Improving the Results Obtained with Current Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices
|
|
|
- Barnaby Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Improving the Results Obtained with Current Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices MICHAEL S. BURNHILL, M.D., and CHARLES H. BIRNBERG, M.D. CAREFUL EXAMINATION of many of the clinical studies on the use of IUD's reveals a primary concern with the detailed analysis of results obtained from the programs. It is extremely difficult to find criteria for organizing a program, or teaching individual physicians to insert IUD's. The purpose of this presentation is to outline criteria for the selection of patients in whom an IUD is to be inserted, for the timing of the insertion, and for the management of side effects and complications. A simple, safe technic of insertion, as well as several pointers in the handling of the devices and instruments, will be discussed. TIMING, CONTRAINDICATIONS, AND SELECTION OF PATIENTS Timing of Insertion The importance of careful timing of the insertion of an IUD lies in two areas. One must be careful that the patient is not pregnant when the device is inserted. Only intramenstrual insertions can eliminate the occasional insertion into a pregnant uterus. No history of a last menses can be relied upon! lntramenstrual insertions are also less traumatic as the cervix is somewhat dilated and the side effects, such as bleeding, are masked by the menstrual flow. The other area requiring attention pertains to insertions in the puerperium. Immediate postpartum and postabortional insertions appear to be safe, although early postpartum insertions ( 3-7 weeks) are prone to end in uterine perforation. There is a great deal of difficulty in picking a safe time to insert devices, because of the various expediencies necessary in managing a large program. It is extremely important that the person inserting the device be made aware of the problems encountered in the course of inserting devices too soon postpartum, or inserting devices into an enlarged uterus. There is greater risk involved in the insertion of devices from 5 to 9 weeks post- 232
2 VoL. 20, No.2, 1969 IMPROVING IUD RESULTS 233 partum. At first impression the patulousness of the cervical canal would appear to make the insertion simple. However, patulousness is associated with an extremely soft myometrium that facilitates perforation in the flexed uterus. The optimum time of insertion is after full involution has occurred postpartum, and during the menstrual period. Contraindications to Insertion Two absolute contraindications to insertion of an IUD are: ( 1) intrauterine pregnancy, and ( 2) acute or subacute pelvic inflammatory disease, whether of tubal, cervical, or endometrial origin (particularly with a history of recent septic abortion). Relative contraindications include the following: 1. A history of gynecologic disease, such as abnormal menses, pelvic pain, genital tumors, or genital tract malignancy 2. Fibromyomas of the uterus, especially if distortion of the uterine cavity is present, or there is a history of menstrual abnormalities 3. Bicornuate or septate uteri 4. Anxiety syndromes or other emotional problems that may be aggravated by the presence of, or side effects from, an IUD 5. Extreme distortions of cervico-uterine anatomy, such as cervical stenosis or fixed, marked, ante-, or retroflexion of the uterus Selection of Patients If the woman has no historical or current contraindications to the insertion of an IUD, a careful pelvic examination should be done to determine if there are any factors that would predispose the patient to uterine perforation or poor results from the IUD. These include: 1. Extreme anteflexion or retroflexion, especially if the uterus does not move with cervical traction 2. Fixed, marked anteversion or retroversion 3. Cervical stenosis or irregular scarring of the cervical canal 4. An enlarged uterus, especially if softened or very irregular in shape 5. Cervical andjor uterine hypoplasia (In general if the cervix is less than ~' in. in circumference andjor the uterus sounds less than 2 in., an IUD cannot be tolerated (though you may be able to insert one) 6. Marked cervical deformities, such as extensive irregular lacerations, or history of repeated midtrimester abortions producing an incompetent cervical os. 7. A hyperinvoluted softened uterus, as seen in lactating women
3 234 BuRNHILL & BIRNBERG FERTILITY & STERILITY TECHNIC OF INSERTING AN IUD Figure 1 shows in schematic fashion the steps to be followed during the insertion of an IUD. Though the device shown is a bow, we strongly urge that a similar technic be employed for the insertion of any IUD. As can be seen from the diagrams, the safe insertion of an IUD requires fixation of the cervix with a tenaculum. This allows traction to be used during the procedure and eliminates most of the difficulties produced by malpositioning of the uterus, such as severe ante- or retroversion. We have found the White tonsil-seizing forcep or the Teale clamp to be the best instruments for this purpose. The teeth of these instruments are similar to those found in an Allis clamp. Much less bleeding and discomfort are encountered when these instruments are used. As can be seen from Fig. 1, a sound is used prior to the introduction of the inserter. This enables one to know the depth and direction of the uterus and gives some indication of whether any problems will be encountered during the insertion of the IUD, such as a tight cervical canal. The use of an appropriately sized dilator is recommended. This assures one that the introducer can be properly placed in the cavity. If difficulty is encountered during the insertion of the dilator, a smaller dilator should be inserted and left in place for a minute. Then the large dilator can usually be inserted. The inserter used for the bow employs a combination plastic sounddilator for its plunger. This instrument affords a simple way of ascertaining the depth of the endometrial cavity and the size of the cervical canal. The dilator end measures 23~ in. If the entire dilator tip fits into the cervicouterine cavity then it is generally possible to insert a large-size device (such as the standard bow or Loop C or D). If more than 3~ in. of the dilator protrudes, no device will be well tolerated. When the inserter is introduced into the cervical canal, care should be taken to inspect the plane in which the device has been loaded into the introducer. The position of the depth stop is of no value since the device can be at right angles to a horizontal stop (as with the loop inserter). The device must fold in the same plane as the uterus and not at right angles to the uterine cavity. Looking at the inserter at the time of introduction will prevent introduction of an IUD in the wrong plane. At the bottom of Fig. 1 are shown several positions that an IUD can assume within the endometrial cavity. As long as no part of the device straddles the cervico-isthmic junction the orientation of the IUD is of no great importance.
