experimer,ts, and more particularly from the fact that adrenalin apnoea
|
|
|
- Winifred Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE ACTION OF ADRENALIN ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. BYA. ST G. HUGGETT (Beit Memorial Research Fellow) AND J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) IN a previous paper (1) we have considered the effects on adrenalin apneea of (1) visceral afferent impulses, (2) varying intracranial pressure, and (3) impulses from the mid brain and cerebrum. As a result of these experimer,ts, and more particularly from the fact that adrenalin apnoea is annulled by a previous intravenous injection of ergotoxin, we concluded that adrenalin apn.cea is due to a vaso-constriction of the blood vessels of the respiratory centre, a view which had been previously put forward by Roberts. On the other hand, Boruttau(2) and later Nice, Rock and Courtright(3) state that adrenalin apncea is due to a direct action of adrenalin on the cells of the respiratory centre, a view which does not demand the presence of local vaso-motor nerves to the cerebral blood vessels. In this paper we record a series of experiments on the action of adrenalin on various reflexes. The bulb contains not only the respiratory centre but also centres associated with the heart, blood vessels and alimentary canal. Therefore on the hypothesis that adrenalin produces constriction of the blood vessels supplying the respiratory centre, the vascular and alimentary reflexes should be effected to some degree simultaneously with the respiration. Further, on the hypothesis of localised vaso-motor innervation, there existed a possibility that the adrenalin would influence other cranial and spinal reflexes. We therefore investigated its action on the conjunctival reflex, the pupillo-motor reflex and the reflex mechanism associated with skeletal muscle. Finally, we determined the influence of afferent nerve stimulation on adrenalin apncea in order to analyse the ultimate mechanism in the causation of adrenalin apncea. Adrenalin on bulbar and midbrain reflexes. At the outset we carried out experiments which conclusively located the action of adrenalin in producing apncea to the bulb or mid brain. The cord of an ainesthetised cat was cut at the level of the 2nd cervical nerve, after which artificial respiration was used. When artificial respiration was suspended as the PH. LIX. 25
2 388 A. Si' G. HUGGETT AND J. MELLANBY. blood became more venous, the alae nasi showed marked respiratory contractions. The intravenous injection of adrenalin at once annulled the contraction of these accessory respiratory muscles. Similarly, we have observed that adrenalin apnoea is readily produced in the decerebrate cat. It is therefore evident that adrenalin apncea is due to the local action of adrenalin on the bulb or mid brain and is independent of the advent of nervous impulses to the respiratory centre either from the cerebrum or periphery. Cardio-inhibitory centre. In order to demonstrate the effect of adrenalin on depressor reflexes, the dose must be less than that required to produce a maximal adrenalin action. Otherwise the central depressor effects are obscured by the peripheral adrenalin action. The absence of effect of adrenalin on this centre is shown in the blood-pressure tracing (Fig. 1) obtained by a Gad manometer. This type of manometer was used to show cardiac effects rather than blood-pressure changes. 1 c.c. of *0033 p.c. adrenalin produced a rate of heart-beat of 212 per min. (A). The same dose of adrenalin immediately followed by central depressor stimulation resulted in a heart-beat of 128 per min. (B). Clearly then, adrenalin does not diminish the sensitivity of the cardio-inhibitory centre in depressor nerve stimulation. Vaso-motor centre. The vagi were cut to limit the lowering of bloodpressure produced by stimulation of the central end of the depressor to I I Fig. 1. Adrenalin on cardio-inhibitory centre. A, adrenalin alone. B, depressor stimulated after adrenalin. Fig. 2. Adrenalin on vaso-motor centre (rabbit). A, depressor stimulated. B, adrenalin injected. C, depressor stimulated after adrenalin.
