Acta Neurologica Belgica Single-centre experience on transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: case series and literature review
|
|
|
- Spencer Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Neurologica Belgica Single-centre experience on transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: case series and literature review --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Corresponding Author: ANEB-D--00 Single-centre experience on transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: case series and literature review Review article Broes Martens Universiteit Gent BELGIUM Corresponding Author Secondary Information: Corresponding Author's Institution: Universiteit Gent Corresponding Author's Secondary Institution: First Author: Broes Martens First Author Secondary Information: Order of Authors: Broes Martens Michel De Pauw Jan De Bleecker Order of Authors Secondary Information: Funding Information: Abstract: Familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP) is a most often length-dependent axonal neuropathy, often part of a multisystem disorder also affecting other organs, such as cardiac, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, renal, meningeal and eye tissue. It is most frequently the result of a mutation in the TTR gene, most commonly a p.val0met mutation. TTR-FAP is a rare autosomal dominant heritable disabling, heterogeneous disease in which early diagnosis is of pivotal importance when attempting treatment. This paper discusses the course of four Belgian FAP patients with different TTR mutations (p.valmet; p.valala; p.alaval; p.val0met). We also review the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of TTR-FAP, diagnostic studies, follow-up, its current treatment and those in development, prognosis and the importance of genetic counselling. At first TTR-FAP is often misdiagnosed as a chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy or chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Genetic testing is obligatory to confirm the diagnosis of TTR-FAP, except in familial cases. Biopsy samples are an asset in diagnosing TTR-FAP but can be falsely negative. At the moment, tafamidis meglumine is considered as first-line treatment in stage I neurological disease. Patients eligible for liver transplantation should be carefully selected when first-line therapy fails. Suggested Reviewers: Powered by Editorial Manager and ProduXion Manager from Aries Systems Corporation
2 Manuscript Single-centre experience on transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: case series and literature review Click here to view linked References Click here to download Manuscript Single-centre experience on TTR-FAP.docx Single-centre experience on transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: case series and literature review Broes Martens, Michel De Pauw², Jan L. De Bleecker Ghent University Hospital, Department of Neurology and Neuromuscular Reference Centre, and ²Department of Cardiology Address for correspondence: Prof. dr. Jan De Bleecker, University Hospital, Neurology Department, De Pintelaan, B000 Gent, Belgium; jan.debleecker@ugent.be; tel. +--
3 Abstract Familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP) is a most often length-dependent axonal neuropathy, often part of a multisystem disorder also affecting other organs, such as cardiac, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, renal, meningeal and eye tissue. It is most frequently the result of a mutation in the TTR gene, most commonly a p.val0met mutation. TTR-FAP is a rare autosomal dominant heritable disabling, heterogeneous disease in which early diagnosis is of pivotal importance when attempting treatment. This paper discusses the course of four Belgian FAP patients with different TTR mutations (p.valmet; p.valala; p.alaval; p.val0met). We also review the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of TTR-FAP, diagnostic studies, follow-up, its current treatment and those in development, prognosis and the importance of genetic counselling. At first TTR-FAP is often misdiagnosed as a chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy or chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Genetic testing is obligatory to confirm the diagnosis of TTR-FAP, except in familial cases. Biopsy samples are an asset in diagnosing TTR-FAP but can be falsely negative. At the moment, tafamidis meglumine is considered as first-line treatment in stage I neurological disease. Patients eligible for liver transplantation should be carefully selected when first-line therapy fails. Key words: transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy; liver transplantation; tafamidis meglumine; genetic testing.
4 Introduction Familial amyloid polyneuropathies (FAPs) are a group of acquired or hereditary, autosomal dominant disorders that affect several organs. Three main types are distinguished, dependent on the precursor protein of amyloid: transthyretin (TTR), being the most prevalent type, gelsolin and apolipoprotein A-. TTR, a homotetrameric protein, is mainly produced in the liver, whereas a small amount is produced by the choroid plexus and retinal cells. Pathogenic mutations induce the dissociation of the tetramer. Subsequent extracellular release of the monomers causes them to self-aggregate and ultimately create insoluble amyloid fibrils which precipitate in multiple tissues. The most frequent mutation is the p.val0met mutation, formerly known as Val0Met [,]. Clinical presentation The main clinical feature of TTR-FAP is a length-dependent sensorimotor polyneuropathy which often precedes marked autonomic dysfunction. The polyneuropathy starts in the feet with loss of temperature and pain sensation, or neuropathic pain. It extends progressively above the ankles with involvement of light touch distally but dissociated sensory loss proximally. Motor deficits also start in the feet and follow a length-dependent pattern. The sensory deficit progresses to the fingers, forearms and eventually the trunk. There are three stages of TTR-FAP. In stage I, the disease is limited to the lower limbs with slight weakness of the extensor hallucis muscles. In stage II, the hand muscles become wasted and weak. In stage III, the patient is bedridden or confined to a wheelchair []. Less frequently the pattern is not length-dependent but focal, resulting from amyloid deposits. Carpal tunnel syndrome, for example, results from endoneurial amyloid deposition in the median nerve. Autonomic dysfunction is often prominent and mostly impairs cardio-circulatory, genitourinary and gastrointestinal systems leading to cardiac conduction failure, orthostatic hypotension, erectile dysfunction, cachexia, gastroparesis, postprandial diarrhoea or constipation. Eye involvement manifestations include vitreous opacities with progressive visual loss, chronic open-angle glaucoma due to trabecular obstruction, and scalloped pupils. Progressive renal failure may occur []. Familial amyloid cardiomyopathy (FAC) occurs when the mutated TTR precipitates in cardiac tissue. FAC should be distinguished from age-related or senile systemic amyloidosis in which misaggregation and subsequent precipitation of wild-type TTR leads to wild-type TTRrelated amyloid cardiomyopathy. This heart disease is slowly progressive and clinically well tolerated until marked conduction disease, ventricular wall thickening and profound diastolic dysfunction occur []. Age of onset for early-onset FAP varies between the third to fourth decade. For late-onset FAP, it may vary between the sixth and eighth decade. It is endemic in Portugal, Sweden and Japan and shows a merely sporadic
5 presentation worldwide. Death occurs within ten years on average [,]. Table shows the main differences between early- and late-onset Val0Met TTR-FAP []. TTR-FAP is a clinically heterogeneous disorder. The factors which influence its phenotype remain unclear. In non-val0met mutations, for example, cardiomyopathy seems to be more common among men with a late onset compared to women with a late onset [,]. Auxiliary investigations Electromyography EMG may initially be normal in cases of small-fibre polyneuropathy. In an advanced stage of the disease, large fibres are also affected, showing a length-dependent axonal sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Demyelinating features are less common but may lead to confusion with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy []. Cerebrospinal Fluid Although usually normal, CSF protein content may be raised in TTR-FAP. TTR itself is predominantly produced in the liver but production in the choroid plexus also occurs. This results in the presence of TTR protein in CSF, sometimes leading to meningeal amyloid deposition [,]. Histology Biopsy samples can be taken from (sural) nerve tissue, heart, muscle, kidney, gastrointestinal tract, the labial salivary gland and, most commonly, subcutaneous abdominal fat [,]. Extracellular amyloid deposits are visualized using Congo red staining. The amyloid deposits display a characteristic apple-green birefringence under polarised light examination. Additional immunohistochemical stains to identify amyloid protein components are mandatory. A negative biopsy, however, does not rule out amyloidosis [,,]. Although the amyloid nature can be demonstrated with staining, the amyloid sub-type has to be proven using massspectroscopy-based proteomic analysis or immunohistochemistry [,]. A high index of suspicion and an experienced pathologist are needed for a correct diagnosis. Neural amyloid deposits are mostly found in the endoneurium and endoneurial capillaries in an asymmetric manner between and in the fascicles. The destruction of unmyelinated fibres may be visualised early on electron microscopy, as well as vanishing of the Schwann cell basal lamina following contact with the amyloid deposits, rendering unmyelinated vessels dystrophic [].