4 VoL. 20, No.2, 1969 IMPROVING IUD RESULTS 235 EQUIPMENT NEEEDED FOR INSERTING AN IUD. Tenaculum Scissors 8 Transverse Fig. 1. Technic for introducing new bow. Steps are: (1) careful bimanual examination; (2) visualization of cervix and traction with tenaculum; (3) sounding uterus; ( 4) dilating cervix (choose proper size of device; if dilator tip protrudes, use junior device); (5) inserting loaded introducer slowly and gently expelling bow (make sure device is in same plane as endometrial cavity); ( 11) removing plunger (wait 30 sec. for bow to resume shape); ( 7) removing introducer (use dilator to seat device, and trim tail to~ in. Final position of bow within endometrial cavity (8) may be vertical, transverse, or oblique.
5 236 BURNHILL & BIRNBERG FERTILITY & STERILITY SPECIAL POINTS ABOUT INSERTION At this point something should be said about the characteristics of the plastic IUD's. None of the plastic IUD's can be boiled. Their ability to return to their original design (their "memory") after placement in an introducer is impaired. The longer a device is left in the tube, the poorer will be its ability to remember its original shape. This is particularly true for the loop, which has a poorer recall than the bow. The devices should be loaded as close as possible to the time of insertion. If possible, no more than 5 min. should elapse between the loading and the introduction of the device. This same loss of memory makes it extremely important to seat the device in the endometrial cavity following its placement in the uterus. This is of special importance in the case of the loop. There is a propensity for the terminal filament of the loop to remain straightened in the upper cervical canal. This can occur whenever the cervical canal is lengthened. One can seat the device by pushing it into the uterine cavity, using a dilator or if necessary the inserter itself. This maneuver can be safely and successfully carried out only if countertraction is being applied to the cervix by a tenaculum. Aside from reducing the expulsion rate and side-effect rate, seating the device assures the physician that the IUD is in the cavity. It is also of great importance to understand that little or no force is needed to insert an introducer and to eject an IUD into the endometrial cavity. Should difficulty be encountered, the ejection should be halted and the initial steps of sounding and dilating repeated to ascertain the source of the difficulty. This should be emphasized, especially if paramedical personnel are involved in IUD programs. Where difficulties are encountered during the insertion the procedure should be stopped. Paramedical personnel should consult the physician in charge of the clinic and if none is available the insertion should be abandoned. A cardinal principle for success with an IUD program is the screeningout of unsuitable candidates and the avoidance of inserting IUD's where any difficulty is encountered. The few additional insertions obtained by relaxing the standards are far outweighed by the poor results obtained, and by the negative effect on the entire program produced by a group of dissatisfied users. THE HANDLING OF SIDE EFFECTS AND COMPLICATIONS Advising the Patient The results obtained with IUD' s can be improved if the patient is given some advice as to what to expect after the insertion of the device. She should be advised:
6 VoL.20,No.2,1969 IMPROVING IUD RESULTS To ignore spotting for the first 3 months after the insertion, as well as other minor menstrual abnormalities 2. To examine her napkins during the period to locate an expelled device 3. To come in for an examination in the event of heavy vaginal bleeding, severe pelvic pain, pelvic infection, or an expulsion 4. To use an additional type of contraception if she has expelled the device or has had extremely heavy menstrual bleeding 5. To avoid checking for the tail of the device, as it may be extremely difficult, if not impossible, to palpate 6. To return for a check-up after 2 menses Side Effects Spotting. The patient should be reassured that spotting is of little importance and will generally disappear. She may benefit from Vitamin C, 500 mg. 1-4 times daily. Menorrhagia. Several heavy periods may be expected if the IUD was slightly larger than the endometrial cavity, and a period of adaptation is required. However, a menstrual How that soaks through a double napkin in less than an hour is of some consequence. This will occur if the device is too large for the cavity. Adaptation cannot occur and it is necessary to shift to a smaller device, such as Loop A for Loop D, or the junior bow for the standard bow. Another cause for menorrhagia is partial expulsion of the IUD with the device straddling the cervico-isthmic junction. This can be handled by removing the device and placing it higher in the endometrial cavity. Mild menorrhagia can frequently be managed with oral vasoconstrictors such as Sudafed, * 60 mg. every 4 hr., Ornadet spansules, 1 capsule every 8 hr., andjor Vitamin C, 1000 mg. 4 times a day. If all of this is of no avail, the IUD should be removed and another method of contraception suggested. Pain. Mild pain (pelvic, back, menstrual, or ovulatory) can be alleviated with aspirin or other analgesics. Severe pain, particularly a persistent low backache, indicates that the device is stimulating the cervico-isthmic junction. Replacing a large device with a smaller one, or replacing a device that is straddling the cervico-isthmic junction should alleviate discomfort. Vaginal Discharge. Since IUD's stimulate ovulation there is frequently a tendency to note increased midcycle discharge. Any discharge associated with either an odor or a color should be specifically investigated and treated *Burroughs Wellcome & Co., Inc., Tuckahoe, N.Y. tsmith, Kline & French Laboratories, Philadelphia, Pa.
