CT and CTA Findings in Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome
|
|
|
- Ophelia Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 6, September: , CT and CTA Findings in Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome TALAL AMER, M.D.*; REHAM ABD EL-WAHAB, M.D.*; AHMAD EL-MORSY, M.D.* and AHMED EL-METWALLY, M.D.** The Departments of Diagnostic Radiology* and Vascular Surgery**, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University Abstract Background: Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome (PAES) is an uncommon anomaly affecting young adults present with calf claudication. It is characterized by various anatomic relations between the muscle and arteries in the popliteal fossa, resulting in arterial compression. Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of CT and CT Angiography (CTA) in the diagnosis of PAES. Material and Methods: Ten patients (12 legs) who underwent surgical treatment for PAES over a 7-years period were evaluated retrospectively. CT and CTA were performed on each affected limb. Results: Characterization and classification based on CT and CTA were consistent with intraoperative results. Conclusion: CT and CTA can show anatomic variations in the popliteal fossa and may be valuable in the diagnosis of PAES in adults presenting with intermittent claudication. Key Words: CT CTA Popliteal Artery Entrapment syndrome. Introduction POPLITEAL Artery Entrapment Syndrome (PAES), despite its rarity, is the most common cause of surgically correctable lower-limb vascular insufficiency among young adults without background atherosclerosis [1]. Two distinct subtypes of PAES, (1) Anatomic and (2) Functional, have been identified [3]. The normal popliteal artery runs between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle in an oblique, medialtolateral orientation, superficial to the popliteus muscle. This normal relation is disturbed in anatomic PAES [3]. PAES occurs when the popliteal artery is compressed secondary to an abnormal relationship to the adjacent muscle and tendons. Compression of Correspondence to: Dr. Talal Amer, The Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University the popliteal artery due to the abnormal position of the adjacent structures may result in repetitive microtrauma and early atherosclerosis, leading to popliteal artery stenosis or occlusion [4]. PAES occurs bilaterally in 27-67% of patients. Several schemes have been described for classification of PAES. The most accepted classification system, proposed by Love and Whelanb [5] and modified by Rich and colleagues [6] (Table 1). Accurate diagnosis of PAES is important. Imaging techniques are necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) has long been the primary imaging technique used to diagnose PAES. Non invasive techniques such as Doppler sonography, CTA, MRI, and MR Angiography (MRA) can be used in addition to DSA. In this study, we evaluated the clinical application of CT and CTA and in the diagnosis of PAES. Table (1): Classification of Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome [7]. Type I II III IV V VI Description Medial head of gastrocnemius muscle is normal; popliteal artery is deviated medially and has an aberrant course. Medial head of gastrocnemius muscle is located laterally; no deviation of popliteal artery. Abnormal muscle bundle from medial head of gastrocnemius muscle surrounding the popliteal artery. Popliteal artery is located deeply and entrapped by the popliteus muscle or a fibrous band. Popliteal vein is also entrapped with any type of popliteal artery. Popliteal artery is normally positioned and entrapped by a normally positioned, hypertrophied gastrocnemius muscle. 2413
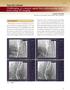
2 2414 CT & CTA Findings in Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome Material and Methods This study is a retrospective one. The CT and CTA of twelve lower limbs (ten patients) with surgically proven and CT documented popliteal artery entrapment at Mansoura University Hospital in the period from October 2007 to May 2014 were reviewed. The mean age was 41.7 years (range, 28 to 60 years). Nine of the study patient were male and one was a female. The clinical presentations were infrapopliteal claudication, rest pain and paraesthesia with symptoms worsening on exercise. The symptoms were bilateral in two of the ten patients. The duration of symptoms varied between 3 months to 5 years. No patient had any previous history of cardiovascular disease. CTA was performed on a 16-MDCT scanner (Phillips Healthcare, Netherland). Patients were placed feet-first and supine on the couch of the scanner. The patient's extremities were positioned with the knee and ankle joints in the neutral position. The scans extended from the aortoiliac superiorly to cover the lower extremity arteries down to the feet distally. The parameters were as follows: A section thickness of 3mm; gantry rotation time, 0.8 second; pitch, 1.375; X-ray tube voltage, 120kV; and the mean tube current, 250mA. Non-ionic high concentration contrast media was used and the dose was determined based on the patient weight (2mg-I/kg). Once the contrast bolus dose has been determined, injection into an antecubital vein via an 18-gauge needle at a flow rate of mL/s was done and followed by saline flush to clear the inflowing veins of contrast medium. The scanning delay was set by an automatic triggering system. Continuous low-dose fluoroscopy (120kV, 120mA) at the level of the lower abdominal aorta was initiated 10 seconds after the biginnig of the contrast material injection. After reaching the preset enhancement level of 100HU, data acquisition was performed in a craniocaudal direction. Delayed images (90-second delay from the initial time of injection) were obtained in patients with poor cardiac output or slow distal runoff. Cross sectional images were reconstructed for both limbs on a workstation with a 1.25-mm slice thickness at 0.7- mm intervals. For each patient, Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP), Multiplanar Reconstruction (MPR), and Volume Rendering (VR) were used. The soft-tissue anatomy and vascular structures around the knee were assessed on the CT cross sectional images. For a more detailed analysis MIP, MPR, and VR were used to assess the arterial tree. The CTAs were evaluated to determine the presence or absence of popliteal artery stenosis (more than 50% diameter reduction by visual estimation), occlusion, or aneurysm. Multisegmental disease or background changes of atherosclerosis were excluded in all patients. The extent of collateral circulation and filling of the distal vessels were assessed. Abnormalities in the course of the popliteal artery and femoral insertion of the gastrocnemius tendons, as well as aberrant muscle slips or fibrous bands compressing the artery, were specifically sought. Popliteal artery entrapments were classified according to modified Love- Wheelan's classification (Table 1). Fig. (1): 52-year-old male with popliteal artery entrapment syndrome of right lower extremity who presented with calf claudication. (A) Axial CT angiography image reveals lateral location of medial head of right gastrocnemius muscle (long arrow) and partial stenosis of popliteal artery consistent with type II anomaly, and caudal portion shows aneurysmal dilatation (B). Results In each patient, both popliteal arteries were well assessed. Abnormalities in the course of the artery and genicular collaterals were best demonstrated in coronal MIP and VR images. There was adequate demonstration of the soft-tissue structures in the popliteal fossa that enabled identification of the cause of entrapment in all limbs.