6 MR Neurography (MRN) A recent study has provided class III evidence that MRN accurately identifies asymptomatic mutated TTR carriers []. Genetic testing The TTR gene is located on chromosome q.-. It contains four exons. One hundred nineteen mutations in the TTR gene have been reported, all of which are missense point mutations except for one microdeletion. One hundred thirteen mutations are amyloidogenic. The p.val0met point mutation is by far the most frequent mutation in endemic areas. DNA testing is mandatory for the diagnosis, except when typical symptoms manifest in cases with a known family history of TTR-FAP []. Own cases We report four cases of TTR-FAP. Three have rare non-val0met TTR mutations. Table shows a summary of the main features of these four patients. Case one concerns a male with a p.valmet TTR mutation who deceased at the age of years. This patient was initially diagnosed as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in based on a sporadic chronic sensorimotor polyneuropathy with areflexia, combined axonal and demyelinating features on EMG, and a markedly elevated protein content in CSF. Several treatment attempts (plasmapheresis, administration of IV immunoglobulins, oral methylprednisolone, oral cyclophosphamide and the anti-cd0- monoclonal antibody rituximab) were of no avail. Early in his disease course, a sural nerve biopsy had been read as mixed axonal and demyelinating, with reportedly negative findings after Congo red staining. Multiple autonomic denervation symptoms developed and dramatically evolved along with marked weight loss. In January 0 no amyloidosis was withheld on a rectal and abdominal fat tissue biopsy. Cardiac and ocular amyloidosis involvement were excluded. Genetic testing revealed a p.valmet (c.g>a) TTR mutation which led to the final diagnosis of TTR-FAP. By the time of the correct diagnosis, the patient was confined to a wheelchair, suffered from extreme muscle wasting and severe autonomic symptoms such as severe orthostatic hypotension, erectile dysfunction and intestinal motility disorders with profound cachexia. He also suffered from a secondary depression. No etiological treatment could be given, resulting in death due to severe autonomic failure in 0.
7 Case two concerns a male with a p.valala TTR mutation who deceased at the age of years. Symptoms started at the age of 0 years with distal leg neuropathic pain, cachexia, gastrointestinal dysmotility, erectile dysfunction and an axonal sensory more than motor neuropathy on EMG, raising suspicion of TTR-FAP. Prompt genetic testing confirmed the diagnosis later that year revealing a p.valala (c.t>c) TTR mutation. Family history was negative. Extensive cardiac evaluation was normal. Tafamidis was administered, and the patient was stable until orthotopic liver transplantation was performed eleven months later. Several bile duct strictures occurred during follow-up, resulting in multiple hospitalizations. Although liver transplantation was judged as successful, autonomic denervation progressed rapidly with severe orthostatic hypotension, cachexia and anorexia. Tafamidis was no longer accepted for reimbursement post-liver transplantation. Diflunisal was used without apparent benefit for months prior to his sudden death in 0. Case three is a -year-old male with a p.alaval TTR mutation. Symptom onset occurred in 0. Initial complaints at age included distal lower limb neuropathic pain, gastrointestinal dysmotility, erectile dysfunction, unexplained orthostatic syncope and rapid weight loss. A cardiac hypertrophy of unknown cause was observed two years earlier. EMG showed a mild length-dependent distal lower limb symmetric sensorimotor axonal neuropathy. Diagnosis of TTR-FAP was based on prompt genetic testing which showed the p.alaval (c.a>t) TTR mutation. His father and paternal uncle had deceased due to a cardiac disorder of unknown etiology. Genetic analysis of his asymptomatic paternal cousin showed the same mutation. Cardiac evaluation demonstrated left ventricular hypertrophy with on the ECG a QS-pattern in the anterior leads compatible with a pseudo-infarct appearance as the anterior segments were still contractile suggesting an infiltrative cardiomyopathy. Endomyocardial biopsy confirmed TTR-immunoreactive amyloid deposition. In June 0, a pacemaker was implanted following a severe syncope and documentation of a high grade AV-block. Tafamidis therapy started in 0 and is continued. The patient was initially stable, then had improved general and neurologic condition with weight gain and improved exercise capability. After years, orthostatic hypotension remains the main symptomatic problem. Cardiac function is stable. Combined heart and liver transplantation was considered but withheld as the clinical condition was generally improved. Case four concerns a -year-old male with a p.val0met TTR mutation. Symptom onset occurred at the age of 0 years with neuropathic pain and autonomic denervation signs in the feet, and intrinsic foot muscle atrophy and weakness, mild bilateral foot drop, sensory ataxia and lower limb areflexia. EMG showed a severe length-
8 dependent distal symmetric sensorimotor axonal neuropathy. Until genetic testing confirmed TTR-FAP diagnosis, the patient was diagnosed with chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. No evidence for cardiac impairment was withheld. Two of his children show the same mutation after DNA testing, one of which experiences a minimal sensory neuropathy. The patient is currently stable under treatment with tafamidis, symptomatic neuropathic pain treatment and physiotherapy. He refuses liver transplantation but is not eligible anyway according to current liver transplantation criteria. Discussion Diagnosis and differential diagnosis In the presence of a positive family history, sensorimotor and autonomic polyneuropathy should raise suspicion of TTR-FAP. In the absence of a positive family history, a length-dependent axonal polyneuropathy predominantly affecting pain and temperature sensation may indicate TTR-FAP, especially when combined with cardiac involvement, prominent autonomic denervation signs and cachexia [,]. There is an average of one to four years between the onset of first symptoms and diagnosis [,]. To confirm amyloidosis, amyloid deposition has to be demonstrated on biopsied tissues and DNA testing should be performed [,]. Another possible cause of amyloidosis is light-chain amyloidosis because of its high incidence in the elderly population. Assessment for serum and urinary free lambda and kappa light chains should be performed [,]. CIDP is the most frequent misdiagnosis. CSF protein content can be raised and nerve conduction velocity may be decreased in FAP, although axonal involvement is most common. The differential diagnosis includes the following disorders: idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy, lumbar spinal stenosis, diabetic polyneuropathy, chronic alcoholism, Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, motor neuron disease and paraneoplastic syndrome [,]. Therapy Targeted therapy Next to symptomatic therapy, targeted therapy should be started as soon as possible to prevent further production of amyloid deposits. Tafamidis meglumine Tafamidis stabilizes the mutant TTR tetramer by binding to the thyroxine binding sites, preventing its dissociation into monomers. For the treatment of TTR-FAP in adult patients with stage I symptomatic polyneuropathy, it is currently in clinical use in Europe in a single daily oral dose of 0 mg. Its efficacy has been
9 proven in both Val0Met and non-val0met TTR mutations. It is well tolerated and increases the quality of life. Its long-term efficacy is currently being assessed [,,,0]. Diflunisal Diflunisal, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, is currently not licensed for the treatment of stage I and stage II TTR-FAP. It prevents the dissociation, misfolding and misassembly of the mutated TTR tetramer. A single multicentre study of Berk et al. has shown that diflunisal inhibits polyneuropathy progression and increases quality of life in TTR-FAP patients with various stages of disease. Gastrointestinal, cardiac and renal side effects may make its use problematic. Further investigations concerning its safety and effect will have to determine its potential use [,]. Liver transplantation Liver transplantation stops the production of the mutated TTR in the liver but not in the choroid plexus and retinal epithelium. Ocular, leptomeningeal and cerebral manifestations such as TIA-like episodes, stroke, auralike episodes and epileptic seizures are thus not influenced by liver transplantation [,,,,]. Survival-rate post-liver transplantation is worse in non-val0met TTR-FAP: the five-year survival rate for non- Val0MetTTR-FAP is 0-0% compared to 0-% in Val0Met TTR-FAP [,,,]. It has been reported that a longer preoperative disease course of FAP is a negative prognostic factor for liver transplantation. It should therefore be performed rather early than late. However, recent guidelines suggest to continue tafamidis therapy as first-line therapy, and keep liver transplantation in reserve until clinical progression under tafamidis occurs [,,,]. Side effects of transplantation and reports of negative neurological evolution despite liver transplant, as in our second patient, were also considered when formulating this guideline []. Contraindications for liver transplantation include: active and uncontrolled cancer; age >0 years for males and >0 years for females; modified body mass index below 00 kg g/l m²; some non-val0met TTR mutations; cardiac insufficiency. However, a combined heart and liver transplantation may be considered in selected cases []. Some mutations are known to frequently cause cardiac or combined cardiac and neurological involvement. The mutation in our third patient is very rare and causes combined cardiac and neuropathic disease. One other published case had combined involvement as well []. In case of domino liver transplantation, where a patient with a severe liver disease receives a liver from a FAP patient, the domino liver transplantation acceptor is at risk of developing FAP. Except for the production of mutated TTR, a normal liver function is required to qualify for domino transplantation. In half of the patients,
10 amyloid deposits were observed in labial salivary glands five years after domino liver transplantation. Nonetheless, it is still done because of the shortage of donor livers []. Therapies in development New therapies that are currently being developed include posttranscriptional gene silencing (using small interfering RNA (sirna) or antisense oligonucleotides), immunotherapy using antibodies and a combination of doxycycline-tauroursodeoxycholic acid [,]. The use of sirna was shown to interfere with gene expression through RNA interference. Substantial and prolonged down-regulation of TTR protein level was observed following treatment with the sirna ALN-TTR0 and ALN-TTR0. The phase APOLLO study with Patisiran (ALN-TTR0) that has recently been completed shows promising results concerning polyneuropathy symptoms, quality of life, exploratory cardiac measures, safety and tolerability (D. Adams, personal communication). Another phase study involving ISIS 0, an antisense oligonucleotide, is in its final stage []. Postponing liver transplantation until results of these studies are known should be considered []. Studies on clinical efficacy and safety of long-term TTR knockdown have not been performed yet. The decrease in retinol-binding protein levels due to TTR knockdown is a possible adverse effect. An advantage compared to liver transplantation is that the sirna ALN-TTR0 knocks down both the mutant and wild-type TTR []. Current treatment guidelines Tafamidis is used as first-line therapy in stage I FAP. Eligibility for liver transplantation should be checked in case of progression of the disease. Off-label use of diflunisal or inclusion in clinical trials should be considered in stage II FAP. Figure shows a treatment algorithm for TTR-FAP, developed by the European Network for TTR-FAP (ATTReuNET) []. Follow-up and prognosis Neurological, cardiac, renal and ocular examination should be done periodically in all TTR-FAP mutation carriers, whether symptomatic or asymptomatic. Neurological examination consists of sensory, motor and reflex evaluation, EMG, assessment of postural blood pressure and heart rate variability, and the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome. Cardiac screening involves performing an electrocardiogram and echocardiogram, and measurement of BNP or NT pro-bnp. Detection of clinical manifestations in TTR-FAP carriers confirms the diagnosis and should result in therapy (Fig. ). Symptomatic treatment and psychological support should also take place [,].
