MiR-1397 Regulates Chicken CARP Gene Expression at Post-transcriptional Level
|
|
|
- Randolph Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MiR-1397 Regulates Chicken CARP Gene Expression at Post-transcriptional Level Chunmei Liang 1, Xusan Xu 2, Liang Huang 2, Xia Zhou 2, Yajun Wang 1, 2, 1, 2, a,* Guoda Ma 1 Guangdong Key Laboratory of Age-Related Cardiac and Cerebral Diseases, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang , China; Abstract 2 Institute of Neurology, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang , China a sihan1107@126.com. Objectvie To identify whether mir-1397 specific targeting chicken carp gene and further analyze its expression pattern under different conditions. Methods Using online softwares, we predict a potential binding site for mir-1397 in chicken carp 3' untranslate region (3'-UTR). Then further confirmed mir-1397 specifically regulate the expression of chicken carp gene by luciferase activity analysis, site-directed mutagenesis, Real time PCR and Western blot. Simultaneously, Realtime PCR was used to analysis the expression of mir-1397 in chicken embryonic myoblasts (CFM) at different developmental stage and in different tissues of adult chicken. Results The mir-1397 can downregulate the activity of carp 3'-UTR luciferase reporter gene and inhibit the expression of endogenous carp, while the binding site mutation in carp 3'-UTR significantly reduced the inhibitory effect of mir In addition, in the CFM cell differentiation process, the expression of carp increased, while the expression of mir-1397 was decreased. Conclusion MiR-1397 can regulate the expression of chicken carp at post-transcriptional level. Keywords Chicken; carp; mir-1397; post-transcriptional regulation. 1. Introduction Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein (carp) is specifically expressed in mammalian cardiac muscle[1] and plays important roles in transcriptional regulation[2], the cytoskeletal architecture[3], and stretch sensing during heart development and pathological processes[4-8]. In contrast to its mammalian homologs, our previous study found that the expression of chicken carp is restricted to skeletal muscle and could be down-regulated by Myostatin[9,10],which a main negative regulator of muscle growth[11-13]. Moreover, our recent functional study demonstrated that carp may play a key role in the myostatin signaling cascade that controls chicken skeletal myogenesis through inducing proliferation and avoiding apoptosis during CFM cells differentiation[10]. However, no reports were shown to investigate chicken carp s expression regulatory mechanisms. MicroRNAs (mirnas) are known to negatively regulate the expression of their target genes[14] and have an important role in myogenesis[15]. Given the large size of the chicken carp 3'-untranslation region (3'-UTR) (2.2 kb)[10], we hypothesized that it was likely to be targeted by mirna. Therefore, we used bioinformatics to predict mir-1397 that would target the carp 3 -UTR, and validated the predictions using quantitative real-time PCR and western blot assays to confirm expression of the mir-1397 in muscle, as well as transfections with exogenous pre-mir-1397 to confirm targeting of the carp 3 -UTR. Moreover, during chicken embryonic myoblasts (CFM) cell differentiation, the expression of carp increased, while the expression of mir-1397 decreased correspondingly. Therefore, we suggest that inhibition of translation by mir-1397 is an important mechanism regulating carp expression and that it could be targeted for improving meat yield in poultry production. 83
2 2. Materials and methods 2.1 Experimental materials Receptive Escherichia coli DH5 alpha, Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent, RIPA lysate purchased from Guangzhou Ding Guo Biotech Corp;The double fluorescent report gene detection kit was bought from Promega company;the antibodies used for Western blot are purchased from Santa Cruz. Xho1 and BamH1 enzymes are purchased from Takara Biology; PCR kit is purchased in Thermo Fisher; Plasmid Extraction Kit and purification kit purchased from Tiangen Biotechnology (Beijing) Co., Ltd Bioinformatic analyses The software mirbase ( and Targetscan ( were used to identify and analyze potential microrna target sequences involved in the regulation of carp gene expression. The 3 -UTR ΔG was calculated with