3 Talal Amer, et al Patient demographics and CTA findings are shown in (Table 2). Popliteal artery entrapment was bilateral in two patients (20%), and unilateral in 8 patient (80%). Type I was diagnosed in 2 limbs, type II in 4 limbs Fig. (1), type III in 4 limbs and type IV in 2 limbs according to Whelan and Rich classification. CTA images revealed stenosis of the popliteal artery in three limbs and occlusion in five limbs. Occlusion of the artery was total in three limbs Fig. (2) and partial in two limbs. Also aneurysm formation was revealed in four limbs of which three were partially thrombosed Fig. (3). Medial displacement of the popliteal artery noted in two limbs. The axial CT images of soft tissue window were carefully evaluated and showed abnormal lateral insertion of the medial head of gastrocnemius muscle in four limbs, medial displacement of popliteal artery in two limbs and aberrant accessory slip of the medial head of gastrocnemius muscle in four limbs. Hypertrophy of medial head of gastrocnemius muscle was noted in one limb of type II. VR and MIP reconstruction showed good genicular collaterals supplying the distal popliteal arterial segments. Three patients were evaluated by both CTA and DSA, there were no significant differences between the length of stenosis, occluded segments and collaterals identified on CTA compared with DSA findings. The abnormalities in the popliteal fossa seen at surgical exploration matched the information gained from CTA in all patients. Fig. (2): 52-year-old male with popliteal artery entrapment syndrome of right lower extremity who presented with calf claudication. (A) Axial CT angiography image reveals lateral location of medial head of right gastrocnemius muscle (arrow) and occlusion of popliteal artery consistent with type II anomaly, and caudal portion shows thrombosed popliteal artery (B). (C) MIP images shows occlusion of right popliteal artery and genicular collateral developments.
4 2416 CT & CTA Findings in Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome Fig. (3): 60-year-old male with popliteal artery entrapment syndrome of right lower extremity who presented with calf claudication. (A) Axial CT angiography image reveals abnormal muscle bundle from medial head of gastrocnemius muscle (arrow) and short segment stenosisof popliteal artery consistent with type III anomaly, and caudal portion shows with partially thrombosed aneurysm (B). (C) MIP image shows the partially thrombosed aneurysm of right popliteal artery. Table (2): Patient demographics, CTA findings and surgical procedure. Case No. Patient Age Sex Affected limb (s) Symptoms Type on CT CTA of popliteal artery Surgery 1 45 M R Intermittent claudication and mild II Aneurysm formation. edema in right leg M R Intermittent right calf III Partially thrombosed aneurysm. Muscle release, claudication. interposition graft and aneurysmecto my M R Intermittent right calf claudication with coldness and numbeness. II Short segment of popliteal artery partial occlusion by a thrombus M R Calf claudication. II Long segment of total occlusion M Bilateral Calf claudication at physical activity. I Medial displacement of PA on both sides M R Calf swelling and pain. III Long segment of partially thrombosed artery M Bilateral Intermittent claudication. III Bilateral partially thrombosed aneurysm F R Rest pain, edema. II Long segment of total occlusion M R Calf swelling and pain. IV Short segment of stenosis 50%. Surgical release M R Calf claudication. IV Total occlusion. Surgical release.