11 Death resulting from progressive cardiac amyloidosis has also been reported post-liver transplantation. This is most probably due to cardiac wild-type TTR deposition. Thus, when considering liver transplantation, assessment of cardiac function and post-transplantation follow-up is of utmost importance. Following liver transplantation, patients with an early onset, Val0Met mutation and shortened duration of the disease have a better prognosis than patients with late onset, non-val0met mutation and prolonged duration of the disease []. Due to the local mutated TTR synthesis in the choroid plexus and retinal epithelium, the ocular and nervous system may deteriorate despite liver transplantation, resulting in, among others, chronic open-angle glaucoma and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. A significant increase of atrial fibrillation, a predictor of cerebrovascular events such as transient ischemic attacks, ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage was observed in Val0Met FAP patients post-liver transplantation. Increased overall survival postliver transplantation enables TTR-FAP patients to develop intracerebral amyloid deposits which increases the risk of brain hemorrhage. Immunosuppressive treatment following transplantation may render the patient susceptible to infections [,,,,,]. Genetic counselling There is an urgent need for genetic counselling for patients and at-risk relatives []. Genetic counselling brings along several stressors for the patient and his or her relatives []. As mentioned, making the diagnosis early may be of pivotal importance in patient outcome. However, genetic testing for TTR-FAP before the age of should not be done since its practice holds no medical benefit. This may change in the future depending on the acquisition of new insights or therapies. Prenatal genetic testing and pre-implantation genetic diagnosis can be considered in some families [,]. In case of a positive genetic test, the gene carrier should not receive presymptomatic treatment since at this time it is not an accepted indication. The gene carrier should, however, be monitored regularly. Suspicion of symptom-onset matching with TTR-FAP should result in treatment []. Conclusion FAP is a heterogeneous disease with a variety of possible symptoms, depending on which tissue is affected. A multiplicity of mutations has been described, each with a diverse expression. It is a rare disorder with major influence on the daily life of patients. When possible, patients that cannot undergo liver transplantation or get tafamidis should be enrolled in clinical trials to test efficacy and safety of new treatment modalities. In an early stage, liver transplantation is a valid option when symptoms are progressive despite tafamidis therapy, although 0
12 it does not eliminate the production of wild-type TTR and TTR production from retinal cells and the choroid plexus. Liver transplantation and the associated immunosuppressive treatment itself holds several risks. Therefore, additional prospective clinical research is necessary to assess the course and outcome of these non- Val0Met TTR mutations, especially in non-endemic regions.
13 Table Course and characteristics of early- and late-onset TTR-FAP. Early-onset Val0Met TTR-FAP Late-onset Val0Met TTR-FAP Age of onset <0 years >0 years Country Portugal, Japan, Brazil Sweden, France, UK, Italy, Japan Positive family history % % Initial clinical presentation Peripheral neuropathy % % Autonomic neuropathy % 0% Mean delay for walking aid >. years years Cardiac Progressive conduction disorders Restrictive cardiomyopathy Heart failure Median survival years. years Causes of death Cachexia, infections Heart failure Sudden death Cachexia or secondary infection TTR-FAP transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Modified from [].
14 Table Summary of cases of TTR-FAP. Case one Case two Case three Case four Sex Male Male Male Male Year of birth TTR mutation p.valmet p.valala p.alaval p.val0met Symptom onset Symptoms First diagnosis Targeted treatment Sensorimotor and autonomic polyneuropathy Neuropathic pain Muscle wasting Impotence Hypotension Intestinal motility disturbance Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy None Sensory more than motor polyneuropathy Neuropathic pain Cachexia Impotence Hypotension Intestinal motility disturbance TTR-FAP Tafamidis Liver transplantation in 0 Diflunisal Symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy in lower limbs Neuropathic pain Impotence Weight loss Hypotension Intestinal motility disturbance TTR-FAP with cardiac amyloidosis Tafamidis Outcome Deceased in 0 Deceased in 0 Doing well on tafamidis therapy Peculiar findings Negative sural Negative evolution Mild improvement nerve, rectal and after liver on tafamidis adipose biopsy for transplantation amyloidosis TTR-FAP transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Sensorimotor and autonomic polyneuropathy Neuropathic pain Chronic idiopathic axonal neuropathy Tafamidis Stable on tafamidis therapy None
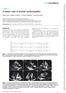
15 Fig. Treatment algorithm for TTR-FAP
16 Legend Fig. Treatment algorithm for TTR-FAP Stage I: walking unaided outside. Stage II: walking with aid. Protocol for clinical trials for antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNA, combination doxycycline-tauroursodeoxycholic acid; or diflunisal offlabel. Modified from [].
17 Compliance with Ethical Standards Funding: The authors declare that no funding was involved. Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
18 References. Plante-Bordeneuve V, Said G (0) Familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Lancet Neurol. doi: 0.0/S-()0-0. Rowczenio DM, Noor I, Gillmore JD, Lachmann HJ, Whelan C, Hawkins PN, et al (0) Online registry for mutations in hereditary amyloidosis including nomenclature recommendations. Hum Mutat. doi: 0.00/humu.. Adams D (0) Recent advances in the treatment of familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. doi: 0./0. Ruberg FL, Berk JL (0) Transthyretin (TTR) Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation. doi: 0./CIRCULATIONAHA..0. Ikeda S, Nakazato M, Ando Y, Sobue G (00) Familial transthyretin-type amyloid polyneuropathy in Japan: clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Neurology. Adams D, Suhr OB, Hund E, Obici L, Tournev I, Campistol JM, et al (0) First European consensus for diagnosis, management, and treatment of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol. doi: 0.0/WCO Chanoine JP, Alex S, Fang SL, Stone S, Leonard JL, Korhle J, et al () Role of transthyretin in the transport of thyroxine from the blood to the choroid plexus, the cerebrospinal fluid, and the brain. Endocrinology.. Schmidt HH-J, Barroso F, Gonzalez-Duarte A, Conceicao I, Obici L, Keohane D, et al (0) Management of asymptomatic gene carriers of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve. doi: 0.00/mus.0. Kollmer J, Sahm F, Hegenbart U, Purrucker JC, Kimmich C, Schonland SO, et al (0) Sural nerve injury in familial amyloid polyneuropathy: MR neurography vs clinicopathologic tools. Neurology. doi: 0./WNL Bulawa CE, Connelly S, DeVit M, Wang L, Weigel C, Fleming JA, et al (0) Tafamidis, a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci. doi: 0.0/pnas.000. Berk JL, Suhr OB, Obici L, Sekijima Y, Zeldenrust SR, Yamashita T, et al (0) Repurposing Diflunisal for Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. doi: 0.00/jama.0.
