Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan
|
|
|
- Todd Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 78 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Assessment of the effects of factors in stroke rehabilitation using eight multiple regression analyses An analysis of the Japan Rehabilitation Database Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD, 1 Mayu Taniguchi, OTR, 1 Keiichi Nakakado, PTR, 1 Taiki Mihono, OTR, 1 Asami Okido, RPT, 1 Takeshi Ushijima, RPT, 1 Gihachiro Eguchi, MD, 1 Susumu Watanabe, MD, PhD, 1 Ryoji Nakanishi, MD, PhD, 1 Hiroaki Yamanaga, MD, PhD 1 1 Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan ABSTRACT Tokunaga M, Taniguchi M, Nakakado K, Mihono T, Okido A, Ushijima T, Eguchi G, Watanabe S, Nakanishi R, Yamanaga H. Assessment of the effects of factors in stroke rehabilitation using eight multiple regression analyses An analysis of the Japan Rehabilitation Database. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2015; 6: Objective: The objective of the present study was to determine via multiple regression analysis what types of patient groups demonstrate large effects for factors in stroke rehabilitation. Methods: The subjects were 1,465 stroke patients in Kaifukuki rehabilitation wards who were registered in the 2014 Japan Rehabilitation Database. The subjects were stratified into eight groups based on age, motor functional independence measure (FIM) score at hospital admission, and cognitive FIM score at admission; multiple regression analysis was then performed with motor FIM score at discharge as the dependent variable. Results: Among the eight groups, the following independent variables were significant: motor FIM score at admission in seven groups, Nichijo-seikatsukino-hyokahyo at admission in five groups, age and post-onset duration of hospitalization in four groups, cognitive FIM score at admission in three groups, and pre-onset modified Rankin Scale in one group. Conclusion: The creation of multiple predictive formulas in multiple regression analysis enables Correspondence: Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD Department of Rehabilitation, Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Yamamuro, Kita-ku, Kumamoto , Japan. tokunaga@juryo.or.jp Accepted: August 5, 2015 No benefits in any form have been or will be received from any commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript. identification of the types of patient groups which demonstrate large effects for factors in stroke rehabilitation. Key words: multiple regression analysis, stroke, stratification, factors, Functional Independence Measure Introduction In our searches of existing literature, we found 12 reports which used multiple regression analysis to predict Functional Independence Measure (FIM) score at hospital discharge in stroke patients who were hospitalized in Kaifukuki rehabilitation wards [1-12]. Of those 12 reports, nine [1-9] created a single predictive formula which was applied to all patients. In contrast, Inouye [10] divided patients into five groups based on age and created five predictive formulas. Similarly, Hirano et al. [11] divided patients into three groups based on FIM score at admission and created three predictive formulas. In addition, Tokunaga et al. [12] divided patients into two groups based on age and three groups based on FIM score at admission, thus creating a total of six groups and six predictive formulas. The use of six predictive formulas rather than one yielded a greater correlation between actual values and predicted values, and thus a smaller residual of actual value minus predicted value. The reason why multiple predictive formulas are preferable to a single predictive formula is the absence of a linear relationship between stroke rehabilitation factors and FIM improvement. Improvement in the total score for the 13 motor-related items of the FIM (motor FIM) is nearly constant in individuals aged 69 years, but declines in a nearly linear fashion in individuals aged 70 years [13, 14]. Motor FIM gain, when plotted on a graph, appears as a curve which peaks at a motor FIM score at admission of [15] or [16]. Multiple regression analysis assumes
2 79 that independent variables and the dependent variable are linearly related; therefore, in the absence of a linear relationship between the independent variables and the dependent variable, the creation of multiple predictive formulas is considered to yield higher predictive accuracy. Recently, Sonoda et al. [17] reported that inhibitory factors in rehabilitation do not necessarily demonstrate uniform effects in all patient groups. Their report described the results of motor FIM score at discharge as predicted by decision tree analysis. Among cognitive FIM items at admission, memory first appeared as a conditional branch at the sixth branch, in regard to patients with a motor FIM score at admission of [17]. Following the decision tree to the fourteenth branch shows that age was involved in patients with a motor FIM score at admission of [17]. Thus, if the effects of the factors affecting motor FIM at discharge differ according to the patient group, failing to create predictive formulas for each patient group in multiple regression analysis would make it impossible to assess accurately the effects of these factors. However, we could find no past reports in which multiple predictive formulas were created in multiple regression analysis to predict motor FIM score at discharge in order to assess which types of patients demonstrate large effects in the factors affecting motor FIM at discharge. In the present study, we used data from stroke patients in Kaifukuki rehabilitation wards registered in the Japan Rehabilitation Database [18] in multiple regression analysis to predict motor FIM at discharge. The objective of the study was to stratify patients based on age, motor FIM score at admission, and cognitive FIM score at admission in order to create multiple predictive formulas to determine which types of patient groups demonstrate large effects for those factors. Subjects and Methods We used patient data from the Japan Rehabilitation Database. The goal behind the creation of the Japan Association of Rehabilitation Database, which was established in September 2012, is to construct and use a rehabilitation database to help improve rehabilitation medicine and care [18]. The groups which comprise the Japan Rehabilitation Database Association are: the Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Japanese Physical Therapy Association, the Japanese Association of Occupational Therapists, and the Japanese Association of Speech-Language-Hearing Therapists. Data on patients who have suffered stroke, hip fracture, or spinal cord injury are collected from participating institutions throughout Japan. The present epidemiologic study is a retrospective investigation. The number of patients registered in the May 2014 Japan Rehabilitation Database (stroke and rehabilitation) was 4,949. After narrowing down these patients according to the conditions shown in Figure 1, we used 1,465 of these patients as subjects. 1. Stratification of patients into 12 groups based on age, motor FIM score at admission, and cognitive FIM score at admission Based on a previous examination in which we found that motor FIM improvement declined beginning at age 70 [13, 14], we divided patients into an age 69 years group and an age 70 years group. Also, because motor FIM improvement declines when cognitive FIM score at admission is 9 [19], we divided patients into groups of those with cognitive FIM scores at admission of 5-9 (cfim 5-9) and (cfim 10-35). Furthermore, motor FIM gain when plotted on a graph appears as a curve which peaks at a motor FIM score at admission of [15] or [16], while Sonoda et al. [17] reported that age and cognitive function exerted effects on patients with motor FIM scores at admission of and 31-69; therefore, we divided patients into groups of those with motor FIM scores at admission of (mfim 13 30), (mfim 31-69), and (mfim 70-91). Thus, based on age, cognitive FIM score at admission, and motor FIM score at admission, we stratified patients into 12 groups (Table 1). 2. Multiple regression analysis with motor FIM score at discharge as the dependent variable We performed multiple regression analysis with motor FIM score at discharge as the dependent variable. Drawing upon variables which previous studies had reported to be correlated with FIM at discharge, we used the following six items as independent variables: age, pre-onset modified Rankin Scale (mrs), postonset duration of hospitalization, motor FIM score at admission, cognitive FIM score at admission, and Nichijo-seikatsu-kino-hyokahyo (NSKH) at admission. We initially elected to perform multiple regression analysis for each of the 12 groups and for all patients together. However, because four of the 12 groups had fewer than 10 patients (Table 1), we excluded those four groups and their 17 patients, therefore ultimately performing multiple regression analysis on eight groups comprising a total of 1,448 patients. In addition, we investigated which of the six independent variables (factors) were significant in which of the eight patient groups. Our creation of a single predictive formula for overall patients also excluded the above-mentioned 17 patients and thus involved a total of 1,448 patients. For multiple regression analysis with patients divided into eight groups and singular multiple regression analysis (for overall patients), we investigated the correlation between actual value and predicted value (Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, p<0.05) and the residual of actual value minus predicted value. In the Japan Rehabilitation Database, all personal