5 Talal Amer, et al Discussion Popliteal entrapment's anatomical basis was first described by Anderson Stuart in 1879 [8]. Its clinical significant was realized in 1965 by Hamming and Vink [9]. In 1965, Love and Wheelan coined the term "popliteal artery entrapment syndrome" [5]. The arterial compression may cause chronic microtrauma with local premature arteriosclerosis and thrombus formation resulting in distal ischemia. In addition, stenosis and turbulent flow can lead to poststenotic ectasia or aneurysmal formation. PAES is a progressive condition so early diagnosis and early treatment may prevent many complications [10]. In our study PAES was bilateral in 20% of cases, frequency of bilateral involvement ranges from 30 to 60%, although values as high as 81% have been quoted [11]. Thus, it is essential to evaluate both limbs even if the clinical symptoms are restricted to a single limb, as the symptoms may be unilateral but with bilateral involvement [1]. The typical presentation is that of a young healthy adult man, in the 20 to 40 year age group, often athletic. There is a strong male predominance [1]. As seen in our study 90% of patient were male and the mean age was Although PAES is difficult to diagnose clinically, it must be considered in any young adult with no cardiovascular risk factors presenting with acute limb ischemia or intermittent claudication [12]. DSA was the reference standard for the diagnosis of PAES, but DSA cannot show the softtissue anatomy cannot identify the underlying cause. An occlusion or aneurysm of the popliteal artery due to PAES is difficult to be differentiated from arteriosclerotic or degenerative causes [5]. DSA may have a role in the evaluation of patients with claudication, but it can't diagnose PAES, especially in cases of arterial occlusion. DSA has been replaced by noninvasive techniques, such as Doppler sonography, CTA, MRI, and MRA [13]. CTA is a novel diagnostic tool for PAES, it can delineate muscles, vessels, fat and bone in the popliteal fossa and their relationship. Also, it provides axial images of the soft-tissue structures which lead to accurate grading of popliteal arterial stenosis or occlusions and evaluation of surrounding muscular anomalies. CTA can also be used for the evaluation of the contralateral limb to rule out bilateral entrapment [12]. Several postprocessing techniques, such as MPR, MIP, and VR, can be used to provide 3D reconstructions and describe vascular abnormalities. MPR is useful for the detection of arterial deviations and aberrant muscles. Lateral and oblique views of CT images can give information about the origin of aberrant muscles and the relationship between the popliteal artery and surrounding structures [12]. The detailed description is useful for clinicians to decide whether surgery is indicated [14]. MIP and VR images give sufficient 3D information about the popliteal artery. The segmental arterial occlusion and the degree of postocclusion refilling are shown by MIP and VR images accurately [5]. In our study, MIP and VR images provided excellent evaluation of vascular lumens. MIP and VR images reconstructed from the volume data acquired during CTA can show internal deviation of the artery, flatness or clinched appearance, narrowing, mural irregularity, and segmental occlusion. Poststenotic dilatation and aneurysms have also been well demonstrated on CTA [15]. CTA is also useful in evaluating occluded arteries. Arterial occlusion is a common complication that may be seen in half of the limbs at presentation [16]. In our study complete occlusion of the popliteal artery with genicular collaterals, seen in 30% of the limbs. In all three patients with occluded popliteal artery, there was CTA evidence to diagnose PAES, as abnormal course of artery, localised single-segment involvement, and obvious abnormality in the anatomy of the popliteal fossa. In contrast, catheter angiography has limited value when the artery is thrombosed, and it cannot differentiate occlusion from other causes. However, CTA can distinguish the occlusion found in PAES from other conditions, such as atherosclerosis, cystic adventitial disease, and popliteal mass. Also, an aneurysm beyond an occluded artery is better seen on CTA than Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) [15]. In this study the angiographic information obtained by CTA was adequate for surgical decision making. There was no discrepancy between the angiographic data obtained on CTA and at surgical exploration, confirming its adequacy as an effective modality for vascular assessment in PAES. Small sample size, retrospective study and lack of direct correlation with catheter angiography or MRI are major limitations of this study, but the
6 2418 CT & CTA Findings in Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome high degree of concordance between surgical and CTA inferences endorses its clinical relevance in the management of PAES. This study also suffers from an inherent selection bias because only surgically proven cases were included. Again, the reviewers were not blinded to the clinical diagnosis. In conclusion, CT and CTA is a novel and readily available imaging modality in the diagnosis, characterization and classification of PAES. References 1- ANIL G., TAY K.H., HOWE T.C. and TAN B.S.: Dynamic Computed Tomography Angiography: Role in the Evaluation of Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol., 34: , LEVIEN L.J.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. Semin. Vasc. Surg., 16: , LAMBERT A.W. and WILKINS D.C.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. Br. J. Surg., 86: , OZKAN U., OGUZKURT L., TERCAN F. and POUR- BAGHER A.: MRI and DSA findings in popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. Diagn. Interv. Radiol., 14: , HAI Z., GUANGRUI S., YUAN Z., ZHUODONG X., CHENG L., JINGMIN L. and YUN S.: CT Angiography and MRI in Patients with Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome. A.J.R., 191: , RICH N.M., COLLINS G.J. Jr., McDONALD P.T., KO- ZLOFF L., CLAGETT G.P. and COLLINS J.T.: Popliteal vascular entrapment: Its increasing interest. Arch. Surg., 114: , TERCAN F., OGUZKURT L., KIZILKILIÇ O., YENIO- CAK A. and GÜLCAN O.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. Diagn. Interv. Radiol., 11 (4): 222-4, GOKKUS K., SAGTAS E., BAKALIM T., TASKAYA E. and AYDIN A.T.: Popliteal entrapment syndrome. A systematic review of the literature and case presentation. Muscles, Ligaments and Tendons Journal, 4 (2): 141, LEJAY A., OHANA M., LEE J.T., GEORG Y., DELAY C., LUCEREAU B., THAVEAU F. and GAERTNER S., CHAKFÉ N.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. J. Cardiovasc. Surg., 1; 55 (2 Suppl 1): , ELIAS D.A., WHITE L.M., RUBENSTEIN J.D., CHRISTAKIS M. and MERCHANT N.: Clinical evaluation and MR imaging features of popliteal artery entrapment and cystic adventitial disease. A.J.R., 180: , KIM H.K., SHIN M.J., KIM S.M., LEE S.H. and HONG H.J.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome: Morphological classification utilizing MR imaging. Skeletal. Radiol., 35: , RADONIC V., KOPLIC S., GIUNIO L., BOZIC I., MASKOVIC J. and BUĆA A.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome: Diagnosis and management, with report of three cases. Tex Heart Inst. J., 27: 3-13, FUJIWARA H., SUGANO T. and FUJII N.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome: Accurate morphological diagnosis utilizing MRI. J. Cardiovasc. Surg., 33: 160-2, ATILLA S., ILGIT E.T., AKPEK S., YÜCEL C., TALI E.T. and IŞIK S.: MR imaging and MR angiography in popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. Eur. Radiol., 8: , BEREGI J.P., DJABBARI M., DESMOUCELLE F., WIL- LOTEAUX S., WATTINNE L. and LOUVEGNY S.: Popliteal vascular disease: Evaluation with spiral CT angiography. Radiology, 203: , ROSSET E., HARTUNG O., BRUNET C., ROCHE P.H., MAGNAN P.E., MATHIEU J.P., et al.: Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome. Anatomic and embryologic bases, diagnostic and therapeutic considerations following a series of 15 cases with a review of the literature. Surg. Radiol. Anat., 17: 161-9, 1995.
