Endocrine System. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
|
|
|
- Jeffery Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endocrine System Kristine Krafts, M.D.
2 Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the pituitary gland. List the hormones produced by the anterior and posterior pituitary and know their general function. Describe the location, histologic components, and embryologic origin of the thyroid gland. List the hormones made by the thyroid gland and know their general function. Describe the location, cell types and hormone of the parathyroid glands.
3 Endocrine System Lecture Objectives Describe the location, cortical layers, and medulla of the adrenal glands. List the hormones made in the cortex and medulla, and know their general function. Describe the location of the pancreas, and the structure and cellular components of a typical pancreatic islet. List the hormones made by the islet cells and know their general function. Describe the location, cell types, and hormone produced by the pineal gland.
4 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas Pineal
5 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction
6 General Features of the Endocrine System Endocrine organs secrete hormones through the blood (no ducts!). Hormones travel elsewhere and have effects on different tissues. The classical endocrine system consists of all the organs we will discuss in this lecture. Male and female reproductive systems also have endocrine functions (we ll discuss these later).
7 Endocrine System in a Nutshell Hypothalamus Pituitary Endocrine organ (for example, thyroid)
8 Endocrine System in a Nutshell Hypothalamus The hypothalamus tells the pituitary what to do Pituitary The pituitary tells the endocrine organ what to do Endocrine organ (thyroid) The endocrine organ releases hormone
9 Endocrine System in a Nutshell The hypothalamus is like a CEO but we don t talk about it much (not many diseases there) The pituitary is like a COO. It basically tells everyone what to do. The endocrine organ is the worker drone. Poor guy.
10 There are negative feedback loops that tell the system when to stop producing hormone. Endocrine System in a Nutshell
11 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary
12 Pituitary Gland Located in the sella turcica (Turkish saddle) in the sphenoid bone. Connected to the hypothalamus Two lobes: Anterior (adenohypophysis) Posterior (neurohypophysis)
13 Pituitary gland
14 Diencephalon Cerebral vesicle Neurohypophysial diverticulum Forming pituitary gland Hypophysial diverticulum (Rathke s pouch) Stomatodeum Former site of buccopharyngeal membrane Notochord Development of the Pituitary Gland
15 Development of the Pituitary Gland Also called craniopharyngeal duct
16 Ugh! Just give me the bottom line. Anterior pituitary: derived from oral ectoderm. Posterior pituitary: derived from floor of developing brain. This makes sense, given what the lobes look like (anterior = glandular epithelium, posterior = neural tissue).
17 Cranial nerves Bones of the head Pharyngeal arches Neural crest Central nervous system Posterior pituitary Neuroectoderm Urogenital system Intermediate plate mesoderm Surface ectoderm Epidermis, hair, and nails Anterior pituitary Paraxial mesoderm Bones of most of the body (everything except the head) Muscles of the entire body Pharyngeal arches Connective tissue Dermis Lateral plate mesoderm Heart Hematopoietic system Pharyngeal arches Connective tissue Endoderm Lining of GI tract
18 Anterior and posterior pituitary
19 Pituitary stalk
20 Anterior and posterior pituitary
21 Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis) Composed of cords of glandular epithelial cells separated by capillaries. Makes and secretes a bunch of hormones. Subdivisions Pars distalis (biggest and most important part) Pars tuberalis (superior extension of pars distalis) Pars intermedia (separates pars distalis from pars nervosa)
22 Anterior pituitary
23 Posterior lobe Anterior lobe Pituitary: super low-power view
24 Pars tuberalis Infundibular stalk Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pituitary: super low-power view
25 Anterior pituitary
26 Anterior pituitary: acidophils, basophils, chromophobes
27 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Anterior pituitary makes and secretes: Growth hormone (GH) Prolactin (PL) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
28 ROS* of Anterior Pituitary Hormones Hormone Growth hormone Prolactin Stimulates growth of bones and many other functions milk secretion Follicle stimulating hormone Luteinizing hormone Adrenocorticotropic hormone Thyroid-stimulating hormone * Ridiculously Oversimplified Summary ovarian follicle development and spermatogenesis ovarian follicle development and testicular hormone secretion secretion of glucocorticoids and androgens by adrenal cortex. secretion of thyroid hormone by thyroid gland
29 Acidophils GH PL Basophils FSH LH ACTH TSH
