SKIN. 3. How is the skin structured around the finger joints to allow for flexible movement of the fingers?
|
|
|
- Gyles Wade
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SKIN Objectives for Exam #1: 1. List various skin structures and describe their functions. 2. Describe skin responses to increases and decreases in body temperature. 3. Provide examples of various skin disorders, including characteristics of skin cancers. Objective for Journal #1: Label different structures found in a model of the skin. Safety Notes: Be careful with the microscope slides, they can break into small sharp pieces. Report any broken glass to your GTA. Avoid placing any food or drink near glass. Part I: Skin Stations You will have an opportunity to cycle through different stations. You can work independently, or with classmates at each station. Station A: Examination of Skin 1. Using a hand magnifier, examine the skin on your forearm, the back of your hand, and fingertips. Describe how the skin differs in appearance at these different locations. Location Skin Appearance Forearm Back of Hand Fingertips 2. What is the advantage of having highly textured fingertips? 3. How is the skin structured around the finger joints to allow for flexible movement of the fingers? 4. Which area of your skin appears to be driest? Why is it important that skin does not become too dry? (consider what happens when skin on parts of the body, like the lips, becomes extremely dry) 19
2 5. After your hands and feet are submerged under water for a long period of time, how do they change in appearance? There is still debate as to why this occurs. From the display, what is the most likely explanation? 6. Most humans have areas of darker skin pigmentation that develop over time ( freckles ), in part due to an increase in the amount of the pigment melanin in cells called melanocytes. Which area of your skin has the most spots of darker pigmentation? Considering these locations, what may be the primary cause of increased changes in pigmentation? 7. What is the role of the protein keratin in the skin? Touch 8. From the Touch poster (bottom left), what can nerve endings in the skin detect? 9. Also from the poster, damaged cells release that activate nerve endings. 10. Look at the heavy pressure touch receptors under the microscope. What is their basic shape? Station B: Skin Models 1. Using the model and The Skin poster as a reference, indicate the three basic layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis (also called subcutaneous layer) on the photo below: 2. From the model and Magnified Cut-Out Section of the Skin poster, list structures that are located in the dermis: 20
3 3. On the photo below, indicate the structural differences between the skin of the scalp and the skin of the sole (bottom) of the foot: Station C: Skin Functions 1. Using the display and the Human Body book, p , for each of the following skin structures, summarize their basic function in the table below. Skin Structure Squamous Epithelial Cell Layer Function Epidermis Prickle Cell Layer Basal Cell Layer Dermal Loose Connective Tissue Blood Vessel Neurons/Nerve Cell Dermis Hair Follicle Arrector Pili Muscle Sweat Gland Sebaceous Oil Gland Subcutaneous Fat Hypodermis Connective Fibrous Tissue Layer Muscle Tissue Layer 21
4 Station D: Hair and Nails Hair 1. From the display, each hair has an muscle and a gland. Examine the miscoscope slide of hair in skin. Are the muscles and glands visible? 2. From The Human Hair mini-poster, what cells produce melanin, which gives hair its color? Looking at the microscope at hairs of different colors, what is missing in the grey hair? 3. Back to The Human Hair mini-poster Each hair follicle goes through a growth cycle. How long does the active growth phase ( anagen ) typically last? Following a 1-2 week transition ( catagen ) phase and the 5-6 week resting ( telogen ) phase, what happens to the hair? What does the hair follicle start to produce? 