Neuromuscular diseases. Judit Boczán MD, PhD
|
|
|
- Nora Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuromuscular diseases Judit Boczán MD, PhD
2 Neuromuscular diseases - Motoneuron (motoneuron diseases) - Spinal roots (pl. disc herniation) - Plexus (brachial, lumbosacral) - Peripheral nerves (mono- and polyneuropathies) - Neuromuscular junction (eg. myasthenia gravis) - Skeletal muscle (myositis, myopathies, muscular dystrophies)
3 Neuromuscular diseases - Motoneuron (motoneuron diseases) - Spinal roots (pl. disc herniation) - Plexus (brachial, lumbosacral) - Peripheral nerves (mono- and polyneuropathies) - Neuromuscular junction (myasthenia gravis) - Skeletal muscle (myositis, myopathies, muscular dystrophies)
4 Anamnesis - Complaints Motor system (YES) weakness fatigue clumsyness Involuntary movements of muscle, cramps Sensory system (NO) numbness pain hypesthesia dysequilibrium
5 Symptoms Motor system Trophism: atrophy Tone: hypotonia Strenght: paresis motor on sign: fasciculation, myokymia Reflexes Decreased deep tendon reflexes No pyramidal signs
6 Examinations Electroneurography (ENG) - Functional examination method of peripheral nerves - Motor, sensory - Axonal? Demyelinisation? - Diagnosis, follow up.. Conduction block
7 Examination Electromyography (EMG) - Differentiation between myogen and neurogen processes - Concentric needle electrode - Activity in relaxed muscle? (no, fibrillation, positive sharp wave, fasciculation) - Voluntary contraction: motor unit potentials (amplitude, duration) normal myopathy neuropathy
8 Neuromuscular diseases - Motoneuron diseases - Diseases of the neuromuscular junction - Skeletal muscle diseases
9 Neuromuscular diseases - Motoneuron diseases - Diseases of the neuromuscular junction - Skeletal muscle diseases
10 Motoneuron diseases (MND) - Upper motoneuron - Upper + Lower motoneuron (ALS) - Lower motoneuron (SMA, SBMA)
11 Motoneuron diseases (MND) - Upper motoneuron - Upper + Lower motoneuron (ALS) - Lower motoneuron (SMA, SBMA)
12 Upper motoneuron diseases - Hereditary spastic paraparesis (HSP) - Lesion of the pyramidal tract - Spasticity (mainly lower extremities) - No or minimal atrophy - Increased tendon reflexes, pyramidal signs - Spastic gait - AD, AR - Diff. DG: other myelopathies (inflammatory, compression, hypovitaminosis B12..)
13 Motoneuron diseases (MND) - Upper motoneuron - Upper + Lower motoneuron (ALS) - Lower motoneuron (SMA, SBMA)
14 Amyotrophic lateralsclerosis (ALS) : Jean-Martin Charcot - Progressive loss of UMN and LMN - Lethal within 3-10 years - Incidence: 1-3/ , Prevalence: 4-10/ Male:Female ratio: 1,5:1 - Onset: majority of cases: years of age - Hereditary: 10% (SOD1 15%, c9orf72.)
15 ALS (Lou Gehrig s disease) Lou Gehrig ( ) - New York Yankees - Onset: Died: 1941 (37 year old) Stephen W. Hawking ( ) Big Bang, black holes Lucas-professor of Cambridge University (like Isaac Newton in the 17 th century)
16 ALS - symptoms - Upper motoneuron (pyramidal tract): spasticity, increased tendon reflexes, pyramidal signs - Lower motoneuron: hypotonic muscles, pronounced muscle atrophy, fasciculation, paresis, bulbar signs (tongue atrophy, fasciculation, dysarthria, dysphagia)
17 Hirano - 4 negative criteria NO: - Sensory signs - Eye movement problems - Vegetative signs (bladder and bowel) - Taint for decubitus
18 Diagnosis - ENG: motor axonal neuropathy (sensory - spared) - EMG: denervation signs at rest (fibrillation, fasciculation), neuropathic potentials, signs of reinnervation - Magnetic evoked potentials (MEP): dysfunction of the pyramidal tract - Brain and cervical MR: negative, BUT precentral gyrus atrophy is possible - Muscle biopsy
19 Subgroups, incidence, prognosis - Primary Lateral Sclerosis (PLS): 5%, UMN + later LMN signs, mean survival: 20 years - Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): 65-70%, UMN+LMN signs, mean survival : 3-4 years - Progressive Muscular Atrophy (PMA): 10%, LMN, later UMN signs, mean survival: 5 years - Primary Bulbar Paresis (PBP): 12-20%, bulbar signs, signs, mean survival: 2 years
20 Therapy - Incurable - Riluzole: slowing progression, increases survival with 3-6 months - Goal: improve the quality of life of the patient and his family - PhysicoTH, exercises, medical aids (eg. handrail, wheelchair..) - Muscle relaxants for decreasing spasticity - Improve communication (eg. camera mouse ) - Dysphagia: pulping, condensation of fluids, percutaneous gastrostomy - Dyspnea: noninvasive ventilation, home ventilation - Psychotherapy (patients, family, alternative Th-s..)