POPLITEAL ARTERY ENTRAPMENT SYNDROME
 POPLITEAL ARTERY ENTRAPMENT SYNDROME Background 1. Definition: Rare cause of exertional leg pain o Due to an abnormal relationship between popliteal artery and surrounding myofascial structures in popliteal
POPLITEAL ARTERY ENTRAPMENT SYNDROME Background 1. Definition: Rare cause of exertional leg pain o Due to an abnormal relationship between popliteal artery and surrounding myofascial structures in popliteal
Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll.
 Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll. For the Department of Vascular Surgery and Kidney Transplantation University Hospital of Strasbourg, FRANCE Popliteal artery entrapment: misdiagnosed Epidemiology Prevalence:
Prof. Nabil CHAKFE et coll. For the Department of Vascular Surgery and Kidney Transplantation University Hospital of Strasbourg, FRANCE Popliteal artery entrapment: misdiagnosed Epidemiology Prevalence:
North American Society of Cardiovascular Imaging Annual Meeting, Baltimore MD, October 15-18, Tips and Tricks in Vascular Imaging
 North American Society of Cardiovascular Imaging Annual Meeting, Baltimore MD, October 15-18, 2016 Tips and Tricks in Vascular Imaging Lower Extremity CTA Dominik Fleischmann, Richard Hallett Division
North American Society of Cardiovascular Imaging Annual Meeting, Baltimore MD, October 15-18, 2016 Tips and Tricks in Vascular Imaging Lower Extremity CTA Dominik Fleischmann, Richard Hallett Division
NADINE R. BARSOUM, M.D.; LAMIAA I.A. METWALLY, M.D. and IMAN M. HAMDY IBRAHIM, M.D.
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, December: 175-183, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Peripheral Arterial Disease of the Lower Limbs: Is Doppler Examination as Efficient in its Diagnosis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, December: 175-183, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Peripheral Arterial Disease of the Lower Limbs: Is Doppler Examination as Efficient in its Diagnosis
B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with 64-MD-CT Angiography
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Long-term outcomes after revascularization for advanced popliteal artery entrapment syndrome with segmental arterial occlusion
 Long-term outcomes after revascularization for advanced popliteal artery entrapment syndrome with segmental arterial occlusion Seong-Yup Kim, MD, Seung-Kee Min, MD, PhD, Sanghyun Ahn, MD, Sang-Il Min,
Long-term outcomes after revascularization for advanced popliteal artery entrapment syndrome with segmental arterial occlusion Seong-Yup Kim, MD, Seung-Kee Min, MD, PhD, Sanghyun Ahn, MD, Sang-Il Min,
Utility of Variable Helical Pitch CT Scanning Technique for CT Angiography of Aortoiliac and Lower Extremity Arteries
 Utility of Variable Helical Pitch CT Scanning Technique for CT Angiography of Aortoiliac and Lower Extremity Arteries Poster No.: C-0863 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Nakamoto,
Utility of Variable Helical Pitch CT Scanning Technique for CT Angiography of Aortoiliac and Lower Extremity Arteries Poster No.: C-0863 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Nakamoto,
CT angiography techniques. Boot camp
 CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
Role of multi-detector computed tomography angiography in the evaluation of lower limb ischemia
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(5): 125-130 Published online September 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140205.16 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print);
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(5): 125-130 Published online September 30, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140205.16 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print);
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
CT Versus MR for the Runoff
 CT Versus MR for the Runoff Robert R. Edelman, M.D. Dept. of Radiology NorthShore University HealthSystem Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University Magnetic Resonance Computed Tomography Radio
CT Versus MR for the Runoff Robert R. Edelman, M.D. Dept. of Radiology NorthShore University HealthSystem Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University Magnetic Resonance Computed Tomography Radio
Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome (PAES) was first characterized
 SE SERIES Popliteal rtery Entrapment Syndrome: ase Series With Variable Timing of Diagnosis and Outcome Jihad. Mustapha, MD, Fadi Saab, MD, Kristopher Danielson, DO, Larry J. Diaz-Sandoval, MD, David ielema,
SE SERIES Popliteal rtery Entrapment Syndrome: ase Series With Variable Timing of Diagnosis and Outcome Jihad. Mustapha, MD, Fadi Saab, MD, Kristopher Danielson, DO, Larry J. Diaz-Sandoval, MD, David ielema,
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Anatomical popliteal artery entrapment syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2288-6575 eissn 2288-6796 https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.94.5.262 Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research Anatomical popliteal artery entrapment syndrome Yong Jae Kwon 1, Tae-Won
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2288-6575 eissn 2288-6796 https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.94.5.262 Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research Anatomical popliteal artery entrapment syndrome Yong Jae Kwon 1, Tae-Won
RC 612B 3 December Richard L. Hallett, MD
 RC 612B 3 December 2015 0830 1000 Richard L. Hallett, MD Chief, Cardiovascular Imaging Northwest Radiology Network Indianapolis, IN Adjunct Assistant Professor Radiology Stanford University Stanford, CA
RC 612B 3 December 2015 0830 1000 Richard L. Hallett, MD Chief, Cardiovascular Imaging Northwest Radiology Network Indianapolis, IN Adjunct Assistant Professor Radiology Stanford University Stanford, CA
