Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
|
|
|
- Veronica Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
2 Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes from text p Complete WB 184
3 Endocrine System
4 Endocrine vs Nervous Cell Communication
5 Nervous vs. Endocrine System
6 Nervous vs. Endocrine System Communication: Electrical impulses Neurotransmitters Hormones Reaction time 1-10 msec Stops immediately Seconds days Response lingers Effects Specific organs Often entire body
7 Endocrine System Anatomy Endocrine glands secrete into blood, lymph Exocrine glands secrete into ducts
8 Major Endocrine Organs Many glands are purely endocrine Anterior pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, parathyroids Some glands are mixed glands endocrine and exocrine functions pancreas, ovaries, testes
9 Endocrine System Functions Regulate metabolic processes Controls rate of chemical reactions Helps transport across membranes Helps regulate water & electrolytes Regulates glucose and calcium concentrations Reproduction, development, growth Mobilization of body defenses
10 Endocrine Hormones Produced by specialized cells (endocrine glands) Blood transfers hormones to target sites Hormones regulate activity of other cells Turns genes on / off
11 The Chemistry of Hormones (2 types) Hormones are classified chemically as Amino acid based (non-steroids): Proteins Peptides Amines Steroids made from cholesterol
12 Hormone Action Hormones alter cellular activity. Typically, one or more occurs: 1. Membrane permeability or electrical state changes 2. Synthesis of proteins (often enzymes) 3. Enzyme activation or inactivation 4. Stimulation of mitosis (cell division) 5. Promotes cell to secrete substance
13 Hormone Action Hormones affect only certain tissues / organs (target cells / target organs) Hormone binding to receptor alters cellular activity Target cells must have specific protein receptors On cell membrane OR Inside the cell
14 Non-Steroid Cell Communication
15 Second-Messenger System (Nonsteroid Hormone Action) 1. Hormone (1 st messenger) binds to membrane receptor 2. Activated receptor sets off a series of reactions Activates an enzyme 3. Enzyme catalyzes a reaction Activates second-messenger molecule (cyclic AMP, Ca 2+ ) 4. Additional intracellular changes promote cellular response
16 Figure 9.1b Mechanisms of hormone action. Slide 5 Nonsteroid hormone (first messenger) Enzyme Cytoplasm ATP camp Second messenger Receptor protein Plasma membrane of target cell 4 Effect on cellular function 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Nonsteroid hormone action
17 Steroid Cell Communication
18 Direct Gene Activation (Steroid Hormone Action) 1. Steroid hormones diffuse through plasma membrane 2. Steroid hormones bind to a receptor protein In the cytoplasm OR In the nucleus 3. Steroid hormones enter the nucleus 4. Hormone-receptor complex binds DNA 5. Activates genes 6. New proteins are made
19 Figure 9.1a Mechanisms of hormone action. Slide 1 Steroid hormone Cytoplasm 1 2 Nucleus Receptor protein 3 Hormone-receptor complex 4 DNA New protein mrna 5 Plasma membrane of target cell Pearson Education, Inc. (a) Steroid hormone action
20 3 Ways to Stimulate Endocrine Glands Neural Hormonal Humoral Feedback Mechanisms Negative Positive HW: Read / take notes from text p Complete Feedback Mechanisms packet
21 Endocrine Gland Stimuli Three categories of stimuli that activate endocrine glands 1. Hormonal 2. Neural 3. Humoral
22 Hormonal Stimuli of Endocrine Glands Most common stimulus Endocrine organs are activated by other hormones
23 Hormonal gland secretion
24 Hormonal stimulus 1 The hypothalamus secretes hormones that Hypothalamus 2 stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to secrete hormones that Anterior pituitary gland Thyroid gland Adrenal cortex Gonad (testis) 3 stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
25 Neural Stimuli of Endocrine Glands Nerve impulses stimulate hormone release Under sympathetic nervous system control (mostly)
26 Figure 9.2c Endocrine gland stimuli. Neural stimulus 1 Sympathetic fiber stimulates adrenal medulla cells CNS (spinal cord) Sympathetic fibers Pearson Education, Inc.