3 80 Figure 1. Inclusion and exclusion criteria. FIM, Functional Independence Measure; mfim, motor FIM; cfim, cognitive FIM; NSKH, Nichijo-seikatsu-kinohyokahyo; mrs, modified Rankin Scale; Numerical value, number of patients. information is converted to data to prevent identification of individuals. The present epidemiologic study was conducted based on the regulations of the institutional review board of the hospital to which the authors belong and with the permission of an employee designated in advance by the institutional review board. Results All eight of the multiple regression analyses were significant (p<0.001). Adjusted R *2, which demonstrates the extent to which independent variables can explain the dependent variable, ranged from 0.15 (Group F) to 0.56 (Group A) (Table 1). No correlations among the six independent variables were greater than 0.8, and no multicollinearity was observed. Motor FIM score at admission was a significant independent variable in seven groups (all except for Group D). Moreover, in comparison with the other five independent variables, motor FIM score at admission demonstrated the largest standardized partial regression coefficient (the relative strength of the association of an independent variable with the dependent variable) (Table 1). Cognitive FIM score at admission was a significant independent variable in three groups (Groups E, J, and L). Age, NSKH at admission, and post-onset duration of hospitalization were significant independent variables in four groups, five groups, and four groups, respectively. However, pre-onset mrs was a significant independent variable only in one group (Group G). When we created eight predictive formulas for the 1,448 patients, the actual value and the predicted value demonstrated a significant strong positive correlation (r = 0.885, p<0.001) (Fig. 2a). The residual (actual value minus predicted value) was 0.01 ± (median: 0.37). When we created only a single predictive formula, the adjusted R *2 was 0.72 (Table 2); all six of the independent variables were significant. The actual value and the predicted value demonstrated a significant strong positive correlation (r = 0.847, p<0.001), while the residual (actual value minus predicted value) was ± (median: ) (Fig. 2b). Discussion In comparison to a single predictive formula, the use of eight predictive formulas resulted in a greater correlation between actual values and predicted values, as well as smaller residual; these results are identical to those of a previous study in which age and FIM score at admission were used to create six predictive formulas [12]. The present study is the fifth to have investigated the correlation between actual
4 81 Table 1. Multiple regression analysis to predict motor FIM score at discharge (eight predictive formulas). Group A B C D E F Age Under 69 cfim at admission cfim 5-9 cfim mfim at admission mfim mfim mfim mfim mfim mfim Number of patients mfim at admission ( 0.417, 1), p < ( 0.202), p = ( 0.428, 1), p < ( 0.334, 1), p < cfim at admission ( 0.041), p = ( 0.017), p = ( 0.118, 3), p < ( 0.028), p = 0.66 Age ( ), p = ( , 2), p < ( , 2), p < ( ), p = 0.15 NSKH at admission ( , 2), p < ( , 1), p < ( ), p = ( ), p = 0.43 Post-onset duration of hospitalization ( , 3), p < ( ), p = ( ), p = ( , 2), p < 0.05 Pre-onset mrs ( 0.042), p = ( ), p = ( ), p = ( ), p = 0.46 Explanatory variables Constant Significance level p < p < p < p < Adjusted coefficient of determination R * Group G H I J K L Age Over 70 cfim at admission cfim 5-9 cfim mfim at admission mfim mfim mfim mfim mfim mfim Number of patients mfim at admission ( 0.390, 1), p < ( 0.269, 1), p < ( 0.429, 1), p < ( 0.461, 1), p < cfim at admission ( 0.749), p = ( 0.184, 3), p < ( 0.074), p = ( 0.161, 2), p < 0.05 Age ( ), p = ( , 2), p < ( , 4), p < ( ), p = 0.06 NSKH at admission ( , 2), p < ( , 4), p < ( , 2), p < ( ), p = 0.45 Post-onset duration of hospitalization ( ), p = ( , 5), p < ( , 3), p < ( ), p = 0.45 Pre-onset mrs ( , 3), p < ( ), p = ( ), p = ( ), p = 0.43 Explanatory variables Constant Significance level p < p < p < p < Adjusted coefficient of determination R* FIM, Functional Independence Measure; mfim, motor FIM; cfim, cognitive FIM; NSKH, Nichijo-seikatsu-kino-hyokahyo; mrs, modified Rankin Scale. Numerical value of independent variables, regression coefficient; circled number, numbers were given in the order of higher standard partial regression coefficient.
5 82 Figure 2. Relationship between actual values and predicted values., each patient; Actual value, actual value of FIM at discharge; Predicted value, predicted value of FIM at discharge. Table 2. Multiple regression analysis to predict motor FIM score at discharge (one predictive formula). Number of patients 1,448 Explanatory variables mfim at admission ( 0.405, 1), p < cfim at admission ( 0.159, 3), p < Age ( , 4), p < NSKH at admission ( , 2), p < Post-onset duration of hospitalization ( , 5), p < Pre-onset mrs ( , 6), p < Constant Significance level p < Adjusted coefficient of determination R* The explanation of this table is the same as in Table 1. and predicted values [1, 2, 9, 12], but yielded the thirdhighest correlation among these studies (Table 3). Similarly, the present study is the fourth to have investigated the residual of actual value minus predicted value [2, 6, 12], but yielded the secondsmallest mean residual, trailing only that reported by Tokunaga et al. [12]; as well as the second-smallest standard deviation in residual, behind only that reported by Sonoda et al. [2]. In the present study, we also investigated which factors among age, pre-onset mrs, post-onset duration of hospitalization, motor FIM score at admission, cognitive FIM score at admission, and NSKH at admission significantly affected motor FIM score at discharge in which of eight groups of patients divided by age, cognitive FIM score at admission, and motor FIM score at admission. When we created only a single predictive formula, all six independent variables were significant. However, in multiple regression analysis with patients divided into eight groups based on age, cognitive FIM score at admission, and motor FIM score at admission, only two to five of the six independent variables were significant in any given group. Of the six independent variables (factors), the factor most frequently found to be significant was motor FIM score at admission (in seven of eight groups), followed by NSKH at admission (five groups), age (four groups), post-onset duration of hospitalization (four groups), and cognitive FIM score at admission (three groups). Pre-onset mrs was significant in only one group (Group G). These results are consistent with a report by Sonoda et al. [17], who stated that inhibitory factors in rehabilitation do not necessarily demonstrate uniform effects in all patient groups. In the report by Sonoda et al. [17], age affected patients with a motor FIM score at admission of In contrast, we found that age was also a significant independent variable in Groups D, E, J, and K; therefore, age was also a significant independent
6 83 Table 3. Reports which used multiple regression analysis to predict FIM score at discharge in stroke patients who were hospitalized in Kaifukuki rehabilitation wards. Reports (Reference numbers) This study Stratification Five groups by age Three groups by FIM at admission Six groups by age and FIM at admission Eight groups by age, mfim and cfim at admission mfim at admission cfim at admission Age Explanatory variables NSKH at admission Post-onset duration of hospitalization Pre-onset mrs Comorbidities SIAS Type of stroke GCS at admission Deviation in tape bisection Neglect Sex Orientation HDS-R Adjusted coefficient of determination R* C orrelation between the measured value and the predicted value Residual 8.06 ± ± ± ± HDS-R, Hasegawa dementia scale-revised; GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; SIAS, Stroke Impairment Assessment Set; Reports, numbers are the reference numbers. Residual, obtained by subtracting the predicted value from the measured value; Other explanations are the same as Table 1. variable for patients whose motor FIM score admission was Moreover, among patients with a motor FIM score at admission of 13-30, age was not a significant independent variable in patients with a cognitive FIM score at admission of 9 (Groups A and G). These results can be summarized as follows: age exerts a significant effect in patients with a cognitive FIM score at admission of 10 and a motor FIM score at admission of Sonoda et al. [17] reported that motor FIM score at admission is useful for predicting motor FIM score at discharge in patients with a motor FIM score at admission of In contrast, in the present study, motor FIM score at admission was a significant independent variable in Group E (age 69 years, cfim 10-35, mfim 31-69), Group J (age 70 years, cfim 10-35, mfim 13-30), and group L (age 70 years, cfim 10-35, mfim 70-91). Sonoda et al. [17] presented a group of patients with motor FIM scores of 31-69, a group which we further stratified in the present study into four groups (Groups B, E, H, and K) based on age and cognitive FIM score at admission. Both Sonoda et al. [17] and the present study found that patients corresponding to our Group E (age 69 years, cfim 10-35, mfim 31-69) were affected by cognitive function. However, among patients with motor FIM scores at admission of 31-69, Groups B and G had few patients, while Group K demonstrated a regression coefficient for motor