Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2011)
|
|
|
- Victor Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 77 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2011) Original Article Relationship between the intensity of stroke rehabilitation and outcome: A survey conducted by the Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward Association in Japan (second report) Shota Nagai, RPT, PhD, 1 Shigeru Sonoda, MD, PhD, 1 Ichiro Miyai, MD, PhD, 1 Atsuo Kakehi, Prof., Dr. Eng, 1 Shinsuke Goto, RPT, 1 Yuko Takayama, ST, 1 Toshio Ota, MD, 1 Isao Itoh, MD, 1 Shinichi Yamamoto, OTR, 1 Yasuki Takizawa, MD, 1 Katsuyuki Kaku, MSW, 1 Yukiko Inoue, PhD, 1 Makoto Ishikawa, MD 1 1 Annual Survey Committee, Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward Association, Shibuya, Tokyo, Japan ABSTRACT Nagai S, Sonoda S, Miyai I, Kakehi A, Goto S, Takayama Y, Ota T, Itoh I, Yamamoto S, Takizawa Y, Kaku K, Inoue Y, Ishikawa M. Relationship between the intensity of stroke rehabilitation and outcome: A survey conducted by the Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward Association in Japan (second report). Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2011: Objective: To verify the scientific basis for additional of rehabilitation programs, 2 new medical remuneration systems that were introduced in Methods: Stroke patients admitted to kaifukuki rehabilitation wards were included in this study. Questionnaire forms were mailed to 11 member facilities of the Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward Association in Japan, and relevant data were collected. The 11 facilities were divided into 3 groups according to the total hours spent on physical, occupational, and speech-language-hearing therapy at each facility. Rehabilitation outcomes were compared between facilities that provided 6 units/day of rehabilitation 7 days per week for each patient (1 unit = a 20-minute rehabilitation) ( 6 units group), those providing 4 and <6 units/day of rehabilitation (4 6 units group), and those providing <4 units/day of rehabilitation (<4 units group). Results: Total scores of the motor and cognitive items of the Functional Independence Measures on admission Correspondence: Shota Nagai, RPT, PhD Faculty of Health Sciences, Kinjo University 1200 Kasama-machi, Hakusan, Ishikawa , Japan s.nagai@mac.com Accepted: November 14, 2011 No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript. were significantly lower in the 6 units group than in the other 2 groups. The number of days spent in the rehabilitation facility was significantly lower, by approximately 12 days, in the 6 units group than in the other groups. Conclusion: These results revealed that facilities providing 6 units/day of rehabilitation even on holidays enabled patients to be discharged from the facility in significantly fewer days, despite accepting patients with more severe stroke, compared to facilities providing fewer units of rehabilitation. Key words: kaifukuki rehabilitation ward, stroke, training time, rehabilitation outcome Introduction The Japanese national insurance system introduced kaifukuki rehabilitation wards in 2000; the term kaifukuki refers to the recovery or convalescent phase [1]. A stay in a kaifukuki rehabilitation ward is approved by the medical remuneration system in Japan when a stroke patient is hospitalized within 2 months of symptom onset, and the patient can receive up to 9 units of 20-minute rehabilitation sessions per day (i.e., up to 180 minutes/day) for 150 days after admission. This system is internationally unique in that it provides as long as 180 minutes of rehabilitation in a single day. The findings of the first investigation of kaifukuki rehabilitation wards conducted by the Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward Association in Japan, the association for kaifukuki rehabilitation wards throughout Japan [2,3], were noteworthy: stroke patients hospitalized in kaifukuki rehabilitation wards who had received 6 units/day of physical/occupational therapy showed markedly improved activities of daily living (ADL) than those shown by patients who had received <6 units/day of therapy [3]. Following the introduction of 2 new medical
2 78 remuneration systems in 2010, namely additional of rehabilitation programs, an environment has been established for more frequent use of rehabilitation services because these new systems are applicable to facilities providing 6 units/day of rehabilitation 7 days a week. However, whether an increased frequency of rehabilitation treatment can in fact improve rehabilitation outcomes has not been adequately investigated. Therefore, the objective of this study was to verify the scientific basis of the aims of these newly introduced additional remuneration systems: providing 6 units/day of rehabilitation 7 days a week, based on the data obtained from our previous investigations. Methods 1. Study population This study included stroke patients admitted to and treated in kaifukuki rehabilitation wards. 2. Survey methods Among the 21 member facilities of the Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward Association in Japan that previously participated in committee activities or other administrative activities, 11 facilities that were evaluable for 3 consecutive years were included in the present survey. The survey was conducted between 2006 and Questionnaire forms were mailed at the end of October in each year to all the patients discharged from the relevant facilities between August and September in the same year, and stroke patients were identified from the returned data. The patient background data evaluated were age, sex, primary disease, number of symptom onsets (primary or recurrence), laterality of lesion (right, left, or bilateral), onset-admission interval (OAI), length of stay in facility (LOS), and discharge disposition (home, sudden change in condition (including death), or other). The discharge disposition was recorded as home even if the patient used home services, such as visiting care (including those discharged to group homes or care houses), and other if the patient was transferred to another hospital or nursing facility. Functional Independence Measures (FIM) [4] were evaluated as parameters of daily activities of living: total score of FIM motor and cognitive items, gained score of FIM motor items (total score of FIM motor items at discharge minus the score on admission), and efficiency of FIM motor items (gained score of FIM motor items divided by LOS) were calculated. The numbers of beds and facility staff (including physicians, occupational therapists, physical therapists, speechlanguage-hearing therapists, social workers, nurses, and care workers) at the time of the 2008 survey were also determined. 3. Analysis methods The number of units, with 1 unit defined as 20 minutes of rehabilitation, was calculated from the data available on hours spent on rehabilitation per week. Average hours of rehabilitation were calculated for each of the 11 facilities evaluated, and rehabilitation outcomes were compared among facilities that provided each patient with 6 units/day of rehabilitation 7 days a week ( 6 units group), those providing 4 and <6 units/day of rehabilitation (4 6 units group), and those providing <4 units/day of rehabilitation (<4 units group). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for the statistical analysis. The Tukey-Kramer honestly significant difference (HSD) test was used for posthoc analysis. Nominal scales were compared using the chi-square test. The average numbers of beds and facility staff at the time of the 2008 survey were compared between facilities. Results 1. Data collected Data were collected from 1,651 stroke patients at the 11 participating facilities. Among the 1,651 patients, 79 with incomplete data were excluded, and data from the remaining 1,572 patients were analyzed. Detailed background data for all patients are presented in Table Comparison of rehabilitation outcomes among the 3 treatment groups When facilities were classified according to the total number of units of physical, occupational, and speechlanguage-hearing therapy given per day; there were 124 patients in 2 facilities that provided <4 units, 560 patients in 4 facilities that provided 4 6 units, and 888 patients in 5 facilities that provided 6 units of therapy. A significant difference in the distribution of sex was found among the 3 groups. In contrast, no significant differences were found in the distributions of diagnosis, laterality of lesion, number of symptom onsets, age, or OAI (Table 2). A significant intergroup difference was also observed in discharge disposition; slightly fewer patients were discharged to home in the <4 units group than in the other 2 groups (Table 2). Total score of FIM motor and cognitive items on admission was significantly lower in the 6 units group than in the other 2 groups. Total score of FIM motor items at discharge was significantly lower in the 6 units group than in the 4 6 units group (Table 3). The same tendency was also observed in the total score of FIM cognitive ability items at discharge as compared to at admission (Table 3). LOS was significantly shorter in the 6 units group, by approximately 12 days, than in the other 2 groups (Table 3). While no significant difference was found among the 3 groups with regard to gained scores of FIM motor and