7 238 BuRNHILL & BIRNBERG FERTILITY & STERILITY with appropriate medicaments if monilial or trichomonal in origin. The use of tampons, particularly in the presence of a tailed device, is an invitation to cervicitis andjor endometritis. Nonspecific persistent leukorrhea associated with the use of a tailed IUD can frequently be cured by removing the device and reinserting one without a tail. Delayed Menses. A persistent corpus luteum or follicle cystosis is occasionally the cause of delayed menses. The patient should be advised to wait a week. If she has still not menstruated a trial of hormonally induced withdrawal bleeding may be attempted. The immunologic KL appears to have a high percentage of false positives with this condition; therefore, a biologic pregnancy test is preferable. Other Side Effects. In general, side effects produced by the introduction of too large a device can be handled by replacing the large device with a smaller one. We have found that about half of the women complaining of either menorrhagia or uterine discomfort following the introduction of a standard bow can be relieved by substituting a junior bow. A chronic expeller can best be handled by inserting a device of different design-i.e., inserting a standard bow when Loop D has been expelled. Acute pelvic infection can best be handled by use of the appropriate antibiotic. We have noted that it may be necessary to remove the device if the infection does not respond rapidly to antibiotics. This is especially true if there is any suspicion of recent septic abortion. The development of side effects some time after the insertion of a device should alert one to the possibility of a smoldering endometritis. This illness begins with either the appearance of spotting, menometrorrhagia, or malodorous vaginal discharge, or bloating and lower abdominal discomfort at any time during the menstrual cycle. Pelvic examination confirms the malodorous discharge, the presence of leukocytes without monilia or trichomonads, and frequently the presence of a foul-smelling agglutinate on the protruding tail of the device. Recently we embarked on a study of the effect of the tail of the IUD on the development of delayed endocervicitis or endometritis. Though this study is in its early stages we are reasonably sure that the addition of a tail has resulted in the development of a genital tract infection in about a fourth of our patients. This tendency appears to be exaggerated in those women who are consistent tampon users. Therapy consists of local medicaments, douching, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and forbidding the use of tampons. Should this therapy fail or the condition recur, the IUD should be removed and cultured. After treatment with the appropriate antibiotic, a reinsertion of a tailless device can be tried after several normal periods have occurred.
8 VoL. 20, No.2, 1969 IMPROVING IUD RESULTS 239 Complications Pregnancy. The patient should be reassured that the presence of the device will not injure the developing fetus. The increased incidence of abortion noted in pregnancies occurring in patients who have an IUD in situ may be induced. There is little doubt that removal of an IUD in the first few weeks of amenorrhea is associated with a very high incidence of abortion. An ectopic pregnancy should be considered in the presence of pain andjor an adnexal mass. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. Acute rapidly fulminating pelvic inflammatory disease or an exacerbation of chronic pelvic inflammatory disease may occur any time after the insertion of a device (though it usually occurs soon after insertion). A tailless device may be left in situ while the patient is treated with the appropriate antibiotics. A tailed device is best removed during treatment. A second occurrence of pelvic inflammatory disease with an IUD in position is generally sufficient reason to remove the IUD permanently. Perforation. Perforations may occur, usually during the insertion of the IUD, particularly in the early puerperium, during lactation, or with a severely flexed uterus. The perforation itself is usually asymptomatic. Frequently the ectopic device is detected only after the patient becomes pregnant, or if she requests removal of the device. The patient should be advised of a perforation as soon as it is detected. A closed device should be removed through either a colpotomy or laparotomy. Open devices appear to be much more benign if left in the peritoneal cavity, since there is no risk of intestinal obstruction. However, some intra-abdominal problems have been reported following perforations with open devices, and the devices are probably best removed if the patient's physical condition permits an operation. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Careful training of the personnel involved with the insertion of IUD's, and the observance of strict criteria for the insertion of the devices, will improve the results being obtained from present national family-planning programs. Particular attention should be given to the dangers of insertion in the early puerperium and during lactation. It is of great importance to develop a consistent ritual for safely inserting devices. This includes a careful history, a bimanual examination, traction on the cervix with a tenaculum, sounding of the uterus, use of a dilator to measure the size of the cervical canal and the depth of the endometrial cavity, slow and gentle insertion of the introducer and expulsion of the
9 240 BuRNHILL & BIRNBERG FERTILITY & STERILITY IUD, and finally, seating of the device to be sure of its placement in the endometrial cavity. The methods outlined for handling the side effects and complications following the use of IUD' s are designed to decrease removal rates. Fewer but better-done insertions on properly selected women may greatly improve the results obtained from an IUD program. 191 Ocean Ave. Brooklyn, N. Y
Example CLINICAL GUIDELINES for Postpartum IUD insertion
 Example CLINICAL GUIDELINES for Postpartum IUD insertion Postpartum Intrauterine Device Insertion 1.0 Indications: 1.1 Insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD) for long-acting reversible contraception
Example CLINICAL GUIDELINES for Postpartum IUD insertion Postpartum Intrauterine Device Insertion 1.0 Indications: 1.1 Insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD) for long-acting reversible contraception
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
Product Information. Confidence that lasts
 Confidence that lasts What is Mirena? Inhibition of sperm motility and function inside the uterus and the fallopian tubes, preventing fertilization (Videla-Rivero et al. 1987). Section of system Levonorgestrel
Confidence that lasts What is Mirena? Inhibition of sperm motility and function inside the uterus and the fallopian tubes, preventing fertilization (Videla-Rivero et al. 1987). Section of system Levonorgestrel
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD
 Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
What s New in Adolescent Contraception?