21 Motoneuron diseases (MND) - Upper motoneuron - Upper + Lower motoneuron (ALS) - Lower motoneuron (SMA, SBMA)
22 Spinal muscular atrophies (SMA) Incidence: 1: / birth 2 nd most frequent AR disease in childhood Survival motor neuron 1 - SMN1 gene 7-8. exon del (5q) carrier fr: 2-3% - SMA0: congenital, reduced movements, respiratory insufficiency, death: 1 st month - SMA I (Werdnig-Hoffmann) onset < 6 m, hypotonia, prox. dominant. paresis, swallowing and respiratory insuff. Death: 1-2 years. - SMA II.: onset: 6 months 2 years - SMA III (Kugelberg-Welander): onset: years, lower extremity dominant, proximal, symmetric weakness and atrophy, cramps, death: adult - SMA IV: onset: adult, norm. lifespan Dg.: EMG, muscle biopsy, genetic test
23 Spinal muscular atrophies (SMA) Therapy: Spinraza (nusinersen) - Antisense oligonucleotide - Intrathecal injection - FDA approval: SMA is caused by loss-of-function mutations in the SMN1 gene which codes for survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. - Patients survive owing to low amounts of the SMN protein produced from the SMN2 gene. - Nusinersen modulates alternate splicing of the SMN2 gene, functionally converting it into SMN1 gene, thus increasing the level of SMN protein in the CNS
24 Kennedy s disease (SBMA) SBMA: spino-bulbar muscular atrophy Prevalence: 1: Androgen receptor (X chromosome) CAG repeat expansion - Onset: years, progression: decades - cramps, atrophy (face, tongue, extremities), paresis, fasciculation - Bulbar muscles (dysarthria, dysphagia) - Gynecomastia, testes atrophy, infertility - CK increased - ENG: sensory-motor PP - EMG: denervation, neurogen - Lifespan is close to normal
25 Neuromuscular diseases - Motoneuron diseases - Diseases of the neuromuscular junction - Skeletal muscle diseases
26 Sanders, Massey: Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol. 91 Myasthenia gravis - Autoimmun appr. 99%, congenital app. 1% - Prevalence: 2-10/ Rare disease - Increasing incidence in elderly (lifespan, better DG workup)
27 Autoantigens in MG No. Antigén Prevalencia MGban 1 nachr Kb. 85% 2 MUSK 4-70% 3 Lrp4? 1-7% 4 Titin 30-75% 5 Ryr 50-90% 6 DHPR 37% 7 TRPC3 36% 8 Tropomyosin 32% Gomez et al., Autoimmunity, 2010; 43(5 6): NMJ: 3x safety factor (EPP generates AP) Others: pl. agrin, cortactin, actomyosin, rapsyn, AChE
28 Pathophysiológy anti-achr antibody (IgG1 és 3, C fixing) No of AChR Ampl. of EPP AP is late or missing - Desorganisation of the postsynaptic membrane - Granulocyta infiltration in the NMJ - Synaptic boutons detach from the sarcolemma - The postsynaptic membrane will be simpler (disappearance of the T-tubule system)
29 Complaints, symptoms Fatigue, skeletal muscle weakness increases with physical exercise, and during the day According to the muscles affected: Ocular - ptosis, diplopia Bulbar masticatory muscles, muscles of facial expression (facies myasthenica), dysarthria, dysphonia, dysphagia Generalized Proximal muscles, neck, respiratory muscles!!!
30 Frequent co-morbidities Thyroid gland diseases Persistent thymus, thymoma (chest CT!)
31 DIAGNOSIS: Edrophonium-chlorid test - Acetylcholine-esterase inhibitor - max. 10 mg iv Positive: - Ocular MG: 60-95% - Generalized MG: 72-95% - BUT: aspecific positive reaction might occur in eg. motoneuron disease, brainstem lesion, other myopathies - Mild symptoms: negative - Side effect: salivation, nausea, fasciculation, sweating, (hypotension, bradycardia)
32 DIAGNOSIS: Ice cube test - 2 minutes chilling with and ice cube ptosis decreases - might be positive in edrophonium negative cases - meta analysis of 6 studies: Sensitivity: 89% Specificity: 100%
33 DIAGNOSIS: Antibody test - Ab titer does NOT correlate with severity BUT: - AB positivity = Myasthenia - Diagnostic kits on the market (AChR, MUSK) - Cell based assays for Lrp4
34 DIAGNOSIS: Repetitive stimulation (3 Hz) More sensitive at proximal muscles! - Axillary nerve deltoid - Accessory nerve trapezius - Ulnar hypothenar Positive: - Ocular MG: 50% - Generalized MG: 75% - anti-musk MG: 57%
35 DIAGNOSIS: single-fiber EMG (SF-EMG) - Most senstivive electrophysiologic test - Often + in a non-paretic muscle - Generalized and ocular MG > 95% sensitivity BUT: ALS, polymyositis: false +
36 CHEST CT - Persistent thymus, thymoma, thymic carcinoma
37 Therapy Inhibition of Ach esterase - quick effect, short T1/2 - pyridostigmine (Mestinon, 0-6x60 mg ), ambenonium chlorid (Mytelase 10mg) - Fit the dose to the patient s actual need - Side effects: muscarinergic: salivation, diarrhoea, vomitus, increased bronchial secretion nicotinergic: muscle twitches, cramps - If symptoms worsen with AChE inhibition: immunosuppression
38 Thymectomy - Persistent thymus, generatlized MG, AChR AT +: up to years of age - Thymoma should be removed due to an oncologic indication - Operation techniques: transsternal transcervical and infraaxillar VAT Robot-assisted operation - In the first year of myasthenia
39 Steroid - Progression despite of high dose of AChE inhibitor - start: 16 mg metilprednizolon per os - increase with 4 mgs every second day - max. 1 mg/kg (! DM, side effects), hold for 1-3 months - taper down with 4 mgs every second week, then stop - Check: RR, glucose, GI complaints, edema!!!!