19 Cavallaro T, Klunk W (0) PiB-PET detects transthyretin-related cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology. doi: 0./WNL Sekijima Y, Yazaki M, Oguchi K, Ezawa N, Yoshinaga T, Yamada M (0) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in posttransplant patients with hereditary ATTR amyloidosis. Neurology. doi: Liepnieks JJ, Zhang LQ, Benson MD (00) Progression of transthyretin amyloid neuropathy after liver transplantation. Neurology. doi: 0./WNL.0b0eead. Franz C, Hoffmann K, Hinz U, Singer R, Hund E, Gotthardt DN, et al (0) Modified body mass index and time interval between diagnosis and operation affect survival after liver transplantation for hereditary amyloidosis: a single-center analysis. Clin Transplant. doi: 0./ctr.. Wange N, Anan I, Ericzon B-G, Pennlert J, Pilebro B, Suhr OB, et al (0) Atrial fibrillation and central nervous complications in liver transplanted hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis patients. Transplantation. doi: 0.0/TP Eriksson M, Buttner J, Todorov T, Yumlu S, Schonland S, Hegenbart U, et al (00) Prevalence of germline mutations in the TTR gene in a consecutive series of surgical pathology specimens with ATTR amyloid. Am J Surg Pathol. doi: 0./jmoldx Coelho T, Adams D, Silva A, Lozeron P, Hawkins PN, Mant T, et al (0) Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. doi: 0.0/NEJMoa00. Obici L, Kuks JB, Buades J, Adams D, Suhr OB, Coelho T, et al (0) Recommendations for presymptomatic genetic testing and management of individuals at risk for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Curr Opin Neurol. doi: 0.0/WCO
20 Table. Course and characteristics of early- and late-onset TTR-FAP. Table Course and characteristics of early- and late-onset TTR-FAP. Early-onset Val0Met TTR-FAP Late-onset Val0Met TTR-FAP Age of onset <0 years >0 years Country Portugal, Japan, Brazil Sweden, France, UK, Italy, Japan Positive family history % % Initial clinical presentation Peripheral neuropathy % % Autonomic neuropathy % 0% Mean delay for walking aid >. years years Cardiac Progressive conduction disorders Restrictive cardiomyopathy Heart failure Median survival years. years Causes of death Cachexia, infections Heart failure Sudden death Cachexia or secondary infection TTR-FAP transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Modified from [].
21 Table. Summary of cases of TTR-FAP. Table Summary of cases of TTR-FAP. Case one Case two Case three Case four Sex Male Male Male Male Year of birth TTR mutation p.valmet p.valala p.alaval p.val0met Symptom onset Symptoms First diagnosis Targeted treatment Sensorimotor and autonomic polyneuropathy Neuropathic pain Muscle wasting Impotence Hypotension Intestinal motility disturbance Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy None Sensory more than motor polyneuropathy Neuropathic pain Cachexia Impotence Hypotension Intestinal motility disturbance TTR-FAP Tafamidis Liver transplantation in 0 Diflunisal Symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy in lower limbs Neuropathic pain Impotence Weight loss Hypotension Intestinal motility disturbance TTR-FAP with cardiac amyloidosis Tafamidis Sensorimotor and autonomic polyneuropathy Neuropathic pain Chronic idiopathic axonal neuropathy Tafamidis Outcome Deceased in 0 Deceased in 0 Doing well on tafamidis therapy Peculiar findings Negative sural Negative evolution Mild improvement nerve, rectal and after liver on tafamidis adipose biopsy for transplantation amyloidosis Stable on tafamidis therapy None TTR-FAP transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy.
22 Fig. Treatment algorithm for TTR-FAP Click here to download Figure Fig.jpg
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: patisiran_onpattro 11/2018 n/a 5/2019 2/2019 Description of Procedure or Service is a double-stranded small
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: patisiran_onpattro 11/2018 n/a 5/2019 2/2019 Description of Procedure or Service is a double-stranded small
Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Polyneuropathy An Overview. Identifying the link can lead to a crucial diagnosis
 Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Polyneuropathy An Overview Identifying the link can lead to a crucial diagnosis Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Polyneuropathy Information about mechanism of disease,
Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Polyneuropathy An Overview Identifying the link can lead to a crucial diagnosis Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Polyneuropathy Information about mechanism of disease,
Neuropathy. Nerves before and after TTR. Márcia Waddington Cruz. CEPARM HUCFF-UFRJ.
 Neuropathy. Nerves before and after TTR. Márcia Waddington Cruz. CEPARM HUCFF-UFRJ. Amyloidosis Amyloid deposit. Precursor proteins. Fibrilar ptn. Lesion to tissues. Mechanism? 2 A TTR. SSA or Wild Type
Neuropathy. Nerves before and after TTR. Márcia Waddington Cruz. CEPARM HUCFF-UFRJ. Amyloidosis Amyloid deposit. Precursor proteins. Fibrilar ptn. Lesion to tissues. Mechanism? 2 A TTR. SSA or Wild Type
Safety and Efficacy of Inotersen in Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Polyneuropathy (NEURO-TTR) Annabel K.
 Safety and Efficacy of Inotersen in Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Polyneuropathy (NEURO-TTR) Annabel K. Wang, MD University of California, Irvine ANA 2017 October 17, 2017 San
Safety and Efficacy of Inotersen in Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Polyneuropathy (NEURO-TTR) Annabel K. Wang, MD University of California, Irvine ANA 2017 October 17, 2017 San
Subject: Patisiran (Onpattro )
 09-J3000-16 Original Effective Date: 12/15/18 Reviewed: 11/14/2018 Revised: 01/01/19 Subject: Patisiran (Onpattro ) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION, EXPLANATION OF
09-J3000-16 Original Effective Date: 12/15/18 Reviewed: 11/14/2018 Revised: 01/01/19 Subject: Patisiran (Onpattro ) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION, EXPLANATION OF
TTR-FAP: Diagnosis and treatment Zürich June 19,2014. Ole B Suhr Umeå University and University Hospital Department of Medicine Umeå Sweden
 TTR-FAP: Diagnosis and treatment Zürich June 19,2014 Ole B Suhr Umeå University and University Hospital Department of Medicine Umeå Sweden Diagnosis of ATTR amyloidosis Clinical symptoms of ATTR- amyloidosis
TTR-FAP: Diagnosis and treatment Zürich June 19,2014 Ole B Suhr Umeå University and University Hospital Department of Medicine Umeå Sweden Diagnosis of ATTR amyloidosis Clinical symptoms of ATTR- amyloidosis
Education Brochure. Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis A closer look at an inherited condition
 Education Brochure Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis A closer look at an inherited condition What is hereditary ATTR (hattr) amyloidosis? hattr amyloidosis is caused by a gene change (mutation) that affects
Education Brochure Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis A closer look at an inherited condition What is hereditary ATTR (hattr) amyloidosis? hattr amyloidosis is caused by a gene change (mutation) that affects
Amyloid Transthyretin (ATTR) Amyloidosis AN OVERVIEW
 Amyloid Transthyretin (ATTR) Amyloidosis AN OVERVIEW AMYLOID TRANSTHYRETIN (ATTR) AMYLOIDOSIS ATTR amyloidosis is a rare, progressive, and fatal disease that manifests clinically with motor and sensory
Amyloid Transthyretin (ATTR) Amyloidosis AN OVERVIEW AMYLOID TRANSTHYRETIN (ATTR) AMYLOIDOSIS ATTR amyloidosis is a rare, progressive, and fatal disease that manifests clinically with motor and sensory
Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Cardiomyopathy An Overview. Identifying the link can lead to a crucial diagnosis
 Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Cardiomyopathy An Overview Identifying the link can lead to a crucial diagnosis Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Cardiomyopathy Information about mechanism of disease,
Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Cardiomyopathy An Overview Identifying the link can lead to a crucial diagnosis Hereditary ATTR (hattr) Amyloidosis: Cardiomyopathy Information about mechanism of disease,
Summary of plenary sessions on October 31, 2015
 4 th ATTR/Familial Amyloidosis Support Meeting October 31 to November 1, 2015 Hilton Chicago O Hare Airport hotel Summary of plenary sessions on October 31, 2015 1 Contents Welcome... 3 Why are we here?