 What s New in Adolescent Contraception? Abby Furukawa, MD Legacy Medical Group Portland Obstetrics and Gynecology April 29, 2017 Objectives Provide an update on contraception options for the adolescent
What s New in Adolescent Contraception? Abby Furukawa, MD Legacy Medical Group Portland Obstetrics and Gynecology April 29, 2017 Objectives Provide an update on contraception options for the adolescent
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
Examining Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptive Methods
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/examining-long-acting-reversible-contraceptivemethods/7078/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/examining-long-acting-reversible-contraceptivemethods/7078/
Application for inclusion of levonorgestrel - releasing IUD for contraception in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines
 Application for inclusion of levonorgestrel - releasing IUD for contraception in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 1. Summary statement of the proposal for inclusion LNG-IUS is an effective contraceptive;
Application for inclusion of levonorgestrel - releasing IUD for contraception in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 1. Summary statement of the proposal for inclusion LNG-IUS is an effective contraceptive;
Family Planning UNMET NEED. The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows
 Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
Bursting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
 www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
Jadelle Contraceptive Implants up to 5 years Insertion and Removal
 Contraceptive Implants up to 5 years Bayer AG Global HealthCare Programs Family Planning 13342 Berlin, Germany www.bayer.com September 2017 Global HealthCare Programs Family Planning Contraceptive Independence»»
Contraceptive Implants up to 5 years Bayer AG Global HealthCare Programs Family Planning 13342 Berlin, Germany www.bayer.com September 2017 Global HealthCare Programs Family Planning Contraceptive Independence»»
Bursting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
 www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
Gynaecology. Pelvic inflammatory disesase
 Gynaecology د.شيماءعبداألميرالجميلي Pelvic inflammatory disesase Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is usually the result of infection ascending from the endocervix causing endometritis, salpingitis, parametritis,
Gynaecology د.شيماءعبداألميرالجميلي Pelvic inflammatory disesase Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is usually the result of infection ascending from the endocervix causing endometritis, salpingitis, parametritis,
1. Ortiz, M. E et al. Mechanisms of action of intrauterine devices. Obstet & Gynl Survey 1996; 51(12), 42S-51S.
 1 2 1. Ortiz, M. E et al. Mechanisms of action of intrauterine devices. Obstet & Gynl Survey 1996; 51(12), 42S-51S. The contraceptive action of all IUDs is mainly in the uterine cavity. The major effect
1 2 1. Ortiz, M. E et al. Mechanisms of action of intrauterine devices. Obstet & Gynl Survey 1996; 51(12), 42S-51S. The contraceptive action of all IUDs is mainly in the uterine cavity. The major effect
ParaGard T 380A INTRAUTERINE COPPER CONTRACEPTIVE PRESCRIBING INFORMATION DESCRIPTION CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY INDICATIONS AND USAGE CONTRAINDICATIONS
 % of Women Experiencing an Accidental Pregnancy within the First Year of Use % of Women Continuing Use at One Year Method (1) Typical Use 1 (2) Perfect Use 2 () (4) ParaGard T 80A INTRAUTERINE COPPER CONTRACEPTIVE
% of Women Experiencing an Accidental Pregnancy within the First Year of Use % of Women Continuing Use at One Year Method (1) Typical Use 1 (2) Perfect Use 2 () (4) ParaGard T 80A INTRAUTERINE COPPER CONTRACEPTIVE
LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraception. Distribution Of Contraception Use By Women In The Us. Unintended Pregnancy is Common
 4:15 5 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
4:15 5 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage:
 Review Article ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com A REVIEW ON INTRAUTERINE DEVICES Boddu Venkata Komali* 1, M. Kalyani
Review Article ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com A REVIEW ON INTRAUTERINE DEVICES Boddu Venkata Komali* 1, M. Kalyani
Welcome to Mirena. The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena. mirena.com. Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S.
 Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S. Welcome to Mirena The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena *Intrauterine Device Supported by 2015-2016 SHS data INDICATIONS FOR MIRENA Mirena
Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S. Welcome to Mirena The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena *Intrauterine Device Supported by 2015-2016 SHS data INDICATIONS FOR MIRENA Mirena
Levonorgestrel Intrauterine Device
 CHAPTER 11 Levonorgestrel Intrauterine Device Key Points for Providers and Clients y Long-term pregnancy protection. Very effective for 5 years, immediately reversible. yinserted into the uterus by a specifically
CHAPTER 11 Levonorgestrel Intrauterine Device Key Points for Providers and Clients y Long-term pregnancy protection. Very effective for 5 years, immediately reversible. yinserted into the uterus by a specifically
LIVE PLACEMENT TRAINING WEBCAST
 REGISTER FOR A LIVE PLACEMENT TRAINING WEBCAST Join us for a training webcast led by an expert speaker who brings extensive background in women s health. On this webcast, you can: Learn the steps for PARAGARD
REGISTER FOR A LIVE PLACEMENT TRAINING WEBCAST Join us for a training webcast led by an expert speaker who brings extensive background in women s health. On this webcast, you can: Learn the steps for PARAGARD
Unintended Pregnancy is Common LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Distribution Of Contraception Use By Women In The Us. Unintended Pregnancy And Contraceptive Use
 3:45 4:30 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
3:45 4:30 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
Frequency of menses. Duration of menses 3 days to 7 days. Flow/amount of menses Average blood loss with menstruation is 60-80cc.