Imaging Strategy For Claudication
 Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
Popliteal vein aneurysm presenting as recurrent pulmonary embolism
 vein aneurysm presenting as recurrent pulmonary embolism Joel Lim 1*, Martin Marshall 2 1. Department of Clinical Services, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia 2. Department of Diagnostic and Radiology,
vein aneurysm presenting as recurrent pulmonary embolism Joel Lim 1*, Martin Marshall 2 1. Department of Clinical Services, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia 2. Department of Diagnostic and Radiology,
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION
 ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
PERIPHERAL CTA. Richard L. Hallett, MD
 RC 812B Lakeside E351 1 December 2017 0830 1000 Richard L. Hallett, MD Chief, Cardiovascular Imaging Northwest Radiology Network Indianapolis, IN Adjunct Assistant Professor Radiology Cardiovascular Imaging
RC 812B Lakeside E351 1 December 2017 0830 1000 Richard L. Hallett, MD Chief, Cardiovascular Imaging Northwest Radiology Network Indianapolis, IN Adjunct Assistant Professor Radiology Cardiovascular Imaging
PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT OF VASCULAR OCCLUSION EXTENT AND LOCALIZATION OF EMBOLI 1. BACKGROUND
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience
 Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Vascular CT Protocols
 Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Popliteal adventitial disease in a triathlete
 Popliteal adventitial disease in a triathlete A 37 year old recreational long distance triathlete complained of right leg pain during running since early 2002. The problems mainly occurred when running
Popliteal adventitial disease in a triathlete A 37 year old recreational long distance triathlete complained of right leg pain during running since early 2002. The problems mainly occurred when running
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
CHALLENGING ILIAC ACCESSES AND THROMBOSIS PREVENTION
 CHALLENGING ILIAC ACCESSES AND THROMBOSIS PREVENTION ARMANDO MANSILHA MD, PhD, FEBVS UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL - PORTO Disclosure of Interest Speaker name: ARMANDO MANSILHA I have the following potential conflicts
CHALLENGING ILIAC ACCESSES AND THROMBOSIS PREVENTION ARMANDO MANSILHA MD, PhD, FEBVS UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL - PORTO Disclosure of Interest Speaker name: ARMANDO MANSILHA I have the following potential conflicts
Cardiac Computed Tomography
 Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
Duplex ultrasound is first-line imaging for all
 Our Protocol for Transabdominal Pelvic Vein Duplex Ultrasound A summary of s protocol for pelvic vein duplex ultrasonography, including equipment, patient positioning, ultrasound settings, and technique.
Our Protocol for Transabdominal Pelvic Vein Duplex Ultrasound A summary of s protocol for pelvic vein duplex ultrasonography, including equipment, patient positioning, ultrasound settings, and technique.
Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options
 Deepak N. Deshmukh DO April 27, 2018 Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options No Disclosures Popliteal Artery Aneurysms (PAAs) Male Predominanace Most common peripheral Aneurysm (70%) 30-50%
Deepak N. Deshmukh DO April 27, 2018 Popliteal Artery Aneurysms: Diagnosis and Repair Options No Disclosures Popliteal Artery Aneurysms (PAAs) Male Predominanace Most common peripheral Aneurysm (70%) 30-50%
The Many Views of PAD: Imaging Modalities for the Interventionist
 The Many Views of PAD: Imaging Modalities for the Interventionist Timothy E. Yates, MD Interventional Vascular & Oncological Radiology Mount Sinai Medical Center 5 December 2015 None Disclosures Objectives
The Many Views of PAD: Imaging Modalities for the Interventionist Timothy E. Yates, MD Interventional Vascular & Oncological Radiology Mount Sinai Medical Center 5 December 2015 None Disclosures Objectives
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach
 Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Visceral aneurysm. Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA
 Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
Visceral aneurysm Diagnosis and Interventions M.NEDEVSKA History 1953 De Bakeyand Cooley Visceral aneurysm VAAs rare, reported incidence of 0.01 to 0.2% on routine autopsies. Clinically important Potentially
Angiographic Imaging of the Lower Extremities with Multidetector CT
 Radiol Clin N Am 43 (2005) 1119 1127 Angiographic Imaging of the Lower Extremities with Multidetector CT Mark D. Hiatt, MD, Dominik Fleischmann, MD, Jeffrey C. Hellinger, MD, Geoffrey D. Rubin, MDT Division
Radiol Clin N Am 43 (2005) 1119 1127 Angiographic Imaging of the Lower Extremities with Multidetector CT Mark D. Hiatt, MD, Dominik Fleischmann, MD, Jeffrey C. Hellinger, MD, Geoffrey D. Rubin, MDT Division
Bilateral Persistent Sciatic Arteries with Failed Iliofemoral Grafts
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 4, December 2012 Bilateral Persistent Sciatic Arteries with Failed Iliofemoral Grafts Hani Al Fadhel, MD, FRCR* Faisal Rafeea, MD, SBEM** Abeer Moustafa Abdul Latif,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 4, December 2012 Bilateral Persistent Sciatic Arteries with Failed Iliofemoral Grafts Hani Al Fadhel, MD, FRCR* Faisal Rafeea, MD, SBEM** Abeer Moustafa Abdul Latif,
Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open techniques.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 14 Number 2 Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open A Rodriguez-Rivera,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 14 Number 2 Management of the persistent sciatic artery with coexistent aortoiliac aneurysms; endovascular and open A Rodriguez-Rivera,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI?
 Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article. DOI: /sjams *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.8.53 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(8D):3009-3014 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.8.53 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(8D):3009-3014 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen. Jonathan Swanson, MD
 Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Vascular Imaging in the Pediatric Abdomen Jonathan Swanson, MD Goals and Objectives To understand the imaging approach, appearance, and clinical manifestations of the common pediatric abdominal vascular
Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:13 17, January 2003 Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT Kohsuke Kudo, Satoshi Terae, Takeshi Asano, Masaki Oka, Kenshi Kaneko,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:13 17, January 2003 Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT Kohsuke Kudo, Satoshi Terae, Takeshi Asano, Masaki Oka, Kenshi Kaneko,
Study of aortic ulcer by using MDCTA
 Study of aortic ulcer by using MDCTA Poster No.: C-3085 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Vascular Authors: L. Saba, R. Sanfilippo, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, R. Montisci, G. Mallarini; Cagliari/IT
Study of aortic ulcer by using MDCTA Poster No.: C-3085 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Vascular Authors: L. Saba, R. Sanfilippo, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, R. Montisci, G. Mallarini; Cagliari/IT
RadRx Your Prescription for Accurate Coding & Reimbursement Copyright All Rights Reserved.
 Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of November 19, 2018 Abdominal Aortogram, Bilateral Runoff
Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of November 19, 2018 Abdominal Aortogram, Bilateral Runoff
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging. Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital
 Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
Internal iliac artery aneurysms: When to intervene and outcomes of EVAR
 Internal iliac artery aneurysms: When to intervene and outcomes of EVAR Frans Moll Wuttichai Saaengprakai, George Georgiadis, Joost van Herwaarden Department of Vascular Surgery, UMC Utrecht, The Netherlands
Internal iliac artery aneurysms: When to intervene and outcomes of EVAR Frans Moll Wuttichai Saaengprakai, George Georgiadis, Joost van Herwaarden Department of Vascular Surgery, UMC Utrecht, The Netherlands
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ABI. See Ankle-brachial index (ABI). Afterload, deconstructing of, in ventricular vascular interaction in heart failure, 449 Air plethysmography
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ABI. See Ankle-brachial index (ABI). Afterload, deconstructing of, in ventricular vascular interaction in heart failure, 449 Air plethysmography
Bottom up cardiac CT for CABG assessment to resolve breathing artefact
 Bottom up cardiac CT for CABG assessment to resolve breathing artefact Poster No.: C-0589 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: P. Glass, P. Donnelly, P. Hanley, D. Higginson,
Bottom up cardiac CT for CABG assessment to resolve breathing artefact Poster No.: C-0589 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: P. Glass, P. Donnelly, P. Hanley, D. Higginson,
Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome
 SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
Popliteal Aneurysm: When is surgical therapy indicated? PROF. GRZEGORZ OSZKINIS
 Popliteal Aneurysm: When is surgical therapy indicated? PROF. GRZEGORZ OSZKINIS Asymptomatic mass - 38-40%will develop symptoms at a rate of 14%/yr Intermittent claudic ation (chronic ischemia) - 25%-40%
Popliteal Aneurysm: When is surgical therapy indicated? PROF. GRZEGORZ OSZKINIS Asymptomatic mass - 38-40%will develop symptoms at a rate of 14%/yr Intermittent claudic ation (chronic ischemia) - 25%-40%
Popliteal artery entrapment: An evolving syndrome
 Popliteal artery entrapment: An evolving syndrome Paul Steven Collins, MD, FACS, Maj, MC, USA, Paul T. McDonald, MD, FACS, Col, MC (Ret), and Robert C. Lim, MD, FACS, Col, MC~ (USAR), San Francisco and
Popliteal artery entrapment: An evolving syndrome Paul Steven Collins, MD, FACS, Maj, MC, USA, Paul T. McDonald, MD, FACS, Col, MC (Ret), and Robert C. Lim, MD, FACS, Col, MC~ (USAR), San Francisco and
Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 297 303 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 297 303 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
Multislice CTA for Renal Artery Stenting
 Multislice CT for Renal rtery Stenting How CT can be a useful modality for diagnosing and managing renal artery stenosis for stent placement. Y MICHEL WHOLEY, MD, M; JMES WU, ; WILLIM C.L. WU, MD, FCC;
Multislice CT for Renal rtery Stenting How CT can be a useful modality for diagnosing and managing renal artery stenosis for stent placement. Y MICHEL WHOLEY, MD, M; JMES WU, ; WILLIM C.L. WU, MD, FCC;
Non-invasive examination
 Non-invasive examination Segmental pressure and Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) The segmental blood pressure (SBP) examination is a simple, noninvasive method for diagnosing and localizing arterial disease.
Non-invasive examination Segmental pressure and Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) The segmental blood pressure (SBP) examination is a simple, noninvasive method for diagnosing and localizing arterial disease.