4 th ATTR/Familial Amyloidosis Support Meeting October 31 to November 1, 2015 Hilton Chicago O Hare Airport hotel Summary of plenary sessions on October 31, 2015 1 Contents Welcome... 3 Why are we here?
reversing familial amyloid polyneuropathy naturally the raw vegan plant based detoxification regeneration workbook for healing patients volume 2
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING FAMILIAL AMYLOID POLYNEUROPATHY NATURALLY THE RAW VEGAN PLANT BASED DETOXIFICATION REGENERATION WORKBOOK FOR HEALING PATIENTS VOLUME 2 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 healing
DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING FAMILIAL AMYLOID POLYNEUROPATHY NATURALLY THE RAW VEGAN PLANT BASED DETOXIFICATION REGENERATION WORKBOOK FOR HEALING PATIENTS VOLUME 2 PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 healing
Progress in the Treatment of Cardiac Amyloidosis
 Progress in the Treatment of Cardiac Amyloidosis Jignesh Patel MD PhD FACC FRCP Director, Cardiac Amyloid Program Medical Director, Heart Transplant Program Clinical Professor Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute,
Progress in the Treatment of Cardiac Amyloidosis Jignesh Patel MD PhD FACC FRCP Director, Cardiac Amyloid Program Medical Director, Heart Transplant Program Clinical Professor Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute,
: A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis
 : A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis 02 November 2015 1 Background and Rationale Cardiac amyloidosis is caused by extracellular
: A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis 02 November 2015 1 Background and Rationale Cardiac amyloidosis is caused by extracellular
Diagnosis of Amyloidosis. Maria M. Picken MD, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Chicago
 Diagnosis of Amyloidosis Maria M. Picken MD, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Chicago mpicken@lumc.edu 1 Outline Diagnosis of amyloidosis Fat pad Other 2 Amyloidoses protein folding disorders protein
Diagnosis of Amyloidosis Maria M. Picken MD, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Chicago mpicken@lumc.edu 1 Outline Diagnosis of amyloidosis Fat pad Other 2 Amyloidoses protein folding disorders protein
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF INOTERSEN IN PATIENTS WITH HEREDITARY TRANSTHYRETIN AMYLOIDOSIS POLYNEUROPATHY (hattr-pn) Teresa Coelho, MD
 SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF INOTERSEN IN PATIENTS WITH HEREDITARY TRANSTHYRETIN AMYLOIDOSIS POLYNEUROPATHY (hattr-pn) Teresa Coelho, MD Centro Hospitalar do Porto Porto, Portugal Disclosures Hospital Santo
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF INOTERSEN IN PATIENTS WITH HEREDITARY TRANSTHYRETIN AMYLOIDOSIS POLYNEUROPATHY (hattr-pn) Teresa Coelho, MD Centro Hospitalar do Porto Porto, Portugal Disclosures Hospital Santo
Amyloidoses are a heterogeneous group of disorders
 REPORT Hereditary ATTR Amyloidosis: Burden of Illness and Diagnostic Challenges Morie A. Gertz, MD, MACP Amyloidoses are a heterogeneous group of disorders with a variety of clinical presentations characterized
REPORT Hereditary ATTR Amyloidosis: Burden of Illness and Diagnostic Challenges Morie A. Gertz, MD, MACP Amyloidoses are a heterogeneous group of disorders with a variety of clinical presentations characterized
YES NO UNKNOWN. Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard Secondary Findings in Adults ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE SIGNIFICANCE/BURDEN OF DISEASE NEXT STEPS
 Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: TTR DISORDER: Hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis HGNC ID: 12405 OMIM ID: 105210 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as
Stage I: Rule-Out Dashboard GENE/GENE PANEL: TTR DISORDER: Hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis HGNC ID: 12405 OMIM ID: 105210 ACTIONABILITY PENETRANCE 1. Is there a qualifying resource, such as
Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis Talking to your healthcare professional about a hereditary condition
 Healthcare Professional Discussion Guide Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis Talking to your healthcare professional about a hereditary condition This guide will give you some tips and strategies to help you start
Healthcare Professional Discussion Guide Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis Talking to your healthcare professional about a hereditary condition This guide will give you some tips and strategies to help you start
Late-onset Transthyretin (TTR)-familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (FAP) with a Long Disease Duration from Non-endemic Areas in Japan
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1457-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Late-onset Transthyretin (TTR)-familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (FAP) with a Long Disease Duration from Non-endemic Areas in Japan Zenshi
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1457-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Late-onset Transthyretin (TTR)-familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (FAP) with a Long Disease Duration from Non-endemic Areas in Japan Zenshi
A Guide to Transthyretin Amyloidosis
 A Guide to Transthyretin Amyloidosis Authored by Teresa Coelho, Bo-Goran Ericzon, Rodney Falk, Donna Grogan, Shu-ichi Ikeda, Mathew Maurer, Violaine Plante-Bordeneuve, Ole Suhr, Pedro Trigo 2016 Edition
A Guide to Transthyretin Amyloidosis Authored by Teresa Coelho, Bo-Goran Ericzon, Rodney Falk, Donna Grogan, Shu-ichi Ikeda, Mathew Maurer, Violaine Plante-Bordeneuve, Ole Suhr, Pedro Trigo 2016 Edition
A Novel Variant Mutation of Transthyretin Ile73Val-Related Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy in Taiwanese
 87 A Novel Variant Mutation of Transthyretin Ile73Val-Related Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy in Taiwanese Ming-Feng Liao, Hong-Shiu Chang Abstract- Purpose: Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) is an
87 A Novel Variant Mutation of Transthyretin Ile73Val-Related Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy in Taiwanese Ming-Feng Liao, Hong-Shiu Chang Abstract- Purpose: Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) is an
Diagnosis and management of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy in Japan: red-flag symptom clusters and treatment algorithm
 Sekijima et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018) 13:6 DOI 10.1186/s13023-017-0726-x REVIEW Diagnosis and management of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy in Japan: red-flag symptom clusters
Sekijima et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018) 13:6 DOI 10.1186/s13023-017-0726-x REVIEW Diagnosis and management of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy in Japan: red-flag symptom clusters
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017
 A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
November 16-18, 2017 Hotel Monteleone New Orleans, LA. Provided by
 November 16-18, 2017 Hotel Monteleone New Orleans, LA Provided by Diabetic Neuropathy: A Global and Growing Problem John D. England, MD Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine
November 16-18, 2017 Hotel Monteleone New Orleans, LA Provided by Diabetic Neuropathy: A Global and Growing Problem John D. England, MD Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy
 Familial amyloid polyneuropathy Violaine Planté-Bordeneuve, Gerard Said Lancet Neurol 2011; 10: 1086 97 Department of Neurology, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Henri-Mondor, Créteil, France (V Planté-Bordeneuve
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy Violaine Planté-Bordeneuve, Gerard Said Lancet Neurol 2011; 10: 1086 97 Department of Neurology, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Henri-Mondor, Créteil, France (V Planté-Bordeneuve
The landscape of ATTR amyloidosis treatment
 The landscape of ATTR amyloidosis treatment Teresa Coelho, M.D. Andrade s Center and Neurophysiology Department Hospital Santo António, Centro Hospitalar do Porto Portugal Disclosures Hospital Santo António
The landscape of ATTR amyloidosis treatment Teresa Coelho, M.D. Andrade s Center and Neurophysiology Department Hospital Santo António, Centro Hospitalar do Porto Portugal Disclosures Hospital Santo António
Update in Nuclear Imaging of Amyloidosis and Sarcoidosis
 Update in Nuclear Imaging of Amyloidosis and Sarcoidosis Balaji Tamarappoo MD, PhD, Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute and Biomedical Imaging Research Institute Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA, USA.
Update in Nuclear Imaging of Amyloidosis and Sarcoidosis Balaji Tamarappoo MD, PhD, Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute and Biomedical Imaging Research Institute Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA, USA.