3 79 Table 1. Background data for all patients Sex M: 905 F: 667 Primary disease CH: 577 CI: 895 SAH: 100 Laterality of lesion Rt: 721 Lt: 716 bilateral: 121 Discharge disposition home: 996 other: 439 sudden change: 137 Number of symptom onsets primary: 1,257 recurrence: 306 unknown: 9 Mean age (years) 68.7 ± 12.9 Mean OAI (days) 39.3 ± 28.8 Mean LOS (days) 86.3 ± 46.3 Admission FIM motor (points) 46.1 ± 23.9 Admission FIM cognitive (points) 21.6 ± 9.5 Units of PT per week (units)* 18.9 ± 7.9 Units of OT per week (units) 17 ± 6.9 Units of ST per week (units) 8.9 ± 6.1 Units of therapy per day (units) 6 ± 2.2 CH: cerebral hemorrhage, CI: cerebral infarction, SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage, OAI: onset-admission interval, LOS: length of stay, FIM motor: total score of FIM motor items, FIM cognitive: total score of FIM cognitive items, PT: physical therapy, OT: occupational therapy, ST: speech-language-hearing therapy * One unit is defined as 20 minutes of rehabilitation Table 2. Comparison of the demographics among the 3 groups defined by the daily number of rehabilitation units provided (i.e., <4 units, 4 6 units, and 6 units groups) <4 units group n = facilities 4 6 units group n = facilities 6 units group n = facilities p value Mean age (years) 67.6 ± ± ± 13.0 N.S. (ANOVA) Mean OAI (days) 41.5 ± ± ± 23.9 N.S. (ANOVA) Sex M: 87 M: 315 M: 503 p < 0.05 (chi-square test) F: 37 F: 245 F: 385 Primary disease CH: 40 CH: 212 CH: 325 N.S. (chi-square test) CI: 70 CI: 318 CI: 507 SAH: 14 SAH: 30 SAH: 56 Laterality of lesion Rt: 62 Rt: 237 Rt: 422 N.S. (chi-square test) Lt: 56 Lt: 277 Lt: 383 bilateral: 6 bilateral: 38 bilateral: 77 unknown: 0 unknown: 8 unknown: 6 Discharge disposition (%) home: 57.3 home: 65.7 home: 62.7 p < 0.05 (chi-square test) sudden change: 5.6 sudden change: 7.0 sudden change: 10.3 others: 37.1 others: 27.3 others: 27.0 Number of symptom onsets primary: 105 primary: 442 primary: 710 N.S. (chi-square test) recurrence: 19 recurrence: 110 recurrence: 177 unknown: 0 unknown: 8 unknown: 1 Units of PT per week (units) 7.6 ± ± ± 6.9 p < (ANOVA)* Units of OT per week (units) 6.3 ± ± ± 5.7 p < (ANOVA)* Units of ST per week (units) 4.9 ± ± ± 6.6 p < (ANOVA)** Total units of therapy per day (units) 2.0 ± ± ± 1.6 p < (ANOVA)* OAI: onset-admission interval, CH: cerebral hemorrhage, CI: cerebral infarction, SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage, PT: physical therapy, OT: occupational therapy, ST: speech-language-hearing therapy, N.S.: not significant Significant difference on Tukey-Kramer HSD test * among 3 groups ** between <4 units and 4 units group, <4 units and 6 units group cognitive items, efficiency of FIM motor items was significant higher in the 6 units group than in the <4 units group (Table 3). The rate of returning home was slightly lower in the <4 units group than in the other groups. Patients in the 6 units group had a slightly higher rate of sudden change in condition than those in the other groups (Table 2). The average numbers of beds and facility staff tended to increase as the number of rehabilitation units increased, although the numbers of beds and nurses were slightly higher in the 4 6 units group than in the 6 units group (Table 4). Discussion In 2010, new remuneration systems for additional
4 80 Table 3. Comparison of treatment outcomes among the <4 units, 4 6 units, and 6 rehabilitation units groups <4 units group n = facilities 4 6 units group n = facilities 6 units group n = facilities ANOVA Mean LOS (days) 93.4 ± ± ± 43.8 p < * Admission FIM motor (points) 51.1 ± ± ± 23.4 p < * Discharge FIM motor (points) 64.8 ± ± ± 26.3 p < 0.01 ** FIM motor gain (points) 13.7 ± ± ± 13.0 N.S. FIM motor efficiency (points/day) 0.15 ± ± ± 0.21 p < 0.01 *** Admission FIM cognitive (points) 24.2 ± ± ± 9.4 p < * Discharge FIM cognitive (points) 27.6 ± ± ± 9.3 p < * FIM cognitive gain (points) 3.5 ± ± ± 4.0 N.S. LOS: length of stay, N.S.: not significant, FIM motor: total score of FIM motor items, FIM motor gain: total score of FIM motor items at discharge minus that on admission, FIM motor efficiency: gained score of FIM motor items divided by LOS, FIM cognitive: total score of FIM cognitive items, FIM cognitive gain: total score of FIM cognitive items at discharge minus that on admission Significant difference in Tukey-Kramer HSD test * between <4 units and 6 units groups, and 4 6 units and 6 units groups ** between 4 6 units and 6 units groups *** between <4 units and 6 units groups Table 4. Average numbers of beds and staff in the facilities of each group Number of beds MD OT <4 units group (2 facilities) units group (3 facilities)* units group (5 facilities) MD: doctor of medicine, OT: occupational therapist, PT: physical therapist, ST: speech-language-hearing therapist, SW: social worker, NS: nurse, CW: care worker * The data for only 3 of the 4 facilities PT ST SW NS CW of rehabilitation programs were introduced into kaifukuki rehabilitation wards that provide 6 units/ day of rehabilitation 7 days a week. However, other than general reports demonstrating the relationship between rehabilitation intensity and rehabilitation outcome [5 8], there is insufficient scientific basis for the substantial increase in medical remuneration that these new systems have brought. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to retrospectively analyze historical data to determine the appropriateness of these new medical remuneration systems. Most previous studies on the number of rehabilitation units have compared groups of patients defined by the number of rehabilitation units performed [3, 9]. One problem with such data is that the unit numbers were not assigned randomly, but were influenced by various factors, such as the treatment strategies adopted by the attending physicians, the number of staff, and the severity of complications. Therefore, the results were affected more by bias due to other factors than by rehabilitation intensity. A previous comparison of rehabilitation intensity within a single facility did not necessarily show an improvement in rehabilitation outcomes with increasing intensity of rehabilitation [9]. Another study demonstrated a significant improvement with increasing intensity of rehabilitation [3] by excluding severe comorbidities and all disorders other than hemiplegia, and stratifying patients by time elapsed since symptom onset; however, the excessive amount of data excluded as a result of stratification might have resulted in a substantial disparity in patient characteristics between the analyzed population and the entire population. The present study is the first to compare rehabilitation outcomes between facilities in Japan. The types of patients admitted and the treatment strategies adopted tend to vary among kaifukuki rehabilitation wards due to regional characteristics and separateness in facilityto-facility relationships [3]. Therefore, to correct for such biases, the participation of multiple facilities is essential; therefore, the present study analyzed patient data from 11 facilities. The present study divided rehabilitation facilities into 3 groups for analysis purposes, resulting in relatively small numbers of facilities in each group and possibly an insufficient statistical power. Nevertheless, a certain trend in rehabilitation outcomes was observed. The results showed that the 6 units group had
5 81 significantly lower total scores of FIM motor and cognitive items on admission, indicating that facilities providing 6 units/day of rehabilitation accept patients with relatively severe ADL and cognitive disorders on admission. These factors are generally associated with poor prognosis and adverse consequences [10]. However, patients in the 6 units group were discharged with significantly shorter LOS (by approximately 12 days) than those in the other 2 groups; in other words, these facilities allowed patients admitted with more severe stroke to be discharged within a shorter period of time. Given a home returning rate of greater than 60%, no significant difference in gained score of FIM motor items among the 3 groups, and significantly higher efficiency of FIM motor items in the 6 units group compared to the <4 units group, it would seem that a shorter LOS does not necessarily imply reduced rehabilitation outcomes. Additionally, in the 6 units group, the rate of sudden change in condition was slightly higher than that in the other 2 groups. This may be because patients with more severe stroke were admitted to facilities providing 6 units/day of rehabilitation, although the involvement of other factors is also possible. In this study, grouping was based only on the number of units of rehabilitation provided. Rehabilitation outcomes in kaifukuki rehabilitation wards are affected, not only by the number of units of rehabilitation provided, but also by many other factors, including the number of staff, ward structure, the equipment/instruments available, and cooperation with medical institutions and welfare agencies. Originally, the grouping should have been done using a comprehensive rehabilitation parameter reflecting all these factors. However, since this was difficult to do in this study, the effects were analyzed by groups based only on the number of rehabilitation units provided. However, in facilities with a higher number of units, the average number of staff tends to be higher for all professionals, except for nurses, and this might have affected the results to some extent. Overall, the present results revealed that facilities providing 6 units/day of rehabilitation even on holidays allowed patients to be discharged from the facility in significantly fewer days, despite accepting patients with more severe stroke, compared to facilities providing fewer units of rehabilitation. Although further investigations are needed, the 2 systems introduced, additional remuneration for providing rehabilitation services on holidays and additional remuneration for enrichment of rehabilitation programs, do appear to be producing the expected effects. References 1. Miyai I, Sonoda S, Nagai S, Takayama Y, Inoue Y, Kakehi A, et al. Results of new policies for inpatient rehabilitation coverage in Japan. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2011; 25: Sonoda S, Miyai I, Nagai S, Yamamoto S, Takizawa Y, Ito I, et al. Relationship between nichijo-seikatsu-kinohyokahyo and the functional Independence measure in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward. Sogo Rihabiriteshon 2009; 37: Nagai S, Sonoda S, Kakehi A, Miyai I, Kurihara M, Ito I, et al. The relationship between intensity of stroke rehabilitation and outcome. Sogo Rihabiriteshon 2009; 37: Data management service of the Uniform Data System for Medical Rehabilitation and the Center for Functional Assessment Research (1990) Guide for use of the uniform data set for medical rehabilitation. version 3.0, State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo. 5. Kwakkel G, Wagenaar RC, Koelman TW, Lankhorst GJ, Koetsier JC. Effects of intensity of rehabilitation after stroke. A research synthesis. Stroke 1997; 28: French B, Thomas LH, Leathley MJ, Sutton CJ, McAdam J, Forster A, et al.: Repetitive task training for improving functional ability after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007; 17: CD Nagai S, Sonoda S, Saitoh E, Okuyama Y, Hasegawa M, Kawakita M, et al. Outcome of the full-time integrated treatment (FIT) program. Sogo Rihabiriteshon 2003; 31: Sonoda S, Saitoh E, Nagai S, Kawakita M, Kanada Y. Full-time integrated treatment program, a new system for stroke rehabilitation in Japan: comparison with conventional rehabilitation. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2004; 83: Okuyama Y, Sonoda S, Nagai S, Tanino G, Nobotachi N, Sakamoto R, et al.: Investigation of the Current Status of the FIT (Full-Time Integrated Treatment) Program for Stroke Patients: Analysis of Rigakuryoho Kagaku 2010; 25: Anderson TP, Bourestom N, Greenberg FR, Hildyard VG. Predictive factors in stroke rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1974; 55:
Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward
 32 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2012) Original Article Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward Makoto
32 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2012) Original Article Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward Makoto
Department of Rehabilitation, Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 2. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 3
 16 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article Increasing the prediction accuracy of FIM gain by adding FIM improvement for one month from admission to the explanatory
16 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article Increasing the prediction accuracy of FIM gain by adding FIM improvement for one month from admission to the explanatory
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan
 86 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article The relationship between measured values and values predicted using multiple regression analysis for mean motor FIM at
86 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article The relationship between measured values and values predicted using multiple regression analysis for mean motor FIM at
Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward in Japan
 Jpn J Rehabil Med 2014 ; : 629.633 Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward in Japan Takatsugu OKAMOTO,,, Seiichi ANDO, Shigeru SONODA,, Ichiro MIYAI,, Makoto ISHIKAWA, Introduction In Japan, the ratio of the people
Jpn J Rehabil Med 2014 ; : 629.633 Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward in Japan Takatsugu OKAMOTO,,, Seiichi ANDO, Shigeru SONODA,, Ichiro MIYAI,, Makoto ISHIKAWA, Introduction In Japan, the ratio of the people
The influence of age on corrected motor FIM effectiveness
 56 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article The influence of age on corrected motor FIM effectiveness Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD, 1 Ryoji Nakanishi, MD, PhD, 1 Gihachiro
56 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article The influence of age on corrected motor FIM effectiveness Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD, 1 Ryoji Nakanishi, MD, PhD, 1 Gihachiro
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan
 78 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Assessment of the effects of factors in stroke rehabilitation using eight multiple regression analyses An analysis of
78 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Assessment of the effects of factors in stroke rehabilitation using eight multiple regression analyses An analysis of
Department of Rehabilitation, Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 2
 7 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Relationship between improvement in GNRI, a nutritional index, and improvement in motor FIM in elderly stroke patients
7 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Relationship between improvement in GNRI, a nutritional index, and improvement in motor FIM in elderly stroke patients
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 2
 66 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article A comparison of the corrected Functional Independence Measure (FIM) effectiveness at Kaifukuki rehabilitation hospitals
66 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article A comparison of the corrected Functional Independence Measure (FIM) effectiveness at Kaifukuki rehabilitation hospitals
Relationship between motor FIM improvement (corrected motor FIM effectiveness) and age in proximal femoral fractures
 131 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Relationship between motor FIM improvement (corrected motor FIM effectiveness) and age in proximal femoral fractures
131 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Relationship between motor FIM improvement (corrected motor FIM effectiveness) and age in proximal femoral fractures
Differences in FIM improvement rate stratified by nutritional status and age in stroke patients in kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation ward
 98 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (217) Original Article Differences in FIM improvement rate stratified by nutritional status and age in stroke patients in kaifukuki (convalescent)
98 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (217) Original Article Differences in FIM improvement rate stratified by nutritional status and age in stroke patients in kaifukuki (convalescent)
Multicenter survey of dysphagia and nutritional status of stroke patients in Kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation wards
 11 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Multicenter survey of dysphagia and nutritional status of stroke patients in Kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation
11 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Multicenter survey of dysphagia and nutritional status of stroke patients in Kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation
Fujihara et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2017) 3:2 DOI /s
 Fujihara et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40780-016-0070-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Development and evaluation of a formula for predicting introduction
Fujihara et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40780-016-0070-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Development and evaluation of a formula for predicting introduction
Falls in the sitting position Characteristics and efficacy of preventive measures
 5 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (205) Original Article Falls in the sitting position Characteristics and efficacy of preventive measures Takayuki Watabe, OTR,,2 Rikitaro Sako,
5 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (205) Original Article Falls in the sitting position Characteristics and efficacy of preventive measures Takayuki Watabe, OTR,,2 Rikitaro Sako,
Influence of Dysphagia on Short-Term Outcome in Patients with Acute Stroke
 Authors: Shinichiro Maeshima, MD, PhD Aiko Osawa, MD Yasuhiro Miyazaki, MA Yasuko Seki, BA Chiaki Miura, BA Yuu Tazawa, BA Norio Tanahashi, MD Affiliations: From the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine
Authors: Shinichiro Maeshima, MD, PhD Aiko Osawa, MD Yasuhiro Miyazaki, MA Yasuko Seki, BA Chiaki Miura, BA Yuu Tazawa, BA Norio Tanahashi, MD Affiliations: From the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine
CLINICAL SURVEY ON 300 APHASIC PATIENTS IN. Shinichi WATABE, Shunichi SASAO and Itaru KIMURA. (Miyagi Byoin National Sanatorium, Miyagi)
 IRYO Vol.41 (10) 52 patients, and they were divided into four groups before admission. They were compared for their limb and hand function (Brunnstrom stage), ambulation, degrees of "ADL" disturbances
IRYO Vol.41 (10) 52 patients, and they were divided into four groups before admission. They were compared for their limb and hand function (Brunnstrom stage), ambulation, degrees of "ADL" disturbances
COMMON GOALS OF REHABILITATION are to decrease
 373 The Relation Between Therapy Intensity and Outcomes of Rehabilitation in Skilled Nursing Facilities Diane U. Jette, PT, DSc, Reg L. Warren, PhD, Christopher Wirtalla, BA ABSTRACT. Jette DU, Warren
373 The Relation Between Therapy Intensity and Outcomes of Rehabilitation in Skilled Nursing Facilities Diane U. Jette, PT, DSc, Reg L. Warren, PhD, Christopher Wirtalla, BA ABSTRACT. Jette DU, Warren
Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community
 Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2009; 4: 24 9 Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community ORIGINAL ARTICLE CKC Chan Bsc, DWC Chan Msc, SKM Wong MBA, MAIS, BA, PDOT ABSTRACT
Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2009; 4: 24 9 Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community ORIGINAL ARTICLE CKC Chan Bsc, DWC Chan Msc, SKM Wong MBA, MAIS, BA, PDOT ABSTRACT
Efficiency, Effectiveness, and Duration of Stroke Rehabilitation
 241 Efficiency, Effectiveness, and Duration of Stroke Rehabilitation Surya Shah, MEd OTR/L, Frank Vanclay, MSocSci, and Betty Cooper, BAppSc This prospective multicenter study identifies the variables
241 Efficiency, Effectiveness, and Duration of Stroke Rehabilitation Surya Shah, MEd OTR/L, Frank Vanclay, MSocSci, and Betty Cooper, BAppSc This prospective multicenter study identifies the variables
Age as a Predictor of Functional Outcome in Anoxic Brain Injury
 Age as a Predictor of Functional Outcome in Anoxic Brain Injury Mrugeshkumar K. Shah, MD, MPH, MS Samir Al-Adawi, PhD David T. Burke, MD, MA Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Spaulding
Age as a Predictor of Functional Outcome in Anoxic Brain Injury Mrugeshkumar K. Shah, MD, MPH, MS Samir Al-Adawi, PhD David T. Burke, MD, MA Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Spaulding
OHTAC Recommendation
 OHTAC Recommendation Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy for Rehabilitation of Arm Dysfunction After Stroke in Adults. Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in May 27, 2011 November
OHTAC Recommendation Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy for Rehabilitation of Arm Dysfunction After Stroke in Adults. Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in May 27, 2011 November
The effects of repetitive task training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on extremities for acute cerebral paralysis
 The effects of repetitive task training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on extremities for acute cerebral paralysis Xingnan Liu 1,2 and Chunli Mei 1,a 1 Department of Nursing, Beihua
The effects of repetitive task training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on extremities for acute cerebral paralysis Xingnan Liu 1,2 and Chunli Mei 1,a 1 Department of Nursing, Beihua
Evaluating inpatient public rehabilitation in Australia using a utilization review tool developed in North America
 University of Wollongong Research Online Graduate School of Medicine - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 Evaluating inpatient public rehabilitation in Australia using a utilization
University of Wollongong Research Online Graduate School of Medicine - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 Evaluating inpatient public rehabilitation in Australia using a utilization
Evidence Tables and References 5.3 Delivery of Inpatient Stroke Rehabilitation
 Evidence Tables and References 5.3 Delivery of Inpatient Stroke Rehabilitation Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care 2011-2013 Update Last Updated: June 12, 2013 Contents Search Strategy...
Evidence Tables and References 5.3 Delivery of Inpatient Stroke Rehabilitation Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care 2011-2013 Update Last Updated: June 12, 2013 Contents Search Strategy...
<INSERT COUNTRY/SITE NAME> All Stroke Events
 WHO STEPS STROKE INSTRUMENT For further guidance on All Stroke Events, see Section 5, page 5-15 All Stroke Events Patient Identification and Patient Characteristics (I 1) Stroke
WHO STEPS STROKE INSTRUMENT For further guidance on All Stroke Events, see Section 5, page 5-15 All Stroke Events Patient Identification and Patient Characteristics (I 1) Stroke
Pattern of Functional Change During Rehabilitation of Patients With Hip Fracture
 111 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of Functional Change During Rehabilitation of Patients With Hip Fracture Nancy K. Latham, PhD, PT, Diane U. Jette, DSc, PT, Reg L. Warren, PhD, Christopher Wirtalla, BA ABSTRACT.
111 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of Functional Change During Rehabilitation of Patients With Hip Fracture Nancy K. Latham, PhD, PT, Diane U. Jette, DSc, PT, Reg L. Warren, PhD, Christopher Wirtalla, BA ABSTRACT.
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Tsang, M. H., Sze, K. H., & Fong, K. N. K. (2008). Occupational therapy treatment with right half-field eye-patching for patients with subacute stroke and unilateral neglect:
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Tsang, M. H., Sze, K. H., & Fong, K. N. K. (2008). Occupational therapy treatment with right half-field eye-patching for patients with subacute stroke and unilateral neglect:
Robot-aided training for upper limbs of sub-acute stroke patients
 27 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Robot-aided training for upper limbs of sub-acute stroke patients Hiroyuki Miyasaka, OTR, PhD, 1, 2 Yutaka Tomita, PhD,
27 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Robot-aided training for upper limbs of sub-acute stroke patients Hiroyuki Miyasaka, OTR, PhD, 1, 2 Yutaka Tomita, PhD,
PURPOSE OF THE SELF-ASSESSMENT TOOLS:
 Pulmonary Rehab s Framework Self-Assessment Tool Inpatient Rehab Survey for Pulmonary Rehab INTRODUCTION: In response to a changing rehab landscape in which rehabilitation is offered in many different
Pulmonary Rehab s Framework Self-Assessment Tool Inpatient Rehab Survey for Pulmonary Rehab INTRODUCTION: In response to a changing rehab landscape in which rehabilitation is offered in many different
Effects of Balance Exercise Assist Robot (BEAR) in independently mobile patients by disease
 1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2019) Original Article Effects of Balance Exercise Assist Robot (BEAR) in independently mobile patients by disease Shinichiro Goto, OTR, 1 Kazuyo
1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2019) Original Article Effects of Balance Exercise Assist Robot (BEAR) in independently mobile patients by disease Shinichiro Goto, OTR, 1 Kazuyo
Fujita Health University Nanakuri Memorial Hospital, Tsu, Mie, Japan 2
 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article The relationship between proximal function of the upper extremity on the paralyzed side and upper extremity skills in daily
Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article The relationship between proximal function of the upper extremity on the paralyzed side and upper extremity skills in daily
Australian, Finland and South Africa - Delving into Data to Investigate Differences in Stroke Rehabilitation
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australasian Rehabilitation Outcomes Centre - AROC Centre for Health Service Development - CHSD 2005 Australian, Finland and South Africa - Delving into Data to
University of Wollongong Research Online Australasian Rehabilitation Outcomes Centre - AROC Centre for Health Service Development - CHSD 2005 Australian, Finland and South Africa - Delving into Data to
VALIDATION OF THE ACTIVITY AND PARTICIPATION COMPONENT OF ICF CORE SETS FOR STROKE PATIENTS IN JAPANESE REHABILITATION WARDS
 J Rehabil Med 2016; 48: 764 768 ORIGINAL REPORT VALIDATION OF THE ACTIVITY AND PARTICIPATION COMPONENT OF ICF CORE SETS FOR STROKE PATIENTS IN JAPANESE REHABILITATION WARDS Shoji Kinoshita, MD 1,2, Masahiro
J Rehabil Med 2016; 48: 764 768 ORIGINAL REPORT VALIDATION OF THE ACTIVITY AND PARTICIPATION COMPONENT OF ICF CORE SETS FOR STROKE PATIENTS IN JAPANESE REHABILITATION WARDS Shoji Kinoshita, MD 1,2, Masahiro
The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity
 863 The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity Tetsuya Tsuji, MD, Meigen Liu, MD, DMSc, Shigeru Sonoda, MD, DMSc, Kazuhisa Domen, MD, DMSc, Naoichi Chino, MD,
863 The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity Tetsuya Tsuji, MD, Meigen Liu, MD, DMSc, Shigeru Sonoda, MD, DMSc, Kazuhisa Domen, MD, DMSc, Naoichi Chino, MD,
REHABILITATION UNIT ANNUAL OUTCOMES REPORT Prepared by
 REHABILITATION UNIT ANNUAL OUTCOMES Prepared by REPORT - 2014 Keir Ringquist, PT, PhD, GCS Rehabilitation Program Manager Director of Occupational and Physical Therapy DEMOGRAPHICS OF THE REHABILITATION
REHABILITATION UNIT ANNUAL OUTCOMES Prepared by REPORT - 2014 Keir Ringquist, PT, PhD, GCS Rehabilitation Program Manager Director of Occupational and Physical Therapy DEMOGRAPHICS OF THE REHABILITATION
Research Report. Key Words: Functional status; Orthopedics, general; Treatment outcomes. Neva J Kirk-Sanchez. Kathryn E Roach
 Research Report Relationship Between Duration of Therapy Services in a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program and Mobility at Discharge in Patients With Orthopedic Problems Background and Purpose. The purpose
Research Report Relationship Between Duration of Therapy Services in a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program and Mobility at Discharge in Patients With Orthopedic Problems Background and Purpose. The purpose
The need to understand what types and intensities of
 Original Contributions Relative Importance of Rehabilitation Therapy Characteristics on Functional Outcomes for Persons With Stroke Rita K. Bode, PhD; Allen W. Heinemann, PhD; Patrick Semik, BS; Trudy
Original Contributions Relative Importance of Rehabilitation Therapy Characteristics on Functional Outcomes for Persons With Stroke Rita K. Bode, PhD; Allen W. Heinemann, PhD; Patrick Semik, BS; Trudy
Measuring Functional Change in Outpatient Therapy Claims-Based Data Collection Reqs. for Outpatient Therapy Services
 Measuring Functional Change in Outpatient Therapy Paulette Niewczyk, MPH, PhD Director of Research Manager of Research, Development, and Analytical Services Manager of CFAR Uniform Data System for Medical
Measuring Functional Change in Outpatient Therapy Paulette Niewczyk, MPH, PhD Director of Research Manager of Research, Development, and Analytical Services Manager of CFAR Uniform Data System for Medical
OUR BRAINS!!!!! Stroke Facts READY SET.