FIM score at admission that, despite being positive, was not significant (p = 0.09). In Groups J and L in the present study, motor FIM score at admission was a significant positive independent variable; this result can be interpreted to mean that, in individuals aged 70 years, cognitive function affects motor FIM score at discharge in patients with a wide range of motor FIM scores at admission. Pre-onset mrs was a significant independent variable only in Group G, thus permitting the conclusion that pre-onset mrs significantly affects severe patients aged 70 years with a cognitive FIM score at admission of 9 and a motor FIM score at admission of 30. Severe patients with low motor FIM and cognitive FIM scores at admission included large numbers of patients who were already severe (in terms of preonset mrs); thus, pre-onset mrs likely exerted a major effect. In fact, while Group G comprised only 7.0% (102/1,465) of all patients in the present study, the group included eight patients with a pre-onset mrs of grade 5, thus accounting for 36.4% (8/22) of all patients with a pre-onset mrs of grade 5. The NSKH, which implies the level of need for nursing care, significantly affected severe patients with a cognitive FIM score at admission of 9 and a motor FIM score at admission of 30 (Groups A and G). Among patients aged 69 years, a cognitive FIM score at admission 10 significantly affected patients with motor FIM scores at admission of 30 (Group
7 84 D); whereas among patients aged 70 years, the same range of cognitive FIM scores significantly affected not only patients with motor FIM scores at admission of 30 (Group J), but also patients with motor FIM scores at admission of (Group K). Thus, for elderly patients with a high level of need for nursing care (i.e. elderly patients with low cognitive FIM and motor FIM scores at admission), NSKH score was considered to be a significant independent variable. Listed below are some of the limitations of the present study. First, multiple regression analysis results vary based on the types of patients examined and the independent variables used. Although past studies (Table 3) often used the six items used in the present study, some studies also included other independent variables such as complications and Stroke Impairment Assessment Set. The Guidelines for Clinical Research and Studies on Stroke state that basic patient information should include the following: sex, age, independence or non-independence in activities of daily living prior to onset, stroke type, lesion of stroke, post-onset duration of hospitalization, presence/absence of hemispatial neglect, and presence/ absence of aphasia [20]. It would be desirable to conduct an investigation similar to the present study but which incorporates all factors which could affect motor FIM score at discharge. Second, four groups (B, C, H, and I) had few patients, thus prohibiting multiple regression analysis. This was due to the fact that motor FIM score at admission and cognitive FIM score at admission are correlated; a cognitive FIM score at admission of 9 combined with a motor FIM score at admission of or is seldom observed. Third, results vary according to the cutoff point used for the strength of the effect of age or cognitive function on outcomes. For example, the conclusion of Sonoda et al. that age affected patients with motor FIM scores at admission of and the conclusion of the present study that age significantly affected patients with a cognitive FIM score at admission of 10 and a motor FIM score of admission of may seem to differ from each other. However, considering that the effect of age was greater in patients with a cognitive FIM score at admission of 10 and a motor FIM score at admission of than in patients with a cognitive FIM score at admission of 10 and a motor FIM score at admission of and that analysis of patients with a motor FIM score at admission of included patients with cognitive FIM scores at admission of both 9 and 10, the conclusion of the present study is in fact identical to the conclusion reached by Sonoda et al. [17]. Fourth, we presumed to divide patients into groups based on continuous variables; therefore, different group divisions may yield different conclusions. We cannot say whether the use of a different group division method, such as quartiles, would yield the same conclusions as those of the present study; this matter should be investigated in a future study. Fifth, the clinical usefulness of the results of the present study is unclear. For example, although there is a conceivable scenario in which multiple regression analysis for predicting motor FIM scores at discharge could be used to identify patients for whom cognitive FIM score at admission is a significant independent variable and thus focus their rehabilitation on cognitive function, further investigation is necessary to determine whether such applications would be useful. Based on the absence of a linear relationship between factors and motor FIM improvement, as well as on the fact that factors do not demonstrate uniform effects in all patient groups, the present study stratified patients based on age, motor FIM score at admission, and cognitive FIM score at admission to create eight predictive formulas; we then used these formulas to determine which of six independent variables (factors) were significant in which patient groups. This method is considered useful in determining the types of patient groups in whom these factors significantly affect motor FIM scores at discharge. Acknowledgements This study used the Japan Rehabilitation Database managed by the Japan Association of Rehabilitation Database, to whom we extend our gratitude. The contents and conclusions of this study are not the opinions of the Association, but rather the viewpoints of the authors. References 1. Jeong S, Inoue Y, Kondo K, Matsumoto D, Shiraishi N. Formula for predicting FIM for stroke patients at discharge from an acute ward or convalescent rehabilitation ward. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2014; 5: Sonoda S, Saitoh E, Nagai S, Okuyama Y, Suzuki T, Suzuki M. Stroke outcome prediction using reciprocal number of initial activities of daily living status. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Diseas 2005; 14: Liu M, Domen K, Chino N. Comorbidity measures for stroke outcome research. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1997; 78: Iwai N, Aoyagi Y. Discharge index and prediction for stroke patients in the post-acute stage. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2012; 3: Tokunaga M, Fukunaga K, Sannomiya K, Imada Y, Hamasaki H, Noguchi D, et al. The difference between measured Nichijo-seikatsu-kino-hyokahyo (NSKH) score and predicted NSKH score derived from ADL is related to FIM gain. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2013; 4: Jeong S, Kondo K, Shiraishi N, Inoue Y. An evaluation of post-stroke rehabilitation in Japan. Clinical Audit 2010; 2: Tsuji T, Liu M, Sonoda S, Domen K, Chino N. The stroke
8 85 impairment assessment set. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000; 81: Mutai H, Furukawa T, Araki K, Misawa K, Hanihara T. Factors associated with functional recovery and home discharge in stroke patients admitted to a convalescent rehabilitation ward. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2012; 12: Sonoda S, Saitoh E, Domen K, Chino N. Prognostication of stroke patients using SIAS and FIM. In: Chino N, Melvin JL (eds.) Functional Evaluation of Stroke Patients. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo, 1995, pp Inouye M. Predicting models of outcome stratified by age after first stroke rehabilitation in Japan. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2001; 80: Hirano Y, Okura Y, Takeuchi M. The influence of ADL severity at admission on ADL at discharge in convalescent stroke rehabilitation. Tohoku Rigaku-ryoho Kagaku 2011; 23: Japanese. 12. Tokunaga M, Ikeda Y, Inoue M, Kodama J, Sakamoto M, Nagatomo M, et al. Multiple regression analysis stratified by age and FIM at admission. J Clin Rehabil 2015; 24: Japanese. 13. Tokunaga M, Nakanishi R, Eguchi G, Kihara K, Tokisato K, Katsura K, et al. The influence of age on corrected motor FIM effectiveness. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2014; 5: Tokunaga M, Watanabe S, Nakanishi R, Yamanaga H, Yonemitsu H, Mita S, et al. The influence of stroke type, gender, and age on FIM improvement. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2014; 5: Tokunaga M, Nakanishi R, Watanabe S, Maeshiro I, Hyakudome A, Sakamoto K, et al. Corrected FIM effectiveness as an index independent of FIM score on admission. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2014; 5: Imada Y, Tokunaga M, Fukunaga K, Sannomiya K, Inoue R, Hamasaki H, et al. Relationship between cognitive FIM score and motor FIM gain in patients with stroke in a Kaifukuki rehabilitation ward. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2014; 5: Sonoda S. The ADL level that is easy to be affected by the inhibitors on stroke rehabilitation. Program for Stroke 2015, p Kondo K. Secondary analysis of the rehabilitation patient database. Jpn J Rehabil Med 2012; 49: Japanese. 19. Tokunaga M, Sannomiya K, Nakashima Y, Nojiri S, Tokisato K, Katsura K, et al. Formula for predicting FIM gain and discharge FIM, methods using median values of FIM gain stratified by admission FIM, age, cognitive function, and transfer interval. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci 2015; 6: The Japanese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine. Guideline for the clinical research and study of stroke. Japanese.