4. What biologically produces straight hair versus wavy hair? Nails 5. Human nails are translucent sheets of dead cells produced by the. Fingernails grow faster than toenails, approximately how much does a nail grow in a month? Station E: Microscope Use 1. Microscopes will be used extensively in BI 103. From the Microscope Focusing Tips poster, the top three tips for successful microscope use are at the top of the poster. What are they? 2. Before examining tissues and cells, you will build microscope skills through a classic color threads focusing activity. Use the following procedure to examine the sample microscope slide (threads): A. Turn on the microscope (with the power dial set between 7 and 8). B. Turn the objective ring to the lowest power of magnification (4X objective). C. Place the slide on the stage and position under the specimen holder. D. Rotate the focus knobs to carefully move the slide into focus. E. Use the stage knobs to move the slide around. F. Carefully move the objective ring to the next higher power objectives (10X and then 40X) and continue examining the slide. G. Which thread (red, blue, or yellow) is on top of the others? (check your answer with your GTA) 3. The eyepieces on your microscope have a magnification of 10X. If you are using a 4X objective, what is the total magnification of the slide you are observing (multiply the two numbers)? With a 10X objective? With a 40X objective? 22
5 Station F: Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1. From the bottom of the Cells poster, animal cells are grouped into. These tissues are groups of cells that work together. Match each tissue with its primary function A. Epithelial Tissue joins the body s tissues together. B. Connective Tissue communication and response to stimulus. C. Muscle Tissue lines body surfaces, both internal and external. D. Nervous Tissue movement. 2. The skin organ primarily contains two tissues. From the display, which two tissue types? Epithelial Tissue: 3. There are three general types of epithelial tissues: simple squamous, simple cuboidal, and simple columnar. a. From the Epithelial Tissue poster, simple squamous epithelial tissue is made up of cells with large central nuclei. Where is simple squamous tissue found in the human body? b. Simple cuboidal cells are -shaped. Where is simple cuboidal tissue found in the human body? c. Columnar epithelial cells are -shaped. Where is simple columnar tissue located in the human body? 4. Epithelial tissues can be combinations of different shaped cells. From the Epithelial Tissue poster, human skin is comprised of and epithelial tissues. The cells start out shaped as cuboidal or columnar in shape at the bottom (basal) layer and become flattened cells as they approach the surface. 5. Sketch the three general types of epithelial tissue at 400X. Add arrows and the labels that are listed under each tissue name. Hint: Start scanning at a low magnification to find an area to sketch and move up to the higher magnification for your drawing. Squamous (400X) Cuboidal (400X) Columnar (400X) Label: plasma membrane & nucleus Label: plasma membrane of cuboidal cells Label: plasma membrane of the squamous cells & the duct they surround of the columnar cells 23
6 Connective Tissue: 6. Connective tissues join other body tissues and are diverse in structure. Connective tissues have three components. From the display, these three components are : 7. Connective tissues are classified in three groups: embryonic connective tissue (found in embryos before birth), proper connective tissue, and special connective tissues. Using the Connective Tissue poster, fill in where different proper and special connective tissues are located in the human body. Group Connective Tissue Location in Human Body Loose (Areolar) Proper Dense (Regular) Dense (Irregular) Cartilage (Hyaline) Special Bone Adipose Blood 8. Skin has three types of connective tissue: dense connective tissue in the dermis and within the hypodermis, loose connective tissue surrounding adipose (fat) tissue. Dense and loose connective tissues are made up of elastic fibers, collagen fibers and fibroblasts, the cells that produce the collagen. The fibers are more tightly packed together in the dense connective tissues than the loose connective tissues. Adipose tissue is comprised of adipose (fat) cells within fibers. What is filling up most of the space within the fat cells? 9. There are a wide variety of connective tissues. In this laboratory you are examining adipose, loose, and dense connective tissue. Hint: make sure you find the correct tissue before you start to draw. Adipose (400x) Loose (400x) Dense (400x) Label: fat cells Label: fibers Label: fibroblasts, collagen 24
7 Station G: Skin Microscope Slides 1. Examine the skin slide. Make sketches (quick drawings) of what you see. Using the display for assistance, label and draw arrows to the following cell structures in your sketch: epidermis, dermis, sweat glands, adipose tissue. 2. The skin slides have been stained with pigments. Why was this staining necessary? Station H: Thermoregulation 1. From your experiences, describe what happens to your skin when your body temperature cools. 2. If not in your previous answer, what specifically happens to the arrector pili muscles, hairs, blood vessels, and the muscle layer in the hypodermis when your body temperature cools? 3. From your experiences, describe what happens to your skin when your body temperature warms. 4. If not in your previous answer, when the body temperature heats up, what happens to the sweat glands and blood vessels? 25