 HealthSouth Rehabilitation Hospital Huntington Dr. Timothy Saxe, Medical Director READY SET. OUR BRAINS!!!!! Stroke Facts 795,000 strokes each year- 600,000 new strokes 5.5 million stroke survivors Leading
HealthSouth Rehabilitation Hospital Huntington Dr. Timothy Saxe, Medical Director READY SET. OUR BRAINS!!!!! Stroke Facts 795,000 strokes each year- 600,000 new strokes 5.5 million stroke survivors Leading
Dominican Scholar. Dominican University of California. Jason Ichimaru Dominican University of California
 Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Occupational Therapy Critically Appraised Papers Series Occupational Therapy 2017 Critcally Appraised Paper for: Is modified constraint-induced movement
Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Occupational Therapy Critically Appraised Papers Series Occupational Therapy 2017 Critcally Appraised Paper for: Is modified constraint-induced movement
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Dahl, A., Askim, T., Stock, R., Langørgen, E., Lydersen, S., & Indredavik, B. (2008). Short- and long-term outcome of constraint-induced movement therapy after stroke:
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Dahl, A., Askim, T., Stock, R., Langørgen, E., Lydersen, S., & Indredavik, B. (2008). Short- and long-term outcome of constraint-induced movement therapy after stroke:
Your Risk for Stroke and How to Be Prepared
 Your Risk for Stroke and How to Be Prepared TABLE OF CONTENTS 01 / 02 / 03 / 04 / 06 / 07 / 08 / 09 / 14 / Stroke Education Stroke: The No. 5 Cause Of Death In The U.S. Is Stroke Preventable? Stroke Risk
Your Risk for Stroke and How to Be Prepared TABLE OF CONTENTS 01 / 02 / 03 / 04 / 06 / 07 / 08 / 09 / 14 / Stroke Education Stroke: The No. 5 Cause Of Death In The U.S. Is Stroke Preventable? Stroke Risk
OUTCOMES AND DATA 2016
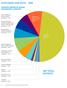 AND DATA 2016 SERVED BY REHAB IMPAIRMENT CATEGORY 20 patients 5.1% MAJOR MULTIPLE TRAUMA W/BRAIN OR SPINAL CORD INJURY 24 patients 6.2% TRAUMATIC 39 patients 10.0% AMPUTATION LOWER EXTREMITY 26 patients
AND DATA 2016 SERVED BY REHAB IMPAIRMENT CATEGORY 20 patients 5.1% MAJOR MULTIPLE TRAUMA W/BRAIN OR SPINAL CORD INJURY 24 patients 6.2% TRAUMATIC 39 patients 10.0% AMPUTATION LOWER EXTREMITY 26 patients
STROKE REHABILITATION: PREDICTING INPATIENT LENGTH OF STAY AND DISCHARGE PLACEMENT
 STROKE HKJOT REHABILITATION 2004;14:3 11 STROKE REHABILITATION: PREDICTING INPATIENT LENGTH OF STAY AND DISCHARGE PLACEMENT Fung Mei Ling Background: Stroke is the third leading cause of death in Hong
STROKE HKJOT REHABILITATION 2004;14:3 11 STROKE REHABILITATION: PREDICTING INPATIENT LENGTH OF STAY AND DISCHARGE PLACEMENT Fung Mei Ling Background: Stroke is the third leading cause of death in Hong
Relationship between weight gain, functional recovery and nutrition monitoring in underweight tube-fed stroke patients
 3 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Relationship between weight gain, functional recovery and nutrition monitoring in underweight tube-fed stroke patients
3 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Relationship between weight gain, functional recovery and nutrition monitoring in underweight tube-fed stroke patients
AROC Reports for Any Health Fund (AHF) January December 2004
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australasian Rehabilitation Outcomes Centre - AROC Centre for Health Service Development - CHSD 2005 AROC Reports for Any Health Fund (AHF) January 2004 - December
University of Wollongong Research Online Australasian Rehabilitation Outcomes Centre - AROC Centre for Health Service Development - CHSD 2005 AROC Reports for Any Health Fund (AHF) January 2004 - December
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION To what extent do the effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) on motor recovery of the upper extremity after stroke persist after the intervention
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION To what extent do the effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) on motor recovery of the upper extremity after stroke persist after the intervention
Rehabilitation in Hospital Authority- Challenges and the Way Ahead
 Rehabilitation in Hospital Authority- Challenges and the Way Ahead Leonard S.W. Li Head, Division of Rehabilitation Medicine Department of Medicine Tung Wah Hospital Rehabilitation Services within Hospital
Rehabilitation in Hospital Authority- Challenges and the Way Ahead Leonard S.W. Li Head, Division of Rehabilitation Medicine Department of Medicine Tung Wah Hospital Rehabilitation Services within Hospital
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Huseyinsinoglu, B. E., Ozdincler, A. R., & Krespi, Y. (2012). Bobath concept versus constraint-induced movement therapy to improve arm functional recovery in stroke patients:
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Huseyinsinoglu, B. E., Ozdincler, A. R., & Krespi, Y. (2012). Bobath concept versus constraint-induced movement therapy to improve arm functional recovery in stroke patients:
Stroke Rehabilitation Intensity Literature Review
 Stroke Rehabilitation Intensity Literature Review Topic Description and Rationale for Choosing the Topic: Providing effective levels of therapy is a major concern post stroke. Patients spend 60% of their
Stroke Rehabilitation Intensity Literature Review Topic Description and Rationale for Choosing the Topic: Providing effective levels of therapy is a major concern post stroke. Patients spend 60% of their
Functional Level During the First Year After Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Course and Predictors of Outcome
 Original Article Elmer ress Functional Level During the First Year After Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Course and Predictors of Outcome Maria Sandhaug a, b, e, Nada Andelic c, Svein A Berntsen
Original Article Elmer ress Functional Level During the First Year After Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Course and Predictors of Outcome Maria Sandhaug a, b, e, Nada Andelic c, Svein A Berntsen
GRADE Tables and Summary of Findings for the recommendations of Rehabilitation in health systems
 GRADE Tables and Summary of Findings for the recommendations of Rehabilitation in health systems REHABILITATION SERVICE DELIVERY For the following PICO questions, Population includes any person who requires
GRADE Tables and Summary of Findings for the recommendations of Rehabilitation in health systems REHABILITATION SERVICE DELIVERY For the following PICO questions, Population includes any person who requires
How to achieve 45 minutes of therapy: Findings from the ReAcT study
 How to achieve 45 minutes of therapy: Findings from the ReAcT study Dr David Clarke, Associate Professor in Stroke Care University of Leeds, UK On behalf of the ReAcT study team: S.Tyson, H.Rodgers, A.Drummond,
How to achieve 45 minutes of therapy: Findings from the ReAcT study Dr David Clarke, Associate Professor in Stroke Care University of Leeds, UK On behalf of the ReAcT study team: S.Tyson, H.Rodgers, A.Drummond,
REHABILITATION UNIT ANNUAL OUTCOMES REPORT
 REHABILITATION UNIT ANNUAL OUTCOMES REPORT - 2013 Prepared by Keir Ringquist, PT, PhD, GCS Rehabilitation Program Manager Director of Occupational and Physical Therapy 1 DEMOGRAPHICS OF THE REHABILITATION
REHABILITATION UNIT ANNUAL OUTCOMES REPORT - 2013 Prepared by Keir Ringquist, PT, PhD, GCS Rehabilitation Program Manager Director of Occupational and Physical Therapy 1 DEMOGRAPHICS OF THE REHABILITATION
Comprehensive Acute. Rehabilitation Unit
 Comprehensive Acute Rehabilitation Unit The Comprehensive Acute Rehabilitation Unit at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital has provided excellence in patient-focused acute rehabilitative care since 1963.