40 Chronic immunosuppression - azathioprin (Imuran): effective steroid lowering drug in MG - 2,5 mg/kg, pregnancy is NOT a contraindication! - Blood cell count, liver function control! - Increases the incidence of non-melanoma skin cancers - Skin protection against UV light is recommended
41 Myasthenic crisis - Respiratory failure requiring intubation, ventilation - Occurence in 15-20% of cases - Provoked by: infection, changes in medication (eg. steroid withdrawal or initiation with high dose; other drugs) - Mortality 4-6% - Treatment: plasma exchange (PLEX) IVIG
42 Neonatal myasthenia - Antibody penetrates the placenta - Respiratory failure and severe dysphagia in newborns - Delivery only at wards with PIC facility! - Temporal mechanical ventilation, nasogastric feeding if necessary - Spontaneous remission
43 Drugs worsening myasthenia Replacement Antibiotics Aminoglycosids, tetracyclin Polymyxin, penicillin (high dose) Anticonvulsants Phenytoin, barbiturate Carbamazepin Cardio- vascular drugs beta blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs, ganglion-inhibitors Cephalosporins, ampicillin Erythromycin, co-trimoxazol Nitrofurantoin digitalis, reserpin Antirheumatics penicillamin Acetylsalicylic acid, phenylbutazon Indomethacin Antiparkinson drugs amantadin L-DOPA Psychiátric drugs Narcotics and musclerelaxants Others Tranquillants, neuroleptics, Lithium Ketamin, aether, Pancuronium, d-tubocurarin corticosteroids, ACTH oral contraceptives thyroid hormones laxans (Mg!) atosil Benzodiazepines (low dose, with care) Halothan, fentanyl N 2 O, suxamethonium
44 Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome - frequently associates with SCLC - AB against the praesynaptic Ca 2+ channel - Repetitive stimulation: differentiates from MG!! 3 Hz: decrement post-activation: amplitude increment 30 Hz stimulation (ulnar nerve): minimum 100% increment
45 Neuromuscular diseases - Motoneuron diseases - Diseases of the neuromuscular junction - Skeletal muscle diseases
46 Skeletal muscle diseases - Myositis - Myopathies - Muscular dystrophies - Ion channel diseases
47 Complaints - Symptoms: - Muscle weakness - Muscle pain - Muscle atrophy - Skin-, joint.. symptoms Subgroups: - Polymyositis (prox.) - Dermatomyositis (prox.) - IBM (distal, BUT: can be hereditary, too) - Associated with other connective tissue disease - Infective
48 Diagnosis: - laboratory: CK, LDH, GOT, GPT, ANA, myositis spec. AB-s - EMG (myogenic potentials, fibrillation - acute) - muscle MRI - biopsy (histochem, IH), myogenic, lymphocytes, MHC expression.. Therapy: steroid, chr. Immunosuppression, IVIG, PLEX
49 Skeletal muscle diseases - Myositis - Myopathies - Muscular dystrophies - Ion channel diseases
50 Weakness of proximal muscles (no sensory!) Causes: - Metabolic (mitochondrial, fat- or carbohydrate) inherited - Endocrine (thyroid gland, parathyroid gland..) - Toxic - Drug induced (statins!) - Critical illness myopathy Diagnosis: - laboratory: t és ica, Mg, phosphate, CK, LDH, GOT, GPT, thyroid function, calcitonin, parathormon.., - EMG (myogen potentials) - biopsy (histochem, IH), myogenic/neurogenic?, deposits?
