By WILDER D. BANCROFT AND JOHN E. RUTZLER, JR.** BAKER CHEMICAL LABORATORY, CORNELL UNIVERSITY Communicated
Do Now pg What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in.
 Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Q: A.1. Answer (b) neurolemma Q: A.2. Answer (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3. Answer (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Q: A.1 (b) neurolemma Q: A.2 (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3 (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.1 (a) Cerebrospinal fluid (b) Synapse (c) Cerebrum (d) Hypothalamus Q: B.2 (a)
NERVOUS SYSTEM Q: A.1 (b) neurolemma Q: A.2 (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3 (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.1 (a) Cerebrospinal fluid (b) Synapse (c) Cerebrum (d) Hypothalamus Q: B.2 (a)
analysis of the known glandular nerves, whether they be for the secretion autonomic system, a ganglion cell relay being placed on their path
 THE INNERVATION OF THE ADRENAL GLANDS. BY T. R. ELLIOTT, M.D., (From the Research Laboratories of University College Hospital Medical School.) RECENT work has proved beyond dqubt that the splanchnic nerves
THE INNERVATION OF THE ADRENAL GLANDS. BY T. R. ELLIOTT, M.D., (From the Research Laboratories of University College Hospital Medical School.) RECENT work has proved beyond dqubt that the splanchnic nerves
Title: Biopsychology Specification: The divisions of the nervous system: central and peripheral (somatic and autonomic). SAMPLE
 Title: Biopsychology Specification: The divisions of the nervous system: central and peripheral (somatic and autonomic). Q1 MCQ: Which of the following responses is caused by an activation of the parasympathetic
Title: Biopsychology Specification: The divisions of the nervous system: central and peripheral (somatic and autonomic). Q1 MCQ: Which of the following responses is caused by an activation of the parasympathetic
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
Fig. 1. The reverse change is shown in Fig. 3. fluid, and then when activity was re-established the fluid replaced by a
 CARDIAC TETANUS. By W. BURRID GE, M.B. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) WALTHER(13) gives complete references to the experiments on cardiac tetanus and in his discussion concludes that superposition
CARDIAC TETANUS. By W. BURRID GE, M.B. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) WALTHER(13) gives complete references to the experiments on cardiac tetanus and in his discussion concludes that superposition
6I2.8I3. preceding paper. Leads were placed on one of the dorsal cutaneous
 6I2.8I3 RESPONSE OF TACTILE RECEPTORS TO INTERMITTENT STIMULATION. BY McKEEN CATTELL1 AND HUDSON HOAGLAND2. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE preceding paper [Adrian, Cattell and Hoagland]
6I2.8I3 RESPONSE OF TACTILE RECEPTORS TO INTERMITTENT STIMULATION. BY McKEEN CATTELL1 AND HUDSON HOAGLAND2. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE preceding paper [Adrian, Cattell and Hoagland]
COURS 8 : THE NERVOUS SYSTEM, PART II
 UE1 Anglais Pr Naguy Le 20/03/2018 à 16h00 Roneotypeur : Bouchamma Imane COURS 8 : THE NERVOUS SYSTEM, PART II Rappel : le CC du 4 mai à lieu sur les cours 7 et 8 «The Nervous System» et sera sous forme
UE1 Anglais Pr Naguy Le 20/03/2018 à 16h00 Roneotypeur : Bouchamma Imane COURS 8 : THE NERVOUS SYSTEM, PART II Rappel : le CC du 4 mai à lieu sur les cours 7 et 8 «The Nervous System» et sera sous forme
Homeostasis. Achievement Criteria. Excellence Criteria. Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment 10/02/2016
 Homeostasis Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment Biology 3.4 AS91604 Achievement Criteria Explain the purpose of the homeostatic mechanism Be able to explain
Homeostasis Demonstrate understanding of how an animal maintains a stable internal environment Biology 3.4 AS91604 Achievement Criteria Explain the purpose of the homeostatic mechanism Be able to explain
MUSCLE. BY C. F. WATTS (Research Student of Gonville
 THE EFFECT OF CURARI AND DENERVATION UPON THE ELECTRICAL EXCITABILITY OF STRIATED MUSCLE. BY C. F. WATTS (Research Student of Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge). (From the Physiological Laboratory,
THE EFFECT OF CURARI AND DENERVATION UPON THE ELECTRICAL EXCITABILITY OF STRIATED MUSCLE. BY C. F. WATTS (Research Student of Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge). (From the Physiological Laboratory,
third, fourth and fifth thoracic nerve roots at their exit from the cord (8-10) of the sympathetic in the frog while studying the vessels in
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ON THE CAPILLARIES DURING PASSIVE CONGESTION By J. HAMILTON CRAWFORD (From the Departments of Physiology and Medicine, Long Island Colege Hospital) (Received
THE INFLUENCE OF THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ON THE CAPILLARIES DURING PASSIVE CONGESTION By J. HAMILTON CRAWFORD (From the Departments of Physiology and Medicine, Long Island Colege Hospital) (Received
capillaries, and a consequent increased transudation, without necessarily altering to any marked extent the total circulation of blood
 612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