27 Figure 9.2c Endocrine gland stimuli. Neural stimulus 1 Adrenal medulla 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 cells secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine
28 Neural Stimuli Results in Release of Epinephrine Increase cardiac output Dilate coronary blood vessels Increase muscle contraction Increase mental alertness Increase glycogen Increase blood sugar
29 Humoral Stimuli of Endocrine Glands Blood levels of certain ions and nutrients stimulate hormone release
30 Regulation of Calcium Ion Concentration in Blood Humoral stimulus 1 Capillary blood contains low concentration of Ca 2+, which stimulates Capillary (low Ca 2+ in blood) Thyroid gland (posterior view) Parathyroid glands PTH Parathyroid glands 2 secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) by parathyroid glands)
31 Control of Hormone Release: Negative Feedback Mechanism (usually) Hormone levels maintained by negative feedback What triggers the release of more hormone? A stimulus Low hormone levels in the blood What stops the release of hormones? Hormone reaches appropriate level in the blood
32 Negative Feedback Mechanism
33 Negative Feedback Mechanism
34 Master Controls of the Endocrine System Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Posterior Pituitary Gland (2 hormones) HW: Read / Take notes from text p
35 Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus
36 Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus Pituitary gland is the size of a pea Hangs by a stalk from the hypothalamus Protected by the sphenoid bone Has two functional lobes Anterior pituitary glandular tissue Posterior pituitary nervous tissue Called the master endocrine gland
37 Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus Hypothalamus makes two hormones: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) oxytocin Neurosecretory cells bring hormones to posterior pituitary Posterior pituitary is a storage site
38 Posterior Pituitary Stores Hormones When stimulated Releases ADH Releases Oxytocin Arterial blood supply Venous drainage ADH Oxytocin
39 Posterior Pituitary - ADH Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Prevents dehydration Inhibits urine production (diuresis) Promotes water reabsorption by the kidneys Alcohol inhibits ADH secretion Therefore increases water loss Large amounts of ADH vasoconstriction of arterioles increases blood pressure ADH is also known as vasopressin ADH hyposecretion results in Diabetes insipidus
40 Posterior Pituitary - Oxytocin Oxytocin Stimulates contractions of the uterus during labor sexual relations breastfeeding Causes milk ejection (let-down reflex) in a breastfeeding woman Increases sense of calmness Pitocin: synthetic oxytocin Used to induce labor Used post labor to stop bleeding
41 Posterior Pituitary When stimulated Releases ADH Prevents water loss Releases Oxytocin Uterine contractions Milk let-down Increases calmness Arterial blood supply Venous drainage ADH Kidney Oxytocin Mammary glands Uterine muscles
42 Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus Hypothalamus produces releasing / inhibiting hormones These hormones are released into portal circulation, which connects hypothalamus to anterior pituitary Hypothalamus also makes two hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone Carried to posterior pituitary via neurosecretory cells for storage
43 Master Controls of the Endocrine System Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Anterior Pituitary Gland (6 hormones) HW: Read / Take notes from text p Complete WB
44 Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus
45 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Six anterior pituitary hormones Hormonal control All amino acid-based hormones Regulated by negative feedback (mostly) Two affect non-endocrine targets: 1. Growth hormone Bones Muscles 2. Prolactin Breast milk production in females Unknown function in males
46 Growth Hormone General metabolic hormone Causes amino acids to be built into proteins Causes fats to be broken down for a source of energy Plays a role in determining final body size Growth of skeletal muscles Growth of long bones
47 Growth Hormone Disorders Pituitary dwarfism hyposecretion of GH during childhood Gigantism hypersecretion of GH during childhood Acromegaly hypersecretion of GH in adulthood continued growth of hand, feet, and facial bones
48 Prolactin (PRL) In females, stimulates and maintains milk production (after childbirth) Positive feedback Function in males is unknown