51 Skeletal muscle diseases - Myositis - Myopathies - Muscular dystrophies - Ion channel diseases
52 Muscular dystrophies - Duchenne/Becker (DMD-BMD, dystrophin) - Limb-girdle (LGMD) - Facio-scapulo-humeral (FSH) - Myotonic dystrophy
53 Duchenne dystrophy - XR, dystrophin gene - Prevalencie: kb. 1 : 7250, 5-24 year old boys - Onset: 2-5 years - Progressive weakness of proximal muscles, Gowers sign - Lumbar hyperodosis, wingigng of the scapula, pseudohypertrophy of the calf, belly sticks out, Achilles contract., scoliosis, CK extremely elevated - Loss of ambulation: 9-13 year - Cardiomyopathy - Respiratory failure - Death: year Therapy: steroid, symptomatic New: CRISPR/Cas9 genetherapy in certain cases
54 Limb girdle muscular dystrophy
55 Facio-scapulo-humeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) - AD: in 70-90% of cases, migt be sporadic, 4q35.2 del - Prevalence: 1 : Onset: 3 rd decade - Facial, periscapular muscles, biceps, leg dorsiflexion, later thigh, linear progression up to year (DG FROM THE DOOR) - Mental retardation, cardiomyopathy might occure - CK: U/l (normal in 25% ) - Wheelchair: only in 20 % - Frequently normal lifespan (spared bulbar and respiratory muscles) - 20% of pts have no symptoms!! Therapy: symptomatic
56 Myotonc dystrophy - AD, myotonin protein kinase (DMPK, CTG triplet expansion) - Prevalence: 13.5 / birth - Frontal baldness - Cataracta - Difficulty in muscle relaxation, paresis - Myopathic face - Cardiomyopathy - Therapy: mexiletin
57 THM Rare diseases: - many rarities - a lot in total - it s 100% for that patient Phenotype: from mild to severe Push the diagnostic workup as much as possible Gene therapy is around the corner Prenatal diagnosis in severe cases Focus on quality of life
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Myasthenia Gravis. Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06
 Myasthenia Gravis Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06 Overview Background Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment Associated Conditions Background Severe muscle disease Most common disorder of neuromuscular
Myasthenia Gravis Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06 Overview Background Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment Associated Conditions Background Severe muscle disease Most common disorder of neuromuscular
Stanley Iyadurai, PhD MD. Assistant Professor of Neurology/Neuromuscular Medicine Nationwide Children s Hospital Myology Course 2015
 1 Stanley Iyadurai, PhD MD Assistant Professor of Neurology/Neuromuscular Medicine Nationwide Children s Hospital Myology Course 2015 Motor unit motor neuron, its axon, and nerve terminals, and muscle
1 Stanley Iyadurai, PhD MD Assistant Professor of Neurology/Neuromuscular Medicine Nationwide Children s Hospital Myology Course 2015 Motor unit motor neuron, its axon, and nerve terminals, and muscle
Faculty Disclosure. Sanjay P. Singh, MD, FAAN. Dr. Singh has listed an affiliation with: Consultant Sun Pharma Speaker s Bureau Lundbeck, Sunovion
 Faculty Disclosure Sanjay P. Singh, MD, FAAN Dr. Singh has listed an affiliation with: Consultant Sun Pharma Speaker s Bureau Lundbeck, Sunovion however, no conflict of interest exists for this conference.
Faculty Disclosure Sanjay P. Singh, MD, FAAN Dr. Singh has listed an affiliation with: Consultant Sun Pharma Speaker s Bureau Lundbeck, Sunovion however, no conflict of interest exists for this conference.
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE
 MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
Myasthenia gravis. Page 1 of 7
 Myasthenia gravis What is myasthenia gravis? Myasthenia gravis (sometimes abbreviated to MG) is a chronic, autoimmune condition that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is rare, affecting
Myasthenia gravis What is myasthenia gravis? Myasthenia gravis (sometimes abbreviated to MG) is a chronic, autoimmune condition that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is rare, affecting
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction
 Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Who is at risk of developing MG? Is MG hereditary? What are the symptoms of MG? What causes MG?
 Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is uncommon, affecting about 15 in every
Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is uncommon, affecting about 15 in every
5.1 Alex.
 5.1 Alex http://tinyurl.com/neuromakessense Alex is a 20-year-old full-time national serviceman. His only past medical history is asthma, presents to A&E with a 4-day history of bilateral finger weakness
5.1 Alex http://tinyurl.com/neuromakessense Alex is a 20-year-old full-time national serviceman. His only past medical history is asthma, presents to A&E with a 4-day history of bilateral finger weakness
Neonatal Hypotonia. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy. Neurology Chapter of IAP
 The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM. Andrzej Sladkowski
 Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Problems of Neurological Function. Unit 10
 Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Myasthenia gravis. David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre
 Myasthenia gravis David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre SWIM, Taunton, 2018 Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of thymus Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of
Myasthenia gravis David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre SWIM, Taunton, 2018 Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of thymus Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Disorders of Muscle. Disorders of Muscle. Muscle Groups Involved in Myopathy. Needle Examination of EMG. History. Muscle Biopsy
 Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Lumbosacral plexus lesion Lumbosacral plexus disorders G54.1 Neuralgic amyotrophy Neuralgic amyotrophy G
 ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 MYASTHENIA GRAVIS INTRODUCTION Most common primary disorder of neuromuscular transmission Usually due to acquired immunological abnormality Also due to genetic abnormalities at neuromuscular junction.
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS INTRODUCTION Most common primary disorder of neuromuscular transmission Usually due to acquired immunological abnormality Also due to genetic abnormalities at neuromuscular junction.
Index. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child
 Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child Basil T. Darras, M.D. Neuromuscular Program Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Classification and General Clinical Evaluation
Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child Basil T. Darras, M.D. Neuromuscular Program Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Classification and General Clinical Evaluation
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference. November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D.
 Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Muscular Dystrophies. Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018
 Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral
 Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
 Page 1 of 6 Title Authored By Course No Contact Hour 1 An Overview of Myasthenia Gravis Ray Lengel RN, FNP, MS MG2061208 Purpose The goal of this course is to provide an understanding about myasthenia
Page 1 of 6 Title Authored By Course No Contact Hour 1 An Overview of Myasthenia Gravis Ray Lengel RN, FNP, MS MG2061208 Purpose The goal of this course is to provide an understanding about myasthenia
Neurology. Brain death. Tests. EEG in Monitoring 3.B.2. Neuromuscular disorders and anaesthesia. Neurology 3.C.6.1 James Mitchell (December 24, 2003)
 Neurology Brain death Tests EEG in Monitoring 3.B.2 Neuromuscular disorders and anaesthesia Neurology 3.C.6.1 James Mitchell (December 24, 2003) Brain death Coma GCS < 8, potential for recovery Persistent
Neurology Brain death Tests EEG in Monitoring 3.B.2 Neuromuscular disorders and anaesthesia Neurology 3.C.6.1 James Mitchell (December 24, 2003) Brain death Coma GCS < 8, potential for recovery Persistent
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer OUTLINE Background Anatomy Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Treatment BACKGROUND Acquired autoimmune disorder Clinically characterized by: Weakness
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer OUTLINE Background Anatomy Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Treatment BACKGROUND Acquired autoimmune disorder Clinically characterized by: Weakness
III./10.4. Diagnosis. Introduction. A.) Laboratory tests. Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques
 III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease. Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine
 Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Motor neuron diseases
 Motor neuron diseases What are motor neuron diseases? The motor neuron diseases (MNDs) are a group of progressive neurological disorders that destroy motor neurons, the cells that control essential voluntary
Motor neuron diseases What are motor neuron diseases? The motor neuron diseases (MNDs) are a group of progressive neurological disorders that destroy motor neurons, the cells that control essential voluntary
Myasthenia Gravis and Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome Michael W. Nicolle, MD
 Review Article Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by maxwo3znzwrcfjddvmduzvysskax4mzb8eymgwvspgpjoz9l+mqfwgfuplwvy+jmyqlpqmifewtrhxj7jpeo+505hdqh14pdzv4lwky42mcrzqckilw0d1o4yvrwmuvvhuyo4rrbviuuwr5dqytbtk/icsrdbt0hfryk7+zagvaltkgnudxdohhaxffu/7kno26hifzu/+bcy16w7w1bdw==
Review Article Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by maxwo3znzwrcfjddvmduzvysskax4mzb8eymgwvspgpjoz9l+mqfwgfuplwvy+jmyqlpqmifewtrhxj7jpeo+505hdqh14pdzv4lwky42mcrzqckilw0d1o4yvrwmuvvhuyo4rrbviuuwr5dqytbtk/icsrdbt0hfryk7+zagvaltkgnudxdohhaxffu/7kno26hifzu/+bcy16w7w1bdw==
Introduction and aims of the study
 Introduction and aims of the study 1 Chapter 1 Motor neuron diseases include the most incapacitating and life-threatening illnesses but also rather benign disorders with only mild symptoms and slow progression.
Introduction and aims of the study 1 Chapter 1 Motor neuron diseases include the most incapacitating and life-threatening illnesses but also rather benign disorders with only mild symptoms and slow progression.
UK practice for electrodiagnosis of MND Review of literature and background
 UK practice for electrodiagnosis of MND Review of literature and background UK practice for electrodiagnosis of MND Review of literature and background EMG Group Mark Baker Stephan Jaiser Stuart Viegas
UK practice for electrodiagnosis of MND Review of literature and background UK practice for electrodiagnosis of MND Review of literature and background EMG Group Mark Baker Stephan Jaiser Stuart Viegas
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
1/28/2019. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team. Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team: Who are we?
 Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Case 1: History of J.H. Outside Evaluation. Outside Labs. Question #1
 Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Myasthenia: Is Medical Therapy in the Grave? Katy Marino, PGY-5
 Myasthenia: Is Medical Therapy in the Grave? Katy Marino, PGY-5 Disclosures Outline History of Thymus Anatomy of Thymus Pathophysiology of Myasthenia Gravis Medical Management of Myasthenia Gravis Surgical
Myasthenia: Is Medical Therapy in the Grave? Katy Marino, PGY-5 Disclosures Outline History of Thymus Anatomy of Thymus Pathophysiology of Myasthenia Gravis Medical Management of Myasthenia Gravis Surgical
CNEMG. Myopathy, Stålberg. At rest denervation and spec spontaneous activity (myotonia, CRD, neuromyotonia) MUP number of fibres in recorded area
 clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG
 Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND OTHER MOTOR NEURON DISEASES Eva L. Feldman
 1 Faculdade de Medicina de São José do Rio Preto Departamento de Ciências Neurológicas Laboratório de Investigação Neuromuscular AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND OTHER MOTOR NEURON DISEASES Eva L. Feldman
1 Faculdade de Medicina de São José do Rio Preto Departamento de Ciências Neurológicas Laboratório de Investigação Neuromuscular AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND OTHER MOTOR NEURON DISEASES Eva L. Feldman
Coexistence of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis
 Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases 1 (2014) 111 115 DOI 10.3233/JND-140007 IOS Press Case Report 111 Coexistence of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis Satoshi Yamashita a,, Akiko Fujimoto
Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases 1 (2014) 111 115 DOI 10.3233/JND-140007 IOS Press Case Report 111 Coexistence of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Myasthenia Gravis Satoshi Yamashita a,, Akiko Fujimoto
2/13/2010. Father hypothyroidismhypothyroidism. Jeffrey W. Ralph, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Director, UCSF Neuropathy Center
 Recent Advances in Neurology: Case Presentations Jeffrey W. Ralph, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Director, UCSF Neuropathy Center Patient 1 23 year-old man Fatigue and weakness in the legs>>arms. No