30 Acidophils GH PL Basophils FSH LH ACTH TSH
31 Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis) Composed of neural tissue (mostly axons). Subdivisions Pars nervosa (biggest and most important part) Median eminence (floor of the hypothalamus) Infundibulum and infundibular stalk (axons traveling from hypothalamus to pars nervosa)
32 Posterior pituitary
33 Pars tuberalis Infundibular stalk Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pituitary: super low-power view
34 Posterior pituitary
35 Posterior pituitary: axons and pituicytes (glial cells)
36 Posterior pituitary: Herring body
37 Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary Posterior pituitary doesn t make hormones! It secretes hormones made by the hypothalamus. Herring bodies are dilated portions of axons containing with hormone-filled vesicles. Hormones: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytocin
38 BAHS* of Posterior Pituitary Hormones Hormone Antidiuretic hormone Oxytocin Stimulates Water reabsorption in the kidney Contraction of uterine smooth muscle in labor. Contraction of breast cells to allow milk let down. * Boring as heck summary
39 VIS* of Oxytocin Situation Interpersonal connection Orgasm Intimate relationship Sports teams Stimulates Trust Pleasure AND connection with that particular person Monogamy Better performance * Very interesting summary
40
41 Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system
42 Control of the Anterior Pituitary Hypothalamus The hypothalamus produces and releases hormones that stimulate or (less commonly) inhibit hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary. Target organs Hormones produced by target organs exert negative feedback on both the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary. Too much hormone turns off production/secretion for a while. Nice!
43 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary Thyroid
44 Development of the Thyroid Gland Originates from foramen cecum; descends along thyroglossal duct (which later disappears), in front of the hyoid and larynx, to its position in front of the trachea (by week 7).
45 Lingual thyroid Thyroglossal duct cyst Developmental abnormalities of the thyroid
46 Thyroid gland gross anatomy
47 Thyroid follicles containing colloid
48 Thyroid Gland Composed of round follicles lined by simple squamous to cuboidal epithelium and filled with colloid. Follicular cells synthesize thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and secrete them into the blood. Hypothalamus releases TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone), which makes pituitary release TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone), which makes thyroid release thyroid hormone.
49 Thyroid hormone synthesis, easy version Follicular cells synthesize thyroglobulin (a protein backbone) and secrete it into the colloid. Follicular cells take up iodide from the blood and attach it to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, forming T3 and T4 (thyroid hormones), which stay attached to thyroglobulin until needed. When stimulated by TSH, follicular cells eat a bit of colloid, digest it in a vesicle, cleave off the T3 and T4 and release it into the blood.
50 Synthesis and Iodination of Thyroglobulin Release of Thyroid Hormone Iodinated thyroglobulin In colloid Uptake of colloid by endocytosis Colloid Lysosomes Apical vesicle containing thyroglobulin Lysosome & colloid droplet fuse Mannose incorporation Digestion by enzymes releases thyroid hormones (T 3, T 4 ) Thyroglobulin synthesis (T 3, T 4 ) Amino acids Iodide Lysosomal enzyme synthesis Thyroid-stimulating hormone bound to receptor
51 What Does Thyroid Hormone Do? Quick answer: increase growth and metabolism. More detailed answer: stimulate mitochondrial protein synthesis, increase absorption of carbohydrates, regulate fat metabolism, promote cell growth. Bottom line: it increases basal metabolic rate and revs up most bodily functions (increases heart rate, raises body temperature, increases nervous reactivity, increases GI motility the list goes on).
52 Parafollicular Cells (C Cells) Derived from neural crest ectoderm. Located between follicular cells and between follicles. Parafollicular cells are larger cells with clear cytoplasm and small secretory granules containing calcitonin. Calcitonin is made in response to high blood calcium (it s not affected by a pituitary hormone!). Calcitonin lowers blood calcium levels by inhibiting osteoclastic resorption.
53 Parafollicular (C) cell
54 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid
55 Parathyroid glands gross anatomy
56 Parathyroid Glands Four glands on posterior surface of thyroid. Main function: secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) to regulate calcium levels. PTH raises calcium levels in response to low serum calcium (it s not under pituitary control!). Two main cell types: chief cells (secrete PTH) and oxyphils (function unknown).