49 Figure 9.5 Hormones of the anterior pituitary and their major target organs. Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary Growth hormone (GH) Bones and muscles Prolactin (PRL) Mammary glands 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
50 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Four are tropic hormones stimulate other endocrine glands to release hormones 1. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) 2. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) 3. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) 4. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
51 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Regulates endocrine activity of the adrenal cortex Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Influences growth and activity of the thyroid gland
52 Figure 9.5 Hormones of the anterior pituitary and their major target organs. Hypothalamus Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenal cortex Thyroid 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
53 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gonadotropic hormones Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation of an egg in females Stimulates testosterone production in males
54 Figure 9.5 Hormones of the anterior pituitary and their major target organs. Hypothalamus Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) Testes or ovaries 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
55 Figure 9.5 Hormones of the anterior pituitary and their major target organs. Releasing hormones secreted into portal circulation Hypothalamus Growth hormone (GH) Anterior pituitary Hypophyseal portal system Posterior pituitary Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Bones and muscles Prolactin (PRL) Mammary glands Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) Thyrotropic hormone (TH) Thyroid Adrenal cortex Testes or ovaries 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
56 Control of Metabolism and Ca 2+ ion concentration Thyroid (3 hormones) Hormonal stimuli Humoral stimuli Parathyroid (1 hormone) Humoral stimuli HW: Read / Take notes from text p Copy Figure 9.10 into notes
57 Thyroid Gland Found at the base of the throat Consists of two lobes and a connecting isthmus Produces two hormones: 1. Thyroid hormone (T 3 and T 4 ) 2. Calcitonin
58 Figure 9.7a The thyroid gland. Thyroid cartilage Epiglottis Common carotid artery Isthmus of thyroid gland Trachea Brachiocephalic artery Left subclavian artery Left lobe of thyroid gland Aorta 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. (a) Gross anatomy of the thyroid gland, anterior view
59 Thyroid Hormone (1 functional hormone) Major metabolic hormone Controls rate of oxidation of glucose Chemical energy (ATP) Body heat Composed of two iodine-containing hormones Thyroxine (T 4 ) Triiodothyronine (T 3 ) converts to T 4 at target cells Needed for tissue growth and development
60
61 Figure 9.7b The thyroid gland. Colloid-filled follicles Follicle cells Parafollicular cells 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. (b) Photomicrograph of thyroid gland follicles (380 )
62 Thyroid Gland Thyroid hormone disorders Goiters Thyroid gland enlarges because of lack of iodine Salt is iodized to prevent goiters Cretinism Caused by hyposecretion of thyroxine Results in dwarfism during childhood
63 Thyroid Gland Thyroid hormone disorders Myxedema Caused by hypothyroidism in adults Results in physical and mental sluggishness Graves disease Caused by hyperthyroidism Results in increased metabolism, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and exophthalmos
64 Thyroid Gland Calcitonin Decreases blood calcium levels Causes calcium deposition on bone Antagonistic to parathyroid hormone Disorder: Calcinosis calcification of soft tissue
65 Parathyroid Glands On the posterior of the thyroid Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Stimulates osteoclasts remove calcium from bone Hypercalcemic hormone ( blood calcium levels) Stimulates the kidneys and intestine absorb more calcium
66
67 Figure 9.10 Hormonal controls of ionic calcium levels in the blood. Calcitonin Calcitonin stimulates calcium salt deposit in bone. Thyroid gland releases calcitonin. Stimulus: Rising blood Ca 2+ levels BALANCE Calcium homeostasis of blood: 9 11 mg/100 ml BALANCE Stimulus Falling blood Ca 2+ levels Osteoclasts degrade bone matrix and release Ca 2+ into blood. PTH Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone (PTH) Pearson Education, Inc.
68 Adrenal Gland (2-in-1) Adrenal Cortex (3 groups of hormones) Hormonal stimuli Humoral stimuli Adrenal Medulla (2 hormones) Neural stimuli HW: Read / Take notes from text p Study all glands / hormones covered so far.