the use of the software mfold ( 2.3 Plasmids construction The 3 -untranslated region (3 -UTR) of mrna sequence of carp containing predicted mir-1397 binding site was amplified by PCR following the protocol of Primer star kit (Takara), the corresponding mutant constructs were created by mutating the seed regions of the mir-1397-binding sites. The primers used in the reaction were listed in Table 1. PCR products were cloned into the pgl3 reporter vector (Promega, USA). Table 1. Primer sequences for building a vector pgl3-ankrd1 3 -UTR primer (5 3 ) 3 UTR-F(CACAACTCGAGCCCGGAGGAAAATAGCCCTG) 3 UTR-R(AAGGATCCGCTTCAGGAACTGTGTGGGA) pgl3-ankrd1 3 -UTR mut 3 UTR-MR (AGATTCGTAACGAATGTAAACTAT) 3 UTR-MF(ACATTCGTTACGAATCTTTGTCAGCAACATGAGCC) 2.4 CFM cells culture and transfection CFMs were prepared from the pectoralis muscles of 10-day-old White Leghorn chicken embryos and cultured as described previously[9,10]. Chicken fibroblast cells were prepared as described by Mar et al [17]. And maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. Chicken fibroblast cells were maintained under 5% CO2 at 37 C in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were cultured to 70% confluence and transiently transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. 2.5 Luciferase reporter assay For identification mir-1397 target chicken carp 3 -UTR, reporter plasmids (pgl3 reporter vector containing carp 3 -UTR) and mir-1397 mimics were cotransfected into 293T cells (60% confluence) using Lipofectamine 2000, control groups here include cells cotransfected with pgl3/carp 3 -UTR and mir-nc, pgl3/carp 3 -UTR mutant and mir-1397 mimics as well as pgl3/carp 3 -UTR mutant and mir-nc. After 48 h cells were lysed and reporter activity was determined using Dual-luciferase report assay system (Promega, USA). Firefly luciferase values were normalized to Renilla, and the ratio of firefly/renilla was presented. 2.6 Tissues collection All experimental procedures were conducted in conformity with institutional guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals, and protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee in Guangdong Medical University. Various tissues including brain, heart, liver, spleen, 84
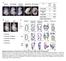
3 lung, kidney, chest muscles, skeletal muscle, pancreas, stomach, ovary, oviduct, skin and fat were collected for RNA extraction. 2.7 Real time PCR and Westernblot analysis Total RNA extraction and quantitative real time PCR was performed as previously described [10]. Primers used were as follow: GAPDH, Forward: 5 -CCTCTCTGGCAAAGTCCAAG-3 ; Reverd: 5 -GGTCACGCTCCTGGAAGATA-3 ; carp, Forward: 5 -CCACTGGCAAACATGATGAC-3 ; Reverse: 5 -CTCGCCTCACGCTTCTTCT-3. MiR-1397 and 5s RNA qpcr primers were purchased from Integrated Biotech Solutions. Fold changes were calculated using the Ct method. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate. Protein expression in CFM was analyzed by western blot as previously described. 2.8 statistical analysis Statistical analysis was analysed by Prism5 software. Data were presented as the means ± s.e. from at least three separate experiments. The two independent sample t-test was used to draw a comparison between groups. All tests were two-tailed, and the significance level was set at P< Results 3.1 mir-1397 combine with carp 3'-UTR sequence The chicken carp gene has a 3 -UTR that is more than twice as long as it s ORF, raising the possibility that it might contain post-transcriptional regulatory elements that would control its protein level. To search for mirna (s) that might regulate chicken carp expression, we used the following target prediction algorithms: miranda ( and Targets can ( These approaches are based on the identification of elements in the 3 -UTR of target genes complementary to the seed sequence of the mirna of interest, calculation of thermodynamic properties of 3 -UTRs. We found a mir-1397 putative binding site (GCAAUGCA) at the 3 -UTR sequence of carp (Fig.1A). This suggested that carp potentially was a regulator target for mir The seed match between mir-1397 and carp 3 -UTR is between bases 168 and 175 (Fig.1A). The free energy required for the interaction between mir-1397 and its cognate carp 3 -UTR binding site is kcal/mol based on the Pictar prediction (Fig.1B). A B Figure 1. Prediction of mir-1397 target sequence in chicken carp-3 '-UTR. (A) Schematic diagram of chicken carp mrna containing the predicted conserved target site of mir-1397 and mutant (carp-3 -mutr) mir-1397 target sequences. (B) Predicted hybridization of mir-1397 (green) and the chicken carp (red) transcript using the RNAhybrid algorithm [16]. The minimum free energy required for the hybridization is indicated. 