57 Parathyroid gland: super low-power view
58 Parathyroid gland: adipose tissue
59 Parathyroid gland: chief cells
60 Parathyroid gland: oxyphil cells
61 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal
62 Adrenal gland gross anatomy
63 The Adrenal Cortex and Medulla Adrenal cortex is on the outside Originates from mesoderm Produces steroids (mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids and sex steroids) Adrenal medulla is on inside Originates from neural crest Produces epinephrine and norepinephrine
64 Cranial nerves Bones of the head Pharyngeal arches Adrenal medulla Neural crest Central nervous system Posterior pituitary Neuroectoderm Urogenital system Intermediate plate mesoderm Surface ectoderm Epidermis, hair, and nails Anterior pituitary Paraxial mesoderm Bones of most of the body (everything except the head) Muscles of the entire body Pharyngeal arches Connective tissue Dermis Lateral plate mesoderm Heart Hematopoietic system Pharyngeal arches Connective tissue Adrenal cortex Endoderm Lining of GI tract
65 Cortex Medulla Adrenal gland histology
66 Zona Glomerulosa Cells form spherical clusters ( glomerula but different than the kidney s glomerula) and produce mineralocorticoids (mostly aldosterone). Aldosterone production is stimulated mostly by angiotensin II (only slightly by ACTH). Aldosterone helps regulate water and electrolytes by stimulating sodium reabsorption by the kidney.
67 Adrenal cortex: glomerulosa
68 Zona Fasciculata Cells form straight columns (fascicles) separated by sinusoids. Cells make glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol), and small amount of androgens. Cortisol synthesis is stimulated by ACTH. Glucocorticoids affect carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism and increase blood glucose levels. Glucocorticoids depress the immune system by decreasing the number of circulating lymphocytes.
69 Zona Reticularis Cells form an irregular network (reticulum). Cells make sex steroids (mostly androgens) and a small amount of glucocorticoids.
70 Adrenal cortex: fasciculata and reticularis
71 Adrenal medulla Contains chromaffin cells (modified sympathetic neurons lacking axons and dendrites) and a few sympathetic ganglion cells. Chromaffin cells produce catecholamines (mostly epinephrine and a little norepinephrine) when stimulated by preganglionic sympathetic neurons. Catecholamines are the fight or flight hormones. They increase blood glucose, increase heart rate, increase blood flow to heart and skeletal muscle, and decrease blood to non-essential organs.
72 Adrenal medulla: ganglion cell and chromaffin cells
73 Capsule Zona glomerulosa Zona fasiculata Medulla Zona reticularis Adrenal gland histology
74 Mineralocorticoids Hormones: Zona glomerulosa Capsule Glucocorticoids Zona fasiculata Sex hormones and Zona reticularis Adrenalin Noradrenalin Medulla Adrenal gland hormones
75 Mineralocorticoids Hormones: Salt Zona glomerulosa Capsule Glucocorticoids Sugar Zona fasiculata Sex hormones and Sex Zona reticularis Adrenalin Noradrenalin Medulla Adrenal gland hormones
76 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas
77 Pancreas The pancreas has both exocrine (ducts) glands and endocrine (ductless) glands. The exocrine glands produce digestive enzymes; we ll discuss these in the Pancreas, Liver and Gallbladder lecture. The endocrine glands produce mostly hormones that regulate blood glucose: glucagon, insulin, and somatostatin. They also produce pancreatic polypeptide, which helps regulate the digestive system.
78 Pancreatic islets (of Langerhans)
79 Pancreatic islet (of Langerhans)
80 Islet Cells and Hormones A (alpha) cells Located at periphery of the islet Secrete glucagon when blood glucose is low Glucagon raises blood glucose B (beta) cells Most numerous type of cell in islet Secrete insulin when blood glucose is high Insulin decreases blood glucose by making cells take up glucose and making the liver synthesize glycogen
81 beta cells alpha cells Aldehyde fuchsin stain (stains insulin dark purple)
82 Other, Less Numerous Islet Cells and Hormones D (delta) cells Secrete somatostatin Somatostatin inhibits release of insulin and glucagon F cells Secrete pancreatic polypeptide Pancreatic polypeptide inhibits release of digestive enzymes Also causes relaxation of gallbladder and decreases secretion of bile
83 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas Pineal
84 Pineal Gland Located in brain near posterior third ventricle Two main cell types: pinealocytes and glial cells Pinealocytes occur in clusters and produce melatonin (which helps induce sleep) in response to light. Brain sand (corpora arenacea) are globules of basophilic calcified material that can be seen radiologically.