69 Adrenal Glands Sit on top of the kidneys Two regions: Adrenal cortex hormonal / humoral control produces 3 corticosteroids Mineralocorticoids Glucocorticoids Sex hormones Adrenal medulla neural control inner neural tissue region
70 Medulla Cortex Figure 9.11 Microscopic structure of the adrenal gland. Adrenal gland Kidney Capsule Mineralocorticoidsecreting area Adrenal gland Medulla Cortex Glucocorticoidsecreting area Adrenal cortex Kidney Sex hormone secreting area Adrenal medulla 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
71 Adrenal Cortex Hormones Mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) Produced in outer adrenal cortex Target organ: kidney Regulate sodium and potassium ion levels in blood Regulate water and electrolyte balance
72 Aldosterone Increases blood pressure by regulating kidney function Causes kidney to Reabsorb sodium Reabsorb water Secrete potassium Release stimulated by: Humoral stimulation level of K + ions in blood Hormonal stimulation (ACTH stress hormone) Inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) Heart-produced hormone when blood pressure is high
73 Figure 9.12 Major mechanisms controlling aldosterone release from the adrenal cortex. Decreased Na + or increased K + in blood Decreased blood volume and/or blood pressure Kidney ACTH Stress Hypothalamus Corticotropinreleasing hormone Anterior pituitary Increased blood pressure or blood volume Direct stimulating effect Renin Indirect stimulating effect via angiotensin Angiotensin II Heart Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) Inhibitory effect Mineralocorticoidproducing part of adrenal cortex Enhanced secretion of aldosterone targets kidney tubules 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Increased absorption of Na + and water; increased K + excretion Increased blood volume and blood pressure
74 Glucocorticoids Cortisone and cortisol Produced by middle layer of adrenal cortex Promote normal cell metabolism Increases blood glucose levels (hyperglycemic) Helps resist long-term stressors Anti-inflammatory properties Released in response to increased ACTH in blood (hormonal stimulus)
75 Sex Hormones Androgens (male sex hormones, ex. testosterone) Some estrogens produced (female sex hormone) Produced in the inner layer of the adrenal cortex Small amounts are made throughout life Role in male development: Testes formation (early regulation) Spermatogenesis Inhibition of fat deposition Enlargement of skeletal muscle cells
76 Sex Hormones Effects of Testosterone
77 Adrenal Medulla Hormones Produces two similar hormones: (catecholamines) 1. Epinephrine (adrenaline) 2. Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Fight or Flight Hormones Prepare the body to deal with short-term stress Increases: heart rate blood pressure blood glucose levels Dilates small passageways of lungs
78 Medulla Cortex Capsule Mineralocorticoid Secreting cells Glucocorticoid Secreting cells Sex hormone Secreting cells Adrenal medulla 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
79 Figure 9.13 Roles of the hypothalamus, adrenal medulla, and adrenal cortex in the stress response. Short term Hypothalamus Nerve impulses Spinal cord Stress Releasing hormones Corticotropic cells of anterior pituitary More prolonged Adrenal medulla Preganglionic sympathetic fibers ACTH Adrenal cortex Mineralocorticoids Glucocorticoids Catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Short-term stress response Increased heart rate Increased blood pressure Liver converts glycogen to glucose and releases glucose to blood Dilation of bronchioles Changes in blood flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive and kidney activity Increased metabolic rate Long-term stress response 1. Retention of sodium and water by kidneys Increased blood volume and blood pressure Proteins and fats converted to glucose or broken down for energy Increased blood sugar Suppression of immune system
80 Regulation of Blood Glucose Levels Pancreas (hidden Islets of Langerhans) Pancreatic Islets (2 hormones) Humoral stimuli Beta cells Alpha cells HW: Read / Take notes from text p Complete Blood Glucose handout.