Comprehensive Acute Rehabilitation Unit The Comprehensive Acute Rehabilitation Unit at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital has provided excellence in patient-focused acute rehabilitative care since 1963.
Blood pressure and total cholesterol level are critical risks especially for hemorrhagic stroke in Akita, Japan.
 Blood pressure and total cholesterol level are critical risks especially for hemorrhagic stroke in Akita, Japan. Manabu Izumi, Kazuo Suzuki, Tetsuya Sakamoto and Masato Hayashi Jichi Medical University
Blood pressure and total cholesterol level are critical risks especially for hemorrhagic stroke in Akita, Japan. Manabu Izumi, Kazuo Suzuki, Tetsuya Sakamoto and Masato Hayashi Jichi Medical University
10/13/2017. The K2A Cycle. Focused Intensive Repetitive Step Training (FIRST)
 Walking the Walk: Translation of Scientific Findings into Clinical Practice September 14 and 15, 2017 State of the Science Chicago, IL T. George Hornby PT, PhD Jennifer Moore PT, DHSc, NCS The K2A Cycle
Walking the Walk: Translation of Scientific Findings into Clinical Practice September 14 and 15, 2017 State of the Science Chicago, IL T. George Hornby PT, PhD Jennifer Moore PT, DHSc, NCS The K2A Cycle
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yasukawa, A., Patel, P., & Sisung, C. (2006). Pilot study: Investigating the effects of Kinesio Taping in an acute pediatric rehabilitation setting. American Journal of
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yasukawa, A., Patel, P., & Sisung, C. (2006). Pilot study: Investigating the effects of Kinesio Taping in an acute pediatric rehabilitation setting. American Journal of
EFFECTIVENESS OF A COMPREHENSIVE DAY TREATMENT PROGRAM FOR REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACQUIRED BRAIN INJURY IN JAPAN
 J Rehabil Med 2006; 38: 20/25 EFFECTIVENESS OF A COMPREHENSIVE DAY TREATMENT PROGRAM FOR REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACQUIRED BRAIN INJURY IN JAPAN Keiji Hashimoto 1,2, Takatsugu Okamoto 1, Shu Watanabe
J Rehabil Med 2006; 38: 20/25 EFFECTIVENESS OF A COMPREHENSIVE DAY TREATMENT PROGRAM FOR REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACQUIRED BRAIN INJURY IN JAPAN Keiji Hashimoto 1,2, Takatsugu Okamoto 1, Shu Watanabe
The Uniform Data System for Medical Rehabilitation Report of Patients with Debility Discharged from Inpatient Rehabilitation Programs in 2000Y2010
 Authors: Rebecca V. Galloway, PT, MPT Carl V. Granger, MD Amol M. Karmarkar, PhD, OTR James E. Graham, PhD, DC Anne Deutsch, RN, PhD, CRRN Paulette Niewczyk, PhD, MPH Margaret A. DiVita, MS Kenneth J.
Authors: Rebecca V. Galloway, PT, MPT Carl V. Granger, MD Amol M. Karmarkar, PhD, OTR James E. Graham, PhD, DC Anne Deutsch, RN, PhD, CRRN Paulette Niewczyk, PhD, MPH Margaret A. DiVita, MS Kenneth J.
Attachment Program for Allied Health Professions in Rehabilitation Services
 Attachment Program for Allied Health Professions in Rehabilitation Services Florence Kwok,TMH ClinPsy; Joshua MAK,TMH SST Peg CHEUNG,TMH OTI; Manfield CHAN,TMH PTI 4 May, 2016 Pathway of a Stroke Patient
Attachment Program for Allied Health Professions in Rehabilitation Services Florence Kwok,TMH ClinPsy; Joshua MAK,TMH SST Peg CHEUNG,TMH OTI; Manfield CHAN,TMH PTI 4 May, 2016 Pathway of a Stroke Patient
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy an effective intervention for improving function in paralyzed upper extremities after a stroke as compared to the standard therapy? Dohle,
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy an effective intervention for improving function in paralyzed upper extremities after a stroke as compared to the standard therapy? Dohle,
Stroke Special Project 640 and 740 Resource For Health Information Management Professionals
 Stroke Special Project 640 and 740 Resource For Health Information Management Professionals Linda Gould RPN Erin Kelleher, BA, CHIM Stefan Pagliuso PT, B.A. Kin(Hon.) Overview of this Resource Overview
Stroke Special Project 640 and 740 Resource For Health Information Management Professionals Linda Gould RPN Erin Kelleher, BA, CHIM Stefan Pagliuso PT, B.A. Kin(Hon.) Overview of this Resource Overview
はじめに 対象と方法 39: , 2017 SAH 183 WFNS
 39:107 原 著 39: 107 112, 2017 1 2 1 1 1 1 要旨 SAH 2010 1 2013 12 SAH 253 183 64 70 WFNS I III 72.7 Fisher CT 3 86.3 19.9 16.6 GR MD 73.2 73.1 80 WFNS Key words: subarachnoid hemorrhage, prognosis, rate of
39:107 原 著 39: 107 112, 2017 1 2 1 1 1 1 要旨 SAH 2010 1 2013 12 SAH 253 183 64 70 WFNS I III 72.7 Fisher CT 3 86.3 19.9 16.6 GR MD 73.2 73.1 80 WFNS Key words: subarachnoid hemorrhage, prognosis, rate of
AROC Intensity of Therapy Project. AFRM Conference 18 September 2013
 AROC Intensity of Therapy Project AFRM Conference 18 September 2013 What is AROC? AROC began as a joint initiative of the whole Australian rehabilitation sector (providers, payers, regulators and consumers)
AROC Intensity of Therapy Project AFRM Conference 18 September 2013 What is AROC? AROC began as a joint initiative of the whole Australian rehabilitation sector (providers, payers, regulators and consumers)
Stroke Rehab Definitions Framework Self-Assessment Tool Acute Integrated Stroke Unit
 rth & East GTA Stroke Network Stroke Rehab Definitions Framework Self-Assessment Tool Acute Integrated Stroke Unit Purpose of the Self-Assessment Tool: The GTA Rehab Network and the GTA regions of the
rth & East GTA Stroke Network Stroke Rehab Definitions Framework Self-Assessment Tool Acute Integrated Stroke Unit Purpose of the Self-Assessment Tool: The GTA Rehab Network and the GTA regions of the
Rehabilitation and Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression
 Rehabilitation and Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression Pradeep Thumbikat MS, MSc, FRCS Consultant in Spinal Cord Injuries Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 1 Evidence for Rehabilitation Differences and similarities
Rehabilitation and Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression Pradeep Thumbikat MS, MSc, FRCS Consultant in Spinal Cord Injuries Sheffield Teaching Hospitals 1 Evidence for Rehabilitation Differences and similarities
Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, Jacksonville, FL. Department of Internal Medicine, Wichita, KS
 in Patients with Respiratory Disease Furqan Shoaib Siddiqi, M.D. 1, Said Chaaban, M.D. 2, Erin Petersen, M.S.N., A.P.R.N. 3, K James Kallail, Ph.D. 2, Mary Hope, B.H.S., A.R.T., R.R.T., C.P.F.T. 3, Daniel
in Patients with Respiratory Disease Furqan Shoaib Siddiqi, M.D. 1, Said Chaaban, M.D. 2, Erin Petersen, M.S.N., A.P.R.N. 3, K James Kallail, Ph.D. 2, Mary Hope, B.H.S., A.R.T., R.R.T., C.P.F.T. 3, Daniel
APPROXIMATELY 500,000 MEDICARE patients are
 934 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Inpatient Rehabilitation for Older Adults With Debility, Hip Fracture, and Myopathy Patrick Kortebein, MD, Carl V. Granger, MD, Dennis H. Sullivan, MD ABSTRACT.