3 ADRBNALIN ON REFLEXES. 389 an effect on the vaso-motor system only. Fig. 2 A shows the fall of blood-presure produced by central stimulation of the left depressor. Fig. 2 B shows the rise of blood-pressure produced by 1 c.c. of *001 p.c. adrenalin. Fig. 2 C shows first the fall of blood-pressure produced by depressor stimulation of the same strength as A, and, at the depth of the depressor fall, the rise of blood-pressure due to the injection of adren,alin of the same strength as produced the rise B. The rise produced by the adrenalin is approximately equal to the depressor fall. From the point of view which we are investigating, the adrenalin rise of bloodpressure may be a resultant of (a) stimulation of the peripheral vasomotor nerve endings, and (b) the central inhibition of the vaso-motor centre in a maer comparable to that observed with the respiratory centre. But, since the adrenalin rise of blood-pressure during depressor nerve stimulation (i.e. during the period in which the vaso-motor centre is inhibited) is of the same height as when the depressor nerve is not stimulated it is evident that the adrlin rise of blood-pressure is not the resultant of a central and peripheral effect but solely to the peripheral action of adrenalin on the nerve endings in the periphery. The experiments with the depressor nerve clearly demonstrate that adrenalin has no action on the cardio-inhibitory centre nor on the vaso-motor centre. Presor nerve stimulation shows precisely the same facts. The central end of the cut right femoral nerve of a cat was stimulated during the rise of pressure produced by the intravenous injection of *01 mgrm. of adrenalin (Fig. 3). The adrenalin rise of blood-pressure (A) was markedly Fig. 3. Adalin on vaso-motor centre (cat). A, adrenalin injected. B, combined adrenalin injection and stimulation of femoral nerve. increased by a simultaneous stimulation of the central end of the right femoral nerve (B), indicating that the bulbar pressor mechanism was unaffected by the adrenalin. Swallowing centre. The experiments were made on a cat decerebrated
4 390 A. ST G. HUGGETT AND J. MELLANBY. by Sherrington's method and on a cat ansesthetised by urethane. The stimulus to swallow was obtained either by placing a drop of alcohol on the fauces or back of the tongue, or by electrical stimulation of the central end of the superior laryngeal nerve. A graphic record was obtained by fixing a hook to the hyoid bone and attaching it to a recording lever. Fig. 4 shows the effect of an intravenous injection of.~~~ Fig. 4. Adrenalin on swallowing centre (cat). Large excursions =swallowing. Small excursions= respiratory. adrenalin on the swallowing reflex provoked by rhythmic stimulation of the central end of the superior laryngeal nerve. The small waves record respiratory movements, the large waves, swallowing movements. It may be observed that the adrenalin produced no effect on the swallowing reflex but almost abolished the respiratory efforts. After the apnoea passed off the tracing shows the usual hyperpncea. Pupillo-motor reflex. The dilatation of the pupil produced by adrenalin might be due in part to central inhibition of the nucleus of the 3rd nerve, and this possibility was investigated. An anesthetised cat was taken into a room with a dim light. The resting size of the pupil was approximately three-quarters of full dilatation and the pupil when illuminated by electrical torch diminished to one-third dilatation. The intravenous injection of 2 c.c. of -004 p.c. adrenalin dilated the pupil from a resting value of three-quarters to five-sixths of full dilatation. This adrenalin pupil when illuminated contracted rapidly from five-sixths to two-thirds dilatation. It is evident, therefore, that the pupil under the influence of adrenalin acts as effectively to the light stimulus as the pupil ofthe normal cat. The light stimulus acts through the nucleus of the 3rd nerve. Consequently the results prove that adrenalin does not diminish the activity of the 3rd nerve nucleus.
5 ADRENALIN ON REFLEXES. 391 Conjunctival reflex. This reflex was tested by lightly touching the corner of the eye under the same conditions as those described for the pupillo-motor reflex. There was no evidence that it was diminished by the intravenous injection of adrenalin. The absence of any demonstrable effect of adrenalin on the bulbar and mid brain centres in general, apart from the respiratory centre, offers strong evidence against the vaso-motor hypothesis of adrenalin apncea. The general association both from an anatomical and physiological point of view, of the bulbar centres renders it very improbable that the blood vessels to one centre should be affected by a substance with so extensive an action as adrenalin, without the blood supply to the adjacent centres being affected. Spinal reflexes. The foregoing experiments show that the respiratory centre is the only cranial centre influenced by the intravenous injection of adrenalin. We therefore investigated the action of adrenalin on spinal reflexes associated with voluntary muscles, to determine whether adrenalin had an action on the cord similar to that observed with the respiratory centre. Knee jerk. A record of the knee jerk was obtained by supporting the knee joint of a cat and attaching the foot to a writing lever. The patellar tendon was mechanically stimulated by light taps at 2 second intervals, and during this stimulation 1 c.c. of *02 p.c. adrenalin was intravenously injected. The record showed that the knee jerk was not influenced by adrenalin. (Crureus muscles. The reflex contractions of the left crureus muscles in a spinal cat were elicited by stimulating the central end of the ipsilateral sciatic nerve, the anterior crural (femoral) nerve being left intact. Tetanic stimuli lasting for 2 seconds repeated at 12 second intervals were used. During the regular series of reflex contractions 1 c.c. of *01 p.c. adrenalin was given intravenously. The tracing showed that the contractions were not effected. The tone of muscles. A spinal cat was prepared and a record was obtained of the tone of the quadriceps extensor before, during and after the injection'of a massive dose of,adrenalin (.05 mgrm.). There was no indication of any change in the tone of the muscles during the general action of adrenalin in the animal. Similar results were obtained from an examination of the effect of adrenalin on the exaggerated postural tonus of the decerebrated cat.