FAMILIAL AMYLOID POLYNEUROPATHY (TTR-FAP): Genetics and Treatment
 FAMILIAL AMYLOID POLYNEUROPATHY (TTR-FAP): Genetics and Treatment Michelle Mezei BSc (Pharm), MDCM, FRCPC Neuromuscular Diseases Unit, VGH Division of Neurology, UBC 1 Learning Objectives To become familiar
FAMILIAL AMYLOID POLYNEUROPATHY (TTR-FAP): Genetics and Treatment Michelle Mezei BSc (Pharm), MDCM, FRCPC Neuromuscular Diseases Unit, VGH Division of Neurology, UBC 1 Learning Objectives To become familiar
Frequencies and geographic distributions of genetic mutations in transthyretinand non-transthyretin-related familial amyloidosis
 Clin Genet 2015: 88: 396 400 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report Frequencies and geographic distributions of genetic mutations in transthyretinand non-transthyretin-related familial
Clin Genet 2015: 88: 396 400 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report Frequencies and geographic distributions of genetic mutations in transthyretinand non-transthyretin-related familial
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat. Dr Hadi Manji
 CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
Guideline of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis for clinicians
 Ando et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2013, 8:31 REVIEW Guideline of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis for clinicians Open Access Yukio Ando 1,13*, Teresa Coelho 2, John L Berk 3, Márcia
Ando et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2013, 8:31 REVIEW Guideline of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis for clinicians Open Access Yukio Ando 1,13*, Teresa Coelho 2, John L Berk 3, Márcia
New approaches in amyloidosis. Philip Hawkins National Amyloidosis Centre UCL & Royal Free Hospital, London
 New approaches in amyloidosis Philip Hawkins National Amyloidosis Centre UCL & Royal Free Hospital, London Systemic Amyloidosis Fatal protein misfolding/aggregation disease caused by accumulation of fibrillar
New approaches in amyloidosis Philip Hawkins National Amyloidosis Centre UCL & Royal Free Hospital, London Systemic Amyloidosis Fatal protein misfolding/aggregation disease caused by accumulation of fibrillar
Clinical history. 73 yo man with chest pain Systemic hypertension and WG Stress EKG N Stress echocardiogram: Cardiac catheterization: no CAD
 CASE 8 Clinical history 73 yo man with chest pain Systemic hypertension and WG Stress EKG N Stress echocardiogram: Concentric hypertrophy Hypokinesis of LV-Inf Cardiac catheterization: no CAD Technique
CASE 8 Clinical history 73 yo man with chest pain Systemic hypertension and WG Stress EKG N Stress echocardiogram: Concentric hypertrophy Hypokinesis of LV-Inf Cardiac catheterization: no CAD Technique
Amyloidosis and Waldenström s Macroglobulinemia
 Amyloidosis and Waldenström s Macroglobulinemia Morie A. Gertz, Giampaolo Merlini, and Steven P. Treon Primary systemic amyloidosis is an immunoglobulin light chain disorder that is 1/5th as common as
Amyloidosis and Waldenström s Macroglobulinemia Morie A. Gertz, Giampaolo Merlini, and Steven P. Treon Primary systemic amyloidosis is an immunoglobulin light chain disorder that is 1/5th as common as
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
A faint in the emergency department (due to primary systemic amyloidosis
 104 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY NEUROLOGICAL RARITIES A faint in the emergency department (due to primary systemic amyloidosis Michele T. M. Hu*, Carolyn M. Gabriel*, Helen J. Lachmann, Rosalind King, Philip N.
104 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY NEUROLOGICAL RARITIES A faint in the emergency department (due to primary systemic amyloidosis Michele T. M. Hu*, Carolyn M. Gabriel*, Helen J. Lachmann, Rosalind King, Philip N.
In vivo detection of nerve injury in familial amyloid polyneuropathy by magnetic resonance neurography
 doi:10.1093/brain/awu344 BRAIN 2015: 138; 549 562 549 In vivo detection of nerve injury in familial amyloid polyneuropathy by magnetic resonance neurography Jennifer Kollmer, 1,2 Ernst Hund, 2,3 Benjamin
doi:10.1093/brain/awu344 BRAIN 2015: 138; 549 562 549 In vivo detection of nerve injury in familial amyloid polyneuropathy by magnetic resonance neurography Jennifer Kollmer, 1,2 Ernst Hund, 2,3 Benjamin
Peripheral Nerve Amyloidosis in Sural Nerve Biopsies. A Clinicopathologic Analysis of 13 Cases
 Peripheral Nerve Amyloidosis in Sural Nerve Biopsies A Clinicopathologic Analysis of 13 Cases Bijal Rajani, MB, BS; Vakesh Rajani, MB, BS; Richard A. Prayson, MD Objective. Amyloidosis is a well-recognized
Peripheral Nerve Amyloidosis in Sural Nerve Biopsies A Clinicopathologic Analysis of 13 Cases Bijal Rajani, MB, BS; Vakesh Rajani, MB, BS; Richard A. Prayson, MD Objective. Amyloidosis is a well-recognized
CARDIAC AMYLOIDOSIS IMAGING ERIC MARTIN MD
 CARDIAC AMYLOIDOSIS IMAGING ERIC MARTIN MD DISCLOSURES Bayer Dalcor Pharma UK LTD Harvard Clinical Research Institute Heartflow Inc. NIH Vascular Dynamics Employee-Iowa Heart Center/Mercy-Des Moines BACKGROUND
CARDIAC AMYLOIDOSIS IMAGING ERIC MARTIN MD DISCLOSURES Bayer Dalcor Pharma UK LTD Harvard Clinical Research Institute Heartflow Inc. NIH Vascular Dynamics Employee-Iowa Heart Center/Mercy-Des Moines BACKGROUND
Xiaoping (Amy) Zhang, Varun Goel, Husain Attarwala, and Gabriel Robbie. Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, USA
 Patisiran Pharmacokinetics (PK), Pharmacodynamics (PD), and Exposure-Response (E-R) Relationship in Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated (hattr) Amyloidosis Xiaoping (Amy) Zhang, Varun Goel,
Patisiran Pharmacokinetics (PK), Pharmacodynamics (PD), and Exposure-Response (E-R) Relationship in Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated (hattr) Amyloidosis Xiaoping (Amy) Zhang, Varun Goel,
Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC
 Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC First, a bit of background Classic CIDP--TREATABLE MADSAM/Asymmetric Neuropathy Chronic Length Dependent Neuropathy-
Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC Jonathan Katz, MD CPMC First, a bit of background Classic CIDP--TREATABLE MADSAM/Asymmetric Neuropathy Chronic Length Dependent Neuropathy-
Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy. Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction
 Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy Chris Edwards, MD Ochsner Neurology, Main Campus Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction A very common complaint in the clinic Presentation is variable Multiple
Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy Chris Edwards, MD Ochsner Neurology, Main Campus Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction A very common complaint in the clinic Presentation is variable Multiple
6/6/2017. Uncommon Etiologies of Heart Failure: Cardiac Amyloidosis. Objectives. Case Presentation
 Uncommon Etiologies of Heart Failure: Cardiac Amyloidosis Maria Fe White, MSN, FNP/ACNP-BC, FHFSA, CHFN Lead Nurse Practitioner Advance Heart Programs Comprehensive Transplant Center Objectives Describe
Uncommon Etiologies of Heart Failure: Cardiac Amyloidosis Maria Fe White, MSN, FNP/ACNP-BC, FHFSA, CHFN Lead Nurse Practitioner Advance Heart Programs Comprehensive Transplant Center Objectives Describe
Evaluation of Myocardial Changes in Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy after Liver Transplantation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Myocardial Changes in Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy after Liver Transplantation Sadahisa Okamoto 1, Taro Yamashita 1, Yukio Ando 2, Mitsuharu Ueda 2, Yohei Misumi 1, Konen
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Myocardial Changes in Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy after Liver Transplantation Sadahisa Okamoto 1, Taro Yamashita 1, Yukio Ando 2, Mitsuharu Ueda 2, Yohei Misumi 1, Konen
Clinical Profile FOR. Indication. Important Safety Information
 Clinical Profile FOR The first and only FDA-approved RNAi treatment for the polyneuropathy of hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis in adults. 1 Indication ONPATTRO (patisiran) is indicated for
Clinical Profile FOR The first and only FDA-approved RNAi treatment for the polyneuropathy of hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis in adults. 1 Indication ONPATTRO (patisiran) is indicated for
Diagnostic approach to cardiac amyloidosis: A case report
 Diagnostic approach to cardiac amyloidosis: A case report Georgia Vogiatzi, MD, MSc, PhD 1 st Cardiology Department, Hippokration Hospital, Athens Medical School Disclosures I have no relevant relationships
Diagnostic approach to cardiac amyloidosis: A case report Georgia Vogiatzi, MD, MSc, PhD 1 st Cardiology Department, Hippokration Hospital, Athens Medical School Disclosures I have no relevant relationships
Amyloidosis: What to do and how to diagnose: An Update 2017
 Amyloidosis: What to do and how to diagnose: An Update 2017 Jonathan L. Kaufman, MD Associate Professor Hematology & Oncology Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Amyloidosis Protein Conformation/Deposition
Amyloidosis: What to do and how to diagnose: An Update 2017 Jonathan L. Kaufman, MD Associate Professor Hematology & Oncology Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Amyloidosis Protein Conformation/Deposition
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression. Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre
 Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Amyloid Polyneuropathy and Myocardial Amyloidosis 10 Years after Domino Liver Transplantation from a Patient with a Transthyretin Ser50Arg Mutation
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8434-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Amyloid Polyneuropathy and Myocardial Amyloidosis 10 Years after Domino Liver Transplantation from a
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8434-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Amyloid Polyneuropathy and Myocardial Amyloidosis 10 Years after Domino Liver Transplantation from a
A Problem with Cardiac Amyloidosis. Defining Amyloidosis. Typical Amyloid Heart. Definition of a double-blind study:
 A disease caused by the deposition of a proteinaceous material, derived from the misfolded breakdown products of a normal or abnormal protein. Typical Amyloid Heart Defining Amyloidosis TYPEOF AMYLOID
A disease caused by the deposition of a proteinaceous material, derived from the misfolded breakdown products of a normal or abnormal protein. Typical Amyloid Heart Defining Amyloidosis TYPEOF AMYLOID
Introduction and aims of the study
 Introduction and aims of the study 1 Chapter 1 Motor neuron diseases include the most incapacitating and life-threatening illnesses but also rather benign disorders with only mild symptoms and slow progression.