934 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Inpatient Rehabilitation for Older Adults With Debility, Hip Fracture, and Myopathy Patrick Kortebein, MD, Carl V. Granger, MD, Dennis H. Sullivan, MD ABSTRACT.
A snapshot of inpatient oncology rehabilitation: Patient profiles and rehab outcomes Rehabilitation Rounds, University of Toronto April 5, 2012
 A snapshot of inpatient oncology rehabilitation: Patient profiles and rehab outcomes Rehabilitation Rounds, University of Toronto April 5, 2012 Sara McEwen, PT, PhD Research Scientist, St. John s Rehab
A snapshot of inpatient oncology rehabilitation: Patient profiles and rehab outcomes Rehabilitation Rounds, University of Toronto April 5, 2012 Sara McEwen, PT, PhD Research Scientist, St. John s Rehab
The relationship between satisfaction in activities of daily living and perceived quality of life in recovery rehabilitation inpatients
 1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article The relationship between satisfaction in activities of daily living and perceived quality of life in recovery rehabilitation
1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article The relationship between satisfaction in activities of daily living and perceived quality of life in recovery rehabilitation
the health outcomes or benefits associated with this procedure.
 Original Issue Date (Created): October 4, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): March 25, 2014 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 I. POLICY Cognitive rehabilitation may be considered medically necessary for
Original Issue Date (Created): October 4, 2002 Most Recent Review Date (Revised): March 25, 2014 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 I. POLICY Cognitive rehabilitation may be considered medically necessary for
Implementing a Structured Cognitive Orientation Program on an Inpatient Rehabilitation Unit: A Pilot Project Lauren Fletcher
 Implementing a Structured Cognitive Orientation Program on an Inpatient Rehabilitation Unit: A Pilot Project Lauren Fletcher The Royal Melbourne Hospital Royal Park Campus Inpatient Rehabilitation Unit
Implementing a Structured Cognitive Orientation Program on an Inpatient Rehabilitation Unit: A Pilot Project Lauren Fletcher The Royal Melbourne Hospital Royal Park Campus Inpatient Rehabilitation Unit
National Stroke Association s Guide to Choosing Stroke. Rehabilitation Services
 National Stroke Association s Guide to Choosing Stroke Rehabilitation Services Rehabilitation, often referred to as rehab, is an important part of stroke recovery. Through rehab, you: Re-learn basic skills
National Stroke Association s Guide to Choosing Stroke Rehabilitation Services Rehabilitation, often referred to as rehab, is an important part of stroke recovery. Through rehab, you: Re-learn basic skills
Risk factors affecting inhospital mortality after hip fracture: retrospective analysis using the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination Database
 Open Access To cite: Shoda N, Yasunaga H, Horiguchi H, et al. Risk factors affecting inhospital mortality after hip fracture: retrospective analysis using the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination Database.
Open Access To cite: Shoda N, Yasunaga H, Horiguchi H, et al. Risk factors affecting inhospital mortality after hip fracture: retrospective analysis using the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination Database.
Dave Ure, OT Reg. (Ont.), CPA, CMA Coordinator
 Dave Ure, OT Reg. (Ont.), CPA, CMA Coordinator Development of the model In response to the request for proposal issued by the Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care in September 2001, the Southwestern Ontario
Dave Ure, OT Reg. (Ont.), CPA, CMA Coordinator Development of the model In response to the request for proposal issued by the Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care in September 2001, the Southwestern Ontario
Clinical outcome of proximal versus total gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer Shiraishi N, Adachi Y, Kitano S, Kakisako K, Inomata M, Yasuda K
 Clinical outcome of proximal versus total gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer Shiraishi N, Adachi Y, Kitano S, Kakisako K, Inomata M, Yasuda K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
Clinical outcome of proximal versus total gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer Shiraishi N, Adachi Y, Kitano S, Kakisako K, Inomata M, Yasuda K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Desrosiers, J., Noreau, L., Rochette, A., Carbonneau, H., Fontaine, L., Viscogliosi, C., & Bravo, G. (2007). Effect of a home leisure education program after stroke: A
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Desrosiers, J., Noreau, L., Rochette, A., Carbonneau, H., Fontaine, L., Viscogliosi, C., & Bravo, G. (2007). Effect of a home leisure education program after stroke: A
MEASUREMENT OF FUNCTIONAL ABILITIES is an. Recovery of Functional Status After Right Hemisphere Stroke: Relationship With Unilateral Neglect
 322 Recovery of Functional Status After Right Hemisphere Stroke: Relationship With Unilateral Neglect Leora R. Cherney, PhD, BC-NCD, Anita S. Halper, MA, BC-NCD, Christina M. Kwasnica, MD, Richard L. Harvey,
322 Recovery of Functional Status After Right Hemisphere Stroke: Relationship With Unilateral Neglect Leora R. Cherney, PhD, BC-NCD, Anita S. Halper, MA, BC-NCD, Christina M. Kwasnica, MD, Richard L. Harvey,
Please make sure that you complete a self-assessment survey for each type of rehab program that your organization provides.