Recent Advances in Neurology: Case Presentations Jeffrey W. Ralph, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Director, UCSF Neuropathy Center Patient 1 23 year-old man Fatigue and weakness in the legs>>arms. No
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease. Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013
 Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
42 y/o woman with unwitnessed episode of loss of consciousness and urinary incontinence
 Top Five Neurological Emergencies: When To Refer February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation 1 CASE 1 42 y/o woman with unwitnessed episode
Top Five Neurological Emergencies: When To Refer February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation 1 CASE 1 42 y/o woman with unwitnessed episode
Muscular System. Disorders & Conditions
 Muscular System Disorders & Conditions Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. Often is described
Muscular System Disorders & Conditions Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues. Often is described
Steps in EMG analysis
 Steps in EMG analysis at rest - spontaneous activity fibs, psw, myotonia, complex rep discharges fasciculations, myokymia at slight voluntary contraction - MUP shape parameters, stability (jiggle), behaviour
Steps in EMG analysis at rest - spontaneous activity fibs, psw, myotonia, complex rep discharges fasciculations, myokymia at slight voluntary contraction - MUP shape parameters, stability (jiggle), behaviour
Problems of Neurological Function
 Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
Problems of Neurological Function Unit 10 Independent Student Review Brain Anatomy and physiology of cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Meninges, ventricles, flow of CSF Blood
Neuromuscular Disease of Infants and Children. A Guide to Diagnosis of Genetic and Acquired Conditions
 Neuromuscular Disease of Infants and Children A Guide to Diagnosis of Genetic and Acquired Conditions Genetic Effects and Infant/Neonatal Neuromuscular Conditions Who did I get this from? Onset, progression,
Neuromuscular Disease of Infants and Children A Guide to Diagnosis of Genetic and Acquired Conditions Genetic Effects and Infant/Neonatal Neuromuscular Conditions Who did I get this from? Onset, progression,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20412 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Niks, E.H. Title: Myasthenia gravis with antibodies to muscle-specific kinase
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20412 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Niks, E.H. Title: Myasthenia gravis with antibodies to muscle-specific kinase
Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in MDs clinical practice
 4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 2 How to proceed with a suspected myopathy? - Level 2 Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in MDs clinical
4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 2 How to proceed with a suspected myopathy? - Level 2 Clinical relevance of autoantibodies in MDs clinical
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
1. Differences in function of the 3 muscle types: a) Skeletal Muscle b) Cardiac Muscle c) Smooth Muscle
 Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. Energetics of muscle
Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. Energetics of muscle
The role of plasmapheresis in Myasthenia Gravis. Ri 陳文科
 The role of plasmapheresis in Myasthenia Gravis Ri 陳文科 Myaasthenia Gravis S/S: 2/3 initial symptoms: Ocular motor disturbances, ptosis or diplopia. 1/6:Oropharyngeal muscle weakness 1/10: limb weakness
The role of plasmapheresis in Myasthenia Gravis Ri 陳文科 Myaasthenia Gravis S/S: 2/3 initial symptoms: Ocular motor disturbances, ptosis or diplopia. 1/6:Oropharyngeal muscle weakness 1/10: limb weakness
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies.
 1 A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies. Available on-line at: Bill Tillier Calgary Alberta September, 2008. Terminology.
1 A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies. Available on-line at: Bill Tillier Calgary Alberta September, 2008. Terminology.
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015
 1 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015 Name: Nursing Case Study: Muscle Weakness Chief Complaint: A 26-year-old woman with muscle weakness in the face. Patient Presentation: A 26-year-old woman
1 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015 Name: Nursing Case Study: Muscle Weakness Chief Complaint: A 26-year-old woman with muscle weakness in the face. Patient Presentation: A 26-year-old woman
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 9 Muscular System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers NEUROMUSCULAR
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers NEUROMUSCULAR
Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of
 Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Diagnosis, management and new treatments for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Special Focus: SMA Type 1
 Diagnosis, management and new treatments for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Special Focus: SMA Type 1 17 th April 2018 Adnan Manzur Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Dubowitz Neuromuscular Centre, GOSH & ICH,
Diagnosis, management and new treatments for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Special Focus: SMA Type 1 17 th April 2018 Adnan Manzur Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Dubowitz Neuromuscular Centre, GOSH & ICH,
Conventional needle electromyography
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 5 Electromyography: Surface, needle conventional and single fiber - Level 1-2 Conventional
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 5 Electromyography: Surface, needle conventional and single fiber - Level 1-2 Conventional
Muscle Disorders. Amber Eker, MD. Assistant Professor Near East University Department of Neurology
 Muscle Disorders Amber Eker, MD Assistant Professor Near East University Department of Neurology Voluntary muscles Involuntary muscles Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle How does skeletal
Muscle Disorders Amber Eker, MD Assistant Professor Near East University Department of Neurology Voluntary muscles Involuntary muscles Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle How does skeletal