3.2 mir-1397 directly targets chicken carp To confirm chicken carp as a real mir-1397 target, the entire wild-type 3 -UTR of carp was inserted downstream of the firefly luciferase reporter gene and cotransfected with mir-1397 mimics into HEK293T cells. As shown in Fig.2A, co-transfection of mir-1397 mimics with the carp 3 UTR reporter resulted in a highly significant decrease (11.8 %, P=0.016) in luciferase activity. To confirm that the predicted target sequence of mir-1397 in the carp 3 -UTR is functional, this 7 bp seed region 85
4 was mutagenized as shown in Fig.1A. Notably, mir-1397 could not inhibit luciferase activity from the mutagenized carp 3 -UTR construct (Fig.2B), indicating that the predicted sequence is indeed a genuine binding site for mir-1397 and it is solely responsible for mir-1397 targeting of the carp 3 -UTR. A B Figure 2. Target validation of mir-1397 using a luciferase assay system. (A-B) carp 3 -UTR reporter vector and Nucleotides in the seed-binding region of the predicted binding site of mir-1397 in the 3 -UTR of the carp was mutated by site directed mutagenesis as depicted in Fig.1 and the reporter-construct was co-transfected with mir-1397 in H9C2 cells. After 24 h the cells were harvested and luciferase activity was measured. Data are presented as percental changes of relative light units (RLU) to control (mir-c) and indicated as mean±s.e. of six triplicates (n= 6; one-way ANOVA, *p< 0.05). 3.3 mir-1397 inhibits the expression of chicken carp Furthermore, Western blotting analyses showed that carp protein levels were decreased after CFM cells received mir Consistently, endogenous level of carp protein was significantly increased in CFM cells (Fig.3A-B) by using this specific inhibitor against mir These results confirm that mir-1397 inhibits carp expression through the 3 -UTR, and further suggest that endogenous mir-1397 actively suppresses carp expression in CFM cells, which could be blocked by mir-1397 inhibitor. A B C Figure 3. MiR-1397 directly reduces carp protein expression. (A) CFM cells were transfected with the indicated concentrations of mir-1397 or anti-mir-1397 inhibitor (2 -Omethyl) or control (scrambled mir sequence) and harvested 48 h later. A representative Western blot using carp antibody is shown. (B) Mean amount of carp measured from three independent experiments was normalized to β-actin.the expression comparisons were significant with p< (C) CFM cells express mir Representative bar shows the products of real-time PCR amplified with primers specific for mir-1397 in CFM cells transfected with scramble or mir-1397 or mir-1397 inhibitor. The amount of starting template for each condition was equilibrated relative to 5S rrna. The expression values were normalized with 5S rrna expression, and are represented as mean±s.e.(n=3, **p< 0.001). 86
5 3.4 Downregulation of mir-1397 during differentiation in CFMs is inversely correlated with the carp expression pattern To gain insight into the function of carp, we examined its expression in adult chicken tissues via real-time PCR analysis. The results revealed that transcript of mir-1397 was widely expressed in all 12 tissues tested adult chicken tissues including skeletal muscle, liver and kideny, but especially predominantly expressed in brain and heart (Fig.4A). To characterize the expression pattern of mir-1397 in vitro, the CFM cells were seeded in 35 mm dishes at 4.0 x 104 cells per dish and harvested. As shown in Fig.4C, carp mrna were increased, whereas the expression of mature mir-1397 was correspondingly reduced during CFMs differentiation (Fig.4B), suggesting that down-regulation of carp protein involves translational inhibition mechanisms, possibly dependent on the corresponding increased accumulation of mir Note that expression of carp is probably a combination of transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms, in keeping with previous reports showing that inhibition of carp accumulation in is due to reduced transcription and to protein destabilization [8, 20]. A B C Figure 4 Expression of mir-1397 in chicken tissues and CFM cells. (A) Expression of mir-1397 in adult chicken tissues. Real-time PCR show that mir-1397 expression is highly expressed in brain and heart. (B-C) mir-1397 expression during myogenesis. Total RNA enriched for mirnas was extracted from chicken myoblasts and myotube (fused myoblasts in differentiation medium for 5 days), and analyzed by real-time PCR to assess mir-1397 and carp expression. The levels of mir-1397 decreased during myogenesis. On the contrary, the expression of carp increased. Representative bar shows the products of real-time PCR amplified with primers specific for mir-1397 and carp in chicken myoblasts and myotube cells. The amount of starting template for each condition was equilibrated relative to 5S rrna or GAPDH. The expression values were normalized with 5S rrna or GAPDH expression, and are represented as mean±s.e. (n=3, p< 0.01). 4. Discussion The chicken carp gene has a 3 -UTR that is more than 2.2 kb [10], which indicated that controlling the promoter activity during transcription is not the only mechanism for carp regulation in muscle. MicroRNAs are known to negatively regulate the expression of their target mrnas via the degradation of the bound mrna target or by directly inhibiting translation of the target mrna [18, 19]. However, while precise regulation of carp levels is an important determinant in defining the biological outcome, the role of mirnas in modulating carp expression has not been extensively analyzed. In this study, we demonstrated that carp is a direct target of mir-1397 in CFMs. Several lines of evidences support this conclusion. First, computational prediction of targets identified a putative binding site on the 3 -UTR of carp mrna. This was experimentally validated by utilizing a luciferase reporter activity assay which showed that the mir-1397 mimic decreased the luciferase activity of the reporter vector containing the mir-1397 response elements; in contrast, the introduction of mutations 87
6 in the mir-1397 binding site of the carp 3 -UTR substantially reduced mir-1397 s inhibitory effects. Second, mir-1397 induction correlated with a reduction in carp protein in CFMs. Third, inhibition of mir-1397 up-regulated, whereas the mir-1397 mimic down-regulated carp protein in CFMs. Together, these results demonstrate a functional significance of mir-1397 induction in inhibition of carp protein expression. However, we found no mir-1397 target sequences exist within the 3 -UTR of mammalian carp homolog genes, which may be correlated with homologous with chicken and mammalian carp is low and 3-'UTR sizes and sequences largely difference. To our knowledge, mir-1397 is the first example of a chicken-specific regulator of carp levels. However, there are no published results on mir-1397 function in any animal or human model. Although our results indicated that mir-1397 is predominant expressed in brain and heart of the adult chicken, which relative lower expressed in skeletal muscle. Our study further contributes to this model and reports for the first time that mir-1397 expression levels are down-regulated during myogenesis. This coincides with the expression pattern of the chicken carp, which was predominantly expressed in chicken postnatal skeletal muscle, and its expression increased during myogenic differentiation in CFM cells [9, 10]. Our previous study demonstrated that carp may play an essential role in governing chicken skeletal myogenesis through promoting proliferation and avoiding apoptosis during CFM cell differentiation. Based on these results, we propose that down-regulated expression of mir-1397 is required during terminal differentiation in order that the positive regulator of myogenesis, carp, is rapidly and efficiently induced, thereby promoting myogenesis (Fig. 4). In summary, our study demonstrated that the mir-1397 is an important factor affecting the carp gene expression in chicken. These data are helpful for elucidating the biological functions of carp and the molecular mechanisms underlying skeletal muscle development in avian. We provided a starting point for examination of the regulation of the chicken carp gene in more detail. Further work is required to elucidate the subtle molecular mechanisms controlling carp expression during myogenesis. Acknowledgements Support for this work includes funding from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No and ), and the third session of the China-Serbia Committee for scientific and technological cooperation (Grant No. 3-13), and Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.2015A ), and Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. A , A , A ), and Scientific research fund of Guangdong Medical University (Grant No.M ). References [1] Chu W., Burns D.K., Swerlick R.A., et al. Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine-inducible nuclear protein from human endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. Vol. 270 (1995), [2] Zou Y., Evans S., Chen J., et al. a cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, is downstream in the Nkx2-5 homeobox gene pathway. Development. Vol. 124 (1997), [3] Miller M.K., Bang M.L., Witt C.C., et al. The muscle ankyrin repeat proteins: CARP, ankrd2/arpp and DARP as a family of titin filament-based stress response molecules. J. Mol. Biol. Vol. 333 (2003), [4] Zhang N., Xie X., Wang J. Multifunctional protein: cardiac ankyrin repeat protein. Journal of Zhejiang University. Science.Vol. B 17 (2016), [5] Zolk O., Frohme M., Maurer A., et al. Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, a negative regulator of cardiac gene expression, is augmented in human heart failure. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. Vol. 293 (2002), [6] Aihara Y., Kurabayashi M., Saito Y., et al. Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein is a novel marker of cardiac hypertrophy: role of M-CAT element within the promoter. Hypertension. Vol. 36 (2000),
7 [7] Arimura T., Bos J., Sato A., et al. Cardiac Ankyrin Repeat Protein Gene (ANKRD1) Mutations in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Vol. 54 (2009), [8] Zolk O., Marx M., Jackel E., et al. Beta-adrenergic stimulation induces cardiac ankyrin repeat protein expression: involvement of protein kinase A and calmodulin-dependent kinase. Cardiovasc. Res. Vol. 59 (2003), [9] Yang W., Zhang Y., Ma G., et al. Identification of gene expression modifications in myostatin-stimulated myoblasts. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. Vol. 326 (2005), [10] Ma G., Wang H., Gu X., et al. CARP, a myostatin-downregulated gene in CFM cells, is a novel essential positive regulator of myogenesis. International Journal of Biological Sciences. Vol. 10 (2014), [11] Lee S. Regulation on muscle mass by myostatin. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. Vol. 20 (2004), [12] Kambadur R., Sharma M., Smith T., et al. Mutations in myostatin (GDF8) in double-muscled Belgian Blue and Piedmontese cattle. Genome Research. Vol. 7 (1997), [13] Lee S. Extracellular Regulation of Myostatin: A Molecular Rheostat for Muscle Mass. Immunology, Endocrine & Metabolic Agents in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 10 (2010), [14] Cannell I., Kong Y., Bushell M.G., et al. How do micrornas regulate gene expression? Biochemical Society Transactions. Vol. 36 (2008), [15] Rao P., Kumar R., Farkhondeh M., et al. Myogenic factors that regulate expression of muscle-specific micrornas. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Vol. 103 (2006), [16] Krüger J., Rehmsmeier M. RNAhybrid: MicroRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Research. Vol. 34 (2006). [17] Mar J., Antin P., Cooper T., et al. Analysis of the upstream regions governing expression of the chicken cardiac troponin T gene in embryonic cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. Journal of Cell Biology. Vol. 107 (1998), [18] Stark A., Brennecke J., Bushati N., et al. Animal micrornas confer robustness to gene expression and have a significant impact on 3 UTR evolution. Cell. Vol. 123 (2005), [19] Callis T., Deng Z., Chen J., et al. Muscling Through the microrna World. Experimental Biology and Medicine.Vol. 233 (2008), [20] Samaras, S. E., Chen, B., Koch, S. R., et al. 26S Proteasome regulation of Ankrd1/CARP in adult rat ventricular myocytes and human microvascular endothelial cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. Vol. 425 (2012),
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 -. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
-. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
HIF-inducible mir-191 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment.