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan
 86 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article The relationship between measured values and values predicted using multiple regression analysis for mean motor FIM at
86 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article The relationship between measured values and values predicted using multiple regression analysis for mean motor FIM at
Department of Rehabilitation, Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 2. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 3
 16 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article Increasing the prediction accuracy of FIM gain by adding FIM improvement for one month from admission to the explanatory
16 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article Increasing the prediction accuracy of FIM gain by adding FIM improvement for one month from admission to the explanatory
Relationship between motor FIM improvement (corrected motor FIM effectiveness) and age in proximal femoral fractures
 131 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Relationship between motor FIM improvement (corrected motor FIM effectiveness) and age in proximal femoral fractures
131 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Relationship between motor FIM improvement (corrected motor FIM effectiveness) and age in proximal femoral fractures
The influence of age on corrected motor FIM effectiveness
 56 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article The influence of age on corrected motor FIM effectiveness Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD, 1 Ryoji Nakanishi, MD, PhD, 1 Gihachiro
56 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article The influence of age on corrected motor FIM effectiveness Makoto Tokunaga, MD, PhD, 1 Ryoji Nakanishi, MD, PhD, 1 Gihachiro
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 2
 66 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article A comparison of the corrected Functional Independence Measure (FIM) effectiveness at Kaifukuki rehabilitation hospitals
66 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article A comparison of the corrected Functional Independence Measure (FIM) effectiveness at Kaifukuki rehabilitation hospitals
Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward
 32 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2012) Original Article Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward Makoto
32 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2012) Original Article Effects of age on functional independence measure score gain in stroke patients in kaifukuki rehabilitation ward Makoto
Fujihara et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2017) 3:2 DOI /s
 Fujihara et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40780-016-0070-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Development and evaluation of a formula for predicting introduction
Fujihara et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2017) 3:2 DOI 10.1186/s40780-016-0070-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Development and evaluation of a formula for predicting introduction
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2011)
 77 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2011) Original Article Relationship between the intensity of stroke rehabilitation and outcome: A survey conducted by the Kaifukuki Rehabilitation
77 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2011) Original Article Relationship between the intensity of stroke rehabilitation and outcome: A survey conducted by the Kaifukuki Rehabilitation
Department of Rehabilitation, Kumamoto Kinoh Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan 2
 7 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Relationship between improvement in GNRI, a nutritional index, and improvement in motor FIM in elderly stroke patients
7 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Relationship between improvement in GNRI, a nutritional index, and improvement in motor FIM in elderly stroke patients
Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward in Japan
 Jpn J Rehabil Med 2014 ; : 629.633 Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward in Japan Takatsugu OKAMOTO,,, Seiichi ANDO, Shigeru SONODA,, Ichiro MIYAI,, Makoto ISHIKAWA, Introduction In Japan, the ratio of the people
Jpn J Rehabil Med 2014 ; : 629.633 Kaifukuki Rehabilitation Ward in Japan Takatsugu OKAMOTO,,, Seiichi ANDO, Shigeru SONODA,, Ichiro MIYAI,, Makoto ISHIKAWA, Introduction In Japan, the ratio of the people
Differences in FIM improvement rate stratified by nutritional status and age in stroke patients in kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation ward
 98 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (217) Original Article Differences in FIM improvement rate stratified by nutritional status and age in stroke patients in kaifukuki (convalescent)
98 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (217) Original Article Differences in FIM improvement rate stratified by nutritional status and age in stroke patients in kaifukuki (convalescent)
Falls in the sitting position Characteristics and efficacy of preventive measures
 5 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (205) Original Article Falls in the sitting position Characteristics and efficacy of preventive measures Takayuki Watabe, OTR,,2 Rikitaro Sako,
5 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (205) Original Article Falls in the sitting position Characteristics and efficacy of preventive measures Takayuki Watabe, OTR,,2 Rikitaro Sako,
The prognosis of stroke patients regarding ADL based on the SIAS and FIMC Preparation of the Stroke ADL Prognostic Assessment Set (SAPAS)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The prognosis of stroke patients regarding ADL based on the SIAS and FIMC Preparation of the Stroke ADL Prognostic Assessment Set (SAPAS) Takashi Ishikura 1), Toshiyuki Wataki 2), Soichiro
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The prognosis of stroke patients regarding ADL based on the SIAS and FIMC Preparation of the Stroke ADL Prognostic Assessment Set (SAPAS) Takashi Ishikura 1), Toshiyuki Wataki 2), Soichiro
The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity
 863 The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity Tetsuya Tsuji, MD, Meigen Liu, MD, DMSc, Shigeru Sonoda, MD, DMSc, Kazuhisa Domen, MD, DMSc, Naoichi Chino, MD,
863 The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity Tetsuya Tsuji, MD, Meigen Liu, MD, DMSc, Shigeru Sonoda, MD, DMSc, Kazuhisa Domen, MD, DMSc, Naoichi Chino, MD,
Factors associated with functional recovery and home discharge in stroke patients admitted to a convalescent rehabilitation ward
 Factors associated with functional recovery and home discharge in stroke patients admitted to a convalescent rehabilitation ward Hitoshi Mutai 1,2, Tomomi Furukawa 1, Kasumi Araki 1, Kousuke Misawa 1,
Factors associated with functional recovery and home discharge in stroke patients admitted to a convalescent rehabilitation ward Hitoshi Mutai 1,2, Tomomi Furukawa 1, Kasumi Araki 1, Kousuke Misawa 1,
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016)
 95 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Effect of adaptations to the living environment on ADL abilities and self-perception of performance/satisfaction Based
95 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Effect of adaptations to the living environment on ADL abilities and self-perception of performance/satisfaction Based
Multicenter survey of dysphagia and nutritional status of stroke patients in Kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation wards
 11 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Multicenter survey of dysphagia and nutritional status of stroke patients in Kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation
11 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Multicenter survey of dysphagia and nutritional status of stroke patients in Kaifukuki (convalescent) rehabilitation
Effects of Balance Exercise Assist Robot (BEAR) in independently mobile patients by disease
 1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2019) Original Article Effects of Balance Exercise Assist Robot (BEAR) in independently mobile patients by disease Shinichiro Goto, OTR, 1 Kazuyo
1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2019) Original Article Effects of Balance Exercise Assist Robot (BEAR) in independently mobile patients by disease Shinichiro Goto, OTR, 1 Kazuyo
Research Report. Key Words: Functional status; Orthopedics, general; Treatment outcomes. Neva J Kirk-Sanchez. Kathryn E Roach
 Research Report Relationship Between Duration of Therapy Services in a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program and Mobility at Discharge in Patients With Orthopedic Problems Background and Purpose. The purpose
Research Report Relationship Between Duration of Therapy Services in a Comprehensive Rehabilitation Program and Mobility at Discharge in Patients With Orthopedic Problems Background and Purpose. The purpose
Fujita Health University Nanakuri Memorial Hospital, Tsu, Mie, Japan 2
 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article The relationship between proximal function of the upper extremity on the paralyzed side and upper extremity skills in daily
Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article The relationship between proximal function of the upper extremity on the paralyzed side and upper extremity skills in daily
Original Paper. Iran J Neurol 2016; 15(4):
 Iranian Journal of Neurology Original Paper Iran J Neurol 2016; 15(4): 202-208 Evaluation of complete functional status of patients with stroke by Functional Independence Measure scale on admission, discharge,
Iranian Journal of Neurology Original Paper Iran J Neurol 2016; 15(4): 202-208 Evaluation of complete functional status of patients with stroke by Functional Independence Measure scale on admission, discharge,
Development of an assessment sheet for fall prediction in stroke inpatients in convalescent rehabilitation wards in Japan
 Environ Health Prev Med (2008) 13:138 147 DOI 10.1007/s12199-007-0023-8 REGULAR ARTICLE Development of an assessment sheet for fall prediction in stroke inpatients in convalescent rehabilitation wards
Environ Health Prev Med (2008) 13:138 147 DOI 10.1007/s12199-007-0023-8 REGULAR ARTICLE Development of an assessment sheet for fall prediction in stroke inpatients in convalescent rehabilitation wards
Robot-aided training for upper limbs of sub-acute stroke patients
 27 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Robot-aided training for upper limbs of sub-acute stroke patients Hiroyuki Miyasaka, OTR, PhD, 1, 2 Yutaka Tomita, PhD,
27 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Robot-aided training for upper limbs of sub-acute stroke patients Hiroyuki Miyasaka, OTR, PhD, 1, 2 Yutaka Tomita, PhD,
The relationship between satisfaction in activities of daily living and perceived quality of life in recovery rehabilitation inpatients
 1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article The relationship between satisfaction in activities of daily living and perceived quality of life in recovery rehabilitation
1 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article The relationship between satisfaction in activities of daily living and perceived quality of life in recovery rehabilitation
AROC Reports for Any Health Fund (AHF) January December 2004
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australasian Rehabilitation Outcomes Centre - AROC Centre for Health Service Development - CHSD 2005 AROC Reports for Any Health Fund (AHF) January 2004 - December
University of Wollongong Research Online Australasian Rehabilitation Outcomes Centre - AROC Centre for Health Service Development - CHSD 2005 AROC Reports for Any Health Fund (AHF) January 2004 - December
Contribution of physical impairment or imaging findings in the prediction of ADL outcome in stroke patients with middle cerebral artery infarction
 119 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Contribution of physical impairment or imaging findings in the prediction of ADL outcome in stroke patients with middle
119 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2016) Original Article Contribution of physical impairment or imaging findings in the prediction of ADL outcome in stroke patients with middle
Original Article. Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2010)
 11 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2010) Original Article A discriminative measure for static postural control ability to prevent in-hospital falls: Reliability and validity of
11 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2010) Original Article A discriminative measure for static postural control ability to prevent in-hospital falls: Reliability and validity of
Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community
 Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2009; 4: 24 9 Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community ORIGINAL ARTICLE CKC Chan Bsc, DWC Chan Msc, SKM Wong MBA, MAIS, BA, PDOT ABSTRACT
Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2009; 4: 24 9 Evaluation of the functional independence for stroke survivors in the community ORIGINAL ARTICLE CKC Chan Bsc, DWC Chan Msc, SKM Wong MBA, MAIS, BA, PDOT ABSTRACT
OUTCOMES AND DATA 2016
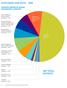 AND DATA 2016 SERVED BY REHAB IMPAIRMENT CATEGORY 20 patients 5.1% MAJOR MULTIPLE TRAUMA W/BRAIN OR SPINAL CORD INJURY 24 patients 6.2% TRAUMATIC 39 patients 10.0% AMPUTATION LOWER EXTREMITY 26 patients
AND DATA 2016 SERVED BY REHAB IMPAIRMENT CATEGORY 20 patients 5.1% MAJOR MULTIPLE TRAUMA W/BRAIN OR SPINAL CORD INJURY 24 patients 6.2% TRAUMATIC 39 patients 10.0% AMPUTATION LOWER EXTREMITY 26 patients
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT. Course Description. Instructional Strategies, Learning Practices, Activities, and Experiences.
 SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Basic Introductory Statistics Grade Level(s): 11-12 Units of Credit: 1 Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles Periods
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Basic Introductory Statistics Grade Level(s): 11-12 Units of Credit: 1 Classification: Elective Length of Course: 30 cycles Periods
IAPT: Regression. Regression analyses
 Regression analyses IAPT: Regression Regression is the rather strange name given to a set of methods for predicting one variable from another. The data shown in Table 1 and come from a student project
Regression analyses IAPT: Regression Regression is the rather strange name given to a set of methods for predicting one variable from another. The data shown in Table 1 and come from a student project
Long-term outcome of severe stroke patients : Is the ADL status at discharge from a stroke center indicative of the long-term outcome?
 227 ORIGINAL Long-term outcome of severe stroke patients : Is the ADL status at discharge from a stroke center indicative of the long-term outcome? Michiharu Kashihara 1, Shigetaka Nakao 2, Jun Kawasaki
227 ORIGINAL Long-term outcome of severe stroke patients : Is the ADL status at discharge from a stroke center indicative of the long-term outcome? Michiharu Kashihara 1, Shigetaka Nakao 2, Jun Kawasaki
Evaluation of the Family - Rated Kinder Infant Development Scale (KIDS) for Disabled Children
 Jikeikai Med J 2012 ; 59 : 5-10 Evaluation of the Family - Rated Kinder Infant Development Scale (KIDS) for Disabled Children Keiji Hashimoto, Naoko Matsui, Hidemi Yakuwa, and Kohei Miyamura Division of
Jikeikai Med J 2012 ; 59 : 5-10 Evaluation of the Family - Rated Kinder Infant Development Scale (KIDS) for Disabled Children Keiji Hashimoto, Naoko Matsui, Hidemi Yakuwa, and Kohei Miyamura Division of
Table 3.1: Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations Screening and Assessment Tools for Acute Stroke Severity
 Table 3.1: Assessment Tool Number and description of Items Neurological Status/Stroke Severity Canadian Neurological Scale (CNS)(1) Items assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech)
Table 3.1: Assessment Tool Number and description of Items Neurological Status/Stroke Severity Canadian Neurological Scale (CNS)(1) Items assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech)
Pattern of Functional Change During Rehabilitation of Patients With Hip Fracture
 111 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of Functional Change During Rehabilitation of Patients With Hip Fracture Nancy K. Latham, PhD, PT, Diane U. Jette, DSc, PT, Reg L. Warren, PhD, Christopher Wirtalla, BA ABSTRACT.
111 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of Functional Change During Rehabilitation of Patients With Hip Fracture Nancy K. Latham, PhD, PT, Diane U. Jette, DSc, PT, Reg L. Warren, PhD, Christopher Wirtalla, BA ABSTRACT.
WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics. What is Statistics and how does it relate to you?
 WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics Time Interval/ Unit 1: Introduction to Statistics 1.1-1.3 2 weeks S-IC-1: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters
WDHS Curriculum Map Probability and Statistics Time Interval/ Unit 1: Introduction to Statistics 1.1-1.3 2 weeks S-IC-1: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters
Evaluation of Preventive Care Program for Cognitive Function Decline among Community-dwelling Frail Elderly People A Pilot Study
 Journal of Japan Academy of Community Health Nursing Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 87 92, 2007 Evaluation of Preventive Care Program for Cognitive Function Decline among Community-dwelling Frail Elderly People A
Journal of Japan Academy of Community Health Nursing Vol. 9, No. 2, pp. 87 92, 2007 Evaluation of Preventive Care Program for Cognitive Function Decline among Community-dwelling Frail Elderly People A
Relationship between sleep disorder and subjective feelings of recovery in convalescent stroke patients
 125 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Relationship between sleep disorder and subjective feelings of recovery in convalescent stroke patients Shuhei Koeda,
125 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Relationship between sleep disorder and subjective feelings of recovery in convalescent stroke patients Shuhei Koeda,
Correlation and regression
 PG Dip in High Intensity Psychological Interventions Correlation and regression Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://martinbland.co.uk/ Correlation Example: Muscle strength
PG Dip in High Intensity Psychological Interventions Correlation and regression Martin Bland Professor of Health Statistics University of York http://martinbland.co.uk/ Correlation Example: Muscle strength
Influence of Dysphagia on Short-Term Outcome in Patients with Acute Stroke
 Authors: Shinichiro Maeshima, MD, PhD Aiko Osawa, MD Yasuhiro Miyazaki, MA Yasuko Seki, BA Chiaki Miura, BA Yuu Tazawa, BA Norio Tanahashi, MD Affiliations: From the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine
Authors: Shinichiro Maeshima, MD, PhD Aiko Osawa, MD Yasuhiro Miyazaki, MA Yasuko Seki, BA Chiaki Miura, BA Yuu Tazawa, BA Norio Tanahashi, MD Affiliations: From the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine
Chapter 1: Exploring Data
 Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
AROC Intensity of Therapy Project. AFRM Conference 18 September 2013
 AROC Intensity of Therapy Project AFRM Conference 18 September 2013 What is AROC? AROC began as a joint initiative of the whole Australian rehabilitation sector (providers, payers, regulators and consumers)
AROC Intensity of Therapy Project AFRM Conference 18 September 2013 What is AROC? AROC began as a joint initiative of the whole Australian rehabilitation sector (providers, payers, regulators and consumers)
Canadian Stroke Best Practices Table 3.3A Screening and Assessment Tools for Acute Stroke
 Canadian Stroke Best Practices Table 3.3A Screening and s for Acute Stroke Neurological Status/Stroke Severity assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech) and motor function (face,
Canadian Stroke Best Practices Table 3.3A Screening and s for Acute Stroke Neurological Status/Stroke Severity assess mentation (level of consciousness, orientation and speech) and motor function (face,
Appendix E: Cohort studies - methodological quality: Non pharmacological risk factors
 Appendix E: studies - methodological quality: n pharmacological risk factors Study Andersson 2001; 51/24 (=2) All patients followed up until discharge but in numbers of number of variables studied; 4/4
Appendix E: studies - methodological quality: n pharmacological risk factors Study Andersson 2001; 51/24 (=2) All patients followed up until discharge but in numbers of number of variables studied; 4/4
Responsiveness, construct and criterion validity of the Personal Care-Participation Assessment and Resource Tool (PC-PART)
 Darzins et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes (2015) 13:125 DOI 10.1186/s12955-015-0322-5 RESEARCH Responsiveness, construct and criterion validity of the Personal Care-Participation Assessment and
Darzins et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes (2015) 13:125 DOI 10.1186/s12955-015-0322-5 RESEARCH Responsiveness, construct and criterion validity of the Personal Care-Participation Assessment and
