THE USE OF TECHNETIUM 99m AS A CLINICAL TRACER ELEMENT
|
|
|
- Buck King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POSTGRAD. MED. J. (1965), 41, 656. THE USE OF TECHNETIUM 99m AS A CLINICAL TRACER ELEMENT R. HERBERT, B.Sc., A.Inst.P. W. KULKE, M.B., B.Ch., D.M.R.T., M.Rad. R. T. H. SHEPHERD, B.M., B.Ch., D.M.R.T., F.F.R. The Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool, 7. THE VARIETY of radioactive tracer chemicals currently available for medical use is almost embarrassingly large and is still increasing. The value of any proposed new isotopes should therefore be carefully considered. No apology however, need be made for the introduction of Technetium 99m by Scheer and Maier-Borst (1963) also by Harper, Beck, Charleston and Lathrop (1964), since this substance has manv advantages in its application to scanning and in the observation of transients. (Clark, Deegan, McKendrick, Herbert and Kulke, 1965). It has been evident for some time that many radioisotopes in common use in medicine are not best suited for scanning purposes. The ideal radioactive agent should usually conform to the following cri,teria:- (a) The gamma ray energy should be such as to permit easy collimation without too much absorption in tissue and at the same time deliver the lowest radiation dose. The optimum energy is then within the range Kev. (b) Beta emission and conversion electrons should preferably be absent as they increase the radiation dose without contributing to the scan. (c) The half life should be a few hours only, permitting biological equilibrium in the body to be obtained with the smallest radiation dose. At the same time this will allow the background to be sufficiently reduced for further tests to be carried out in a few days. (d) The radioisotope should be available carrier free or at least in high specific activity to avoid toxic or hypersensitivity reactions. A radioisotope with these properties may be administered in millicurie quantities with a hazard no greater than that of conventional X-ray investigations. Since Technetium 99m epitomises these criteria it seemed worthy of further investigation as a tracer isotope. It will be shown that multimillicurie doses may safely be used to obtain high counting rates which can give results of high statistical significance. Production and Physical Properties Tc99m is most conveniently produced carrier free as a pertechnetate (TcO4) in isotonic saline from a Mo99 generator which has a half-life of 67 hours. These generators in which the Mo99 is incorporated in an alumina column, are regularly available from the Radiochemical Centre, Amersham, England and other suppliers. Tc99m decays to Tc99 by isomeric transition with a half-life of 6.0 hours emitting a MeV gamma ray which is 8-11% converted. (Strominger, Hollander and Seaborg, 1958). Tc99 itself decays by beta emission to stable Ru99, and has a half-life of 2.1 x 105 years so that only millimicrocurie quantities of this isotope are produced by a tracer dose. The Specific Gamma Ray Emission r is 0.61 r/mch at 1 cm, and the half-value layers in lead and water are cms and 5.0 cms respectively. Since the gamma ray energy is near that which gives minimum r and there is no beta emission, adequate counting rates can be obtained with a comparatively small radiation dose. Conventional instruments give efficient collimation, but due to the low gamma ray energy, shielding and collimator length may be reduced to make a high sensitivity lightweight detector (Harper, Beck and others, 1964). Metabolism After some initial experiments on rats, three human subjects were investigated and some results of plasma clearance tests are presented in Fig. 1. Two of the subjects received approximately two millicuries of Tc99m as pertechnetate in isotonic saline by intravenous injection while the same dose was given orally to a third. After two hours the plasma concentration was in each case between 3% and 5% per litre and the mean long term component was 3.5% per litre with a half clearance time of 9 hours. Urine excretion was approximately 30o/% at 24 hours and 40%/, at two days while 10% has been collected in the faeces in two days. (Fig. 2). This is in agreement with the results of Sorensen and Archambault (1963 and 1964), who)
2 November, 1965 HERBERT, KULKE and SHEPHERD: Technetium 99m 657 I hours FIG. 1.-Plasma clearance of Tc99m. 0. Intravenous administration. X. Oral administration. recovered 58% in the urine and 24% in faeces after three days, and also with Harper, Lathrop, McCardle and Andros (1964) who found 50% total excretion in 1.8 days with 10%-15% in the stools. The activity remaining in the bodv should be obtainable by subtracting the total known excretion from 100% and this is shown in Fig. 3. The biological half-life is approximately 60 hours. While radiopertechnetate is sufficiently concentrated in the thyroid to produce good scans, the thyroid uptake is small by comparison with radioiodine and it is more rapidly released, the maximum uptake occurring within an hour. One normal showed a peak uptake of 4%/, (Fig. 3); another had 3% in the gland at three hours. We have not been able to demonstrate protein binding and it appears that the uptake follows a similar pattern to that of the '"blocked" gland for iodine (Foss and Herbert, 1952), where the percentage uptake for normals is within the range 2.1%-7.3%. This is also in agreement with observations of Harper, Lathrop, McCardle and Andros (1964) who found that the uptake of Tc99m in normals was 2%. Brown-Grant (1961) describes the concentration of iodine in the stomach after intravenous injection of iodine. Similarly, if the trunk is scanned after intravenous injection of radiopertechnetate the concentration of Tc99m is clearly seen, first in the stomach and later in hours FIG. 2.- Excretion of Tc99m. 0. Faeces. X. Urine I 10hours FIG. 3.-Metabolism of Tc99m. (a) Total retained (whole body) (b) Stomach. (c) Plasma clearance (% per litre) i(d) Thyroid. Oh
3 658 POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL November, 1965 ;.;...,~.'... *4..: ; :... >:8:;; ~~~~~~~~~~~~~.. :::... ;f.:...::.:::: :. :.. ;4k...:::..:.... :::::S : ::... ::..:.:::.::... ::;: :. : ::I::.. the gut. A series of such scans is shown in Fig. 4. By measuring the density of the stomach scan, subtracting the background over adjacent areas, and then comparing with a standard phantom, it has been possible to make an estimate of the uptake (Fig. 3 and 4). The maximum of 6% occurs at 5 hours and decays with a half-time of 13 hours. It is not known whether this results from secretion in the gastric juices or swallowed saliva, for the concentration in saliva reached 46% per litre at 3 hours and *thereafter dropped sharply. Uptake of Tc99m in the parotid and submaxilliary glands has been demonstrated by Harper, Beck, Charleston and Lathrop (1964) in their thyroid scans. No other significant concentration has been observed. Dosimetry The above information is sufficient to make a fair estimate of the radiation hazard resulting ~~...i..~ :.;:t ' :: :: ::. FIG. 4.-Serial scans of stomach after intravenous injection of Tc99m. from a tracer dose of Tc99m. The critical organs appear to be the thyroid and stomach. In our calculations it has been assumed that the gamma ray energy is Mev, the specific gamma ray emission is 0.61 r/mch at 1 cm, and there is 9% electron conversion in which the Mev is dissipated as beta like radiation. Whole body-uptake 100%; T eff = 0.23 days; w = 70 Kg; g = 125 cms. D y oc x 0.61 x 125 x 1000 x 0.23 = r/mc D,f oc 73.8 x x 1000 x 0.23 x 0.09 = rads/mc Total efjective dose = rem/imc. Calculating as above; Thyroid (normal)-uptake = 5%; T eff = 0.14 days; w= 20 g; g = 15 cms. D ycc = 0.11 r/mc. D 3 a = 0.32 rad/mc. Total dose = 0.43 rem/imc. Stomach-Uptake = 6%; T eff 0.17 days; w = 250 g; g = 94 ems. D y cc = r/mc. D 8 a = rad/mc. Total dose = rem/imc.