Introduction and aims of the study 1 Chapter 1 Motor neuron diseases include the most incapacitating and life-threatening illnesses but also rather benign disorders with only mild symptoms and slow progression.
A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
 Joturnal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 88-93 A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease A P BROOKS* AND A E H EMERY From the University Department of Human Genetics, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh
Joturnal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 88-93 A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease A P BROOKS* AND A E H EMERY From the University Department of Human Genetics, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh
A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies
 Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Varun Goel 1, Nathalie H Gosselin 2, Claudia Jomphe 2, Husain Attarwala 1, Xiaoping (Amy) Zhang 1, JF Marier 2, Gabriel Robbie 1
 Population Pharmacokinetic (PK) / Pharmacodynamic (PD) Model of Serum Transthyretin (TTR) Following Patisiran Administration in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Hereditary TTR-Mediated (hattr) Amyloidosis
Population Pharmacokinetic (PK) / Pharmacodynamic (PD) Model of Serum Transthyretin (TTR) Following Patisiran Administration in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Hereditary TTR-Mediated (hattr) Amyloidosis
Family Tree. Family Health Tree Map your family s history of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis
 Family Tree Family Health Tree Map your family s history of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis Chart your family s health history This chart can help you map your family s health history and determine who may
Family Tree Family Health Tree Map your family s history of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis Chart your family s health history This chart can help you map your family s health history and determine who may
ESC 2018 Tafamidis Analyst Briefing. August 27, 2018
 ESC 2018 Tafamidis Analyst Briefing August 27, 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements This presentation includes forward-looking statements about, among other things, a potential indication for Tafamidis for
ESC 2018 Tafamidis Analyst Briefing August 27, 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements This presentation includes forward-looking statements about, among other things, a potential indication for Tafamidis for
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
A celebration of 10 years of THAOS
 Newsletter December 17 Transthyretin Amyloidosis Outcomes Survey Spotlight Fabio Barroso Page 2 A celebration of 10 years of THAOS This October saw the third THAOS Investigator meeting, along with the
Newsletter December 17 Transthyretin Amyloidosis Outcomes Survey Spotlight Fabio Barroso Page 2 A celebration of 10 years of THAOS This October saw the third THAOS Investigator meeting, along with the
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Reflecting on THAOS in 2016, and looking forward to 2017
 Newsletter December 2016 Transthyretin Amyloidosis Outcomes Survey Scientific Board Meeting Summary Page 2 Spotlight Dr Arnt Kristen Page 3 THAOS today Page 4 Recent research from THAOS Page 5 ICON Project
Newsletter December 2016 Transthyretin Amyloidosis Outcomes Survey Scientific Board Meeting Summary Page 2 Spotlight Dr Arnt Kristen Page 3 THAOS today Page 4 Recent research from THAOS Page 5 ICON Project
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen First European consensus for diagnosis, management, and treatment of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy Adams, David; Suhr, Ole B.; Hund, Ernst; Obici, Laura; Tournev,
University of Groningen First European consensus for diagnosis, management, and treatment of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy Adams, David; Suhr, Ole B.; Hund, Ernst; Obici, Laura; Tournev,
Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic
 HISTORY OF PF-NCS Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic diagnosis remains unclear. EMG/NCV
HISTORY OF PF-NCS Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic diagnosis remains unclear. EMG/NCV
Primary Amyloidosis. Kihyun Kim Div. of Hematology/Oncology, Dept. of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan Univ. School of Medidine Samsung Medical Center
 Primary Amyloidosis Kihyun Kim Div. of Hematology/Oncology, Dept. of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan Univ. School of Medidine Samsung Medical Center Systemic Amyloidosis A group of complex diseases caused by tissue
Primary Amyloidosis Kihyun Kim Div. of Hematology/Oncology, Dept. of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan Univ. School of Medidine Samsung Medical Center Systemic Amyloidosis A group of complex diseases caused by tissue
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE
 MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
Neurologic Manifestations of Systemic Disease (N Scolding and C Rice, Section Editors)
 Curr Treat Options Neurol (2016) 18:53 DOI 10.1007/s11940-016-0436-z Neurologic Manifestations of Systemic Disease (N Scolding and C Rice, Section Editors) Current and Future Treatment Approaches in Transthyretin
Curr Treat Options Neurol (2016) 18:53 DOI 10.1007/s11940-016-0436-z Neurologic Manifestations of Systemic Disease (N Scolding and C Rice, Section Editors) Current and Future Treatment Approaches in Transthyretin
Amyloidosis. Philip Hawkins National Amyloidosis Centre UCL & Royal Free Hospital, London
 Amyloidosis Philip Hawkins National Amyloidosis Centre UCL & Royal Free Hospital, London Amyloid Abnormal extracellular fibrillar protein deposit in tissues Pathognomonic red-green birefringence after
Amyloidosis Philip Hawkins National Amyloidosis Centre UCL & Royal Free Hospital, London Amyloid Abnormal extracellular fibrillar protein deposit in tissues Pathognomonic red-green birefringence after
Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of
 Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
David Adams 1*, Ole B. Suhr 2, Peter J. Dyck 3, William J. Litchy 3, Raina G. Leahy 4, Jihong Chen 4, Jared Gollob 4 and Teresa Coelho 5
 Adams et al. BMC Neurology (2017) 17:181 DOI 10.1186/s12883-017-0948-5 STUDY PROTOCOL Open Access Trial design and rationale for APOLLO, a Phase 3, placebo-controlled study of patisiran in patients with
Adams et al. BMC Neurology (2017) 17:181 DOI 10.1186/s12883-017-0948-5 STUDY PROTOCOL Open Access Trial design and rationale for APOLLO, a Phase 3, placebo-controlled study of patisiran in patients with
A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy
 Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
OBSERVATION. Akira Yoshioka, MD; Yoko Yamaya, MD; Shinji Saiki, MD; Genjiro Hirose, MD; Kohei Shimazaki, MD; Masaaki Nakamura, MD; Yukio Ando, MD
 OBSERVATION A Case of Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy Homozygous for the Transthyretin Val30Met Gene With Motor-Dominant Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy and Unusual Sural Nerve Pathological Findings Akira
OBSERVATION A Case of Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy Homozygous for the Transthyretin Val30Met Gene With Motor-Dominant Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy and Unusual Sural Nerve Pathological Findings Akira
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Vague Neurological Conditions
 Vague Neurological Conditions Dr. John Lefebre, MD, FRCPC Chief Regional Medical Director Europe, India, South Africa, Middle East and Turkey Canada 2014 2 3 4 Agenda Dr. John Lefebre, M.D., FRCPC 1. TIA
Vague Neurological Conditions Dr. John Lefebre, MD, FRCPC Chief Regional Medical Director Europe, India, South Africa, Middle East and Turkey Canada 2014 2 3 4 Agenda Dr. John Lefebre, M.D., FRCPC 1. TIA
Update on Treatments for Systemic Amyloidosis
 Update on Treatments for Systemic Amyloidosis Laura M. Dember, M.D. Renal, Electrolyte and Hypertension Division University of Pennsylvania ANZSN Update Course Darwin, Australia September 2, 2017 Disclosure
Update on Treatments for Systemic Amyloidosis Laura M. Dember, M.D. Renal, Electrolyte and Hypertension Division University of Pennsylvania ANZSN Update Course Darwin, Australia September 2, 2017 Disclosure
Cardiac Involvement is Underdiagnosed in Patients with Biopsy-Proven Systemic AL Amyloidosis
 Original Article 41 Cardiac Involvement is Underdiagnosed in Patients with Biopsy-Proven Systemic AL Amyloidosis Haoyi Zheng 1, Amitabha Mazumder 2, Stuart D. Katz 3 1. Cardiac Imaging, The Heart Center,
Original Article 41 Cardiac Involvement is Underdiagnosed in Patients with Biopsy-Proven Systemic AL Amyloidosis Haoyi Zheng 1, Amitabha Mazumder 2, Stuart D. Katz 3 1. Cardiac Imaging, The Heart Center,
Repurposing Diflunisal for Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy A Randomized Clinical Trial
 Research Original Investigation Repurposing Diflunisal for Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy A Randomized Clinical Trial John L. Berk, MD; Ole B. Suhr, MD, PhD; Laura Obici, MD; Yoshiki Sekijima, MD, PhD;