6 392 A. ST G. HUGGETT AND J. MELLANBY. The antagonistic action of adrenalin and afferent nerve stimulation on the respiratory centre. Afferent nerve stimulation produces an exaggerated discharge of the respiratory centre resulting in hyperpnoea. This hyperpuoea may be diminished or annulled by adrenalin. Fig. 5 shows the hyperpnoea produced by faradic stimulation of the central end of the right femoral Fig. 5. Adrenalin on hyperpnuea produced by afferent nerve. F, femoral nerve stimulated. A, adrenalin injected. Fig. 6. Afferent nerve stimulation in adrenalin apncea. A, adrenalin injected. B, femoral nerve stimulated with increasing strength of currents. nerve and the marked diminution in respiratory movements produced during nerve stimulation by the intravenous injection, *02 mgrm. of adrenalin. The contrary effect may be demonstrated with equal certainty. Fig. 6 A shows the apncea produced by *01 mgrm. of adrenalin. At B a faradic current was applied to the central end of the cut femoral nerve with the secondary coil at 12-no effect was produced; at B the secondary coil was moved up to 10 with a resultant return to normal respiration; at C the secondary coil was placed at 8 with a production of hyperpncea.
7 ADRENALIN ON REFLEXES. 393 DISCUSSION. From the foregoing experiments it is evident that adrenalin effects the respiratory centre only and has no action on other bulbar centres or on parts of the brain concerned with the eye reflexes. These facts render the hypothesis of localised vaso-constrictor nerves to the cerebral vesels improbable. On the other hand, no evidence has been obtained from a study of muscle tone and limb reflexes that adrenalin has a direct action on the cells of the brain or the spinal cord. Therefore we must asume that adrenalin acts directly on the cells of the respiratory centre and apparently on the cells of the respiratory centre only. This hypothesis is supported by the mutual antagonistic actions of adrenalin and afferent nerve stimulation on the activity of the respiratory centre. Afferent nerve hyperpncea may be diminished by adrenalin, or adrenalin apncea may be annulled by afferent nerve stimulation. Since afferent nerve hyperpncea is due to impulses affecting the cells of the respiratory centre it follows that the antagonistic action of adrenalin must be also due to an action of adrenalin on the same cells. In a previous paper it has been indicated that the facts of adrenalin apncea form an apparent contradiction to the generalisation that adrenalin acts as a defence mechanism in the body. The mutual antagonistic action of adrenalin and afferent nerve stimuli on the respiratory mechanism clears up this apparent difficulty. On the occurrence of danger afferent impulses tend to discharge the respiratory centre, and the resultant hyperpncea, if not controlled would lead to a depletion of C02 from the blood with a production of acapnia. But the simultaneous output of adrenalin diminishes the sensitivity to these stimuli and hyperpncea is produced only when the C02 of the blood has accumulated to a sufficient degree to overcome this diminished sensitivity. The facts of adrenalin apncea does not favour the hypothesis of Lumsden(4) that respiration is controlled by four distinct centres. These centres of different function, localisation and development should be effected in varying degrees by adrenalin and corresponding variations in respiration be produced. In point of fact, adrenalin only diminishes to a greater or less degree the movements of respiration-inspiratory apncea or gasping never being produced. This uniformity of adrenalin apncea, and the absence of adrenalin action on any other nerve cell in the mid brain, bulb, or spinal cord indicate the existence of one centre only for the nervous control of the respiratory mechanism.
8 394 A. ST G. HUGGETT AND J. MELLANBY. SUMMARY. (1) Adrenalin apncea is not accompanied by any change in the activity of the cardio-inhibitory centre, the vaso-motor centre or the swallowing centre. It is improbable, therefore, that adrenalin produces local vaso-constriction of the blood vessels to the bulb. (2) Adrenalin does not influence the normal tone of muscles, the exaggerated tonus of decerebrate rigidity, the pupillo-motor reflex, the conjunctival reflex, or the reflex movements of the limbs. (3) These experiments indicate that adrenalin effects respiratory movements by a specific action on the cells of the respitatory centre. REFERENCES. (1) Mellanby and Huggett. This Journ. 57. p (2) Boruttau. Pfliiger's Arch. p (3) Nice, Rock and Courtright. Amer. Journ. Physiol. 34. p (4) Lumsden. This Joum. 57. p Errata. Nos. 2 and 38 Vol. 59. p The Figure inscribed 'coil 6 cm.' is8 Fig. 5 (not Fig. 4), and that inscribed 'coil 6.75' iu Fig. 4 (not Fig. 5) in accordance with the description in the text. p. 248, line 20 from top. For '.1 to 2 mg.' read '41 to *2 mg.'