V.A. is a 62-year-old male who presents in referral
 , LLC an HMP Communications Holdings Company Clinical Case Update Latest Trends in Critical Limb Ischemia Imaging Amit Srivastava, MD, FACC, FABVM Interventional Cardiologist Bay Area Heart Center St.
, LLC an HMP Communications Holdings Company Clinical Case Update Latest Trends in Critical Limb Ischemia Imaging Amit Srivastava, MD, FACC, FABVM Interventional Cardiologist Bay Area Heart Center St.
Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
 Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings
 Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out (tro) examination
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):21898-21905 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015005 Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):21898-21905 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015005 Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Lee et al. CT of Chronic Total and Subtotal Occlusive rterial Disease Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Jung Eun Lee 1 Hee
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Lee et al. CT of Chronic Total and Subtotal Occlusive rterial Disease Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Jung Eun Lee 1 Hee
Ultrasound-guided percutaneous aspiration of adventitial cysts in the occluded popliteal artery clinical results and MR findings at 5-year follow-up
 Case report Cite as: Rosiak G, Milczarek K, Cieszanowski A, Rowiński O: Ultrasound-guided percutaneous aspiration of adventitial cysts in the occluded popliteal artery clinical results and MR findings
Case report Cite as: Rosiak G, Milczarek K, Cieszanowski A, Rowiński O: Ultrasound-guided percutaneous aspiration of adventitial cysts in the occluded popliteal artery clinical results and MR findings
PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM. By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai
 PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai Defintions True Aneurysm Involves all three layers of the vessel. Have two basic shapes; Fusiform = symmetric widening of the vessels
PERPHERAL ARTERY ANEURYSM By Pooja Sharma and Susanna Sebastianpillai Defintions True Aneurysm Involves all three layers of the vessel. Have two basic shapes; Fusiform = symmetric widening of the vessels
University Journal of Medicine and Medical Specialities
 ISSN 2455-2852 2018, Vol. 4(5) Imaging Assessment of Vascular Thoracic Outlet Syndrome BALAJI A AYYAMPERUMAL Department of Radio Diagnosis,MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND GOVERNMENT GENERAL HOSPITAL Abstract
ISSN 2455-2852 2018, Vol. 4(5) Imaging Assessment of Vascular Thoracic Outlet Syndrome BALAJI A AYYAMPERUMAL Department of Radio Diagnosis,MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND GOVERNMENT GENERAL HOSPITAL Abstract
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels
 CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
MayeThurner syndrome: Correlation between digital subtraction and computed tomography venography
 Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2015) 114, 363e368 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE MayeThurner syndrome: Correlation between
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2015) 114, 363e368 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE MayeThurner syndrome: Correlation between
Median arcuate ligament syndrome. An unfrequent cause of abdominal pain.
 Median arcuate ligament syndrome. An unfrequent cause of abdominal pain. Poster No.: C-2093 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Caminero, M. L. Rozas, M. E. Banegas Illescas, J. A.
Median arcuate ligament syndrome. An unfrequent cause of abdominal pain. Poster No.: C-2093 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Caminero, M. L. Rozas, M. E. Banegas Illescas, J. A.
Vascular Imaging Original Research
 MDCT Angiography of Renal Arteries Vascular Imaging Original Research Adam D. Talenfeld 1 Ryan B. Schwope Huntley J. Alper Emil I. Cohen Robert A. Lookstein Talenfeld AD, Schwope RB, Alper HJ, Cohen EI,
MDCT Angiography of Renal Arteries Vascular Imaging Original Research Adam D. Talenfeld 1 Ryan B. Schwope Huntley J. Alper Emil I. Cohen Robert A. Lookstein Talenfeld AD, Schwope RB, Alper HJ, Cohen EI,
Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants)
 Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants) Siddharth P. Jadhav, MD Director, Body CT and MRI Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures None Objectives
Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants) Siddharth P. Jadhav, MD Director, Body CT and MRI Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures None Objectives
, David Stultz, MD. Cardiac CT. David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 March 28, 2006
 Cardiac CT David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 March 28, 2006 Courtesy Tom Kracus Courtesy Kettering Tom Medical Kracus Cente Kettering Medical Center 2003-2006, David Stultz, MD Courtesy Tom Kracus
Cardiac CT David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 6 March 28, 2006 Courtesy Tom Kracus Courtesy Kettering Tom Medical Kracus Cente Kettering Medical Center 2003-2006, David Stultz, MD Courtesy Tom Kracus
Endovascular treatment of popliteal artery aneurysm: preliminary results
 Endovascular treatment of popliteal artery aneurysm: preliminary results Poster No.: C-0483 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: G. Guzzardi, R. Fossaceca, P. Cerini, C. Stanca, I. Di Gesù,
Endovascular treatment of popliteal artery aneurysm: preliminary results Poster No.: C-0483 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: G. Guzzardi, R. Fossaceca, P. Cerini, C. Stanca, I. Di Gesù,
THE popliteal artery is the second most common site of aneurysm. The
 POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
KNEE DISLOCATION. The most common injury will be an anterior dislocation, and this usually results from a hyperextension mechanism.
 KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
KNEE DISLOCATION Introduction Dislocation of the knee is a severe injury associated with major soft tissue injury and a high incidence of damage to the popliteal artery. There is displacement of the tibia
Indications: following: embolization. artery that has diseases 5. The evaluation. of suspected. such entities. a cold hand. biopsy
 Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Challenging of contrast agent-free endovascular treatment using 3D imaging
 AC17-0010 Challenging of contrast agent-free endovascular treatment using 3D imaging Amane Kozuki Department of Cardiology, Osaka Saiseikai Nakatsu Hospital Introduction With advances in devices and techniques,
AC17-0010 Challenging of contrast agent-free endovascular treatment using 3D imaging Amane Kozuki Department of Cardiology, Osaka Saiseikai Nakatsu Hospital Introduction With advances in devices and techniques,
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L.
 Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Functional Orthopedic Imaging Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion. Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy.
 Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Imagerie pré-thérapeutique de l aorte
 Imagerie pré-thérapeutique de l aorte Gilles Soulez, MD, MSc, FSIR Professeur Titulaire et Chairman Dpt Radiologie, Radio-Oncologie et Medecine Nucléaire Université de Montréal Current challenges of EVAR
Imagerie pré-thérapeutique de l aorte Gilles Soulez, MD, MSc, FSIR Professeur Titulaire et Chairman Dpt Radiologie, Radio-Oncologie et Medecine Nucléaire Université de Montréal Current challenges of EVAR
Case Report Abstracts Presented to the Peripheral Vascular Society - Winter Meeting 2009
 Case Report Abstracts Presented to the Peripheral Vascular Society - Winter Meeting 2009 Intermittent Foot Claudication with Active Dorsiflexion: The Seminal Case of Dorsalis Pedis Artery Entrapment Katie
Case Report Abstracts Presented to the Peripheral Vascular Society - Winter Meeting 2009 Intermittent Foot Claudication with Active Dorsiflexion: The Seminal Case of Dorsalis Pedis Artery Entrapment Katie
MR Angiography in the evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 March 2001 MR Angiography in the evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Ted Mau, Harvard Medical School Year III Objectives We will cover: Indications for Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Basic
March 2001 MR Angiography in the evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Ted Mau, Harvard Medical School Year III Objectives We will cover: Indications for Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Basic
Peripheral Arterial Disease. Westley Smith MD Vascular Fellow
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Westley Smith MD Vascular Fellow Background (per 10,000) Goodney P, et al. Regional intensity of vascular care and lower extremity amputation rates. JVS. 2013; 6: 1471-1480.
Peripheral Arterial Disease Westley Smith MD Vascular Fellow Background (per 10,000) Goodney P, et al. Regional intensity of vascular care and lower extremity amputation rates. JVS. 2013; 6: 1471-1480.
Chungbuk Regional Cardiovascular Center, Division of Cardiology, Departments of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital Sangmin Kim
 Endovascular Procedures for Isolated Common Iliac and Internal Iliac Aneurysm Chungbuk Regional Cardiovascular Center, Division of Cardiology, Departments of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University
Endovascular Procedures for Isolated Common Iliac and Internal Iliac Aneurysm Chungbuk Regional Cardiovascular Center, Division of Cardiology, Departments of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
Renal Artery Stenosis With Severe Hypertension: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Renal Artery Stenosis With Severe Hypertension: A Case Report Suwaid MA ABSTRACT Background: Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is found in 77% of hypertensive patients and is responsible for 1-2%
CASE REPORT Renal Artery Stenosis With Severe Hypertension: A Case Report Suwaid MA ABSTRACT Background: Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is found in 77% of hypertensive patients and is responsible for 1-2%
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement
 Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Disclosures. Critical Limb Ischemia. Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient. Vascular Testing in Critical Limb Ischemia UCSF Vascular Symposium
 Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
Methods of Arterial and Venous Assessment CHAPTER 1. Peter Gorman, Mario De Nunzio, Richard Donnelly. Principles of vascular ultrasound
 CHAPTER 1 Methods of Arterial and Venous Assessment Peter Gorman, Mario De Nunzio, Richard Donnelly OVERVIEW This chapter describes the main investigative techniques used in arterial and venous disease.
CHAPTER 1 Methods of Arterial and Venous Assessment Peter Gorman, Mario De Nunzio, Richard Donnelly OVERVIEW This chapter describes the main investigative techniques used in arterial and venous disease.
A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
IVUS Guided Case Review Case Performed by Frank R. Arko III, MD Charlotte, NC
 IVUS Guided Case Review Case Performed by Frank R. Arko III, MD Charlotte, NC The opinions and clinical experiences presented herein are for informational purposes only. Dr. Arko is a paid consultant for
IVUS Guided Case Review Case Performed by Frank R. Arko III, MD Charlotte, NC The opinions and clinical experiences presented herein are for informational purposes only. Dr. Arko is a paid consultant for
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
Length Measurements of the Aorta After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 18, 481 486 (1999) Article No. ejvs.1999.0882 Length Measurements of the Aorta After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair J. J. Wever, J. D. Blankensteijn, I. A. M. J.
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 18, 481 486 (1999) Article No. ejvs.1999.0882 Length Measurements of the Aorta After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair J. J. Wever, J. D. Blankensteijn, I. A. M. J.
New Horizons in the Imaging of the Lung
 New Horizons in the Imaging of the Lung Postprocessing. How to do it and when do we need it? Peter M.A. van Ooijen, MSc, PhD Principal Investigator, Radiology, UMCG Discipline Leader Medical Imaging Informatics
New Horizons in the Imaging of the Lung Postprocessing. How to do it and when do we need it? Peter M.A. van Ooijen, MSc, PhD Principal Investigator, Radiology, UMCG Discipline Leader Medical Imaging Informatics
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