4 November, 1965 HERBERT, KULKE and SHEPHERD: Technetium 99m 659 ~~~~~. - w{~g ::: FIG. 5.-Hand held collimated scintillation detector for low energy gamma rays :.7t... Im c99mh Zc&:.7. '::.,. X A S ~... ~ These values are in reasonable agreement with those of 'McAfee, Fueger, Stern, Wagner and Migita (1964) who quote rads/mc whole body and 0.08 rads/mc for stomach but the thyroid dose is higher than that given by Harper, Beck and others (1964) (0.1 rad/mc). Measuring and Detecting Apparatus For dispensing tracer doses, a well-type ionisation chamber Type 1383A with a brass liner has been used and calibrated with a standardised Ce-141 source. In our instrument the sensitivity was 5.1 pico-amps. per millicurie for a 10 ml sample. Harper, Beck and others (1964) have shown that optimum collimation for brain scanning is obtained at a gamma ray energy of about 100 Kev. By using a I" thick Nal crystal with a 180 hole focussed collimator i" thick we have made a detector which is lighter and cheaper than the conventional detectors for medium energy, yet for the same resolution the sensitivity is increased by a factor of 5. Since only a comparatively thin crystal is required, CsI may also be used. A hand held scintillation detector with a simple collimator suitable for measuring transients is shown in Fig. 5. This particular counter 'weighs only 4 lbs. compared with nearly 1 cwt. which is necessary to provide similar collimation for I131. Clinical Application of Technetium-99m The clinical uses of this new isotope are ;'~~~~~.:.. G.f,...' '..d,..t-..:.:.>w.a : '... FIG. 6.-Comparison of thyroid scanning with Tc99m and Sg
5 660 POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL November, 1965 self-evident from the above considerations and our expectations have been borne out in practice. (a) Thyroid studies: For the reasons alreadv stated massive quantities relative to Ils' can safely be administered and sufficient isotope accumulates in thyroid cells to yield very accurate thyroid scans. In scanning a small organ the low energy monochromatic radiation of Tc9om, yields much superior scans than can be obtained with IJ31. This fact is illustrated in Fig. 6 which compares a thyroid scan with 1131 with a scan using Tc99m in a gland containing functioning adenomata, normal tissue and inactive cysts. The isotope is therefore of use to determine the position, size and shape of the thyroid gland preoperatively or for calculation of I131 dosage in thyrotoxicosis, to determine retrosternal extension of 'the thyroid gland and to determine the position of any ectopic thyroid tissue. Its reliability in the diagnosis of tumours has not yet been fully determined, but it appears to be of the same order as I131. Some concentration of the isotope does occur in malignant conditions of the thyroid, but it is not to the same extent as the concentration in normal thyroid tissue, and it is not yet clear whether this represents active isotope trapping by the neoplastic cells, or is non-specific and due to a breakdown in blood-tissue barrier in the tumour. Functioning thyroid metastases will concentrate Tc99m but apparently not to any greater extent than would be expected from metastases of other origins. Harper, Lathrop and others (1964) quote the thyroid uptake of Tc99m in hyperthyroid individuals as 6-30 /, which might suggest that it is suitable for use as a thyroid function test. This has not been confirmed in our studies and indeed it would be surprising on theoretical grounds if this were possible as technetium uptake can onlv represent the size and vascularity of the gland and the size of the iodide compartments of the body, and high uptakes might be expected equally from puberty goitres, iodide deficiency goitres, and thyrotoxic goitres. The great value of Tco9m in thyrotoxicosis is that it enables scans to be performed routinelv in all cases without any great radiation exposure to the individual or to the population. Thus using 131, 50,ucs needs to be administered to obtain uptake and survey studies, yielding thyroid doses of the order of 50 rems and whole body and gonad doses of rems. Using Tc99m for survey, 10,ucs Il31 is sufficient for uptake studies giving a large reduction in exposure, whilst for the combination of 10 Ucs of I132 and 1 mc Tc9om the dosages are reduced to 0.5 rem (thyroid) and 0.01 rem (whole body). Both isotopes can be given coincidently if a gamma ray spectrometer is used for the uptake measurements. (b) Brain tumour localisation: The use of Tc99m as pertechnetate has been reported by Harper, Beck and others (1964) and Anger, Van Dyke, Gottschalk, Yano and Scheer (1965). McAfee, Fueger and others (1964) prefer this isotope to most other agents. Although the radiation energy is suitable for brain scanning and very high counting rates are obtainable, retention of the isotope in tumours may not be prolonged and it is necessary to scan at a time when the level of isotope in the circulating blood is high. This obscures localisation in parts of the base and occipital regions of the brain in a manner resembling the scan pro. duced by R.I.131S.A. It is possible that a more suitable technetium compound would give improved results. (c) The observation of transients in a small volume of tissue presents collimator problems similar to those of scanning. Clark and others (1965) have shown that the increased counting rate and improved collimation achieved by using Tc99m as pertechnetate instead of Ils' has increased the accuracy of the detection of intra-cardiac shunts by external counting over a lung field. Pertechnetate clears too rapidly from the blood for use in cardiac output measurement, but Tc9om albumin, which has been prepared by Stern, Zolle and McAfee (1965) would be eminently suitable for this purpose. (d) Multimillicurie quantities of technetium may be safely injected rapidly to act as a radioactive bolus, yielding a high count rate. This could be of value in the study of dynamic processes with scintillation cameras as described by Bender and Blau (1963) and Anger (1965).