 HIF-inducible mir-9 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment. Neha Nagpal, Hafiz M Ahmad, Shibu Chameettachal3, Durai Sundar, Sourabh
HIF-inducible mir-9 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment. Neha Nagpal, Hafiz M Ahmad, Shibu Chameettachal3, Durai Sundar, Sourabh
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting
 MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
mir-132 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4
 Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Inhibition of Autophagy by MiR-30A Induced by Mycobacteria tuberculosis as a Possible Mechanism of Immune Escape in Human Macrophages
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 68, 420 424, 2015 Short Communication Inhibition of Autophagy by MiR-30A Induced by Mycobacteria tuberculosis as a Possible Mechanism of Immune Escape in Human Macrophages Zhi Chen
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 68, 420 424, 2015 Short Communication Inhibition of Autophagy by MiR-30A Induced by Mycobacteria tuberculosis as a Possible Mechanism of Immune Escape in Human Macrophages Zhi Chen
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
P. Mathijs Voorhoeve, Carlos le Sage, Mariette Schrier, Ad J.M. Gillis, Hans Stoop,
 Supplemental Data A Genetic Screen Implicates mirna-372 and mirna-373 As Oncogenes in Testicular Germ Cell Tumors P. Mathijs Voorhoeve, Carlos le Sage, Mariette Schrier, Ad J.M. Gillis, Hans Stoop, Remco
Supplemental Data A Genetic Screen Implicates mirna-372 and mirna-373 As Oncogenes in Testicular Germ Cell Tumors P. Mathijs Voorhoeve, Carlos le Sage, Mariette Schrier, Ad J.M. Gillis, Hans Stoop, Remco
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Cross species analysis of genomics data. Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets
 02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supp. Fig. 1. Autoimmunity. Tolerance APC APC. T cell. T cell. doi: /nature06253 ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 TCR CD28
 Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: , 2019
 326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression
 1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Identification of target genes for adenohypophysis-prefer mir-7 and mir-375 in cattle
 Identification of target genes for adenohypophysis-prefer mir-7 and mir-375 in cattle B. Yuan 1, G.J. Sun 1, G.L. Zhang 2, J. Wu 2, C. Xu 1, L.S. Dai 1, J. Chen 1, X.F. Yu 1, Z.H. Zhao 1 and J.B. Zhang
Identification of target genes for adenohypophysis-prefer mir-7 and mir-375 in cattle B. Yuan 1, G.J. Sun 1, G.L. Zhang 2, J. Wu 2, C. Xu 1, L.S. Dai 1, J. Chen 1, X.F. Yu 1, Z.H. Zhao 1 and J.B. Zhang
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 15: , 2018
 10098 MicroRNA 154 functions as a tumor suppressor in non small cell lung cancer through directly targeting B cell specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1 SIDA LIU 1, YANG YANG 2, LU CHEN
10098 MicroRNA 154 functions as a tumor suppressor in non small cell lung cancer through directly targeting B cell specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1 SIDA LIU 1, YANG YANG 2, LU CHEN
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro
 Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
Research Article MiR-15b Targets Cyclin D1 to Regulate Proliferation and Apoptosis in Glioma Cells
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 687826, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/687826 Research Article MiR-15b Targets to Regulate Proliferation and Apoptosis in Glioma Cells Guan Sun, 1 Lei Shi,
BioMed Research International, Article ID 687826, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/687826 Research Article MiR-15b Targets to Regulate Proliferation and Apoptosis in Glioma Cells Guan Sun, 1 Lei Shi,
RESEARCH ARTICLE. MiR-130a Overcomes Gefitinib Resistance by Targeting Met in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.3.1391 MiR-130a Overcomes Gefitinib Resistance by Targeting Met in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines RESEARCH ARTICLE MiR-130a Overcomes Gefitinib Resistance
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.3.1391 MiR-130a Overcomes Gefitinib Resistance by Targeting Met in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines RESEARCH ARTICLE MiR-130a Overcomes Gefitinib Resistance
The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by upregulating mirna-487a
 Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis. Midbrain Forebrain/ Forebrain/ Hindbrain Spinal cord Hindbrain Hindbrain
 A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
Molecular BioSystems PAPER. Gene module based regulator inference identifying mir-139 as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer.