 Frequency of menses 24 days (0.5%) to 35 days (0.9%) Age 25, 40% are between 25 and 28 days Age 25-35, 60% are between 25 and 28 days Teens and women over 40 s cycles may be longer apart Duration of menses
Frequency of menses 24 days (0.5%) to 35 days (0.9%) Age 25, 40% are between 25 and 28 days Age 25-35, 60% are between 25 and 28 days Teens and women over 40 s cycles may be longer apart Duration of menses
VirtaMed GynoS hysteroscopy Module descriptions
 VirtaMed GynoS hysteroscopy Module descriptions VirtaMed AG Rütistr. 12, 8952 Zurich Switzerland info@virtamed.com www.virtamed.com Phone: +41 44 500 9690 Table of contents Table of contents... 1 Essential
VirtaMed GynoS hysteroscopy Module descriptions VirtaMed AG Rütistr. 12, 8952 Zurich Switzerland info@virtamed.com www.virtamed.com Phone: +41 44 500 9690 Table of contents Table of contents... 1 Essential
Acute Salpingitis. Fallopian Tubes. Uterus
 Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTION. Summary Tables
 LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTION Summary Tables Bridging the Divide: A Project of the Jacobs Institute of Women s Health June 2016 Table 1. Summary of LARC Methods Available Years Since Effective Copper
LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTION Summary Tables Bridging the Divide: A Project of the Jacobs Institute of Women s Health June 2016 Table 1. Summary of LARC Methods Available Years Since Effective Copper
Family Planning and Infertility
 Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
The use of long-acting reversible contraceptive
 Overcoming LARC complications: 7 case challenges The strings to your patient s intrauterine device (IUD) are missing. Clinical experience and ACOG direction guide the management plans for this and more
Overcoming LARC complications: 7 case challenges The strings to your patient s intrauterine device (IUD) are missing. Clinical experience and ACOG direction guide the management plans for this and more
Essure By Mayo Clinic staff
 Page 1 of 5 Reprints A single copy of this article may be reprinted for personal, noncommercial use only. Essure By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/essure/my00999 Definition
Page 1 of 5 Reprints A single copy of this article may be reprinted for personal, noncommercial use only. Essure By Mayo Clinic staff Original Article: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/essure/my00999 Definition
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion
 Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Treatment of Cervical Precancerous Lesions using Thermocoagulation(Cold Coagulation) and Cryotherapy General Principles All high grade CIN should be
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Treatment of Cervical Precancerous Lesions using Thermocoagulation(Cold Coagulation) and Cryotherapy General Principles All high grade CIN should be
maybe it s time to With Your Current And move on to 100% hormone free, more than 99% effective Paragard (intrauterine copper contraceptive) IUD.
 maybe it s time to With Your Current And move on to 100% hormone free, more than 99% effective Paragard (intrauterine copper contraceptive) IUD. thinking about ParaGard (INTRAUTERINE COPPER CONTRACEPTIVE)?
maybe it s time to With Your Current And move on to 100% hormone free, more than 99% effective Paragard (intrauterine copper contraceptive) IUD. thinking about ParaGard (INTRAUTERINE COPPER CONTRACEPTIVE)?
THE WOMAN-FRIENDLY STERILIZATION METHOD
 THE WOMAN-FRIENDLY STERILIZATION METHOD Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE MOST WOMAN-FRIENDLY STERILIZATION METHOD
THE WOMAN-FRIENDLY STERILIZATION METHOD Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE MOST WOMAN-FRIENDLY STERILIZATION METHOD
HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF INFERTILITY (STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF 3437 CASES)
 FERTILITY AND STERIUTY Copyright 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 2:3, ~o. 11, November 1972 Printed in U.S.A. HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF INFERTILITY (STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF 337
FERTILITY AND STERIUTY Copyright 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 2:3, ~o. 11, November 1972 Printed in U.S.A. HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF INFERTILITY (STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF 337
ESSURE A RESOURCE FOR CODING
 ESSURE REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE A RESOURCE FOR CODING INDICATION Essure is indicated for women who desire permanent birth control (female sterilization) by bilateral occlusion of fallopian tubes. IMPORTANT
ESSURE REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE A RESOURCE FOR CODING INDICATION Essure is indicated for women who desire permanent birth control (female sterilization) by bilateral occlusion of fallopian tubes. IMPORTANT
Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders
 Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders Episode Overview: 1. Describe the presentation and RF for Adnexal torsion 2. List the imaging findings of adnexal torsion (US vs CT) 3. What is the management of adnexal
Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders Episode Overview: 1. Describe the presentation and RF for Adnexal torsion 2. List the imaging findings of adnexal torsion (US vs CT) 3. What is the management of adnexal
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that
 The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES?
 CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
IS PARAGARD RIGHT FOR YOU?
 IS PARAGARD RIGHT FOR YOU? Ask your doctor about the only reversible birth control that s more than % effective and 100% hormone free. What to Tell your Doctor How you feel about hormones How you feel
IS PARAGARD RIGHT FOR YOU? Ask your doctor about the only reversible birth control that s more than % effective and 100% hormone free. What to Tell your Doctor How you feel about hormones How you feel
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
Example Clinical Guideline for Immediate Postpartum LARC Insertion
 Example Clinical Guideline for Immediate Postpartum LARC Insertion RATIONALE Delay in contraceptive provision until the six week postpartum appointment can leave some women at risk for rapid repeat pregnancy.
Example Clinical Guideline for Immediate Postpartum LARC Insertion RATIONALE Delay in contraceptive provision until the six week postpartum appointment can leave some women at risk for rapid repeat pregnancy.
Transcervical Sterilization
 Q UESTIONS & ANSWERS A BOUT Transcervical Sterilization A New Choice in Permanent Birth Control Choosing a Birth Control Method Women and their partners now have more birth control choices than ever. How
Q UESTIONS & ANSWERS A BOUT Transcervical Sterilization A New Choice in Permanent Birth Control Choosing a Birth Control Method Women and their partners now have more birth control choices than ever. How
Question Bank III - BHMS
 Question Bank III - BHMS Sub:- Ob/Gy -Paper-II 1. Give the definition of Puberty. 2. Enumerate five important physical changes evident during puberty. 3. Write down the vaginal changes during puberty.
Question Bank III - BHMS Sub:- Ob/Gy -Paper-II 1. Give the definition of Puberty. 2. Enumerate five important physical changes evident during puberty. 3. Write down the vaginal changes during puberty.
17. Preventing pregnancy
 17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
For more information, visit us online at PARAGARDAccessSolutions.com. To speak with a representative call PARAGARD ( ).