81 Pancreatic Islets Pancreas Located in the abdomen, close to stomach Mixed gland, with both endocrine and exocrine functions The pancreatic islets produce hormones Insulin produced by beta cells Glucagon produced by alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis
82 Figure 9.14a Pancreatic tissue. Stomach Pancreas (a) 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
83 Figure 9.14c Pancreatic tissue. Exocrine cells of pancreas Alpha (α) cells Capillaries 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. (c) Cord of beta (β) cells secreting insulin into capillaries
84 Pancreatic Islets Insulin Released when blood glucose levels are high Increases the rate of glucose uptake and metabolism by body cells Glucagon Released when blood glucose levels are low Stimulates the liver to release glucose to blood, thus increasing blood glucose levels
85 BioFlix : Homeostasis
86
87 Figure 9.15 Regulation of blood glucose levels by a negative feedback mechanism involving pancreatic hormones. Insulin-secreting cells of the pancreas activated; release insulin into the blood Pancreas Elevated blood sugar level Insulin Tissue cells Glucose Glycogen Liver takes up glucose and stores as glycogen Uptake of glucose from blood is enhanced in most body cells Blood glucose falls to homeostatic set point; stimulus for insulin release diminishes Stimulus Blood glucose level (e.g., after eating four jelly doughnuts) Blood glucose rises to homeostatic set point; stimulus for glucagon release diminishes Stimulus Blood glucose level (e.g., after skipping a meal) Low blood sugar level Liver breaks down glycogen stores and releases glucose to the blood Glucose Glycogen Liver Glucagon Glucagon-releasing cells of pancreas activated; release glucagon into blood 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
88 Diabetes mellitus Occurs in the absence of insulin Blood sugar levels increase dramatically Blood glucose is lost in the urine; water follows Three cardinal signs: 1. Polyuria production of abnormally large volumes of dilute urine. 2. Polydipsia excessive thirst 3. Polyphagia excessive hunger
89 Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
90 Pineal Gland (1 hormone) Neural stimuli Thymus (1 hormone) Humoral stimuli Gonads (endocrine function same as adrenal cortex) Testes (1 group, 1 main hormone) Ovaries (2 groups) Placenta (3 hormones) HW: Read / Take notes from text p Study all glands and hormones. Complete WB , 189
91 Figure 9.3 Location of the major endocrine organs of the body. Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Thymus Adrenal glands Pancreas Ovary (female) Testis (male) 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
92 Pineal Gland Located in the middle of the brain Stimulated by light Secretes melatonin Helps establish the body s sleep/wake cycles Establishes biological rhythms Coordinates fertility hormones in humans
93 Circadian Rhythms
94 Thymus Gland Located posterior to the sternum Largest in infants and children Produces thymosin Matures some types of white blood cells Important in developing the immune system
95 Gonads Ovaries Produce eggs Produce two groups of steroid hormones: 1. Estrogens 2. Progesterone Testes Produce sperm Produce androgens Ex. testosterone
96 Hormones of the Ovaries Estrogens Development of secondary female characteristics Mature female reproductive organs Progesterone Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus Helps prepare breasts for lactation In combination, progesterone and estrogens Promote breast development Regulate menstrual cycle
97 Hormones of the Testes Produce several androgens Testosterone is the most important androgen Responsible for male secondary sex characteristics Promotes growth Promotes maturation of male reproductive system Required for sperm cell production
98 Testosterone levels Optimal vs. Low (exaggerated illustration)
99 Placenta Hormones maintain pregnancy Progesterone hcg (human chorionic gonadotropin) Estrogen Some hormones help during childbirth
100 Endocrine System Videos as Review Endocrine System Video Support Hormone song Watch the following videos to review the endocrine system, hormones and gland functions. CC Endocrine system part 1 A&P CC Endocrine system part 2 A&P CC Endocrine system Biology
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
BIOLOGY. CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition. Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor. CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation
 BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Intro to the Endocrine System Chief Complaint:8-year-old girl with excessive thirst, frequent
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Intro to the Endocrine System Chief Complaint:8-year-old girl with excessive thirst, frequent
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
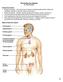 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Endocrine Control. Chapter 35
 Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books)
 Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Art labeling Activity: Figure 16.1
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