however, to have been directly studied in any of the numerous observations
 ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
Cambridge. University of Cambridge.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, abnormally low blood-pressure to a normal height, that is to say the
 THE EFFECT OF ADRENALIN UPON RESPIRATION. BY FF. ROBERTS, M.D., M.R.C.P., Fellow of Clare College, Cambridge. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Cambridge.) IT has long been known that adrenalin,
THE EFFECT OF ADRENALIN UPON RESPIRATION. BY FF. ROBERTS, M.D., M.R.C.P., Fellow of Clare College, Cambridge. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Cambridge.) IT has long been known that adrenalin,
College). Sherrington(6), and Adrian and Zottermannl)). The pain of cramp. obtained results by using mechanical stimuli such as passive stretch
 REFLEX EFFECTS OF ACTIVE MUSCULAR CON- TRACTION. BY SYBIL COOPER (Research Fellow of St Hilda's College) AND R. S. CREED (Fellow of New College). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) INTRODUCTION.
REFLEX EFFECTS OF ACTIVE MUSCULAR CON- TRACTION. BY SYBIL COOPER (Research Fellow of St Hilda's College) AND R. S. CREED (Fellow of New College). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) INTRODUCTION.
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S
 The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
University of Leeds.)
 6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
closely resembling that following an antidromic impulse [Eccles and
 185 6I2.833. 96 REFLEX INTERRUPTIONS OF RHYTHMIC DISCHARGE. By E. C. HOFF, H. E. HOFF AND D. SHEEHAN1. (New Haven, Conn.) (From the Laboratory of Physiology, Yale University School of Medicine.) (Received
185 6I2.833. 96 REFLEX INTERRUPTIONS OF RHYTHMIC DISCHARGE. By E. C. HOFF, H. E. HOFF AND D. SHEEHAN1. (New Haven, Conn.) (From the Laboratory of Physiology, Yale University School of Medicine.) (Received
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses
 Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
milliamperes, and the frequency of interruption to be varied from 2 to action(1). reflex effects on the heart. It is advisable to do this previous to
 STUDIES OF REFLEX ACTIVITY IN THE INVOLUNTARY NERVOUS SYSTEM. I. Depressor Reflexes. BY SAMSON WRIGHT, (Physiological Laboratory, Middlesex Hospital.) THE vaso-motor effects of stimulating the central
STUDIES OF REFLEX ACTIVITY IN THE INVOLUNTARY NERVOUS SYSTEM. I. Depressor Reflexes. BY SAMSON WRIGHT, (Physiological Laboratory, Middlesex Hospital.) THE vaso-motor effects of stimulating the central
Name Date Period. Human Reflexes Lab
 Name Date Period Introduction: Human Reflexes Lab Neurons communicate in many ways, but much of what the body must do every day is programmed as reflexes. Reflexes are rapid, predictable, involuntary motor
Name Date Period Introduction: Human Reflexes Lab Neurons communicate in many ways, but much of what the body must do every day is programmed as reflexes. Reflexes are rapid, predictable, involuntary motor
(From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
(Received February 6, 1934.)
 218 6I2.327:6I2.826 THE EFFECTS OF HYPOTHALAMIC STIMULATION ON GASTRIC MOTILITY. BY J. BEATTIE AND D. SHE E HAN (Rockefeller Research Fellow). (From the Department of Anatomy, McGill University, Montreal.)
218 6I2.327:6I2.826 THE EFFECTS OF HYPOTHALAMIC STIMULATION ON GASTRIC MOTILITY. BY J. BEATTIE AND D. SHE E HAN (Rockefeller Research Fellow). (From the Department of Anatomy, McGill University, Montreal.)
Rosenthal(4), Hill(5), Lumsden(6), J. F. and C. Heymans(l, Gesell(7m, C. F. Schmidt(s)). These facts are taken by several authors
 6I2.288:6II.I33 6I2.284.2:577.I74.5 SINUS CALOTICUS AND RESPIRATORY REFLEXES. I. Cerebral blood flow and respiration. Adrenaline apnceal. BY C. HEYMANS AND JEAN J. BOUCKAERT. (From the Department of Pharmacology,
6I2.288:6II.I33 6I2.284.2:577.I74.5 SINUS CALOTICUS AND RESPIRATORY REFLEXES. I. Cerebral blood flow and respiration. Adrenaline apnceal. BY C. HEYMANS AND JEAN J. BOUCKAERT. (From the Department of Pharmacology,
King's College, London.)
 THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
show-n to give off a branch, and sometimes two or three branches, to
 THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Rothlin(12) noted in the rabbit under urethane anesthesia that ergotamine. validity of their conclusion is discussed below. phosphate was used.