 Molecular BioSystems PAPER Cite this: Mol. BioSyst., 2014, 10, 3249 Gene module based regulator inference identifying mir-139 as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer Jin Gu, * a Yang Chen, a Huiya Huang,
Molecular BioSystems PAPER Cite this: Mol. BioSyst., 2014, 10, 3249 Gene module based regulator inference identifying mir-139 as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer Jin Gu, * a Yang Chen, a Huiya Huang,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: , YULIN XIONG, CHANGJIANG ZHANG, JING YUAN, YAN ZHU, ZHAOXIA TAN, XUEMEI KUANG and XIAOHONG WANG
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 1733-1737, 2015 Hepatitis C virus represses the cellular antiviral response by upregulating the expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 through sponging
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 1733-1737, 2015 Hepatitis C virus represses the cellular antiviral response by upregulating the expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 through sponging
microrna 761 regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3β expression and promotes the proliferation and cell cycle of human gastric cancer cells
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 16: 3459-3464, 2018 microrna 761 regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3β expression and promotes the proliferation and cell cycle of human gastric cancer cells XINFANG SUN, HONGTAO HOU,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 16: 3459-3464, 2018 microrna 761 regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3β expression and promotes the proliferation and cell cycle of human gastric cancer cells XINFANG SUN, HONGTAO HOU,
Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs
 Protein Cell 15, 6(1):1 5 DOI 1.17/s13238-14-116-2 Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs Jie Xu, Xi Chen, Donghai Li, Qun Chen, Zhen Zhou, Dongxia
Protein Cell 15, 6(1):1 5 DOI 1.17/s13238-14-116-2 Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs Jie Xu, Xi Chen, Donghai Li, Qun Chen, Zhen Zhou, Dongxia
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Supplemental Figure 1
 1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SYPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Figure S1. Phylogenic studies of the mir-183/96/182 cluster and 3 -UTR of Casp2. (A) Genomic arrangement of the mir-183/96/182 cluster in vertebrates.
SYPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Figure S1. Phylogenic studies of the mir-183/96/182 cluster and 3 -UTR of Casp2. (A) Genomic arrangement of the mir-183/96/182 cluster in vertebrates.
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
Prediction of micrornas and their targets
 Prediction of micrornas and their targets Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Computational Methods Mature and precursor mirna prediction mirna target gene prediction Summary micrornas? RNA can
Prediction of micrornas and their targets Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Computational Methods Mature and precursor mirna prediction mirna target gene prediction Summary micrornas? RNA can
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences. mirna-711-sp1-collagen-i pathway is involved in the anti-fibrotic effect of pioglitazone in myocardial infarction
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER May 2013 Vol.56 No.5: 431 439 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4477-1 mirna-711-sp1-collagen-i pathway is involved in the anti-fibrotic effect of pioglitazone in myocardial
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER May 2013 Vol.56 No.5: 431 439 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4477-1 mirna-711-sp1-collagen-i pathway is involved in the anti-fibrotic effect of pioglitazone in myocardial
Posttranscriptional upregulation of HER3 by HER2 mrna induces trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer
 Li et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:113 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0862-5 RESEARCH Open Access Posttranscriptional upregulation of HER3 by HER2 mrna induces trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer
Li et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:113 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0862-5 RESEARCH Open Access Posttranscriptional upregulation of HER3 by HER2 mrna induces trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues. suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by
 Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 10: , 2015
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 10: 1103-1108, 2015 As one of the most common malignant cancers, bladder cancer severely threatens the health of individuals worldwide. Downregulation of tumor suppressors
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 10: 1103-1108, 2015 As one of the most common malignant cancers, bladder cancer severely threatens the health of individuals worldwide. Downregulation of tumor suppressors