 Oncology Rehab s Framework Self-Assessment Tool Inpatient Rehab Survey for Oncology Rehab INTRODUCTION: In response to a changing rehab landscape in which rehabilitation is offered in many different settings
Oncology Rehab s Framework Self-Assessment Tool Inpatient Rehab Survey for Oncology Rehab INTRODUCTION: In response to a changing rehab landscape in which rehabilitation is offered in many different settings
Functional Independent Recovery among Stroke Patients at King Hussein Medical Center
 Functional Independent Recovery among Stroke Patients at King Hussein Medical Center Ali Al-Hadeed MD*, Amjad Banihani MD**, Tareq Al-Marabha MD* ABSTRACT Objective: To describe the functional independent
Functional Independent Recovery among Stroke Patients at King Hussein Medical Center Ali Al-Hadeed MD*, Amjad Banihani MD**, Tareq Al-Marabha MD* ABSTRACT Objective: To describe the functional independent
Texas Administrative Code
 RULE 19.1301 Provision of Rehabilitative Services (a) Provision of services. If rehabilitative services, such as, but not limited to, physical therapy, speech/language pathology, occupational therapy,
RULE 19.1301 Provision of Rehabilitative Services (a) Provision of services. If rehabilitative services, such as, but not limited to, physical therapy, speech/language pathology, occupational therapy,
AN ESTIMATED 500,000 to 1.5 million patients are admitted
 1441 The Relationship Between Therapy Intensity and Rehabilitative Outcomes After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multicenter Analysis David X. Cifu, MD, Jeffrey S. Kreutzer, PhD, ABPP, Stephanie A. Kolakowsky-Hayner,
1441 The Relationship Between Therapy Intensity and Rehabilitative Outcomes After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multicenter Analysis David X. Cifu, MD, Jeffrey S. Kreutzer, PhD, ABPP, Stephanie A. Kolakowsky-Hayner,
Outcomes in GEM models of geriatric care: How do we measure success? Disclosure. Objectives. Geriatric Grand Rounds
 Geriatric Grand Rounds Tuesday, October 7, 2008 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital Outcomes in GEM models of geriatric care: How do we measure success? In keeping with
Geriatric Grand Rounds Tuesday, October 7, 2008 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital Outcomes in GEM models of geriatric care: How do we measure success? In keeping with
The relationship between quality of care and hospital costs in Europe. Unto Häkkinen and EuroDRG teams in Finland, France, Germany, Spain and Sweden
 The relationship between quality of care and hospital costs in Europe Unto Häkkinen and EuroDRG teams in Finland, France, Germany, Spain and Sweden 1 Aims and data Motivation: Does introduction of cost
The relationship between quality of care and hospital costs in Europe Unto Häkkinen and EuroDRG teams in Finland, France, Germany, Spain and Sweden 1 Aims and data Motivation: Does introduction of cost
Construction and Quality Evaluation of the Japanese Rehabilitation Nutrition Database
 J Nutr Sci Vitaminol, 6, 5 57, 08 Construction and Quality Evaluation of the Japanese Rehabilitation Nutrition Database Miyuki Takasaki, Ryo Momosaki, Hidetaka Wakabayashi and Shinta Nishioka Division
J Nutr Sci Vitaminol, 6, 5 57, 08 Construction and Quality Evaluation of the Japanese Rehabilitation Nutrition Database Miyuki Takasaki, Ryo Momosaki, Hidetaka Wakabayashi and Shinta Nishioka Division
Using the AcuteFIM Instrument for Discharge Placement
 Using the AcuteFIM Instrument for Discharge Placement Paulette Niewczyk, MPH, PhD Manager of CFAR / Director of Research Center for Functional Assessment Research Uniform Data System for Medical Rehabilitation
Using the AcuteFIM Instrument for Discharge Placement Paulette Niewczyk, MPH, PhD Manager of CFAR / Director of Research Center for Functional Assessment Research Uniform Data System for Medical Rehabilitation
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 FOCUSED QUESTION CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Will adults diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis who participate in an intensive hand exercise program improve in areas of hand strength, joint mobility,
FOCUSED QUESTION CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Will adults diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis who participate in an intensive hand exercise program improve in areas of hand strength, joint mobility,
REVIEW OF REHABILITATION OF ISCHAEMIC STROKE PATIENTS
 REVIEW OF REHABILITATION OF ISCHAEMIC STROKE PATIENTS MAHMOOD K 1, HOSSAIN MS2, RAHMAN S 3 Abstract: Rehabilitation of stroke patient is a continuum, starting within days of onset and ending only when
REVIEW OF REHABILITATION OF ISCHAEMIC STROKE PATIENTS MAHMOOD K 1, HOSSAIN MS2, RAHMAN S 3 Abstract: Rehabilitation of stroke patient is a continuum, starting within days of onset and ending only when
Integrating Medical and Social Support for Elderly System & Technology Enabled Service Innovations. Dr Christina MAW Hospital Authority, Hong Kong
 Integrating Medical and Social Support for Elderly System & Technology Enabled Service Innovations Dr Christina MAW Hospital Authority, Hong Kong Hospital Authority (HA) of Hong Kong A statutory body responsible
Integrating Medical and Social Support for Elderly System & Technology Enabled Service Innovations Dr Christina MAW Hospital Authority, Hong Kong Hospital Authority (HA) of Hong Kong A statutory body responsible
Evaluation of the Family - Rated Kinder Infant Development Scale (KIDS) for Disabled Children
 Jikeikai Med J 2012 ; 59 : 5-10 Evaluation of the Family - Rated Kinder Infant Development Scale (KIDS) for Disabled Children Keiji Hashimoto, Naoko Matsui, Hidemi Yakuwa, and Kohei Miyamura Division of
Jikeikai Med J 2012 ; 59 : 5-10 Evaluation of the Family - Rated Kinder Infant Development Scale (KIDS) for Disabled Children Keiji Hashimoto, Naoko Matsui, Hidemi Yakuwa, and Kohei Miyamura Division of
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016)
 95 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Effect of adaptations to the living environment on ADL abilities and self-perception of performance/satisfaction Based
95 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Effect of adaptations to the living environment on ADL abilities and self-perception of performance/satisfaction Based
International Congress Series 1232 (2002)
 International Congress Series 1232 (2002) 549-554 Measurement of Cerebral Circulation Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Topography during Music-Exercise (trampoline) Therapy as a Method of Brain Rehabilitation
International Congress Series 1232 (2002) 549-554 Measurement of Cerebral Circulation Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Topography during Music-Exercise (trampoline) Therapy as a Method of Brain Rehabilitation
AROC Outcome Targets Report Inpatient Pathway 3
 AROC Outcome Targets Report Inpatient Pathway 3 Anywhere Hospital January 2013 December 2013 Australasian Faculty of Rehabilitation Medicine AROC impairment specific benchmarking process...3 Introducing
AROC Outcome Targets Report Inpatient Pathway 3 Anywhere Hospital January 2013 December 2013 Australasian Faculty of Rehabilitation Medicine AROC impairment specific benchmarking process...3 Introducing
Poststroke Rehabilitation Outcomes and Reimbursement of Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities and Subacute Rehabilitation Programs
 Poststroke Rehabilitation Outcomes and Reimbursement of Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities and Subacute Rehabilitation Programs Anne Deutsch, PhD, RN, CRRN; Carl V. Granger, MD; Allen W. Heinemann, PhD,
Poststroke Rehabilitation Outcomes and Reimbursement of Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities and Subacute Rehabilitation Programs Anne Deutsch, PhD, RN, CRRN; Carl V. Granger, MD; Allen W. Heinemann, PhD,
Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SSNAP)
 Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SSNAP) Changes over Time: 4 years of data April 2013 March 2017 National results Based on stroke patients admitted to and/or discharged from hospital between April
Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SSNAP) Changes over Time: 4 years of data April 2013 March 2017 National results Based on stroke patients admitted to and/or discharged from hospital between April
Meta Analysis. David R Urbach MD MSc Outcomes Research Course December 4, 2014
 Meta Analysis David R Urbach MD MSc Outcomes Research Course December 4, 2014 Overview Definitions Identifying studies Appraising studies Quantitative synthesis Presentation of results Examining heterogeneity
Meta Analysis David R Urbach MD MSc Outcomes Research Course December 4, 2014 Overview Definitions Identifying studies Appraising studies Quantitative synthesis Presentation of results Examining heterogeneity
Canadian Stroke Best Practices Table 3.3A Screening and Assessment Tools for Acute Stroke
 Canadian Stroke Best Practices Table 3.3A Screening and s for Acute Stroke Neurological Status/Stroke Severity assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech) and motor function (face,
Canadian Stroke Best Practices Table 3.3A Screening and s for Acute Stroke Neurological Status/Stroke Severity assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech) and motor function (face,
Table 3.1: Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations Screening and Assessment Tools for Acute Stroke Severity
 Table 3.1: Assessment Tool Number and description of Items Neurological Status/Stroke Severity Canadian Neurological Scale (CNS)(1) Items assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech)
Table 3.1: Assessment Tool Number and description of Items Neurological Status/Stroke Severity Canadian Neurological Scale (CNS)(1) Items assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech)
Angela Colantonio, PhD 1, Gary Gerber, PhD 2, Mark Bayley, MD, FRCPC 1, Raisa Deber, PhD 3, Junlang Yin, MSc 1 and Hwan Kim, PhD candidate 1
 J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 311 315 ORIGINAL REPORT Differential Profiles for Patients with Traumatic and Non- Traumatic Brain Injury Angela Colantonio, PhD 1, Gary Gerber, PhD 2, Mark Bayley, MD, FRCPC 1,
J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 311 315 ORIGINAL REPORT Differential Profiles for Patients with Traumatic and Non- Traumatic Brain Injury Angela Colantonio, PhD 1, Gary Gerber, PhD 2, Mark Bayley, MD, FRCPC 1,
Gender and Ethnic Differences in Rehabilitation Outcomes After Hip-Replacement Surgery
 Authors: Ivonne-Marie Bergés, PhD Yong-Fang Kuo, PhD Glenn V. Ostir, PhD Carl V. Granger, MD James E. Graham, PhD Kenneth J. Ottenbacher, PhD, OTR Affiliations: From the Sealy Center on Aging, University
Authors: Ivonne-Marie Bergés, PhD Yong-Fang Kuo, PhD Glenn V. Ostir, PhD Carl V. Granger, MD James E. Graham, PhD Kenneth J. Ottenbacher, PhD, OTR Affiliations: From the Sealy Center on Aging, University