6 November, 1965 HERBERT, KULKE and SHEPHERD: Technetium 99m 661 TABLE 1 COMPARISON OF Tc99m WiTH IODINE ISOTOPES. RADIATION DOSES. Tc99m 1123 I125 I Thyroid dose rem/mc injected Whole body dose rem/mc injected TABLE 2 COMPARISON OF Tc99m WITH IODINE ISOTOPES. DATA RELEVANT TO SENSITIVITY AND COLLIMATION. Tc99m I132 H. V. L. in Sodium iodide (mm) H. V. L. in lead (mm) Relative weights of collimators for 1" crystal (transmission 0.1 %) (e) Gastric scans. If technetium is actively secreted by gastric mucosal cells, then useful scans may be feasible. Normal gastric scans have been made but positive pathological scans have not yet been attempted. (f) Placentography. Excellent scans of the placenta have been made by McAfee, Stern, Fueger, Baggish, Holzman and Zolle,(1964) using Tc99m tagged albumin. Comparison with Other Radioisotopes As Tco9m has been used for scanning the thyroid gland, it is instructive to compare its properties with 1125, IBli and I132, all of which are in common use for thyroid studies. I123 (Myers and Anger, 1962) has also been included as its emissions are most like those of Tc99m and if this radioisotope becomes readily available it should be the agent of choice for thyroid scanning, combining optimum physical properties with true iodide metabolism. For brain scanning, placentography and other applications where iodide is not specifically required, Tc99m has the advantage of a much smaller thyroid and whole body dose. The data relevant to radiation dose are shown in Table 1 and it will be seen that while tracer doses of J125 and 1131 should be kept much less than 1 millicurie, severely limiting the counting rate obtainable for scanning purposes, multimillicurie doses of Tc99m may be safely given. In Table 2 the data relevant to detector sensitivity and collimation are given including relative weights of typical collimators. The high penetration of I132 makes it unsuitable for any but the crudest collimation, while for the low energy radiations of Tc99m, I123 and I125 the weight of lead screening can be less than 1/20 of that for I'31. Also crystals of a few millimetres thickness can provide adequate detection efficiency, resulting in a reduction in the cost and a further reduction in weight of collimators. With the thickness required Caesium iodide crystals have been used with advantage. Summary The physical properties, metabolism and radiation dose of Tc99m are discussed and compared with those of I123, and 1132.
7 662 POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL November, 1965 It is shown that with Tc99m the highest "in vivo" counting rates are obtained for a given internal radiation dose, so that measurements of high statistical accuracy may safely be made. The gamma ray energy is near optimum for scanning and the observation of transients allowing light-weight collimators to be used. While Tc99m tagged albumin is considered superior to R.I.S.A. for applications such as brain scanning, placentography and the measurement of cardiac output, 1123 if it becomes available will be preferable for thyroid scanning. We are greatly indebted to Dr. F. D. S. Butement of the Department *of Inorganic, Physical and Industrial Chemistry, University of Liverpool for supplying us with the separated Te99m in the earlv stages of the development and to Dr. T. A. Chalmers, Lecturer in Radiology, University of Liverpool for helpful discussion and advice. Also to Mr. Andrews for preparing the diagrams and photographs. REFERENCES ANGER, H. O., VAN DYKE, D. G., GOTrTSC:ALK, A., YANO, Y., and SCHEER, L. R. (1965): The Scintillation Camera in Diagnosis and Research, Nucleonics, 23, No. 1, 57. BENDER, M. A., and BLAU, M. (1963): The Autofluoroscope, Nucleonics, 21, No. 10, 52. BROWN-GRANT, K. (1961): Extra Thyroidal Iodide Concentrating Mechanisms, Physiol. Rev., 41, 189. CLARK, J., DEEGAN, T., imckendrick, C., HERBERT, R., and KULKE, W. (1965): Use of Technetium99m for Diagnosis of Intra-cardiac Shunts, Thorax, in press. Foss, G. L., and HERBERT, R. (1952): An JInvestigation of 80 Cases of Doubtful Thyrotoxicosis by a Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test, Clin. Sci., 2, 33. HARPER, P. V., BECK, R., CHARLESTON, D., and LATHROP, K. A. (1964): Optimization of a Scanning Method using Tc99m, Nucleonics, 22, No. 1, 50. HARPER, P. V., LATHROP, K. A., MCCARDLE, R. J., and ANDROS, G. (1964): The Use of Technetium 99m as a Clinical Scanning Agent for Thyroid, Liver and Brain. Symposium on Medical Radioisotope Scanning, I.A.E.A., Vienna, 2, 33. MCAFEE, J. G., FUEGER, IG. F., STERN, H. S., WAGNER, J. N., Jr., and MIGITA, T. (1964): Tc99m Pertechnetate for Brain Scanning, J. nucl. Med., 5, 811. MCAFEE, J. G., STERN, H. S., FUEGER, G. F., 'BAGGISH, M. S., HOLZMAN, G. B., and ZOLLE, I. (1964): 99mTc Labelled Serum Alibumin for Scintillation Scanning of 'Placenta, J. nucl. Med., 5, 936. MYERS, W. G., and ANGER 'H. 0. ((1962): Radioiodine 123, J. nucl. Med., 4, 183. SCHEER, 'K. E., and MAIER-BORST, W. '(1963): Zur Darstellung von Tc99m fuir Medizinische Zwecke, Nucl.-Med. (Stuttg.), 3, 214. SORENSEN, L. B. '(1964): Liver Scanning with Radiomolybdenum. Symposium on Medical Radioisotope Scanning, I.A.E.A., Vienna, 2, 431. SORENSEN, L. B., and ARCHAMBAULT, M. (1963): Visualization of the Liver (by Scanning with Mo99 (Molybdate) as a Tracer, J. lab. Clin. Med., 62, 330. STERN, H. S., ZOLLE, I., and MCAFEE, J. G. (1965): Preparation of Technetium(Tc99m)-Labelled Serum Albumin i(human), Int. J. appl. Radiat., 16, 283. STROMINGER, D., HOLLANDER, J. M., and SEABORG, G. T. (1958): Table of Isotopes, Revs. Modern Phys., 30, 673. Postgrad Med J: first published as /pgmj on 1 November Downloaded from on 11 March 2019 by guest. Protected
Time of maximum uptake of Technetium-99m pertechnetate (TcO4) in the thyroid gland and its correlation with thyroid functional status
 Time of maximum uptake of Technetium-99m pertechnetate (TcO4) in the thyroid gland and its correlation with thyroid functional status Md. Mizanur Rahman 1*, Dr. Shankar Kumar Dey 2 1 Center For Research
Time of maximum uptake of Technetium-99m pertechnetate (TcO4) in the thyroid gland and its correlation with thyroid functional status Md. Mizanur Rahman 1*, Dr. Shankar Kumar Dey 2 1 Center For Research
Chapter 22 THYROID UPTAKE TEST. R.D. Ganatra
 XA9847619 Chapter 22 THYROID UPTAKE TEST R.D. Ganatra Measurement of the uptake of the radioiodine by the thyroid gland was one of the earliest applications of the radioisotopes in medicine but in advanced
XA9847619 Chapter 22 THYROID UPTAKE TEST R.D. Ganatra Measurement of the uptake of the radioiodine by the thyroid gland was one of the earliest applications of the radioisotopes in medicine but in advanced
Medical Physics 4 I3 Radiation in Medicine
 Name: Date: 1. This question is about radiation dosimetry. Medical Physics 4 I3 Radiation in Medicine Define exposure. A patient is injected with a gamma ray emitter. The radiation from the source creates
Name: Date: 1. This question is about radiation dosimetry. Medical Physics 4 I3 Radiation in Medicine Define exposure. A patient is injected with a gamma ray emitter. The radiation from the source creates
PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5)
 PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5) 1. (a) A radioisotope is an isotope that is unstable and will emit particles from the nucleus
PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5) 1. (a) A radioisotope is an isotope that is unstable and will emit particles from the nucleus
Internal Dosimetry of Human Brain for 99m tc and 131 I Using Nuclear Imaging in Bangladesh
 Sri Lankan Journal of Physics, Vol. 6 (2005) 33-41 Institute of Physics - Sri Lanka Internal Dosimetry of Human Brain for 99m tc and 131 I Using Nuclear Imaging in Bangladesh M. M. Alam a, M. I. Kabir
Sri Lankan Journal of Physics, Vol. 6 (2005) 33-41 Institute of Physics - Sri Lanka Internal Dosimetry of Human Brain for 99m tc and 131 I Using Nuclear Imaging in Bangladesh M. M. Alam a, M. I. Kabir
Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution. Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to
Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to
Radio-isotopes in Clinical Medicine
 Radio-isotopes in Clinical Medicine Radiactive isotopes, whether naturally occurring or artificially produced, have a number of different uses in clinical medicine. These include: (1) Diagnostic and research
Radio-isotopes in Clinical Medicine Radiactive isotopes, whether naturally occurring or artificially produced, have a number of different uses in clinical medicine. These include: (1) Diagnostic and research
2. RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS UTILIZED
 1. OVERVIEW AND INDICATIONS (adapted from Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Thyroid Uptake Measurement, Version 3.0; reprinted from http://snmmi.files.cmsplus.com/docs/thyroid%20uptake%20measure%20v3%200.pdf,
1. OVERVIEW AND INDICATIONS (adapted from Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Thyroid Uptake Measurement, Version 3.0; reprinted from http://snmmi.files.cmsplus.com/docs/thyroid%20uptake%20measure%20v3%200.pdf,
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION USP DIAGNOSTIC. For Oral Use DESCRIPTION
 DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution is an aqueous solution of sodium iodide I-131 for diagnostic use by oral administration. The
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution is an aqueous solution of sodium iodide I-131 for diagnostic use by oral administration. The
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure THYROID UPTAKE MEASUREMENT (I-123 or I-131 as Sodium Iodide)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure THYROID UPTAKE MEASUREMENT (I-123 or I-131 as Sodium Iodide) Overview Indications The Thyroid Uptake Measurement measures the metabolic activity
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure THYROID UPTAKE MEASUREMENT (I-123 or I-131 as Sodium Iodide) Overview Indications The Thyroid Uptake Measurement measures the metabolic activity
Radiation Detection and Measurement
 Radiation Detection and Measurement Range of charged particles (e.g.,!: µm; ": mm) Range of high energy photons (cm) Two main types of interactions of high energy photons Compton scatter Photoelectric
Radiation Detection and Measurement Range of charged particles (e.g.,!: µm; ": mm) Range of high energy photons (cm) Two main types of interactions of high energy photons Compton scatter Photoelectric
METROLOGY TO SUPPORT INNOVATION IN MOLECULAR RADIOTHERAPY. Glenn Flux
 METROLOGY TO SUPPORT INNOVATION IN MOLECULAR RADIOTHERAPY Glenn Flux Head of Radioisotope Physics Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK CGPM 2018 glenn.flux@icr.ac.uk Overview
METROLOGY TO SUPPORT INNOVATION IN MOLECULAR RADIOTHERAPY Glenn Flux Head of Radioisotope Physics Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK CGPM 2018 glenn.flux@icr.ac.uk Overview
Radioactivity. Alpha particles (α) :
 Radioactivity It is the property of an element that causes it to emit radiation Discovered by Becquerel (1896) Radiation comes from the nucleus of the atom There are three types of radiation : alpha particles
Radioactivity It is the property of an element that causes it to emit radiation Discovered by Becquerel (1896) Radiation comes from the nucleus of the atom There are three types of radiation : alpha particles
Radiopharmacy. Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL. CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı
 Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
I-123 Thyroid Scintigraphy
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 6 I-123 Thyroid Scintigraphy Primary Indications: Thyroid scintigraphy with I-123 is indicated to evaluate thyroid morphology and global and/or regional function
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 6 I-123 Thyroid Scintigraphy Primary Indications: Thyroid scintigraphy with I-123 is indicated to evaluate thyroid morphology and global and/or regional function
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC. For Oral Use DESCRIPTION
 DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules, USP are color-coded capsules containing sodium iodide I 131 for diagnostic use by oral administration.
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules, USP are color-coded capsules containing sodium iodide I 131 for diagnostic use by oral administration.
1. OVERVIEW AND INDICATIONS
 1. OVERVIEW AND INDICATIONS (adapted from Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Thyroid Scintigraphy and other sources) a) Evaluation of the general structure of the thyroid gland (e.g. nodular
1. OVERVIEW AND INDICATIONS (adapted from Society of Nuclear Medicine Procedure Guideline for Thyroid Scintigraphy and other sources) a) Evaluation of the general structure of the thyroid gland (e.g. nodular
GLUCEPTATE. Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION
 27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
KEYWORDS: nuclear medicine; gamma camera; radiopharmaceutical activities.
 Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in the First Six Months of the Gamma Camera Use in the Clinical Center of Montenegro - Podgorica Nevenka Antovic
Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in the First Six Months of the Gamma Camera Use in the Clinical Center of Montenegro - Podgorica Nevenka Antovic
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region. Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE WITH RESPECT TO THYROID DISORDERS By: B.Shafiei MD Nuclear Physician Taleghani Medical Center Radioactive: An element with Unstable Nucleus (Excess Energy), can achieve
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MEDICINE WITH RESPECT TO THYROID DISORDERS By: B.Shafiei MD Nuclear Physician Taleghani Medical Center Radioactive: An element with Unstable Nucleus (Excess Energy), can achieve
Spleen Scintiphotography with Technetium-99m Sulfur Colloid and the Gamma Ray Scintillation Camera1'2
 JOURNA OF NUCEAR MEDICINE 7:733-739, 1966 Spleen Scintiphotography with Technetium-99m Sulfur Colloid and the Gamma Ray Scintillation Camera1'2 Jerry P. Petasnick, M.D. and Alexander Gottschalk, M.D. Chicago,
JOURNA OF NUCEAR MEDICINE 7:733-739, 1966 Spleen Scintiphotography with Technetium-99m Sulfur Colloid and the Gamma Ray Scintillation Camera1'2 Jerry P. Petasnick, M.D. and Alexander Gottschalk, M.D. Chicago,
An investigation of the effect of ionising radiation on nurses and their patients during dialysis
 International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
OTHER NON-CARDIAC USES OF Tc-99m CARDIAC AGENTS Tc-99m Sestamibi for parathyroid imaging, breast tumor imaging, and imaging of other malignant tumors.
 DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
Medical Use of Radioisotopes
 Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
Robert N. Beck Memorial Presentation
 Robert N. Beck Memorial Presentation A. Bertrand (Randy) Brill MD, PhD Vanderbilt University With extensive contributions from Nick Yasillo, Chin-Tu Chen, Don Gunter, John N Aarsvold, & Adriadne Beck Robert
Robert N. Beck Memorial Presentation A. Bertrand (Randy) Brill MD, PhD Vanderbilt University With extensive contributions from Nick Yasillo, Chin-Tu Chen, Don Gunter, John N Aarsvold, & Adriadne Beck Robert
Applications of radioactivity in medicine
 Lec.3 Applications of radioactivity in medicine -Nuclear medicine (N.M) -Applications of radioactive material in medicine Nuclear Medicine:- The clinical uses of radioactivity for the diagnosis of disease.
Lec.3 Applications of radioactivity in medicine -Nuclear medicine (N.M) -Applications of radioactive material in medicine Nuclear Medicine:- The clinical uses of radioactivity for the diagnosis of disease.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
 BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS L/4739/0 1 CHOLETEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin For Diagnostic Use DESCRIPTION Each reaction vial contains a nonradioactive, sterile, nonpyrogenic mixture
BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS L/4739/0 1 CHOLETEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin For Diagnostic Use DESCRIPTION Each reaction vial contains a nonradioactive, sterile, nonpyrogenic mixture
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure THERAPY FOR THYROID CANCER (I-131 as Sodium Iodide)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure THERAPY FOR THYROID CANCER (I-131 as Sodium Iodide) Overview Indications I-131 therapy for Thyroid Cancer, of the papillo-follicular type, is
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure THERAPY FOR THYROID CANCER (I-131 as Sodium Iodide) Overview Indications I-131 therapy for Thyroid Cancer, of the papillo-follicular type, is
R: March, E D T P A. Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection. DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use
 R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION
 511945-0903 September 2003 USA Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging 331 Treble Cove Road N. Billerica, MA 01862 USA GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE DESCRIPTION: Gallium Citrate Ga 67
511945-0903 September 2003 USA Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging 331 Treble Cove Road N. Billerica, MA 01862 USA GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE DESCRIPTION: Gallium Citrate Ga 67
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry
 Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Nuclear Medicine and PET. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Monitoring of iodine-125 and iodine-131 in thyroid of individuals in nuclear medicine centers of North West provinces of Iran
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 2 (3): 141-147 Monitoring of iodine-125 and iodine-131 in thyroid of individuals in nuclear medicine centers of North West provinces of Iran G.H. Heravi, H. Garshasbi *, J.
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 2 (3): 141-147 Monitoring of iodine-125 and iodine-131 in thyroid of individuals in nuclear medicine centers of North West provinces of Iran G.H. Heravi, H. Garshasbi *, J.
STATE ENTERPRISE «RADIOPREPARAT» Generator of 99 Mo/ 99m Tc TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTIONS ТSH
 INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS, ACADEMY OF SCIENCE OF UZBEKISTAN STATE ENTERPRISE «RADIOPREPARAT» Generator of 99 Mo/ 99m Tc TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTIONS ТSH 42-006-2008 Description and Composition
INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS, ACADEMY OF SCIENCE OF UZBEKISTAN STATE ENTERPRISE «RADIOPREPARAT» Generator of 99 Mo/ 99m Tc TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTIONS ТSH 42-006-2008 Description and Composition
Martin Law, PhD, DABSNM, DABMP Physicist ic Radiology/QMH
 A practical measure in personnel dose reduction for 90 Y-micropsheres liverdirected radioembolization: from radiology department to patient ward Martin Law, PhD, DABSNM, DABMP Physicist ic Radiology/QMH
A practical measure in personnel dose reduction for 90 Y-micropsheres liverdirected radioembolization: from radiology department to patient ward Martin Law, PhD, DABSNM, DABMP Physicist ic Radiology/QMH
THYROID IMAGING STUDY (Tc-99m as Sodium Pertechnetate)
 THYROID IMAGING STUDY (Tc-99m as Sodium Pertechnetate) Overview Indications The Thyroid Imaging Study with Tc-99m-pertechnetate demonstrates the distribution of tissues that take up anions. Such tissues
THYROID IMAGING STUDY (Tc-99m as Sodium Pertechnetate) Overview Indications The Thyroid Imaging Study with Tc-99m-pertechnetate demonstrates the distribution of tissues that take up anions. Such tissues
Isotopes in Functional Cancer Imaging
 Seeing and Believing: i Medical Isotopes in Functional Cancer Imaging François Bénard, MD, FRCPC BCCancer Cancer Agency and University of British Columbia Nuclear Medicine 101 A radioactive atom is produced
Seeing and Believing: i Medical Isotopes in Functional Cancer Imaging François Bénard, MD, FRCPC BCCancer Cancer Agency and University of British Columbia Nuclear Medicine 101 A radioactive atom is produced
Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: US and Radionuclide imaging. Deepa R Biyyam, MD Attending Pediatric Radiologist
 Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: US and Radionuclide imaging Deepa R Biyyam, MD Attending Pediatric Radiologist Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: Imaging modalities Outline ACR-SNM-SPR guidelines
Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: US and Radionuclide imaging Deepa R Biyyam, MD Attending Pediatric Radiologist Imaging in Pediatric Thyroid disorders: Imaging modalities Outline ACR-SNM-SPR guidelines
Basics of nuclear medicine
 Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility
 Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 8, No. 2, December 2013 1 Editorial Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility Taalab, Kh; and Mohsen, Z Department of Nuclear Medicine, International Medical Center;
Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 8, No. 2, December 2013 1 Editorial Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility Taalab, Kh; and Mohsen, Z Department of Nuclear Medicine, International Medical Center;
45 Hr PET Registry Review Course
 45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
Summary of Patient Release after Radioiodine Therapy Research Review
 Summary of Patient Release after Radioiodine Therapy Research Review Introduction This report provides a summary of the Office of Research (RES) staff s efforts to evaluate radiation exposure to members