examination in the initial assessment of overdose patients
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1988, 5, 139-145 Use of abbreviated mental status examination in the initial assessment of overdose patients K. S. MERIGIAN,1 J. R. HEDGES,1 J. R. ROBERTS,1 R. A. CHILDRESS,'
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1988, 5, 139-145 Use of abbreviated mental status examination in the initial assessment of overdose patients K. S. MERIGIAN,1 J. R. HEDGES,1 J. R. ROBERTS,1 R. A. CHILDRESS,'
Fitting a Single-Phase Model to the Post-Exercise Changes in Heart Rate and Oxygen Uptake
 Fitting a Single-Phase Model to the Post-Exercise Changes in Heart Rate and Oxygen Uptake R. STUPNICKI, T. GABRYŚ, U. SZMATLAN-GABRYŚ, P. TOMASZEWSKI University of Physical Education, Warsaw, Poland Summary
Fitting a Single-Phase Model to the Post-Exercise Changes in Heart Rate and Oxygen Uptake R. STUPNICKI, T. GABRYŚ, U. SZMATLAN-GABRYŚ, P. TOMASZEWSKI University of Physical Education, Warsaw, Poland Summary
Dysphagia associated with acute-phase brainstem cerebrovascular disorder
 43 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Dysphagia associated with acute-phase brainstem cerebrovascular disorder Ryoko Akahori, MD, 1 Hitoshi Kagaya, MD, DMSc,
43 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Dysphagia associated with acute-phase brainstem cerebrovascular disorder Ryoko Akahori, MD, 1 Hitoshi Kagaya, MD, DMSc,
BED BLOCKERS: A STUDY ON THE ELDERLY PATIENTS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL IN INDIA
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 1 BED BLOCKERS: A STUDY ON THE ELDERLY PATIENTS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL IN INDIA P N., N Shinge, P S. Citation P N., N Shinge, P S.. BED BLOCKERS:
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 1 BED BLOCKERS: A STUDY ON THE ELDERLY PATIENTS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL IN INDIA P N., N Shinge, P S. Citation P N., N Shinge, P S.. BED BLOCKERS:
Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2017;41(1):16-24 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.1.16 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Effect of a Caregiver s Education Program
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2017;41(1):16-24 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.1.16 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Effect of a Caregiver s Education Program
Prism Adaptation Therapy Enhances Rehabilitation of Stroke Patients With Unilateral Spatial Neglect: A Randomized, Controlled Trial
 407516NNRXXX10.1177/1545968311407516Miz uno et alneurorehabilitation and Neural Repair The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: http://www. sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav Research Articles Prism
407516NNRXXX10.1177/1545968311407516Miz uno et alneurorehabilitation and Neural Repair The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: http://www. sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav Research Articles Prism
The Uniform Data System for Medical Rehabilitation Report of Patients with Debility Discharged from Inpatient Rehabilitation Programs in 2000Y2010
 Authors: Rebecca V. Galloway, PT, MPT Carl V. Granger, MD Amol M. Karmarkar, PhD, OTR James E. Graham, PhD, DC Anne Deutsch, RN, PhD, CRRN Paulette Niewczyk, PhD, MPH Margaret A. DiVita, MS Kenneth J.
Authors: Rebecca V. Galloway, PT, MPT Carl V. Granger, MD Amol M. Karmarkar, PhD, OTR James E. Graham, PhD, DC Anne Deutsch, RN, PhD, CRRN Paulette Niewczyk, PhD, MPH Margaret A. DiVita, MS Kenneth J.
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting data to assist in making effective decisions
 Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Functional Level During the First Year After Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Course and Predictors of Outcome
 Original Article Elmer ress Functional Level During the First Year After Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Course and Predictors of Outcome Maria Sandhaug a, b, e, Nada Andelic c, Svein A Berntsen
Original Article Elmer ress Functional Level During the First Year After Moderate and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Course and Predictors of Outcome Maria Sandhaug a, b, e, Nada Andelic c, Svein A Berntsen
TOTAL HIP AND KNEE REPLACEMENTS. FISCAL YEAR 2002 DATA July 1, 2001 through June 30, 2002 TECHNICAL NOTES
 TOTAL HIP AND KNEE REPLACEMENTS FISCAL YEAR 2002 DATA July 1, 2001 through June 30, 2002 TECHNICAL NOTES The Pennsylvania Health Care Cost Containment Council April 2005 Preface This document serves as
TOTAL HIP AND KNEE REPLACEMENTS FISCAL YEAR 2002 DATA July 1, 2001 through June 30, 2002 TECHNICAL NOTES The Pennsylvania Health Care Cost Containment Council April 2005 Preface This document serves as
William C Miller, PhD, FCAOT Professor Occupational Science & Occupational Therapy University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada
 William C Miller, PhD, FCAOT Professor Occupational Science & Occupational Therapy University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada THE L TEST MANUAL Version: November 2014 Table of Contents Introduction...
William C Miller, PhD, FCAOT Professor Occupational Science & Occupational Therapy University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada THE L TEST MANUAL Version: November 2014 Table of Contents Introduction...
Statistical analysis plan the Oslo Orthogeriatrics Study
 Statistical analysis plan the Oslo Orthogeriatrics Study Note: This statistical analysis plan was written prior to any unblinding of treatment allocation 1. Introduction The aim of the Oslo Orthogeriatrics
Statistical analysis plan the Oslo Orthogeriatrics Study Note: This statistical analysis plan was written prior to any unblinding of treatment allocation 1. Introduction The aim of the Oslo Orthogeriatrics
A Study of relationship between frailty and physical performance in elderly women
 Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2015;11(4):215-219 A Study of relationship between frailty and physical performance in elderly women Bog Ja Jeoung 1, *, Yang Chool Lee 2 1 Department
Original Article Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation 2015;11(4):215-219 A Study of relationship between frailty and physical performance in elderly women Bog Ja Jeoung 1, *, Yang Chool Lee 2 1 Department
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Kapadia, N. M., Zivanovic, V., Furlan, J. C., Craven, B. C., McGillivray, C., & Popovic, M. R. (2011). Functional electrical stimulation therapy for grasping in traumatic
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Kapadia, N. M., Zivanovic, V., Furlan, J. C., Craven, B. C., McGillivray, C., & Popovic, M. R. (2011). Functional electrical stimulation therapy for grasping in traumatic
APPROXIMATELY 500,000 MEDICARE patients are
 934 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Inpatient Rehabilitation for Older Adults With Debility, Hip Fracture, and Myopathy Patrick Kortebein, MD, Carl V. Granger, MD, Dennis H. Sullivan, MD ABSTRACT.
934 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Inpatient Rehabilitation for Older Adults With Debility, Hip Fracture, and Myopathy Patrick Kortebein, MD, Carl V. Granger, MD, Dennis H. Sullivan, MD ABSTRACT.