 612. I85:547*945*1 STUDIES OF REFLEX ACTIVITY IN INVOLUNTARY NERVOUS SYSTEM. II. Action of ergotamine on vaso-motor reflexes. BY SAMSON WRIGHT. (Physiology Laboratory, King's College, Lonuon.) LITERATURE
612. I85:547*945*1 STUDIES OF REFLEX ACTIVITY IN INVOLUNTARY NERVOUS SYSTEM. II. Action of ergotamine on vaso-motor reflexes. BY SAMSON WRIGHT. (Physiology Laboratory, King's College, Lonuon.) LITERATURE
Neurophysiology Lab (Adapted From the Joy of Lab )
 Neurophysiology Lab (Adapted From the Joy of Lab ) Introduction: The nervous system operates by receiving input, processing information, and then providing output. The input is detected by structures called
Neurophysiology Lab (Adapted From the Joy of Lab ) Introduction: The nervous system operates by receiving input, processing information, and then providing output. The input is detected by structures called
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
following its stimulation. joined each superior thyroid artery and was found just cephalad to
 612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
Cannon(3) and Elliott(4). The action of these fibres has thrown a new
 ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of
![McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of](/thumbs/83/87976616.jpg) 6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
Circulation," Anrep and Starling(l) were unable to obtain evidence of
 CARDIOVASCULAR REFLEXES. BY I. DE BURGH DALY AND E. B. VERNEY (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Physiology Institute, Cardi.) DURING an investigation of the "Central and Reflex Regulation of the
CARDIOVASCULAR REFLEXES. BY I. DE BURGH DALY AND E. B. VERNEY (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Physiology Institute, Cardi.) DURING an investigation of the "Central and Reflex Regulation of the
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION
 Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
The sympathetic nerve fibres which originate in the thoracic part of. postganglionic but does not affect preganglionic nerve fibres, Langley has
 532 PHYSIOLOGY: S. J. MELTZER PROC. N. A. S. ARE THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANLIA INDISPENSABLE TO THE MAINTENANCE OF LIFE? By S. J. MULTZUR ROCKUPSLLUR INSTITUTh FOR MUDICAL RuSZARCH Read before the Academy,
532 PHYSIOLOGY: S. J. MELTZER PROC. N. A. S. ARE THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANLIA INDISPENSABLE TO THE MAINTENANCE OF LIFE? By S. J. MULTZUR ROCKUPSLLUR INSTITUTh FOR MUDICAL RuSZARCH Read before the Academy,
Nervous System. Lesson 11
 Nervous System Lesson 11 Reflex Arcs 1. Patellar reflex Causes leg to kick up 2. Achilles reflex Causes foot to jerk forward 3. Triceps reflex Causes arm to straighten 4. Babinski reflex 4. Pupil Dilation
Nervous System Lesson 11 Reflex Arcs 1. Patellar reflex Causes leg to kick up 2. Achilles reflex Causes foot to jerk forward 3. Triceps reflex Causes arm to straighten 4. Babinski reflex 4. Pupil Dilation
Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION
 Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION (a) The Reflex Arc ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (b) Proprioception and Proprioceptors 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 What Are Reflexes? Reflexes
Lesson 6.4 REFLEXES AND PROPRIOCEPTION (a) The Reflex Arc ~ ~ ~ TOPICS COVERED IN THIS LESSON (b) Proprioception and Proprioceptors 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 What Are Reflexes? Reflexes
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5
 NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
Pfluiger's Archiv, LXIV
 THE PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF EXTRACTS OF THE PITUITARY BODY. BY E. A. SCHAFER, F.R.S., AND SWALE VINCENT, M.B. (Six Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) Results
THE PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF EXTRACTS OF THE PITUITARY BODY. BY E. A. SCHAFER, F.R.S., AND SWALE VINCENT, M.B. (Six Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) Results
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) heart-lung preparation. The object of this communication is to show that
 6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33 III. THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. The dependence of changes in the coronary blood flow on cardiac and local vascular factors. BY H. HA.USLER (Rockefeller Travelling Fellow). (From the Physiological
6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33 III. THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. The dependence of changes in the coronary blood flow on cardiac and local vascular factors. BY H. HA.USLER (Rockefeller Travelling Fellow). (From the Physiological
Chapters 9 & 10. Cardiorespiratory System. Cardiovascular Adjustments to Exercise. Cardiovascular Adjustments to Exercise. Nervous System Components
 Cardiorespiratory System Chapters 9 & 10 Cardiorespiratory Control Pulmonary ventilation Gas exchange Left heart Arterial system Tissues Right heart Lungs Pulmonary ventilation Cardiovascular Regulation-
Cardiorespiratory System Chapters 9 & 10 Cardiorespiratory Control Pulmonary ventilation Gas exchange Left heart Arterial system Tissues Right heart Lungs Pulmonary ventilation Cardiovascular Regulation-
INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS DRUGS ON THE ACTION SYSTEM OF THE CAT OF CURARE ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1952), 7, 14. INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS DRUGS ON THE ACTION OF CURARE ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THE CAT BY S. SALAMA* AND SAMSON WRIGHT From the Department of Physiology, Middlesex