Summary of Patient Release after Radioiodine Therapy Research Review Introduction This report provides a summary of the Office of Research (RES) staff s efforts to evaluate radiation exposure to members
Theragnostics for bone metastases. Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK
 Theragnostics for bone metastases Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK NPL 2015 Ra-223 Biodistribution & dosimetry Ra-223: 11.4 days half-life, range of 100 µm Six
Theragnostics for bone metastases Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK NPL 2015 Ra-223 Biodistribution & dosimetry Ra-223: 11.4 days half-life, range of 100 µm Six
Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153
 APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
Determination of Beta Radiation Dose to the Thyroid Gland from the Ingestion of 131 I by Patients
 American Journal of Environmental Protection 2016; 5(6): 168-178 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajep doi: 10.11648/j.ajep.20160506.14 ISSN: 2328-5680 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5699 (Online) Determination
American Journal of Environmental Protection 2016; 5(6): 168-178 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajep doi: 10.11648/j.ajep.20160506.14 ISSN: 2328-5680 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5699 (Online) Determination
Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals
 Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals 1. Generator & Reactors 2. Cyclotrons & PET tracer 3. Quality control 4. Renal 5. GIT 6. CNS & Psychiatrics 7. Tumor Diagnosis & Treatment 8. Bones & joints 9. Thyroid
Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals 1. Generator & Reactors 2. Cyclotrons & PET tracer 3. Quality control 4. Renal 5. GIT 6. CNS & Psychiatrics 7. Tumor Diagnosis & Treatment 8. Bones & joints 9. Thyroid
Ultra-TechneKow FM. Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Ultra-TechneKow FM Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
Ultra-TechneKow FM Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
New single photon radiopharmaceuticals for renal scintigraphy
 New single photon radiopharmaceuticals for renal scintigraphy Andrew Taylor, M.D.* Malgorzata Lipowska, Ph.D.* Luigi Marzilli, Ph.D. # *Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA # Louisiana State
New single photon radiopharmaceuticals for renal scintigraphy Andrew Taylor, M.D.* Malgorzata Lipowska, Ph.D.* Luigi Marzilli, Ph.D. # *Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA # Louisiana State
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 TechneScan SULFUR COLLOID Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
TechneScan SULFUR COLLOID Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging. Danielle Wilson
 Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
Individualised Treatment Planning for Radionuclide therapy (Molecular Radiotherapy)
 Individualised Treatment Planning for Radionuclide therapy (Molecular Radiotherapy) FMU/ICRP workshop 2017 Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK ICRP Task Group 101
Individualised Treatment Planning for Radionuclide therapy (Molecular Radiotherapy) FMU/ICRP workshop 2017 Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK ICRP Task Group 101
8.05 days 138 days 7.60 days 0.22 mr/h at 1.0 meter per millicurie 124,068 curies/gram 2 mm = 0.20 cm = 0.08 in 165 cm = 65.0 in = 5.
 Iodine-131 Radiological Safety Guidance Physical Data GAMMA ENERGIES 364 kev (82% abundance) 637 kev (7% abundance) 284 kev (6% abundance) 80 kev (3% abundance) 723 kev (2% abundance) 29-34 kev (4.5%/x-rays)
Iodine-131 Radiological Safety Guidance Physical Data GAMMA ENERGIES 364 kev (82% abundance) 637 kev (7% abundance) 284 kev (6% abundance) 80 kev (3% abundance) 723 kev (2% abundance) 29-34 kev (4.5%/x-rays)
Distribution Pattern of Radioactive Labelled Lipiodoi-UF Following I ntralymphatic Application for Therapy
 122 Lymphology 9 (1976) 122-126 Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart Distribution Pattern of Radioactive Labelled Lipiodoi-UF Following I ntralymphatic Application for Therapy H. Weissleder, P. Pfannenstiel,
122 Lymphology 9 (1976) 122-126 Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart Distribution Pattern of Radioactive Labelled Lipiodoi-UF Following I ntralymphatic Application for Therapy H. Weissleder, P. Pfannenstiel,
Part 7: Regulatory Issues and Quality Control. Part 1: Current NRC Regulations Related to Radiation Safety
 Part 7: Regulatory Issues and Quality Control Part 1: Current NRC Regulations Related to Radiation Safety 1. Secretarial space, hallways, and certain other areas of a department must qualify as an UNRESTRICTED
Part 7: Regulatory Issues and Quality Control Part 1: Current NRC Regulations Related to Radiation Safety 1. Secretarial space, hallways, and certain other areas of a department must qualify as an UNRESTRICTED
RULES AND REGULATIONS
 RI-12 RI-12 BIOASSAYS FOR INTERNAL RADIOACTIVITY PURPOSE This procedure specifies the requirements, responsibilities and methods for performing and reporting measurements for detecting and verifying the
RI-12 RI-12 BIOASSAYS FOR INTERNAL RADIOACTIVITY PURPOSE This procedure specifies the requirements, responsibilities and methods for performing and reporting measurements for detecting and verifying the
Observations on the emission of radioactive J-131 during its application on a patient as a treatment against hyperthyroid
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VI 545 Observations on the emission of radioactive J-131 during its application on a patient as a treatment against hyperthyroid I. Vgenopoulou 1 & A. Vgenopoulos 2 1
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VI 545 Observations on the emission of radioactive J-131 during its application on a patient as a treatment against hyperthyroid I. Vgenopoulou 1 & A. Vgenopoulos 2 1
Ultra-TechneKow DTE. Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Ultra-TechneKow DTE Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
Ultra-TechneKow DTE Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system. Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine Imaging tehniques Anatomy Physiology Metabolism Molecular Rtg. / CT PET / SPECT MRI MR spectroscopy fmri Ultrasound
Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine Imaging tehniques Anatomy Physiology Metabolism Molecular Rtg. / CT PET / SPECT MRI MR spectroscopy fmri Ultrasound
Calculation methods in Hermes Medical Solutions dosimetry software
 Calculation methods in Hermes Medical Solutions dosimetry software Helena McMeekin MSc. Clinical Applications Scientist, Hermes Medical Solutions MRTDosimetry Scientific Workshop The Principals and Clinical
Calculation methods in Hermes Medical Solutions dosimetry software Helena McMeekin MSc. Clinical Applications Scientist, Hermes Medical Solutions MRTDosimetry Scientific Workshop The Principals and Clinical
Cambridge CB2 3EG. ['25I]L-thyroxine. Experiments were performed after 24 hr had elapsed.