8 Station I: Skin Disorders Acne 1. From the display, describe the differences between each of the different forms of acne: Acne Type Blackhead What is occurring in the skin Whitehead Pimple Burns 2. From the display, fill in what happens to the skin in different degree burns: Degree First What happens to the skin Second Third Fourth Station J: Skin Cancer Ultraviolet light 1. One of the leading causes of skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet light. From display, how does the skin change when exposed to UVB light? 2. What type of ultraviolet radiation is most likely to cause the genetic mutations that lead to skin cancer (UVA or UVB)? 3. How can UVA damage skin? 4. Most people think they are mostly exposed to UV light at mid-day and that it is completely blocked by glass. When can you have high exposure to UVB? When can you be exposed to UVA? 5. Are tanning beds safe for skin? 6. What is the difference between a sunscreen and a sunblock? 7. Your GTA can provide you with a UV bead. These stay white unless exposed to a range of UV light, typically 360 nm to 300 nm. This includes the high-energy part of UV Type A ( nm) and the low energy part of UV Type B ( nm). Are the beads currently detecting UV light? 26
9 Skin Cancer 8. From the Skin Cancer poster, moles are malformations which mean they are unlikely to spread from their location. However; growth, changes in color, inflammation, or bleeding may indicate the presence of. Cancer is a disease in which cells grow uncontrollably in the body. What is the most frequent (and least deadly) type of skin cancer? (also called basal cell carcinoma). Malignant melanoma is the most malignant type of skin cancer, meaning it is the most likely to. 9. Staging is the process of identifying how far a cancer has progressed in the body. From the display, what happens to melanoma cancer cells at each of the following five stages? Stage What is happening to the tumor (group of cancer cells)? 10. The model has representations of three skin cancers (two types of basal cell, and one melanoma) and other abnormal pre-cancerous skin growths that may in some cases develop into skin cancer. In the table below, describe what each of these look like on the surface of the skin, thinking about which of these may be easiest or most difficult to detect. Skin Disorder Pre-cancer: Dysplastic Nevi (DN) Cancer: Malignant Melanoma (MM) Pre-cancer: Actinic Keratosis (AK) Cancer: Keratoacanthoma (KA) Cancer: Nodular Basal Cell (NBC) Cancer: Morpheic Basal Cell (MBC) What is Happening in the Skin Melanocytes are growing excessively, leaving dark patches of skin like a large irregular mole Melanocytes are growing excessively, this can spread (metastasize) and is the most deadly skin cancer Cells are growing abnormally producing a rough and dry lesion. This may develop into cancer. Cell in skin glands grow excessively, this can bleed and spread (metastasize) like squamous cell carcinoma Excessive growth of cells in the basal layer of the skin forms a threedimensional tumor Excessive growth of cells in the basal layer of the skin, these can be flat and shine like a pearl What the disorder looks like on the surface of the skin (color, shape, etc.) 11. From the handout, what are the A, B, C, D, E s of detecting skin cancer? 27
10 12. Basal cell carcinoma is illustrated on p. 312 of Human Body. Examine the basal cell carcinoma slide under the microscope at 400X magnification. The cancerous area typically has irregular structure ( spreading finger-like projections of cells into surrounding tissue). You can also see this in the skin cancer model you examined for the previous question. Draw what you see and label the skin structures that you are able to observe, including the basal cell carcinoma cancer cells. 400X Part II: Labeled Skin Structures (For Journal #1, stamp required) Using the large skin model as a reference, label the Skin Anatomy illustrations on pages 4 and 5 of your Biology Journal. A stamp is required; your GTA will stamp the journal page to confirm that the labels were completed in lab. Journal assignments represent your individual skills. Do not submit an assignment that is a duplication of any other individual s work. 28
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Your Skin. Section 14.2 Your Skin, Hair, and Nails
 Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
Warm Up. You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class.