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described
 Supplemental Methods In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described previously 1 2 using 32P-labeled 211 bp fragment from 3 HS1. Footprinting reaction mixes contained
Supplemental Methods In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described previously 1 2 using 32P-labeled 211 bp fragment from 3 HS1. Footprinting reaction mixes contained
MicroRNA 761 is downregulated in colorectal cancer and regulates tumor progression by targeting Rab3D
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE MicroRNA 761 is downregulated in colorectal cancer and regulates tumor progression by targeting Rab3D YUPENG REN, GANG SHI, PENG JIANG and QINGKAI MENG Department
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE MicroRNA 761 is downregulated in colorectal cancer and regulates tumor progression by targeting Rab3D YUPENG REN, GANG SHI, PENG JIANG and QINGKAI MENG Department
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 35: 1757-1763, 2016 MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy Ruida Xu, Shuzhong Liu, Haihong Chen
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 35: 1757-1763, 2016 MicroRNA-30a downregulation contributes to chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through activating Beclin-1-mediated autophagy Ruida Xu, Shuzhong Liu, Haihong Chen
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
microrna 200a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FOXA1 in glioma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE microrna 200a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FOXA1 in glioma XIAOFENG CHEN 1, KUN LIU 1, PING YANG 2, WEIPING KUANG 1, HONGXING HUANG 1, EWEN TU 3, BO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE microrna 200a functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting FOXA1 in glioma XIAOFENG CHEN 1, KUN LIU 1, PING YANG 2, WEIPING KUANG 1, HONGXING HUANG 1, EWEN TU 3, BO
s u p p l e m e n ta ry i n f o r m at i o n
 Figure S1 Characterization of tet-off inducible cell lines expressing GFPprogerin and GFP-wt lamin A. a, Western blot analysis of GFP-progerin- or GFP-wt lamin A- expressing cells before induction (0d)
Figure S1 Characterization of tet-off inducible cell lines expressing GFPprogerin and GFP-wt lamin A. a, Western blot analysis of GFP-progerin- or GFP-wt lamin A- expressing cells before induction (0d)
NOVEL FUNCTION OF mirnas IN REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION. Ana M. Martinez
 NOVEL FUNCTION OF mirnas IN REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION Ana M. Martinez Switching from Repression to Activation: MicroRNAs can Up-Regulate Translation. Shoba Vasudevan, Yingchun Tong, Joan A. Steitz AU-rich
NOVEL FUNCTION OF mirnas IN REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION Ana M. Martinez Switching from Repression to Activation: MicroRNAs can Up-Regulate Translation. Shoba Vasudevan, Yingchun Tong, Joan A. Steitz AU-rich
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 1977-1984, 2017 mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9 Hua Liang, Ruoyu Luo, Xiaoqi Chen, Yuzi Zhao and Aili Tan Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 1977-1984, 2017 mir-187 inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells by targeting FGF9 Hua Liang, Ruoyu Luo, Xiaoqi Chen, Yuzi Zhao and Aili Tan Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
*** DMSO DAPT. JAG-FC (ug/ml) Fold change in RLU. Fold change in RLU JAG1-Fc Wnt1 CM 1.2. Fold change in expression
 A 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DMSO DAPT 1..8.6.4.2 C 1 2 3 4 JAGFC (ug/ml) D 5 6 JAG1Fc Wnt1 CM Fold change in expression 1..8.6.4.2 *** 1..8.6.4.2 * JAG1Fc Wnt1 CM JAG1Fc Dvl2 Fig. S1. Dishevelled inhibits Notch signalling.
A 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DMSO DAPT 1..8.6.4.2 C 1 2 3 4 JAGFC (ug/ml) D 5 6 JAG1Fc Wnt1 CM Fold change in expression 1..8.6.4.2 *** 1..8.6.4.2 * JAG1Fc Wnt1 CM JAG1Fc Dvl2 Fig. S1. Dishevelled inhibits Notch signalling.
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat. synovial cells
 Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets PUMA to promote host cell survival
 An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Published online 17 July 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, No doi: /nar/gkq637
 Published online 17 July 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, No. 21 7673 7688 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq637 GAM/ZFp/ZNF512B is central to a gene sensor circuitry involving cell-cycle regulators, TGFb
Published online 17 July 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, No. 21 7673 7688 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq637 GAM/ZFp/ZNF512B is central to a gene sensor circuitry involving cell-cycle regulators, TGFb
MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