 Improve patient access with PARAGARD Access Solutions TM A comprehensive range of support services and resources designed to make access easier for your patients who choose PARAGARD. PARAGARD Direct is
Improve patient access with PARAGARD Access Solutions TM A comprehensive range of support services and resources designed to make access easier for your patients who choose PARAGARD. PARAGARD Direct is
Types of Hysterectomy for Non-cancerous Conditions: Understanding Your Doctor s Recommendations
 Types of Hysterectomy for Non-cancerous Conditions: Understanding Your Doctor s Recommendations Who can benefit from this information? The decision to have a hysterectomy is one of the many important decisions
Types of Hysterectomy for Non-cancerous Conditions: Understanding Your Doctor s Recommendations Who can benefit from this information? The decision to have a hysterectomy is one of the many important decisions
The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings.
 The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings Counseling Cards Checklist to be reasonably sure a woman is not pregnant
The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings Counseling Cards Checklist to be reasonably sure a woman is not pregnant
In vitro fertilization outcome relative to embryo transfer difficulty: a novel approach to the forbidding cervix
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 72, NO. 2, AUGUST 1999 Copyright 1999 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. In vitro fertilization
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 72, NO. 2, AUGUST 1999 Copyright 1999 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. In vitro fertilization
INTRAUTERINE DEVICES AND INFECTIONS. Tips for Evaluation and Management
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICES AND INFECTIONS Tips for Evaluation and Management Objectives At the end of this presentation, the participant should be able to: 1. Diagnose infection after IUD placement 2. Provide
INTRAUTERINE DEVICES AND INFECTIONS Tips for Evaluation and Management Objectives At the end of this presentation, the participant should be able to: 1. Diagnose infection after IUD placement 2. Provide
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. Pr MIRENA. Levonorgestrel-releasing Intrauterine System (52 mg) to deliver. up to 20 mcg levonorgestrel per day.
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Pr MIRENA Levonorgestrel-releasing Intrauterine System (52 mg) to deliver up to 20 mcg levonorgestrel per day Progestogen Bayer Inc. 2920 Matheson Blvd East Mississauga, Ontario L4W 5R6
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Pr MIRENA Levonorgestrel-releasing Intrauterine System (52 mg) to deliver up to 20 mcg levonorgestrel per day Progestogen Bayer Inc. 2920 Matheson Blvd East Mississauga, Ontario L4W 5R6
Levosert levonorgestrel 20mcg/24hour intrauterine device
 Levosert levonorgestrel 20mcg/24hour intrauterine device Verdict: Formulary inclusion: Formulary category: Restrictions: Reason for inclusion: Link to formulary: Link to medicine review summary: Levosert
Levosert levonorgestrel 20mcg/24hour intrauterine device Verdict: Formulary inclusion: Formulary category: Restrictions: Reason for inclusion: Link to formulary: Link to medicine review summary: Levosert
Fitting of an Intrauterine Device (IUD)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an IUD? An IUD is a small T-shaped plastic and copper device that is put into
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an IUD? An IUD is a small T-shaped plastic and copper device that is put into
Female Sterilization. Kavita Nanda, MD, MHS FHI 360 Expanding Contraceptive Choice December 6, 2018
 Female Sterilization Kavita Nanda, MD, MHS FHI 360 Expanding Contraceptive Choice December 6, 2018 What is female sterilization? Family planning method that provides permanent contraception to women and
Female Sterilization Kavita Nanda, MD, MHS FHI 360 Expanding Contraceptive Choice December 6, 2018 What is female sterilization? Family planning method that provides permanent contraception to women and
Hydrotuhation. Separate Examination of the Patency of Each Tube with Isotonic Saline Solution. Hideo Yagi, M.D.
 Hydrotuhation Separate Examination of the Patency of Each Tube with sotonic Saline Solution Hideo Yagi M.D. HYDROTUBATON is a tenn which introduced in 1929 to describe a new technic for diagnosing patency
Hydrotuhation Separate Examination of the Patency of Each Tube with sotonic Saline Solution Hideo Yagi M.D. HYDROTUBATON is a tenn which introduced in 1929 to describe a new technic for diagnosing patency
Birth Control- an Overview. Keith Merritt, MD. Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy
 Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Evidence Based Guideline Intrauterine Ablation or Resection of the Endometrium
 Evidence Based Guideline Intrauterine Ablation or Resection of the Endometrium File Name: intrauterine_ablation_or_resection_of_the_endometrium Guideline Number: EBG.OBGYN3030 Origination: 4/1993 Last
Evidence Based Guideline Intrauterine Ablation or Resection of the Endometrium File Name: intrauterine_ablation_or_resection_of_the_endometrium Guideline Number: EBG.OBGYN3030 Origination: 4/1993 Last
One Thousand Cases of Infertility
 One Thousand Cases of Infertility Clinical Review of a Five-Year Series Robert B. Wilson, M.D. THE RECORDS of 1032 women who complained of infertility have been reviewed. These patients were seen by various
One Thousand Cases of Infertility Clinical Review of a Five-Year Series Robert B. Wilson, M.D. THE RECORDS of 1032 women who complained of infertility have been reviewed. These patients were seen by various
Instruction for the patient
 WS 4 Case 3 STI and IUD Your situation Instruction for the patient You are 32 years old, divorced and have one child; you have just started a new relationship You underwent surgical resection of the left
WS 4 Case 3 STI and IUD Your situation Instruction for the patient You are 32 years old, divorced and have one child; you have just started a new relationship You underwent surgical resection of the left
Fertility Following Myomectomy
 Fertility Following Myomectomy FRANCIS M. INGERSOLL, M.D. MYOMECTOMY is an operation frequently indicated in both the maitied and the single woman who desires to preserve her child-bearing function. The
Fertility Following Myomectomy FRANCIS M. INGERSOLL, M.D. MYOMECTOMY is an operation frequently indicated in both the maitied and the single woman who desires to preserve her child-bearing function. The
Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle?
 Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle? Introduction: The menstrual cycle (changes within the uterus) is an approximately 28-day cycle that
Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle? Introduction: The menstrual cycle (changes within the uterus) is an approximately 28-day cycle that
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Contraceptives. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Hysteroscopy Clinic. Patient Information. Women and Children - Gynaecology
 8 Hysteroscopy Clinic Patient Information Women and Children - Gynaecology When a woman is first told that she has a gynaecological condition that requires further investigation at a specialised hospital
8 Hysteroscopy Clinic Patient Information Women and Children - Gynaecology When a woman is first told that she has a gynaecological condition that requires further investigation at a specialised hospital
100% Highly effective No cost No side effects
 effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
Contraception: I. Non-Hormonal Methods
 Contraception: I. Non-Hormonal Methods Prof. Karim Hassanein I. Abd- El-Maeboud OB/GYN Department Ain Shams University Family Planning A Branch of Reproductive Health Service (RHS). Def.: In advance regulation
Contraception: I. Non-Hormonal Methods Prof. Karim Hassanein I. Abd- El-Maeboud OB/GYN Department Ain Shams University Family Planning A Branch of Reproductive Health Service (RHS). Def.: In advance regulation
reproductive organs. Malignant neoplasms. 4. Inflammatory disorders of female reproductive organs 2 5. Infertility. Family planning.
 Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
유일하게 100% 무호르몬인 IUD( 자궁내피임장치 ) 입니다!
 PARAGARD 사용을고려중이십니까? ( 동제자궁내피임장치 ) 유일하게 100% 무호르몬인 IUD( 자궁내피임장치 ) 입니다! PARAGARD 란? PARAGARD 는자궁내에삽입되어구리를배출함으로써최대 10 년까지임신을방지하는장치입니다. 이는자궁내장치 (Intrauterine Device,IUD) 라고도불리는피임방법입니다. PARAGARD 의작용방법 PARAGARD
PARAGARD 사용을고려중이십니까? ( 동제자궁내피임장치 ) 유일하게 100% 무호르몬인 IUD( 자궁내피임장치 ) 입니다! PARAGARD 란? PARAGARD 는자궁내에삽입되어구리를배출함으로써최대 10 년까지임신을방지하는장치입니다. 이는자궁내장치 (Intrauterine Device,IUD) 라고도불리는피임방법입니다. PARAGARD 의작용방법 PARAGARD
Notes to Teacher continued Contraceptive Considerations
 Abstinence a conscious decision to refrain from sexual intercourse 100% pregnancy will not occur if close contact between the penis and vagina does not take place. The risk of a number of STDs, including
Abstinence a conscious decision to refrain from sexual intercourse 100% pregnancy will not occur if close contact between the penis and vagina does not take place. The risk of a number of STDs, including
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS. fallopian tube instead of the uterus), constant pelvic pain, and other problems.
 PID can be treated and cured with Pelvic antibiotics. If left untreated, PID can lead to serious problems like infertility (not being able to get pregnant), ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy in the Inflammatory
PID can be treated and cured with Pelvic antibiotics. If left untreated, PID can lead to serious problems like infertility (not being able to get pregnant), ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy in the Inflammatory
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID) SALIM ABDUL-RAZAK (INTERN RADIOGRAPHER) TAMALE TEACHING HOSPITAL
 PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID) SALIM ABDUL-RAZAK (INTERN RADIOGRAPHER) TAMALE TEACHING HOSPITAL OBJECTIVES Definition of PID Prevalence rate of PID Causes of PID Symptoms of PID Risk factors Investigations
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID) SALIM ABDUL-RAZAK (INTERN RADIOGRAPHER) TAMALE TEACHING HOSPITAL OBJECTIVES Definition of PID Prevalence rate of PID Causes of PID Symptoms of PID Risk factors Investigations
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
DIP.G.O. EXAMINATION 2007
 DIP.G.O. EXAMINATION 2007 GYNAECOLOGY Batch A/07 Time : 2 hrs. Question 1. a. Define Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding 10 b. What are the various terms used to describe menstrual disorder? 10 Question 2.
DIP.G.O. EXAMINATION 2007 GYNAECOLOGY Batch A/07 Time : 2 hrs. Question 1. a. Define Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding 10 b. What are the various terms used to describe menstrual disorder? 10 Question 2.
M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH
 Unrestricted M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH Patients at imminent risk of exsanguination Manual aortic compression Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta Uterine tourniquet
Unrestricted M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH Patients at imminent risk of exsanguination Manual aortic compression Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta Uterine tourniquet
Contraception and gynecological pathologies
 1 Contraception and gynecological pathologies 18 years old, 2 CMI normal First menstruation at 14 years old Irregular (every 2/3 months), painful + She does not need contraception She is worried about
1 Contraception and gynecological pathologies 18 years old, 2 CMI normal First menstruation at 14 years old Irregular (every 2/3 months), painful + She does not need contraception She is worried about
(Received 5th July 1968)
 EFFECT OF AN INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE ON CONCEPTION AND OVULATION IN THE RHESUS MONKEY W. A. KELLY, J. H. MARSTON and P. ECKSTEIN Department of Anatomy, Medical School, Birmingham 15 (Received 5th July 1968)
EFFECT OF AN INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE ON CONCEPTION AND OVULATION IN THE RHESUS MONKEY W. A. KELLY, J. H. MARSTON and P. ECKSTEIN Department of Anatomy, Medical School, Birmingham 15 (Received 5th July 1968)
Laparoscopy-Hysteroscopy
 Laparoscopy-Hysteroscopy Patient Information Laparoscopy The laparoscope, a surgical instrument similar to a telescope, is inserted through a small incision (cut) in the belly button during laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy-Hysteroscopy Patient Information Laparoscopy The laparoscope, a surgical instrument similar to a telescope, is inserted through a small incision (cut) in the belly button during laparoscopy.