 Warm Up You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class. Reflection 1. What were 2 similarities between your classification scheme and others in the
Warm Up You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class. Reflection 1. What were 2 similarities between your classification scheme and others in the
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems
 Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
BI 121 LAB. WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System
 BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Skin The Integumentary System
 Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
The Integementary System. The Skin & Its Parts
 The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integumentary System. Chapter 6
 The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body.
 Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma
 Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4
 Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4 CHAPTER 3: Cells and Tissues 1. The smallest unit of living tissue is called a. All living organisms are composed of these basic units where all life processes
Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4 CHAPTER 3: Cells and Tissues 1. The smallest unit of living tissue is called a. All living organisms are composed of these basic units where all life processes
Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems Welcome to Lesson 3 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. I
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems Welcome to Lesson 3 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. I
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Figure 4.1. Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 115
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
All the Rest. What is All the Rest? Integumentary System. First are the FUNCTI0NS. THERMOREGULATION function. PROTECTION function 10/12/16
 What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015. Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 14.
 Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015 Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 11. 19. 20. 8. 7. 14. 15. 12. 17. 9. 13.
Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015 Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 11. 19. 20. 8. 7. 14. 15. 12. 17. 9. 13.
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
What is a tissue? Points to ponder. Tissues Connective Tissue. 1. Connective tissue 2/23/2019. Organization and Regulation of Body Systems
 Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Skin Cancer. There are many types of diseases. From a simple cold to the deadly disease
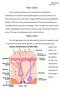 Skin Cancer Skin Cancer 1 There are many types of diseases. From a simple cold to the deadly disease Mesothelioma. Some diseases are almost harmless and some can kill you in less than a year. There are
Skin Cancer Skin Cancer 1 There are many types of diseases. From a simple cold to the deadly disease Mesothelioma. Some diseases are almost harmless and some can kill you in less than a year. There are
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE
 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
II. Skin and Its Tissues. I. Introduction. Unit Two. Integument URLs.
 6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
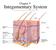 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Student Objectives. 7. Describe the structure of nails.
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
Integumentary System. Study of the Skin
 Integumentary System Study of the Skin Skin is used to: Maintain homeostasis Provide a protective covering Slow down water loss from deeper tissues House sensory receptors Synthesize various biochemicals
Integumentary System Study of the Skin Skin is used to: Maintain homeostasis Provide a protective covering Slow down water loss from deeper tissues House sensory receptors Synthesize various biochemicals
The INTEGUMENTARY System
 The INTEGUMENTARY System Functions of the Skin Protection Vitamin D Production Sensory Organ Temperature Regulation Protection against UV Light Layers of the Skin Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Epidermis
The INTEGUMENTARY System Functions of the Skin Protection Vitamin D Production Sensory Organ Temperature Regulation Protection against UV Light Layers of the Skin Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Epidermis
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Mitosis Models 3-5. Chromosome. #1 Prophase. #2 Prophase. 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids. 2n = 4
 MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
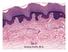 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
The Integumentary System: ANATOMY Includes: - Skin (integument) MEMBRANES. PHYSIOLOGY (functions) Protection. EPITHELIAL (cont.
 Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue? a. It
BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue? a. It
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
Sensory System Continued
 Sensory System Continued Skin The skin is the largest organ of the body, covering its entire surface Technically skin is no longer the largest organ. it s the interstitium What is the skin s purpose? Purpose
Sensory System Continued Skin The skin is the largest organ of the body, covering its entire surface Technically skin is no longer the largest organ. it s the interstitium What is the skin s purpose? Purpose
3. Dense connective tissue is found in skin, & surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs.
 Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