85 pinealocytes corpus arenaceum Pineal gland
86 Endocrine System Lecture Outline Introduction Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas Pineal
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
The endocrine system
 The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
The endocrine system Overview I. Pituitary II. Adrenals III. Pancreas IV. Thyroid V. Parathyroids VI. Ovaries, testis fenestrated capillaries are general structures http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/7157.html
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB
 Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Endocrine Histology Lab GUIDE TO MICROSCOPES IN LAB The micrographs that appear on this review page are typical views of the tissues seen in the laboratory. The descriptions that accompany them are designed
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU
 The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
The Endocrine System WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, HKU Objectives: 1. Be able to identify the endocrine glands and tissues. 2. Be able to describe their locations in the body and the functions of
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System: An Overview. A system of ductless glands. Interacts closely with the nervous system Endocrinology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 17 Part 1 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless s Secrete messenger
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG
 Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
The endocrine system -- a brief overview.
 The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system
 Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Histology of the Thyroid Gland
 Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome)
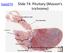 histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
histo074 Slide 74: Pituitary (Masson s trichrome) Infundibular stalk Pars tuberlaris Carcinoma Pars nervosa Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Pars Pars intermedia
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Classic Endocrine Glands
 1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
1 Endocrine system regulates metabolic activities help in bring out homeostasis 3 Nervous & endocrine systems functions in different way interact to modulate & coordinate metabolic activities of body 3
21 Endocrine organs and cells
 21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
Chapter 23 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Comparison of Nervous and Endocrine Systems (see Table 23.1): (p. 704) 1. The nervous and endocrine systems together coordinate functions of
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
Lecture 7 General Medicine_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE, HISTOPHYSIOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Hormones classification Components of the endocrine system Principles of humoral regulation
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland
 Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Embryology and Histology of Pituitary and Adrenal gland Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com ituitary gland, is a pea-sized gland that sits in a
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Endocrine System. Always willing to lend a helping gland
 Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Fig The Endocrine System The connective tissue will be very well vascularized. Due to their need to distribute their products by the blood, the
 Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
Chapter 17 Endocrine System 17.1. Introduction The organs of the endocrine system are multicellular glands of epithelial origin. The parenchyma of endocrine organs is composed almost exclusively of epithelial
Endocrine System. Collection of glands that secrete hormones.
 Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture. Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises
 A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
A&P 2 Endocrine Pre-Lab Guide Information from Videos and Exercises Read Me In this Pre-lab, we are going over some basic concepts regarding endocrine glands. These notes cover important concepts found
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Thyroid Gland. Chapter 18 Part 2. Thyroid gland. Thyroid Gland. Thyroid Gland. Parathyroid Gland. Adrenal Gland. Pancreas
 Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
11/26/2007. The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System. NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Lecture Series
 The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System
 Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
The Endocrine System. Qian XiaoJing. Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE QIAN
 The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
The Endocrine System Qian XiaoJing Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology PUMC pumc_he@126.com 69156461 Symptoms Failure of lactation Breast atrophy Lack of menstrual bleeding Loss of pubic & axillary
Chapter 11. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Gross anatomy. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran
 Gross anatomy Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Glands drain ipsillaterally by superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran In the fifth week, epithelium of
Gross anatomy Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran Glands drain ipsillaterally by superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins. Dr. Shatarat & Dr. Badran In the fifth week, epithelium of
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-22
 Chapter-22 CHEMICAL COORDINATION AND INTEGRATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Endocrine glands : These are ductless glands which secrete hormones directly into the blood stream. Hormones : Non-nutrient chemicals,
Chapter-22 CHEMICAL COORDINATION AND INTEGRATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Endocrine glands : These are ductless glands which secrete hormones directly into the blood stream. Hormones : Non-nutrient chemicals,
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45. Intercellular communication. Paracrine and Autocrine Signaling. Signaling by local regulators 11/26/2017
 Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
HIHIM 409. Endocrine system. Differences between systems. Hormone effects. Similarities. Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system
 The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
BIOLOGY. CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition. Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor. CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation
 BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
Endocrine System. Human Physiology Unit 3
 Endocrine System Human Physiology Unit 3 Endocrine System Various glands located throughout the body Some organs may also have endocrine functions Endocrine glands/organs synthesize and release hormones
Endocrine System Human Physiology Unit 3 Endocrine System Various glands located throughout the body Some organs may also have endocrine functions Endocrine glands/organs synthesize and release hormones
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
54a A&P: Endocrine System
 54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