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1952), 7, 14. INFLUENCE OF VARIOUS DRUGS ON THE ACTION OF CURARE ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THE CAT BY S. SALAMA* AND SAMSON WRIGHT From the Department of Physiology, Middlesex
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
gland, the tongue and the sweat glands of the cat. The submaxillary
 306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
M1. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A 1. in dim light / low light levels 1. because circular muscles (in iris) relax 1
 M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Chapter 13. The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
ansesthesia; an oncometer was used for measurement of the splenic Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
products2. Clearly, if similar results to those obtained by Ginezinsky
 THE EFFECT ON MUSCLE CONTRACTION O1NJ.j SYMPATHETIC STIMULATION AND OF VARIOUS MODIFICATIONS OF CONDITIONS. BY DR HELENE WASTL (VIENNA). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE question, whether
THE EFFECT ON MUSCLE CONTRACTION O1NJ.j SYMPATHETIC STIMULATION AND OF VARIOUS MODIFICATIONS OF CONDITIONS. BY DR HELENE WASTL (VIENNA). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE question, whether
Reflexes. Dr. Baizer
 Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Tenth Biology Control and Coordination I. Conceptual Understanding
 Tenth Biology Control and Coordination I. Conceptual Understanding 1. Reaching for a pencil, grasping a doorknob, walking or running, driving etc., involve some movements. What are they? A: Whenever we
Tenth Biology Control and Coordination I. Conceptual Understanding 1. Reaching for a pencil, grasping a doorknob, walking or running, driving etc., involve some movements. What are they? A: Whenever we
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III Small Review Review What is this? A neuron What does it do? Receives and transmits information Sending a signal How are signals sent in the nervous system? Message travels from neuron
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM III Small Review Review What is this? A neuron What does it do? Receives and transmits information Sending a signal How are signals sent in the nervous system? Message travels from neuron
Many authors (Hering, 1927; Koch 1931; Heymans, Bouckaert & Regniers,
 259 J. Physiol. (I949) I09, 259-27I 6I2.0I4.424.089:6I2.I4 PRESSOR RESPONSES TO ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE CAROTID SINUS NERVE IN CATS BY E. NEIL AND C. R. M. REDWOOD Department of Physiology, School
259 J. Physiol. (I949) I09, 259-27I 6I2.0I4.424.089:6I2.I4 PRESSOR RESPONSES TO ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE CAROTID SINUS NERVE IN CATS BY E. NEIL AND C. R. M. REDWOOD Department of Physiology, School
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
DR. JITENDRA PATEL (MBBS, MD) Medical Educator & Researcher
 1 DR. JITENDRA PATEL (MBBS, MD) Medical Educator & Researcher Associate Professor in Physiology Email: dr.jrpatel84@gmail.com Web: www.esphys.weebly.com 2 OUTLINE Stretch reflex overview Muscle spindle
1 DR. JITENDRA PATEL (MBBS, MD) Medical Educator & Researcher Associate Professor in Physiology Email: dr.jrpatel84@gmail.com Web: www.esphys.weebly.com 2 OUTLINE Stretch reflex overview Muscle spindle
possibility of a secretion of adrenaline from the suprarenal glands resulting
 355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
612.I73:6I2.I3. mammary and mediastinal vessels tied off. The thoracic wall on the left
 612.I73:6I2.I3 CARDIAC OUTPUT AND BLOOD DISTRIBUTION. By H. BAR CROFT (Harmsworth Scholar, St Mary's Hospital, London). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE methods for the measurement of
612.I73:6I2.I3 CARDIAC OUTPUT AND BLOOD DISTRIBUTION. By H. BAR CROFT (Harmsworth Scholar, St Mary's Hospital, London). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE methods for the measurement of
Gasping. The influences affecting gasping may best be studied after
 THE REGULATION OF RESPIRATION. Part I. BY THOMAS LUMSDEN, M.D. (ABERD.). (From the Department of Experimental Pathology, Lister Institute.) IN two previous articles (1), four respiratory centres were located,
THE REGULATION OF RESPIRATION. Part I. BY THOMAS LUMSDEN, M.D. (ABERD.). (From the Department of Experimental Pathology, Lister Institute.) IN two previous articles (1), four respiratory centres were located,
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
J. Physiol. (I956) I33,
 232 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 232-242 A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF THE PATTERN OF ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE AORTIC NERVE ON THE REFLEX DEPRESSOR RESPONSES By W. W. DOUGLAS, J. M. RITCHIE AND W. SCHAUMANN*
232 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 232-242 A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF THE PATTERN OF ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE AORTIC NERVE ON THE REFLEX DEPRESSOR RESPONSES By W. W. DOUGLAS, J. M. RITCHIE AND W. SCHAUMANN*
(Received 26 September 1958)
 438 J. Physiol. (I959) I46, 438-458 THE EFFECTS OF DISTENSION OF THE BLADDER ON SOMATIC REFLEXES IN THE CAT BY M. H. EVANS* AND A. McPHERSON* From the National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill,
438 J. Physiol. (I959) I46, 438-458 THE EFFECTS OF DISTENSION OF THE BLADDER ON SOMATIC REFLEXES IN THE CAT BY M. H. EVANS* AND A. McPHERSON* From the National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill,
University College, Cork.)