![Cambridge CB2 3EG. ['25I]L-thyroxine. Experiments were performed after 24 hr had elapsed. Cambridge CB2 3EG. ['25I]L-thyroxine. Experiments were performed after 24 hr had elapsed.](/thumbs/95/125304458.jpg) J. Physiol. (1971), 212, pp. 447-454 447 With 2 text-ftgurea Printed in Great Britain AN EXAMINATION OF THE EXTENT OF REVERSIBILITY OF THYROXINE BINDING WITHIN THE THYROXINE DISTRIBUTION SPACE IN THE RABBIT
J. Physiol. (1971), 212, pp. 447-454 447 With 2 text-ftgurea Printed in Great Britain AN EXAMINATION OF THE EXTENT OF REVERSIBILITY OF THYROXINE BINDING WITHIN THE THYROXINE DISTRIBUTION SPACE IN THE RABBIT
The Physics of Medical Imaging
 VEA Bringing Learning to Life Program Support Notes Senior Secondary The Physics of Medical Imaging 27mins Program Support Notes by Ian Walter, Dip.App.Chem.; G.Dip.Ed.Admin.; TTTC Produced by VEA Pty
VEA Bringing Learning to Life Program Support Notes Senior Secondary The Physics of Medical Imaging 27mins Program Support Notes by Ian Walter, Dip.App.Chem.; G.Dip.Ed.Admin.; TTTC Produced by VEA Pty
Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis
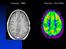 Anatomy : MRI Fonction : Nucl Med Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis Functional imaging = distribution of a (radio)- tracer in organs Each tracer is a SPY of a function, usually through a metabolic pathway flow
Anatomy : MRI Fonction : Nucl Med Nuclear Medicine Diagnosis Functional imaging = distribution of a (radio)- tracer in organs Each tracer is a SPY of a function, usually through a metabolic pathway flow
Gastric emptying following vagotomy and antrectomy and proximal gastric vagotomy
 Gut, 1975, 16, 509-513 Gastric emptying following vagotomy and antrectomy and proximal gastric vagotomy H. KALBASI, F. R. HUDSON, A. HERRING, S. MOSS, H. I. GLASS, AND J. SPENCER From the Departments of
Gut, 1975, 16, 509-513 Gastric emptying following vagotomy and antrectomy and proximal gastric vagotomy H. KALBASI, F. R. HUDSON, A. HERRING, S. MOSS, H. I. GLASS, AND J. SPENCER From the Departments of
SafeTview Syringe Shields Models to Latchkey Syringe Shields Models to Nuclear Medicine. Specifications.
 SafeTview Syringe Shields Models 56-342 to 56-345! Best shielding syringe shield with a window. Window is reset into offset solid tungsten barrel to prevent shine-through as occurs with other designs!
SafeTview Syringe Shields Models 56-342 to 56-345! Best shielding syringe shield with a window. Window is reset into offset solid tungsten barrel to prevent shine-through as occurs with other designs!
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 317e322. Available online at ScienceDirect
 Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 317e322 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage:
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 317e322 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage:
Poltechnet GBq, radionuclide generator Sodium pertechnetate ( 99m Tc) solution
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Poltechnet 8.0-175 GBq, radionuclide generator Sodium pertechnetate ( 99m Tc) solution Read all of the leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Poltechnet 8.0-175 GBq, radionuclide generator Sodium pertechnetate ( 99m Tc) solution Read all of the leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because
International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN) INFORMATION on Nuclear accidents and radioactive contamination of foods 30.
 Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN) INFORMATION on Nuclear accidents and radioactive contamination of foods 30. March 2011 This
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations International Food Safety Authorities Network (INFOSAN) INFORMATION on Nuclear accidents and radioactive contamination of foods 30. March 2011 This
Quantitative Theranostics in Nuclear Medicine
 Quantitative Theranostics in Nuclear Medicine M. Lassmann Klinik und Poliklinik für Nuklearmedizin Direktor: Prof. Dr. A. Buck Contents What is Theranostics? Potential Targets Basic Principles of Quantitative
Quantitative Theranostics in Nuclear Medicine M. Lassmann Klinik und Poliklinik für Nuklearmedizin Direktor: Prof. Dr. A. Buck Contents What is Theranostics? Potential Targets Basic Principles of Quantitative
General Nuclear Medicine
 General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
Introduction. Measurement of Secondary Radiation for Electron and Proton Accelerators. Introduction - Photons. Introduction - Neutrons.
 Measurement of Secondary Radiation for Electron and Proton Accelerators D. Followill, Ph.D. Radiological Physics Center U. T. M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Introduction Patients undergoing radiation therapy
Measurement of Secondary Radiation for Electron and Proton Accelerators D. Followill, Ph.D. Radiological Physics Center U. T. M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Introduction Patients undergoing radiation therapy
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Erythrocyte and Plasma Volume Measurement
 Erythrocyte and Plasma Volume Measurement JP Esser, Meander Medical Centre, Amersfoort NOTE: no changes have been made since the version of 2007 Warning: I human serum albumin and 131 I human serum albumin
Erythrocyte and Plasma Volume Measurement JP Esser, Meander Medical Centre, Amersfoort NOTE: no changes have been made since the version of 2007 Warning: I human serum albumin and 131 I human serum albumin
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism With Iodine-131
 Treatment of Hyperthyroidism With Iodine-131 Pages with reference to book, From 29 To 33 Sbeeda Asghar, Mumtaz-ul-Haq, Maqbool Ahmad Shahid ( Atomic Energy Nuclear Medicine Centre, Mayo Hospital, Lahore.
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism With Iodine-131 Pages with reference to book, From 29 To 33 Sbeeda Asghar, Mumtaz-ul-Haq, Maqbool Ahmad Shahid ( Atomic Energy Nuclear Medicine Centre, Mayo Hospital, Lahore.