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
FERTILITY & TCM. On line course provided by. Taught by Clara Cohen
 FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
Sexual differentiation:
 Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
Abnormal Development of Female Genitalia Dr. Maryam Fetal development of gonads, external genitalia, Mullerian ducts and Wolffian ducts can be disrupted at a variety of points, leading to a wide range
JHPIEGO. IUD Training Site Assessment for Key Social Marketing Project, Pakistan
 JHPIEGO IUD Training Site Assessment for Key Social Marketing Project, Pakistan The development and use of objective and measurable performance standards are essential factors in improving job performance.
JHPIEGO IUD Training Site Assessment for Key Social Marketing Project, Pakistan The development and use of objective and measurable performance standards are essential factors in improving job performance.
38 OBG Management August 2012 Vol. 24 No. 8 obgmanagement.com
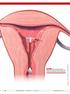 FIGURE 1 Copper intrauterine device displaced in the lower uterine segment with the left arm embedded in the myometrium. illustrations: craig zuckerman for obg management 38 OBG Management August 2012
FIGURE 1 Copper intrauterine device displaced in the lower uterine segment with the left arm embedded in the myometrium. illustrations: craig zuckerman for obg management 38 OBG Management August 2012
Review of IUCD Complications: Lessons from CAT. Dr FG Mhlanga CAT Meeting 24 September 2016
 Review of IUCD Complications: Lessons from CAT Dr FG Mhlanga CAT Meeting 24 September 2016 INTRODUCTION The intrauterine device (IUD) is a reliable long term reversible, cost-effective,easy to use and
Review of IUCD Complications: Lessons from CAT Dr FG Mhlanga CAT Meeting 24 September 2016 INTRODUCTION The intrauterine device (IUD) is a reliable long term reversible, cost-effective,easy to use and
GLOBAL ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY
 GLOBAL ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY Training: Part 1 Anatomy and Physiology Female Anatomy Normal Uterus Female Anatomy Normal Uterus Female Anatomy Uterine Positions Abnormal Uterus Retroflexed Normal
GLOBAL ENDOMETRIAL ABLATION TECHNOLOGY Training: Part 1 Anatomy and Physiology Female Anatomy Normal Uterus Female Anatomy Normal Uterus Female Anatomy Uterine Positions Abnormal Uterus Retroflexed Normal
Safety, Efficacy, and Patient Acceptability of the Copper T-380A Intrauterine Contraceptive Device
 Clinical Medicine Insights: Women s Health Review Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Safety, Efficacy, and Patient Acceptability of the Copper
Clinical Medicine Insights: Women s Health Review Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Safety, Efficacy, and Patient Acceptability of the Copper
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Information leaflet on. Laparoscopic Treatment of Endometriosis
 Information leaflet on Laparoscopic Treatment of Endometriosis 1 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition, which affects many women. It is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside
Information leaflet on Laparoscopic Treatment of Endometriosis 1 What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition, which affects many women. It is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Laparoscopy. Patient Information. Womens Health
 Laparoscopy Patient Information Womens Health What is a Laparoscopy Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive or key hole surgical procedure performed under general anaesthetic. It enables the surgeon to look
Laparoscopy Patient Information Womens Health What is a Laparoscopy Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive or key hole surgical procedure performed under general anaesthetic. It enables the surgeon to look
Contraceptive case studies. Dr Christine Roke National Medical Advisor Family Planning June 2015
 Contraceptive case studies Dr Christine Roke National Medical Advisor Family Planning June 2015 Case 1 Mary is a 47 year old who has come in for a routine cervical smear. She asks when her Multiload IUD
Contraceptive case studies Dr Christine Roke National Medical Advisor Family Planning June 2015 Case 1 Mary is a 47 year old who has come in for a routine cervical smear. She asks when her Multiload IUD
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
THE INTRA--UTERINE DEVICE
 CANADIAN CONSENSUS CONFERENCE THE INTRA--UTERINE DEVICE WHY CONSIDER THIS METHOD? Use of an IUD should be considered for all women who seek a reversible, effective, coitally-independent method of contraception.
CANADIAN CONSENSUS CONFERENCE THE INTRA--UTERINE DEVICE WHY CONSIDER THIS METHOD? Use of an IUD should be considered for all women who seek a reversible, effective, coitally-independent method of contraception.
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust
 Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Contraception. Objectives. Unintended Pregnancy. Unintended Pregnancy in the US. What s the Impact? 10/7/2014
 Contraception Tami Allen, RNC OB, MHA Robin Petersen, RN, MSN Perinatal Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Discuss the impact of unintended pregnancy in the United States Discuss the risks and benefits
Contraception Tami Allen, RNC OB, MHA Robin Petersen, RN, MSN Perinatal Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Discuss the impact of unintended pregnancy in the United States Discuss the risks and benefits
CASE 41. What is the pathophysiologic cause of her amenorrhea? Which cells in the ovary secrete estrogen?
 CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
Sperm Survival in Women. Motile Sperm in the Fundus and Tubes of Surgical Cases
 Sperm Survival in Women Motile Sperm in the Fundus and Tubes of Surgical Cases Boris B. Rubenstein, M.D., Ph.D.; Hermann Strauss, M.D.; Maurice L. Lazarus, M.D., and Henry Hankin, M.D. THE DURATION of
Sperm Survival in Women Motile Sperm in the Fundus and Tubes of Surgical Cases Boris B. Rubenstein, M.D., Ph.D.; Hermann Strauss, M.D.; Maurice L. Lazarus, M.D., and Henry Hankin, M.D. THE DURATION of
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
LARC. sample. ask brook about. Are any of them right for me? How effective is it? How long does it last? long acting reversible contraception
 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates
 University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
University Gynecologic Oncology Associates Medical History Form Date: Name: Date of Birth: / / GYNE HISTORY Age of first period? If you no longer have periods, at what age did they stop? Are you pregnant