 612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
The Neurologic Examination
 The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
Smith, Miller and Grab er(4) state that the maintenance of an efficient
 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
striking difference between these two animals in respect of the sympathetic
 THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
University College, London.)
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE BLOOD SUPPLY ON PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY B. P. BABKIN. (From the Physiological Institute, University College, London.) THE importance of the normal blood supply of a gland for its
THE INFLUENCE OF THE BLOOD SUPPLY ON PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY B. P. BABKIN. (From the Physiological Institute, University College, London.) THE importance of the normal blood supply of a gland for its
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
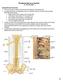 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System 1 Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors and Sensation Respond to changes (stimuli) in the environment Generate graded potentials that can trigger an action potential that is carried
Peripheral Nervous System 1 Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors and Sensation Respond to changes (stimuli) in the environment Generate graded potentials that can trigger an action potential that is carried
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Q: A.1. Answer (b) neurolemma Q: A.2. Answer (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3. Answer (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Q: A.1 (b) neurolemma Q: A.2 (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3 (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.1 (a) Cerebrospinal fluid (b) Synapse (c) Cerebrum (d) Hypothalamus Q: B.2 (a)
NERVOUS SYSTEM Q: A.1 (b) neurolemma Q: A.2 (d) Pons - consciousness Q: A.3 (b) Contains both sensory and motor fibres Q: B.1 (a) Cerebrospinal fluid (b) Synapse (c) Cerebrum (d) Hypothalamus Q: B.2 (a)
disappears; by fresh additions of cocaine the blocking may be repeated blocking of conduction is obtained almost at once, but it quickly
 THE SELECTIVE ACTION OF COCAINE ON NERVE FIBRES. BY W. E. DIXON, M.k, M.D. (Five Figures in Text.) (From the Pharmacological Laboratory, Cambridge.) v. AN RE P first clearly showed that a localised anaesthesia
THE SELECTIVE ACTION OF COCAINE ON NERVE FIBRES. BY W. E. DIXON, M.k, M.D. (Five Figures in Text.) (From the Pharmacological Laboratory, Cambridge.) v. AN RE P first clearly showed that a localised anaesthesia
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Peripheral nervous system and nerve plexus Dr. Abbas Garib Alla PNS Terminology Ganglia neuron cell bodies Peripheral nerves neuronal axons PNS neuroglia Satellite
(Received March 21, 1934.)
 382 612. I78.4 THE PRODUCTION OF CARDIAC IRREGULARITIES BY EXCITATION OF THE HYPOTHALMIC CENTRES. BY B. B. DIKSHIT. (From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh.) (Received March 21, 1934.)
382 612. I78.4 THE PRODUCTION OF CARDIAC IRREGULARITIES BY EXCITATION OF THE HYPOTHALMIC CENTRES. BY B. B. DIKSHIT. (From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh.) (Received March 21, 1934.)
UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES
 [218] UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES BY S. WOLDRING AND M. N. J. DIRKEN Physiological Institute, Groningen, Netherlands (Received 17 July 1950) (With Plate 2 and one Text-figure) Adrian
[218] UNIT ACTIVITY IN THE MEDULLA OBLONGATA OF FISHES BY S. WOLDRING AND M. N. J. DIRKEN Physiological Institute, Groningen, Netherlands (Received 17 July 1950) (With Plate 2 and one Text-figure) Adrian
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
that tyramine has no dilator action on the denervated pupil of
 459 J. Physiol. (1938) 91, 459-473 547.562-233-262:6 I 2.896 THE ACTION OF TYRAMINE AND ADRENALINE ON THE DENERVATED NICTITATING MEMBRANE BY EDITH BtTLBRING AND J. H. BURN From the Pharmacological Laboratory,
459 J. Physiol. (1938) 91, 459-473 547.562-233-262:6 I 2.896 THE ACTION OF TYRAMINE AND ADRENALINE ON THE DENERVATED NICTITATING MEMBRANE BY EDITH BtTLBRING AND J. H. BURN From the Pharmacological Laboratory,
Nervous System CHAPTER 9. Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc.