Y90 SIRT Therapy Dosimetric Aspects
 Y90 SIRT Therapy Dosimetric Aspects David Chee-Eng Ng MBBS, BSc, MSc, MRCP, FAMS, FRCP (Edin) Head and Senior Consultant, Department of Nuclear Medicine and PET Singapore General Hospital Adjunct Assistant
Y90 SIRT Therapy Dosimetric Aspects David Chee-Eng Ng MBBS, BSc, MSc, MRCP, FAMS, FRCP (Edin) Head and Senior Consultant, Department of Nuclear Medicine and PET Singapore General Hospital Adjunct Assistant
Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles. Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine NUCLEAR MEDICINE Application of the radioactive isotopes in the diagnostics and in the
Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine NUCLEAR MEDICINE Application of the radioactive isotopes in the diagnostics and in the
M A A. Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Albumin Aggregated Injection. DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use
 R: March 1998 27248 0001E m TM M A A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Albumin Aggregated Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain
R: March 1998 27248 0001E m TM M A A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Albumin Aggregated Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden
 Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
TABLE 1 Principal Radiation Emission Data Radiation Mean % per Disintegration Mean Energy (kev) Gamma
 KIT FOR THE PREPARATION OF TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEBROFENIN - mebrofenin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution ---------- Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin DESCRIPTION Each multidose
KIT FOR THE PREPARATION OF TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEBROFENIN - mebrofenin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution ---------- Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin DESCRIPTION Each multidose
Nuclear Medicine: Basics to therapy
 Nuclear Medicine: Basics to therapy RCP Medical careers day Dr Sabina Dizdarevic MD MSc PhD FRCP Dr Deena Neriman MBBS FRCR Ms Charlotte Weston CEO BNMS On behalf of the British Nuclear Medicine Society
Nuclear Medicine: Basics to therapy RCP Medical careers day Dr Sabina Dizdarevic MD MSc PhD FRCP Dr Deena Neriman MBBS FRCR Ms Charlotte Weston CEO BNMS On behalf of the British Nuclear Medicine Society
IPPE Iron shell transmission experiment with 14 MeV neutron source and its analysis by the Monte-Carlo method
 IPPE Iron shell transmission experiment with 14 MeV neutron source and its analysis by the Monte-Carlo method S.P. Simakov 1,2, M.G. Kobozev 1, A.A. Lychagin 1, V.A. Talalaev 1, U. Fischer 2, U. von Möllendorff
IPPE Iron shell transmission experiment with 14 MeV neutron source and its analysis by the Monte-Carlo method S.P. Simakov 1,2, M.G. Kobozev 1, A.A. Lychagin 1, V.A. Talalaev 1, U. Fischer 2, U. von Möllendorff
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate)
 Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
DRAXIMAGE MDP-25 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Medronate Injection. For Intravenous Use DIAGNOSTIC FOR SKELETAL IMAGING
 TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEDRONATE - medronic acid injection, powder, for solution Jubilant DraxImage Inc ---------- DRAXIMAGE MDP-25 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Medronate Injection For Intravenous
TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEDRONATE - medronic acid injection, powder, for solution Jubilant DraxImage Inc ---------- DRAXIMAGE MDP-25 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Medronate Injection For Intravenous
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
 1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE a) Axumin is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE a) Axumin is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following
Hazards + uses of emissions; Background radiation
 Hazards + uses of emissions; Background radiation Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Physics Exam Board AQA Topic 4.4 Atomic structure Sub-Topic Hazards uses of emissions; Background radiation Difficulty
Hazards + uses of emissions; Background radiation Question Paper 1 Level GCSE (9-1) Subject Physics Exam Board AQA Topic 4.4 Atomic structure Sub-Topic Hazards uses of emissions; Background radiation Difficulty
Thyroid remnant volume and Radioiodine ablation in Differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thyroid remnant volume and Radioiodine ablation in Differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Md. Sayedur Rahman Miah, Md. Reajul Islam, Tanjim Siddika Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Allied Sciences,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thyroid remnant volume and Radioiodine ablation in Differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Md. Sayedur Rahman Miah, Md. Reajul Islam, Tanjim Siddika Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Allied Sciences,
Warning: The intravenous administration of sodium perchlorate mentioned in this recommendation is a non-registered application.
 Thyroid Scintigraphy JAF de Jong, Instituut Verbeeten, Tilburg B de Keizer, University Medical Centre, Utrecht Warning: The intravenous administration of sodium perchlorate mentioned in this recommendation
Thyroid Scintigraphy JAF de Jong, Instituut Verbeeten, Tilburg B de Keizer, University Medical Centre, Utrecht Warning: The intravenous administration of sodium perchlorate mentioned in this recommendation
might be due to a direct action on the thyroid, like that of the thiouracil
 288 J. Physiol. (1953) I20, 288-297 COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF THIOURACIL, THY- ROXINE AND CORTISONE ON THE THYROID FUNCTION OF RABBITS BY N. B. MYANT* From the Department of Clinical Research, University
288 J. Physiol. (1953) I20, 288-297 COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF THIOURACIL, THY- ROXINE AND CORTISONE ON THE THYROID FUNCTION OF RABBITS BY N. B. MYANT* From the Department of Clinical Research, University
RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING
 RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING RAYMOND TAILLEFER, M.D. FRCP(c), ABNM DIRECTOR, DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE HOPITAL ST-JEAN-SUR-RICHELIEU Disclosures to Report: Grant Research Support:
RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING RAYMOND TAILLEFER, M.D. FRCP(c), ABNM DIRECTOR, DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE HOPITAL ST-JEAN-SUR-RICHELIEU Disclosures to Report: Grant Research Support:
GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3
 GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3 WARNING: Store below 25ºC Store away from radiation sources Avoid exposure of film to sunlight Handle film carefully, creasing may cause damage Do not expose to temperatures
GAFCHROMIC DOSIMETRY MEDIA TYPE MD-V3 WARNING: Store below 25ºC Store away from radiation sources Avoid exposure of film to sunlight Handle film carefully, creasing may cause damage Do not expose to temperatures
Nuclear Medicine: Manuals. Nuclear Medicine. Nuclear imaging. Emission imaging: study types. Bone scintigraphy - technique
 Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Single Photon Emission Tomography Approach for Online Patient Dose Assessment in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy
 Single Photon Emission Tomography Approach for Online Patient Dose Assessment in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Daniel M Minsky a,b,c*, Alejandro Valda a,b, Andrés J Kreiner a,b,c and Alejandro A Burlon
Single Photon Emission Tomography Approach for Online Patient Dose Assessment in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Daniel M Minsky a,b,c*, Alejandro Valda a,b, Andrés J Kreiner a,b,c and Alejandro A Burlon
Study of Performance of Thyroid Counter for Monitoring of Intake of Iodine-131 among Radiation Workers in Malaysia
 ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Study of Performance of Thyroid Counter for Monitoring of Intake of Iodine-131 among Radiation Workers
ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Study of Performance of Thyroid Counter for Monitoring of Intake of Iodine-131 among Radiation Workers
CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations. Sarah Bell
 CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations Sarah Bell Sarah.bell14@nhs.net Outline 1. Introduction 2. Aims and Objectives 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion 6. Conclusions 7. References Introduction
CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations Sarah Bell Sarah.bell14@nhs.net Outline 1. Introduction 2. Aims and Objectives 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion 6. Conclusions 7. References Introduction
BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS. MAGROTEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium To 99m Albumin Aggregated Diagnostic For Intravenous Use
 BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS MAGROTEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium To 99m Albumin Aggregated Diagnostic For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION Macrotec is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, lyophilized preparation of albumin
BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS MAGROTEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium To 99m Albumin Aggregated Diagnostic For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION Macrotec is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, lyophilized preparation of albumin
ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER
 ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER Bro. Dr. Collie Miller IARC/WHO Based on trends in the incidence of cancer, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and WHO
ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER Bro. Dr. Collie Miller IARC/WHO Based on trends in the incidence of cancer, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and WHO
b) Tc-99m MAA may be used in adults as an imaging agent to aid in the evaluation of peritoneovenous (LeVeen) shunt patency.
 1. OVERVIEW a) Tc 99m Macroaggregated Albumin (MAA) is a lung imaging agent which may be used as an adjunct in the evaluation of pulmonary perfusion in adults and pediatric patients. b) Tc-99m MAA may
1. OVERVIEW a) Tc 99m Macroaggregated Albumin (MAA) is a lung imaging agent which may be used as an adjunct in the evaluation of pulmonary perfusion in adults and pediatric patients. b) Tc-99m MAA may