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) epidural anesthesia-related, 825 826 ACE inhibitors. See Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Acetaminophen for
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) epidural anesthesia-related, 825 826 ACE inhibitors. See Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Acetaminophen for
Facts about Myasthenia Gravis
 The information in this fact sheet was adapted by the MDNSW (06/06) from the MDA USA fact sheet (updated 11/05) with their kind permission. Facts about Myasthenia Gravis Myasthenia Gravis (MG), Lambert-Eaton
The information in this fact sheet was adapted by the MDNSW (06/06) from the MDA USA fact sheet (updated 11/05) with their kind permission. Facts about Myasthenia Gravis Myasthenia Gravis (MG), Lambert-Eaton
Muscle Physiology. Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College
 Muscle Physiology Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College Muscle tissue Muscle is an excitable tissue capable of force production Three types Skeletal- striated, voluntary Cardiac- non-striated, involuntary
Muscle Physiology Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College Muscle tissue Muscle is an excitable tissue capable of force production Three types Skeletal- striated, voluntary Cardiac- non-striated, involuntary
4/16/2018. Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis. Objectives. Disclosures. Off-label uses for medications will be discussed
 Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis Jemima Albayda, MD Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins Myositis center Disclosures Off-label uses for medications will be discussed Objectives To
Demystifying weakness: how to approach refractory myositis Jemima Albayda, MD Assistant Professor Johns Hopkins Myositis center Disclosures Off-label uses for medications will be discussed Objectives To
TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart
 TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart Below you find a list of the information that is asked in the CTSR of all registered neuromuscular disease sites. For more information please visit
TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart Below you find a list of the information that is asked in the CTSR of all registered neuromuscular disease sites. For more information please visit
The Floppy Baby. Clare Betteridge
 The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
Radiculopathies Carpal tunnel syndrome Tarsal tunnel syndrome Trauma to nerves Motor/sensory deficits Hot/cold sensation Neuritis
 Contact: Toll-free: 1-877-268-1346 Locals: 404-814-0161 Forms: www.pmdtesting.com NCVs aid in the evaluation of: Herniated Disks Peripheral neuropathies Numbness and tingling Pain in the extremities Atrophy
Contact: Toll-free: 1-877-268-1346 Locals: 404-814-0161 Forms: www.pmdtesting.com NCVs aid in the evaluation of: Herniated Disks Peripheral neuropathies Numbness and tingling Pain in the extremities Atrophy
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES
 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 5(5): September-October 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Pharmaceutical Sciences Review Article!!!
International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 5(5): September-October 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Pharmaceutical Sciences Review Article!!!
A 61 year-old man with exercise-induced muscle spasms
 A 61 year-old man with exercise-induced muscle spasms Jeffrey Ralph, MD RAIN 2017 Case Presentation 61 year-old man with hypertension 1 year ago: tingling in the hands, which then spread to neck, arms,
A 61 year-old man with exercise-induced muscle spasms Jeffrey Ralph, MD RAIN 2017 Case Presentation 61 year-old man with hypertension 1 year ago: tingling in the hands, which then spread to neck, arms,
Symptomatic pain treatments (carbamazepine and gabapentin) were tried and had only a transient and incomplete effect on the severe pain syndrome.
 Laurencin 1 Appendix e-1 Supplementary Material: Clinical observations Patient 1 (48-year-old man) This patient, who was without a notable medical history, presented with thoracic pain and cough, which
Laurencin 1 Appendix e-1 Supplementary Material: Clinical observations Patient 1 (48-year-old man) This patient, who was without a notable medical history, presented with thoracic pain and cough, which
Successive magnifications
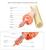 Successive magnifications Skeletal ("striated" = striped) muscle cell ("fiber" = cell) 10-100 microns (huge) and long (tendon to tendon) There are smaller units within fiber called "myofibrils" (1-2 microns
Successive magnifications Skeletal ("striated" = striped) muscle cell ("fiber" = cell) 10-100 microns (huge) and long (tendon to tendon) There are smaller units within fiber called "myofibrils" (1-2 microns
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Neuromuscular Junction Testing ELBA Y. GERENA MALDONADO, MD ACTING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER
 Neuromuscular Junction Testing ELBA Y. GERENA MALDONADO, MD ACTING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER Objectives Neurophysiology Electrodiagnostic Evaluation Clinical Application
Neuromuscular Junction Testing ELBA Y. GERENA MALDONADO, MD ACTING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER Objectives Neurophysiology Electrodiagnostic Evaluation Clinical Application
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis
 Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis 1 Shannon Venance 1 and Rabi Tawil 2 1 Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada 2 University
Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis 1 Shannon Venance 1 and Rabi Tawil 2 1 Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada 2 University
Phenotypic Variability in ALS
 Phenotypic Variability in ALS Michael A. Elliott, MD, FAAN Medical Director, ALS Clinic Swedish Neuroscience Institute 1 Outline ALS Background Description Typical Presentation Clinical Phenotype Motor
Phenotypic Variability in ALS Michael A. Elliott, MD, FAAN Medical Director, ALS Clinic Swedish Neuroscience Institute 1 Outline ALS Background Description Typical Presentation Clinical Phenotype Motor
Randomized Trial of Thymectomy in Myasthenia Gravis. New England Journal of Medicine - August 11, 2016
 Randomized Trial of Thymectomy in Myasthenia Gravis New England Journal of Medicine - August 11, 2016 Disclosures None At all. Example Case 38 year-old female with no pertinent PMH who presents with a