 Nervous System CHAPTER 9 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. Neurons and Supporting Cells Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. 2 Communication and Control Systems nervous system endocrine system uses chemicals
Nervous System CHAPTER 9 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. Neurons and Supporting Cells Copyright 2016 by Elsevier, Inc. 2 Communication and Control Systems nervous system endocrine system uses chemicals
Spinal Cord Protection. Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. External Anatomy of Spinal Cord. Structures Covering the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
Scheminzky's phenomenon was attempted by studying the actions of galvanic. Scheminzky (see Scheminzky, 1940, 1947, and the papers quoted therein) has
 316 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 3I6-32I EFFECTS OF DIRECT CURRENTS ON THE ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF THE SPINAL CORD BY C. AJMONE MARSAN, M. G. F. FUORTES AND F. MAROSSERO From the Clinica Malattie Nervose e Mentali,
316 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 3I6-32I EFFECTS OF DIRECT CURRENTS ON THE ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF THE SPINAL CORD BY C. AJMONE MARSAN, M. G. F. FUORTES AND F. MAROSSERO From the Clinica Malattie Nervose e Mentali,
J. Physiol. (I957) I35, (Received 20 July 1956) The interpretation ofthe experimental results ofthe preceding paper (Matthews
 263 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 263-269 THE RELATIVE SENSITIVITY OF MUSCLE NERVE FIBRES TO PROCAINE BY PETER B. C. MATTHEWS AND GEOFFREY RUSHWORTH From the Laboratory of Physiology, University of Oxford (Received
263 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 263-269 THE RELATIVE SENSITIVITY OF MUSCLE NERVE FIBRES TO PROCAINE BY PETER B. C. MATTHEWS AND GEOFFREY RUSHWORTH From the Laboratory of Physiology, University of Oxford (Received
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
The Interaction between Two Trains o f Impulses Converging on. (Communicated by Sir Charles Sherrington, F.R.S. Received June 25, 1929.
 363 612. 816. 3 The Interaction between Two Trains o f Impulses Converging on the Same Moto By Sybil Cooper, Research Fellow of St. Hilda s College, Oxford, and D. D e n n y -B row n, Beit Memorial Research
363 612. 816. 3 The Interaction between Two Trains o f Impulses Converging on the Same Moto By Sybil Cooper, Research Fellow of St. Hilda s College, Oxford, and D. D e n n y -B row n, Beit Memorial Research
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Orbeli are of sympathetic origin. Moreover he found relatively little
 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE SKIN OF THE TOAD. BY K. UYENO. THE general scheme of sympathetic innervation in the frog has been determined by Langley and Orbeli(i) on the basis of the visceromotor
THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE SKIN OF THE TOAD. BY K. UYENO. THE general scheme of sympathetic innervation in the frog has been determined by Langley and Orbeli(i) on the basis of the visceromotor
Spinal nerves. Aygul Shafigullina. Department of Morphology and General Pathology
 Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
London, N.W. 7. Tubocurarine perfused through the cerebral ventricles of cats produces
 J. Physiol. (1962), 164, pp. 301-317 301 With 7 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE RELATION BETWEEN SEIZURE DISCHARGE AND MYOCLONUS DURING PERFUSION OF THE CEREBRAL VENTRICLES WITH TUBOCURARINE
J. Physiol. (1962), 164, pp. 301-317 301 With 7 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE RELATION BETWEEN SEIZURE DISCHARGE AND MYOCLONUS DURING PERFUSION OF THE CEREBRAL VENTRICLES WITH TUBOCURARINE
Prom the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
 365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
6I :6I2.I83 BY ALISON S. DALE. concluded that the apparent vaso-constriction obtained by F r6 hli c h and
 6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Regulation of respiration
 Regulation of respiration Breathing is controlled by the central neuronal network to meet the metabolic demands of the body Neural regulation Chemical regulation Respiratory center Definition: A collection
Regulation of respiration Breathing is controlled by the central neuronal network to meet the metabolic demands of the body Neural regulation Chemical regulation Respiratory center Definition: A collection
2 Answer all the questions.
 2 Answer all the questions. 1 The human eye is an organ of the nervous system. (a) The eye is stimulated by light. Which structure in the eye contains the light receptor cells?.. [1] (b) The pupil reflex
2 Answer all the questions. 1 The human eye is an organ of the nervous system. (a) The eye is stimulated by light. Which structure in the eye contains the light receptor cells?.. [1] (b) The pupil reflex
Observing Nervous Responses
 Lab #15H Observing Nervous Responses Introduction The nervous system is a series of conducting tissues that carries impulses to all parts of the body. Your nervous system initiates many types of reflex
Lab #15H Observing Nervous Responses Introduction The nervous system is a series of conducting tissues that carries impulses to all parts of the body. Your nervous system initiates many types of reflex