ORIGINAL PAPER. Measures and effects on prevention of fall: the role of a fall working group at a university hospital
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 497 ~ 504, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.497 ORIGINAL PAPER Measures and effects on prevention of fall: the role of a fall working group at a university hospital Kazuyoshi Kobayashi
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 497 ~ 504, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.497 ORIGINAL PAPER Measures and effects on prevention of fall: the role of a fall working group at a university hospital Kazuyoshi Kobayashi
The Development of a Japanese Version of the Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire
 Original Article Makoto YAMAGUCHI *1 Hiroaki KUMANO *2 Yuichi YAMAUCHI *3 Yoshiaki KADOTA *4,5 Masako ISEKI *4 Abstract Though has been translated into several languages and validated, a Japanese version
Original Article Makoto YAMAGUCHI *1 Hiroaki KUMANO *2 Yuichi YAMAUCHI *3 Yoshiaki KADOTA *4,5 Masako ISEKI *4 Abstract Though has been translated into several languages and validated, a Japanese version
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data
 Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Unit 1 Exploring and Understanding Data Area Principle Bar Chart Boxplot Conditional Distribution Dotplot Empirical Rule Five Number Summary Frequency Distribution Frequency Polygon Histogram Interquartile
Gender and Ethnic Differences in Rehabilitation Outcomes After Hip-Replacement Surgery
 Authors: Ivonne-Marie Bergés, PhD Yong-Fang Kuo, PhD Glenn V. Ostir, PhD Carl V. Granger, MD James E. Graham, PhD Kenneth J. Ottenbacher, PhD, OTR Affiliations: From the Sealy Center on Aging, University
Authors: Ivonne-Marie Bergés, PhD Yong-Fang Kuo, PhD Glenn V. Ostir, PhD Carl V. Granger, MD James E. Graham, PhD Kenneth J. Ottenbacher, PhD, OTR Affiliations: From the Sealy Center on Aging, University
Angela Colantonio, PhD 1, Gary Gerber, PhD 2, Mark Bayley, MD, FRCPC 1, Raisa Deber, PhD 3, Junlang Yin, MSc 1 and Hwan Kim, PhD candidate 1
 J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 311 315 ORIGINAL REPORT Differential Profiles for Patients with Traumatic and Non- Traumatic Brain Injury Angela Colantonio, PhD 1, Gary Gerber, PhD 2, Mark Bayley, MD, FRCPC 1,
J Rehabil Med 2011; 43: 311 315 ORIGINAL REPORT Differential Profiles for Patients with Traumatic and Non- Traumatic Brain Injury Angela Colantonio, PhD 1, Gary Gerber, PhD 2, Mark Bayley, MD, FRCPC 1,
A newly developed assessment scale for attentional disturbance based on behavioral problems: Behavioral Assessment of Attentional Disturbance (BAAD)
 Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 31, No. 1, pp. 29-33, 2006 A newly developed assessment scale for attentional disturbance based on behavioral problems: Behavioral Assessment of Attentional Disturbance (BAAD)
Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 31, No. 1, pp. 29-33, 2006 A newly developed assessment scale for attentional disturbance based on behavioral problems: Behavioral Assessment of Attentional Disturbance (BAAD)
Subacute inpatient rehabilitation across a range of impairments: intensity of therapy received and outcomes
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Health Services Research Institute Faculty of Business 2013 Subacute inpatient rehabilitation across a range of impairments: intensity of therapy received
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Health Services Research Institute Faculty of Business 2013 Subacute inpatient rehabilitation across a range of impairments: intensity of therapy received
The Long-term Prognosis of Delirium
 The Long-term Prognosis of Jane McCusker, MD, DrPH, Professor, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McGill University; Head, Clinical Epidemiology and Community Studies, St. Mary s Hospital, Montreal, QC. Nine
The Long-term Prognosis of Jane McCusker, MD, DrPH, Professor, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McGill University; Head, Clinical Epidemiology and Community Studies, St. Mary s Hospital, Montreal, QC. Nine
What is Occupational Therapy?
 Introduction to Occupational Therapy Services What is Occupational Therapy? Alice Chan, OTI Tai Po Hospital a health profession that focuses on promoting health and well being through engagement in meaningful
Introduction to Occupational Therapy Services What is Occupational Therapy? Alice Chan, OTI Tai Po Hospital a health profession that focuses on promoting health and well being through engagement in meaningful
M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points Total 60
 M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points 1-10 10 11 3 12 4 13 3 14 10 15 14 16 10 17 7 18 4 19 4 Total 60 Multiple choice questions (1 point each) For questions
M 140 Test 1 A Name SHOW YOUR WORK FOR FULL CREDIT! Problem Max. Points Your Points 1-10 10 11 3 12 4 13 3 14 10 15 14 16 10 17 7 18 4 19 4 Total 60 Multiple choice questions (1 point each) For questions
BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN
 Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Review Article Relationship of Activity of Daily Living with Quality of Life Debalina Datta 1, Pratyay Pratim Datta* 2 and KunalKanti Majumdar
Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Review Article Relationship of Activity of Daily Living with Quality of Life Debalina Datta 1, Pratyay Pratim Datta* 2 and KunalKanti Majumdar
DESIGN TYPE AND LEVEL OF EVIDENCE: Level I: Pilot randomized controlled trial. Limitations (appropriateness of study design):
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Does the Cognitive Orientation to daily Occupational Performance (CO-OP) approach increase clients performance on goals more than a standard occupational
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Does the Cognitive Orientation to daily Occupational Performance (CO-OP) approach increase clients performance on goals more than a standard occupational
STATISTICS INFORMED DECISIONS USING DATA
 STATISTICS INFORMED DECISIONS USING DATA Fifth Edition Chapter 4 Describing the Relation between Two Variables 4.1 Scatter Diagrams and Correlation Learning Objectives 1. Draw and interpret scatter diagrams
STATISTICS INFORMED DECISIONS USING DATA Fifth Edition Chapter 4 Describing the Relation between Two Variables 4.1 Scatter Diagrams and Correlation Learning Objectives 1. Draw and interpret scatter diagrams
Management of the Frail Older Patients: What Are the Outcomes
 Management of the Frail Older Patients: What Are the Outcomes Professor Edwina Brown Imperial College Renal and Transplant Centre Hammersmith Hospital, London Increasing prevalence of old old on RRT RRT
Management of the Frail Older Patients: What Are the Outcomes Professor Edwina Brown Imperial College Renal and Transplant Centre Hammersmith Hospital, London Increasing prevalence of old old on RRT RRT
Lowest-Low Fertility and Governmental Actions in Japan: A Comment
 Lowest-Low Fertility and Governmental Actions in Japan: A Comment Hiroshi Yoshida * Graduate School of Economics and Management, Tohoku University, 980-8576 Sendai, JAPAN 1. Introduction The reasons of
Lowest-Low Fertility and Governmental Actions in Japan: A Comment Hiroshi Yoshida * Graduate School of Economics and Management, Tohoku University, 980-8576 Sendai, JAPAN 1. Introduction The reasons of
2.75: 84% 2.5: 80% 2.25: 78% 2: 74% 1.75: 70% 1.5: 66% 1.25: 64% 1.0: 60% 0.5: 50% 0.25: 25% 0: 0%
 Capstone Test (will consist of FOUR quizzes and the FINAL test grade will be an average of the four quizzes). Capstone #1: Review of Chapters 1-3 Capstone #2: Review of Chapter 4 Capstone #3: Review of
Capstone Test (will consist of FOUR quizzes and the FINAL test grade will be an average of the four quizzes). Capstone #1: Review of Chapters 1-3 Capstone #2: Review of Chapter 4 Capstone #3: Review of
MEASUREMENT OF FUNCTIONAL ABILITIES is an. Recovery of Functional Status After Right Hemisphere Stroke: Relationship With Unilateral Neglect
 322 Recovery of Functional Status After Right Hemisphere Stroke: Relationship With Unilateral Neglect Leora R. Cherney, PhD, BC-NCD, Anita S. Halper, MA, BC-NCD, Christina M. Kwasnica, MD, Richard L. Harvey,
322 Recovery of Functional Status After Right Hemisphere Stroke: Relationship With Unilateral Neglect Leora R. Cherney, PhD, BC-NCD, Anita S. Halper, MA, BC-NCD, Christina M. Kwasnica, MD, Richard L. Harvey,
National Hospital Organization Shimoshizu Hospital, Yotsukaido City, Chiba, Japan
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2018;42(4):569-574 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.569 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Correlation Between Walking Ability and
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2018;42(4):569-574 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.569 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Correlation Between Walking Ability and
Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression
 Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression Linear relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these relationships.
Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression Linear relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these relationships.