Research Original Investigation Repurposing Diflunisal for Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy A Randomized Clinical Trial John L. Berk, MD; Ole B. Suhr, MD, PhD; Laura Obici, MD; Yoshiki Sekijima, MD, PhD;
Familial amyloidotic polineuropathy and systemic lupus
 (2012) 21, 1455 1458 http://lup.sagepub.com CASE REPORT AC Ferreira, F Carvalho and F Nolasco Department of Nephrology, Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central, Hospital de Curry Cabral, Lisbon, Portugal Familial
(2012) 21, 1455 1458 http://lup.sagepub.com CASE REPORT AC Ferreira, F Carvalho and F Nolasco Department of Nephrology, Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central, Hospital de Curry Cabral, Lisbon, Portugal Familial
Immune Mediated Neuropathies
 Immune Mediated Neuropathies Hernan Gatuslao, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine AIDP and CIDP Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Immune Mediated Neuropathies Hernan Gatuslao, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine AIDP and CIDP Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Heart Failure Syndromes related to Unusual Cardiomyopathies
 Heart Failure Syndromes related to Unusual Cardiomyopathies Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine
Heart Failure Syndromes related to Unusual Cardiomyopathies Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012
 Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
Nicolas Bianchi M.D. May 15th, 2012 New concepts in TIA Differential Diagnosis Stroke Syndromes To learn the new definitions and concepts on TIA as a condition of high risk for stroke. To recognize the
Conference Call to Discuss FDA Approval of ONPATTRO (patisiran)
 Conference Call to Discuss FDA Approval of ONPATTRO (patisiran) August 10, 2018 1 Agenda Welcome Christine Lindenboom Vice President, Investor Relations & Corporate Communications Introduction John Maraganore,
Conference Call to Discuss FDA Approval of ONPATTRO (patisiran) August 10, 2018 1 Agenda Welcome Christine Lindenboom Vice President, Investor Relations & Corporate Communications Introduction John Maraganore,
Systemic amyloidosis with cardiac involvement
 034 Cardiology Systemic amyloidosis with cardiac involvement Amyloidosis is a term used to describe a group of disorders consisting of abnormalities in and the accumulation of amyloid protein. This protein
034 Cardiology Systemic amyloidosis with cardiac involvement Amyloidosis is a term used to describe a group of disorders consisting of abnormalities in and the accumulation of amyloid protein. This protein
APOLLO Phase 3 Study of Patisiran Complete Results
 Leo Living with hattr Amyloidosis APOLLO Phase 3 Study of Patisiran Complete Results November 2, 2017 Agenda Welcome Christine Lindenboom Vice President, Investor Relations & Corporate Communications Introduction
Leo Living with hattr Amyloidosis APOLLO Phase 3 Study of Patisiran Complete Results November 2, 2017 Agenda Welcome Christine Lindenboom Vice President, Investor Relations & Corporate Communications Introduction
Lactic Acidosis and Ascending Neuromuscular Syndrome. Mina Hosseinipour, M.D, MPH. University of North Carolina Project, Lilongwe Malawi
 Lactic Acidosis and Ascending Neuromuscular Syndrome Mina Hosseinipour, M.D, MPH. University of North Carolina Project, Lilongwe Malawi Introduction ART is rapidly scaling up in resource poor countries
Lactic Acidosis and Ascending Neuromuscular Syndrome Mina Hosseinipour, M.D, MPH. University of North Carolina Project, Lilongwe Malawi Introduction ART is rapidly scaling up in resource poor countries
Letter of Medical Necessity The Use of SPINRAZA (nusinersen) for Spinal Muscular Atrophy
 TEMPLATE Letter of Medical Necessity The Use of SPINRAZA (nusinersen) for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Date: [Insert Name of Medical Director] RE: Patient Name [ ] [Insurance Company] Policy Number [ ] [Address]
TEMPLATE Letter of Medical Necessity The Use of SPINRAZA (nusinersen) for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Date: [Insert Name of Medical Director] RE: Patient Name [ ] [Insurance Company] Policy Number [ ] [Address]
C. Quarta, L. Obici, S. Longhi, S. Perlini, A. Milandri, F. Del Corso, F. Perfetto, F. Cappelli, G. Merlini, C. Rapezzi
 Hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis with exclusively cardiac phenotype: disease profile and differential diagnosis with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and senile systemic amyloidosis C. Quarta, L.
Hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis with exclusively cardiac phenotype: disease profile and differential diagnosis with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and senile systemic amyloidosis C. Quarta, L.
Disease specific examination in the diabetic neuropathies. Christopher Gibbons MD, MMSc
 Disease specific examination in the diabetic neuropathies Christopher Gibbons MD, MMSc Overview Review the details examination development Review the current status of diabetic neuropathy examinations
Disease specific examination in the diabetic neuropathies Christopher Gibbons MD, MMSc Overview Review the details examination development Review the current status of diabetic neuropathy examinations
Phase 2 Open-Label Extension Study of Patisiran An RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy
 Phase 2 Open-Label Extension Study of Patisiran An RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy American Neurological Association Annual Meeting October 13, 2014 Agenda Welcome
Phase 2 Open-Label Extension Study of Patisiran An RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy American Neurological Association Annual Meeting October 13, 2014 Agenda Welcome
Cardiac amyloidosis an easy, but usually delayed diagnosis
 M K pag 46 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine CASE REPORTS Cardiac amyloidosis an easy, but usually delayed diagnosis R. SILISTE, MD a ; I. CALANGEA, MD a ; F. VOINEA, MD a ; I. SAVULESCU-FIEDLER,
M K pag 46 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine CASE REPORTS Cardiac amyloidosis an easy, but usually delayed diagnosis R. SILISTE, MD a ; I. CALANGEA, MD a ; F. VOINEA, MD a ; I. SAVULESCU-FIEDLER,
04 July 2016 ISA Uppsala, Sweden
 Phase 2 Open-Label Extension (OLE) Study of Revusiran An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Patients with Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Cardiomyopathy 04 July 2016 ISA Uppsala, Sweden
Phase 2 Open-Label Extension (OLE) Study of Revusiran An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Patients with Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Cardiomyopathy 04 July 2016 ISA Uppsala, Sweden
Amyloidosis. Maria M. Picken MD, PhD
 Amyloidosis Goals: To explain how amyloid forms and what diseases are caused by it Objectives 1. Explain why amyloid forms 2. When to suspect amyloidosis 3. How to diagnose amyloidosis 4. What are the
Amyloidosis Goals: To explain how amyloid forms and what diseases are caused by it Objectives 1. Explain why amyloid forms 2. When to suspect amyloidosis 3. How to diagnose amyloidosis 4. What are the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Received May 28, 2010; accepted August 21, 2010.
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 17:122-128, 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Continuous Development of Arrhythmia Is Observed in Swedish Transplant Patients With Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy (Amyloidogenic Transthyretin
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 17:122-128, 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Continuous Development of Arrhythmia Is Observed in Swedish Transplant Patients With Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy (Amyloidogenic Transthyretin
Cardiomyopathy Related to Transthyretin Val30met Mutation in Hereditary Systemic Amyloidosis
 Cardiomyopathy Related to Transthyretin Val30met Mutation in Hereditary Systemic Amyloidosis Caio Passos Cordeiro, Rodrigo Roitman Pozzatti, Suzane Garcia Ferreira, Marcella Severiano de Freitas, Alexandre
Cardiomyopathy Related to Transthyretin Val30met Mutation in Hereditary Systemic Amyloidosis Caio Passos Cordeiro, Rodrigo Roitman Pozzatti, Suzane Garcia Ferreira, Marcella Severiano de Freitas, Alexandre
Eidos Therapeutics, Inc.
 Eidos Therapeutics, Inc. Precision medicine for transthyretin amyloidosis September 2018 update Eidos forward-looking statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements about Eidos Therapeutics,
Eidos Therapeutics, Inc. Precision medicine for transthyretin amyloidosis September 2018 update Eidos forward-looking statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements about Eidos Therapeutics,
CNS third year med students Summary of midterm material H Awad
 CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
CNS third year med students 2018 Summary of midterm material H Awad Dear All This presentation summaries the main important topics covered in the midterm material ( lectures 1-6) There will be two questions
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy
 The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS. 1. Cardiovascular Disease
 THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
Case 3. Your Diagnosis?
 Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