Randomized Trial of Thymectomy in Myasthenia Gravis New England Journal of Medicine - August 11, 2016 Disclosures None At all. Example Case 38 year-old female with no pertinent PMH who presents with a
High Yield Neurological Examination
 High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
3/17/2015. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Nerve conduction studies/electromyography Differential diagnosis Other motor neuron syndromes
 B. Jane Distad, MD Associate Professor Department of Neurology 2015 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Nerve conduction studies/electromyography Differential diagnosis Other motor neuron syndromes Spinal muscular
B. Jane Distad, MD Associate Professor Department of Neurology 2015 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Nerve conduction studies/electromyography Differential diagnosis Other motor neuron syndromes Spinal muscular
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer
 AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
PRIMARY DISEASES OF MYELIN. By: Shifaa Al Qa qa
 PRIMARY DISEASES OF MYELIN By: Shifaa Al Qa qa Most diseases of myelin are primarily white matter disorders??? Myelinated axons most diseases of CNS myelin do not involve the peripheral nerves to any significant
PRIMARY DISEASES OF MYELIN By: Shifaa Al Qa qa Most diseases of myelin are primarily white matter disorders??? Myelinated axons most diseases of CNS myelin do not involve the peripheral nerves to any significant
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: nusinersen_spinraza 03/2017 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal muscular atrophy
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: nusinersen_spinraza 03/2017 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Spinal muscular atrophy
Updates on Neuromuscular Disorders Who is This Guy? Why is he Keeping me Awake? Disclosures 10/19/2016
 Updates on Neuromuscular Disorders 2016 J. Douglas Miles, M.D., Ph.D. University of Hawai i John A. Burns School of Medicine October 22, 2016 Who is This Guy? Why is he Keeping me Awake? Neurologist Fellowship
Updates on Neuromuscular Disorders 2016 J. Douglas Miles, M.D., Ph.D. University of Hawai i John A. Burns School of Medicine October 22, 2016 Who is This Guy? Why is he Keeping me Awake? Neurologist Fellowship
Effects of Temperature on Neuromuscular Function. Jon Marsden School of Health Professions University of Plymouth
 Effects of Temperature on Neuromuscular Function Jon Marsden School of Health Professions University of Plymouth http://www.visualphotos.com/image/2x2696104/test_tube_over_a_bunsen_burner http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~nd/surprise_95/journal/vol4/ykl/report.html
Effects of Temperature on Neuromuscular Function Jon Marsden School of Health Professions University of Plymouth http://www.visualphotos.com/image/2x2696104/test_tube_over_a_bunsen_burner http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~nd/surprise_95/journal/vol4/ykl/report.html
ME Farrugia Consultant Neurologist, Institute of Neurological Sciences, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow, UK
 CME doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2011.111 2011 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Myasthenic syndromes Consultant Neurologist, Institute of Neurological Sciences, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow, UK ABSTRACT
CME doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2011.111 2011 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Myasthenic syndromes Consultant Neurologist, Institute of Neurological Sciences, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow, UK ABSTRACT
Surgery for the treatment of myasthenia gravis. Tim Batchelor Department of Thoracic Surgery Bristol Royal Infirmary
 Surgery for the treatment of myasthenia gravis Tim Batchelor Department of Thoracic Surgery Bristol Royal Infirmary The role of thymectomy It is of considerable interest to find a relationship between
Surgery for the treatment of myasthenia gravis Tim Batchelor Department of Thoracic Surgery Bristol Royal Infirmary The role of thymectomy It is of considerable interest to find a relationship between
Pediatric Aspects of EDX
 Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal
 HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
PART 2 VII XII. Horner Syndrome
 PART 2 CN V VII V XII Horner Syndrome 1 Neuromuscular Disease Clinical presentations, signs and symptoms Lecture presented at the EAN Teaching Course in Burkinje Faso, Nov. 2017 Wolfgang Grisold (1) Anna
PART 2 CN V VII V XII Horner Syndrome 1 Neuromuscular Disease Clinical presentations, signs and symptoms Lecture presented at the EAN Teaching Course in Burkinje Faso, Nov. 2017 Wolfgang Grisold (1) Anna
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Part I Curriculum & Weights
 American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
EMG; clinical practice. Erik Stålberg
 EMG; clinical practice Erik Stålberg What do we want to express Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping N-M transmission
EMG; clinical practice Erik Stålberg What do we want to express Muscle membrane function - spontaneous Muscle fibre characteristics; diameter MU organisation number of fibres grouping N-M transmission
LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN?
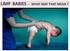 LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN? ARE WE LOOKING WHERE WE SHOULD? FLOPPY = LIMP = FLACCID = WEAK Poor head control when pulled C-posture sitting, or in ventral susp. Frog-leg lying Dropping arms Casey
LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN? ARE WE LOOKING WHERE WE SHOULD? FLOPPY = LIMP = FLACCID = WEAK Poor head control when pulled C-posture sitting, or in ventral susp. Frog-leg lying Dropping arms Casey
Neuroimmunology. Innervation of lymphoid organs. Neurotransmitters. Neuroendocrine hormones. Cytokines. Autoimmunity
 Neuroimmunology Innervation of lymphoid organs Neurotransmitters Neuroendocrine hormones Cytokines Autoimmunity CNS has two ways of contacting and regulating structures in the periphery Autonomic
Neuroimmunology Innervation of lymphoid organs Neurotransmitters Neuroendocrine hormones Cytokines Autoimmunity CNS has two ways of contacting and regulating structures in the periphery Autonomic
Muscle Physiology. Dr. Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