Bupa care home census 2012
 A profile of residents in care homes: results from the 2012 Bupa census Margaret Butterworth Care HomeForum Nat Lievesley Centre for Policy on Ageing November 2013 Bupa care home census 2012 This presentation
A profile of residents in care homes: results from the 2012 Bupa census Margaret Butterworth Care HomeForum Nat Lievesley Centre for Policy on Ageing November 2013 Bupa care home census 2012 This presentation
Knowledge discovery tools 381
 Knowledge discovery tools 381 hours, and prime time is prime time precisely because more people tend to watch television at that time.. Compare histograms from di erent periods of time. Changes in histogram
Knowledge discovery tools 381 hours, and prime time is prime time precisely because more people tend to watch television at that time.. Compare histograms from di erent periods of time. Changes in histogram
2019 COLLECTION TYPE: MIPS CLINICAL QUALITY MEASURES (CQMS) MEASURE TYPE: Patient Reported Outcome High Priority
 Quality ID #220 (NQF 0425): Functional Status Change for Patients with Low Back Impairments National Quality Strategy Domain: Communication and Care Coordination Meaningful Measure Area: Patient Reported
Quality ID #220 (NQF 0425): Functional Status Change for Patients with Low Back Impairments National Quality Strategy Domain: Communication and Care Coordination Meaningful Measure Area: Patient Reported
Hybrid Assistive Limb (HAL) Rehabilitation in Patients with Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 55, 901 906, 2015 doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2015-0209 Online October 28, 2015 Hybrid Assistive Limb (HAL) Rehabilitation in Patients with Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke Toshiyasu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 55, 901 906, 2015 doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2015-0209 Online October 28, 2015 Hybrid Assistive Limb (HAL) Rehabilitation in Patients with Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke Toshiyasu
Comparison of clock drawing with Mini Mental State Examination as a screening test in elderly acute hospital admissions
 Postgrad Med J (1993) 69, 696-700 A) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 199: Comparison of clock drawing with Mini Mental State Examination as a screening test in elderly acute hospital admissions
Postgrad Med J (1993) 69, 696-700 A) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 199: Comparison of clock drawing with Mini Mental State Examination as a screening test in elderly acute hospital admissions
Critical Review: The Efficacy of Animal-Assisted Therapy for Improving Communication Skills in Adults with Aphasia or Apraxia
 Critical Review: The Efficacy of Animal-Assisted Therapy for Improving Communication Skills in Adults with Aphasia or Apraxia McDermid, Julie M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School
Critical Review: The Efficacy of Animal-Assisted Therapy for Improving Communication Skills in Adults with Aphasia or Apraxia McDermid, Julie M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School
AN ESTIMATED 500,000 to 1.5 million patients are admitted
 1441 The Relationship Between Therapy Intensity and Rehabilitative Outcomes After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multicenter Analysis David X. Cifu, MD, Jeffrey S. Kreutzer, PhD, ABPP, Stephanie A. Kolakowsky-Hayner,
1441 The Relationship Between Therapy Intensity and Rehabilitative Outcomes After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multicenter Analysis David X. Cifu, MD, Jeffrey S. Kreutzer, PhD, ABPP, Stephanie A. Kolakowsky-Hayner,
Relationship between weight gain, functional recovery and nutrition monitoring in underweight tube-fed stroke patients
 3 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Relationship between weight gain, functional recovery and nutrition monitoring in underweight tube-fed stroke patients
3 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2018) Original Article Relationship between weight gain, functional recovery and nutrition monitoring in underweight tube-fed stroke patients
Peterborough Community Rehabilitation Schemes. Martyn Parker
 Peterborough Community Rehabilitation Schemes Martyn Parker Peterborough Hospital at Home Established 1987 Provided home care for patients Initially used by for hip fracture patients and after hysterectomy
Peterborough Community Rehabilitation Schemes Martyn Parker Peterborough Hospital at Home Established 1987 Provided home care for patients Initially used by for hip fracture patients and after hysterectomy
What is Occupational Therapy? Introduction to Occupational Therapy. World Federation of Occupational Therapists 2012
 World Federation of Occupational Therapists 2012 Introduction to Occupational Therapy Suki HUI Occupational Therapist I Statement on Occupational Therapy Occupational therapy is a client-centred health
World Federation of Occupational Therapists 2012 Introduction to Occupational Therapy Suki HUI Occupational Therapist I Statement on Occupational Therapy Occupational therapy is a client-centred health
Changes in subjective Quality of Life after making a Daruma doll and recreation in elderly patients with dementia
 71 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Changes in subjective Quality of Life after making a Daruma doll and recreation in elderly patients with dementia Keiko
71 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2015) Original Article Changes in subjective Quality of Life after making a Daruma doll and recreation in elderly patients with dementia Keiko
Statistics: Making Sense of the Numbers
 Statistics: Making Sense of the Numbers Chapter 9 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including
Statistics: Making Sense of the Numbers Chapter 9 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including
Development of the Sydney Falls Risk Screening Tool: phase two
 Development of the Sydney Falls Risk Screening Tool: phase two Presented by Duncan McKechnie Coinvestigators Murray Fisher, Julie Pryor, Jhoven de Jesus, Melissa Bonser The University of Sydney Page 1
Development of the Sydney Falls Risk Screening Tool: phase two Presented by Duncan McKechnie Coinvestigators Murray Fisher, Julie Pryor, Jhoven de Jesus, Melissa Bonser The University of Sydney Page 1
Psychology Research Process
 Psychology Research Process Logical Processes Induction Observation/Association/Using Correlation Trying to assess, through observation of a large group/sample, what is associated with what? Examples:
Psychology Research Process Logical Processes Induction Observation/Association/Using Correlation Trying to assess, through observation of a large group/sample, what is associated with what? Examples:
Effect of Mobility on Community Participation at 1 year Post-Injury in Individuals with Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
 Effect of Mobility on Community Participation at 1 year Post-Injury in Individuals with Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Irene Ward, PT, DPT, NCS Brain Injury Clinical Research Coordinator Kessler Institute
Effect of Mobility on Community Participation at 1 year Post-Injury in Individuals with Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Irene Ward, PT, DPT, NCS Brain Injury Clinical Research Coordinator Kessler Institute
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting data to assist in making effective decisions
 Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Readings: OpenStax Textbook - Chapters 1 5 (online) Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 1, 5, 6, 13 (online) Introductory comments Describe how familiarity with statistical methods can - be associated
Acute Rehabilitation. Giving Courage l Creating Hope l Building Strength
 Acute Rehabilitation Giving Courage l Creating Hope l Building Strength What is Acute Rehabilitation? Rehabilitation is a team of healthcare professionals working together to help people regain function
Acute Rehabilitation Giving Courage l Creating Hope l Building Strength What is Acute Rehabilitation? Rehabilitation is a team of healthcare professionals working together to help people regain function
Audit of perioperative management of patients with fracture neck of femur
 Audit of perioperative management of patients with fracture neck of femur *M Dissanayake 1, N Wijesuriya 2 Registrar in Anaesthesia 1, Consultant Anaesthetist 2, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama,
Audit of perioperative management of patients with fracture neck of femur *M Dissanayake 1, N Wijesuriya 2 Registrar in Anaesthesia 1, Consultant Anaesthetist 2, North Colombo Teaching Hospital, Ragama,
Understandable Statistics
 Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
Understandable Statistics correlated to the Advanced Placement Program Course Description for Statistics Prepared for Alabama CC2 6/2003 2003 Understandable Statistics 2003 correlated to the Advanced Placement
Medico-Social Impact of Fragility Fracture 11/2/2014. Dr David Dai Consultant Geriatrician Prince of Wales Hospital 24 th January, 2014
 Medico-Social Impact of Fragility Fracture Dr David Dai Consultant Geriatrician Prince of Wales Hospital 24 th January, 2014 2014 Policy Agenda As Hong Kong moves steadily to an ageing society (with the
Medico-Social Impact of Fragility Fracture Dr David Dai Consultant Geriatrician Prince of Wales Hospital 24 th January, 2014 2014 Policy Agenda As Hong Kong moves steadily to an ageing society (with the
Alectinib Versus Crizotinib for Previously Untreated Alk-positive Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer : A Meta-Analysis
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 30 2, 309 315, June 2018 Original Alectinib Versus Crizotinib for Previously Untreated Alk-positive Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer : A Meta-Analysis Ryo MANABE 1, Koichi ANDO
Showa Univ J Med Sci 30 2, 309 315, June 2018 Original Alectinib Versus Crizotinib for Previously Untreated Alk-positive Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer : A Meta-Analysis Ryo MANABE 1, Koichi ANDO
